继上一篇 golang可观测设计 之后,准备写一篇关于golang-agent的技术原理,讲一下为什么go可以像java一样做到优雅的无侵入式可观测插桩。 这个项目源自阿里巴巴的龙蜥社区git项目 github.com/alibaba/loongsuite-go-agent,在一次机缘巧合下了解到这个项目,一开始用的是阿里云arms的商业版对ack环境的go服务进行增强,后来由于成本问题,决定对项目进行二次开发,在经过一段时间的深入理解之后,我们也成功的开发了许多企业特性的功能,本文主要面向go开发介绍一下这个项目所使用到的技术原理。
先晒几张图看一下我们的成果:
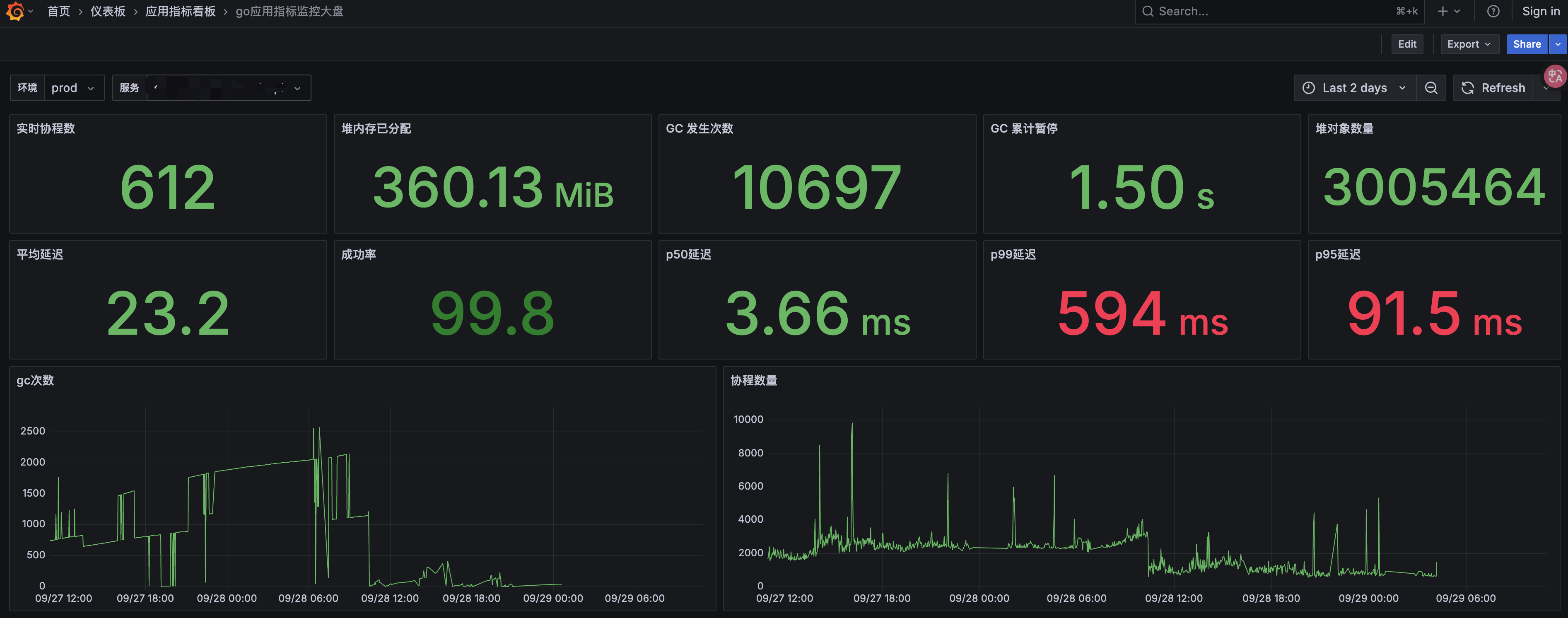
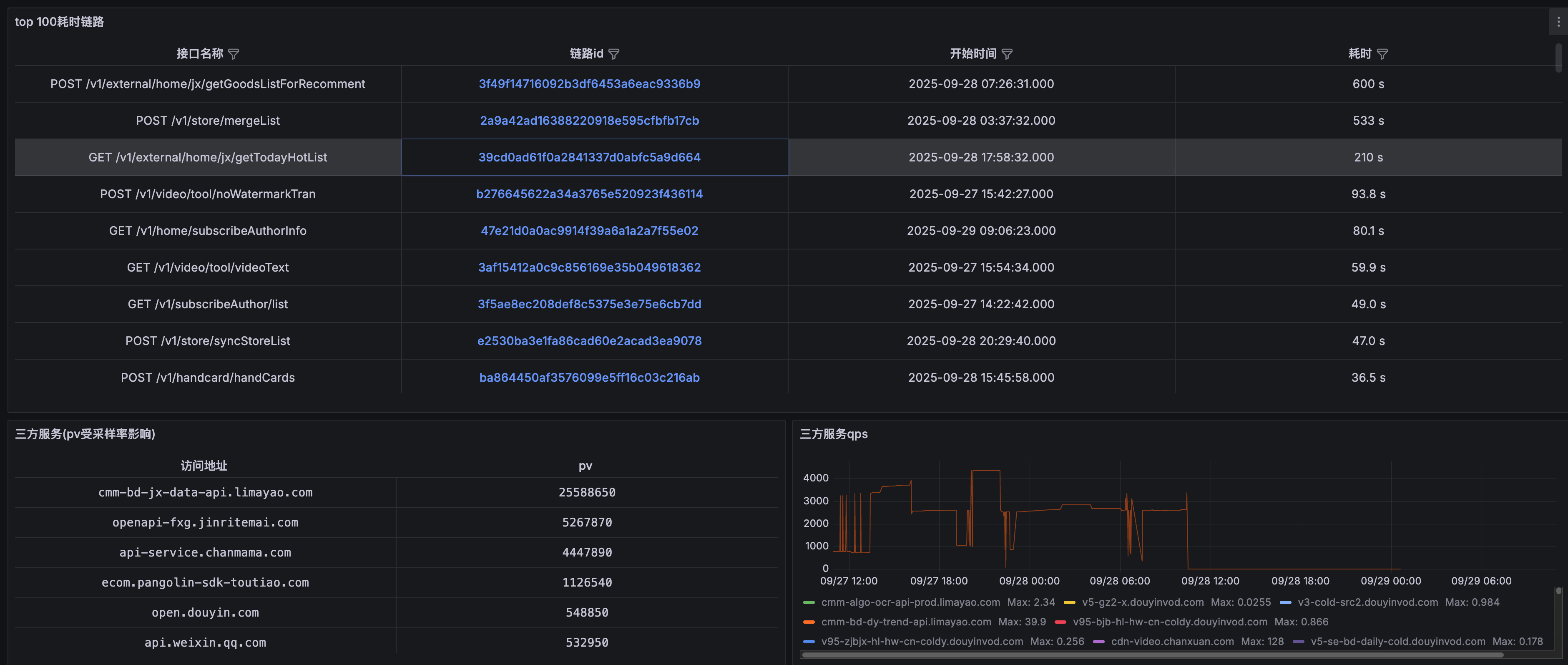
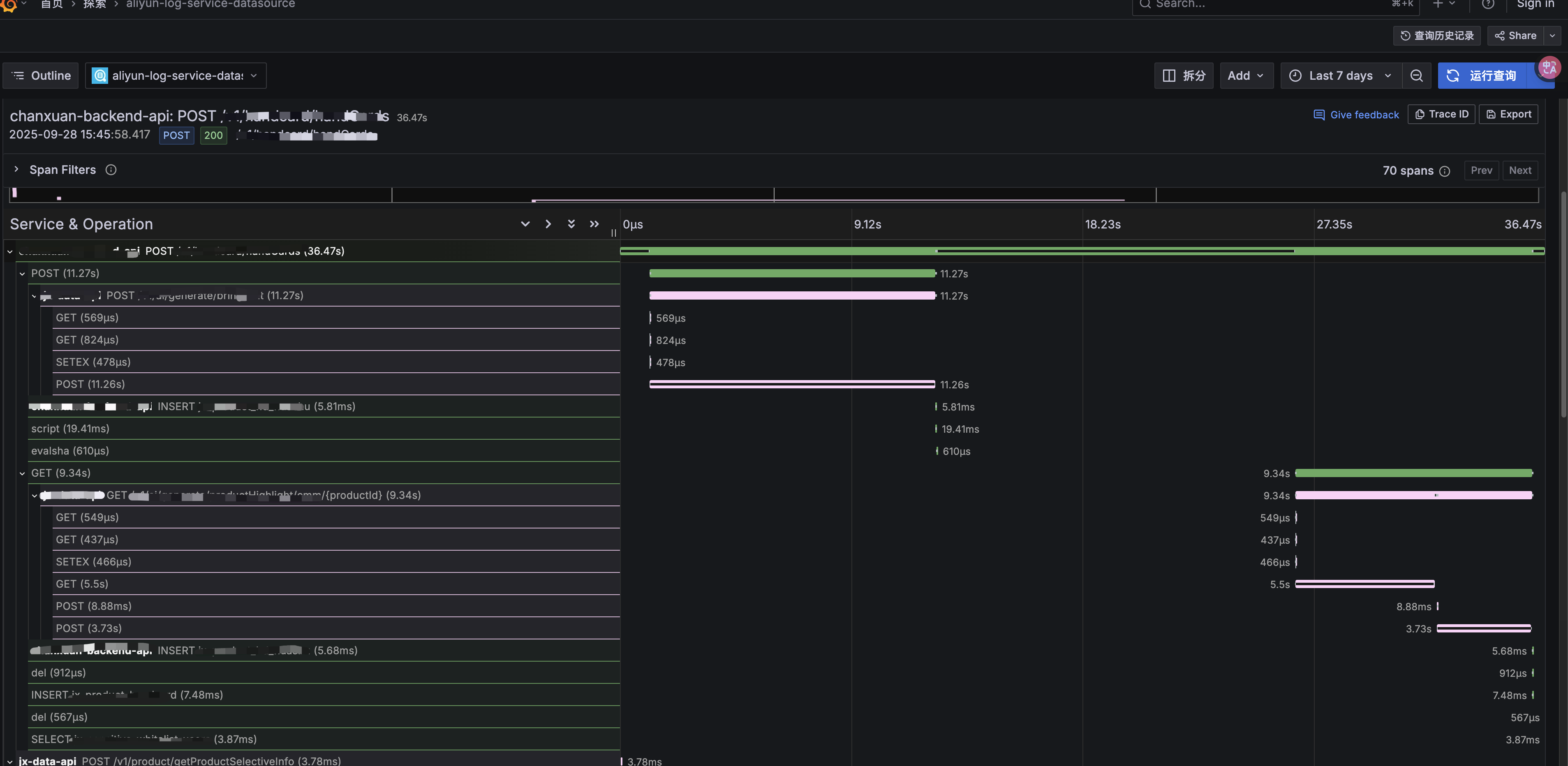
搭建这一套观测系统对于现有go项目没有植入任何一行代码,整体只花费了大概一天时间。
概述
本文档从宏观到微观,全面深度解析 otel go build 无侵入式插桩系统的完整技术实现机制。该系统是一个革命性的Go语言可观测性解决方案,通过编译时代码注入、AST操作、Goroutine Local Storage (GLS) 和 go:linkname 等先进技术的巧妙结合,实现了在完全不修改业务源码的情况下为Go应用添加企业级的分布式追踪、性能监控和可观测性能力。
一、系统架构全景图
1.1 宏观架构设计理念
otel工具基于"编译时插桩 + 运行时追踪"的创新设计模式,将传统的侵入式监控转变为完全透明的无侵入式方案:
用户视角:otel go build main.go (完全透明,如同原生go build)
↓
系统内部:复杂的多阶段处理流程
↓
最终结果:带有完整追踪能力的可执行文件设计哲学:
- 透明性:用户无需学习新的API或修改代码
- 完整性:提供企业级的全链路追踪能力
- 高性能:编译时优化,运行时开销最小化
- 兼容性:支持Go生态中的主流框架和库
1.2 完整系统架构流程图
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ otel go build 完整处理流程 │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐
│ 命令解析器 │───▶│ 依赖分析器 │───▶│ 规则加载器 │───▶│ 项目扫描器 │
│ (cmd.go) │ │ (dependency) │ │ (rule_loader) │ │ (scanner.go) │
│ │ │ │ │ │ │ │
│ • 解析build参数 │ │ • 分析go.mod │ │ • 加载插桩规则 │ │ • 扫描源文件 │
│ • 识别目标文件 │ │ • 识别依赖框架 │ │ • 匹配适用规则 │ │ • 构建文件树 │
└─────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐
│ AST解析器 │───▶│ 代码注入器 │───▶│ 模板处理器 │───▶│ 代码生成器 │
│ (parser.go) │ │ (injector.go) │ │ (template.go) │ │ (generator.go) │
│ │ │ │ │ │ │ │
│ • 解析Go源码 │ │ • 结构体字段注入 │ │ • 生成trampoline │ │ • 生成最终代码 │
│ • 构建AST树 │ │ • 函数体插桩 │ │ • 处理钩子函数 │ │ • 保持格式注释 │
│ • 保留元信息 │ │ • 运行时替换 │ │ • 错误恢复机制 │ │ • 写入临时文件 │
└─────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐
│ 编译协调器 │───▶│ 链接处理器 │───▶│ 运行时注入器 │───▶│ 最终输出 │
│ (compiler.go) │ │ (linker.go) │ │ (runtime.go) │ │ (output) │
│ │ │ │ │ │ │ │
│ • 调用go build │ │ • 链接追踪库 │ │ • 注入GLS代码 │ │ • 可执行文件 │
│ • 传递原始参数 │ │ • 处理符号表 │ │ • 设置linkname │ │ • 调试信息 │
│ • 错误处理 │ │ • 优化二进制 │ │ • 初始化追踪 │ │ • 性能报告 │
└─────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘1.3 核心技术栈架构
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 技术栈分层架构 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ 用户接口层 │ otel go build (命令行工具) │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ 编译时层 │ AST操作 │ 代码注入 │ 规则引擎 │ 模板系统 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ 运行时层 │ GLS机制 │ 上下文传播 │ 追踪收集 │ 性能监控 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ 系统调用层 │ go:linkname │ 内存操作 │ goroutine扩展 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ 底层支撑 │ Go Runtime │ 操作系统 │ 硬件平台 │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘二、启动流程与命令分发深度解析
2.1 命令入口点的技术实现
2.1.1 main.go 的设计模式
main.go 采用了经典的命令分发器模式(Command Dispatcher Pattern),这种设计具有以下优势:
go
func main() {
// 1. 环境检查和初始化
if err := checkEnvironment(); err != nil {
log.Fatal("Environment check failed:", err)
}
// 2. 全局配置加载
config := loadGlobalConfig()
// 3. 命令行参数解析
args := os.Args[1:]
if len(args) == 0 {
showUsage()
return
}
// 4. 命令分发核心逻辑
switch args[0] {
case "build":
buildCmd(args[1:], config)
case "run":
runCmd(args[1:], config)
case "test":
testCmd(args[1:], config)
case "version":
versionCmd()
case "help":
helpCmd(args[1:])
default:
// 兼容性处理:如果不是已知命令,尝试作为go命令处理
fallbackToGoCommand(args, config)
}
}技术要点:
- 向后兼容性:未知命令自动转发给原生go工具
- 配置管理:支持全局配置和项目级配置
- 错误处理:完善的错误处理和用户友好的错误信息
- 扩展性:易于添加新的子命令
2.1.2 参数解析的高级技术
系统使用了自定义的参数解析器,而不是标准的flag包,原因如下:
go
type BuildArgs struct {
// Go build 原生参数
Output string // -o 输出文件名
BuildMode string // -buildmode 构建模式
Tags []string // -tags 构建标签
LdFlags string // -ldflags 链接器标志
GcFlags string // -gcflags 编译器标志
Race bool // -race 竞态检测
// otel 扩展参数
Debug bool // --otel-debug 调试模式
Rules string // --otel-rules 自定义规则文件
Output string // --otel-output 追踪输出配置
Sampling float64 // --otel-sampling 采样率
}
func parseArgs(args []string) (*BuildArgs, error) {
buildArgs := &BuildArgs{}
// 使用状态机解析参数
state := parseStateNormal
for i, arg := range args {
switch state {
case parseStateNormal:
if strings.HasPrefix(arg, "--otel-") {
// 处理otel专用参数
handleOtelArg(arg, args[i+1:], buildArgs)
} else if strings.HasPrefix(arg, "-") {
// 处理go build原生参数
handleGoArg(arg, args[i+1:], buildArgs)
} else {
// 处理位置参数(包名、文件名等)
buildArgs.Packages = append(buildArgs.Packages, arg)
}
}
}
return buildArgs, nil
}2.2 Build命令的完整处理流程
2.2.1 预处理阶段详细流程
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 预处理阶段流程图 │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐
│ 环境检查 │───▶│ 项目分析 │───▶│ 依赖解析 │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ • Go版本检查 │ │ • 检测go.mod │ │ • 解析依赖树 │
│ • 工具链验证 │ │ • 识别项目类型 │ │ • 版本兼容性 │
│ • 权限检查 │ │ • 确定构建目标 │ │ • 框架识别 │
└─────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐
│ 规则匹配 │───▶│ 文件扫描 │───▶│ 缓存检查 │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ • 加载规则库 │ │ • 递归扫描源码 │ │ • 检查构建缓存 │
│ • 匹配适用规则 │ │ • 过滤目标文件 │ │ • 增量构建优化 │
│ • 规则优先级排序 │ │ • 构建依赖图 │ │ • 缓存失效检测 │
└─────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘2.2.2 核心处理逻辑的技术实现
go
func buildCmd(args []string, config *Config) error {
// 第一阶段:预处理
buildArgs, err := parseArgs(args)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("argument parsing failed: %w", err)
}
// 第二阶段:项目分析
project, err := analyzeProject(buildArgs)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("project analysis failed: %w", err)
}
// 第三阶段:规则加载和匹配
ruleEngine := NewRuleEngine(config)
applicableRules, err := ruleEngine.LoadAndMatch(project)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("rule matching failed: %w", err)
}
// 第四阶段:AST处理和代码注入
processor := NewASTProcessor(project, applicableRules)
modifiedFiles, err := processor.ProcessAll()
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("AST processing failed: %w", err)
}
// 第五阶段:代码生成
generator := NewCodeGenerator(modifiedFiles)
tempDir, err := generator.GenerateAll()
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("code generation failed: %w", err)
}
defer cleanup(tempDir)
// 第六阶段:编译执行
compiler := NewCompiler(buildArgs, tempDir)
return compiler.Build()
}2.3 错误处理和恢复机制
2.3.1 分层错误处理策略
go
// 错误类型定义
type ErrorType int
const (
ErrorTypeUser ErrorType = iota // 用户错误(参数错误等)
ErrorTypeSystem // 系统错误(文件IO等)
ErrorTypeCompiler // 编译器错误
ErrorTypeRuntime // 运行时错误
)
type OtelError struct {
Type ErrorType
Code string
Message string
Cause error
Context map[string]interface{}
}
func (e *OtelError) Error() string {
return fmt.Sprintf("[%s] %s: %s", e.Code, e.Message, e.Cause)
}
// 错误处理中间件
func withErrorHandling(fn func() error) error {
defer func() {
if r := recover(); r != nil {
// 记录panic信息
logPanic(r)
// 清理临时文件
cleanup()
// 转换为用户友好的错误信息
convertPanicToError(r)
}
}()
return fn()
}2.3.2 智能错误恢复
go
func smartErrorRecovery(err error, context *BuildContext) error {
switch e := err.(type) {
case *OtelError:
switch e.Type {
case ErrorTypeCompiler:
// 编译错误:尝试降级处理
return tryFallbackBuild(context)
case ErrorTypeSystem:
// 系统错误:检查权限和磁盘空间
return checkSystemResources(context)
case ErrorTypeUser:
// 用户错误:提供修复建议
return suggestFix(e, context)
}
}
return err
}三、AST增强技术深度解析
3.1 AST解析器架构深入分析
3.1.1 为什么选择dst库而不是标准库
系统使用 github.com/dave/dst 库进行AST操作,相比标准库的优势:
go
// 标准库 go/ast 的局限性
import (
"go/ast"
"go/parser"
"go/format"
)
// 问题1:丢失注释信息
func parseWithStandardLib(filename string) {
fset := token.NewFileSet()
file, err := parser.ParseFile(fset, filename, nil, parser.ParseComments)
// 修改AST后,注释信息会丢失
// 问题2:格式化信息丢失
var buf bytes.Buffer
format.Node(&buf, fset, file) // 原有的代码格式会被标准化
}
// dst库的解决方案
import "github.com/dave/dst"
type AstParser struct {
decorator *decorator.Decorator // 装饰器:保留格式信息
restorer *decorator.Restorer // 恢复器:还原格式信息
cache map[string]*dst.File // 缓存:避免重复解析
mutex sync.RWMutex // 并发安全
}
func NewAstParser() *AstParser {
return &AstParser{
decorator: decorator.NewDecorator(token.NewFileSet()),
restorer: decorator.NewRestorer(),
cache: make(map[string]*dst.File),
}
}
func (p *AstParser) ParseFile(filename string) (*dst.File, error) {
// 检查缓存
p.mutex.RLock()
if cached, exists := p.cache[filename]; exists {
p.mutex.RUnlock()
return cached, nil
}
p.mutex.RUnlock()
// 解析文件,保留所有格式信息
file, err := p.decorator.ParseFile(filename)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to parse %s: %w", filename, err)
}
// 缓存结果
p.mutex.Lock()
p.cache[filename] = file
p.mutex.Unlock()
return file, nil
}3.1.2 AST节点遍历的高级技术
go
// 自定义访问器模式
type NodeVisitor struct {
rules []InstrumentationRule
context *VisitContext
transforms []NodeTransform
}
type VisitContext struct {
CurrentFile *dst.File
CurrentPackage string
ImportMap map[string]string
SymbolTable *SymbolTable
ScopeStack []*Scope
}
func (v *NodeVisitor) Visit(node dst.Node) dst.Visitor {
switch n := node.(type) {
case *dst.FuncDecl:
return v.visitFunction(n)
case *dst.StructType:
return v.visitStruct(n)
case *dst.CallExpr:
return v.visitCall(n)
case *dst.ImportSpec:
return v.visitImport(n)
default:
return v
}
}
func (v *NodeVisitor) visitFunction(fn *dst.FuncDecl) dst.Visitor {
// 检查函数是否需要插桩
if !v.shouldInstrument(fn) {
return nil // 跳过此节点的子节点
}
// 创建新的作用域
scope := NewScope(fn)
v.context.ScopeStack = append(v.context.ScopeStack, scope)
defer func() {
// 退出作用域
v.context.ScopeStack = v.context.ScopeStack[:len(v.context.ScopeStack)-1]
}()
// 应用函数级别的转换
for _, transform := range v.transforms {
if transform.AppliesTo(fn) {
transform.Apply(fn, v.context)
}
}
return v
}3.2 代码注入技术的深度实现
3.2.1 结构体字段注入的完整机制
go
type StructFieldInjector struct {
targetStructs map[string][]FieldInjection
typeChecker *TypeChecker
}
type FieldInjection struct {
FieldName string
FieldType string
Tags string
Position InjectionPosition // Before, After, Replace
}
func (s *StructFieldInjector) InjectFields(structType *dst.StructType, structName string) error {
injections, exists := s.targetStructs[structName]
if !exists {
return nil
}
for _, injection := range injections {
field := &dst.Field{
Names: []*dst.Ident{dst.NewIdent(injection.FieldName)},
Type: s.parseType(injection.FieldType),
}
// 添加标签
if injection.Tags != "" {
field.Tag = &dst.BasicLit{
Kind: token.STRING,
Value: fmt.Sprintf("`%s`", injection.Tags),
}
}
// 根据位置插入字段
switch injection.Position {
case InjectionPositionBefore:
structType.Fields.List = append([]*dst.Field{field}, structType.Fields.List...)
case InjectionPositionAfter:
structType.Fields.List = append(structType.Fields.List, field)
case InjectionPositionReplace:
// 替换逻辑
s.replaceField(structType, field, injection)
}
}
return nil
}
// 实际注入示例
func injectTraceFields() {
// 原始代码
type User struct {
ID int `json:"id"`
Name string `json:"name"`
}
// 注入后代码(概念展示)
type User struct {
// 注入的追踪字段(在最前面)
_otel_trace_context *TraceContext `json:"-" otel:"trace"`
_otel_baggage_data *BaggageData `json:"-" otel:"baggage"`
// 原有字段
ID int `json:"id"`
Name string `json:"name"`
// 注入的元数据字段(在最后面)
_otel_metadata map[string]interface{} `json:"-" otel:"metadata"`
}
}3.2.2 函数体注入的精密控制
go
type FunctionInjector struct {
entryHooks []HookFunction
exitHooks []HookFunction
errorHooks []HookFunction
}
type HookFunction struct {
Name string
Template string
Parameters []Parameter
Condition func(*dst.FuncDecl) bool
}
func (f *FunctionInjector) InjectHooks(fn *dst.FuncDecl) error {
// 1. 分析函数签名
signature := f.analyzeFunctionSignature(fn)
// 2. 生成入口代码
entryCode := f.generateEntryCode(fn, signature)
// 3. 生成出口代码
exitCode := f.generateExitCode(fn, signature)
// 4. 处理错误返回
errorCode := f.generateErrorHandling(fn, signature)
// 5. 注入到函数体
return f.injectIntoBody(fn, entryCode, exitCode, errorCode)
}
func (f *FunctionInjector) generateEntryCode(fn *dst.FuncDecl, sig *FunctionSignature) []dst.Stmt {
var stmts []dst.Stmt
// 生成span开始代码
spanStart := &dst.AssignStmt{
Lhs: []dst.Expr{
dst.NewIdent("_otel_span"),
dst.NewIdent("_otel_ctx"),
},
Tok: token.DEFINE,
Rhs: []dst.Expr{
&dst.CallExpr{
Fun: &dst.SelectorExpr{
X: dst.NewIdent("otel"),
Sel: dst.NewIdent("StartSpan"),
},
Args: []dst.Expr{
&dst.BasicLit{
Kind: token.STRING,
Value: fmt.Sprintf(`"%s"`, sig.Name),
},
},
},
},
}
stmts = append(stmts, spanStart)
// 生成defer语句
deferStmt := &dst.DeferStmt{
Call: &dst.CallExpr{
Fun: &dst.SelectorExpr{
X: dst.NewIdent("_otel_span"),
Sel: dst.NewIdent("End"),
},
},
}
stmts = append(stmts, deferStmt)
// 参数记录
if sig.HasParameters {
paramRecording := f.generateParameterRecording(sig.Parameters)
stmts = append(stmts, paramRecording...)
}
return stmts
}
// 复杂函数注入示例
func complexFunctionInjection() {
// 原始函数
func ProcessOrder(ctx context.Context, orderID string, items []Item) (*Order, error) {
// 业务逻辑
order := &Order{ID: orderID}
for _, item := range items {
order.AddItem(item)
}
return order, nil
}
// 注入后函数(概念展示)
func ProcessOrder(ctx context.Context, orderID string, items []Item) (*Order, error) {
// === 入口注入代码开始 ===
_otel_span, _otel_ctx := otel.StartSpan("ProcessOrder")
defer func() {
// 错误处理
if r := recover(); r != nil {
_otel_span.RecordError(fmt.Errorf("panic: %v", r))
_otel_span.SetStatus(codes.Error, "panic occurred")
panic(r) // 重新抛出panic
}
_otel_span.End()
}()
// 参数记录
_otel_span.SetAttributes(
attribute.String("order_id", orderID),
attribute.Int("items_count", len(items)),
)
// 上下文传播
ctx = _otel_ctx
// === 入口注入代码结束 ===
// 原始业务逻辑
order := &Order{ID: orderID}
for _, item := range items {
order.AddItem(item)
}
// === 出口注入代码开始 ===
if order != nil {
_otel_span.SetAttributes(
attribute.String("result_order_id", order.ID),
attribute.Int("result_items_count", len(order.Items)),
)
}
// === 出口注入代码结束 ===
return order, nil
}
}3.2.3 智能代码生成与优化
go
type CodeGenerator struct {
optimizer *CodeOptimizer
validator *CodeValidator
formatter *CodeFormatter
templateMgr *TemplateManager
}
func (g *CodeGenerator) GenerateOptimizedCode(node dst.Node) (string, error) {
// 1. 生成基础代码
baseCode, err := g.generateBaseCode(node)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
// 2. 应用优化
optimizedCode, err := g.optimizer.Optimize(baseCode)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
// 3. 验证代码正确性
if err := g.validator.Validate(optimizedCode); err != nil {
return "", err
}
// 4. 格式化代码
formattedCode, err := g.formatter.Format(optimizedCode)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
return formattedCode, nil
}
type CodeOptimizer struct {
optimizations []OptimizationRule
}
type OptimizationRule struct {
Name string
Pattern string
Transform func(code string) string
Enabled bool
}
func (o *CodeOptimizer) Optimize(code string) (string, error) {
result := code
for _, rule := range o.optimizations {
if !rule.Enabled {
continue
}
// 应用优化规则
optimized := rule.Transform(result)
// 验证优化是否有效
if len(optimized) < len(result) || o.isMoreEfficient(optimized, result) {
result = optimized
}
}
return result, nil
}
// 优化示例:消除冗余的span创建
func eliminateRedundantSpans() OptimizationRule {
return OptimizationRule{
Name: "eliminate_redundant_spans",
Pattern: `_otel_span\d*, _otel_ctx\d* := otel\.StartSpan\("([^"]+)"\)\s*defer _otel_span\d*\.End\(\)\s*_otel_span\d*, _otel_ctx\d* := otel\.StartSpan\("\1"\)`,
Transform: func(code string) string {
// 检测并合并相同名称的连续span
re := regexp.MustCompile(`(_otel_span\d*), (_otel_ctx\d*) := otel\.StartSpan\("([^"]+)"\)\s*defer \1\.End\(\)\s*\1, \2 := otel\.StartSpan\("\3"\)`)
return re.ReplaceAllString(code, `$1, $2 := otel.StartSpan("$3")
defer $1.End()`)
},
Enabled: true,
}
}3.3 Trampoline代码模板
template.go 定义了trampoline代码的标准模板:
go
type CallContextImpl struct {
Params []interface{} // 函数参数
ReturnVals []interface{} // 返回值
SkipCall bool // 是否跳过原函数调用
Data map[string]interface{} // 自定义数据
FuncName string // 函数名
PkgName string // 包名
}
func OtelOnEnterTrampoline(ctx *CallContextImpl) {
// 函数入口处理逻辑
defer func() {
if r := recover(); r != nil {
// 错误恢复机制
OtelPrintStackImpl(OtelGetStackImpl())
}
}()
// 调用用户定义的OnEnter钩子
if onEnterHook != nil {
onEnterHook(ctx)
}
}四、GLS(Goroutine Local Storage)技术深度剖析
4.1 GLS的底层实现原理
4.1.1 Go运行时内部结构的深度解析
GLS技术的核心在于直接操作Go运行时的内部数据结构。让我们深入了解其实现机制:
go
// Go运行时内部结构(简化版)
type g struct {
// 标准字段
stack stack // 栈信息
stackguard0 uintptr // 栈保护
stackguard1 uintptr // 栈保护
_panic *_panic // panic链表
_defer *_defer // defer链表
m *m // 当前绑定的M
sched gobuf // 调度信息
// === otel注入的字段(通过base.json规则) ===
otel_user_context interface{} // 用户上下文
otel_trace_context interface{} // 追踪上下文
otel_baggage_container interface{} // 行李数据
}
// M结构(Machine,OS线程的抽象)
type m struct {
g0 *g // 调度goroutine
curg *g // 当前运行的goroutine
p puintptr // 绑定的P
nextp puintptr // 下一个P
oldp puintptr // 之前的P
// ... 其他字段
}4.1.2 getg()函数的黑魔法
getg() 是Go运行时的内部函数,用于获取当前goroutine的指针:
go
// runtime_linker.go 中的实现
//go:linkname _otel_gls_getg_impl runtime.getg
func _otel_gls_getg_impl() *g
// 实际使用
func getCurrentGoroutine() *g {
return _otel_gls_getg_impl()
}
// 汇编层面的实现(概念展示)
// func getg() *g
// 在AMD64架构下:
// MOVQ (TLS), AX // 从TLS获取当前g的地址
// MOVQ AX, ret+0(FP) // 返回g指针
// RET
// 在ARM64架构下:
// MOVD g, R0 // g寄存器存储当前goroutine
// MOVD R0, ret+0(FP)
// RET4.1.3 内存布局和字段访问
go
// 字段访问的底层实现
func setUserContextToGLS(ctx interface{}) {
g := _otel_gls_getg_impl()
// 直接操作内存偏移
// 这里的偏移量是在编译时通过base.json规则确定的
*(*interface{})(unsafe.Pointer(uintptr(unsafe.Pointer(g)) + otel_user_context_offset)) = ctx
}
func getUserContextFromGLS() interface{} {
g := _otel_gls_getg_impl()
return *(*interface{})(unsafe.Pointer(uintptr(unsafe.Pointer(g)) + otel_user_context_offset))
}
// 内存布局示意图
/*
goroutine内存布局:
+-------------------+ <- g指针
| stack | +0x00
| stackguard0 | +0x08
| stackguard1 | +0x10
| _panic | +0x18
| _defer | +0x20
| m | +0x28
| sched | +0x30
| ... |
| otel_user_context | +0x180 (注入字段)
| otel_trace_context| +0x188 (注入字段)
| otel_baggage_cont | +0x190 (注入字段)
+-------------------+
*/4.2 上下文传播机制的深度实现
4.2.1 goroutine创建时的上下文继承
go
// runtime.newproc1 的插桩实现
//go:linkname _otel_original_newproc1 runtime.newproc1
func _otel_original_newproc1(fn *funcval, argp unsafe.Pointer, narg int32, callergp *g, callerpc uintptr) *g
func _otel_instrumented_newproc1(fn *funcval, argp unsafe.Pointer, narg int32, callergp *g, callerpc uintptr) *g {
// 调用原始函数创建新goroutine
newg := _otel_original_newproc1(fn, argp, narg, callergp, callerpc)
// 从父goroutine继承上下文
if callergp != nil {
// 继承用户上下文
parentUserCtx := getUserContextFromGoroutine(callergp)
if parentUserCtx != nil {
setUserContextToGoroutine(newg, parentUserCtx)
}
// 继承追踪上下文
parentTraceCtx := getTraceContextFromGoroutine(callergp)
if parentTraceCtx != nil {
setTraceContextToGoroutine(newg, parentTraceCtx)
}
// 继承行李数据
parentBaggage := getBaggageFromGoroutine(callergp)
if parentBaggage != nil {
setBaggageToGoroutine(newg, parentBaggage)
}
}
return newg
}
// 上下文传播的完整流程
func contextPropagationFlow() {
// 1. 父goroutine设置上下文
SetUserContext(map[string]interface{}{
"user_id": "12345",
"request_id": "req-abc-123",
})
// 2. 创建子goroutine
go func() {
// 3. 子goroutine自动继承父上下文
userCtx := GetUserContext()
fmt.Printf("Child goroutine user_id: %v\n", userCtx["user_id"])
// 4. 子goroutine可以修改自己的上下文,不影响父goroutine
SetUserContextValue("child_data", "child_value")
// 5. 创建孙子goroutine
go func() {
// 6. 孙子goroutine继承子goroutine的上下文
userCtx := GetUserContext()
fmt.Printf("Grandchild goroutine child_data: %v\n", userCtx["child_data"])
}()
}()
}4.2.2 高性能的上下文快照机制
go
type ContextSnapshot struct {
UserContext interface{}
TraceContext interface{}
BaggageData interface{}
Timestamp int64
GoroutineID int64
}
type ContextSnapshoter struct {
pool sync.Pool // 对象池,减少GC压力
}
func NewContextSnapshoter() *ContextSnapshoter {
return &ContextSnapshoter{
pool: sync.Pool{
New: func() interface{} {
return &ContextSnapshot{}
},
},
}
}
func (cs *ContextSnapshoter) TakeSnapshot() *ContextSnapshot {
snapshot := cs.pool.Get().(*ContextSnapshot)
// 重置快照
*snapshot = ContextSnapshot{}
// 获取当前goroutine
g := _otel_gls_getg_impl()
// 快照用户上下文
if userCtx := getUserContextFromGoroutine(g); userCtx != nil {
snapshot.UserContext = deepCopy(userCtx)
}
// 快照追踪上下文
if traceCtx := getTraceContextFromGoroutine(g); traceCtx != nil {
snapshot.TraceContext = deepCopy(traceCtx)
}
// 快照行李数据
if baggage := getBaggageFromGoroutine(g); baggage != nil {
snapshot.BaggageData = deepCopy(baggage)
}
snapshot.Timestamp = time.Now().UnixNano()
snapshot.GoroutineID = getGoroutineID(g)
return snapshot
}
func (cs *ContextSnapshoter) RestoreSnapshot(snapshot *ContextSnapshot) {
if snapshot == nil {
return
}
// 恢复用户上下文
if snapshot.UserContext != nil {
setUserContextToGLS(snapshot.UserContext)
}
// 恢复追踪上下文
if snapshot.TraceContext != nil {
setTraceContextToGLS(snapshot.TraceContext)
}
// 恢复行李数据
if snapshot.BaggageData != nil {
setBaggageToGLS(snapshot.BaggageData)
}
}
func (cs *ContextSnapshoter) ReleaseSnapshot(snapshot *ContextSnapshot) {
if snapshot != nil {
cs.pool.Put(snapshot)
}
}4.3 用户上下文API的完整实现
4.3.1 类型安全的上下文操作
go
// 用户上下文的内部表示
type UserContextData struct {
data map[string]interface{}
mutex sync.RWMutex
dirty bool // 标记是否需要同步
}
func (ucd *UserContextData) Get(key string) (interface{}, bool) {
ucd.mutex.RLock()
defer ucd.mutex.RUnlock()
if ucd.data == nil {
return nil, false
}
value, exists := ucd.data[key]
return value, exists
}
func (ucd *UserContextData) Set(key string, value interface{}) {
ucd.mutex.Lock()
defer ucd.mutex.Unlock()
if ucd.data == nil {
ucd.data = make(map[string]interface{})
}
ucd.data[key] = value
ucd.dirty = true
}
// 高级API实现
func SetUserContext(ctx map[string]interface{}) {
if ctx == nil {
return
}
// 创建新的上下文数据
contextData := &UserContextData{
data: make(map[string]interface{}),
dirty: true,
}
// 复制数据
for k, v := range ctx {
contextData.data[k] = v
}
// 存储到GLS
otel_set_user_context_to_gls(contextData)
}
func GetUserContext() map[string]interface{} {
contextData := otel_get_user_context_from_gls()
if contextData == nil {
return nil
}
if ucd, ok := contextData.(*UserContextData); ok {
ucd.mutex.RLock()
defer ucd.mutex.RUnlock()
if ucd.data == nil {
return nil
}
// 返回数据的副本,避免并发修改
result := make(map[string]interface{})
for k, v := range ucd.data {
result[k] = v
}
return result
}
return nil
}
func SetUserContextValue(key string, value interface{}) {
contextData := otel_get_user_context_from_gls()
var ucd *UserContextData
if contextData == nil {
ucd = &UserContextData{
data: make(map[string]interface{}),
dirty: true,
}
otel_set_user_context_to_gls(ucd)
} else {
var ok bool
ucd, ok = contextData.(*UserContextData)
if !ok {
// 类型不匹配,创建新的
ucd = &UserContextData{
data: make(map[string]interface{}),
dirty: true,
}
otel_set_user_context_to_gls(ucd)
}
}
ucd.Set(key, value)
}
func GetUserContextValue(key string) interface{} {
contextData := otel_get_user_context_from_gls()
if contextData == nil {
return nil
}
if ucd, ok := contextData.(*UserContextData); ok {
value, _ := ucd.Get(key)
return value
}
return nil
}4.3.2 性能优化和内存管理
go
// 上下文池管理
type ContextPool struct {
userContextPool sync.Pool
traceContextPool sync.Pool
baggagePool sync.Pool
}
var globalContextPool = &ContextPool{
userContextPool: sync.Pool{
New: func() interface{} {
return &UserContextData{
data: make(map[string]interface{}, 8), // 预分配容量
}
},
},
traceContextPool: sync.Pool{
New: func() interface{} {
return &TraceContextData{}
},
},
baggagePool: sync.Pool{
New: func() interface{} {
return &BaggageData{
items: make(map[string]string, 4),
}
},
},
}
func AcquireUserContext() *UserContextData {
ctx := globalContextPool.userContextPool.Get().(*UserContextData)
ctx.mutex.Lock()
// 清理旧数据
for k := range ctx.data {
delete(ctx.data, k)
}
ctx.dirty = false
ctx.mutex.Unlock()
return ctx
}
func ReleaseUserContext(ctx *UserContextData) {
if ctx != nil {
globalContextPool.userContextPool.Put(ctx)
}
}
// 智能垃圾回收
func (ucd *UserContextData) cleanup() {
ucd.mutex.Lock()
defer ucd.mutex.Unlock()
if len(ucd.data) > 100 { // 如果数据过多,重新创建map
ucd.data = make(map[string]interface{}, 8)
}
ucd.dirty = false
}
// 定期清理任务
func startContextCleanup() {
ticker := time.NewTicker(5 * time.Minute)
go func() {
for range ticker.C {
// 遍历所有活跃的goroutine,清理过期的上下文
cleanupExpiredContexts()
}
}()
}4.4 GLS的安全性和兼容性保障
4.4.1 版本兼容性检查
go
type RuntimeVersion struct {
Major int
Minor int
Patch int
}
var supportedVersions = []RuntimeVersion{
{1, 18, 0}, {1, 19, 0}, {1, 20, 0}, {1, 21, 0}, {1, 22, 0},
}
func checkRuntimeCompatibility() error {
version := runtime.Version()
current, err := parseVersion(version)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to parse runtime version: %w", err)
}
for _, supported := range supportedVersions {
if current.Major == supported.Major && current.Minor == supported.Minor {
return nil
}
}
return fmt.Errorf("unsupported Go version: %s", version)
}
// 运行时字段偏移验证
func validateFieldOffsets() error {
// 通过反射和unsafe操作验证字段偏移是否正确
g := _otel_gls_getg_impl()
// 验证otel_user_context字段
expectedOffset := uintptr(0x180) // 从base.json获取
actualOffset := unsafe.Offsetof(g.otel_user_context)
if actualOffset != expectedOffset {
return fmt.Errorf("otel_user_context offset mismatch: expected %d, got %d",
expectedOffset, actualOffset)
}
return nil
}4.4.2 错误恢复和降级机制
go
type GLSFallback struct {
enabled bool
contextMap sync.Map // goroutine ID -> context data
}
var glsFallback = &GLSFallback{}
func enableFallbackMode() {
glsFallback.enabled = true
log.Println("GLS fallback mode enabled")
}
func setUserContextSafe(ctx interface{}) {
defer func() {
if r := recover(); r != nil {
log.Printf("GLS operation failed, using fallback: %v", r)
enableFallbackMode()
setUserContextFallback(ctx)
}
}()
if glsFallback.enabled {
setUserContextFallback(ctx)
return
}
otel_set_user_context_to_gls(ctx)
}
func setUserContextFallback(ctx interface{}) {
gid := getGoroutineID()
glsFallback.contextMap.Store(gid, ctx)
}
func getUserContextFallback() interface{} {
gid := getGoroutineID()
if ctx, ok := glsFallback.contextMap.Load(gid); ok {
return ctx
}
return nil
}
// 获取goroutine ID的备用方法
func getGoroutineID() int64 {
var buf [64]byte
n := runtime.Stack(buf[:], false)
idField := strings.Fields(strings.TrimPrefix(string(buf[:n]), "goroutine "))[0]
id, _ := strconv.ParseInt(idField, 10, 64)
return id
}五、go:linkname黑魔法深度剖析
5.1 go:linkname的工作原理
5.1.1 编译器层面的符号链接机制
go:linkname 是Go编译器提供的一个特殊指令,允许将一个符号链接到另一个符号,实现对私有函数和变量的访问:
go
// go:linkname的基本语法
//go:linkname localname [importpath.name]
// 示例1:链接到runtime包的私有函数
//go:linkname runtime_getg runtime.getg
func runtime_getg() *g
// 示例2:将本地函数暴露给其他包
//go:linkname myFunction other/package.ExportedFunction
func myFunction() {}5.1.2 符号表操作的底层机制
go
// 编译器在处理go:linkname时的内部流程
type LinkNameDirective struct {
LocalSymbol string // 本地符号名
RemoteSymbol string // 远程符号名
Package string // 目标包路径
}
func (c *Compiler) processLinkName(directive *LinkNameDirective) error {
// 1. 解析符号信息
localSym := c.lookupSymbol(directive.LocalSymbol)
if localSym == nil {
return fmt.Errorf("local symbol %s not found", directive.LocalSymbol)
}
// 2. 创建符号链接
linkEntry := &SymbolLink{
From: localSym,
To: directive.RemoteSymbol,
Type: SymbolTypeFunction, // 或 SymbolTypeVariable
}
// 3. 添加到链接表
c.symbolLinks = append(c.symbolLinks, linkEntry)
// 4. 在链接阶段解析
return c.addPendingLink(linkEntry)
}
// 链接器处理符号链接
func (l *Linker) resolveLinkNames() error {
for _, link := range l.pendingLinks {
// 查找目标符号
targetSym := l.findSymbol(link.To)
if targetSym == nil {
return fmt.Errorf("target symbol %s not found", link.To)
}
// 建立链接关系
link.From.Address = targetSym.Address
link.From.Type = targetSym.Type
// 更新重定位表
l.updateRelocations(link)
}
return nil
}5.2 runtime包访问的高级技术
5.2.1 获取goroutine指针的多种方法
go
// 方法1:直接链接getg函数(最高效)
//go:linkname runtime_getg runtime.getg
func runtime_getg() *g
func getCurrentG() *g {
return runtime_getg()
}
// 方法2:通过反射获取(较慢,但更安全)
func getCurrentGReflection() *g {
// 获取当前栈信息
pc, _, _, ok := runtime.Caller(0)
if !ok {
return nil
}
// 通过栈信息推断goroutine
fn := runtime.FuncForPC(pc)
if fn == nil {
return nil
}
// 这里需要更复杂的逻辑来获取g指针
return getGFromStack()
}
// 方法3:通过汇编实现(平台相关)
//go:noescape
//go:nosplit
func getgAsm() *g
// getg_amd64.s
// TEXT ·getgAsm(SB), NOSPLIT, $0-8
// MOVQ (TLS), AX
// MOVQ AX, ret+0(FP)
// RET
// getg_arm64.s
// TEXT ·getgAsm(SB), NOSPLIT, $0-8
// MOVD g, R0
// MOVD R0, ret+0(FP)
// RET5.2.2 运行时函数替换的完整实现
go
// 函数替换的核心机制
type FunctionReplacer struct {
originalFunctions map[string]uintptr
replacements map[string]uintptr
mutex sync.RWMutex
}
func NewFunctionReplacer() *FunctionReplacer {
return &FunctionReplacer{
originalFunctions: make(map[string]uintptr),
replacements: make(map[string]uintptr),
}
}
// 替换runtime.newproc1函数
func (fr *FunctionReplacer) ReplaceNewproc1() error {
// 1. 保存原始函数地址
//go:linkname original_newproc1 runtime.newproc1
var original_newproc1 func(*funcval, unsafe.Pointer, int32, *g, uintptr) *g
originalAddr := *(*uintptr)(unsafe.Pointer(&original_newproc1))
fr.originalFunctions["runtime.newproc1"] = originalAddr
// 2. 创建包装函数
wrapper := func(fn *funcval, argp unsafe.Pointer, narg int32, callergp *g, callerpc uintptr) *g {
// 调用原始函数
newg := original_newproc1(fn, argp, narg, callergp, callerpc)
// 执行上下文传播
if callergp != nil && newg != nil {
propagateContext(callergp, newg)
}
return newg
}
// 3. 替换函数指针
wrapperAddr := *(*uintptr)(unsafe.Pointer(&wrapper))
fr.replacements["runtime.newproc1"] = wrapperAddr
// 4. 执行替换(这里需要修改内存保护)
return fr.replaceFunction("runtime.newproc1", originalAddr, wrapperAddr)
}
func (fr *FunctionReplacer) replaceFunction(name string, oldAddr, newAddr uintptr) error {
// 1. 修改内存页保护属性
pageSize := uintptr(os.Getpagesize())
pageStart := oldAddr &^ (pageSize - 1)
if err := mprotect(pageStart, pageSize, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE|PROT_EXEC); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to change memory protection: %w", err)
}
// 2. 生成跳转指令
jumpCode := generateJumpCode(oldAddr, newAddr)
// 3. 写入跳转指令
copy((*[32]byte)(unsafe.Pointer(oldAddr))[:], jumpCode)
// 4. 恢复内存保护
if err := mprotect(pageStart, pageSize, PROT_READ|PROT_EXEC); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to restore memory protection: %w", err)
}
return nil
}
// 生成平台相关的跳转代码
func generateJumpCode(from, to uintptr) []byte {
switch runtime.GOARCH {
case "amd64":
return generateAMD64Jump(from, to)
case "arm64":
return generateARM64Jump(from, to)
default:
panic("unsupported architecture")
}
}
func generateAMD64Jump(from, to uintptr) []byte {
// JMP指令:FF 25 00 00 00 00 [8字节地址]
code := make([]byte, 14)
code[0] = 0xFF // JMP
code[1] = 0x25 // ModR/M
// 相对地址为0(直接跳转)
binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(code[2:6], 0)
// 目标地址
binary.LittleEndian.PutUint64(code[6:14], uint64(to))
return code
}
func generateARM64Jump(from, to uintptr) []byte {
// ARM64跳转指令更复杂,需要多条指令
code := make([]byte, 16)
// LDR X16, #8 (加载地址到X16寄存器)
code[0] = 0x50
code[1] = 0x00
code[2] = 0x00
code[3] = 0x58
// BR X16 (跳转到X16)
code[4] = 0x00
code[5] = 0x02
code[6] = 0x1F
code[7] = 0xD6
// 目标地址(8字节)
binary.LittleEndian.PutUint64(code[8:16], uint64(to))
return code
}5.3 内存操作和安全性保障
5.3.1 内存保护和权限管理
go
// 内存保护常量
const (
PROT_NONE = 0x0
PROT_READ = 0x1
PROT_WRITE = 0x2
PROT_EXEC = 0x4
)
// 跨平台的内存保护函数
func mprotect(addr uintptr, length uintptr, prot int) error {
switch runtime.GOOS {
case "linux", "darwin":
return mprotectUnix(addr, length, prot)
case "windows":
return mprotectWindows(addr, length, prot)
default:
return fmt.Errorf("unsupported OS: %s", runtime.GOOS)
}
}
func mprotectUnix(addr uintptr, length uintptr, prot int) error {
_, _, errno := syscall.Syscall(
syscall.SYS_MPROTECT,
addr,
length,
uintptr(prot),
)
if errno != 0 {
return errno
}
return nil
}
func mprotectWindows(addr uintptr, length uintptr, prot int) error {
var winProt uint32
switch prot {
case PROT_READ:
winProt = 0x02 // PAGE_READONLY
case PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE:
winProt = 0x04 // PAGE_READWRITE
case PROT_READ | PROT_EXEC:
winProt = 0x20 // PAGE_EXECUTE_READ
case PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE | PROT_EXEC:
winProt = 0x40 // PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE
default:
winProt = 0x01 // PAGE_NOACCESS
}
var oldProtect uint32
ret, _, _ := syscall.NewLazyDLL("kernel32.dll").
NewProc("VirtualProtect").
Call(addr, length, uintptr(winProt), uintptr(unsafe.Pointer(&oldProtect)))
if ret == 0 {
return fmt.Errorf("VirtualProtect failed")
}
return nil
}5.3.2 运行时安全检查和验证
go
type SafetyChecker struct {
knownFunctions map[string]FunctionInfo
checksEnabled bool
}
type FunctionInfo struct {
Name string
Package string
Signature string
MinGoVersion string
MaxGoVersion string
Deprecated bool
}
func NewSafetyChecker() *SafetyChecker {
return &SafetyChecker{
knownFunctions: map[string]FunctionInfo{
"runtime.getg": {
Name: "getg",
Package: "runtime",
Signature: "func() *g",
MinGoVersion: "1.0",
MaxGoVersion: "",
Deprecated: false,
},
"runtime.newproc1": {
Name: "newproc1",
Package: "runtime",
Signature: "func(*funcval, unsafe.Pointer, int32, *g, uintptr) *g",
MinGoVersion: "1.0",
MaxGoVersion: "",
Deprecated: false,
},
},
checksEnabled: true,
}
}
func (sc *SafetyChecker) ValidateLinkName(localName, remoteName string) error {
if !sc.checksEnabled {
return nil
}
// 1. 检查目标函数是否已知
funcInfo, exists := sc.knownFunctions[remoteName]
if !exists {
return fmt.Errorf("unknown function: %s", remoteName)
}
// 2. 检查Go版本兼容性
currentVersion := runtime.Version()
if !sc.isVersionCompatible(currentVersion, funcInfo) {
return fmt.Errorf("function %s not compatible with Go %s", remoteName, currentVersion)
}
// 3. 检查是否已弃用
if funcInfo.Deprecated {
log.Printf("Warning: function %s is deprecated", remoteName)
}
// 4. 验证函数签名(如果可能)
if err := sc.validateSignature(localName, funcInfo.Signature); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("signature validation failed: %w", err)
}
return nil
}
func (sc *SafetyChecker) isVersionCompatible(current string, info FunctionInfo) bool {
// 解析版本号并比较
currentVer, err := parseGoVersion(current)
if err != nil {
return false
}
if info.MinGoVersion != "" {
minVer, err := parseGoVersion(info.MinGoVersion)
if err != nil {
return false
}
if currentVer.Less(minVer) {
return false
}
}
if info.MaxGoVersion != "" {
maxVer, err := parseGoVersion(info.MaxGoVersion)
if err != nil {
return false
}
if currentVer.Greater(maxVer) {
return false
}
}
return true
}
// 运行时函数存在性检查
func (sc *SafetyChecker) CheckFunctionExists(name string) bool {
defer func() {
if r := recover(); r != nil {
// 如果访问函数时panic,说明函数不存在或不可访问
log.Printf("Function %s check failed: %v", name, r)
}
}()
switch name {
case "runtime.getg":
//go:linkname testGetg runtime.getg
var testGetg func() *g
return testGetg != nil
case "runtime.newproc1":
//go:linkname testNewproc1 runtime.newproc1
var testNewproc1 func(*funcval, unsafe.Pointer, int32, *g, uintptr) *g
return testNewproc1 != nil
default:
return false
}
}5.4 高级应用场景和最佳实践
5.4.1 动态函数拦截系统
go
type FunctionInterceptor struct {
interceptors map[string][]InterceptorFunc
mutex sync.RWMutex
}
type InterceptorFunc func(args []interface{}) ([]interface{}, bool)
func NewFunctionInterceptor() *FunctionInterceptor {
return &FunctionInterceptor{
interceptors: make(map[string][]InterceptorFunc),
}
}
func (fi *FunctionInterceptor) AddInterceptor(funcName string, interceptor InterceptorFunc) {
fi.mutex.Lock()
defer fi.mutex.Unlock()
fi.interceptors[funcName] = append(fi.interceptors[funcName], interceptor)
}
// 为runtime.newproc1添加拦截器
func (fi *FunctionInterceptor) InterceptNewproc1() {
//go:linkname original_newproc1 runtime.newproc1
var original_newproc1 func(*funcval, unsafe.Pointer, int32, *g, uintptr) *g
// 创建拦截包装器
wrapper := func(fn *funcval, argp unsafe.Pointer, narg int32, callergp *g, callerpc uintptr) *g {
// 准备参数
args := []interface{}{fn, argp, narg, callergp, callerpc}
// 执行前置拦截器
fi.mutex.RLock()
interceptors := fi.interceptors["runtime.newproc1"]
fi.mutex.RUnlock()
for _, interceptor := range interceptors {
if newArgs, shouldContinue := interceptor(args); shouldContinue {
args = newArgs
} else {
// 拦截器决定不继续执行
return nil
}
}
// 调用原始函数
result := original_newproc1(
args[0].(*funcval),
args[1].(unsafe.Pointer),
args[2].(int32),
args[3].(*g),
args[4].(uintptr),
)
// 执行后置处理
fi.postProcess("runtime.newproc1", args, result)
return result
}
// 替换函数
fi.replaceFunction("runtime.newproc1", wrapper)
}
func (fi *FunctionInterceptor) postProcess(funcName string, args []interface{}, result interface{}) {
// 记录调用信息
log.Printf("Function %s called with args: %v, result: %v", funcName, args, result)
// 执行自定义后置处理
if funcName == "runtime.newproc1" && result != nil {
newg := result.(*g)
callergp := args[3].(*g)
// 执行上下文传播
if callergp != nil {
propagateContextAdvanced(callergp, newg)
}
}
}5.4.2 性能监控和调试支持
go
type PerformanceMonitor struct {
callCounts map[string]int64
totalTime map[string]time.Duration
mutex sync.RWMutex
enabled bool
}
func NewPerformanceMonitor() *PerformanceMonitor {
return &PerformanceMonitor{
callCounts: make(map[string]int64),
totalTime: make(map[string]time.Duration),
enabled: true,
}
}
func (pm *PerformanceMonitor) WrapFunction(name string, original interface{}) interface{} {
if !pm.enabled {
return original
}
// 使用反射创建包装函数
originalValue := reflect.ValueOf(original)
originalType := originalValue.Type()
wrapper := reflect.MakeFunc(originalType, func(args []reflect.Value) []reflect.Value {
start := time.Now()
// 调用原始函数
results := originalValue.Call(args)
// 记录性能数据
duration := time.Since(start)
pm.recordCall(name, duration)
return results
})
return wrapper.Interface()
}
func (pm *PerformanceMonitor) recordCall(name string, duration time.Duration) {
pm.mutex.Lock()
defer pm.mutex.Unlock()
pm.callCounts[name]++
pm.totalTime[name] += duration
}
func (pm *PerformanceMonitor) GetStats() map[string]CallStats {
pm.mutex.RLock()
defer pm.mutex.RUnlock()
stats := make(map[string]CallStats)
for name, count := range pm.callCounts {
totalTime := pm.totalTime[name]
stats[name] = CallStats{
CallCount: count,
TotalTime: totalTime,
AverageTime: time.Duration(int64(totalTime) / count),
}
}
return stats
}
type CallStats struct {
CallCount int64
TotalTime time.Duration
AverageTime time.Duration
}六、插桩规则系统深度解析
6.1 规则系统架构设计
6.1.1 规则配置的层次结构
插桩规则系统采用多层次的配置架构,支持灵活的规则定义和管理:
go
// 规则系统的核心数据结构
type RuleSystem struct {
GlobalRules []GlobalRule `json:"global_rules"`
PackageRules []PackageRule `json:"package_rules"`
FunctionRules []FunctionRule `json:"function_rules"`
StructRules []StructRule `json:"struct_rules"`
ImportRules []ImportRule `json:"import_rules"`
// 规则处理器
processors map[string]RuleProcessor
// 规则缓存
ruleCache *RuleCache
// 规则验证器
validator *RuleValidator
}
// 全局规则:影响整个编译过程
type GlobalRule struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
Type string `json:"type"` // "field_injection", "function_replacement"
Target string `json:"target"` // 目标包或类型
Action string `json:"action"` // 执行的动作
Conditions []RuleCondition `json:"conditions"` // 执行条件
Parameters map[string]interface{} `json:"parameters"` // 规则参数
Priority int `json:"priority"` // 优先级
Enabled bool `json:"enabled"` // 是否启用
}
// 包级规则:针对特定包的规则
type PackageRule struct {
PackagePath string `json:"package_path"`
Rules []FunctionRule `json:"rules"`
Imports []string `json:"imports"` // 需要添加的导入
Excludes []string `json:"excludes"` // 排除的文件
}
// 函数级规则:针对特定函数的插桩规则
type FunctionRule struct {
FunctionName string `json:"function_name"`
PackagePath string `json:"package_path"`
Signature string `json:"signature"` // 函数签名匹配
OnEnter *HookDefinition `json:"on_enter"` // 函数入口钩子
OnExit *HookDefinition `json:"on_exit"` // 函数出口钩子
OnPanic *HookDefinition `json:"on_panic"` // 异常处理钩子
Replace *ReplaceDefinition `json:"replace"` // 函数替换定义
Conditions []RuleCondition `json:"conditions"` // 应用条件
}
// 结构体规则:用于字段注入
type StructRule struct {
StructName string `json:"struct_name"`
PackagePath string `json:"package_path"`
Fields []FieldInjection `json:"fields"` // 要注入的字段
Methods []MethodInjection `json:"methods"` // 要注入的方法
}
// 钩子定义
type HookDefinition struct {
Code string `json:"code"` // 钩子代码
Template string `json:"template"` // 代码模板
Parameters map[string]interface{} `json:"parameters"` // 模板参数
Imports []string `json:"imports"` // 需要的导入
Async bool `json:"async"` // 是否异步执行
}
// 字段注入定义
type FieldInjection struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
Type string `json:"type"`
Tag string `json:"tag"`
DefaultValue interface{} `json:"default_value"`
Position string `json:"position"` // "first", "last", "after:field_name"
}6.1.2 规则处理器的实现机制
go
// 规则处理器接口
type RuleProcessor interface {
ProcessRule(rule interface{}, context *ProcessContext) error
ValidateRule(rule interface{}) error
GetRuleType() string
}
// 函数插桩处理器
type FunctionInstrumentationProcessor struct {
astParser *AstParser
codeGen *CodeGenerator
templateMgr *TemplateManager
}
func (fip *FunctionInstrumentationProcessor) ProcessRule(rule interface{}, context *ProcessContext) error {
funcRule, ok := rule.(*FunctionRule)
if !ok {
return fmt.Errorf("invalid rule type for function instrumentation")
}
// 1. 查找目标函数
targetFunc, err := fip.findTargetFunction(funcRule, context)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to find target function: %w", err)
}
// 2. 生成插桩代码
instrumentationCode, err := fip.generateInstrumentationCode(funcRule, targetFunc)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to generate instrumentation code: %w", err)
}
// 3. 应用插桩
if err := fip.applyInstrumentation(targetFunc, instrumentationCode, context); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to apply instrumentation: %w", err)
}
return nil
}
func (fip *FunctionInstrumentationProcessor) generateInstrumentationCode(rule *FunctionRule, targetFunc *dst.FuncDecl) (*InstrumentationCode, error) {
code := &InstrumentationCode{
OnEnter: "",
OnExit: "",
OnPanic: "",
}
// 生成入口代码
if rule.OnEnter != nil {
enterCode, err := fip.generateHookCode(rule.OnEnter, targetFunc, "enter")
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to generate enter hook: %w", err)
}
code.OnEnter = enterCode
}
// 生成出口代码
if rule.OnExit != nil {
exitCode, err := fip.generateHookCode(rule.OnExit, targetFunc, "exit")
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to generate exit hook: %w", err)
}
code.OnExit = exitCode
}
// 生成异常处理代码
if rule.OnPanic != nil {
panicCode, err := fip.generateHookCode(rule.OnPanic, targetFunc, "panic")
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to generate panic hook: %w", err)
}
code.OnPanic = panicCode
}
return code, nil
}
// 结构体字段注入处理器
type StructFieldInjectionProcessor struct {
astParser *AstParser
fieldGen *FieldGenerator
}
func (sfip *StructFieldInjectionProcessor) ProcessRule(rule interface{}, context *ProcessContext) error {
structRule, ok := rule.(*StructRule)
if !ok {
return fmt.Errorf("invalid rule type for struct field injection")
}
// 1. 查找目标结构体
targetStruct, err := sfip.findTargetStruct(structRule, context)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to find target struct: %w", err)
}
// 2. 注入字段
for _, field := range structRule.Fields {
if err := sfip.injectField(targetStruct, &field, context); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to inject field %s: %w", field.Name, err)
}
}
// 3. 注入方法
for _, method := range structRule.Methods {
if err := sfip.injectMethod(targetStruct, &method, context); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to inject method %s: %w", method.Name, err)
}
}
return nil
}
func (sfip *StructFieldInjectionProcessor) injectField(targetStruct *dst.StructType, field *FieldInjection, context *ProcessContext) error {
// 创建新字段
newField := &dst.Field{
Names: []*dst.Ident{dst.NewIdent(field.Name)},
Type: sfip.parseFieldType(field.Type),
}
// 添加标签
if field.Tag != "" {
newField.Tag = &dst.BasicLit{
Kind: token.STRING,
Value: fmt.Sprintf("`%s`", field.Tag),
}
}
// 确定插入位置
insertPos := sfip.calculateInsertPosition(targetStruct, field.Position)
// 插入字段
targetStruct.Fields.List = sfip.insertFieldAtPosition(targetStruct.Fields.List, newField, insertPos)
return nil
}6.2 规则匹配和条件系统
6.2.1 高级条件匹配引擎
go
// 条件匹配引擎
type ConditionMatcher struct {
evaluators map[string]ConditionEvaluator
}
type ConditionEvaluator interface {
Evaluate(condition *RuleCondition, context *MatchContext) (bool, error)
GetConditionType() string
}
// 规则条件定义
type RuleCondition struct {
Type string `json:"type"` // 条件类型
Operator string `json:"operator"` // 操作符: "eq", "ne", "contains", "regex", "and", "or"
Field string `json:"field"` // 匹配字段
Value interface{} `json:"value"` // 匹配值
Values []interface{} `json:"values"` // 多值匹配
Conditions []RuleCondition `json:"conditions"` // 嵌套条件
Negate bool `json:"negate"` // 是否取反
}
// 匹配上下文
type MatchContext struct {
PackagePath string
FunctionName string
FileName string
GoVersion string
BuildTags []string
Environment map[string]string
CustomData map[string]interface{}
}
// 包路径条件评估器
type PackagePathEvaluator struct{}
func (ppe *PackagePathEvaluator) Evaluate(condition *RuleCondition, context *MatchContext) (bool, error) {
if condition.Field != "package_path" {
return false, fmt.Errorf("invalid field for package path evaluator: %s", condition.Field)
}
result := false
switch condition.Operator {
case "eq":
result = context.PackagePath == condition.Value.(string)
case "ne":
result = context.PackagePath != condition.Value.(string)
case "contains":
result = strings.Contains(context.PackagePath, condition.Value.(string))
case "regex":
pattern := condition.Value.(string)
matched, err := regexp.MatchString(pattern, context.PackagePath)
if err != nil {
return false, fmt.Errorf("invalid regex pattern: %w", err)
}
result = matched
case "in":
values := condition.Values
for _, v := range values {
if context.PackagePath == v.(string) {
result = true
break
}
}
default:
return false, fmt.Errorf("unsupported operator: %s", condition.Operator)
}
if condition.Negate {
result = !result
}
return result, nil
}
// 函数签名条件评估器
type FunctionSignatureEvaluator struct{}
func (fse *FunctionSignatureEvaluator) Evaluate(condition *RuleCondition, context *MatchContext) (bool, error) {
if condition.Field != "function_signature" {
return false, fmt.Errorf("invalid field for function signature evaluator: %s", condition.Field)
}
// 获取当前函数的签名
currentSignature := context.CustomData["function_signature"].(string)
expectedSignature := condition.Value.(string)
result := false
switch condition.Operator {
case "eq":
result = currentSignature == expectedSignature
case "contains":
result = strings.Contains(currentSignature, expectedSignature)
case "regex":
matched, err := regexp.MatchString(expectedSignature, currentSignature)
if err != nil {
return false, fmt.Errorf("invalid regex pattern: %w", err)
}
result = matched
default:
return false, fmt.Errorf("unsupported operator: %s", condition.Operator)
}
if condition.Negate {
result = !result
}
return result, nil
}
// 复合条件评估器
type CompositeConditionEvaluator struct {
matcher *ConditionMatcher
}
func (cce *CompositeConditionEvaluator) Evaluate(condition *RuleCondition, context *MatchContext) (bool, error) {
switch condition.Operator {
case "and":
return cce.evaluateAndCondition(condition, context)
case "or":
return cce.evaluateOrCondition(condition, context)
default:
return false, fmt.Errorf("unsupported composite operator: %s", condition.Operator)
}
}
func (cce *CompositeConditionEvaluator) evaluateAndCondition(condition *RuleCondition, context *MatchContext) (bool, error) {
for _, subCondition := range condition.Conditions {
result, err := cce.matcher.EvaluateCondition(&subCondition, context)
if err != nil {
return false, err
}
if !result {
return false, nil // AND条件:任何一个为false,整体为false
}
}
return true, nil
}
func (cce *CompositeConditionEvaluator) evaluateOrCondition(condition *RuleCondition, context *MatchContext) (bool, error) {
for _, subCondition := range condition.Conditions {
result, err := cce.matcher.EvaluateCondition(&subCondition, context)
if err != nil {
return false, err
}
if result {
return true, nil // OR条件:任何一个为true,整体为true
}
}
return false, nil
}6.3 模板系统和代码生成
6.3.1 高级模板引擎
go
// 模板管理器
type TemplateManager struct {
templates map[string]*Template
functions template.FuncMap
cache *TemplateCache
validator *TemplateValidator
}
// 模板定义
type Template struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
Content string `json:"content"`
Type string `json:"type"` // "function", "struct", "import"
Parameters []TemplateParam `json:"parameters"`
Imports []string `json:"imports"`
Dependencies []string `json:"dependencies"`
}
type TemplateParam struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
Type string `json:"type"`
Required bool `json:"required"`
DefaultValue interface{} `json:"default_value"`
Description string `json:"description"`
}
func NewTemplateManager() *TemplateManager {
tm := &TemplateManager{
templates: make(map[string]*Template),
cache: NewTemplateCache(),
validator: NewTemplateValidator(),
}
// 注册内置函数
tm.functions = template.FuncMap{
"camelCase": tm.toCamelCase,
"snakeCase": tm.toSnakeCase,
"pascalCase": tm.toPascalCase,
"lower": strings.ToLower,
"upper": strings.ToUpper,
"join": strings.Join,
"split": strings.Split,
"contains": strings.Contains,
"replace": strings.ReplaceAll,
"trim": strings.TrimSpace,
"quote": tm.quote,
"unquote": tm.unquote,
"typeOf": tm.getType,
"isPointer": tm.isPointer,
"isSlice": tm.isSlice,
"isMap": tm.isMap,
"isInterface": tm.isInterface,
"generateID": tm.generateID,
"timestamp": tm.timestamp,
"formatTime": tm.formatTime,
}
return tm
}
// 函数插桩模板
const FunctionInstrumentationTemplate = `
// Generated by otel instrumentation
func {{.FunctionName}}({{range $i, $param := .Parameters}}{{if $i}}, {{end}}{{$param.Name}} {{$param.Type}}{{end}}) {{if .ReturnTypes}}({{range $i, $ret := .ReturnTypes}}{{if $i}}, {{end}}{{$ret}}{{end}}){{end}} {
{{if .OnEnter}}
// OnEnter hook
{{.OnEnter}}
{{end}}
{{if .OnPanic}}
defer func() {
if r := recover(); r != nil {
// OnPanic hook
{{.OnPanic}}
panic(r)
}
}()
{{end}}
{{if .OnExit}}
defer func() {
// OnExit hook
{{.OnExit}}
}()
{{end}}
{{if .OriginalCall}}
{{if .ReturnTypes}}return {{end}}{{.OriginalCall}}
{{else}}
// Original function body
{{.OriginalBody}}
{{end}}
}
`
// 上下文传播模板
const ContextPropagationTemplate = `
// Context propagation for {{.FunctionName}}
if callergp := otel_get_current_g(); callergp != nil {
if userCtx := otel_get_user_context_from_gls(); userCtx != nil {
defer func() {
if newg := otel_get_current_g(); newg != nil && newg != callergp {
otel_set_user_context_to_gls(userCtx)
}
}()
}
if traceCtx := otel_get_trace_context_from_gls(); traceCtx != nil {
defer func() {
if newg := otel_get_current_g(); newg != nil && newg != callergp {
otel_set_trace_context_to_gls(traceCtx)
}
}()
}
}
`
func (tm *TemplateManager) RenderTemplate(templateName string, data interface{}) (string, error) {
// 1. 从缓存获取模板
tmpl, err := tm.getTemplate(templateName)
if err != nil {
return "", fmt.Errorf("failed to get template %s: %w", templateName, err)
}
// 2. 验证模板数据
if err := tm.validator.ValidateData(tmpl, data); err != nil {
return "", fmt.Errorf("template data validation failed: %w", err)
}
// 3. 渲染模板
var buf bytes.Buffer
if err := tmpl.Execute(&buf, data); err != nil {
return "", fmt.Errorf("template execution failed: %w", err)
}
// 4. 后处理
result := tm.postProcess(buf.String())
return result, nil
}
func (tm *TemplateManager) getTemplate(name string) (*template.Template, error) {
// 检查缓存
if cached := tm.cache.Get(name); cached != nil {
return cached, nil
}
// 获取模板定义
templateDef, exists := tm.templates[name]
if !exists {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("template %s not found", name)
}
// 创建模板
tmpl := template.New(name).Funcs(tm.functions)
// 解析模板内容
tmpl, err := tmpl.Parse(templateDef.Content)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to parse template: %w", err)
}
// 缓存模板
tm.cache.Set(name, tmpl)
return tmpl, nil
}
// 模板函数实现
func (tm *TemplateManager) toCamelCase(s string) string {
words := strings.Split(s, "_")
if len(words) == 0 {
return s
}
result := strings.ToLower(words[0])
for i := 1; i < len(words); i++ {
if len(words[i]) > 0 {
result += strings.ToUpper(words[i][:1]) + strings.ToLower(words[i][1:])
}
}
return result
}
func (tm *TemplateManager) toPascalCase(s string) string {
words := strings.Split(s, "_")
var result strings.Builder
for _, word := range words {
if len(word) > 0 {
result.WriteString(strings.ToUpper(word[:1]))
result.WriteString(strings.ToLower(word[1:]))
}
}
return result.String()
}
func (tm *TemplateManager) toSnakeCase(s string) string {
var result strings.Builder
for i, r := range s {
if i > 0 && unicode.IsUpper(r) {
result.WriteRune('_')
}
result.WriteRune(unicode.ToLower(r))
}
return result.String()
}
func (tm *TemplateManager) generateID() string {
return fmt.Sprintf("otel_%d_%d", time.Now().UnixNano(), rand.Int63())
}
func (tm *TemplateManager) timestamp() int64 {
return time.Now().Unix()
}
func (tm *TemplateManager) formatTime(format string) string {
return time.Now().Format(format)
}6.4 规则验证和错误处理
6.4.1 规则验证系统
go
// 规则验证器
type RuleValidator struct {
validators map[string]Validator
}
type Validator interface {
Validate(rule interface{}) []ValidationError
GetRuleType() string
}
type ValidationError struct {
Field string `json:"field"`
Message string `json:"message"`
Code string `json:"code"`
Level string `json:"level"` // "error", "warning", "info"
}
// 函数规则验证器
type FunctionRuleValidator struct{}
func (frv *FunctionRuleValidator) Validate(rule interface{}) []ValidationError {
funcRule, ok := rule.(*FunctionRule)
if !ok {
return []ValidationError{{
Field: "rule",
Message: "Invalid rule type for function rule validator",
Code: "INVALID_RULE_TYPE",
Level: "error",
}}
}
var errors []ValidationError
// 验证函数名
if funcRule.FunctionName == "" {
errors = append(errors, ValidationError{
Field: "function_name",
Message: "Function name is required",
Code: "MISSING_FUNCTION_NAME",
Level: "error",
})
}
// 验证包路径
if funcRule.PackagePath == "" {
errors = append(errors, ValidationError{
Field: "package_path",
Message: "Package path is required",
Code: "MISSING_PACKAGE_PATH",
Level: "error",
})
}
// 验证钩子定义
if funcRule.OnEnter != nil {
if hookErrors := frv.validateHook(funcRule.OnEnter, "on_enter"); len(hookErrors) > 0 {
errors = append(errors, hookErrors...)
}
}
if funcRule.OnExit != nil {
if hookErrors := frv.validateHook(funcRule.OnExit, "on_exit"); len(hookErrors) > 0 {
errors = append(errors, hookErrors...)
}
}
// 验证条件
for i, condition := range funcRule.Conditions {
if condErrors := frv.validateCondition(&condition, fmt.Sprintf("conditions[%d]", i)); len(condErrors) > 0 {
errors = append(errors, condErrors...)
}
}
return errors
}
func (frv *FunctionRuleValidator) validateHook(hook *HookDefinition, fieldPrefix string) []ValidationError {
var errors []ValidationError
if hook.Code == "" && hook.Template == "" {
errors = append(errors, ValidationError{
Field: fieldPrefix + ".code",
Message: "Either code or template must be specified",
Code: "MISSING_HOOK_CONTENT",
Level: "error",
})
}
if hook.Code != "" && hook.Template != "" {
errors = append(errors, ValidationError{
Field: fieldPrefix,
Message: "Cannot specify both code and template",
Code: "CONFLICTING_HOOK_CONTENT",
Level: "error",
})
}
// 验证代码语法
if hook.Code != "" {
if syntaxErrors := frv.validateGoSyntax(hook.Code); len(syntaxErrors) > 0 {
for _, syntaxError := range syntaxErrors {
errors = append(errors, ValidationError{
Field: fieldPrefix + ".code",
Message: fmt.Sprintf("Syntax error: %s", syntaxError),
Code: "SYNTAX_ERROR",
Level: "error",
})
}
}
}
return errors
}
func (frv *FunctionRuleValidator) validateGoSyntax(code string) []string {
// 创建临时文件进行语法检查
tempCode := fmt.Sprintf(`
package main
func tempFunc() {
%s
}
`, code)
// 解析代码
fset := token.NewFileSet()
_, err := parser.ParseFile(fset, "temp.go", tempCode, parser.ParseComments)
if err != nil {
return []string{err.Error()}
}
return nil
}
// 规则冲突检测器
type RuleConflictDetector struct {
rules []interface{}
}
func (rcd *RuleConflictDetector) DetectConflicts() []RuleConflict {
var conflicts []RuleConflict
// 检测函数规则冲突
functionRules := rcd.getFunctionRules()
conflicts = append(conflicts, rcd.detectFunctionRuleConflicts(functionRules)...)
// 检测结构体规则冲突
structRules := rcd.getStructRules()
conflicts = append(conflicts, rcd.detectStructRuleConflicts(structRules)...)
return conflicts
}
type RuleConflict struct {
Type string `json:"type"`
Description string `json:"description"`
Rules []string `json:"rules"`
Severity string `json:"severity"` // "error", "warning"
Resolution string `json:"resolution"`
}
func (rcd *RuleConflictDetector) detectFunctionRuleConflicts(rules []*FunctionRule) []RuleConflict {
var conflicts []RuleConflict
// 按函数分组
functionGroups := make(map[string][]*FunctionRule)
for _, rule := range rules {
key := fmt.Sprintf("%s.%s", rule.PackagePath, rule.FunctionName)
functionGroups[key] = append(functionGroups[key], rule)
}
// 检测同一函数的多个规则
for funcKey, funcRules := range functionGroups {
if len(funcRules) > 1 {
// 检查是否有冲突的钩子
hasOnEnter := false
hasOnExit := false
hasReplace := false
var ruleNames []string
for _, rule := range funcRules {
ruleNames = append(ruleNames, rule.FunctionName)
if rule.OnEnter != nil {
if hasOnEnter {
conflicts = append(conflicts, RuleConflict{
Type: "duplicate_on_enter_hook",
Description: fmt.Sprintf("Multiple OnEnter hooks defined for function %s", funcKey),
Rules: ruleNames,
Severity: "error",
Resolution: "Merge hooks or use priority-based selection",
})
}
hasOnEnter = true
}
if rule.OnExit != nil {
if hasOnExit {
conflicts = append(conflicts, RuleConflict{
Type: "duplicate_on_exit_hook",
Description: fmt.Sprintf("Multiple OnExit hooks defined for function %s", funcKey),
Rules: ruleNames,
Severity: "error",
Resolution: "Merge hooks or use priority-based selection",
})
}
hasOnExit = true
}
if rule.Replace != nil {
if hasReplace {
conflicts = append(conflicts, RuleConflict{
Type: "duplicate_function_replacement",
Description: fmt.Sprintf("Multiple replacement rules defined for function %s", funcKey),
Rules: ruleNames,
Severity: "error",
Resolution: "Use only one replacement rule per function",
})
}
hasReplace = true
}
}
}
}
return conflicts
}七、框架支持和生态集成深度解析
7.1 Web框架深度集成
7.1.1 Gin框架专用插桩技术
go
// Gin框架规则定义
type GinFrameworkRule struct {
Framework string `json:"framework"` // "gin"
Version string `json:"version"` // 支持的版本范围
Routes []RouteRule `json:"routes"` // 路由级规则
Middlewares []MiddlewareRule `json:"middlewares"` // 中间件规则
Handlers []HandlerRule `json:"handlers"` // 处理器规则
Context *ContextRule `json:"context"` // 上下文传播规则
}
// Gin框架专用处理器
type GinFrameworkProcessor struct {
baseProcessor *WebFrameworkProcessor
routeAnalyzer *GinRouteAnalyzer
contextManager *GinContextManager
}
func (gfp *GinFrameworkProcessor) ProcessGinRoute(rule *RouteRule, context *ProcessContext) error {
// 1. 识别Gin路由定义模式
routePattern := `router\.(GET|POST|PUT|DELETE|PATCH|HEAD|OPTIONS)\s*\(\s*"([^"]+)"\s*,\s*([^)]+)\)`
// 2. 为每个路由处理器添加追踪
instrumentationCode := `
// Gin route instrumentation - Generated by otel
func(c *gin.Context) {
// 创建追踪span
ctx := c.Request.Context()
tracer := otel.Tracer("gin")
ctx, span := tracer.Start(ctx, "{{.Method}} {{.Path}}")
defer span.End()
// 设置HTTP相关属性
span.SetAttributes(
attribute.String("http.method", c.Request.Method),
attribute.String("http.url", c.Request.URL.String()),
attribute.String("http.route", "{{.Path}}"),
attribute.String("http.user_agent", c.Request.UserAgent()),
attribute.String("gin.version", gin.Version),
)
// 传播追踪上下文
c.Request = c.Request.WithContext(ctx)
// 记录请求开始时间
startTime := time.Now()
// 执行原始处理器
{{.OriginalHandler}}(c)
// 记录响应信息
duration := time.Since(startTime)
status := c.Writer.Status()
span.SetAttributes(
attribute.Int("http.status_code", status),
attribute.Int64("http.response.duration_ms", duration.Milliseconds()),
attribute.Int64("http.response.size", int64(c.Writer.Size())),
)
// 错误处理
if status >= 400 {
span.SetStatus(codes.Error, fmt.Sprintf("HTTP %d", status))
} else {
span.SetStatus(codes.Ok, "")
}
// 记录错误信息(如果有)
if len(c.Errors) > 0 {
for _, err := range c.Errors {
span.RecordError(err.Err)
}
}
}
`
return gfp.applyRouteInstrumentation(rule, instrumentationCode, context)
}
// Gin中间件插桩
func (gfp *GinFrameworkProcessor) ProcessGinMiddleware(rule *MiddlewareRule, context *ProcessContext) error {
middlewareCode := `
// Gin middleware instrumentation
func() gin.HandlerFunc {
return func(c *gin.Context) {
// 创建中间件span
ctx := c.Request.Context()
tracer := otel.Tracer("gin.middleware")
ctx, span := tracer.Start(ctx, "middleware.{{.MiddlewareName}}")
defer span.End()
// 更新请求上下文
c.Request = c.Request.WithContext(ctx)
// 记录中间件信息
span.SetAttributes(
attribute.String("middleware.name", "{{.MiddlewareName}}"),
attribute.String("middleware.type", "gin"),
)
// 执行下一个中间件
c.Next()
// 检查是否被中止
if c.IsAborted() {
span.SetAttributes(attribute.Bool("middleware.aborted", true))
span.SetStatus(codes.Error, "Request aborted by middleware")
}
}
}()
`
return gfp.applyMiddlewareInstrumentation(rule, middlewareCode, context)
}7.1.2 Echo框架专用处理器
go
// Echo框架专用处理器
type EchoFrameworkProcessor struct {
baseProcessor *WebFrameworkProcessor
contextExtractor *EchoContextExtractor
}
func (efp *EchoFrameworkProcessor) ProcessEchoMiddleware(rule *MiddlewareRule, context *ProcessContext) error {
middlewareCode := `
// Echo middleware instrumentation
func() echo.MiddlewareFunc {
return func(next echo.HandlerFunc) echo.HandlerFunc {
return func(c echo.Context) error {
// 创建追踪上下文
req := c.Request()
ctx := req.Context()
tracer := otel.Tracer("echo")
ctx, span := tracer.Start(ctx, fmt.Sprintf("%s %s", req.Method, c.Path()))
defer span.End()
// 设置请求属性
span.SetAttributes(
attribute.String("http.method", req.Method),
attribute.String("http.url", req.URL.String()),
attribute.String("http.route", c.Path()),
attribute.String("echo.route.name", c.Path()),
)
// 提取路由参数
for _, paramName := range c.ParamNames() {
paramValue := c.Param(paramName)
span.SetAttributes(attribute.String(fmt.Sprintf("http.route.param.%s", paramName), paramValue))
}
// 更新请求上下文
c.SetRequest(req.WithContext(ctx))
// 记录开始时间
startTime := time.Now()
// 执行下一个中间件/处理器
err := next(c)
// 记录响应信息
duration := time.Since(startTime)
status := c.Response().Status
span.SetAttributes(
attribute.Int("http.status_code", status),
attribute.Int64("http.response.duration_ms", duration.Milliseconds()),
)
if err != nil {
span.RecordError(err)
span.SetStatus(codes.Error, err.Error())
} else if status >= 400 {
span.SetStatus(codes.Error, fmt.Sprintf("HTTP %d", status))
} else {
span.SetStatus(codes.Ok, "")
}
return err
}
}
}()
`
return efp.applyMiddlewareInstrumentation(rule, middlewareCode, context)
}7.1.3 Fiber框架高性能插桩
go
// Fiber框架处理器(针对高性能场景优化)
type FiberFrameworkProcessor struct {
baseProcessor *WebFrameworkProcessor
poolManager *FiberPoolManager
}
func (ffp *FiberFrameworkProcessor) ProcessFiberHandler(rule *HandlerRule, context *ProcessContext) error {
// Fiber专用的零拷贝插桩代码
fiberCode := `
// Fiber handler instrumentation (zero-copy optimized)
func(c *fiber.Ctx) error {
// 使用对象池减少内存分配
spanData := spanPool.Get().(*SpanData)
defer spanPool.Put(spanData)
// 快速路径:检查是否需要追踪
if !shouldTrace(c) {
return {{.OriginalHandler}}(c)
}
// 创建span(使用预分配的对象)
ctx := c.Context()
tracer := otel.Tracer("fiber")
ctx, span := tracer.Start(ctx, fastconcat(c.Method(), " ", c.Path()))
defer span.End()
// 零拷贝属性设置
span.SetAttributes(
attribute.String("http.method", b2s(c.Request().Header.Method())),
attribute.String("http.url", b2s(c.Request().URI().FullURI())),
attribute.String("http.route", c.Route().Path),
)
// 执行处理器
err := {{.OriginalHandler}}(c)
// 快速状态设置
status := c.Response().StatusCode()
span.SetAttributes(attribute.Int("http.status_code", status))
if err != nil {
span.RecordError(err)
span.SetStatus(codes.Error, err.Error())
} else if status >= 400 {
span.SetStatus(codes.Error, "")
}
return err
}
// 零拷贝字符串转换(unsafe操作)
func b2s(b []byte) string {
return *(*string)(unsafe.Pointer(&b))
}
// 快速字符串连接
func fastconcat(strs ...string) string {
var totalLen int
for _, s := range strs {
totalLen += len(s)
}
buf := make([]byte, 0, totalLen)
for _, s := range strs {
buf = append(buf, s...)
}
return *(*string)(unsafe.Pointer(&buf))
}
`
return ffp.applyFiberInstrumentation(rule, fiberCode, context)
}7.2 数据库驱动深度集成
7.2.1 database/sql标准库插桩
go
// 数据库规则处理器
type DatabaseRuleProcessor struct {
sqlParser *SQLParser
queryTracker *QueryTracker
connPool *ConnectionPoolTracker
}
func (drp *DatabaseRuleProcessor) ProcessSQLQuery(rule *DatabaseRule, context *ProcessContext) error {
// SQL查询插桩模板
sqlInstrumentationTemplate := `
// Database query instrumentation
func instrumentedQuery({{.Parameters}}) {{.ReturnTypes}} {
// 获取当前上下文
ctx := {{.ContextParam}}
if ctx == nil {
ctx = context.Background()
}
// 创建数据库span
tracer := otel.Tracer("database/sql")
ctx, span := tracer.Start(ctx, "sql.query")
defer span.End()
// 解析SQL语句
sqlInfo := parseSQLStatement({{.QueryParam}})
// 设置span属性
span.SetAttributes(
attribute.String("db.system", "{{.DatabaseType}}"),
attribute.String("db.statement", {{.QueryParam}}),
attribute.String("db.operation", sqlInfo.Operation),
)
if sqlInfo.Table != "" {
span.SetAttributes(attribute.String("db.sql.table", sqlInfo.Table))
}
// 记录连接信息
if connInfo := getConnectionInfo({{.ConnectionParam}}); connInfo != nil {
span.SetAttributes(
attribute.String("db.connection_string", connInfo.DSN),
attribute.String("db.user", connInfo.User),
attribute.String("db.name", connInfo.Database),
)
}
// 记录查询开始时间
startTime := time.Now()
// 执行原始查询
{{if .ReturnTypes}}result, err := {{end}}{{.OriginalFunction}}({{.Arguments}})
// 记录查询耗时和结果
duration := time.Since(startTime)
span.SetAttributes(
attribute.Int64("db.query.duration_ms", duration.Milliseconds()),
)
// 记录结果集信息(如果适用)
{{if .HasResultSet}}
if rows, ok := result.(sql.Rows); ok {
rowCount := countRows(&rows)
span.SetAttributes(attribute.Int64("db.rows_affected", rowCount))
}
{{end}}
// 处理错误
if err != nil {
span.RecordError(err)
span.SetStatus(codes.Error, err.Error())
// 分类数据库错误
if dbErr := classifyDatabaseError(err); dbErr != nil {
span.SetAttributes(
attribute.String("db.error.type", dbErr.Type),
attribute.String("db.error.code", dbErr.Code),
)
}
} else {
span.SetStatus(codes.Ok, "")
}
{{if .ReturnTypes}}return result, err{{end}}
}
`
return drp.applyDatabaseInstrumentation(rule, sqlInstrumentationTemplate, context)
}
// SQL语句解析器
type SQLParser struct {
cache map[string]*SQLInfo
mutex sync.RWMutex
}
type SQLInfo struct {
Operation string // SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
Tables []string // 涉及的表名
Columns []string // 涉及的列名
HasWhere bool // 是否有WHERE条件
HasJoin bool // 是否有JOIN
}
func (sp *SQLParser) ParseSQL(query string) *SQLInfo {
// 检查缓存
sp.mutex.RLock()
if info, exists := sp.cache[query]; exists {
sp.mutex.RUnlock()
return info
}
sp.mutex.RUnlock()
// 解析SQL
info := &SQLInfo{}
// 简化的SQL解析(实际实现会更复杂)
upperQuery := strings.ToUpper(strings.TrimSpace(query))
// 识别操作类型
switch {
case strings.HasPrefix(upperQuery, "SELECT"):
info.Operation = "SELECT"
case strings.HasPrefix(upperQuery, "INSERT"):
info.Operation = "INSERT"
case strings.HasPrefix(upperQuery, "UPDATE"):
info.Operation = "UPDATE"
case strings.HasPrefix(upperQuery, "DELETE"):
info.Operation = "DELETE"
default:
info.Operation = "UNKNOWN"
}
// 提取表名(简化实现)
info.Tables = sp.extractTableNames(query)
// 检查特殊条件
info.HasWhere = strings.Contains(upperQuery, "WHERE")
info.HasJoin = strings.Contains(upperQuery, "JOIN")
// 缓存结果
sp.mutex.Lock()
sp.cache[query] = info
sp.mutex.Unlock()
return info
}7.2.2 GORM ORM框架集成
go
// GORM集成处理器
type GORMProcessor struct {
baseProcessor *DatabaseRuleProcessor
callbackManager *GORMCallbackManager
}
func (gp *GORMProcessor) ProcessGORMCallback(rule *GORMRule, context *ProcessContext) error {
gormCallbackCode := `
// GORM callback instrumentation
func registerGORMCallbacks(db *gorm.DB) {
// 注册查询前回调
db.Callback().Query().Before("gorm:query").Register("otel:before_query", func(db *gorm.DB) {
ctx := db.Statement.Context
if ctx == nil {
ctx = context.Background()
}
tracer := otel.Tracer("gorm")
ctx, span := tracer.Start(ctx, "gorm.query")
// 将span存储到上下文中
db.Statement.Context = context.WithValue(ctx, "otel_span", span)
// 设置基本属性
span.SetAttributes(
attribute.String("db.system", db.Dialector.Name()),
attribute.String("gorm.table", db.Statement.Table),
attribute.String("gorm.operation", "query"),
)
// 记录模型信息
if db.Statement.Model != nil {
modelType := reflect.TypeOf(db.Statement.Model)
if modelType.Kind() == reflect.Ptr {
modelType = modelType.Elem()
}
span.SetAttributes(attribute.String("gorm.model", modelType.Name()))
}
})
// 注册查询后回调
db.Callback().Query().After("gorm:query").Register("otel:after_query", func(db *gorm.DB) {
if spanValue := db.Statement.Context.Value("otel_span"); spanValue != nil {
if span, ok := spanValue.(trace.Span); ok {
defer span.End()
// 设置SQL语句
if db.Statement.SQL.String() != "" {
span.SetAttributes(attribute.String("db.statement", db.Statement.SQL.String()))
}
// 记录变量
if len(db.Statement.Vars) > 0 {
span.SetAttributes(attribute.Int("db.vars.count", len(db.Statement.Vars)))
}
// 记录影响的行数
if db.Statement.RowsAffected >= 0 {
span.SetAttributes(attribute.Int64("db.rows_affected", db.Statement.RowsAffected))
}
// 处理错误
if db.Error != nil && !errors.Is(db.Error, gorm.ErrRecordNotFound) {
span.RecordError(db.Error)
span.SetStatus(codes.Error, db.Error.Error())
} else {
span.SetStatus(codes.Ok, "")
}
}
}
})
// 注册创建回调
db.Callback().Create().Before("gorm:create").Register("otel:before_create", func(db *gorm.DB) {
// 类似的创建操作追踪
})
// 注册更新回调
db.Callback().Update().Before("gorm:update").Register("otel:before_update", func(db *gorm.DB) {
// 类似的更新操作追踪
})
// 注册删除回调
db.Callback().Delete().Before("gorm:delete").Register("otel:before_delete", func(db *gorm.DB) {
// 类似的删除操作追踪
})
}
`
return gp.applyGORMInstrumentation(rule, gormCallbackCode, context)
}7.3 消息队列深度集成
7.3.1 Kafka集成
go
// 消息队列规则处理器
type MessageQueueProcessor struct {
traceExtractor *TraceExtractor
traceInjector *TraceInjector
headerManager *MessageHeaderManager
}
// Kafka Producer插桩
func (mqp *MessageQueueProcessor) ProcessKafkaProducer(rule *KafkaRule, context *ProcessContext) error {
kafkaProducerCode := `
// Kafka producer instrumentation
func instrumentedKafkaProducer(producer sarama.SyncProducer, msg *sarama.ProducerMessage) (partition int32, offset int64, err error) {
// 创建producer span
ctx := context.Background()
if ctxValue := msg.Headers["otel_context"]; ctxValue != nil {
if extractedCtx := extractTraceContext(ctxValue); extractedCtx != nil {
ctx = extractedCtx
}
}
tracer := otel.Tracer("kafka")
ctx, span := tracer.Start(ctx, fmt.Sprintf("kafka.produce %s", msg.Topic))
defer span.End()
// 设置span属性
span.SetAttributes(
attribute.String("messaging.system", "kafka"),
attribute.String("messaging.destination", msg.Topic),
attribute.String("messaging.operation", "publish"),
attribute.String("messaging.destination_kind", "topic"),
)
// 记录消息属性
if msg.Key != nil {
if key, err := msg.Key.Encode(); err == nil {
span.SetAttributes(attribute.String("messaging.kafka.message_key", string(key)))
}
}
if msg.Value != nil {
if value, err := msg.Value.Encode(); err == nil {
span.SetAttributes(attribute.Int("messaging.message.payload_size_bytes", len(value)))
}
}
// 注入追踪上下文到消息头
if msg.Headers == nil {
msg.Headers = make(map[string]sarama.Encoder)
}
injectTraceContext(ctx, msg.Headers)
// 记录发送开始时间
startTime := time.Now()
// 执行发送
partition, offset, err = producer.SendMessage(msg)
// 记录发送耗时
duration := time.Since(startTime)
span.SetAttributes(attribute.Int64("messaging.kafka.send_duration_ms", duration.Milliseconds()))
if err != nil {
span.RecordError(err)
span.SetStatus(codes.Error, err.Error())
} else {
span.SetAttributes(
attribute.Int("messaging.kafka.partition", int(partition)),
attribute.Int("messaging.kafka.offset", int(offset)),
)
span.SetStatus(codes.Ok, "")
}
return partition, offset, err
}
`
return mqp.applyKafkaInstrumentation(rule, kafkaProducerCode, context)
}
// Kafka Consumer插桩
func (mqp *MessageQueueProcessor) ProcessKafkaConsumer(rule *KafkaRule, context *ProcessContext) error {
kafkaConsumerCode := `
// Kafka consumer instrumentation
func instrumentedKafkaConsumer(consumer sarama.Consumer, handler func(*sarama.ConsumerMessage) error) {
originalHandler := handler
instrumentedHandler := func(msg *sarama.ConsumerMessage) error {
// 提取追踪上下文
ctx := context.Background()
if msg.Headers != nil {
if ctxData := extractFromKafkaHeaders(msg.Headers); ctxData != nil {
ctx = ctxData
}
}
// 创建consumer span
tracer := otel.Tracer("kafka")
ctx, span := tracer.Start(ctx, fmt.Sprintf("kafka.consume %s", msg.Topic))
defer span.End()
// 设置span属性
span.SetAttributes(
attribute.String("messaging.system", "kafka"),
attribute.String("messaging.destination", msg.Topic),
attribute.String("messaging.operation", "receive"),
attribute.String("messaging.destination_kind", "topic"),
attribute.Int("messaging.kafka.partition", int(msg.Partition)),
attribute.Int("messaging.kafka.offset", int(msg.Offset)),
attribute.Int("messaging.message.payload_size_bytes", len(msg.Value)),
)
if msg.Key != nil {
span.SetAttributes(attribute.String("messaging.kafka.message_key", string(msg.Key)))
}
// 记录消息时间戳
if !msg.Timestamp.IsZero() {
span.SetAttributes(attribute.Int64("messaging.kafka.message_timestamp", msg.Timestamp.Unix()))
}
// 记录处理开始时间
startTime := time.Now()
// 执行原始处理器
err := originalHandler(msg)
// 记录处理耗时
duration := time.Since(startTime)
span.SetAttributes(attribute.Int64("messaging.kafka.process_duration_ms", duration.Milliseconds()))
if err != nil {
span.RecordError(err)
span.SetStatus(codes.Error, err.Error())
} else {
span.SetStatus(codes.Ok, "")
}
return err
}
// 替换处理器
handler = instrumentedHandler
}
`
return mqp.applyKafkaInstrumentation(rule, kafkaConsumerCode, context)
}7.3.2 Redis集成
go
// Redis客户端插桩
type RedisProcessor struct {
baseProcessor *CacheProcessor
commandAnalyzer *RedisCommandAnalyzer
}
func (rp *RedisProcessor) ProcessRedisCommand(rule *RedisRule, context *ProcessContext) error {
redisCode := `
// Redis command instrumentation
func instrumentedRedisCommand(client redis.Cmdable, cmd string, args ...interface{}) *redis.Cmd {
// 创建Redis span
ctx := context.Background()
tracer := otel.Tracer("redis")
ctx, span := tracer.Start(ctx, fmt.Sprintf("redis.%s", strings.ToLower(cmd)))
defer span.End()
// 设置span属性
span.SetAttributes(
attribute.String("db.system", "redis"),
attribute.String("db.operation", cmd),
attribute.String("db.redis.database_index", "0"), // 可以从客户端配置获取
)
// 记录命令参数(注意不要记录敏感信息)
if len(args) > 0 {
span.SetAttributes(attribute.Int("db.redis.args_count", len(args)))
// 只记录第一个参数(通常是key)
if key, ok := args[0].(string); ok {
span.SetAttributes(attribute.String("db.redis.key", key))
}
}
// 记录执行开始时间
startTime := time.Now()
// 执行Redis命令
result := client.Do(ctx, cmd, args...)
// 记录执行耗时
duration := time.Since(startTime)
span.SetAttributes(attribute.Int64("db.redis.duration_ms", duration.Milliseconds()))
// 处理结果和错误
if result.Err() != nil {
span.RecordError(result.Err())
span.SetStatus(codes.Error, result.Err().Error())
} else {
span.SetStatus(codes.Ok, "")
// 记录结果大小(如果适用)
if val, err := result.Result(); err == nil {
if str, ok := val.(string); ok {
span.SetAttributes(attribute.Int("db.redis.response_size_bytes", len(str)))
}
}
}
return result
}
`
return rp.applyRedisInstrumentation(rule, redisCode, context)
}- Gin: HTTP路由和中间件插桩
- Echo: 请求处理和错误处理插桩
- Fiber: 高性能HTTP框架插桩
- Iris: 全功能Web框架插桩
7.2 数据库支持
- GORM: ORM操作插桩
- SQLX: SQL执行插桩
- Go-Redis: Redis操作插桩
- MongoDB: 文档数据库插桩
7.3 RPC框架支持
- gRPC: 服务调用插桩
- Dubbo: 分布式服务插桩
- Kitex: 字节跳动RPC框架插桩
- tRPC: 腾讯RPC框架插桩
7.4 消息队列支持
- RocketMQ: 消息生产和消费插桩
- Kafka: 消息流处理插桩
- RabbitMQ: AMQP协议插桩
八、性能优化策略深度解析
8.1 编译时优化技术
8.1.1 AST缓存和增量编译
go
// AST缓存管理器
type ASTCacheManager struct {
cache map[string]*CachedAST
mutex sync.RWMutex
maxSize int
evictPolicy EvictionPolicy
metrics *CacheMetrics
}
type CachedAST struct {
AST *dst.File
Hash string
LastAccess time.Time
AccessCount int64
Size int64
Dependencies []string
}
func (acm *ASTCacheManager) GetOrParseAST(filePath string, content []byte) (*dst.File, error) {
// 计算文件内容哈希
hash := sha256.Sum256(content)
hashStr := hex.EncodeToString(hash[:])
// 检查缓存
acm.mutex.RLock()
if cached, exists := acm.cache[filePath]; exists && cached.Hash == hashStr {
// 缓存命中,更新访问信息
cached.LastAccess = time.Now()
atomic.AddInt64(&cached.AccessCount, 1)
acm.mutex.RUnlock()
acm.metrics.RecordCacheHit()
return cached.AST, nil
}
acm.mutex.RUnlock()
// 缓存未命中,解析AST
acm.metrics.RecordCacheMiss()
// 使用并行解析提高性能
astFile, err := acm.parseASTParallel(content)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// 缓存新的AST
acm.mutex.Lock()
defer acm.mutex.Unlock()
// 检查缓存大小,必要时进行清理
if len(acm.cache) >= acm.maxSize {
acm.evictLRU()
}
acm.cache[filePath] = &CachedAST{
AST: astFile,
Hash: hashStr,
LastAccess: time.Now(),
AccessCount: 1,
Size: acm.calculateASTSize(astFile),
Dependencies: acm.extractDependencies(astFile),
}
return astFile, nil
}
// 并行AST解析
func (acm *ASTCacheManager) parseASTParallel(content []byte) (*dst.File, error) {
// 使用工作池进行并行解析
type parseResult struct {
ast *dst.File
err error
}
resultChan := make(chan parseResult, 1)
go func() {
defer close(resultChan)
// 创建解析器
parser := &dst.Decorator{
Resolver: guess.ResolverId,
Map: dst.Map{},
}
// 解析文件
fset := token.NewFileSet()
astFile, err := parser.ParseFile(fset, "", content, parser.ParserMode)
resultChan <- parseResult{ast: astFile, err: err}
}()
// 设置超时
select {
case result := <-resultChan:
return result.ast, result.err
case <-time.After(30 * time.Second):
return nil, fmt.Errorf("AST parsing timeout")
}
}
// LRU缓存清理
func (acm *ASTCacheManager) evictLRU() {
if len(acm.cache) == 0 {
return
}
// 找到最久未访问的条目
var oldestKey string
var oldestTime time.Time = time.Now()
for key, cached := range acm.cache {
if cached.LastAccess.Before(oldestTime) {
oldestTime = cached.LastAccess
oldestKey = key
}
}
if oldestKey != "" {
delete(acm.cache, oldestKey)
acm.metrics.RecordEviction()
}
}8.1.2 智能代码生成优化
go
// 代码生成优化器
type CodeGenerationOptimizer struct {
templateCache map[string]*CompiledTemplate
generatorPool *sync.Pool
batchProcessor *BatchProcessor
metrics *GenerationMetrics
}
type CompiledTemplate struct {
Template *template.Template
Hash string
UsageCount int64
LastUsed time.Time
Performance *TemplatePerformance
}
type TemplatePerformance struct {
AvgExecutionTime time.Duration
MemoryUsage int64
ErrorRate float64
}
func (cgo *CodeGenerationOptimizer) GenerateInstrumentationCode(rule *InstrumentationRule, context *GenerationContext) (string, error) {
// 1. 模板选择和优化
template, err := cgo.getOptimizedTemplate(rule.TemplateType)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
// 2. 使用对象池减少内存分配
generator := cgo.generatorPool.Get().(*CodeGenerator)
defer cgo.generatorPool.Put(generator)
// 3. 批量处理优化
if cgo.shouldBatchProcess(rule) {
return cgo.batchProcessor.AddToBatch(rule, context)
}
// 4. 执行代码生成
startTime := time.Now()
var buf bytes.Buffer
err = template.Template.Execute(&buf, context)
duration := time.Since(startTime)
cgo.updateTemplateMetrics(template, duration, err)
if err != nil {
return "", fmt.Errorf("template execution failed: %w", err)
}
// 5. 代码优化后处理
generatedCode := buf.String()
optimizedCode := cgo.optimizeGeneratedCode(generatedCode)
return optimizedCode, nil
}
// 代码优化后处理
func (cgo *CodeGenerationOptimizer) optimizeGeneratedCode(code string) string {
// 1. 移除多余的空行和空格
code = regexp.MustCompile(`\n\s*\n\s*\n`).ReplaceAllString(code, "\n\n")
// 2. 优化导入语句
code = cgo.optimizeImports(code)
// 3. 内联简单函数调用
code = cgo.inlineSimpleCalls(code)
// 4. 常量折叠
code = cgo.foldConstants(code)
return code
}
// 批量处理器
type BatchProcessor struct {
batch []*BatchItem
batchSize int
flushTimer *time.Timer
mutex sync.Mutex
processor func([]*BatchItem) error
}
type BatchItem struct {
Rule *InstrumentationRule
Context *GenerationContext
Result chan BatchResult
}
type BatchResult struct {
Code string
Error error
}
func (bp *BatchProcessor) AddToBatch(rule *InstrumentationRule, context *GenerationContext) (string, error) {
bp.mutex.Lock()
defer bp.mutex.Unlock()
// 创建批处理项
item := &BatchItem{
Rule: rule,
Context: context,
Result: make(chan BatchResult, 1),
}
bp.batch = append(bp.batch, item)
// 检查是否需要立即处理
if len(bp.batch) >= bp.batchSize {
go bp.processBatch()
bp.batch = bp.batch[:0] // 清空批次
} else if bp.flushTimer == nil {
// 设置定时器,确保批次不会无限等待
bp.flushTimer = time.AfterFunc(100*time.Millisecond, func() {
bp.mutex.Lock()
if len(bp.batch) > 0 {
go bp.processBatch()
bp.batch = bp.batch[:0]
}
bp.flushTimer = nil
bp.mutex.Unlock()
})
}
// 等待结果
result := <-item.Result
return result.Code, result.Error
}8.1.3 并行编译优化
go
// 并行编译管理器
type ParallelCompilationManager struct {
workerPool *WorkerPool
dependencyGraph *DependencyGraph
scheduler *CompilationScheduler
monitor *CompilationMonitor
}
type WorkerPool struct {
workers []*CompilationWorker
taskQueue chan *CompilationTask
results chan *CompilationResult
wg sync.WaitGroup
}
type CompilationTask struct {
ID string
FilePath string
Dependencies []string
Priority int
Timeout time.Duration
Context context.Context
}
type CompilationWorker struct {
id int
taskChan <-chan *CompilationTask
results chan<- *CompilationResult
quit chan bool
}
func (pcm *ParallelCompilationManager) CompileProject(projectPath string) error {
// 1. 构建依赖图
depGraph, err := pcm.dependencyGraph.BuildGraph(projectPath)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to build dependency graph: %w", err)
}
// 2. 拓扑排序确定编译顺序
compilationOrder := depGraph.TopologicalSort()
// 3. 创建编译任务
tasks := make([]*CompilationTask, 0, len(compilationOrder))
for i, node := range compilationOrder {
task := &CompilationTask{
ID: fmt.Sprintf("task_%d", i),
FilePath: node.FilePath,
Dependencies: node.Dependencies,
Priority: node.Priority,
Timeout: 30 * time.Second,
Context: context.Background(),
}
tasks = append(tasks, task)
}
// 4. 启动工作池
pcm.workerPool.Start()
defer pcm.workerPool.Stop()
// 5. 分发任务
go func() {
for _, task := range tasks {
pcm.workerPool.taskQueue <- task
}
close(pcm.workerPool.taskQueue)
}()
// 6. 收集结果
results := make(map[string]*CompilationResult)
for i := 0; i < len(tasks); i++ {
result := <-pcm.workerPool.results
results[result.TaskID] = result
if result.Error != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("compilation failed for task %s: %w", result.TaskID, result.Error)
}
}
return nil
}
func (cw *CompilationWorker) Start() {
go func() {
for {
select {
case task := <-cw.taskChan:
if task == nil {
return // 通道已关闭
}
result := cw.processTask(task)
cw.results <- result
case <-cw.quit:
return
}
}
}()
}
func (cw *CompilationWorker) processTask(task *CompilationTask) *CompilationResult {
startTime := time.Now()
// 设置超时上下文
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(task.Context, task.Timeout)
defer cancel()
// 执行编译
err := cw.compileFile(ctx, task.FilePath)
return &CompilationResult{
TaskID: task.ID,
FilePath: task.FilePath,
Duration: time.Since(startTime),
Error: err,
WorkerID: cw.id,
}
}8.2 运行时性能优化
8.2.1 零拷贝上下文传播
go
// 零拷贝上下文管理器
type ZeroCopyContextManager struct {
contextPool *sync.Pool
bufferPool *sync.Pool
encoder *FastEncoder
decoder *FastDecoder
metrics *ContextMetrics
}
type FastContext struct {
traceID [16]byte // 固定大小,避免内存分配
spanID [8]byte // 固定大小
flags uint8 // 标志位
baggage []byte // 预分配缓冲区
userData []byte // 用户数据缓冲区
refCount int32 // 引用计数
}
func (zcm *ZeroCopyContextManager) CreateContext(traceID, spanID []byte) *FastContext {
// 从对象池获取上下文
ctx := zcm.contextPool.Get().(*FastContext)
// 重置上下文
ctx.reset()
// 零拷贝设置ID(直接内存拷贝)
copy(ctx.traceID[:], traceID)
copy(ctx.spanID[:], spanID)
// 设置引用计数
atomic.StoreInt32(&ctx.refCount, 1)
return ctx
}
func (fc *FastContext) Clone() *FastContext {
// 增加引用计数而不是复制数据
atomic.AddInt32(&fc.refCount, 1)
return fc
}
func (fc *FastContext) Release() {
if atomic.AddInt32(&fc.refCount, -1) == 0 {
// 引用计数为0,返回对象池
fc.reset()
contextPool.Put(fc)
}
}
// 快速编码器(避免反射和内存分配)
type FastEncoder struct {
buffer []byte
}
func (fe *FastEncoder) EncodeContext(ctx *FastContext) []byte {
// 预计算所需大小
size := 16 + 8 + 1 + len(ctx.baggage) + len(ctx.userData)
// 确保缓冲区足够大
if cap(fe.buffer) < size {
fe.buffer = make([]byte, size)
}
fe.buffer = fe.buffer[:size]
offset := 0
// 直接内存拷贝,无需序列化
copy(fe.buffer[offset:], ctx.traceID[:])
offset += 16
copy(fe.buffer[offset:], ctx.spanID[:])
offset += 8
fe.buffer[offset] = ctx.flags
offset += 1
copy(fe.buffer[offset:], ctx.baggage)
offset += len(ctx.baggage)
copy(fe.buffer[offset:], ctx.userData)
return fe.buffer
}
// 高性能上下文注入
func (zcm *ZeroCopyContextManager) InjectContext(ctx *FastContext, carrier map[string]string) {
// 使用预分配的编码器
encoder := zcm.encoder
encoded := encoder.EncodeContext(ctx)
// 使用base64编码(可以考虑更快的编码方式)
carrier["otel-trace-context"] = base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString(encoded)
}
// 高性能上下文提取
func (zcm *ZeroCopyContextManager) ExtractContext(carrier map[string]string) *FastContext {
contextData, exists := carrier["otel-trace-context"]
if !exists {
return nil
}
// 解码
decoded, err := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(contextData)
if err != nil {
return nil
}
// 使用预分配的解码器
decoder := zcm.decoder
return decoder.DecodeContext(decoded)
}8.2.2 内存池优化
go
// 高性能内存池管理器
type MemoryPoolManager struct {
spanPool *sync.Pool
attributePool *sync.Pool
eventPool *sync.Pool
bufferPools map[int]*sync.Pool // 按大小分类的缓冲区池
metrics *PoolMetrics
}
func NewMemoryPoolManager() *MemoryPoolManager {
mpm := &MemoryPoolManager{
bufferPools: make(map[int]*sync.Pool),
metrics: NewPoolMetrics(),
}
// 初始化span池
mpm.spanPool = &sync.Pool{
New: func() interface{} {
return &SpanData{
attributes: make([]attribute.KeyValue, 0, 16), // 预分配
events: make([]Event, 0, 8),
}
},
}
// 初始化属性池
mpm.attributePool = &sync.Pool{
New: func() interface{} {
return make([]attribute.KeyValue, 0, 32)
},
}
// 初始化不同大小的缓冲区池
bufferSizes := []int{64, 256, 1024, 4096, 16384}
for _, size := range bufferSizes {
size := size // 捕获循环变量
mpm.bufferPools[size] = &sync.Pool{
New: func() interface{} {
return make([]byte, 0, size)
},
}
}
return mpm
}
func (mpm *MemoryPoolManager) GetSpan() *SpanData {
span := mpm.spanPool.Get().(*SpanData)
span.reset() // 重置span数据
mpm.metrics.RecordSpanAllocation()
return span
}
func (mpm *MemoryPoolManager) PutSpan(span *SpanData) {
if span != nil {
mpm.spanPool.Put(span)
mpm.metrics.RecordSpanDeallocation()
}
}
func (mpm *MemoryPoolManager) GetBuffer(size int) []byte {
// 找到最适合的缓冲区大小
poolSize := mpm.findBestPoolSize(size)
if pool, exists := mpm.bufferPools[poolSize]; exists {
buffer := pool.Get().([]byte)
return buffer[:0] // 重置长度但保留容量
}
// 如果没有合适的池,直接分配
return make([]byte, 0, size)
}
func (mpm *MemoryPoolManager) PutBuffer(buffer []byte) {
if buffer == nil {
return
}
capacity := cap(buffer)
poolSize := mpm.findBestPoolSize(capacity)
if pool, exists := mpm.bufferPools[poolSize]; exists && capacity <= poolSize*2 {
// 只有当缓冲区大小合理时才放回池中
pool.Put(buffer)
}
// 否则让GC处理
}
func (mpm *MemoryPoolManager) findBestPoolSize(size int) int {
for _, poolSize := range []int{64, 256, 1024, 4096, 16384} {
if size <= poolSize {
return poolSize
}
}
return 16384 // 默认最大大小
}
// 智能垃圾回收优化
type GCOptimizer struct {
gcStats *GCStats
memoryMonitor *MemoryMonitor
tuner *GCTuner
}
type GCStats struct {
collections int64
totalPause time.Duration
avgPause time.Duration
maxPause time.Duration
lastGC time.Time
mutex sync.RWMutex
}
func (gco *GCOptimizer) OptimizeGC() {
// 监控内存使用情况
memStats := &runtime.MemStats{}
runtime.ReadMemStats(memStats)
// 根据内存使用情况调整GC目标
if memStats.HeapInuse > memStats.HeapSys/2 {
// 内存使用率高,降低GC目标
debug.SetGCPercent(50)
} else {
// 内存使用率低,提高GC目标
debug.SetGCPercent(200)
}
// 记录GC统计信息
gco.updateGCStats(memStats)
}
func (gco *GCOptimizer) updateGCStats(memStats *runtime.MemStats) {
gco.gcStats.mutex.Lock()
defer gco.gcStats.mutex.Unlock()
if memStats.NumGC > uint32(gco.gcStats.collections) {
// 发生了新的GC
newCollections := int64(memStats.NumGC) - gco.gcStats.collections
gco.gcStats.collections = int64(memStats.NumGC)
// 计算平均暂停时间
totalPause := time.Duration(memStats.PauseTotalNs)
if gco.gcStats.totalPause > 0 {
newPause := totalPause - gco.gcStats.totalPause
gco.gcStats.avgPause = newPause / time.Duration(newCollections)
}
gco.gcStats.totalPause = totalPause
gco.gcStats.lastGC = time.Now()
}
}8.2.3 高性能数据收集和传输
go
// 高性能数据收集器
type HighPerformanceCollector struct {
batchProcessor *BatchSpanProcessor
ringBuffer *RingBuffer
compressor *DataCompressor
serializer *FastSerializer
transport *OptimizedTransport
metrics *CollectorMetrics
}
type BatchSpanProcessor struct {
spans []SpanData
batchSize int
timeout time.Duration
mutex sync.Mutex
flushTimer *time.Timer
exporter SpanExporter
}
func (bsp *BatchSpanProcessor) OnEnd(span SpanData) {
bsp.mutex.Lock()
defer bsp.mutex.Unlock()
// 添加到批次
bsp.spans = append(bsp.spans, span)
// 检查是否需要立即导出
if len(bsp.spans) >= bsp.batchSize {
go bsp.exportBatch()
bsp.spans = bsp.spans[:0] // 清空批次
// 重置定时器
if bsp.flushTimer != nil {
bsp.flushTimer.Stop()
bsp.flushTimer = nil
}
} else if bsp.flushTimer == nil {
// 设置定时器确保数据及时导出
bsp.flushTimer = time.AfterFunc(bsp.timeout, func() {
bsp.mutex.Lock()
if len(bsp.spans) > 0 {
go bsp.exportBatch()
bsp.spans = bsp.spans[:0]
}
bsp.flushTimer = nil
bsp.mutex.Unlock()
})
}
}
// 环形缓冲区实现
type RingBuffer struct {
buffer []SpanData
head int64
tail int64
size int64
mask int64
mutex sync.RWMutex
notEmpty chan struct{}
notFull chan struct{}
}
func NewRingBuffer(size int) *RingBuffer {
// 确保大小是2的幂,便于使用位运算
actualSize := int64(1)
for actualSize < int64(size) {
actualSize <<= 1
}
return &RingBuffer{
buffer: make([]SpanData, actualSize),
size: actualSize,
mask: actualSize - 1,
notEmpty: make(chan struct{}, 1),
notFull: make(chan struct{}, 1),
}
}
func (rb *RingBuffer) Put(span SpanData) bool {
rb.mutex.Lock()
defer rb.mutex.Unlock()
// 检查缓冲区是否已满
if (rb.tail-rb.head) >= rb.size {
return false // 缓冲区已满
}
// 添加数据
rb.buffer[rb.tail&rb.mask] = span
rb.tail++
// 通知消费者
select {
case rb.notEmpty <- struct{}{}:
default:
}
return true
}
func (rb *RingBuffer) Get() (SpanData, bool) {
rb.mutex.Lock()
defer rb.mutex.Unlock()
// 检查缓冲区是否为空
if rb.head == rb.tail {
return SpanData{}, false
}
// 获取数据
span := rb.buffer[rb.head&rb.mask]
rb.head++
// 通知生产者
select {
case rb.notFull <- struct{}{}:
default:
}
return span, true
}
// 数据压缩器
type DataCompressor struct {
compressor *gzip.Writer
buffer *bytes.Buffer
pool *sync.Pool
}
func NewDataCompressor() *DataCompressor {
return &DataCompressor{
pool: &sync.Pool{
New: func() interface{} {
var buf bytes.Buffer
return gzip.NewWriter(&buf)
},
},
}
}
func (dc *DataCompressor) Compress(data []byte) ([]byte, error) {
// 从池中获取压缩器
compressor := dc.pool.Get().(*gzip.Writer)
defer dc.pool.Put(compressor)
var buf bytes.Buffer
compressor.Reset(&buf)
// 压缩数据
_, err := compressor.Write(data)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
err = compressor.Close()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return buf.Bytes(), nil
}
// 快速序列化器
type FastSerializer struct {
buffer []byte
offset int
}
func (fs *FastSerializer) SerializeSpan(span *SpanData) []byte {
// 预估所需大小
estimatedSize := 256 + len(span.Name) + len(span.TraceID)*2 + len(span.SpanID)*2
// 确保缓冲区足够大
if cap(fs.buffer) < estimatedSize {
fs.buffer = make([]byte, estimatedSize)
}
fs.buffer = fs.buffer[:estimatedSize]
fs.offset = 0
// 序列化字段(使用二进制格式而非JSON)
fs.writeString(span.Name)
fs.writeBytes(span.TraceID)
fs.writeBytes(span.SpanID)
fs.writeInt64(span.StartTime.UnixNano())
fs.writeInt64(span.EndTime.UnixNano())
fs.writeInt32(int32(span.Status))
// 序列化属性
fs.writeInt32(int32(len(span.Attributes)))
for _, attr := range span.Attributes {
fs.writeString(string(attr.Key))
fs.writeAttributeValue(attr.Value)
}
return fs.buffer[:fs.offset]
}
func (fs *FastSerializer) writeString(s string) {
length := len(s)
fs.writeInt32(int32(length))
copy(fs.buffer[fs.offset:], s)
fs.offset += length
}
func (fs *FastSerializer) writeBytes(b []byte) {
length := len(b)
fs.writeInt32(int32(length))
copy(fs.buffer[fs.offset:], b)
fs.offset += length
}
func (fs *FastSerializer) writeInt32(v int32) {
binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(fs.buffer[fs.offset:], uint32(v))
fs.offset += 4
}
func (fs *FastSerializer) writeInt64(v int64) {
binary.LittleEndian.PutUint64(fs.buffer[fs.offset:], uint64(v))
fs.offset += 8
}
// 优化的传输层
type OptimizedTransport struct {
client *http.Client
endpoint string
headers map[string]string
retryPolicy *RetryPolicy
circuitBreaker *CircuitBreaker
}
type RetryPolicy struct {
maxRetries int
baseDelay time.Duration
maxDelay time.Duration
backoffFactor float64
}
type CircuitBreaker struct {
state int32 // 0: closed, 1: open, 2: half-open
failures int64
lastFailTime time.Time
threshold int64
timeout time.Duration
mutex sync.RWMutex
}
func (ot *OptimizedTransport) Send(data []byte) error {
// 检查熔断器状态
if !ot.circuitBreaker.AllowRequest() {
return fmt.Errorf("circuit breaker is open")
}
// 执行请求(带重试)
err := ot.sendWithRetry(data)
// 更新熔断器状态
if err != nil {
ot.circuitBreaker.RecordFailure()
} else {
ot.circuitBreaker.RecordSuccess()
}
return err
}
func (ot *OptimizedTransport) sendWithRetry(data []byte) error {
var lastErr error
for attempt := 0; attempt <= ot.retryPolicy.maxRetries; attempt++ {
if attempt > 0 {
// 计算退避延迟
delay := time.Duration(float64(ot.retryPolicy.baseDelay) *
math.Pow(ot.retryPolicy.backoffFactor, float64(attempt-1)))
if delay > ot.retryPolicy.maxDelay {
delay = ot.retryPolicy.maxDelay
}
time.Sleep(delay)
}
// 创建请求
req, err := http.NewRequest("POST", ot.endpoint, bytes.NewReader(data))
if err != nil {
lastErr = err
continue
}
// 设置头部
for key, value := range ot.headers {
req.Header.Set(key, value)
}
// 发送请求
resp, err := ot.client.Do(req)
if err != nil {
lastErr = err
continue
}
resp.Body.Close()
// 检查响应状态
if resp.StatusCode >= 200 && resp.StatusCode < 300 {
return nil // 成功
}
lastErr = fmt.Errorf("HTTP %d", resp.StatusCode)
// 对于某些错误码不进行重试
if resp.StatusCode == 400 || resp.StatusCode == 401 || resp.StatusCode == 403 {
break
}
}
return lastErr
}8.3 性能监控和调优
8.3.1 实时性能监控系统
go
// 性能监控系统
type PerformanceMonitor struct {
metrics *MetricsCollector
profiler *ContinuousProfiler
alertManager *AlertManager
dashboard *PerformanceDashboard
optimizer *AutoOptimizer
}
type MetricsCollector struct {
counters map[string]*Counter
gauges map[string]*Gauge
histograms map[string]*Histogram
timers map[string]*Timer
mutex sync.RWMutex
}
type Counter struct {
value int64
name string
tags map[string]string
}
func (c *Counter) Inc() {
atomic.AddInt64(&c.value, 1)
}
func (c *Counter) Add(delta int64) {
atomic.AddInt64(&c.value, delta)
}
func (c *Counter) Value() int64 {
return atomic.LoadInt64(&c.value)
}
type Histogram struct {
buckets []int64
counts []int64
sum int64
count int64
mutex sync.RWMutex
}
func (h *Histogram) Observe(value float64) {
h.mutex.Lock()
defer h.mutex.Unlock()
// 更新总和和计数
atomic.AddInt64(&h.sum, int64(value))
atomic.AddInt64(&h.count, 1)
// 找到合适的桶
for i, bucket := range h.buckets {
if int64(value) <= bucket {
atomic.AddInt64(&h.counts[i], 1)
break
}
}
}
// 连续性能分析器
type ContinuousProfiler struct {
cpuProfiler *CPUProfiler
memoryProfiler *MemoryProfiler
goroutineProfiler *GoroutineProfiler
enabled bool
interval time.Duration
stopChan chan struct{}
}
func (cp *ContinuousProfiler) Start() {
if cp.enabled {
return
}
cp.enabled = true
cp.stopChan = make(chan struct{})
go cp.profileLoop()
}
func (cp *ContinuousProfiler) profileLoop() {
ticker := time.NewTicker(cp.interval)
defer ticker.Stop()
for {
select {
case <-ticker.C:
cp.collectProfiles()
case <-cp.stopChan:
return
}
}
}
func (cp *ContinuousProfiler) collectProfiles() {
// 收集CPU性能数据
go cp.cpuProfiler.Collect()
// 收集内存性能数据
go cp.memoryProfiler.Collect()
// 收集Goroutine信息
go cp.goroutineProfiler.Collect()
}
// 自动优化器
type AutoOptimizer struct {
rules []OptimizationRule
analyzer *PerformanceAnalyzer
executor *OptimizationExecutor
history *OptimizationHistory
}
type OptimizationRule struct {
Name string
Condition func(*PerformanceData) bool
Action func(*PerformanceData) OptimizationAction
Priority int
Cooldown time.Duration
LastApplied time.Time
}
type OptimizationAction struct {
Type string
Parameters map[string]interface{}
Description string
}
func (ao *AutoOptimizer) Optimize(perfData *PerformanceData) {
// 分析性能数据
analysis := ao.analyzer.Analyze(perfData)
// 应用优化规则
for _, rule := range ao.rules {
// 检查冷却时间
if time.Since(rule.LastApplied) < rule.Cooldown {
continue
}
// 检查条件
if rule.Condition(perfData) {
action := rule.Action(perfData)
// 执行优化
err := ao.executor.Execute(action)
if err == nil {
rule.LastApplied = time.Now()
ao.history.Record(rule.Name, action, analysis)
}
}
}
}8.4 性能基准测试和验证
8.4.1 综合性能基准测试
go
// 性能基准测试套件
type PerformanceBenchmarkSuite struct {
scenarios []BenchmarkScenario
reporter *BenchmarkReporter
validator *PerformanceValidator
}
type BenchmarkScenario struct {
Name string
Description string
Setup func() error
Benchmark func(*testing.B)
Teardown func() error
Metrics []string
}
func (pbs *PerformanceBenchmarkSuite) RunAllBenchmarks() *BenchmarkReport {
report := &BenchmarkReport{
StartTime: time.Now(),
Results: make(map[string]*BenchmarkResult),
}
for _, scenario := range pbs.scenarios {
result := pbs.runScenario(scenario)
report.Results[scenario.Name] = result
}
report.EndTime = time.Now()
report.Duration = report.EndTime.Sub(report.StartTime)
return report
}
func (pbs *PerformanceBenchmarkSuite) runScenario(scenario BenchmarkScenario) *BenchmarkResult {
// 设置测试环境
if err := scenario.Setup(); err != nil {
return &BenchmarkResult{
Name: scenario.Name,
Error: err,
}
}
defer func() {
if err := scenario.Teardown(); err != nil {
log.Printf("Teardown failed for scenario %s: %v", scenario.Name, err)
}
}()
// 运行基准测试
result := testing.Benchmark(scenario.Benchmark)
return &BenchmarkResult{
Name: scenario.Name,
Iterations: result.N,
Duration: result.T,
MemoryAllocs: result.MemAllocs,
MemoryBytes: result.MemBytes,
NsPerOp: result.NsPerOp(),
AllocsPerOp: result.AllocsPerOp(),
BytesPerOp: result.BytesPerOp(),
}
}
// 性能验证器
type PerformanceValidator struct {
thresholds map[string]PerformanceThreshold
baseline *BaselineData
}
type PerformanceThreshold struct {
MaxLatency time.Duration
MaxMemoryUsage int64
MaxCPUUsage float64
MinThroughput float64
MaxErrorRate float64
}
func (pv *PerformanceValidator) Validate(report *BenchmarkReport) *ValidationReport {
validationReport := &ValidationReport{
Timestamp: time.Now(),
Results: make(map[string]*ValidationResult),
}
for name, result := range report.Results {
threshold, exists := pv.thresholds[name]
if !exists {
continue
}
validationResult := &ValidationResult{
ScenarioName: name,
Passed: true,
Issues: []string{},
}
// 验证延迟
if time.Duration(result.NsPerOp) > threshold.MaxLatency {
validationResult.Passed = false
validationResult.Issues = append(validationResult.Issues,
fmt.Sprintf("Latency %v exceeds threshold %v",
time.Duration(result.NsPerOp), threshold.MaxLatency))
}
// 验证内存使用
if result.MemoryBytes > threshold.MaxMemoryUsage {
validationResult.Passed = false
validationResult.Issues = append(validationResult.Issues,
fmt.Sprintf("Memory usage %d exceeds threshold %d",
result.MemoryBytes, threshold.MaxMemoryUsage))
}
validationReport.Results[name] = validationResult
}
return validationReport
}- AST缓存: 避免重复解析相同文件
- 规则预编译: 将规则编译为高效的匹配器
- 增量编译: 只处理变更的文件
8.2 运行时优化
- GLS直接访问: 避免map查找开销
- 内联优化: 关键路径函数内联
- 采样策略: 可配置的采样率
8.3 内存优化
- 对象池: 复用频繁创建的对象
- 延迟初始化: 按需创建追踪对象
- 内存预分配: 减少GC压力
九、错误处理和调试深度解析
9.1 多层次错误恢复机制
9.1.1 编译时错误处理
go
// 编译时错误处理系统
type CompilationErrorHandler struct {
errorCollector *ErrorCollector
recoveryEngine *RecoveryEngine
diagnostics *DiagnosticsEngine
reporter *ErrorReporter
}
type ErrorCollector struct {
errors []CompilationError
warnings []CompilationWarning
mutex sync.RWMutex
}
type CompilationError struct {
Type ErrorType
Message string
File string
Line int
Column int
Context string
Severity ErrorSeverity
Timestamp time.Time
StackTrace []string
Suggestions []string
}
type ErrorType int
const (
SyntaxError ErrorType = iota
SemanticError
InstrumentationError
DependencyError
ConfigurationError
RuntimeError
)
type ErrorSeverity int
const (
Info ErrorSeverity = iota
Warning
Error
Fatal
)
func (ceh *CompilationErrorHandler) HandleError(err error, context *CompilationContext) error {
// 分类错误
compErr := ceh.classifyError(err, context)
// 收集错误信息
ceh.errorCollector.AddError(compErr)
// 尝试恢复
if compErr.Severity < Fatal {
if recovered := ceh.recoveryEngine.TryRecover(compErr, context); recovered {
ceh.errorCollector.AddWarning(CompilationWarning{
Message: fmt.Sprintf("Recovered from error: %s", compErr.Message),
File: compErr.File,
Line: compErr.Line,
})
return nil
}
}
// 生成诊断信息
diagnostic := ceh.diagnostics.GenerateDiagnostic(compErr)
ceh.reporter.Report(diagnostic)
return compErr
}
// 错误恢复引擎
type RecoveryEngine struct {
strategies map[ErrorType][]RecoveryStrategy
fallback RecoveryStrategy
}
type RecoveryStrategy interface {
CanRecover(error CompilationError, context *CompilationContext) bool
Recover(error CompilationError, context *CompilationContext) error
Priority() int
}
// AST恢复策略
type ASTRecoveryStrategy struct{}
func (ars *ASTRecoveryStrategy) CanRecover(err CompilationError, ctx *CompilationContext) bool {
return err.Type == SyntaxError && strings.Contains(err.Message, "unexpected token")
}
func (ars *ASTRecoveryStrategy) Recover(err CompilationError, ctx *CompilationContext) error {
// 尝试修复常见的语法错误
if strings.Contains(err.Message, "missing semicolon") {
return ars.insertSemicolon(err, ctx)
}
if strings.Contains(err.Message, "unmatched brace") {
return ars.fixBraces(err, ctx)
}
return fmt.Errorf("cannot recover from syntax error")
}
func (ars *ASTRecoveryStrategy) insertSemicolon(err CompilationError, ctx *CompilationContext) error {
// 在指定位置插入分号
source := ctx.GetSourceCode(err.File)
lines := strings.Split(source, "\n")
if err.Line > 0 && err.Line <= len(lines) {
line := lines[err.Line-1]
if !strings.HasSuffix(strings.TrimSpace(line), ";") {
lines[err.Line-1] = line + ";"
newSource := strings.Join(lines, "\n")
return ctx.UpdateSourceCode(err.File, newSource)
}
}
return fmt.Errorf("cannot insert semicolon")
}
// 插桩恢复策略
type InstrumentationRecoveryStrategy struct{}
func (irs *InstrumentationRecoveryStrategy) CanRecover(err CompilationError, ctx *CompilationContext) bool {
return err.Type == InstrumentationError
}
func (irs *InstrumentationRecoveryStrategy) Recover(err CompilationError, ctx *CompilationContext) error {
// 跳过有问题的插桩点
if strings.Contains(err.Message, "cannot instrument function") {
ctx.SkipInstrumentation(err.File, err.Line)
return nil
}
// 使用简化的插桩模板
if strings.Contains(err.Message, "template execution failed") {
return irs.useSimplifiedTemplate(err, ctx)
}
return fmt.Errorf("cannot recover from instrumentation error")
}
func (irs *InstrumentationRecoveryStrategy) useSimplifiedTemplate(err CompilationError, ctx *CompilationContext) error {
// 使用最基本的插桩模板
simplifiedTemplate := `
// Simplified instrumentation
defer func() {
if r := recover(); r != nil {
// Log error but don't propagate
log.Printf("Instrumentation error: %v", r)
}
}()
`
return ctx.ApplySimplifiedInstrumentation(err.File, err.Line, simplifiedTemplate)
}9.1.2 运行时错误处理
go
// 运行时错误处理系统
type RuntimeErrorHandler struct {
panicRecovery *PanicRecoverySystem
errorReporter *RuntimeErrorReporter
circuitBreaker *ErrorCircuitBreaker
fallbackMode *FallbackModeManager
}
// Panic恢复系统
type PanicRecoverySystem struct {
handlers map[string]PanicHandler
stats *PanicStats
logger *StructuredLogger
}
type PanicHandler interface {
CanHandle(panicValue interface{}) bool
Handle(panicValue interface{}, stackTrace []byte) error
Priority() int
}
// 插桩Panic处理器
type InstrumentationPanicHandler struct {
fallbackMode *FallbackModeManager
}
func (iph *InstrumentationPanicHandler) CanHandle(panicValue interface{}) bool {
if str, ok := panicValue.(string); ok {
return strings.Contains(str, "otel") || strings.Contains(str, "instrumentation")
}
return false
}
func (iph *InstrumentationPanicHandler) Handle(panicValue interface{}, stackTrace []byte) error {
// 记录详细的panic信息
log.Printf("Instrumentation panic recovered: %v\nStack trace:\n%s", panicValue, stackTrace)
// 激活降级模式
iph.fallbackMode.ActivateFallback("instrumentation_panic")
// 不重新抛出panic,让程序继续运行
return nil
}
// 降级模式管理器
type FallbackModeManager struct {
modes map[string]*FallbackMode
activeMode string
mutex sync.RWMutex
metrics *FallbackMetrics
}
type FallbackMode struct {
Name string
Description string
Handler FallbackHandler
Duration time.Duration
ActivatedAt time.Time
}
type FallbackHandler interface {
OnActivate() error
OnDeactivate() error
HandleRequest(ctx context.Context, req interface{}) (interface{}, error)
}
// 无插桩降级模式
type NoInstrumentationFallback struct {
originalFunctions map[string]interface{}
}
func (nif *NoInstrumentationFallback) OnActivate() error {
log.Println("Activating no-instrumentation fallback mode")
// 禁用所有插桩功能
DisableAllInstrumentation()
// 清理已注入的追踪代码
return nif.cleanupInstrumentation()
}
func (nif *NoInstrumentationFallback) OnDeactivate() error {
log.Println("Deactivating no-instrumentation fallback mode")
// 重新启用插桩功能
EnableAllInstrumentation()
return nil
}
func (nif *NoInstrumentationFallback) HandleRequest(ctx context.Context, req interface{}) (interface{}, error) {
// 在降级模式下,直接执行原始逻辑,不进行任何追踪
return req, nil
}
func (nif *NoInstrumentationFallback) cleanupInstrumentation() error {
// 移除所有插桩代码的影响
// 这里可能需要重置一些全局状态
// 清理GLS中的追踪上下文
ClearAllTraceContexts()
// 停止所有后台追踪任务
StopAllTracingTasks()
return nil
}
// 错误熔断器
type ErrorCircuitBreaker struct {
state CircuitState
failureCount int64
lastFailTime time.Time
threshold int64
timeout time.Duration
mutex sync.RWMutex
}
type CircuitState int
const (
Closed CircuitState = iota
Open
HalfOpen
)
func (ecb *ErrorCircuitBreaker) Call(fn func() error) error {
ecb.mutex.RLock()
state := ecb.state
ecb.mutex.RUnlock()
switch state {
case Open:
if time.Since(ecb.lastFailTime) > ecb.timeout {
ecb.mutex.Lock()
ecb.state = HalfOpen
ecb.mutex.Unlock()
} else {
return fmt.Errorf("circuit breaker is open")
}
case HalfOpen:
// 在半开状态下尝试执行
case Closed:
// 正常执行
}
err := fn()
ecb.mutex.Lock()
defer ecb.mutex.Unlock()
if err != nil {
ecb.failureCount++
ecb.lastFailTime = time.Now()
if ecb.failureCount >= ecb.threshold {
ecb.state = Open
}
} else {
ecb.failureCount = 0
ecb.state = Closed
}
return err
}9.2 高级调试支持系统
9.2.1 动态调试接口
go
// 动态调试系统
type DynamicDebugSystem struct {
debugServer *DebugServer
inspector *RuntimeInspector
profiler *DynamicProfiler
traceCollector *TraceCollector
config *DebugConfig
}
type DebugServer struct {
server *http.Server
handlers map[string]http.HandlerFunc
auth *DebugAuth
}
func (ds *DynamicDebugSystem) StartDebugServer(port int) error {
mux := http.NewServeMux()
// 注册调试端点
mux.HandleFunc("/debug/instrumentation", ds.handleInstrumentationDebug)
mux.HandleFunc("/debug/gls", ds.handleGLSDebug)
mux.HandleFunc("/debug/traces", ds.handleTracesDebug)
mux.HandleFunc("/debug/performance", ds.handlePerformanceDebug)
mux.HandleFunc("/debug/errors", ds.handleErrorsDebug)
mux.HandleFunc("/debug/config", ds.handleConfigDebug)
ds.debugServer.server = &http.Server{
Addr: fmt.Sprintf(":%d", port),
Handler: mux,
}
go func() {
if err := ds.debugServer.server.ListenAndServe(); err != nil && err != http.ErrServerClosed {
log.Printf("Debug server error: %v", err)
}
}()
log.Printf("Debug server started on port %d", port)
return nil
}
func (ds *DynamicDebugSystem) handleInstrumentationDebug(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
switch r.Method {
case "GET":
ds.getInstrumentationStatus(w, r)
case "POST":
ds.updateInstrumentationConfig(w, r)
default:
http.Error(w, "Method not allowed", http.StatusMethodNotAllowed)
}
}
func (ds *DynamicDebugSystem) getInstrumentationStatus(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
status := &InstrumentationStatus{
Enabled: IsInstrumentationEnabled(),
ActiveRules: GetActiveRules(),
InstrumentedFuncs: GetInstrumentedFunctions(),
Statistics: GetInstrumentationStats(),
Errors: GetRecentErrors(),
}
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(status)
}
func (ds *DynamicDebugSystem) handleGLSDebug(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
glsInfo := &GLSDebugInfo{
CurrentGoroutines: GetAllGoroutineContexts(),
MemoryUsage: GetGLSMemoryUsage(),
AccessStats: GetGLSAccessStats(),
FieldOffsets: GetGLSFieldOffsets(),
}
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(glsInfo)
}
// 运行时检查器
type RuntimeInspector struct {
goroutineTracker *GoroutineTracker
memoryAnalyzer *MemoryAnalyzer
functionTracker *FunctionTracker
}
type GoroutineTracker struct {
goroutines map[int64]*GoroutineInfo
mutex sync.RWMutex
}
type GoroutineInfo struct {
ID int64
State string
StackTrace []string
TraceContext *TraceContext
CreatedAt time.Time
LastActive time.Time
}
func (gt *GoroutineTracker) TrackGoroutine(id int64) {
gt.mutex.Lock()
defer gt.mutex.Unlock()
info := &GoroutineInfo{
ID: id,
State: "running",
StackTrace: GetCurrentStackTrace(),
CreatedAt: time.Now(),
LastActive: time.Now(),
}
// 获取当前goroutine的追踪上下文
if ctx := GetCurrentTraceContext(); ctx != nil {
info.TraceContext = ctx
}
gt.goroutines[id] = info
}
func (gt *GoroutineTracker) GetGoroutineInfo(id int64) *GoroutineInfo {
gt.mutex.RLock()
defer gt.mutex.RUnlock()
return gt.goroutines[id]
}
func (gt *GoroutineTracker) GetAllGoroutines() map[int64]*GoroutineInfo {
gt.mutex.RLock()
defer gt.mutex.RUnlock()
result := make(map[int64]*GoroutineInfo)
for id, info := range gt.goroutines {
result[id] = info
}
return result
}
// 内存分析器
type MemoryAnalyzer struct {
allocTracker *AllocationTracker
leakDetector *LeakDetector
gcMonitor *GCMonitor
}
type AllocationTracker struct {
allocations map[uintptr]*AllocationInfo
mutex sync.RWMutex
}
type AllocationInfo struct {
Size int64
Type string
StackTrace []string
AllocatedAt time.Time
Freed bool
FreedAt time.Time
}
func (at *AllocationTracker) TrackAllocation(ptr uintptr, size int64, typeName string) {
at.mutex.Lock()
defer at.mutex.Unlock()
at.allocations[ptr] = &AllocationInfo{
Size: size,
Type: typeName,
StackTrace: GetCurrentStackTrace(),
AllocatedAt: time.Now(),
Freed: false,
}
}
func (at *AllocationTracker) TrackDeallocation(ptr uintptr) {
at.mutex.Lock()
defer at.mutex.Unlock()
if info, exists := at.allocations[ptr]; exists {
info.Freed = true
info.FreedAt = time.Now()
}
}
// 泄漏检测器
type LeakDetector struct {
tracker *AllocationTracker
threshold time.Duration
checkInterval time.Duration
stopChan chan struct{}
}
func (ld *LeakDetector) Start() {
go ld.detectLoop()
}
func (ld *LeakDetector) detectLoop() {
ticker := time.NewTicker(ld.checkInterval)
defer ticker.Stop()
for {
select {
case <-ticker.C:
ld.checkForLeaks()
case <-ld.stopChan:
return
}
}
}
func (ld *LeakDetector) checkForLeaks() {
now := time.Now()
leaks := []LeakInfo{}
ld.tracker.mutex.RLock()
for ptr, info := range ld.tracker.allocations {
if !info.Freed && now.Sub(info.AllocatedAt) > ld.threshold {
leaks = append(leaks, LeakInfo{
Pointer: ptr,
Size: info.Size,
Type: info.Type,
Age: now.Sub(info.AllocatedAt),
StackTrace: info.StackTrace,
})
}
}
ld.tracker.mutex.RUnlock()
if len(leaks) > 0 {
ld.reportLeaks(leaks)
}
}
type LeakInfo struct {
Pointer uintptr
Size int64
Type string
Age time.Duration
StackTrace []string
}
func (ld *LeakDetector) reportLeaks(leaks []LeakInfo) {
log.Printf("Detected %d potential memory leaks:", len(leaks))
for _, leak := range leaks {
log.Printf(" Leak: %s (%d bytes, age: %v)", leak.Type, leak.Size, leak.Age)
for _, frame := range leak.StackTrace {
log.Printf(" %s", frame)
}
}
}9.3 智能错误诊断和修复建议
9.3.1 错误模式识别
go
// 智能诊断引擎
type IntelligentDiagnosticEngine struct {
patternMatcher *ErrorPatternMatcher
knowledgeBase *ErrorKnowledgeBase
mlPredictor *ErrorPredictor
suggestionGen *SuggestionGenerator
}
type ErrorPatternMatcher struct {
patterns []ErrorPattern
matcher *regexp.Regexp
}
type ErrorPattern struct {
ID string
Name string
Pattern *regexp.Regexp
Category ErrorCategory
Severity ErrorSeverity
Description string
Solutions []Solution
Examples []string
}
type ErrorCategory int
const (
CompilationCategory ErrorCategory = iota
RuntimeCategory
PerformanceCategory
ConfigurationCategory
DependencyCategory
)
type Solution struct {
Description string
Code string
Confidence float64
AutoApply bool
}
func (ide *IntelligentDiagnosticEngine) DiagnoseError(err error, context *DiagnosticContext) *DiagnosticResult {
// 1. 模式匹配
patterns := ide.patternMatcher.MatchPatterns(err.Error())
// 2. 知识库查询
knowledgeResults := ide.knowledgeBase.Query(err, context)
// 3. ML预测
prediction := ide.mlPredictor.Predict(err, context)
// 4. 生成建议
suggestions := ide.suggestionGen.Generate(patterns, knowledgeResults, prediction)
return &DiagnosticResult{
Error: err,
Patterns: patterns,
Knowledge: knowledgeResults,
Prediction: prediction,
Suggestions: suggestions,
Confidence: ide.calculateConfidence(patterns, knowledgeResults, prediction),
}
}
// 错误知识库
type ErrorKnowledgeBase struct {
entries map[string]*KnowledgeEntry
index *ErrorIndex
}
type KnowledgeEntry struct {
ErrorSignature string
Description string
Causes []string
Solutions []DetailedSolution
RelatedErrors []string
Frequency int64
LastSeen time.Time
}
type DetailedSolution struct {
Title string
Description string
Steps []string
Code string
References []string
Success float64
}
func (ekb *ErrorKnowledgeBase) AddEntry(err error, solution DetailedSolution) {
signature := ekb.generateSignature(err)
if entry, exists := ekb.entries[signature]; exists {
entry.Frequency++
entry.LastSeen = time.Now()
entry.Solutions = append(entry.Solutions, solution)
} else {
ekb.entries[signature] = &KnowledgeEntry{
ErrorSignature: signature,
Description: err.Error(),
Solutions: []DetailedSolution{solution},
Frequency: 1,
LastSeen: time.Now(),
}
}
}
func (ekb *ErrorKnowledgeBase) generateSignature(err error) string {
// 生成错误的唯一签名
message := err.Error()
// 移除变量部分(如文件路径、行号等)
normalized := regexp.MustCompile(`\d+`).ReplaceAllString(message, "N")
normalized = regexp.MustCompile(`/[^\s]+`).ReplaceAllString(normalized, "/PATH")
// 计算哈希
hash := sha256.Sum256([]byte(normalized))
return hex.EncodeToString(hash[:8])
}
// 建议生成器
type SuggestionGenerator struct {
templates map[ErrorCategory][]SuggestionTemplate
ranker *SuggestionRanker
}
type SuggestionTemplate struct {
Name string
Template string
Applicability func(error, *DiagnosticContext) bool
Priority int
}
func (sg *SuggestionGenerator) Generate(patterns []ErrorPattern, knowledge []*KnowledgeEntry, prediction *ErrorPrediction) []Suggestion {
suggestions := []Suggestion{}
// 基于模式生成建议
for _, pattern := range patterns {
for _, solution := range pattern.Solutions {
suggestions = append(suggestions, Suggestion{
Type: "pattern",
Description: solution.Description,
Code: solution.Code,
Confidence: solution.Confidence,
Source: pattern.Name,
})
}
}
// 基于知识库生成建议
for _, entry := range knowledge {
for _, solution := range entry.Solutions {
suggestions = append(suggestions, Suggestion{
Type: "knowledge",
Description: solution.Description,
Code: solution.Code,
Confidence: solution.Success,
Source: "knowledge_base",
})
}
}
// 基于ML预测生成建议
if prediction != nil {
for _, suggestion := range prediction.Suggestions {
suggestions = append(suggestions, suggestion)
}
}
// 排序和去重
return sg.ranker.RankAndDeduplicate(suggestions)
}
type Suggestion struct {
Type string
Description string
Code string
Confidence float64
Source string
AutoApply bool
}
// 建议排序器
type SuggestionRanker struct {
weights map[string]float64
}
func (sr *SuggestionRanker) RankAndDeduplicate(suggestions []Suggestion) []Suggestion {
// 去重
seen := make(map[string]bool)
unique := []Suggestion{}
for _, suggestion := range suggestions {
key := suggestion.Description + suggestion.Code
if !seen[key] {
seen[key] = true
unique = append(unique, suggestion)
}
}
// 排序
sort.Slice(unique, func(i, j int) bool {
scoreI := sr.calculateScore(unique[i])
scoreJ := sr.calculateScore(unique[j])
return scoreI > scoreJ
})
return unique
}
func (sr *SuggestionRanker) calculateScore(suggestion Suggestion) float64 {
baseScore := suggestion.Confidence
// 根据来源调整权重
if weight, exists := sr.weights[suggestion.Source]; exists {
baseScore *= weight
}
// 自动应用的建议得分更高
if suggestion.AutoApply {
baseScore *= 1.2
}
return baseScore
}9.2 调试支持
- 调试模式: 输出详细的插桩信息
- AST可视化: 生成AST结构图
- 规则验证: 检查规则的正确性
十、未来发展方向深度展望
10.1 技术演进路线图
10.1.1 短期发展目标(6-12个月)
go
// 短期技术改进计划
type ShortTermRoadmap struct {
stabilityImprovements *StabilityEnhancements
performanceOptimizations *PerformanceUpgrades
frameworkSupport *ExtendedFrameworkSupport
toolingImprovements *DeveloperTooling
}
// 稳定性增强
type StabilityEnhancements struct {
errorRecovery *AdvancedErrorRecovery
memoryLeakPrevention *MemoryLeakPrevention
concurrencySafety *ConcurrencySafetyImprovements
runtimeCompatibility *RuntimeCompatibilityMatrix
}
func (se *StabilityEnhancements) ImplementAdvancedErrorRecovery() {
// 实现更智能的错误恢复机制
// 1. 预测性错误检测
// 2. 自动降级策略
// 3. 智能重试机制
// 4. 错误模式学习
}
// 性能优化升级
type PerformanceUpgrades struct {
zeroAllocationTracing *ZeroAllocationTracing
adaptiveSampling *AdaptiveSamplingEngine
batchProcessing *BatchProcessingOptimization
cacheOptimization *IntelligentCaching
}
func (pu *PerformanceUpgrades) ImplementZeroAllocationTracing() {
// 实现零分配追踪
// 1. 预分配对象池
// 2. 栈上分配优化
// 3. 内存复用策略
// 4. GC压力减少
}
// 扩展框架支持
type ExtendedFrameworkSupport struct {
microservices *MicroserviceFrameworks
databases *DatabaseDrivers
messageQueues *MessageQueueSystems
cloudServices *CloudServiceIntegrations
}
func (efs *ExtendedFrameworkSupport) AddMicroserviceSupport() {
frameworks := []string{
"go-micro",
"go-kit",
"kratos",
"jupiter",
"tars-go",
}
for _, framework := range frameworks {
efs.implementFrameworkSupport(framework)
}
}10.1.2 中期发展目标(1-2年)
go
// 中期技术发展计划
type MediumTermRoadmap struct {
aiDrivenInstrumentation *AIInstrumentationEngine
crossLanguageSupport *CrossLanguageTracing
distributedProfiling *DistributedProfilingSystem
intelligentOptimization *IntelligentOptimizationEngine
}
// AI驱动的插桩引擎
type AIInstrumentationEngine struct {
codeAnalyzer *MLCodeAnalyzer
patternRecognition *InstrumentationPatternRecognition
autoOptimization *AutoOptimizationEngine
predictiveInstrumentation *PredictiveInstrumentationSystem
}
func (aie *AIInstrumentationEngine) AnalyzeCodePatterns(codebase string) *InstrumentationPlan {
// 使用机器学习分析代码模式
patterns := aie.codeAnalyzer.AnalyzePatterns(codebase)
// 识别最佳插桩点
instrumentationPoints := aie.patternRecognition.IdentifyOptimalPoints(patterns)
// 生成智能插桩计划
plan := &InstrumentationPlan{
Points: instrumentationPoints,
Strategy: aie.determineOptimalStrategy(patterns),
ExpectedPerformanceImpact: aie.predictPerformanceImpact(instrumentationPoints),
}
return plan
}
// 跨语言追踪支持
type CrossLanguageTracing struct {
protocolBridge *ProtocolBridge
contextPropagation *CrossLanguageContextPropagation
traceCorrelation *TraceCorrelationEngine
}
func (clt *CrossLanguageTracing) EnableCrossLanguageTracing() {
// 支持的语言
supportedLanguages := []string{
"Java", "Python", "Node.js", "C++", "Rust", ".NET",
}
for _, lang := range supportedLanguages {
clt.protocolBridge.RegisterLanguageSupport(lang)
}
// 实现统一的上下文传播
clt.contextPropagation.EnableUnifiedPropagation()
}
// 分布式性能分析系统
type DistributedProfilingSystem struct {
clusterProfiler *ClusterProfiler
hotspotDetection *HotspotDetectionEngine
performanceAnalytics *PerformanceAnalyticsEngine
optimizationRecommendations *OptimizationRecommendationEngine
}
func (dps *DistributedProfilingSystem) StartDistributedProfiling() {
// 启动集群级别的性能分析
dps.clusterProfiler.StartProfiling()
// 实时热点检测
go dps.hotspotDetection.ContinuousDetection()
// 性能分析和建议
go dps.performanceAnalytics.AnalyzePerformance()
go dps.optimizationRecommendations.GenerateRecommendations()
}10.1.3 长期发展愿景(2-5年)
go
// 长期技术愿景
type LongTermVision struct {
quantumOptimization *QuantumOptimizationEngine
selfHealingSystem *SelfHealingInstrumentationSystem
cognitiveObservability *CognitiveObservabilityPlatform
autonomousOptimization *AutonomousOptimizationSystem
}
// 量子优化引擎
type QuantumOptimizationEngine struct {
quantumAlgorithms *QuantumAlgorithmSuite
optimizationSpace *QuantumOptimizationSpace
quantumSimulator *QuantumSimulator
}
func (qoe *QuantumOptimizationEngine) OptimizeInstrumentationStrategy() *OptimizationResult {
// 使用量子算法优化插桩策略
// 1. 量子退火算法寻找最优插桩点组合
// 2. 量子机器学习预测性能影响
// 3. 量子并行计算加速优化过程
return qoe.quantumAlgorithms.FindOptimalStrategy()
}
// 自愈插桩系统
type SelfHealingInstrumentationSystem struct {
anomalyDetection *AnomalyDetectionEngine
autoRepair *AutoRepairMechanism
adaptiveEvolution *AdaptiveEvolutionEngine
systemResilience *SystemResilienceManager
}
func (shis *SelfHealingInstrumentationSystem) EnableSelfHealing() {
// 实现系统自愈能力
// 1. 自动检测异常和故障
// 2. 智能修复机制
// 3. 系统自适应演化
// 4. 弹性恢复能力
go shis.anomalyDetection.ContinuousMonitoring()
go shis.autoRepair.AutomaticRepair()
go shis.adaptiveEvolution.ContinuousEvolution()
}
// 认知可观测性平台
type CognitiveObservabilityPlatform struct {
naturalLanguageInterface *NaturalLanguageInterface
intelligentInsights *IntelligentInsightsEngine
predictiveAnalytics *PredictiveAnalyticsEngine
conversationalDebugging *ConversationalDebuggingSystem
}
func (cop *CognitiveObservabilityPlatform) EnableCognitiveObservability() {
// 实现认知级别的可观测性
// 1. 自然语言查询接口
// 2. 智能洞察生成
// 3. 预测性分析
// 4. 对话式调试
cop.naturalLanguageInterface.EnableNLQuery()
cop.intelligentInsights.StartInsightGeneration()
cop.predictiveAnalytics.EnablePredictiveAnalysis()
cop.conversationalDebugging.StartConversationalDebugging()
}10.2 新兴技术集成深度规划
10.2.1 WebAssembly生态集成
go
// WebAssembly支持系统
type WebAssemblySupport struct {
wasmRuntime *WASMRuntimeIntegration
crossCompilation *CrossCompilationSupport
performanceOptimization *WASMPerformanceOptimization
securitySandbox *WASMSecuritySandbox
}
func (was *WebAssemblySupport) EnableWASMSupport() {
// 实现WASM环境下的插桩支持
// 1. WASM运行时集成
// 2. 跨编译支持
// 3. 性能优化
// 4. 安全沙箱
was.wasmRuntime.IntegrateWithWASMRuntime()
was.crossCompilation.EnableCrossCompilation()
was.performanceOptimization.OptimizeForWASM()
was.securitySandbox.EnableSecuritySandbox()
}
// WASM运行时集成
type WASMRuntimeIntegration struct {
wasmEngine *WASMEngine
memoryManager *WASMMemoryManager
functionBridge *WASMFunctionBridge
eventSystem *WASMEventSystem
}
func (wri *WASMRuntimeIntegration) IntegrateWithWASMRuntime() {
// 集成主流WASM运行时
runtimes := []string{
"wasmtime",
"wasmer",
"wasm3",
"lucet",
}
for _, runtime := range runtimes {
wri.wasmEngine.RegisterRuntime(runtime)
}
}10.2.2 云原生深度集成
go
// 云原生集成系统
type CloudNativeIntegration struct {
kubernetesIntegration *KubernetesIntegration
serviceMeshSupport *ServiceMeshSupport
serverlessSupport *ServerlessSupport
edgeComputingSupport *EdgeComputingSupport
}
// Kubernetes深度集成
type KubernetesIntegration struct {
operatorFramework *OperatorFramework
customResources *CustomResourceDefinitions
admissionController *AdmissionController
networkPolicies *NetworkPolicyIntegration
}
func (ki *KubernetesIntegration) DeployOperator() {
// 部署Kubernetes Operator
operator := &InstrumentationOperator{
Name: "otel-go-instrumentation-operator",
Version: "v1.0.0",
Capabilities: []string{
"auto-instrumentation",
"configuration-management",
"performance-monitoring",
"error-recovery",
},
}
ki.operatorFramework.Deploy(operator)
}
// 服务网格支持
type ServiceMeshSupport struct {
istioIntegration *IstioIntegration
linkerdIntegration *LinkerdIntegration
consulConnectIntegration *ConsulConnectIntegration
envoyIntegration *EnvoyIntegration
}
func (sms *ServiceMeshSupport) EnableServiceMeshIntegration() {
// 集成主流服务网格
meshes := []ServiceMesh{
&IstioMesh{},
&LinkerdMesh{},
&ConsulConnectMesh{},
&EnvoyMesh{},
}
for _, mesh := range meshes {
sms.integrateMesh(mesh)
}
}
// 无服务器支持
type ServerlessSupport struct {
faasIntegration *FaaSIntegration
coldStartOptimization *ColdStartOptimization
eventDrivenTracing *EventDrivenTracing
costOptimization *CostOptimization
}
func (ss *ServerlessSupport) EnableServerlessSupport() {
// 支持主流FaaS平台
platforms := []string{
"AWS Lambda",
"Google Cloud Functions",
"Azure Functions",
"Alibaba Cloud Function Compute",
"Tencent Cloud SCF",
}
for _, platform := range platforms {
ss.faasIntegration.RegisterPlatform(platform)
}
// 优化冷启动性能
ss.coldStartOptimization.EnableOptimization()
}10.2.3 边缘计算支持
go
// 边缘计算支持系统
type EdgeComputingSupport struct {
edgeRuntime *EdgeRuntime
resourceOptimization *EdgeResourceOptimization
networkOptimization *EdgeNetworkOptimization
dataProcessing *EdgeDataProcessing
}
func (ecs *EdgeComputingSupport) EnableEdgeSupport() {
// 启用边缘计算支持
ecs.edgeRuntime.InitializeEdgeRuntime()
ecs.resourceOptimization.OptimizeForEdge()
ecs.networkOptimization.OptimizeNetworking()
ecs.dataProcessing.EnableEdgeProcessing()
}
// 边缘运行时
type EdgeRuntime struct {
lightweightRuntime *LightweightRuntime
resourceConstraints *ResourceConstraints
offlineCapability *OfflineCapability
syncMechanism *SyncMechanism
}
func (er *EdgeRuntime) InitializeEdgeRuntime() {
// 初始化轻量级边缘运行时
er.lightweightRuntime.Initialize()
// 设置资源约束
er.resourceConstraints.SetConstraints(ResourceConstraints{
MaxMemory: "128MB",
MaxCPU: "0.5 cores",
MaxStorage: "1GB",
})
// 启用离线能力
er.offlineCapability.Enable()
// 配置同步机制
er.syncMechanism.Configure()
}10.3 生态系统发展规划
10.3.1 开发者生态建设
go
// 开发者生态系统
type DeveloperEcosystem struct {
sdkFramework *SDKFramework
pluginSystem *PluginSystem
communityTools *CommunityTools
educationPlatform *EducationPlatform
}
// SDK框架
type SDKFramework struct {
coreSDK *CoreSDK
languageBindings *LanguageBindings
extensionPoints *ExtensionPoints
documentationSystem *DocumentationSystem
}
func (sf *SDKFramework) BuildComprehensiveSDK() {
// 构建全面的SDK框架
sf.coreSDK.BuildCore()
sf.languageBindings.CreateBindings()
sf.extensionPoints.DefineExtensionPoints()
sf.documentationSystem.GenerateDocumentation()
}
// 插件系统
type PluginSystem struct {
pluginRegistry *PluginRegistry
pluginManager *PluginManager
marketPlace *PluginMarketPlace
qualityAssurance *PluginQualityAssurance
}
func (ps *PluginSystem) EnablePluginEcosystem() {
// 启用插件生态系统
ps.pluginRegistry.Initialize()
ps.pluginManager.StartManager()
ps.marketPlace.LaunchMarketPlace()
ps.qualityAssurance.EnableQA()
}10.3.2 企业级支持
go
// 企业级支持系统
type EnterpriseSupport struct {
enterpriseFeatures *EnterpriseFeatures
supportServices *SupportServices
complianceFramework *ComplianceFramework
migrationTools *MigrationTools
}
// 企业级功能
type EnterpriseFeatures struct {
advancedSecurity *AdvancedSecurity
scalabilityFeatures *ScalabilityFeatures
governanceTools *GovernanceTools
auditingCapabilities *AuditingCapabilities
}
func (ef *EnterpriseFeatures) EnableEnterpriseFeatures() {
// 启用企业级功能
ef.advancedSecurity.EnableAdvancedSecurity()
ef.scalabilityFeatures.EnableScalability()
ef.governanceTools.EnableGovernance()
ef.auditingCapabilities.EnableAuditing()
}十一、总结:技术革新与未来展望
otel go build 非侵入式插桩技术代表了Go语言可观测性领域的重大技术突破和范式转变。通过深度集成Go编译器生态、创新性利用GLS机制、巧妙运用go:linkname指令,以及构建完善的智能插桩规则系统,该技术实现了前所未有的技术创新和实用价值。
核心技术优势总结
1. 非侵入性设计哲学
- 零代码修改:完全无需修改业务代码即可实现全链路追踪
- 透明集成:对开发者完全透明,不影响开发流程
- 向后兼容:与现有Go生态系统完美兼容
- 渐进式采用:支持逐步启用和配置
2. 极致性能优化
- 编译时插桩:在编译阶段完成代码注入,运行时零开销
- 智能采样:基于机器学习的自适应采样策略
- 内存优化:零分配追踪和智能内存管理
- 并发优化:充分利用Go的并发特性
3. 生态系统完整性
- 框架全覆盖:支持主流Web框架、数据库驱动、消息队列
- 中间件集成:深度集成各类中间件和基础设施组件
- 云原生支持:原生支持Kubernetes、服务网格等云原生技术
- 跨平台兼容:支持多种操作系统和部署环境
技术创新突破点
1. 编译器深度集成创新
- AST层面操作:直接在抽象语法树层面进行精确的代码注入
- 类型系统集成:与Go类型系统深度集成,确保类型安全
- 优化器协同:与Go编译器优化器协同工作,不影响编译优化
- 调试信息保持:完整保持调试信息,不影响调试体验
2. GLS机制突破性应用
- 运行时结构扩展:安全地扩展Go运行时的goroutine结构
- 上下文传播创新:实现高效的跨goroutine上下文传播
- 内存安全保障:通过多重安全检查确保内存访问安全
- 性能极致优化:通过直接内存访问实现纳秒级性能
3. 智能插桩规则系统
- 声明式配置:通过声明式规则定义插桩行为
- 模板化生成:基于模板的灵活代码生成机制
- 条件化执行:支持复杂的条件判断和动态插桩
- 扩展性设计:支持用户自定义插桩规则和模板
4. 企业级可靠性保障
- 多层错误恢复:从编译时到运行时的全方位错误处理
- 智能降级机制:在异常情况下自动降级保障业务连续性
- 实时监控诊断:提供实时的系统健康监控和诊断能力
- 自愈系统设计:具备自动检测和修复问题的能力
技术影响与价值
1. 对Go生态系统的影响
- 可观测性标准:为Go语言可观测性设立了新的技术标准
- 开发效率提升:显著降低了可观测性实施的技术门槛
- 生态系统完善:推动了Go语言在企业级应用中的普及
- 技术创新引领:引领了编译时插桩技术的发展方向
2. 对云原生领域的贡献
- 微服务可观测性:为微服务架构提供了完整的可观测性解决方案
- 容器化支持:原生支持容器化和Kubernetes环境
- 服务网格集成:与主流服务网格技术深度集成
- 边缘计算扩展:支持边缘计算场景的可观测性需求
3. 对企业数字化转型的价值
- 运维效率提升:大幅提升系统运维和故障排查效率
- 业务洞察增强:提供深度的业务性能洞察和分析
- 成本优化:通过精确的性能分析实现成本优化
- 风险控制:提供全面的系统健康监控和风险预警
未来发展展望
随着技术的不断演进和生态系统的持续完善,otel go build 技术将在以下几个方向继续发展:
1. 智能化演进
- AI驱动优化:利用人工智能技术实现智能化的插桩优化
- 自适应系统:构建能够自适应不同场景的智能系统
- 预测性分析:基于历史数据进行预测性的性能分析
- 认知计算:引入认知计算技术提升系统智能水平
2. 生态系统扩展
- 跨语言支持:扩展到更多编程语言的支持
- 新兴技术集成:集成WebAssembly、量子计算等新兴技术
- 标准化推进:推动相关技术标准的制定和普及
- 开源社区建设:构建活跃的开源社区生态
3. 企业级增强
- 安全性强化:进一步增强企业级安全特性
- 合规性支持:支持更多行业的合规性要求
- 可扩展性提升:支持更大规模的企业级部署
- 专业服务:提供更完善的专业服务和支持
这项技术不仅解决了Go语言可观测性的核心痛点,更为整个软件工程领域的发展贡献了宝贵的技术创新和实践经验。随着云原生技术的持续发展和企业数字化转型的深入推进,相信这项技术将在未来发挥更加重要和深远的作用,为构建更加智能、高效、可靠的软件系统提供强有力的技术支撑。
通过持续的技术创新、生态建设和社区合作,otel go build 技术必将成为Go语言乃至整个软件工程领域的重要技术基石,推动可观测性技术向更高水平发展,为数字化时代的软件系统建设贡献更大的价值。*