假设在画布中,我们有这样一个道路路线
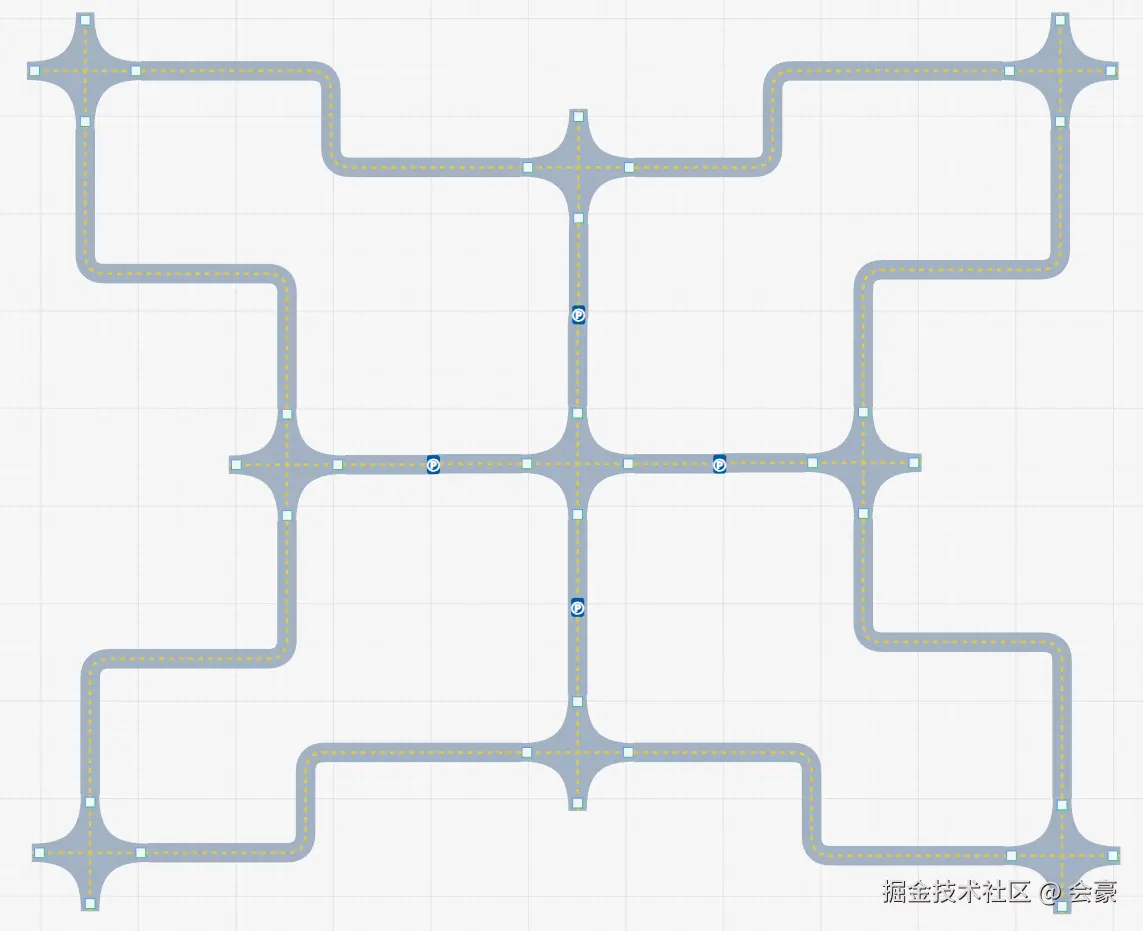
我们要如何把这样一个路线转为json结构呢,并且我们可以看到,在最中间的十字路所相连的道路上都有一个P点标志,这是用户自定义的停靠点标识
道路的本质是path字符串,格式如下
M 644 398.5 L 644 278 C 644 264.67 650.67 258 664 258 L 826 258 C 839.33 258 846 251.33 846 238 L 846 113.5
在这个字符串里面并不包含用户自定义的停靠点,停靠点是一个数组结构的数据,格式如下
labels?: {
text: string
distance: number
}[]
停靠点可以设置多个,如下图
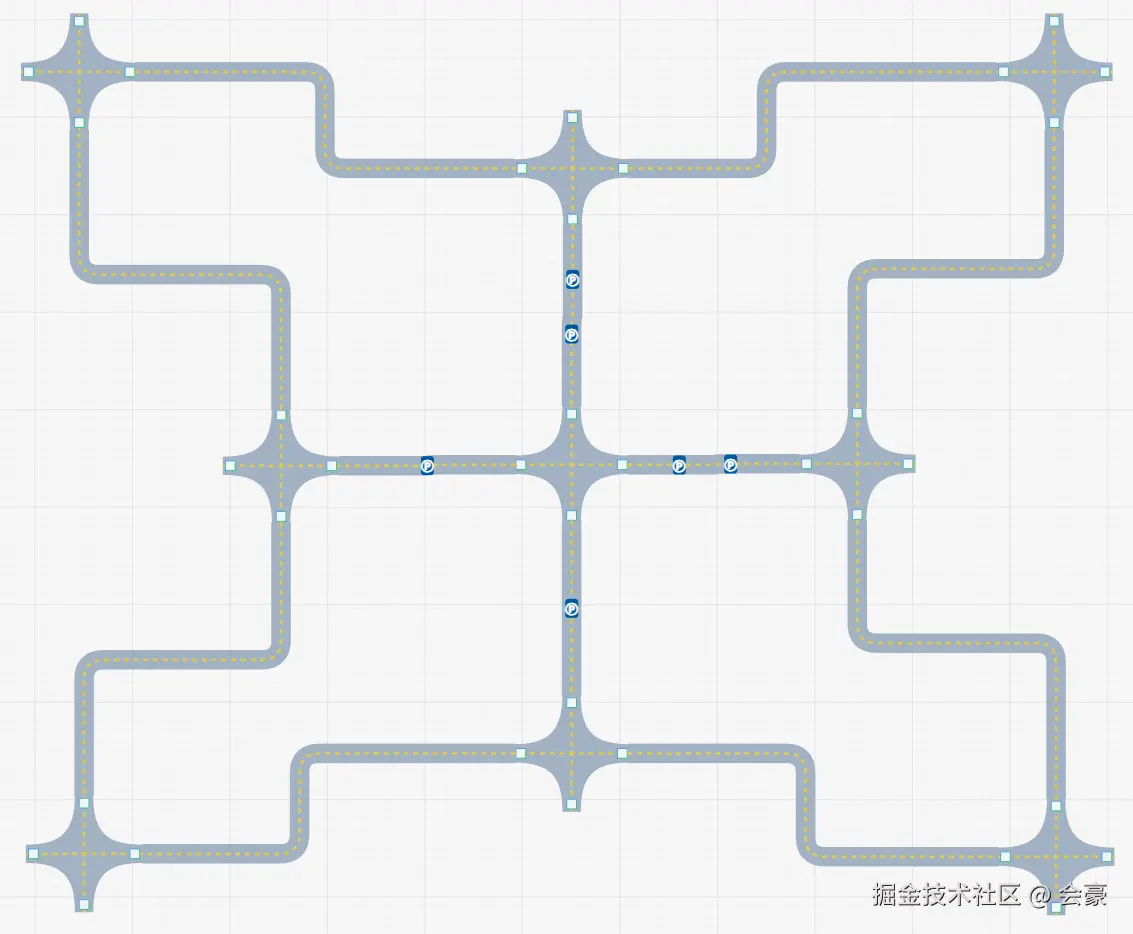
接下来我们需要解析path字符串,以及解析用户自定义的停靠点,并且将两者结合起来,形成一个图结构的数据,方便后面的A 算法寻找最优路径*
设计思路
-
获取画布里面所有的【十字路,道路】
-
遍历所有的道路
2.1 解析道路的path字符串,解析成下面的格式
ts
export interface PathPoint {
x: number
y: number
type: string
t: number
}x表示在画布上,该点位的绝对坐标值
y同理
type表示 带点为的类型
t是相对坐标【0-1】
比如说这样一个path字符串
M 644 398.5 L 644 278 C 644 264.67 650.67 258 664 258 L 826 258 C 839.33 258 846 251.33 846 238 L 846 113.5
经过解析后
ts
[
{ x: 644, y: 398.5, type: 'moveto', t: 0 },
{ x: 644, y: 278, type: 'lineto', t: 0.25597 },
{ x: 644, y: 264.67, type: 'control1', t: 0.281994 },
{ x: 650.67, y: 258, type: 'control2', t: 0.298011 },
{ x: 664, y: 258, type: 'curveto', t: 0.324004 },
{ x: 826, y: 258, type: 'lineto', t: 0.667972 },
{ x: 839.33, y: 258, type: 'control1', t: 0.693992 },
{ x: 846, y: 251.33, type: 'control2', t: 0.71001 },
{ x: 846, y: 238, type: 'curveto', t: 0.736006 },
{ x: 846, y: 113.5, type: 'lineto', t: 1 }
]可以看到每个点位的绝对坐标,和相对位置
2.2 然后这时,我们再去解析用户自定义的停靠点,停靠点的格式我们已经知道,接下来就是解析成上面的格式,停靠点的相对位置我们已经有了,只需要根据相对坐标获取到绝对位置,type不重要,方法如下
ts
import { svgPathProperties } from 'svg-path-properties'
private getPointByAt(
path: string,
t: number
): {
x: number
y: number
t: number
} {
if (t < 0 || t > 1) {
throw new Error('参数 t 必须在 0 到 1 之间')
}
const properties = new svgPathProperties(path)
const totalLength = properties.getTotalLength()
// 获取指定位置的坐标点
const point = properties.getPointAtLength(totalLength * t)
return {
x: point.x,
y: point.y,
t
}
}2.3 接下来我们只需要将这两个数组进行一个融合即可,但是要注意,融合后,要根据 t 值进行从小到大排序
ts
const allPoints = [...pathPoints, ...labelPoints].sort((p1, p2) => p1.t - p2.t)2.4 到这时我们的所有点位都解析完毕,到下一步就需要串接所有的点位,形成一个类似双向链表的数据结构,此时我们需要注意,要记录开始点位和结束点位,因为后面的十字路节点需要和道路的开始点位和结束点位进行串接
代码如下
ts
let sourceId = '' //记录开始点位
let targetId = '' //记录结束点位
const graphRouting = {} as any
//是一个元素的id
let preUUID = ''
allPoints.forEach((point, index) => {
const uuid = generateUUID()
if (index > 0) {
graphRouting[uuid] = {
position: [point.x, point.y],
route: [preUUID]
}
graphRouting[preUUID].route.push(uuid)
} else {
graphRouting[uuid] = {
position: [point.x, point.y],
route: []
}
}
if (index === 0 && typeof edge.sourceId === 'string') {
graphRouting[uuid].route.push(edge.sourceId)
}
if (index === allPoints.length - 1 && typeof edge.targetId === 'string') {
graphRouting[uuid].route.push(edge.targetId)
}
if (index === 0) {
sourceId = uuid
}
if (index === allPoints.length - 1) {
targetId = uuid
}
preUUID = uuid
})以这个数据结构为例
ts
[
{ x: 644, y: 398.5, type: 'moveto', t: 0 },
{ x: 644, y: 278, type: 'lineto', t: 0.25597 },
{ x: 644, y: 264.67, type: 'control1', t: 0.281994 },
{ x: 650.67, y: 258, type: 'control2', t: 0.298011 },
{ x: 664, y: 258, type: 'curveto', t: 0.324004 },
{ x: 826, y: 258, type: 'lineto', t: 0.667972 },
{ x: 839.33, y: 258, type: 'control1', t: 0.693992 },
{ x: 846, y: 251.33, type: 'control2', t: 0.71001 },
{ x: 846, y: 238, type: 'curveto', t: 0.736006 },
{ x: 846, y: 113.5, type: 'lineto', t: 1 }
]经过整合后,得到下面的数据结构
ts
{
'0-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx': { position: [ 644, 398.5 ], route: [ '1-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx' ] },
'1-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx': {
position: [ 644, 278 ],
route: [ '0-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx', '2-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx' ]
},
'2-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx': {
position: [ 644, 264.67 ],
route: [ '1-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx', '3-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx' ]
},
'3-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx': {
position: [ 650.67, 258 ],
route: [ '2-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx', '4-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx' ]
},
'4-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx': {
position: [ 664, 258 ],
route: [ '3-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx', '5-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx' ]
},
'5-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx': {
position: [ 826, 258 ],
route: [ '4-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx', '6-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx' ]
},
'6-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx': {
position: [ 839.33, 258 ],
route: [ '5-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx', '7-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx' ]
},
'7-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx': {
position: [ 846, 251.33 ],
route: [ '6-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx', '8-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx' ]
},
'8-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx': {
position: [ 846, 238 ],
route: [ '7-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx', '9-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx' ]
},
'9-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx': { position: [ 846, 113.5 ], route: [ '8-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx' ] }
}-
然后我们再去遍历所有的十字路节点,将十字路和道路相连起来,十字路可以看作一个点位,然后查看有哪些道路和当前的十字路连接
-
如果有连接,就查看连接的是起点还是终点,如果是起点就将十字路与道路的sourceId 连接起来,如果是终点,就将十字路和道路的targetId连接起来
-
最后我们将道路的数据和十字路的数据整合到一起,就构成了整个的路径网络
完整源代码
ts
//初始化交通网络
public parsePathWithAccurateT(pathData: string): PathPoint[] {
const props = new svgPathProperties(pathData)
const segments: PathPoint[] = []
// 获取路径采样点,用于计算累积长度
const totalSamples = 500
const samplePoints: { x: number; y: number; length: number }[] = []
let totalLength = 0
let last = props.getPointAtLength(0)
samplePoints.push({ ...last, length: 0 })
for (let i = 1; i <= totalSamples; i++) {
const p = props.getPointAtLength((i / totalSamples) * props.getTotalLength())
const d = Math.hypot(p.x - last.x, p.y - last.y)
totalLength += d
samplePoints.push({ ...p, length: totalLength })
last = p
}
// 查找最接近某个点在路径中的累积长度
function findT(x: number, y: number): number {
let minDist = Infinity
let bestLength = 0
for (const p of samplePoints) {
const dist = Math.hypot(p.x - x, p.y - y)
if (dist < minDist) {
minDist = dist
bestLength = p.length
}
}
return +(bestLength / totalLength).toFixed(6)
}
// 解析 path 命令,提取关键点
const commands = pathData.match(/[a-df-z][^a-df-z]*/gi) || []
let current = { x: 0, y: 0 }
for (const cmd of commands) {
const type = cmd[0]
const nums = cmd
.slice(1)
.trim()
.split(/[\s,]+/)
.map(Number)
if (type.toLowerCase() === 'm' || type.toLowerCase() === 'l') {
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i += 2) {
const [x, y] = [nums[i], nums[i + 1]]
current = { x, y }
segments.push({ x, y, type: type === 'M' ? 'moveto' : 'lineto', t: findT(x, y) })
}
} else if (type.toLowerCase() === 'c') {
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i += 6) {
const [x1, y1, x2, y2, x, y] = nums.slice(i, i + 6)
segments.push({ x: x1, y: y1, type: 'control1', t: findT(x1, y1) })
segments.push({ x: x2, y: y2, type: 'control2', t: findT(x2, y2) })
segments.push({ x, y, type: 'curveto', t: findT(x, y) })
current = { x, y }
}
}
}
return segments
}
private getPointByAt(
path: string,
t: number
): {
x: number
y: number
t: number
} {
if (t < 0 || t > 1) {
throw new Error('参数 t 必须在 0 到 1 之间')
}
const properties = new svgPathProperties(path)
const totalLength = properties.getTotalLength()
// 获取指定位置的坐标点
const point = properties.getPointAtLength(totalLength * t)
return {
x: point.x,
y: point.y,
t
}
}
public initTrafficNet() {
const canvas = Canvas.getCanvas()
//过滤出所有十字路口的节点
const crossingNodes = canvas.nodes.filter((node) => node.shape === 'cross-node')
//过滤出所有的道路
const roadEdges = canvas.edges.filter((edge) => edge.shape === 'road-edge')
//返回结果
const edgeResult = [] as { id: string; sourceId: string; targetId: string; data: any }[]
//遍历所有的道路
roadEdges.forEach((edge) => {
//获取path的所有端点
const path = edge.simData?.path || ''
// 这是path的所有点位
const pathPoints = this.parsePathWithAccurateT(path)
/**
* 获取所有用户自定义的点位
*/
const labels = edge.labels || []
const labelPoints = labels.map((item) => {
return this.getPointByAt(path, item.distance)
})
const allPoints = [...pathPoints, ...labelPoints].sort((p1, p2) => p1.t - p2.t)
let sourceId = '' //记录开始点位
let targetId = '' //记录结束点位
const graphRouting = {} as any
//是一个元素的id
let preUUID = ''
allPoints.forEach((point, index) => {
const uuid = generateUUID()
if (index > 0) {
graphRouting[uuid] = {
position: [point.x, point.y],
route: [preUUID]
}
graphRouting[preUUID].route.push(uuid)
} else {
graphRouting[uuid] = {
position: [point.x, point.y],
route: []
}
}
if (index === 0 && typeof edge.sourceId === 'string') {
graphRouting[uuid].route.push(edge.sourceId)
}
if (index === allPoints.length - 1 && typeof edge.targetId === 'string') {
graphRouting[uuid].route.push(edge.targetId)
}
if (index === 0) {
sourceId = uuid
}
if (index === allPoints.length - 1) {
targetId = uuid
}
preUUID = uuid
})
edgeResult.push({
id: edge.id,
sourceId: sourceId,
targetId: targetId,
data: graphRouting
})
})
const nodeResult = {} as any
//遍历所有的十字路
crossingNodes.forEach((node) => {
//整理输入
const inputEdges = roadEdges.filter((edge) => edge.targetId === node.id)
const inputEdgeIds = inputEdges.map((item) => item.id)
//整理输出
const outputEdges = roadEdges.filter((edge) => edge.sourceId === node.id)
const outputEdgeIds = outputEdges.map((item) => item.id)
const inputRoute = inputEdgeIds.map((id) => {
return edgeResult.find((item) => item.id === id)?.targetId
})
const outputRoute = outputEdgeIds.map((id) => {
return edgeResult.find((item) => item.id === id)?.sourceId
})
const totalRoute = [...inputRoute, ...outputRoute]
nodeResult[node.id] = {
position: [node.x + 60, node.y + 60],
route: totalRoute
}
})
const result = edgeResult
.map((item) => {
return item.data
})
.concat(nodeResult)
// 合并两个数据源
const mergeRouteData = (data: RouteObject[]): RouteObject => {
return data.reduce((acc, curr) => {
// 将当前对象的每个元素合并到结果中
for (const key in curr) {
if (curr.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
acc[key] = curr[key]
}
}
return acc
}, {} as RouteObject)
}
// 调用合并函数
this._trafficGraph = mergeRouteData(result)
return this._trafficGraph
}根据这个网络,我们就可以让AGV小车沿着这个路径网络去运送物品
下面我附加一个A算法,寻找最优路径,不属性A算法的小伙伴可以看我这篇文章
ts
// 获取两个点之间的距离(这里使用欧几里得距离作为启发式估算)
private calculateDistance(position1: Point, position2: Point): number {
const dx = position2[0] - position1[0]
const dy = position2[1] - position1[1]
return Math.sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy) // 欧几里得距离
}
//获取到最优路径
public getOptimalPath(startId: string, targetId: string) {
const openList: Set<string> = new Set()
const closedList: Set<string> = new Set()
const gScores: { [key: string]: number } = {}
const fScores: { [key: string]: number } = {}
const cameFrom: { [key: string]: string | null } = {}
// 初始化
for (const nodeId in this._trafficGraph) {
if (this._trafficGraph.hasOwnProperty(nodeId)) {
gScores[nodeId] = Infinity
fScores[nodeId] = Infinity
cameFrom[nodeId] = null
openList.add(nodeId)
}
}
gScores[startId] = 0
fScores[startId] = this.calculateDistance(
this._trafficGraph[startId].position,
this._trafficGraph[targetId].position
)
while (openList.size > 0) {
// 从 openList 中选择 f 值最小的节点
let currentId = ''
let lowestFScore = Infinity
for (const nodeId of openList) {
if (fScores[nodeId] < lowestFScore) {
lowestFScore = fScores[nodeId]
currentId = nodeId
}
}
if (currentId === targetId) {
// 找到目标节点,重建路径
const path: string[] = []
let current = targetId
while (current !== null) {
path.unshift(current)
current = cameFrom[current]!
}
return path
}
// 从 openList 移除当前节点并加入到 closedList
openList.delete(currentId)
closedList.add(currentId)
// 遍历邻居节点
const currentNode = this._trafficGraph[currentId]
for (const neighborId of currentNode.route) {
if (closedList.has(neighborId)) {
continue // 如果该邻居已在 closedList 中,跳过
}
if (!this._trafficGraph[neighborId]?.position) {
new Error('搬运设备未找到对应点位')
}
const tentativeGScore =
gScores[currentId] +
this.calculateDistance(currentNode.position, this._trafficGraph[neighborId].position)
if (!openList.has(neighborId)) {
openList.add(neighborId)
}
if (tentativeGScore < gScores[neighborId]) {
cameFrom[neighborId] = currentId
gScores[neighborId] = tentativeGScore
fScores[neighborId] =
gScores[neighborId] +
this.calculateDistance(
this._trafficGraph[neighborId].position,
this._trafficGraph[targetId].position
)
}
}
}
// 如果 openList 为空,表示没有路径
return []
}