文章目录
一、红⿊树的概念
红⿊树是⼀棵⼆叉搜索树,他的每个结点增加⼀个存储位来表⽰结点的颜⾊,可以是红⾊或者⿊⾊。
通过对任何⼀条从根到叶⼦的路径上各个结点的颜⾊进⾏约束,红⿊树确保没有⼀条路径会⽐其他路径⻓出2倍,因⽽是接近平衡的。
1、红⿊树的规则
- 每个结点不是红⾊就是⿊⾊。
- 根结点是⿊⾊的。
- 如果⼀个结点是红⾊的,则它的两个孩⼦结点必须是⿊⾊的,也就是说任意⼀条路径不会有连续的红⾊结点。
- 对于任意⼀个结点,从该结点到其所有NULL结点的简单路径上,均包含相同数量的⿊⾊结点。
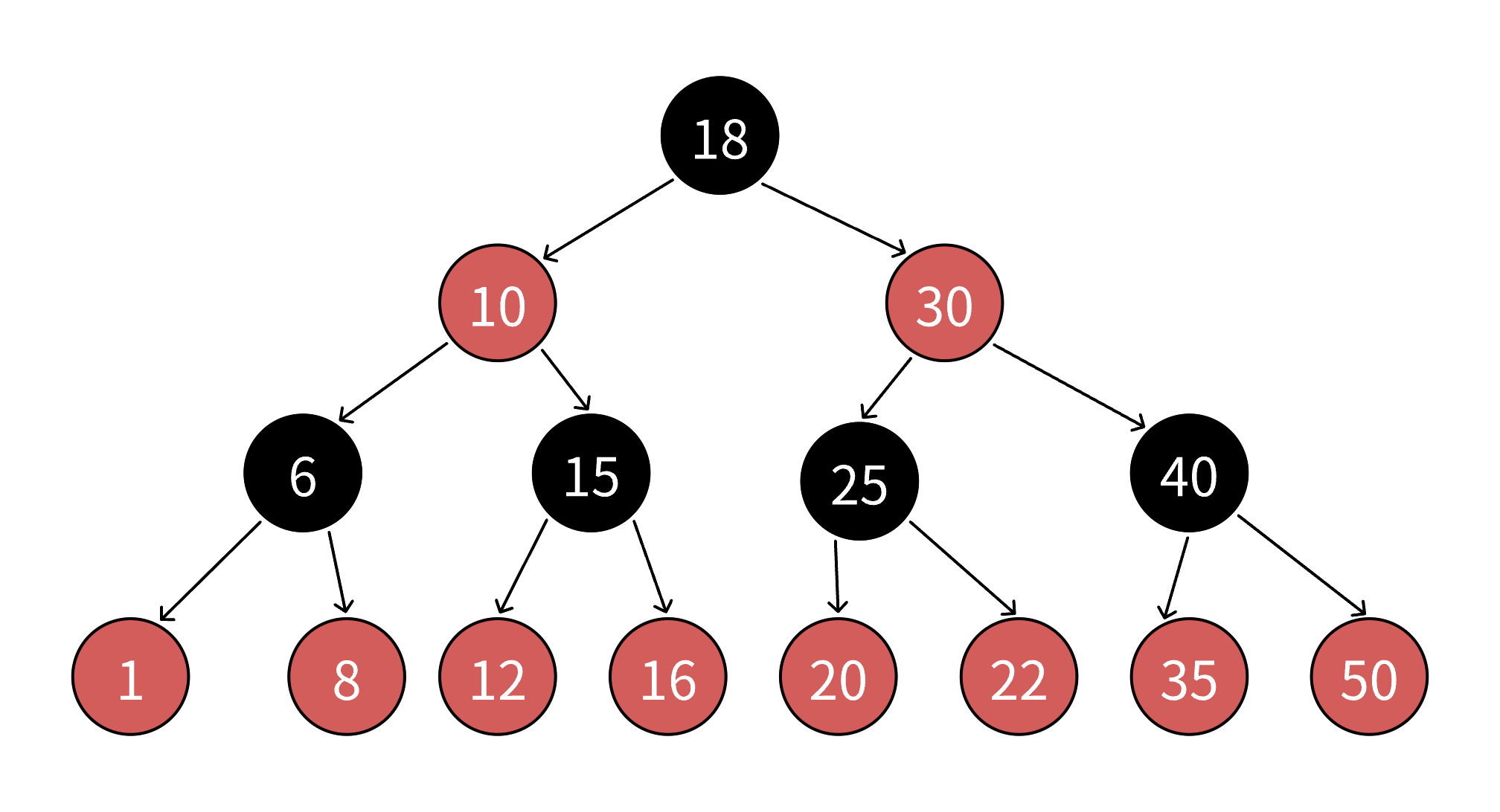
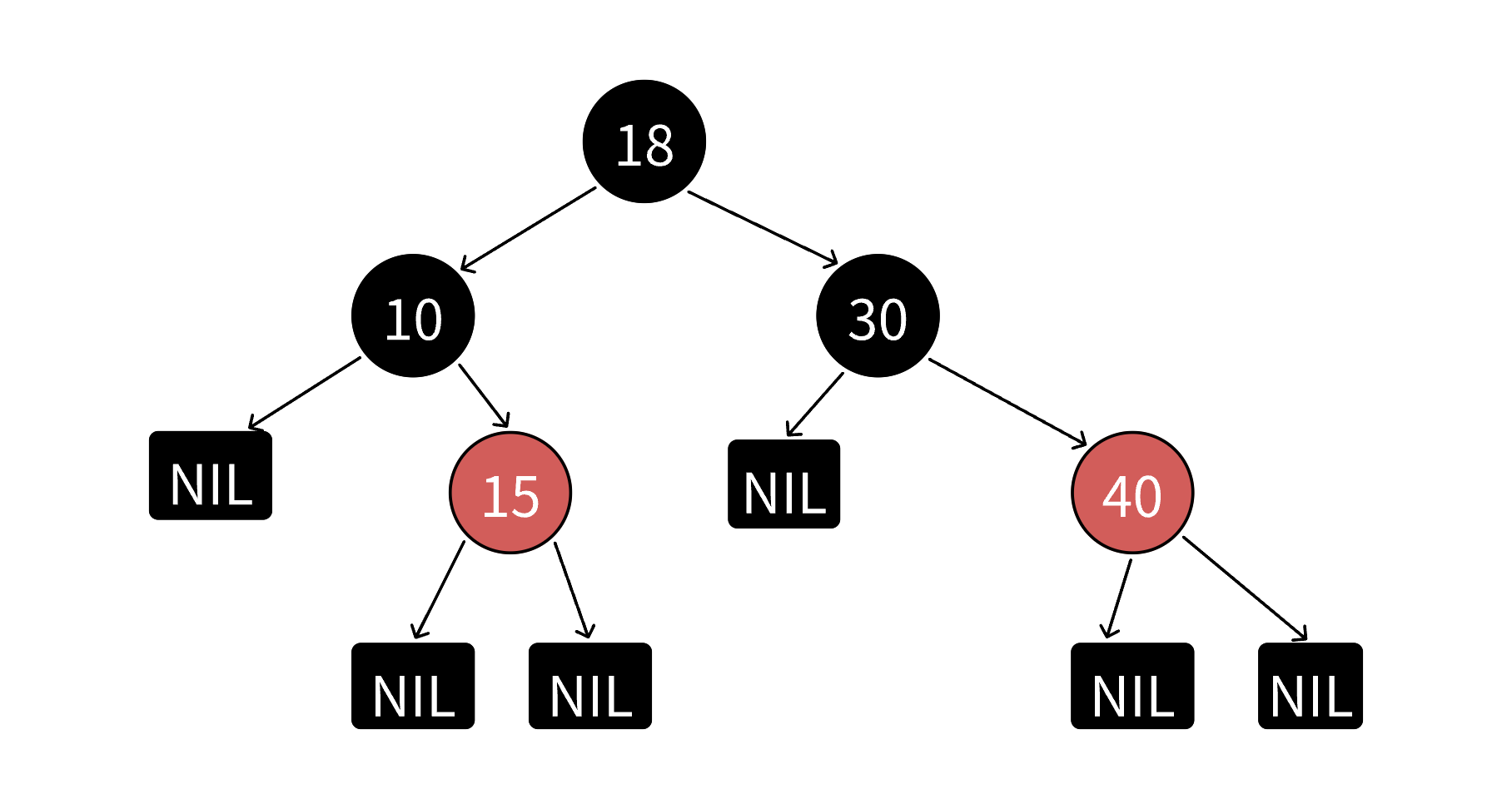
说明: 《算法导论》等书籍上补充了⼀条每个叶⼦结点(NIL)都是⿊⾊的规则。他这⾥所指的叶⼦结点不是传统的意义上的叶⼦结点,⽽是我们说的空结点,有些书籍上也把NIL叫做外部结点。NIL是为了⽅便准确的标识出所有路径。
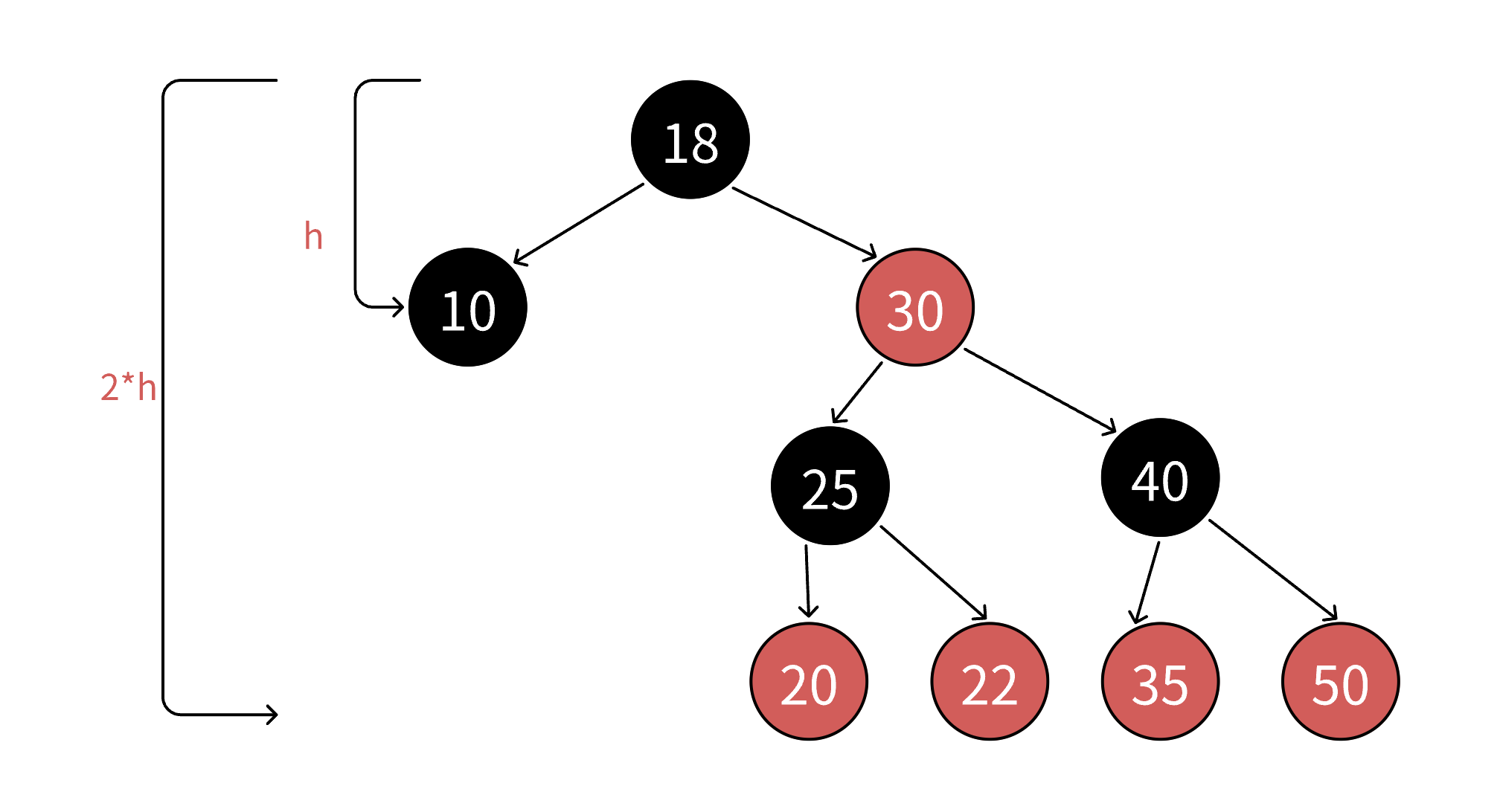
2、红⿊树如何确保最⻓路径不超过最短路径的2倍?
-
由规则4可知,从根到NULL结点的每条路径都有相同数量的⿊⾊结点,所以极端场景下,最短路径就是全是⿊⾊结点的路径,假设最短路径⻓度为bh(black height)。
-
由规则2和规则3可知,任意⼀条路径不会有连续的红⾊结点,所以极端场景下,最⻓的路径就是⼀⿊⼀红间隔组成,那么最⻓路径的⻓度为2*bh。
-
综合红⿊树的4点规则⽽⾔,理论上的全⿊最短路径和⼀⿊⼀红的最⻓路径并不是在每棵红⿊树都存在的。假设任意⼀条从根到NULL结点路径的⻓度为x,那么
bh<= x <=2*bh。
3、红⿊树的效率
假设N是红⿊树树中结点数量,h最短路径的⻓度,那么 2h-1<= N <22*h-1,由此推出h ≈ logN ,也就是意味着红⿊树增删查改最坏也就是⾛最⻓路径2 ∗ logN ,那么时间复杂度还是O(logN)。
红⿊树的表达相对AVL树要抽象⼀些,AVL树通过⾼度差直观的控制了平衡。红⿊树通过4条规则的颜⾊约束,间接的实现了近似平衡,他们效率都是同⼀档次,但是相对⽽⾔,插⼊相同数量的结点,红⿊树的旋转次数是更少的,因为他对平衡的控制没那么严格。
二、红⿊树的实现
1、红⿊树的结构
cpp
//枚举表示颜色
enum Colour
{
RED,
BALCK
};
//默认按key/value结构实现
template<class K,class V>
struct RBTreeNode
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _left;
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _right;
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _parent;
Colour _col;
RBTreeNode(const pair<K, V>& kv)
:_kv(kv)
,_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
_parent(nullptr)
{}
};
template<class K,class V>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public:
//...
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};2、红⿊树的插⼊
1)红⿊树插入的过程
-
插⼊⼀个值按⼆叉搜索树规则进⾏插⼊,插⼊后我们只需要观察是否符合红⿊树的4条规则。
-
如果是空树插⼊,新增结点是⿊⾊结点。如果是⾮空树插⼊,新增结点必须红⾊结点,因为⾮空树插⼊,新增⿊⾊结点就破坏了规则4,规则4是很难维护的。
-
⾮空树插⼊后,新增结点必须红⾊结点,如果⽗亲结点是⿊⾊的,则没有违反任何规则,插⼊结束。
-
⾮空树插⼊后,新增结点必须红⾊结点,如果⽗亲结点是红⾊的,则违反规则3。进⼀步分析,c是红⾊,p为红,g必为⿊,这三个颜⾊都固定了,关键的变化看u的情况,需要根据u分为以下⼏种情况分别处理。
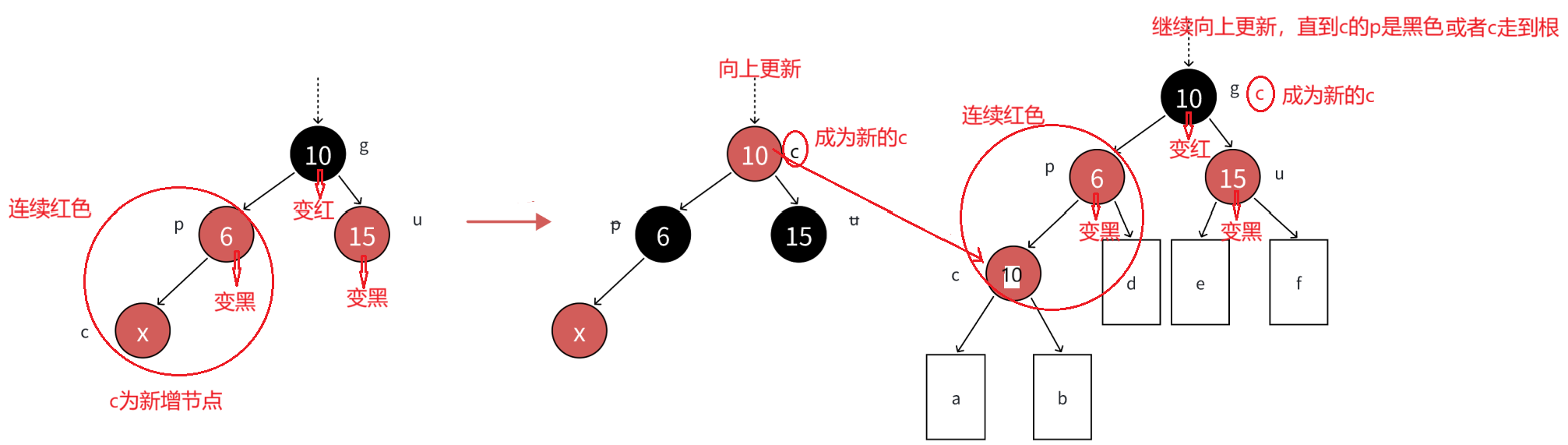
说明: 下图中假设我们把新增结点标识为c(cur),c的⽗亲标识为p(parent),p的⽗亲标识为g(grandfather),p的兄弟标识为u(uncle)。
2)情况1:变⾊
c为红,p为红,g为⿊,u存在且为红,则将p和u变⿊,g变红。在把g当做新的c,继续往上更新。
分析: 因为p和u都是红⾊,g是⿊⾊,把p和u变⿊,左边⼦树路径各增加⼀个⿊⾊结点,g再变红,相当于保持g所在⼦树的⿊⾊结点的数量不变,同时解决了c和p连续红⾊结点的问题,需要继续往上更新是因为,g是红⾊,如果g的⽗亲还是红⾊,那么就还需要继续处理;如果g的⽗亲是⿊⾊,则处理结束了;如果g就是整棵树的根,再把g变回⿊⾊。
下面这种情况,只变⾊,不旋转。所以⽆论c是p的左还是右,p是g的左还是右,都是这种变⾊处理⽅式。
3)情况2:单旋+变⾊
c为红,p为红,g为⿊,u不存在或者u存在且为⿊,u不存在,则c⼀定是新增结点。u存在且为⿊,则c⼀定不是新增,c之前是⿊⾊的,是在c的⼦树中插⼊,变⾊将c从⿊⾊变成红⾊,更新上来的。
分析: p必须变⿊,才能解决,连续红⾊结点的问题,这⾥单纯的变⾊⽆法解决问题,需要旋转+变⾊。
如果p是g的左,c是p的左,那么以g为旋转点进⾏右单旋,再把p变⿊,g变红即可。p变成课这颗树新的根,这样⼦树⿊⾊结点的数量不变,没有连续的红⾊结点了,且不需要往上更新,因为p的⽗亲是⿊⾊还是红⾊或者空都不违反规则。
cpp
g
p u
c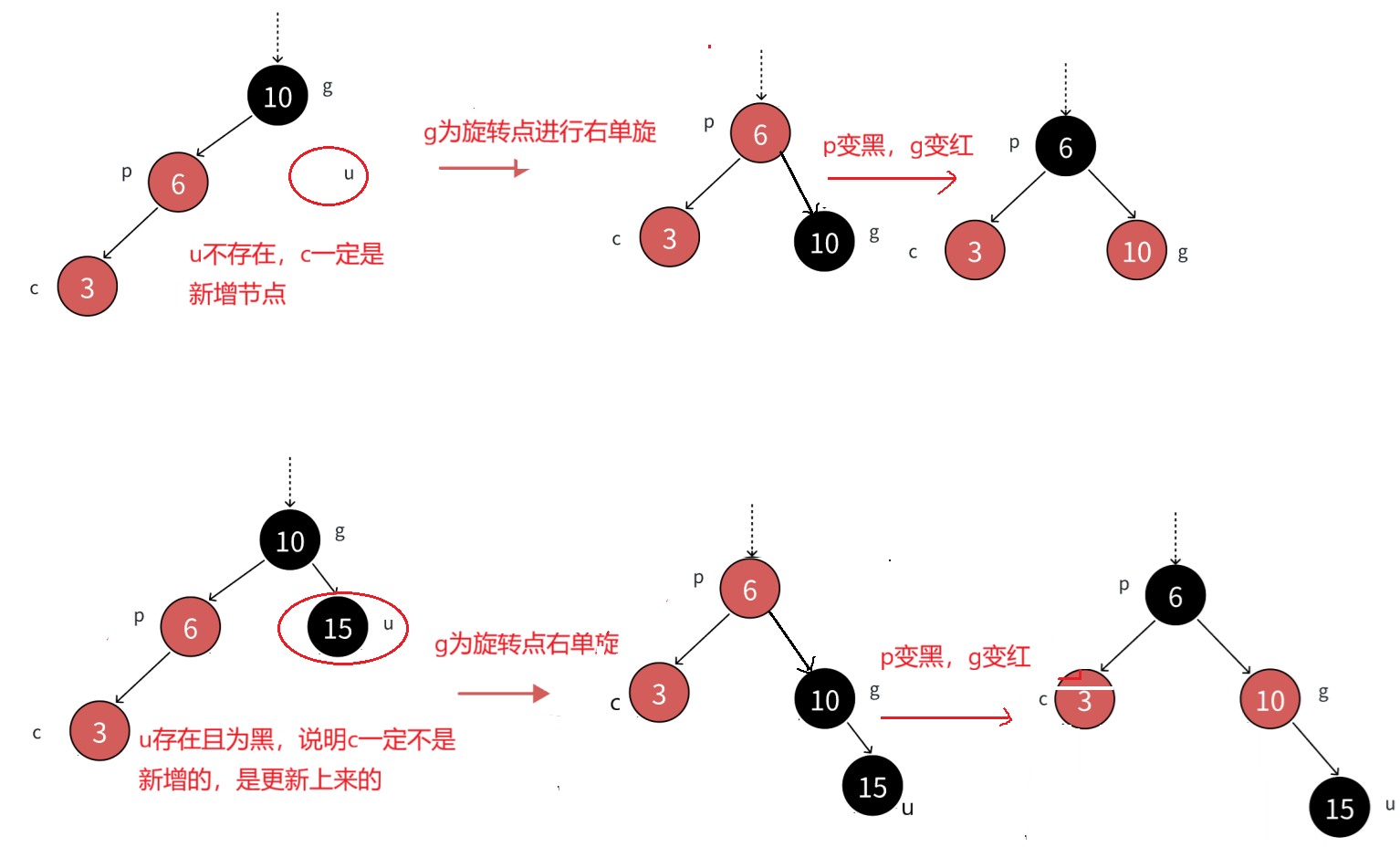
cpp
g
u p
c如果p是g的右,c是p的右,那么以g为旋转点进⾏左单旋,再把p变⿊,g变红即可。p变成课这颗树新的根,这样⼦树⿊⾊结点的数量不变,没有连续的红⾊结点了,且不需要往上更新,因为p的⽗亲是⿊⾊还是红⾊或者空都不违反规则。
4)情况2:双旋+变⾊
c为红,p为红,g为⿊,u不存在或者u存在且为⿊,u不存在,则c⼀定是新增结点。u存在且为⿊,则c⼀定不是新增,c之前是⿊⾊的,是在c的⼦树中插⼊,变⾊将c从⿊⾊变成红⾊,更新上来的。
分析: p必须变⿊,才能解决,连续红⾊结点的问题,u不存在或者是⿊⾊的,这⾥单纯的变⾊⽆法解决问题,需要旋转+变⾊。
如果p是g的左,c是p的右,那么先以p为旋转点进⾏左单旋,再以g为旋转点进⾏右单旋,再把c变⿊,g变红即可。c变成课这颗树新的根,这样⼦树⿊⾊结点的数量不变,没有连续的红⾊结点了,且不需要往上更新,因为c的⽗亲是⿊⾊还是红⾊或者空都不违反规则。
cpp
g
p u
c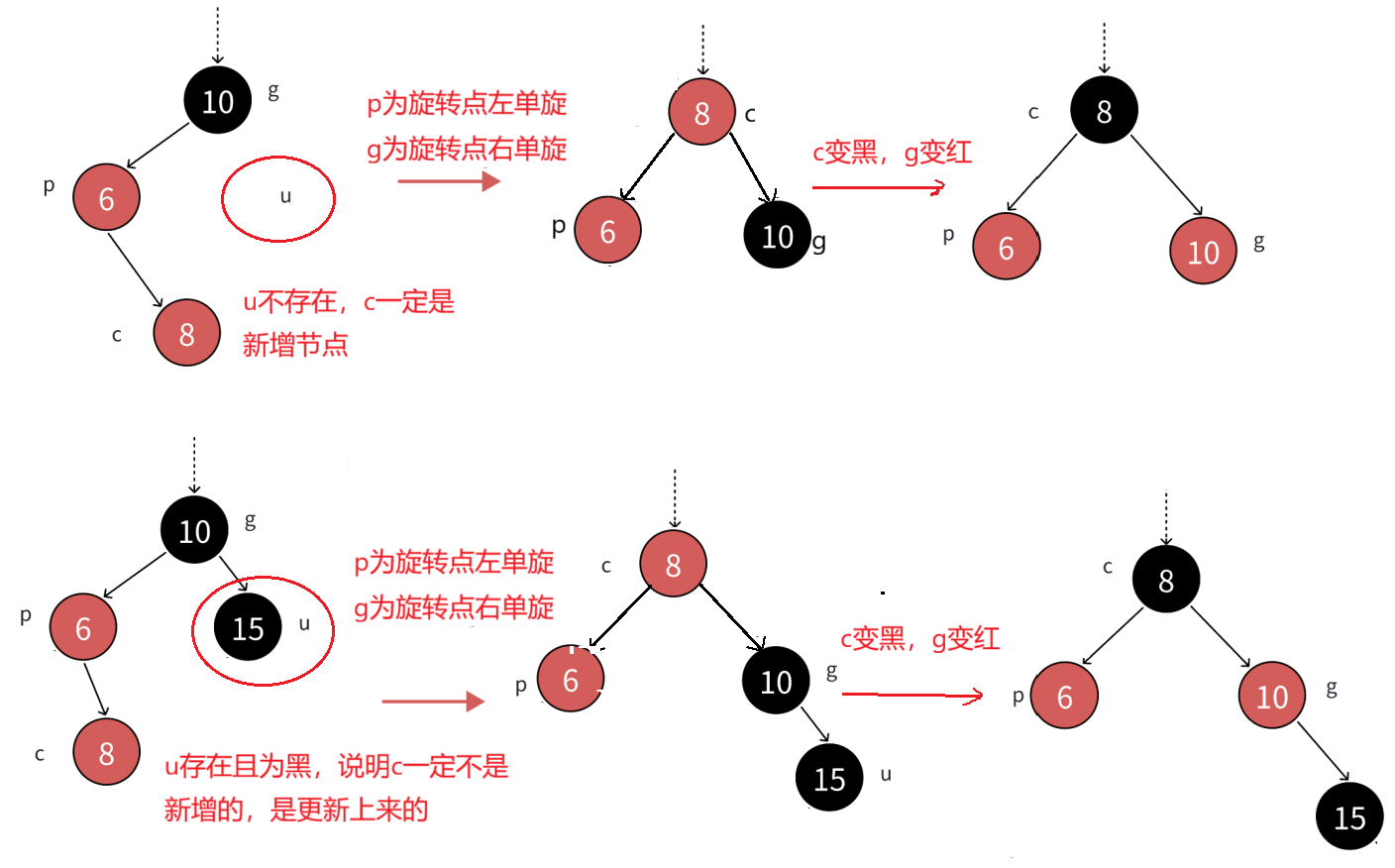
如果p是g的右,c是p的左,那么先以p为旋转点进⾏右单旋,再以g为旋转点进⾏左单旋,再把c变⿊,g变红即可。c变成课这颗树新的根,这样⼦树⿊⾊结点的数量不变,没有连续的红⾊结点了,且不需要往上更新,因为c的⽗亲是⿊⾊还是红⾊或者空都不违反规则。
cpp
g
u p
c3、红⿊树的插⼊代码
注意:旋转代码的实现跟AVL树是⼀样的,只是不需要更新平衡因⼦ 。
cpp
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
//插入
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(kv);
_root->_col = BLACK;//根节点为黑色
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (kv.first > cur->_kv.first)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kv.first < cur->_kv.first)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(kv);
cur->_col = RED;//只能插入红色节点
//链接父节点
if (kv.first > parent->_kv.first)
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
cur->_parent = parent;
//处理颜色
//插入节点的父亲是红色
while (parent && parent->_col == RED)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
if (parent == grandfather->_left)
{
// g
//p u
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
//uncle存在且为红
if (uncle&& uncle->_col == RED)
{
//变色
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
//向上更新
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
//uncle不存在或为存在为黑
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
// g
// p u
//c
RotateR(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else
{
// g
// p u
// c
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
else//uncle在左边
{
// g
//u p
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
// g
//u p
// c
RotateL(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else
{
// g
//u p
// c
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
}
//走到根了,根置为黑
_root->_col = BLACK;
return true;
}
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
Node* pParent = parent->_parent;
parent->_left = subLR;
if (subLR)
subLR->_parent = parent;
subL->_right = parent;
parent->_parent = subL;
if (pParent == nullptr)
{
_root = subL;
subL->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
//原parent在父节点的左边
if (pParent->_left == parent)
{
pParent->_left = subL;
}
else
{
pParent->_right = subL;
}
subL->_parent = pParent;
}
}
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
Node* pParent = parent->_parent;
parent->_right = subRL;
if (subRL)
subRL->_parent = parent;
subR->_left = parent;
parent->_parent = subR;
if (pParent == nullptr)
{
_root = subR;
subR->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (pParent->_left == parent)
{
pParent->_left = subR;
}
else
{
pParent->_right = subR;
}
subR->_parent = pParent;
}
}4、红⿊树的查找
按⼆叉搜索树逻辑实现即可,搜索效率为O(logN)。
cpp
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (key > cur->_kv.first)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (key < cur->_kv.first)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return cur;
}
}
return nullptr;
}5、红⿊树的验证
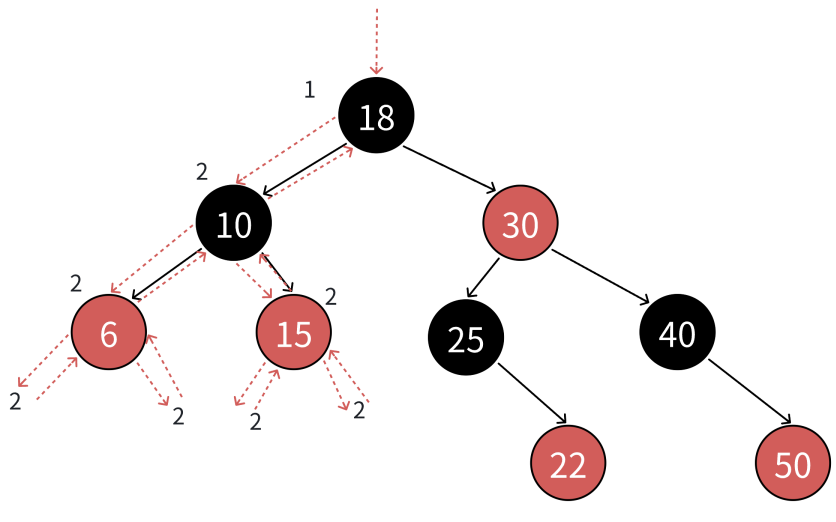
这⾥获取最⻓路径和最短路径,检查最⻓路径不超过最短路径的2倍是不可⾏的,因为就算满⾜这个条件,红⿊树也可能颜⾊不满⾜规则,当前暂时没出问题,后续继续插⼊还是会出问题的。所以我们还是去检查4点规则,满⾜这4点规则,⼀定能保证最⻓路径不超过最短路径的2倍。
- 枚举颜⾊类型,天然实现保证了颜⾊不是⿊⾊就是红⾊。
- 直接检查根即可。
- 前序遍历检查,遇到红⾊结点查孩⼦不太⽅便,因为孩⼦有两个,且不⼀定存在,反过来检查⽗亲的颜⾊更方便。
- 规则4前序遍历,遍历过程中⽤形参记录跟到当前结点的blackNum(⿊⾊结点数量),前序遍历遇到⿊⾊结点就++blackNum,⾛到空就计算出了⼀条路径的⿊⾊结点数量。再任意⼀条路径⿊⾊结点数量作为参考值,依次⽐较即可。
cpp
bool Check(Node* root, int blackNum, const int refNum)
{
//前序遍历走到空,意味着一条路径走完
if (root == nullptr)
{
if (refNum != blackNum)
{
cout << "存在黑色节点数量不相等的路径" << endl;
return false;
}
return true;
}
//检查父亲更方便
if (root->_col == RED && root->_parent->_col == RED)
{
cout << "存在连续的红色节点:" << root->_kv.first << endl;
return false;
}
if (root->_col == BLACK)
{
++blackNum;
}
return Check(root->_left, blackNum, refNum)
&& Check(root->_right, blackNum, refNum);
}
bool IsBalance()
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
return true;
}
if (_root->_col == RED)
{
return false;
}
//参考值
int refNum = 0;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_col == BLACK)
{
++refNum;
}
cur = cur->_left;
}
return Check(_root, 0, refNum);
}6、红黑树实现的完整代码
1)RBTree.h
cpp
//枚举表示颜色
enum Colour
{
RED,
BLACK
};
//默认按key/value结构实现
template<class K,class V>
struct RBTreeNode
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _left;
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _right;
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _parent;
Colour _col;
RBTreeNode(const pair<K, V>& kv)
:_kv(kv)
,_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_parent(nullptr)
{}
};
template<class K,class V>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public:
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
//插入
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(kv);
_root->_col = BLACK;//根节点为黑色
return true;
}
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (kv.first > cur->_kv.first)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kv.first < cur->_kv.first)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(kv);
cur->_col = RED;//只能插入红色节点
//链接父节点
if (kv.first > parent->_kv.first)
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
cur->_parent = parent;
//处理颜色
//插入节点的父亲是红色
while (parent && parent->_col == RED)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
if (parent == grandfather->_left)
{
// g
//p u
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
//uncle存在且为红
if (uncle&& uncle->_col == RED)
{
//变色
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
//向上更新
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
//uncle不存在或为存在为黑
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
// g
// p u
//c
RotateR(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else
{
// g
// p u
// c
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
else//uncle在左边
{
// g
//u p
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
// g
//u p
// c
RotateL(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else
{
// g
//u p
// c
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
}
//走到根了,根置为黑
_root->_col = BLACK;
return true;
}
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
Node* pParent = parent->_parent;
parent->_left = subLR;
if (subLR)
subLR->_parent = parent;
subL->_right = parent;
parent->_parent = subL;
if (pParent == nullptr)
{
_root = subL;
subL->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
//原parent在父节点的左边
if (pParent->_left == parent)
{
pParent->_left = subL;
}
else
{
pParent->_right = subL;
}
subL->_parent = pParent;
}
}
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
Node* pParent = parent->_parent;
parent->_right = subRL;
if (subRL)
subRL->_parent = parent;
subR->_left = parent;
parent->_parent = subR;
if (pParent == nullptr)
{
_root = subR;
subR->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (pParent->_left == parent)
{
pParent->_left = subR;
}
else
{
pParent->_right = subR;
}
subR->_parent = pParent;
}
}
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (key > cur->_kv.first)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (key < cur->_kv.first)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return cur;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
bool IsBalance()
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
return true;
}
if (_root->_col == RED)
{
return false;
}
//参考值
int refNum = 0;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_col == BLACK)
{
++refNum;
}
cur = cur->_left;
}
return Check(_root, 0, refNum);
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
int Height()
{
return _Height(_root);
}
int Size()
{
return _Size(_root);
}
private:
bool Check(Node* root, int blackNum, const int refNum)
{
//前序遍历走到空,意味着一条路径走完
if (root == nullptr)
{
if (refNum != blackNum)
{
cout << "存在黑色节点数量不相等的路径" << endl;
return false;
}
return true;
}
//检查父亲更方便
if (root->_col == RED && root->_parent->_col == RED)
{
cout << "存在连续的红色节点:" << root->_kv.first << endl;
return false;
}
if (root->_col == BLACK)
{
++blackNum;
}
return Check(root->_left, blackNum, refNum)
&& Check(root->_right, blackNum, refNum);
}
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_kv.first << ":" << root->_kv.second << endl;
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
int _Height(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = _Height(root->_left);
int rightHeight = _Height(root->_right);
return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;
}
int _Size(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return 0;
}
return _Size(root->_left) + _Size(root->_right) + 1;
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};2)Test.cpp
再对实现的各种方法进行测试:
cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include"RBTree.h"
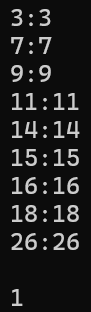
void TestRBTree1()
{
RBTree<int, int> t;
int a[] = { 16, 3, 7, 11, 9, 26, 18, 14, 15 };//常规场景
//int a[] = { 4, 2, 6, 1, 3, 5, 15, 7, 16, 14 };//带有双旋场景
for (auto e : a)
{
t.Insert({ e,e });
}
t.InOrder();
cout << t.IsBalance() << endl;
}运行结果:
学习了红黑树之后,我们再将其与AVL树进行对比。
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<time.h>
using namespace std;
#include"RBTree.h"
#include"AVLTree.h"
void TestRBTree2()
{
const int N = 10000000;
vector<int> v;
v.reserve(N);
srand(time(0));
for (size_t i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
v.push_back(rand() + i);
}
size_t begin1 = clock();
AVLTree<int, int> t;
for (auto e : v)
{
t.Insert(make_pair(e, e));
}
size_t end1 = clock();
size_t begin2 = clock();
RBTree<int, int> r;
for (auto e : v)
{
r.Insert(make_pair(e, e));
}
size_t end2 = clock();
cout << "AVLTree Insert:" << end1 - begin1 << endl;
cout << "RB Insert:" << end2 - begin2 << endl;
cout << "AVL IsBalance:" << t.IsBalanceTree() << endl;
cout << "RB IsBalance:" << r.IsBalance() << endl;
cout << "AVL Height:" << t.Height() << endl;
cout << "RB Height:" << r.Height() << endl;
cout << "AVL Size:" << t.Size() << endl;
cout << "RB Size:" << r.Size() << endl;
size_t begin3 = clock();
//确定值
for (auto e : v)
{
t.Find(e);
}
// 随机值
/*for (size_t i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
t.Find((rand() + i));
}*/
size_t end3 = clock();
cout << "AVL Find:" << end3 - begin3 << endl;
size_t begin4 = clock();
// 确定在的值
for (auto e : v)
{
r.Find(e);
}
// 随机值
/*for (size_t i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
t.Find((rand() + i));
}*/
size_t end4 = clock();
cout << "RB Find:" << end4 - begin4 << endl;
}运行结果:
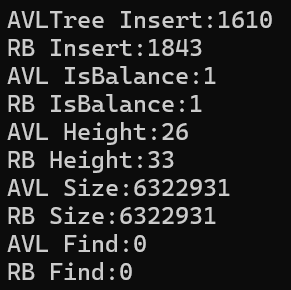
实践上一般使用红黑树更多,因为AVL树需要维护每个节点的平衡因子,且需额外存储高度信息。红黑树仅需维护节点的颜色。