作者:翟天保Steven
版权声明:著作权归作者所有,商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处
前言
图像配准是医学图像处理中一项基础且重要的任务,它的目标是将不同时间、不同模态或不同视角下获取的图像对齐到同一坐标系下。ITK (Insight Segmentation and Registration Toolkit) 作为开源的医学图像处理工具包,提供了强大的图像配准功能。
本文将通过一段完整的ITK代码(参考ITK官方例程),详细介绍基于欧拉变换与质心对齐的二维刚性配准算法的实现过程。
环境准备
参见:Windows下用CMake编译ITK及配置测试_itk配置-CSDN博客
功能说明
图像配准的本质是寻找最优空间变换,使浮动图像与固定图像的 "相似度最高"。本方案的核心组件及原理如下:
1.空间变换:2D 欧拉变换(Euler2DTransform)
欧拉变换是 2D 配准中常用的刚性变换(不改变图像尺度),包含 3 个自由度,能解决 "旋转 + 平移" 类错位问题:
- 旋转:围绕图像质心(或指定中心点)的角度调整(单位:弧度);
- 平移:X 轴、Y 轴方向的位移调整(单位:像素 / 物理毫米,取决于图像间距)。
适用于:医学影像中因患者轻微移动导致的图像旋转、平移错位(如 MRI、CT 切片)。
2.相似度度量:均方误差(MeanSquares)
均方误差(Mean Squared Error, MSE)通过计算 "固定图像与浮动图像对应像素值差的平方和" 衡量相似度:
- 特点:计算速度快,适合灰度分布相似的图像(如同一模态的 MRI 切片);值越小,说明图像对齐越精准。
3.优化器:正则步长梯度下降(RegularStepGradientDescentv4)
优化器的作用是 "最小化相似度度量值"(均方误差需最小化),找到最优变换参数。正则步长梯度下降的优势在于:
- 自适应步长:初始步长较大(快速接近最优解),随着迭代逐步减小步长(避免在最优解附近震荡);
- 早停机制:当步长小于预设最小值,或达到最大迭代次数时自动停止,兼顾效率与精度。
4.变换初始化:质心对齐(CenteredTransformInitializer)
直接随机初始化变换参数易导致 "局部最优解"(如配准陷入局部最小值,无法找到全局最优)。本方案通过质心对齐初始化解决此问题:
- 计算固定图像与浮动图像的灰度质心;
- 初始化变换参数,使两图像的质心先对齐,为后续优化提供 "优质初始点"。
代码模块解析
1. 配准框架搭建
代码首先定义了配准所需的核心组件类型,并完成实例化与关联,构建起完整的配准流水线:
- 变换模型 :
Euler2DTransform定义了 2D 空间的欧拉变换,考虑旋转+平移。 - 相似性度量 :
MeanSquaresImageToImageMetricv4通过计算两幅图像综合像素差值,来评估相似程度。 - 优化器 :
RegularStepGradientDescentOptimizerv4通过沿梯度方向迭代更新参数,自适应调整步长,寻找最优解。
2. 图像读取与预处理
通过itk::ImageFileReader读取固定图像和浮动图像,其中固定图像是作为参考的标准图像,浮动图像是需要变换的图像。代码支持PNG 格式输出,通过注册 IO 工厂确保格式支持。
3. 优化过程配置
优化器参数直接影响配准收敛速度和精度,本文对梯度下降优化器的关键参数进行了配置:
- 学习率:设为 0.1,控制每次迭代的步长大小,过大可能导致震荡,过小则收敛缓慢。
- 迭代次数:设为 200 次,避免无限制迭代。
此外,代码中还创建了一个迭代观察者 (CommandIterationUpdate),用于在每次迭代时输出当前的迭代次数、度量值和变换参数,便于监控配准过程。
4. 中心变换初始化器配置
采用质心模式,快速对齐固定图像质心和浮动图像质心,提高配准效率和准确度。
5. 配准结果处理
配准完成后,代码获取最终的变换参数,并使用itk::ResampleImageFilter将浮动图像重采样到固定图像的空间坐标系中。然后通过类型转换和强度重映射,将结果保存为 PNG 图像。
6. 配准效果可视化
为直观对比配准效果,代码生成了配准前后的图像。
使用说明
- 需安装ITK库及相关依赖。
- 将ITK官方项目中Examples\Data中的图像文件(文件名字与例程中名字一致),复制到你项目的路径下,并更改代码。
- 编译时需链接 ITK的库文件。
完整代码
#include "itkImageRegistrationMethodv4.h"
#include "itkMeanSquaresImageToImageMetricv4.h"
#include "itkRegularStepGradientDescentOptimizerv4.h"
// Euler2D变换和中心变换初始化器的头文件
#include "itkEuler2DTransform.h"
#include "itkCenteredTransformInitializer.h"
#include "itkImageFileReader.h"
#include "itkImageFileWriter.h"
#include "itkResampleImageFilter.h"
#include "itkCastImageFilter.h"
#include "itkRescaleIntensityImageFilter.h"
#include "itkSubtractImageFilter.h"
#include "itkPNGImageIOFactory.h"
// 实现命令观察者类,用于监控配准过程
#include "itkCommand.h"
class CommandIterationUpdate : public itk::Command
{
public:
// ITK智能指针相关定义
using Self = CommandIterationUpdate;
using Superclass = itk::Command;
using Pointer = itk::SmartPointer<Self>;
itkNewMacro(Self);
protected:
CommandIterationUpdate() = default;
public:
// 优化器类型定义
using OptimizerType = itk::RegularStepGradientDescentOptimizerv4<double>;
using OptimizerPointer = const OptimizerType*;
// 执行函数,用于处理事件
void Execute(itk::Object* caller, const itk::EventObject& event) override
{
Execute((const itk::Object*)caller, event);
}
void Execute(const itk::Object* object, const itk::EventObject& event) override
{
// 检查事件类型是否为迭代事件
auto optimizer = static_cast<OptimizerPointer>(object);
if (!itk::IterationEvent().CheckEvent(&event))
{
return;
}
// 输出当前迭代信息:迭代次数、度量值、当前位置参数
std::cout << optimizer->GetCurrentIteration() << " ";
std::cout << optimizer->GetValue() << " ";
std::cout << optimizer->GetCurrentPosition() << std::endl;
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
// 固定输入输出文件名(使用固定字符串而非命令行参数)
const char* fixedImageFile = "ExampleData\\BrainProtonDensitySliceBorder20.png";
const char* movingImageFile = "ExampleData\\BrainProtonDensitySliceR10X13Y17.png";
const char* outputImageFile = "Output\\ImageRegistration6Output.png";
const char* differenceBeforeFile = "Output\\ImageRegistration6DifferenceBefore.png";
const char* differenceAfterFile = "Output\\ImageRegistration6DifferenceAfter.png";
const int defaultPixelValue = 100; // 重采样时的默认像素值
// 注册PNG图像IO工厂,确保能正确读写PNG文件
itk::PNGImageIOFactory::RegisterOneFactory();
// 定义图像维度和像素类型
constexpr unsigned int Dimension = 2;
using PixelType = float;
// 定义固定图像和移动图像类型
using FixedImageType = itk::Image<PixelType, Dimension>;
using MovingImageType = itk::Image<PixelType, Dimension>;
// 定义变换类型:2D欧拉变换(包含旋转和平移)
using TransformType = itk::Euler2DTransform<double>;
// 定义优化器、度量和配准方法类型
using OptimizerType = itk::RegularStepGradientDescentOptimizerv4<double>;
using MetricType = itk::MeanSquaresImageToImageMetricv4<FixedImageType, MovingImageType>;
using RegistrationType = itk::ImageRegistrationMethodv4<FixedImageType, MovingImageType>;
// 创建各组件实例
auto metric = MetricType::New();
auto optimizer = OptimizerType::New();
auto registration = RegistrationType::New();
// 为配准方法设置度量和优化器
registration->SetMetric(metric);
registration->SetOptimizer(optimizer);
// 创建变换对象
auto transform = TransformType::New();
// 定义图像读取器类型并创建实例
using FixedImageReaderType = itk::ImageFileReader<FixedImageType>;
using MovingImageReaderType = itk::ImageFileReader<MovingImageType>;
auto fixedImageReader = FixedImageReaderType::New();
auto movingImageReader = MovingImageReaderType::New();
// 设置读取器的文件名
fixedImageReader->SetFileName(fixedImageFile);
movingImageReader->SetFileName(movingImageFile);
// 为配准方法设置固定图像和移动图像
registration->SetFixedImage(fixedImageReader->GetOutput());
registration->SetMovingImage(movingImageReader->GetOutput());
// 定义并创建中心变换初始化器
using TransformInitializerType = itk::CenteredTransformInitializer<TransformType, FixedImageType, MovingImageType>;
auto initializer = TransformInitializerType::New();
// 为初始化器设置变换和图像
initializer->SetTransform(transform);
initializer->SetFixedImage(fixedImageReader->GetOutput());
initializer->SetMovingImage(movingImageReader->GetOutput());
// 设置使用质心模式计算初始变换参数
initializer->MomentsOn();
// 执行变换初始化
initializer->InitializeTransform();
// 初始化旋转角度为0
transform->SetAngle(0.0);
// 将初始化后的变换设置为配准的初始变换
registration->SetInitialTransform(transform);
registration->InPlaceOn();
// 设置优化器的参数缩放因子
using OptimizerScalesType = OptimizerType::ScalesType;
OptimizerScalesType optimizerScales(transform->GetNumberOfParameters());
const double translationScale = 1.0 / 1000.0; // 平移参数的缩放因子
optimizerScales[0] = 1.0; // 旋转角度的缩放因子
optimizerScales[1] = translationScale; // X平移的缩放因子
optimizerScales[2] = translationScale; // Y平移的缩放因子
optimizer->SetScales(optimizerScales);
// 设置优化器参数
optimizer->SetLearningRate(0.1); // 学习率
optimizer->SetMinimumStepLength(0.001); // 最小步长
optimizer->SetNumberOfIterations(200); // 最大迭代次数
// 创建并注册迭代观察者,用于监控配准过程
auto observer = CommandIterationUpdate::New();
optimizer->AddObserver(itk::IterationEvent(), observer);
// 配置单级配准
constexpr unsigned int numberOfLevels = 1;
RegistrationType::ShrinkFactorsArrayType shrinkFactorsPerLevel;
shrinkFactorsPerLevel.SetSize(1);
shrinkFactorsPerLevel[0] = 1; // 收缩因子(1表示不收缩)
RegistrationType::SmoothingSigmasArrayType smoothingSigmasPerLevel;
smoothingSigmasPerLevel.SetSize(1);
smoothingSigmasPerLevel[0] = 0; // 平滑系数(0表示不平滑)
registration->SetNumberOfLevels(numberOfLevels);
registration->SetSmoothingSigmasPerLevel(smoothingSigmasPerLevel);
registration->SetShrinkFactorsPerLevel(shrinkFactorsPerLevel);
// 执行配准过程
try
{
registration->Update();
std::cout << "优化器停止条件: "
<< registration->GetOptimizer()->GetStopConditionDescription()
<< std::endl;
}
catch (const itk::ExceptionObject& err)
{
std::cerr << "捕获到异常!" << std::endl;
std::cerr << err << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// 获取最终配准参数
TransformType::ParametersType finalParameters = transform->GetParameters();
const double finalAngle = finalParameters[0];
const double finalTranslationX = finalParameters[1];
const double finalTranslationY = finalParameters[2];
// 获取旋转中心
const double rotationCenterX = registration->GetOutput()->Get()->GetFixedParameters()[0];
const double rotationCenterY = registration->GetOutput()->Get()->GetFixedParameters()[1];
// 获取迭代次数和最佳度量值
const unsigned int numberOfIterations = optimizer->GetCurrentIteration();
const double bestValue = optimizer->GetValue();
// 打印配准结果
const double finalAngleInDegrees = finalAngle * 180.0 / itk::Math::pi;
std::cout << "结果 = " << std::endl;
std::cout << " 旋转角度 (弧度) = " << finalAngle << std::endl;
std::cout << " 旋转角度 (度) = " << finalAngleInDegrees << std::endl;
std::cout << " X方向平移 = " << finalTranslationX << std::endl;
std::cout << " Y方向平移 = " << finalTranslationY << std::endl;
std::cout << " 旋转中心 X = " << rotationCenterX << std::endl;
std::cout << " 旋转中心 Y = " << rotationCenterY << std::endl;
std::cout << " 迭代次数 = " << numberOfIterations << std::endl;
std::cout << " 度量值 = " << bestValue << std::endl;
// 打印变换矩阵和偏移量
TransformType::MatrixType matrix = transform->GetMatrix();
TransformType::OffsetType offset = transform->GetOffset();
std::cout << "变换矩阵 = " << std::endl << matrix << std::endl;
std::cout << "偏移量 = " << std::endl << offset << std::endl;
// 重采样移动图像到固定图像空间
using ResampleFilterType = itk::ResampleImageFilter<MovingImageType, FixedImageType>;
auto resample = ResampleFilterType::New();
resample->SetTransform(transform);
resample->SetInput(movingImageReader->GetOutput());
FixedImageType::Pointer fixedImage = fixedImageReader->GetOutput();
resample->SetSize(fixedImage->GetLargestPossibleRegion().GetSize());
resample->SetOutputOrigin(fixedImage->GetOrigin());
resample->SetOutputSpacing(fixedImage->GetSpacing());
resample->SetOutputDirection(fixedImage->GetDirection());
resample->SetDefaultPixelValue(defaultPixelValue);
// 定义输出图像类型和转换滤波器
using OutputPixelType = unsigned char;
using OutputImageType = itk::Image<OutputPixelType, Dimension>;
using CastFilterType = itk::CastImageFilter<FixedImageType, OutputImageType>;
using WriterType = itk::ImageFileWriter<OutputImageType>;
auto writer = WriterType::New();
auto caster = CastFilterType::New();
// 写入配准结果图像
writer->SetFileName(outputImageFile);
caster->SetInput(resample->GetOutput());
writer->SetInput(caster->GetOutput());
writer->Update();
// 计算并写入差异图像
using DifferenceImageType = itk::Image<float, Dimension>;
using DifferenceFilterType = itk::SubtractImageFilter<
FixedImageType, FixedImageType, DifferenceImageType>;
auto difference = DifferenceFilterType::New();
// 定义强度重缩放滤波器,将差异图像映射到0-255范围
using RescalerType = itk::RescaleIntensityImageFilter<
DifferenceImageType, OutputImageType>;
auto intensityRescaler = RescalerType::New();
intensityRescaler->SetOutputMinimum(0);
intensityRescaler->SetOutputMaximum(255);
difference->SetInput1(fixedImageReader->GetOutput());
difference->SetInput2(resample->GetOutput());
resample->SetDefaultPixelValue(1);
intensityRescaler->SetInput(difference->GetOutput());
auto writer2 = WriterType::New();
writer2->SetInput(intensityRescaler->GetOutput());
try
{
// 写入配准后的差异图像
writer2->SetFileName(differenceAfterFile);
writer2->Update();
// 写入配准前的差异图像(使用恒等变换)
auto identityTransform = TransformType::New();
identityTransform->SetIdentity();
resample->SetTransform(identityTransform);
writer2->SetFileName(differenceBeforeFile);
writer2->Update();
}
catch (const itk::ExceptionObject& excp)
{
std::cerr << "写入差异图像时出错" << std::endl;
std::cerr << excp << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}测试效果
官方给定的浮动图像在 X 轴方向偏移了 13 像素,Y 轴方向偏移了 17 像素,并旋转了10度,理想情况下配准结果应该接近这三个值。在实际运行中,优化器会找到最优的变换参数,输出类似如下的结果:
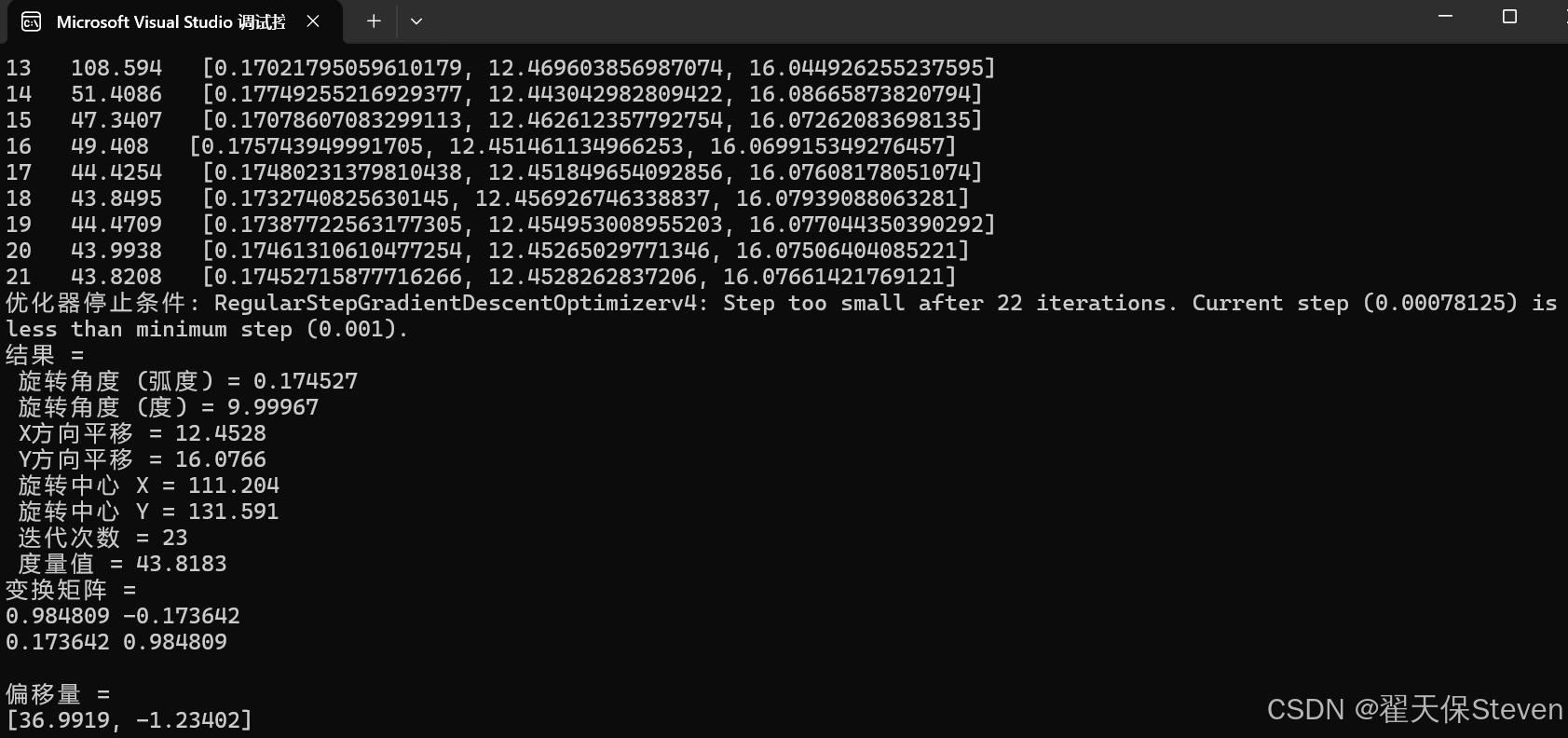
从结果可以看出,配准得到的平移量非常接近真实偏移量,说明配准算法成功地找到了最优变换参数。但也能看出仍存在一定位移偏差,官方也给出了解释,因为配准示例中采用了质心对齐的方法,而人为创造偏差时并不是这样处理的,所以整体的平移会有偏差。
过程图像如下:
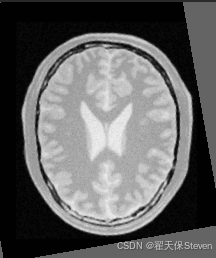
配准后图像
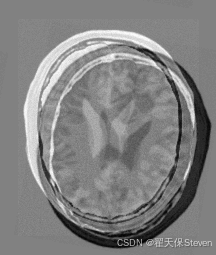
配准前两图差值

配准后两图差值
如果文章帮助到你了,可以点个赞让我知道,我会很快乐~加油!
