C++范围操作(2)
主要介绍c++23中的范围操作
ranges相关
1、std::ranges::to
在c++20中,想要将结果转成最终的容器,需要手动操作,c++23中提供了常用容器的转换操作
cpp
int main() {
// 转成vector
std::vector vec = std::views::iota(1, 21)
| std::views::filter([](int it) { return it % 3 == 0; })
| std::ranges::to<std::vector>();
std::cout << endl << "-------------vector-----------------" << endl;
for (int x : vec) {
std::cout << x << ", ";
}
// 转成list
std::list list1 = std::views::iota(1, 21)
| std::views::filter([](int it) { return it % 3 == 0; })
| std::ranges::to<std::list>();
std::cout << endl << "-------------list-----------------" << endl;
for (int x : list1) {
std::cout << x << ", ";
}
// 转成forward_list
std::forward_list list2 = std::views::iota(1, 21)
| std::views::filter([](int it) { return it % 3 == 0; })
| std::ranges::to<std::forward_list>();
std::cout << endl << "-------------forward_list-----------------" << endl;
for (int x : list2) {
std::cout << x << ", ";
}
// 转成set
std::set set = std::views::iota(1, 21)
| std::views::filter([](int it) { return it % 3 == 0; })
| std::ranges::to<std::set>();
std::cout << endl << "-------------set-----------------" << endl;
for (int x : set) {
std::cout << x << ", ";
}
// 转成map
std::map map1 = std::views::iota(1, 21)
| std::views::filter([](int it) { return it % 3 == 0; })
| std::views::enumerate // 生成索引
| std::ranges::to<std::map>();
std::cout << endl << "-------------map-----------------" << endl;
for (auto entry : map1) {
std::cout << "(" << entry.first << "," << entry.second << ") , ";
}
// 转成queue
std::queue que1 = std::views::iota(1, 21)
| std::views::filter([](int it) { return it % 3 == 0; })
| std::ranges::to<std::queue>();
std::cout << endl << "-------------queue-----------------" << endl;
while (!que1.empty())
{
cout << que1.front() << ", ";
que1.pop();
}
// 转成deque
std::deque que2 = std::views::iota(1, 21)
| std::views::filter([](int it) { return it % 3 == 0; })
| std::ranges::to<std::deque>();
std::cout << endl << "-------------deque-----------------" << endl;
while (!que2.empty())
{
cout << que2.front() << ", ";
que2.pop_front();
}
// 转成priority_queue
std::priority_queue que3 = std::views::iota(1, 21)
| std::views::filter([](int it) { return it % 3 == 0; })
| std::ranges::to<std::priority_queue>();
std::cout << endl << "-------------priority_queue-----------------" << endl;
while (!que3.empty())
{
cout << que3.top() << ", ";
que3.pop();
}
// 转成stack
std::stack stk = std::views::iota(1, 21)
| std::views::filter([](int it) { return it % 3 == 0; })
| std::ranges::to<std::stack>();
std::cout << endl << "-------------stack-----------------" << endl;
while (!stk.empty())
{
cout << stk.top() << ", ";
stk.pop();
}
return 0;
}2、std::ranges::fold_left与std::ranges::fold_right
- std::ranges::fold_left
- 左折叠顺序 :操作顺序为
f(f(f(init, x1), x2), ..., xn) - 灵活参数:支持迭代器对或直接传入范围对象
- 类型安全 :提供编译时类型检查,比传统
std::accumulate更安全
- 左折叠顺序 :操作顺序为
- std::ranges::fold_right、
- 左折叠顺序 :操作顺序为
f(x1, f(x2, f(..., f(xn, init)...)) - 灵活参数:支持迭代器对或直接传入范围对象
- 类型安全 :提供编译时类型检查,比传统
std::accumulate更安全
c++
- 左折叠顺序 :操作顺序为
cpp
int main()
{
system("chcp 65001");
auto view = std::views::iota(1, 11)
| std::views::filter([](int it) { return it > 0; });
// 加法
int result1 = std::ranges::fold_left(view, 0, std::plus<int>());
int result2 = std::ranges::fold_right(view, 0, std::plus<int>());
std::cout << "result2= " << result2 << endl;
std::cout << "result2= " << result2 << endl;
// 减法
result1 = std::ranges::fold_left(view, 0, std::minus<int>());
result2 = std::ranges::fold_right(view, 0, std::minus<int>());
std::cout << "result1= " << result1 << endl;
std::cout << "result2= " << result2 << endl;
// 乘法
result1 = std::ranges::fold_left(view, 1, std::multiplies<int>());
result2 = std::ranges::fold_right(view, 1, std::multiplies<int>());
std::cout << "result1= " << result1 << endl;
std::cout << "result2= " << result2 << endl;
// 除法
double db1 = std::ranges::fold_left(view, 1, std::divides<double>());
double db2 = std::ranges::fold_right(view, 1, std::divides<double>());
std::cout << "db1= " << db1 << endl;
std::cout << "db2= " << db2 << endl;
// 自定义操作
auto opt = [](int a, int b) {return 2 * a + b * 3; };
result1 = std::ranges::fold_left(view, 0, opt);
result2 = std::ranges::fold_right(view, 0, opt);
std::cout << "result1= " << result1 << endl;
std::cout << "result2= " << result2 << endl;
// 字符串拼接
auto view1 = view | std::views::transform([](int i) {return std::to_string(i) + ", "; });
string str1 = std::ranges::fold_left(view1, std::string(), std::plus<string>());
string str2 = std::ranges::fold_right(view1, std::string(), std::plus<string>());
std::cout << "str1= " << str1 << endl;
std::cout << "str2= " << str2 << endl;
return 0;
}java
java
// 加法
int result = IntStream.rangeClosed(1, 10)
.boxed()
.reduce(0, Integer::sum);
System.out.println("result-> " + result);
// 减法
result = IntStream.rangeClosed(1, 10)
.boxed()
.reduce(0, (a, b) -> a - b);
System.out.println("result-> " + result);
// 乘法
result = IntStream.rangeClosed(1, 10)
.boxed()
.reduce(1, (a, b) -> a * b);
System.out.println("result-> " + result);
// 除法
result = IntStream.rangeClosed(1, 10)
.boxed()
.reduce(1, (a, b) -> a / b);
System.out.println("result-> " + result);
// 字符串拼接
String str1 = IntStream.rangeClosed(1, 10)
.boxed()
.map(String::valueOf)
.collect(Collectors.joining(", ", "[", "]"));
System.out.println("str1-> " + str1);3、std::ranges::distance
用于计算范围或迭代器对之间距离
c++
cpp
int main()
{
system("chcp 65001");
auto view = std::views::iota(1, 11)
| std::views::filter([](int it) { return it % 3 == 0; });
std::cout << "distance= " << std::ranges::distance(view) << endl;
return 0;
}java
java
long count = IntStream.rangeClosed(1, 10)
.boxed()
.filter(it -> it % 3 == 0) // 过滤
.count();
System.out.println("count-> " + count);4、std::ranges::find_if与std::ranges::find_last_if
c++
cpp
int main()
{
system("chcp 65001");
auto view = std::views::iota(1, 11)
| std::views::filter([](int it) { return it % 2 == 0; });
// find_if
auto result = std::ranges::find_if(view, [](int a) { return a > 5; });
if (result != view.end()) {
std::cout << "find_if= " << *result << endl;
}
// find_if_not
result = std::ranges::find_if_not(view, [](int a) { return a > 5; });
if (result != view.end()) {
std::cout << "find_if_not= " << *result << endl;
}
// find_if_not
auto ll = std::ranges::find_last_if(view, [](int a) { return a > 5; });
if (!ll.empty())
{
std::cout << "find_last_if= " << *ll.begin() << endl;
}
// find_last_if_not
ll = std::ranges::find_last_if_not(view, [](int a) { return a > 5; });
if (!ll.empty())
{
std::cout << "find_last_if_not= " << *ll.begin() << endl;
}
return 0;
}java
java
int result = IntStream.rangeClosed(1, 20)
.boxed()
.filter(it -> it % 2 == 0) // 过滤
.findFirst()
.orElse(0);
System.out.println("result-> " + result);
result = IntStream.rangeClosed(1, 20)
.boxed()
.filter(it -> it % 2 != 0) // 过滤
.findFirst()
.orElse(0);
System.out.println("result-> " + result);5、std::ranges::all_of与std::ranges::any_of
c++
cpp
int main()
{
system("chcp 65001");
auto view = std::views::iota(1, 11)
| std::views::filter([](int it) { return it % 2 == 0; });
// all_of
bool result = std::ranges::all_of(view, [](int a) { return a > 5; });
std::cout << "all_of= " << boolalpha << result << endl;
// any_of
result = std::ranges::all_of(view, [](int a) { return a > 5; });
std::cout << "any_of= " << boolalpha << result << endl;
return 0;
}java
java
boolean result = IntStream.rangeClosed(1, 20)
.boxed()
.filter(it -> it % 2 == 0) // 过滤
.allMatch(it -> it > 5);
System.out.println("result-> " + result);
result = IntStream.rangeClosed(1, 20)
.boxed()
.filter(it -> it % 2 != 0) // 过滤
.anyMatch(it -> it > 5);
System.out.println("result-> " + result);
result = IntStream.rangeClosed(1, 20)
.boxed()
.filter(it -> it % 2 != 0) // 过滤
.noneMatch(it -> it > 5);
System.out.println("result-> " + result);6、std::ranges::for_each_n与std::ranges::for_each
| 特性 | std::ranges::for_each |
std::ranges::for_each_n |
|---|---|---|
| 输入 | 整个范围或迭代器对 | 起始迭代器 + 元素数量 |
| 适用场景 | 处理所有元素 | 处理指定数量的元素 |
| 边界安全 | 自动处理到范围结束 | 如果数量超过范围,行为未定义(需确保数量有效) |
| 返回值 | {end_iterator, function_object} |
{advanced_iterator, function_object} |
| 范围版本 | ✅ 有 | ❌ 无(需手动传迭代器) |
cpp
int main() {
// for_each
auto view = std::views::iota(1, 21)
| std::views::filter([](int it) { return it % 3 == 0; });
std::ranges::for_each(view, [](const int it) {std::cout << "for_each-> " << it << endl; });
// for_each_n [0,2]
std::ranges::for_each_n(view.begin(), 2, [](const int it) {std::cout << "for_each_n [0,2]-> " << it << endl; });
// for_each_n [1,3]
std::ranges::for_each_n(++view.begin(), 2, [](const int it) {std::cout << "for_each_n [1,3]-> " << it << endl; });
// for_each_n [2,4]
std::ranges::for_each_n(std::next(view.begin(), 2), 2, [](const int it) {std::cout << "for_each_n [2,4]-> " << it << endl; });
// for_each_n [end-2, end]
std::ranges::for_each_n(std::prev(view.end(), 2), 2, [](const int it) {std::cout << "for_each_n [end-2, end]-> " << it << endl; });
return 0;
}views相关
| 适配器 | C++23 | 描述 | Java Stream 等价 |
|---|---|---|---|
std::views::chunk |
✅ | 将范围分割为固定大小的块 | 自定义 Collector |
std::views::chunk_by |
✅ | 根据谓词分组连续元素 | Collectors.groupingBy() |
std::views::slide |
✅ | 创建滑动窗口视图 | 自定义实现 |
std::views::join_with |
✅ | 连接范围并插入分隔符 | Collectors.joining(delimiter) |
std::views::adjacent |
✅ | 创建相邻元素元组 | 自定义实现 |
std::views::adjacent_transform |
✅ | 对相邻元素应用函数 | 自定义实现 |
std::views::cartesian_product |
✅ | 笛卡尔积 | 嵌套循环 |
std::views::zip_transform |
✅ | zip + transform 组合 | Stream.zip() + map() |
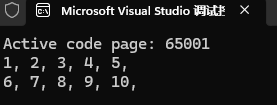
1、std::views::chunk
固定长度分块
cpp
int main()
{
system("chcp 65001");
// 固定长度分块
auto chunks = std::views::iota(1, 11)
| std::views::chunk(5);
for (auto chunk : chunks)
{
for (auto it : chunk)
{
std::cout << it << ", ";
}
std::cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
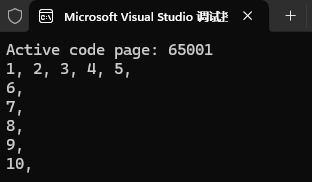
2、std::views::chunk_by
根据条件将相邻的满足条件的元素分组到同一个块中
cpp
int main()
{
system("chcp 65001");
// 按条件将相邻的满足条件的元素划分到一组
auto chunks = std::views::iota(1, 11)
| std::views::chunk_by([](int a, int b) {return a + b < 10; });
for (auto chunk : chunks)
{
for (auto it : chunk)
{
std::cout << it << ", ";
}
std::cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
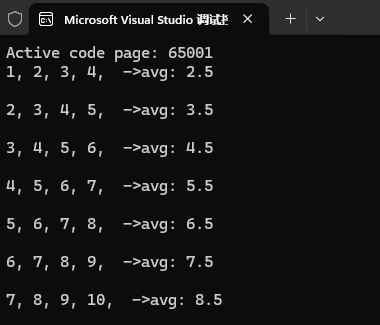
3、std::views::slide
将范围分割成多个重叠的固定大小子范围,每个子窗口相对于前一个窗口滑动一个位置
cpp
int main()
{
system("chcp 65001");
// 指定元素个数划分
auto wins = std::views::iota(1, 11)
| std::views::slide(4);
for (auto win : wins)
{
for (auto it : win)
{
std::cout << it << ", ";
}
// 计算窗口内元素的平均值
double avg = std::accumulate(win.begin(), win.end(), 0.0) / win.size();
std::cout << " ->avg: " << avg << std::endl;
std::cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
4、std::views::join_with
主要作用是将二维容器(如
vector<vector<T>>)转换为一维视图,并在每个子范围之间插入指定的分隔符元素或子范围。它是std::ranges::views::join的扩展版本,提供了更灵活的连接逻辑
cpp
int main()
{
system("chcp 65001");
// 字符作为分割符号
auto line1 = std::views::iota(1, 11)
| std::views::transform([](int a) {return std::to_string(a); })
| std::views::join_with(',');
for (auto it : line1)
{
std::cout << it;
}
std::cout << endl;
// 字符串作为分割符号
auto str = std::views::iota(1, 11)
| std::views::transform([](int a) { std::vector<std::string> vec = { std::to_string(a) }; return vec; })
| std::views::join_with(", ");
for (auto it : str)
{
std::cout << it;
}
std::cout << endl;
// 字符作为分割符号
std::vector<std::string> words = { "hello", "world" };
auto sentence1 = words | std::views::join_with(',');
for (auto it : sentence1)
{
std::cout << it;
}
std::cout << endl;
// 字符串作为分割符号
auto sentence2 = words
| std::views::transform([](string a) {std::vector<std::string> vec = { a }; return vec; })
| std::views::join_with(", ");
for (auto it : sentence2)
{
std::cout << it;
}
std::cout << endl;
// std::vector作为分隔符
std::vector<std::vector<int>> matrix = { {1, 2}, {3, 4}, {5, 6} };
auto flattened = matrix | std::views::join_with(0);
// auto flattened = matrix | std::views::join_with(std::vector<int>{0});
for (auto it : flattened)
{
std::cout << it;
}
std::cout << endl;
return 0;
}5、std::views::adjacent
将输入范围转换为一个由相邻元素组成的元组视图
cpp
int main()
{
system("chcp 65001");
// 生成二元组
auto tuple2List = std::views::iota(1, 11)
| std::views::adjacent<2>;
for (auto [a, b] : tuple2List)
{
std::cout << "[" << a << ", " << b << "], ";
std::cout << endl;
}
// 生成三元组
auto tuple3List = std::views::iota(1, 11)
| std::views::adjacent<3>;
for (auto [a, b, c] : tuple3List)
{
std::cout << "[" << a << ", " << b << ", " << c << "], ";
std::cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}6、std::views::adjacent_transform
可以std::views::adjacent 与 std::views::transform组合使用
cpp
int main()
{
system("chcp 65001");
// adjacent_transform
auto avgList = std::views::iota(1, 11)
| std::views::adjacent_transform<3>(
[](auto... args) {
return (args + ...) / 3.0;
}
);
for (double avg : avgList) {
std::cout << "auto-> avg: " << avg << std::endl;
}
// 指定参数
auto aaa = std::views::iota(1, 11)
| std::views::adjacent_transform<3>(
[](int a, int b, int c) {
return (a + b + c) / 3.0;
}
);
for (double avg : aaa) {
std::cout << "aaa-> avg: " << avg << std::endl;
}
// std::views::adjacent + std::views::transform组合使用
auto bbb = std::views::iota(1, 11)
| std::views::adjacent<3>
| std::views::transform([](auto tuple) { auto [a, b, c] = tuple; return (a + b + c) / 3.0; });
for (double avg : bbb) {
std::cout << "bbb-> avg: " << avg << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}7、std::views::cartesian_product
生成多个范围的笛卡尔积视图
cpp
int main()
{
system("chcp 65001");
std::vector<char> aaa = { 'a', 'b' };
std::vector<int> bbb = { 1, 2 };
std::vector<std::string> ccc = { "hello", "world" };
// 生成笛卡尔积
auto result = std::views::cartesian_product(aaa, bbb, ccc);
for (const auto& tuple : result) {
char a = std::get<0>(tuple);
int b = std::get<1>(tuple);
std::string c = std::get<2>(tuple);
std::cout << a << " - " << b << " - " << c << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}8、std::views::zip_transform
可以使用std::views::zip 与 std::views::transform组合
cpp
int main()
{
system("chcp 65001");
std::vector<int> aa = { 1, 2, 3 };
std::vector<char> bb = { 'A', 'B', 'C' };
std::vector<std::string> cc = { "one", "two", "three" };
// 将三个范围的对应元素打包成元组
auto abc = std::views::zip(aa, bb, cc);
for (auto [a, b, c] : abc) {
std::cout << a << " - " << b << " - " << c << std::endl;
}
// std::views::zip_transform
auto result = std::views::zip_transform([](int a, char b, string c) { return std::to_string(a) + b + c; },
aa, bb, cc);
for (auto it : result)
{
std::cout << it << endl;
}
// std::views::zip + std::views::transform
auto rtn = std::views::zip(aa, bb, cc)
| std::views::transform([](auto pair) {
auto [a, b, c] = pair;
return std::to_string(a) + b + c;
});
for (auto it : rtn)
{
std::cout << it << endl;
}
return 0;
}