目录
[deque 双端队列](#deque 双端队列)
[priority_queue 优先级队列](#priority_queue 优先级队列)
stack、queue是容器适配器,库里给的默认适配容器是deque
没有迭代器,不支持随便遍历
广度优先遍历要用queue
stack

模板不一定是普通类型,也可能是容器
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
void test_stack_queue()
{
stack<int> st;
st.push(1);
st.push(2);
st.push(3);
st.push(4);
while (!st.empty())
{
cout << st.top() << " ";
st.pop();
}
cout << endl; // 4 3 2 1
queue<int> q;
q.push(1);
q.push(2);
q.push(3);
q.push(4);
while (!q.empty())
{
cout << q.front() << " ";
q.pop();
}
cout << endl; // 1 2 3 4
deque<int> dq;
dq.push_back(1);
dq.push_back(2);
dq.push_back(3);
dq.push_back(4);
dq.push_back(5);
dq.push_back(6);
for (size_t i = 0; i < dq.size(); i++)
{
cout << dq[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl; // 1 2 3 4 5 6
}模拟实现
不用写默认成员函数,因为_con是自定义类型的容器,已经实现好了
我们不写,编译器会自动调用 这个容器的构造、析构、拷贝构造、赋值
stack.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include<vector>
#include<list>
namespace qtw
{
// 容器适配器
//template<class T, class Container = vector<T>>
template<class T, class Container = deque<T>>
class stack
{
public:
void push(const T& x)
{
_con.push_back(x);
}
void pop()
{
_con.pop_back();
}
T& top()
{
return _con.back();
}
size_t size()
{
return _con.size();
}
bool empty()
{
return _con.empty();
}
private:
Container _con;
};
void test_stack()
{
//stack<int, vector<int>> st1;
stack<int> st1;
st1.push(1);
st1.push(2);
st1.push(3);
st1.push(4);
while (!st1.empty())
{
cout << st1.top() << " ";
st1.pop();
}
cout << endl;
stack<int, list<int>> st2;
st2.push(1);
st2.push(2);
st2.push(3);
st2.push(4);
while (!st2.empty())
{
cout << st2.top() << " ";
st2.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
}queue

模拟实现
queue.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include<vector>
#include<list>
namespace qtw
{
// 容器适配器
//template<class T, class Container = list<T>>
template<class T, class Container = deque<T>>
class queue
{
public:
void push(const T& x)
{
_con.push_back(x);
}
void pop()
{
_con.pop_front();
//_con.erase(_con.begin());
}
T& front()
{
return _con.front();
}
T& back()
{
return _con.back();
}
size_t size()
{
return _con.size();
}
bool empty()
{
return _con.empty();
}
private:
Container _con;
};
void test_queue()
{
queue<int, list<int>> q;
//queue<int, vector<int>> q;
//这样写报错,vector没有提供pop_front
//所以上面有_con.erase(_con.begin());
q.push(1);
q.push(2);
q.push(3);
q.push(4);
while (!q.empty())
{
cout << q.front() << " ";
q.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
}deque 双端队列
deque 双端队列(严格来说不是队列)。双向开口,两边都可以插入、删除数据的容器。随机迭代器
vector :
优点:下标随机访问、排序
缺点:扩容、头部、中间插入删除
list:
优点:按需申请、任意位置插入删除
缺点:不支持下标随机访问
deque:库里支持了头尾插删、下标随机访问,是不是完美了呢?不是!
排序消耗的时间,deque拷贝到vector排序再拷贝到deque(拷贝这一下消耗很小) 比 deque对象调用算法sort 快
算法sort要大量下标访问数据,肯定是 deque 的下标访问没那么快。
看看deque的底层:
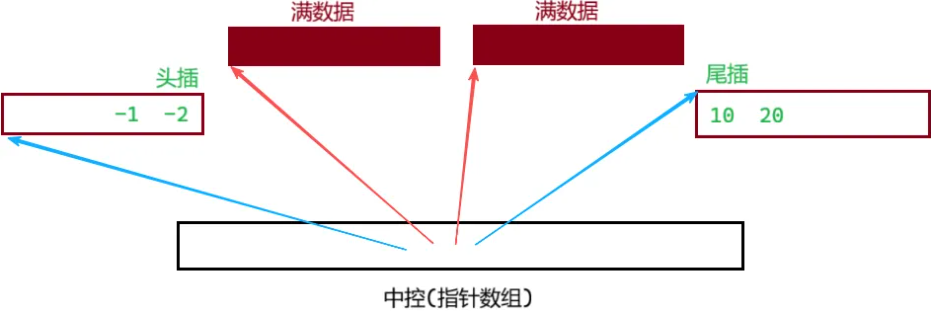
中控指针数组满了,像 vector 一样扩容+拷贝数据即可
相比 vector:deque 极大缓解了扩容、头删插问题。但[ ]不够极致,要计算在哪个 buff,在这个 buff 的第几个
cpp
operator[](size_t i) // 假设是有效地址
{
1.先看在不在第一个buff数组,在就找位置访问
2.不在第一个buff,i -= 第一个buff数组的size
第几个buff = i/buffsize(每个buff数组的size是固定的)
在这个buff的第几个 = i%=buffersize
}相比 list :
deque支持下标随机访问
CPU高速缓存效率不错,不用频繁申请小量内存
deque头尾删插不错,但中间插入删除很拉胯
总结:deque不适合高频下标随机访问,所以用的不多。但高频的头尾删插 deque 很合适
所以 deque 适配 stack 和 queue 很合适
priority_queue 优先级队列
要给头文件**#include <queue>**
也是容器适配器,默认适配容器是 vector。没有提供迭代器,不支持遍历
不是先进先出的队列,是按优先级出的。默认是大的优先级高
给仿函数 Compare 可以自己控制 大/小 谁的优先级高
底层:堆**。做 Top-k 不用写堆,直接用 priority_queue**
数组中最大的第K个元素:https://leetcode.cn/problems/kth-largest-element-in-an-array/
cpp
void test_priority_queue()
{
// 默认是大堆 -- less
priority_queue<int> pq;
// 5 4 3 1
// 仿函数控制实现小堆
//priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> pq;
// 1 3 4 5
pq.push(3);
pq.push(5);
pq.push(1);
pq.push(4);
while (!pq.empty())
{
cout << pq.top() << " ";
pq.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}less 是小于的比较,实现的大堆
greater 是小堆
模拟实现
这样就写死了。只能是大堆
priority_queue.h
cpp
namespace qtw
{
template <class T, class Container = vector<T>>
class priority_queue
{
private:
void AdjustDown(int parent)
{
size_t child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < _con.size())
{
if (child + 1 < _con.size() && _con[child + 1] > _con[child])
{
child++;
}
if (_con[child] > _con[parent])
{
swap(_con[child], _con[parent]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void AdjustUp(int child)
{
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if (_con[parent] < _con[child])
{
swap(_con[parent], _con[child]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
public:
priority_queue()
{ }
template <class InputIterator>
priority_queue(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
{
while (first != last)
{
_con.push_back(*first);
first++;
}
for (int i = (_con.size() - 2) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
AdjustDown(i);
}
}
bool empty()
{
return _con.empty();
}
size_t size()
{
return _con.size();
}
const T& top()
{
return _con[0];
}
void push(const T& x)
{
_con.push_back(x);
AdjustUp(_con.size() - 1);
}
void pop()
{
swap(_con[0], _con[_con.size() - 1]);
_con.pop_back();
AdjustDown(0);
}
private:
Container _con;
};
void test_priority_queue1()
{
priority_queue<int> pq;
pq.push(3);
pq.push(5);
pq.push(1);
pq.push(4);
while (!pq.empty())
{
cout << pq.top() << " ";
pq.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
}优化
(先看仿函数第一个分割线以上的部分)
只是向上、向下调整变了
priority_queue.h
cpp
namespace qtw
{
template <class T, class Container = vector<T>, class Compare = less<T>>
class priority_queue
{
private:
void AdjustDown(int parent)
{
Compare com;
size_t child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < _con.size())
{
//if (child + 1 < _con.size() && _con[child] < _con[child + 1])
if (child + 1 < _con.size() && com(_con[child], _con[child + 1]))
{
child++;
}
if (com(_con[parent], _con[child]))
{
swap(_con[child], _con[parent]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void AdjustUp(int child)
{
Compare com;
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if (com(_con[parent], _con[child]))
{
swap(_con[parent], _con[child]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
// 省略了一些代码
};
void test_priority_queue1()
{
priority_queue<int> pq;
// 大堆
pq.push(3);
pq.push(5);
pq.push(1);
pq.push(4);
while (!pq.empty())
{
cout << pq.top() << " ";
pq.pop();
}
cout << endl; // 5 4 3 1
}
void test_priority_queue2()
{
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> pq;
// 小堆
pq.push(3);
pq.push(5);
pq.push(1);
pq.push(4);
while (!pq.empty())
{
cout << pq.top() << " ";
pq.pop();
}
cout << endl; // 1 3 4 5
}
}仿函数
就是重载了 operator( ) 的普通类
意义:1. 用库里的控制大堆小堆 2. 如果类型不符合我们的比较意愿,可以控制它
cpp
// 仿函数/函数对象
class Less // 防止和库里的less冲突
{
public:
bool operator()(int x, int y)
{
return x < y;
}
};
int main()
{
Less lessfunc;
cout << lessfunc(1, 2) << endl; // 1
cout << lessfunc.operator()(1, 2) << endl; // 1
return 0;
}只看第14行,会觉得lessfunc是函数名
仿函数的真正意义:类对象可以像函数一样使用
库里面把它写成了类模板, 可以支持更多类型。前提:这个类型支持了 < 的比较
cpp
// 仿函数/函数对象
template <class T>
class Less // 防止和库里的less冲突
{
public:
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x < y;
}
};
int main()
{
Less<int> lessfunc;
cout << lessfunc(1, 2) << endl;
cout << lessfunc.operator()(1, 2) << endl;
return 0;
}如果是日期类呢?我们重载了日期类的 < >,不会报错
cpp
namespace qtw
{
template <class T, class Container = vector<T>, class Compare = less<T>>
class priority_queue
{ };
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
: _year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{ }
bool operator<(const Date& d)const
{
return (_year < d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month < d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day);
}
bool operator>(const Date& d)const
{
return (_year > d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month > d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day);
}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d);
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d)
{
_cout << d._year << "-" << d._month << "-" << d._day;
return _cout;
}
void test_priority_queue3()
{
priority_queue<Date> pq;
pq.push(Date(2015, 9, 3));
pq.push(Date(2019, 10, 1));
pq.push(Date(1949, 10, 1));
while (!pq.empty())
{
cout << pq.top() << " ";
pq.pop();
}
cout << endl; // 2019-10-1 2015-9-3 1949-10-1
}
void test_priority_queue4()
{
priority_queue<Date, vector<Date>, greater<Date>> pq;
pq.push(Date(2015, 9, 3));
pq.push(Date(2019, 10, 1));
pq.push(Date(1949, 10, 1));
while (!pq.empty())
{
cout << pq.top() << " ";
pq.pop();
}
cout << endl; // 1949-10-1 2015-9-3 2019-10-1
}
}有些情况要自己写仿函数
eg:优先级队列里存节点的指针
cpp
void test_priority_queue5()
{
priority_queue<Date*> pq;
pq.push(new Date(2015, 9, 3));
pq.push(new Date(2019, 10, 1));
pq.push(new Date(1949, 10, 1));
while (!pq.empty())
{
cout << *pq.top() << " ";
pq.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}每次结果都不一样,为什么?
默认按类型比较排序,类型是指针,就按指针比,且 new 出的地址大小不定
Date* 是内置类型,不能重载运算符
cpp
struct LessPDate // 仿函数控制比较规则
{
bool operator()(const Date* p1, const Date* p2)
{
return *p1 < *p2;
}
};
void test_priority_queue6()
{
priority_queue<Date*, vector<Date*>, LessPDate> pq;
pq.push(new Date(2015, 9, 3));
pq.push(new Date(2019, 10, 1));
pq.push(new Date(1949, 10, 1));
while (!pq.empty())
{
cout << *pq.top() << " ";
pq.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}本篇的分享就到这里了,感谢观看 ,如果对你有帮助,别忘了点赞+收藏+关注 。
小编会以自己学习过程中遇到的问题为素材,持续为您推送文章