在现代几何建模与逆向工程中,点云数据的处理是构建精确 CAD 模型的关键环节。OpenCASCADE Technology(OCCT)作为一款功能强大的开源几何建模内核,提供了从离散点集拟合出光滑 B-Spline 曲线与曲面的能力。本文以 OCCT 7.9.0 为背景,结合 Windows 11 + Visual Studio 2022 开发环境,深入剖析 GeomAPI_PointsToBSpline 与 GeomAPI_PointsToBSplineSurface 的使用方法,解决新版 API 变更带来的兼容性问题,并提供可独立运行的完整代码示例。
曲线拟合:从螺旋点云生成 B-Spline 曲线
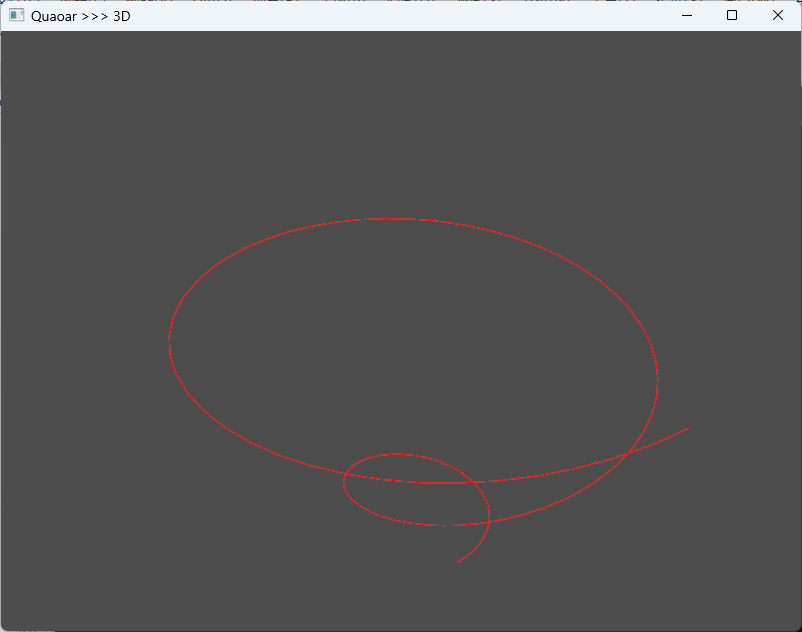
我们首先构造一个典型的三维螺旋线点云,模拟从扫描设备获取的数据。螺旋线的参数方程为:
{x(t)=tcost10y(t)=tsint10z(t)=t10,t∈[0,4π] \begin{cases} x(t) = \frac{t \cos t}{10} \\ y(t) = \frac{t \sin t}{10} \\ z(t) = \frac{t}{10} \end{cases}, \quad t \in [0, 4\pi] ⎩ ⎨ ⎧x(t)=10tcosty(t)=10tsintz(t)=10t,t∈[0,4π]
该点云将作为输入,使用 GeomAPI_PointsToBSpline 拟合出一条 C2C^2C2 连续的 B-Spline 曲线。注意在 OCCT 7.9.0 中,GeomAPI_PointsToBSpline 的构造函数接受点数组、最小/最大次数和连续性等级。
cpp
// main_curve.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
// OpenCASCADE 核心头文件
#include <gp_Pnt.hxx>
#include <TColgp_Array1OfPnt.hxx>
#include <TColgp_HArray1OfPnt.hxx>
#include <GeomAPI_PointsToBSpline.hxx>
#include <Geom_BSplineCurve.hxx>
#include <BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge.hxx>
#include <TopoDS_Edge.hxx>
#include <TopoDS_Shape.hxx>
// 可视化封装(假设已实现)
#include "Viewer.h"
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
Viewer vout(50, 50, 800, 600);
std::vector<TopoDS_Shape> prts;
// 生成螺旋点云
std::vector<gp_Pnt> points;
for (double t = 0; t < 4 * M_PI; t += 0.1) {
double x = t * cos(t) / 10.0;
double y = t * sin(t) / 10.0;
double z = t / 10.0;
points.emplace_back(x, y, z);
}
// 转换为 OCCT 数组
int nPts = static_cast<int>(points.size());
Handle(TColgp_HArray1OfPnt) hPoints = new TColgp_HArray1OfPnt(1, nPts);
for (int i = 0; i < nPts; ++i) {
hPoints->SetValue(i + 1, points[i]);
}
// 拟合 B-Spline 曲线(最小次数 3,最大 8,C2 连续)
GeomAPI_PointsToBSpline curveFitter(hPoints->Array1(), 3, 8, GeomAbs_C2);
if (!curveFitter.IsDone()) {
std::cerr << "曲线拟合失败!" << std::endl;
return 1;
}
Handle(Geom_BSplineCurve) fittedCurve = curveFitter.Curve();
TopoDS_Edge curveEdge = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeEdge(fittedCurve);
prts.push_back(curveEdge);
// 可视化
for (const auto& shape : prts) {
vout << shape;
}
vout.StartMessageLoop();
return 0;
}此代码独立运行后将在窗口中显示一条光滑的螺旋曲线。关键在于 GeomAPI_PointsToBSpline 自动完成了参数化(默认为弦长法)和节点向量生成,用户只需关注输入点集与期望的光滑性。
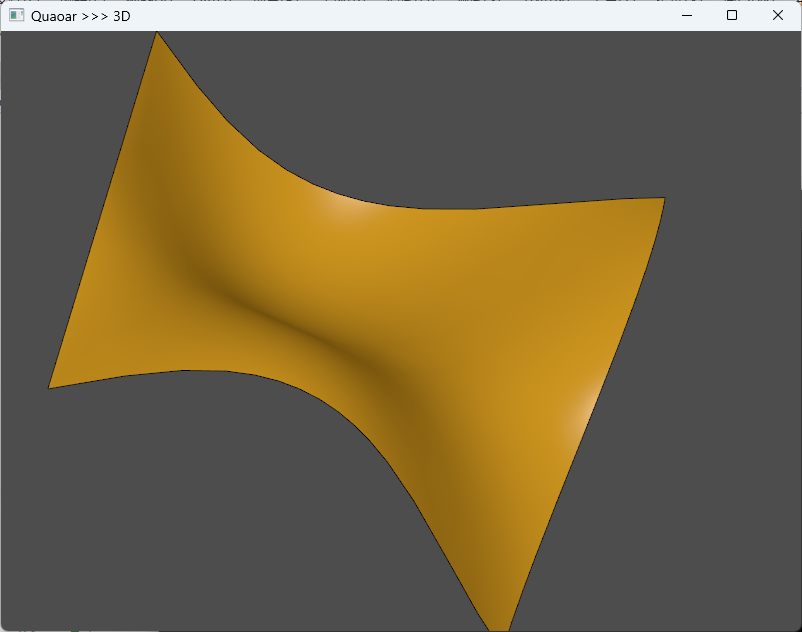
曲面拟合:从网格点云重建 B-Spline 曲面
曲面拟合比曲线更复杂,需处理二维点阵。我们构造一个波浪形曲面,其高度由 z=sinu⋅cosvz = \sin u \cdot \cos vz=sinu⋅cosv 定义,形成 20×2020 \times 2020×20 的规则网格。在 OCCT 7.9.0 中,GeomAPI_PointsToBSplineSurface::Init 的签名已变更,不再接受闭合性标志,而是通过 Approx_ParametrizationType 控制参数化方式。
cpp
// main_surface.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
// OpenCASCADE 核心头文件
#include <gp_Pnt.hxx>
#include <TColgp_Array2OfPnt.hxx>
#include <GeomAPI_PointsToBSplineSurface.hxx>
#include <Geom_BSplineSurface.hxx>
#include <BRepBuilderAPI_MakeFace.hxx>
#include <TopoDS_Face.hxx>
#include <TopoDS_Shape.hxx>
// 可视化封装
#include "Viewer.h"
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
Viewer vout(50, 50, 800, 600);
std::vector<TopoDS_Shape> prts;
// 生成网格点云 (20x20)
const int nbU = 20, nbV = 20;
TColgp_Array2OfPnt pointsArray(1, nbU, 1, nbV);
for (int i = 0; i < nbU; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < nbV; ++j) {
double u = i * 0.2;
double v = j * 0.2;
double x = u;
double y = v;
double z = sin(u) * cos(v);
pointsArray.SetValue(i + 1, j + 1, gp_Pnt(x, y, z));
}
}
// 创建曲面拟合器并初始化
GeomAPI_PointsToBSplineSurface surfaceFitter;
surfaceFitter.Init(
pointsArray, // 点阵数据
Approx_ChordLength, // 参数化方法:弦长法
3, // 最小次数
8, // 最大次数
GeomAbs_C2, // 连续性要求
1.0e-3 // 3D 容差
);
if (!surfaceFitter.IsDone()) {
std::cerr << "曲面拟合失败!" << std::endl;
return 1;
}
// 获取拟合结果(返回 Handle(Geom_BSplineSurface))
Handle(Geom_BSplineSurface) fittedSurface = surfaceFitter.Surface();
TopoDS_Face surfaceFace = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeFace(fittedSurface, 1e-6);
prts.push_back(surfaceFace);
// 可视化
for (const auto& shape : prts) {
vout << shape;
}
vout.StartMessageLoop();
return 0;
}此处关键修正点是:
- 使用
TColgp_Array2OfPnt而非Handle(TColgp_HArray2OfPnt),因为Init接受引用而非句柄。 - 将
Handle(Geom_BoundedSurface)改为Handle(Geom_BSplineSurface),因为Surface()方法返回的是具体类型。 - 参数化类型
Approx_ChordLength明确指定,避免默认值歧义。
深度解析:OCCT 7.9.0 的 API 变更与数学原理
在 OCCT 7.7 之后,GeomAPI_PointsToBSplineSurface 移除了对闭合性的直接支持,这反映了其设计哲学的转变:拟合与拓扑应分离 。闭合性(周期性)现在需通过后处理实现,例如使用 GeomConvert::SurfaceToBSplineSurface 并调用 SetUNotPeriodic() 或 SetVPeriodic()。
B-Spline 曲面拟合的数学本质是求解一个最小二乘问题。给定点集 {P_{i,j}} \\in \\mathbb{R}\^3 ,寻找控制点 {Q_{k,l}} 和节点向量 U, V ,使得:
min∑i,j∥S(ui,vj)−Pi,j∥2 \min \sum_{i,j} \left\| S(u_i, v_j) - P_{i,j} \right\|^2 mini,j∑∥S(ui,vj)−Pi,j∥2
其中 S(u,v) = \\sum_{k,l} N_{k,p}(u) N_{l,q}(v) Q_{k,l} 是 B-Spline 曲面, N_{k,p} 是第 kkk 个 ppp 次基函数。OCCT 使用 chord length 参数化确定 (u_i, v_j) ,即:
ui=∑m=1i∥Pm,j−Pm−1,j∥∑m=1n∥Pm,j−Pm−1,j∥,vj=∑n=1j∥Pi,n−Pi,n−1∥∑n=1m∥Pi,n−Pi,n−1∥ u_i = \frac{\sum_{m=1}^{i} \|P_{m,j} - P_{m-1,j}\|}{\sum_{m=1}^{n} \|P_{m,j} - P_{m-1,j}\|}, \quad v_j = \frac{\sum_{n=1}^{j} \|P_{i,n} - P_{i,n-1}\|}{\sum_{n=1}^{m} \|P_{i,n} - P_{i,n-1}\|} ui=∑m=1n∥Pm,j−Pm−1,j∥∑m=1i∥Pm,j−Pm−1,j∥,vj=∑n=1m∥Pi,n−Pi,n−1∥∑n=1j∥Pi,n−Pi,n−1∥
容差 Tol3DTol3DTol3D 控制拟合精度,通常设为 10−310^{-3}10−3 至 10−610^{-6}10−6,取决于点云密度和模型尺度。
实际应用:从文件读取点云并拟合曲面
在工业场景中,点云通常来自 .txt 或 .ply 文件。以下代码演示如何从文本文件读取 x y z 格式的点并拟合曲面。
cpp
// main_from_file.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <sstream>
#include <gp_Pnt.hxx>
#include <TColgp_Array2OfPnt.hxx>
#include <GeomAPI_PointsToBSplineSurface.hxx>
#include <Geom_BSplineSurface.hxx>
#include <BRepBuilderAPI_MakeFace.hxx>
#include <TopoDS_Face.hxx>
#include <TopoDS_Shape.hxx>
#include "Viewer.h"
// 假设点云文件为规则网格,每行一个点,按行优先顺序存储
std::vector<std::vector<gp_Pnt>> loadGridFromTxt(const std::string& filename, int rows, int cols)
{
std::ifstream file(filename);
if (!file.is_open()) {
throw std::runtime_error("无法打开文件: " + filename);
}
std::vector<std::vector<gp_Pnt>> grid(rows, std::vector<gp_Pnt>(cols));
double x, y, z;
for (int i = 0; i < rows; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; ++j) {
if (!(file >> x >> y >> z)) {
throw std::runtime_error("文件数据不足或格式错误");
}
grid[i][j] = gp_Pnt(x, y, z);
}
}
file.close();
return grid;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
Viewer vout(50, 50, 800, 600);
try {
// 假设有一个 10x10 的点云文件 "points.txt"
auto grid = loadGridFromTxt("points.txt", 10, 10);
int nbU = grid.size(), nbV = grid[0].size();
TColgp_Array2OfPnt pointsArray(1, nbU, 1, nbV);
for (int i = 0; i < nbU; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < nbV; ++j) {
pointsArray.SetValue(i + 1, j + 1, grid[i][j]);
}
}
GeomAPI_PointsToBSplineSurface surfaceFitter;
surfaceFitter.Init(pointsArray, Approx_ChordLength, 3, 8, GeomAbs_C2, 1e-3);
Handle(Geom_BSplineSurface) surface = surfaceFitter.Surface();
TopoDS_Face face = BRepBuilderAPI_MakeFace(surface, 1e-6);
vout << face;
vout.StartMessageLoop();
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
std::cerr << "错误: " << e.what() << std::endl;
return 1;
}
return 0;
}此版本增强了鲁棒性,包含文件异常处理,并可通过 MaxDistance() 查询拟合质量。