一.基础查询
1.查询常量,表达式,函数
select 100;
select 'jonw';
select 100%98;
select VERSION();
2.为字段起别名
select id,name as 名字 from stu;
select id 编号,name 名字 from stu;
注:变名尽量加双引号,或者单引号。
3.去重
select distinctid from stu; //一次只能去重一个字段
4.+号的作用
只有充当运算符的功能
select '123'+90 ; 结果为213
select 'jos'+90; 结果为90
select null +90; 结果为null
注:null和任意字段拼接都为null
5.拼接
select concat(xin,ming)as 姓名 from stu;
6.判断是否为null
select ifnull(name ,0 ) ,name from stu;
二.条件查询
语句:
select 查询列表 from 表名 where 筛选条件;
条件:
运算符:> < = (!= , <>) =
逻辑表达式:&& || ! and or not
例子:
select * from stu where age>=10;
select * from stu where age>20 and age<30;
三.模糊查询
关键字:
like betweent...and... in (is null)
安全等于 可以用来判断是否等于null
例子:
select * from stu where name like '%z%'; //匹配name中是否有z的信息
select * from stu where name like '_h__s%'; //匹配name第二个字符为h,第五个字符为s的信息
select * from stu where name like 'h\%';//用\来作为转义字符,将后面的_作为一个字符
select * from stu where name like '_h_s%' ESCAPE ''; //定义转义符为$
select * from stu where age BETWEEN 20 and 30; //包含临界值,不能调换两个临界值
select * from stu where age in (20,23,'30'); //in里面的数据类型必须相同或者兼容,且不支持通配符
select * from stu where age is null; //=,<> 不能判断null值
四.排序查询
select * from stu ORDER BY age asc; //升序排列。默认为升序
select * from stu ORDER BY age desc;//降序排列
select *,IFNULL(age,0)+10 年龄 from stu ORDER BY 年龄 desc;
select name,LENGTH(name) 字节长度,address from stu ORDER BY 字节长度 asc;
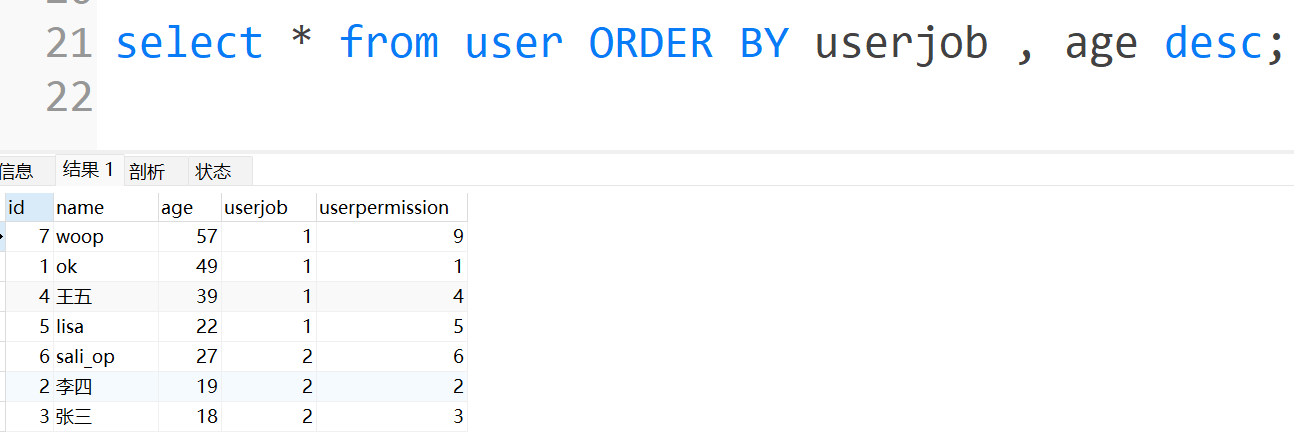
select LENGTH(name) 名字长度, SUBSTR(name,1,1) 首字符,name from stu ORDER BY 首字符 , 名字长度;
注:可以有两个或多个字段排序,即在一个字段的数据有相同的情况下,按第二个排序条件排序。
五.分组查询
语句

案例1
查询名字中含有字符'a'的,每个部门的平均工资:
select avg(salary) ,bumenid from stu where name like '%a%' order by bumenid;
案例2
查询哪个部门的员工个数大于2:
select count(*) , workid from work order by workid having count(*)>2;
案例3
查询每个工种有奖金的员工的最高工资>12000的工种编号和最高工资
select max(salary),工种id from stu where 奖金 is not null order by 工种id having max(salary>12000);
案例4
查询每个部门,每个工种的员工的平均工资
select avg(salary),bumenid,workid from stu group by bumenid,workid //多个字段分组用,分开
注:having只能用在分组查询(group by)后面
六.连接查询

定义:
也叫多表连接,需要增加条件让两个表连一起
1.内连接
语句:
select 查询列表 from 表1 别名 inner join·表2 别名 on 连接条件;(99sql格式)
案例:
查询名字中包含字符e的员工名和工种名:
select e.name,j.job_title from emploee e inner join job j on e.id=j.id where e.name like '%e%';
注:三表连接:如果三个表以上的表连接,则可以多写几个join job..on 语句且连接条件应该都与from后的表有连接
1.1等值连接:
select name,username from login,staff where staff.id=login.id;
select l.id,t.id from login as l,tb_user t where l.password=t.password;//可以给表起别名,但是之后只能用别名
select COUNT(*) ,t.password from login l,tb_user t where l.password=t.password GROUP BY t.password;//查询两个表中密码相等的数量
多表连接和双表连接相似,需要用and 来连接条件
1.2非等值连接(用between and或者逻辑符来筛选来条件):
select salary,level_grade from tab1 t1,tab2 t2 where salary between t1.maxsalary and t1,minsalary; //查询员工的工资和工资等级
1.3自连接(自己表连接自己):
查询员工名,员工id,上级名,上级id(用manager_id在同表来找上司)
select e.employee_id,e.last_name, m.employee_id,m.last_name from employee e ,employee m where m.manger_id=employee_id;
2.外连接
**作用:**用于查询一个表有,另一个表没有的数据
**结果:**外连接结果=内连接结果+主表中有而从表中没有的数据
**左连接:**left outer join中left左边为主表,join右边是从表
右连接:right outer join中right左边是从表,join右边是主表
**全外连接:**full outer join //结果=内连接结果+表1有但表2没有+表2有但表1没有
例子:select c.city_name,l.* from location l left outer join city c on l.id=c,id where c.deparementid is null
3.交叉连接
**语句:**select 查询内容 from table1 cross join table2;=select 查询内容 from table1 ,table2;
**结果:**也就是两个表的笛卡尔乘积。
七.子查询

标量子查询:
例子1查询谁年龄大于张三的年龄:
select * from stu where age>(select age from stu where name='zhangsan');
例子2查询最低工资的员工信息:
select * from stu where salary=(select MIN(salary) from stu);
列子查询:
in :在多行一列中等于其中的任意一个 id in(10,20,30) = id=any(10,20,30)
any:只要满足其中的一个。比如 a>any(10,20,30)=a>min(10,20,30)
all:要满足其中的所有。比如 a>all(10,20,30)=a>max(10,20,30)
行字查询(了解):
查询员工编号最小的,工资最高的员工信息:
select * from emploee where emploee_id = (select min(emploee_id) from emploee) and salary =(select max(salary) from emploee);
====
select * from emploee where (emploee_id,salary) = (select min(emploee_id) ,max(salary) from emploee);
select后面子查询:
查询每个部门的员工的个数
select d.*,(select count(*) from emploee e where e.department _id = d.department_id) 个数 from department d;
from后面子查询:
说明:将子查询的结果集充当一张表,且要为该表起别名才能被找到。
exists后面子查询:
语句:exists(查询语句)。如果查询语句有结果有值则查询结果为1,否则为0。相对于一个布尔类型条件。
例如。查询有员工的部门名:
select department_name from department d where exists (select emplomee_id from emploee e where d.department_id=e.emplomee_id);
select department_name from department d where d.depaetment_id in(select emplomee_id from emploee );
八.分页查询
语句1:
select 查询列表 from 表 【
on 连接条件
where 筛选条件
group by 分组字段
having 分组后的筛选
order by 排序的字段】 limit 要显示条目的起始索引 要显示的条目个数。
语句2:
select 查询列表 from 表 limit (页码-1)*每页数,每页数;
页码:page 每页数:size
例子:
显示前五条员工信息:select * from stu limit 0,2;
显示2到4条员工信息:select * from stu limit 1,3;
九.联合查询
**作用:**将多个查询结果合并成一个结果
**语句:**查询语句 union 查询语句
注:
1.联合查询中,查询语句的结果的列数需要一致
2.union联合查询默认自动去重,如果不想去重用union all