前言
链表和顺序表是经常被拿出来对比的东西,就更要知道这两个的区别和如何使用,链表分为八种,带不带头(哨兵位的头结点),双不双向(C++里的list 和forward_list),循不循环(尾指针指向的是空,还是指向头结点,参考list中的begin和end迭代器)
本次实现双向带头循环和单向不带头不循环链表,这样所有的类型基本上都可以写出来了.
一、单向链表
单向链表没啥说的,一张图介绍一下
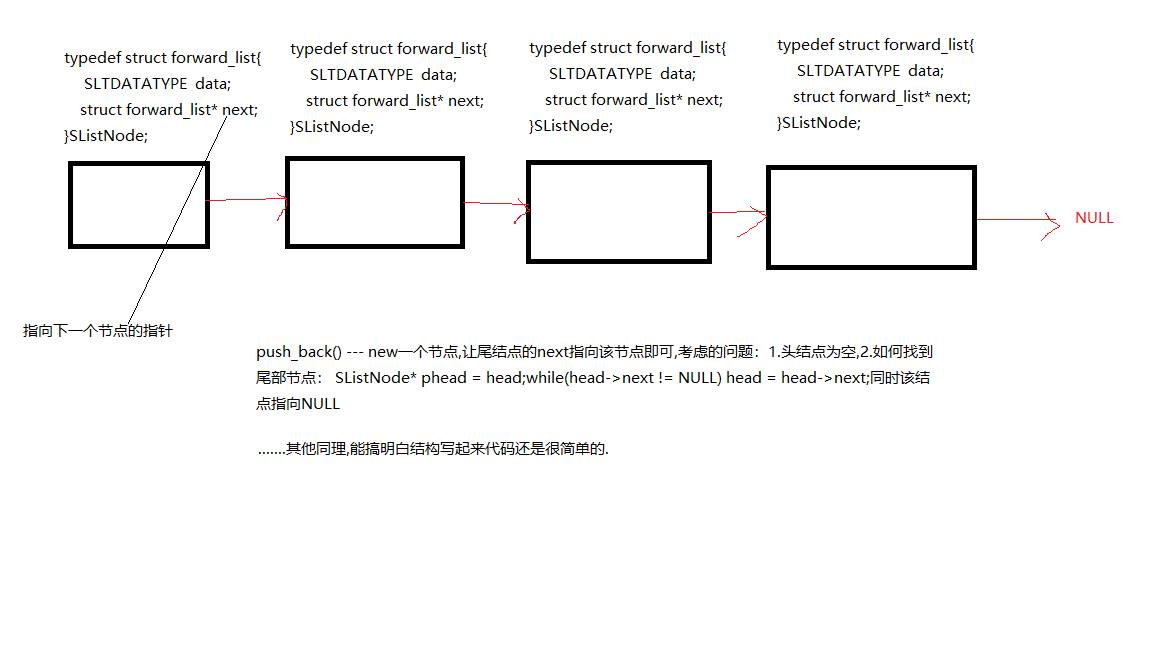
有一个问题关于二级指针的, 比如push_back(SListNode *head,SLTDATATYPE val) 这样对吗?当然不对,你可能会问,这本身就是指针为什么需要二级指针,为什么不对?因为当单链表是空的时候要修改头指针!所以这里要注意:1.使用二级指针,2:使用引用来玩
注意: 在pos后插入和pos前插入不需要二级指针,因为没有对指针本身进行修改,就不需要二级
如果有可能修改原来的指针,一定要用二级指针!!!
这里提到一下C++里的关于形参类型的标准
1.输入型参数 const xxx
2.输出型 * xxx
3.输入输出型 & xxxx
二、单链表的具体实现
c
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<assert.h>
#define SLTDATATYPE int
typedef struct SlistNode
{
SLTDATATYPE data;
struct SlistNode* next;
//SLTNode* next; //这种方式不行 因为得现有下面的名称SLTNode
//SLT Single list
}SLTNode;
void Print(SLTNode * pHead);
void SLPushBack(SLTNode** ppHead, SLTDATATYPE x);
void SLTPushFront(SLTNode** ppHead, SLTDATATYPE x);
SLTNode* BuySLTNode(SLTDATATYPE x);
//搞结点用的
void SLPopBack(SLTNode** ppHead);
void SLTPopFront(SLTNode** ppHead);
//查找-----也可以修改
SLTNode* SListFind(SLTNode* phead, SLTDATATYPE x);
SLTNode* SListFind(SLTNode* phead, SLTDATATYPE x);
//pos之前插入
void SListInsert(SLTNode** ppHead,SLTNode* pos, SLTDATATYPE x);
//pos位置删除
void SListErase(SLTNode** ppHead,SLTNode* pos);
//pos后面插入
void SListInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDATATYPE x);
//pos位置后面删除
void SListEraseAfter(SLTNode* pos);
void SLTDestroy(SLTNode** pHead);
void Print(SLTNode* pHead)
{
//不需要断言 assert 本身就是空
SLTNode* cur = pHead;
while (cur)
{
printf("%d->", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
void SLTPushFront(SLTNode** ppHead, SLTDATATYPE x)
{
SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTNode(x);
newnode->next = *ppHead;
*ppHead = newnode;
}
void SLPopBack(SLTNode** ppHead)
{
assert(*ppHead!=NULL);
if ((*ppHead)->next == NULL)
{
free(*ppHead);
*ppHead = NULL;
}
else
{
SLTNode* prev = NULL;
SLTNode* tail = *ppHead;
while (tail->next)
{
prev = tail;
tail = tail->next;
}
free(tail);
tail = NULL;
prev->next = NULL;
}
}
void SLTPopFront(SLTNode** ppHead)
{
assert(*ppHead);
SLTNode* first = *ppHead;
*ppHead = first->next;
free(first);
first = NULL;
}
SLTNode* SListFind(SLTNode* phead, SLTDATATYPE x);
SLTNode* SListFind(SLTNode* phead, SLTDATATYPE x)
{
SLTNode* find = phead;
while (find)
{
if (find->data == x)
{
return find;
}
find = find->next;
}
return NULL;
}
void SListInsert(SLTNode** ppHead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDATATYPE x)
{
assert(ppHead);
assert(pos);
SLTNode* cur = *ppHead;
if (pos == *ppHead)
{
SLTPushFront(ppHead, x);
}
else
{
while (cur->next != pos)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTNode(x);
cur->next = newnode;
newnode->next = pos;
}
}
//pos位置删除
// pos
//0->1->//2//->3->4->5
void SListErase(SLTNode** ppHead, SLTNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
assert(ppHead);
assert(*ppHead);
SLTNode* cur = *ppHead;
if (*ppHead == pos)
{
SLTPopFront(ppHead);
}
while (cur->next != pos)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = pos->next;
free(pos);
}
void SListInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDATATYPE x)
{
assert(pos);
SLTNode* newNode = BuySLTNode(x);
newNode->next = pos->next;
pos->next = newNode;
}
//pos位置后面删除
void SListEraseAfter(SLTNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
assert(pos->next);
//pos->next = pos->next->next;//这样做不行
SLTNode* del = pos->next;
pos->next = pos->next->next;
free(del);
del = NULL;
// pos
}
void SLPushBack(SLTNode** ppHead, SLTDATATYPE x)
{
SLTNode * cur=BuySLTNode(x);
//如果本身为空
if (*ppHead == NULL)
{
*ppHead = cur;
}
else
{
SLTNode* tail = *ppHead;
while (tail->next)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = cur;
cur->next = NULL;
}
}
SLTNode* BuySLTNode(SLTDATATYPE x)
{
SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc");
return NULL;
}
newnode->next = NULL;
newnode->data = x;
return newnode;
}
void SLTDestroy(SLTNode** ppHead)
{
SLTNode* cur = *ppHead;
while (cur)
{
SLTNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
*ppHead = NULL;
}数据结构作业
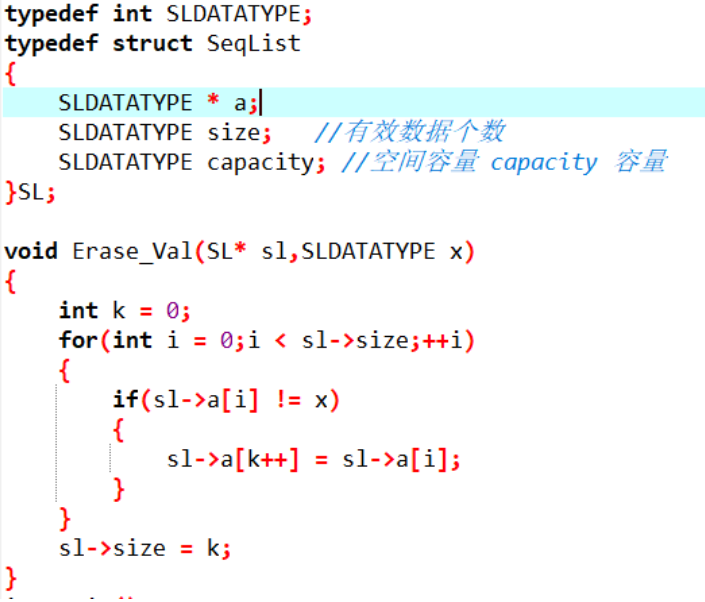
1.正好数据结构留了这个作业,就写一下,思路不是很难,遇到不是x的值直接从开始去覆盖即可.
2、定义三元组(a, b, c)(a、b、c均为正数)的距离D = |a - b| + |b - c| + |c - a|。给定3个非空整数集合S1、S2和S3,按升序分别存储在3个数组中。请设计一个尽可能高效的算法,计算并输出所有可能的三元组(a, b, c)(a ∈ S1, b ∈ S2, c ∈ S3)中的最小距离。例如 S1 = { -1, 0, 9},S2 = {-25, -10, 10, 11}, S3 = {2, 9, 17, 30, 41},则最小距离为2,相应的三元组为(9,10,9)。要求:
(1)给出算法的基本设计思想
(2)根据设计思想,采用C语言或C++语言描述算法,关键之处给出注释。
(3)说明你所设计算法的时间复杂度和空间复杂度。
思路和代码如下
cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5;
int a[N], b[N], c[N];
// 思路:D = |a - b| + |b - c | + |c - a| -> D = 2 max(a,b,c) - min(a,b,c)
// 算法:用三指针来遍历
// 每次记录一个max和min,如果ans更小就更新,
// 每次移动最小的指针,因为是升序,这样才有可能更小,有一个停止就结束
// 因为要记录三元组,所以需要遍历两次
// 时间复杂度O(posa + posb + posc) 其中posa,posb,posc为三个数组中的长度
// 空间复杂度O(1) 不需要开额外空间
int main()
{
int na, nb, nc;
cin >> na >> nb >> nc;
int posa = 0, posb = 0, posc = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < na; ++i)
{
int x;cin >> x;
if (x > 0) a[posa++] = x;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nb; ++i)
{
int x;cin >> x;
if (x > 0) b[posb++] = x;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nc; ++i)
{
int x;cin >> x;
if (x > 0) c[posc++] = x;
}
int maxi = 0, mini = 0, ans = 1e9;
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
while (i < posa && j < posb && k < posc)
{
int maxi = max(max(a[i], b[j]), c[k]);
int mini = min(min(a[i], b[j]), c[k]);
ans = min(ans, (maxi - mini) * 2);
if (ans == 0) { break; }
if (a[i] == mini) i++;
else if (b[j] == mini) j++;
else k++;
}
cout << "最小的D为" << ans << '\n';
//输出三元组
i = j = k = 0;
while (i < posa && j < posb && k < posc)
{
int maxi = max(max(a[i], b[j]), c[k]);
int mini = min(min(a[i], b[j]), c[k]);
if(2 * (maxi - mini) == ans)
{
cout << "符合条件的三元组之一为" << a[i] << ',' << b[j] << ',' << c[k] << '\n';
}
if (a[i] == mini) i++;
else if (b[j] == mini) j++;
else k++;
}
return 0;
}三、双向链表
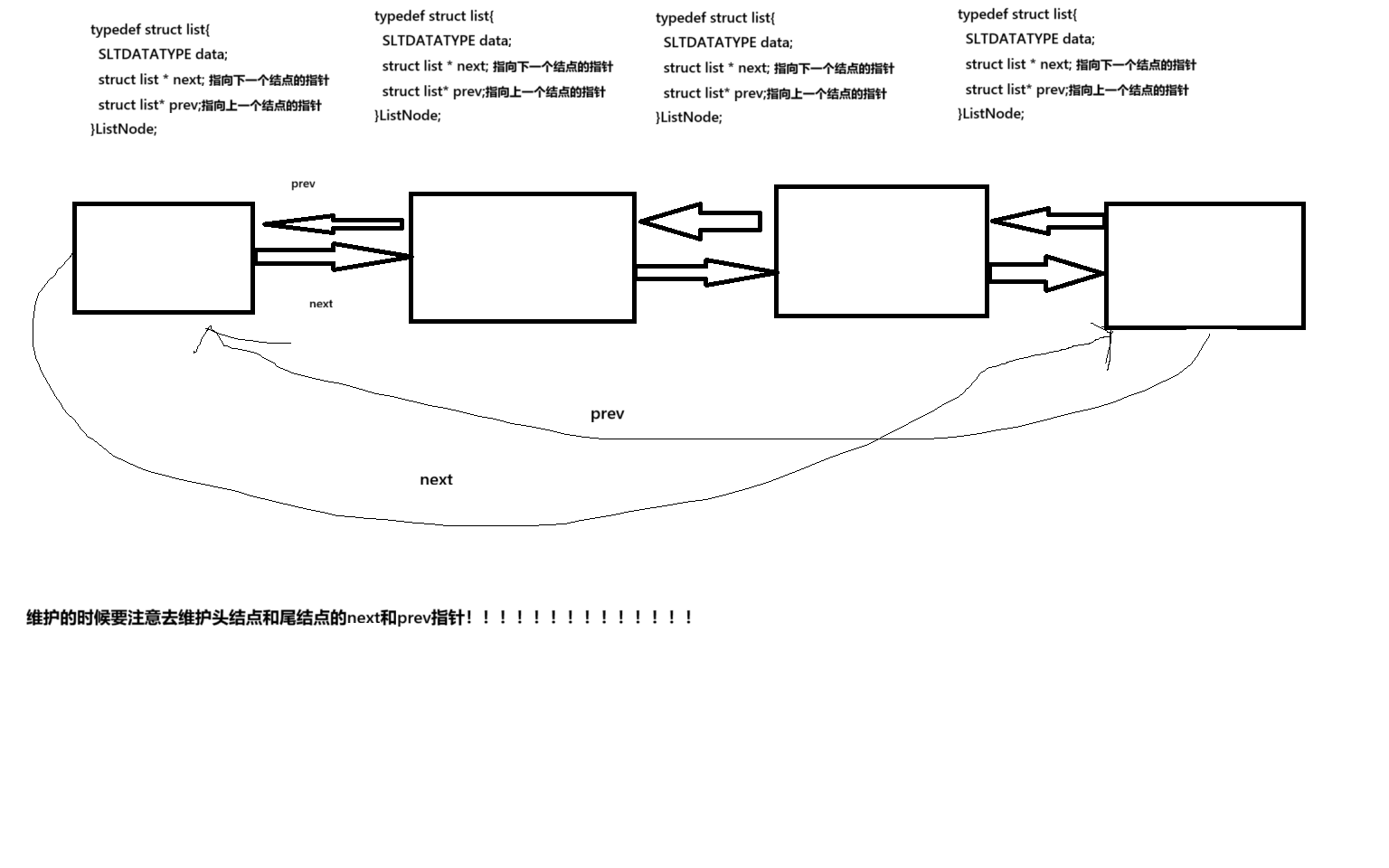
其实和单向链表的差别不是很大,多了一个prev指针,来指向上一个结点,这里我画图画的是双向不带头循环链表
四、代码实现
我实现的是带头双向循环链表,带头的情况下一些函数就不需要传二级指针了。
既然带头了,就要控制好,头结点的next结点实际上才是真正的数据,记住这一点还是比较好维护的。也要记得维护next和prev指针,不要忘了某一个.
cpp
//链表--双向
#include <stdlib.h>//system //qsort //malloc
#include <stdio.h>//return 0
#include <assert.h>//assert 断言
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
typedef int LTDATATYPE;
typedef struct DlistNode
{
struct DlistNode* next;
struct DlistNode* prev;
LTDATATYPE data;
}LTNode;
LTNode* LTInit();
//可以传二级指针,也可以用返回值去接受
void Destory(LTNode* phead);
void LTPushback(LTNode* phead, LTDATATYPE x);
void LTPopback(LTNode* phead, LTDATATYPE x);
LTNode *BuyListnode(LTDATATYPE x);
void LTPrint(LTNode* phead);
bool LTEmpty(LTNode* phead);
void LTPushfront(LTNode* phead, LTDATATYPE x);
void LTPopfront(LTNode* phead);
void LTErase(LTNode* pos);
void LTInsert(LTNode* pos, LTDATATYPE x);
LTNode* find(LTNode* phead, LTDATATYPE x);
LTNode* LTInit()//**ppHead
{
LTNode * head = BuyListnode(-1);
head->next = head;
head->prev = head;
return head;
}
void LTPrint(LTNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
LTNode* cur = phead->next;
printf("<=head=>");
while (cur != phead)
{
printf("%d <=>", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
}
LTNode *BuyListnode(LTDATATYPE x)
{
LTNode* node =(LTNode*) malloc(sizeof(LTNode));
if (node == NULL)
{
perror("malloc");
return NULL;
}
node->next = NULL;
node->prev = NULL;
node->data = x;
return node;
}
void Destory(LTNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
LTNode* cur = phead;
while (cur != phead)
{
LTNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
free(phead);
phead = NULL;
}
void LTPushback(LTNode* phead, LTDATATYPE x)
{
assert(phead);
LTNode* newnode = BuyListnode(x);
LTNode* tail = phead->prev;
tail->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = tail;
newnode->next =phead;
phead->prev = newnode;
}
bool LTEmpty(LTNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
return phead->next == phead;
}
//phead tailprev tail
void LTPopback(LTNode* phead, LTDATATYPE x)
{
assert(phead);
assert(!LTEmpty(phead));
LTNode* tail = phead->prev;
LTNode* tailprev = tail->prev;
tailprev->next = phead;
phead->prev = tailprev;
free(tail);
tail = NULL;
}
//phead node p1
void LTPushfront(LTNode* phead, LTDATATYPE x)
{
assert(phead);
LTNode* node = BuyListnode(x);
node->next = phead->next;
phead->next->prev = node;
phead->next = node;
node->prev = phead;
}
//head next
//head 1 2 3 4 5
void LTPopfront(LTNode* phead)
{
assert(phead);
assert(!LTEmpty(phead));
LTNode* next = phead->next;
phead->next = next->next;
next->next->prev = phead;
}
//pos
//head 1 2 3
void LTErase(LTNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
LTNode* prev = pos->prev;
LTNode* next = pos->next;
prev->next = next;
next->prev = prev;
free(pos);
pos = NULL; //形参的改变不影响实参,给pos置空没有意义
}// pos
//head 1 2 3 pos 4 5
//pos newnode next
//head 1 2 3 4 5
void LTInsert(LTNode* pos, LTDATATYPE x)
{
LTNode* newnode = BuyListnode(x);
LTNode * next = pos->next;
//pos newnode next
pos->next = newnode;
newnode->prev = pos;
newnode->next = next;
next->prev = newnode;
}
LTNode* find(LTNode* phead, LTDATATYPE x)
{
LTNode *find = phead->next;
while (find != phead)
{
if (find->data == x)
{
return find;
}
find = find->next;
}
return NULL;
}总结
下次应该是栈和队列