设计模式-命令模式
命令模式的英文翻译是 Command Design Pattern。它是这么定义的:The command pattern encapsulates a request as an object, thereby letting us parameterize other objects with different requests, queue or log requests, and support undoable operations. 翻译一下就是命令模式将请求(命令)封装为一个对象,这样可以使用不同的请求参数化其他对象(将不同请求依赖注入到其他对象),并且能够支持请求(命令)的排队执行、记录日志、撤销等(附加控制)功能。
案例分析
一般客户只需要把需求提交给公司,公司内有不同的部门,一般这个需求需要公司的某个部门执行,但是客户是不关注这些的,抽象理解其实是客户端(client)不需要关注请求的具体处理者(Receiver)。
首先定义一个命令接口
java
public interface Command {
void execute();
}假设前端传递来的请求可以封装为A和B两大类,A类请求由部门A实现,B类请求由部门B实现
java
public class RequestA implements Command {
private DepartmentA receiver;
public RequestA(DepartmentA receiver) {
this.receiver = receiver;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
receiver.computeRequestA();
}
}
public class RequestB implements Command {
private DepartmentB receiver;
public RequestB(DepartmentB receiver) {
this.receiver = receiver;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
receiver.computeRequestB();
}
}定义部门A和部门B,部门A可以处理A类请求,部门B可以处理B类请求
java
public class DepartmentA {
public void computeRequestA() {
System.out.println("DepartmentA compute RequestA");
}
}
public class DepartmentB {
public void computeRequestB() {
System.out.println("DepartmentB compute RequestB");
}
}其实如果只是为了实现上述功能,其他设计模式也可以达到,但是需要支持命令的排队,延时,就要靠调用者类(invoker)了
java
public class Invoker {
private List<Command> commandList = new ArrayList<>();
public boolean addCommand(Command request) {
return commandList.add(request);
}
public void invoke() {
for (Command command : commandList) {
command.execute();
}
commandList.clear();
}
}Invoker 类中 commandList 存储了所有待执行的命令,因此可以支持撤销、排队等功能
只有在真正调用 invoke() 方法时,命令才真正的被执行,以下是测试代码:
java
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DepartmentA departmentA = new DepartmentA();
DepartmentB departmentB = new DepartmentB();
Command requestA = new RequestA(departmentA);
Command requestB = new RequestB(departmentB);
Invoker invoker = new Invoker();
invoker.addCommand(requestA);
invoker.addCommand(requestB);
invoker.invoke();
}
}上述代码中省略了将前端传递的参数封装为 RequestA 或 RequestB 的实现。
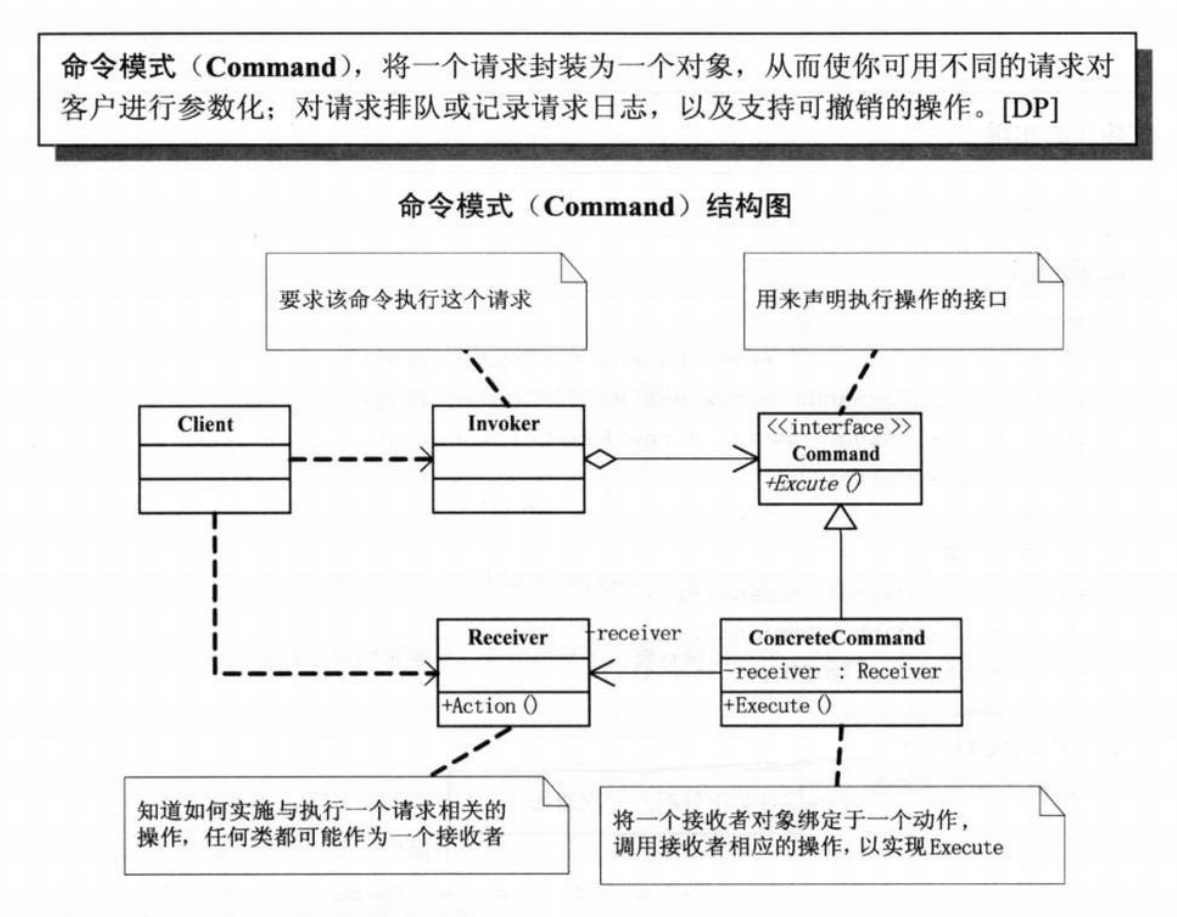
如上图所示,结合本例,Request 对象其实就是 Command 的具体表现类,内部引用了可以处理其需求的执行者 Receiver(Department),最终由 Invoker 调用执行。