目录
[* type列](#* type列)
[* Extra 列](#* Extra 列)
[* Using temporary](#* Using temporary)
[Using filesort](#Using filesort)
[Using where](#Using where)
[Using index](#Using index)
MySQL的优化涉及多个级别的配置、调优和性能评估。根据职位(开发人员或DBA),可以在单个 SQL语句、整个应用程序、单个数据库服务器或多个联网数据库服务器的级别进行优化;
别影响性能的重要因素:表结构、查询语句和数据库配置。
软件级别的因素会导致硬件级别的CPU和I/O操作。在优化数据库性能时,首先要学习软件级别的规则,但在真实的企业中,通常数据库遇到瓶颈 首先考虑换⼀个高性能的存储设置,比如把机械硬盘换成SSD,再考虑软件层面,最后考虑操作系 统层面的优化;
这里只讨论索引级别的优化;本文将介绍一些性能分析的方法;
压力测试工具
使用MySQL自带的压测工具(mysqlslap)模拟多个客户端同时查询,观察测试结果:
bash
# 使用主键查询 查询100w次
mysqlslap -uroot -proot123 \
--concurrency=100 \
--iterations=100 \
--create-schema="test" \
--engine="innodb" \
--number-of-queries=10000 \
--query="SELECT id, sn, name, mail, age, gender, class_id FROM test.index_demo WHERE id = 1020000"
mysqlslap: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
Benchmark
Running for engine innodb
Average number of seconds to run all queries: 0.257 seconds
Minimum number of seconds to run all queries: 0.169 seconds
Maximum number of seconds to run all queries: 0.345 seconds
Number of clients running queries: 100
Average number of queries per client: 100
# 使⽤⾮索引列查询 查询300次
mysqlslap -uroot -proot123 --concurrency=30 --iterations=3 --create-schema="test" --engine="innodb" --number-of-queries=100 --query="SELECT id, sn, name, mail, age, gender, class_id FROM test.index_demo WHERE sn = '1020000';"
mysqlslap: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
Benchmark
Running for engine innodb
Average number of seconds to run all queries: 3.982 seconds
Minimum number of seconds to run all queries: 3.956 seconds
Maximum number of seconds to run all queries: 3.997 seconds
Number of clients running queries: 30
Average number of queries per client: 3命令参数解析:
基本连接选项
-
-uroot:使用 root 用户连接 MySQL -
-proot123:使用密码 "root123"
性能测试核心参数
-
--concurrency=100:模拟 100个并发客户端 同时连接数据库。这个值越高,测试压力越大。 -
--iterations=100:整个测试将 重复执行100次,用于获取更稳定的平均性能数据。 -
--create-schema="test":测试将在名为 "test" 的数据库中执行(如果数据库不存在会自动创建) -
--engine="innodb":指定使用 InnoDB 存储引擎 进行测试(如果表已存在,会临时改为使用InnoDB) -
--number-of-queries=10000:整个测试期间将 总共执行10000次查询(所有客户端总查询数,比如:示例中100个客户端一轮总共需要执行1w次,执行100轮)
测试查询定义
-
--query="SELECT id, sn, name, mail, age, gender, class_id FROM test.index_demo WHERE id = 1020000"要测试的SQL查询语句:从test数据库的index_demo表中查询id=1020000的记录;
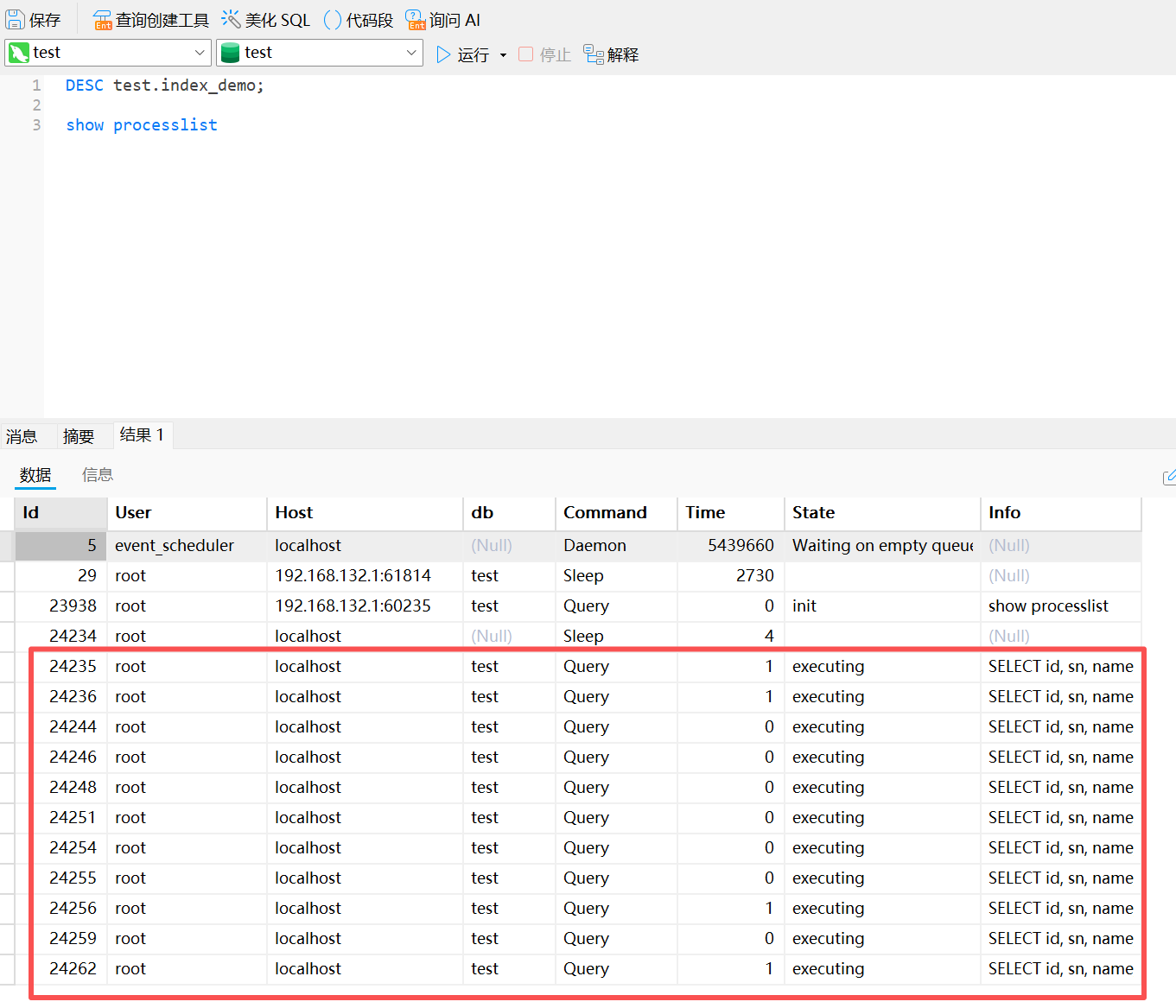
使用 show processlist 命令查看正在运行的线程:
SQL语句性能分析
在执行 SELECT , DELETE , INSERT , REPLACE ,和 UPDATE 之前都可以用执行计划分析SQL语句的执行情况,以便优化SQL语句。
注意:并不会真正的执行SQL,只是对SQL进行分析,最终返回一个分析结果
bash
# 索引列
mysql> EXPLAIN select id, sn, name, mail, age, gender, class_id from index_demo where id = 1020000\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1 # SELECT标识符,表示查询序列号,如果使用子查询或联表查询就会查到多个执行计划id也会递增;
select_type: SIMPLE # 查询类型,简单查询(无子查询/UNION)
table: index_demo # 查询的表名
partitions: NULL # 查询涉及的分区(未分区则为NULL)
type: const # 连接类型,const表示通过主键/唯一索引查找
possible_keys: PRIMARY # 可能使用的索引(此处显示主键索引可用)
key: PRIMARY # 实际使用的索引(最终选择主键索引)
key_len: 8 # 使用的索引长度(字节)
ref: const # 与索引比较的列/常量
rows: 1 # 预估需要检查的行数
filtered: 100.00 # 按条件过滤后剩余行的百分比
Extra: NULL # 附加执行信息
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
# 非索引列
mysql> EXPLAIN select id, sn, name, mail, age, gender, class_id from index_demo where sn = '1020000'\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: index_demo
partitions: NULL
type: ALL
possible_keys: NULL
key: NULL
key_len: NULL
ref: NULL
rows: 993231
filtered: 10.00
Extra: Using where
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)在性能分析时主要关注以下字段:
bash
# 使用非索引列
type: ALL # 全表扫描
key: NULL # 未用索引
rows: 100000 # 扫描10万行
Extra: Using where # 存储引擎层未过滤
# 使用索引列
type: const # 主键精准定位
key: PRIMARY # 使用主键
rows: 1 # 扫描1行
Extra: NULL # 无额外操作分析上边两个查询语句,第一个查询:实际用到的索引是主键索引,索引长度为8字节,索引比较的列是常量,估算要检查的行数为1行,按条件筛选率是100%;
第二个查询:没有用到索引,估算要检查的行数为993231行,按条件筛选率仅为10%;
select_type
|---------------|------------------------|
| select_type 值 | 说明 |
| SIMPLE | 简单SELECT(不使用UNION或子查询) |
| PRIMARY | 外层查询 |
| UNION | UNION中的第⼆个及之后的SELECT语句 |
| UNION RESULT | UNION的结果。 |
| SUBQUERY | 子查询中 |
| INSERT | INSERT 语句 |
| UPDATE | UPDATE 语句 |
| DELETE | DELETE 语句 |
测试语句:
bash
explain select * from student where id = (select id from student1 where name = '宋江')\G
explain select * from student union select * from student1\G* type列
性能排序与说明
EXPLAIN输出的type列描述了表是如何连接的,性能从最高往低依次降低;
| 类型 | 名称 | 触发场景 | 性能 | 优化建议 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| system | 系统表 | 查询系统表或只有1行的表 | ★★★★★ | 无需优化 |
| const | 常量 | 用主键/唯一索引精确匹配 (WHERE id = 1) |
★★★★★ | 理想状态 |
| eq_ref | 等值引用 | JOIN时用主键/唯一索引关联 (A.id = B.id) |
★★★★☆ | 检查JOIN字段索引 |
| ref | 普通索引 | 用非唯一索引查找 (WHERE age = 20) |
★★★☆☆ | 确保索引选择性高 |
| fulltext | 全文索引 | 使用全文索引搜索 | ★★★☆☆ | 优化MATCH条件 |
| ref_or_null | 含NULL的索引 | 索引查询包含NULL值 (WHERE age = 20 OR age IS NULL) |
★★☆☆☆ | 避免字段允许NULL |
| index_merge | 索引合并 | 合并多个索引的结果 (WHERE a=1 OR b=2) |
★★☆☆☆ | 改用复合索引 |
| unique_subquery | 唯一子查询 | 子查询使用主键 (WHERE id IN (SELECT...)) |
★★☆☆☆ | 改写成JOIN |
| index_subquery | 索引子查询 | 子查询使用普通索引 | ★★☆☆☆ | 改写成JOIN |
| range | 范围扫描 | 索引范围查询 (WHERE id > 100) |
★☆☆☆☆ | 控制范围数据量 |
| index | 全索引扫描 | 遍历整个索引树 (SELECT indexed_col FROM table) |
☆☆☆☆☆ | 避免SELECT无覆盖索引 |
| ALL | 全表扫描 | 无索引可用 | ⚠️最差 | 必须加索引 |
-
system:查询系统表或只有1行的表;
-
const:用主键/唯一索引精确匹配 (WHERE id = 1),结果最多有⼀个匹配的行,类型显示 为 const ,这种类型查询性能极高,且只会返回一行数据;
-
eq_ref:应⽤于多表连接的场景,表关联条件是主键索引或唯一非空索引时使⽤等号 ( = ) 进行索引列的比较,每行只匹配⼀条记录
sql
select * from student s, account a where s.id = a.id;- ref:使用了普通索引,返回的结果可能是多行组成的结果集(
WHERE age = 20) - fulltext:使用全文索引搜索
- ref_or_null:索引查询包含NULL值(
WHERE age = 20 OR age IS NULL) - index_merge:在查询中使用了多个索引,OR 两边必须是单独索引,最终通过不同索引检索数据,然后对结果集进行合并,Key_len显示最长的索引长度。
sql
select * from index_demo where name = 'user_1020021' or id = 1030300\G
-- name 和 id 都是单独的索引列- unique_subquery:子查询使用主键(
WHERE id IN (SELECT...))
sql
-- ⼦查询中返回的是外层表的主键索引或唯⼀索引
value IN (SELECT primary_key FROM single_table WHERE some_expr)- index_subquery:类似于unique_subquery,只不过子查询中返回的是普通索引列;
- range:使用索引列进行范围查询,当使用<>、>、>=、<、<=、is NULL、<=>、BETWEEN、LIKE或IN()操作符,索引列与常量进行较时为range;
- index:扫描整个索引树而不扫描整个表,比如只使用索引排序而不使用条件查询时:
sql
select * from index_demo order by sn limit 10\G- ALL:最差的情况,表示MySQL必须对全表进行逐行扫描才可以以找到匹配行;
针对这些type类型,在全文索引(fulltext)性能之下的其实都可以根据业务进行调整优化,尽可能的使用索引;特别需要避免的就是全表扫描;
* Extra 列
Extra 列中如果出现 Using filesort 和 Using temporary ,将会对查询效率有比较严重的影响;
Using filesort:使用文件排序,该场景必须要进行优化;
Using temporary:使用临时表排序,临时表所占用的是内存中的一片区域,当内存占满之后,就需要申请临时文件此时发生磁盘IO;
* Using temporary
当使用非索引列进行分组时,会用临时表进行排序,优化时可以考虑为分组的列加索引;
sql
mysql> explain select avg(age) from index_demo group by gender\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: index_demo
partitions: NULL
type: ALL
possible_keys: NULL
key: NULL
key_len: NULL
ref: NULL
rows: 993231
filtered: 100.00
Extra: Using temporary
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.01 sec)
-- 使用索引列,减少内存的使用
mysql> explain select avg(age) from index_demo group by class_id\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: index_demo
partitions: NULL
type: index
possible_keys: class_id
key: class_id
key_len: 8
ref: NULL
rows: 993231
filtered: 100.00
Extra: NULL
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)Using filesort
当使用非索引列进行排序时会用到文件内排序,优化时可以考虑为排序的列加索引;
sql
mysql> explain select * from index_demo where id < 1020000 order by age limit 10\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: index_demo
partitions: NULL
type: range
possible_keys: PRIMARY
key: PRIMARY
key_len: 8
ref: NULL
rows: 496615
filtered: 100.00
Extra: Using where; Using filesort -- 使用了文件内排序,进行了磁盘IO
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> explain select * from index_demo where id < 1020000 order by class_id limit 10\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: index_demo
partitions: NULL
type: index
possible_keys: PRIMARY
key: class_id
key_len: 8
ref: NULL
rows: 20
filtered: 50.00
Extra: Using where
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)Using where
使用了非索引列进行检索数据,且进行了全表扫描;
sql
-- gender 非索引列
explain select * from index_demo where gender = 1\G当使用索引列进行检索数据时,行范围查找,此时扫描的是索引树,也显示的是 Using where;
sql
mysql> explain select * from index_demo where id < 102000\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: index_demo
partitions: NULL
type: range
possible_keys: PRIMARY
key: PRIMARY
key_len: 8
ref: NULL
rows: 3674
filtered: 100.00
Extra: Using where -- 扫描索引树,使用了索引
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)Using index
发生索引覆盖时显示using index,表示这是⼀个高效查询;
主键索引:主键索引的B+树叶子节点中,保存的是完整的数据行;
普通索引:普通索引生成的索引树的叶子节点中,保存的是索引列的值和主键值;
索引覆盖
当查询可以完全通过索引获取所需数据 时,性能会有显著提升;查询的所有字段都包含在某个索引中,引擎无需回表查数据文件。
比如:
sql
-- 创建一个包含 mail, age, class_id 的复合索引
create index idx_mail_age_classId on index_demo(mail, age, class_id);
-- 查询 mail,age,class_id 这三个列,判定条件也是索引中最左前缀列
mysql> explain select mail,age,class_id from index_demo where mail = '1020000@qq.com'\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: index_demo
partitions: NULL
type: ref
possible_keys: idx_mail_age_classId
key: idx_mail_age_classId
key_len: 83
ref: const
rows: 1
filtered: 100.00
Extra: Using index
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)如果新增一个列:
sql
select mail,age,class_id,sn from index_demo where mail = '1020000@qq.com'\G由于sn 不是索引中的列,只能通过索引记录中的主键ID,再到主表中查询所有的数据,最终返回结果集,这个现象叫回表查询;
回表查询
当使用索引检索数据时,查询的列不只包含索引列,这时需要通过索引中记录的主键值到主表中进行查询,这个现象叫做回表查询;
sql
mysql> explain select * from index_demo where mail = '1020000@qq.com'\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: index_demo
partitions: NULL
type: ref
possible_keys: idx_mail_age_classId
key: idx_mail_age_classId
key_len: 83
ref: const
rows: 1
filtered: 100.00
Extra: NULL
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)即使使用了复合索引,但也发生了回表查询;回表查询需要额外的磁盘I/O(如果数据页不在缓冲池中),对于高频查询,建议优化为覆盖索引查询;