文章目录
- SpringMVC
- [Spring IoC详解](#Spring IoC详解)
SpringMVC
应用分层
-
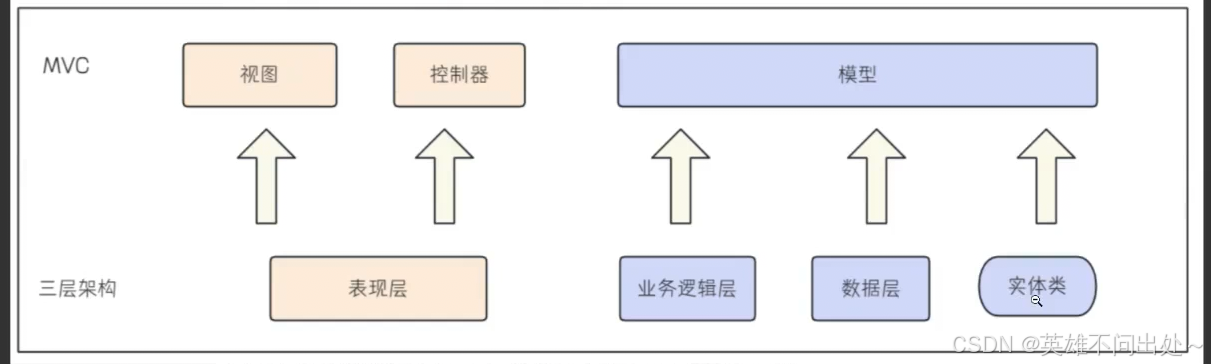
MVC和三层架构之间是什么样的关系?
MVC模式强调数据和视图分离
三层架构是不同维度的数据处理(业务逻辑处理,数据处理,表现层处理数据的校验和数据的返回)
MVC是一种三层架构的实现
三层架构是MVC的一种替代
MVC是一种思想,三层架构是一种实现
-
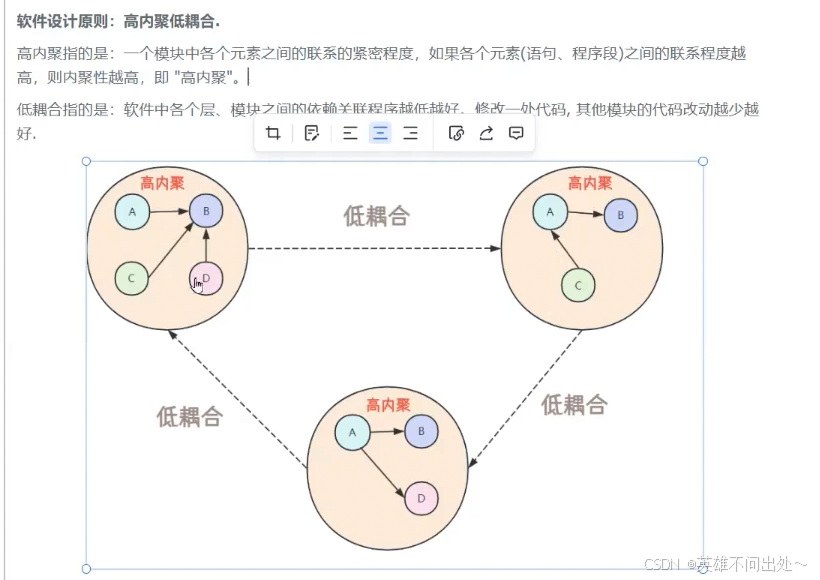
软件的设计原则:高内聚低耦合
高内聚低耦合:指的是一个模块之内是要高内聚的(关系紧密),模块与模块之间是要低耦合的(它们之间的影响不要那么大),比如A要调用B,B改了一个代码,A就跟着改,这就是高耦合
-
MVC和三层架构的共同目的都是为了解耦,分层和代码复用
-
应用分层的好处:

企业的命名规范
- 类名,变量名,数据库中的命名,串形Java中很少用到(在前端中比较常用到)


总结
- SpringBoot和SpringMVC之间的关系?
使用SpringBoot创建SpringMVC框架(SpringMVC是一个web框架)
Spring IoC详解

- Spring是一个包含众多工具的IoC容器
- Spring两大核心思想:
(1) IoC
(2) AOP
这两个是重要的面试题 - 对于Spring是IoC容器的理解:

控制反转的例子:比如一个公司要裁员,公司老板把权力交给了hr,hr就可以进行裁员了
写注解就是为了把控制权交给Spring,让Spring进行对象的管理
- IoC的目的也是为了解耦:
举一个耦合性高的例子:
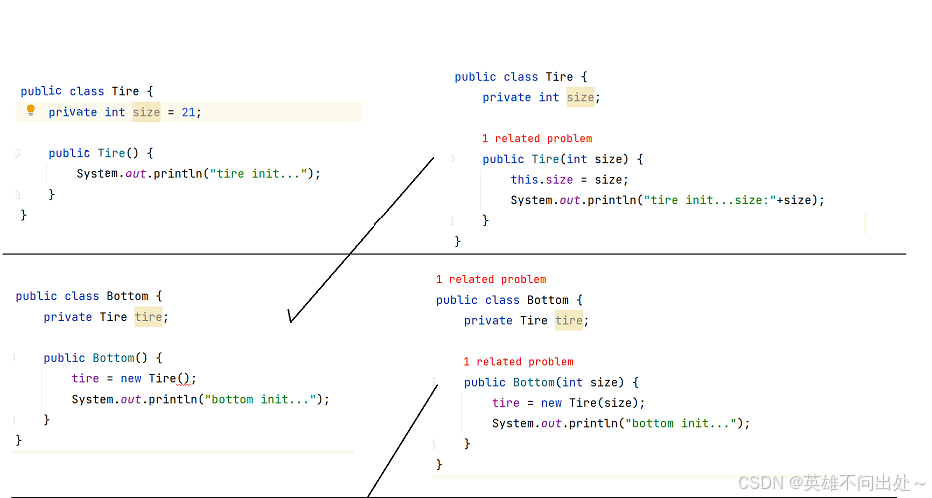
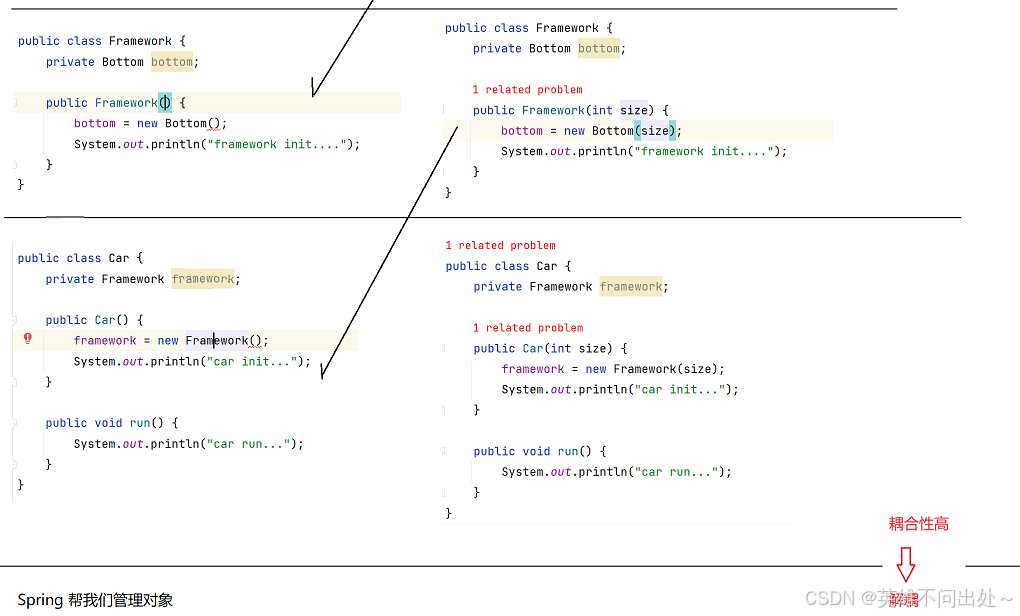
ioc如何进行解耦呢?
全都在Main这个类中,new很多个需要的对象,然后把这些对象传给后面的类使用,后面的类各自封装好这些类,它们之间只需要传这些封装好的类即可,不需传Main中的构造好的属性了
Main
java
package com.example.ioc.demos.ioc.v2;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int size = 19;
String color = "red";
int price = 100;
Tire tire = new Tire(19,color);
Bottom bottom = new Bottom(tire,100);
Framework framework = new Framework(bottom);
Car car = new Car(framework);
car.run();
}
}Car
java
package com.example.ioc.demos.ioc.v2;
public class Car {
private Framework framework;
// 之前是自己去new的,现在不再new了
// 现在是你给我提供一个,我就用你提供给我的这个
public Car(Framework framework){
this.framework = framework;
System.out.println("Car init...");
}
public void run(){
System.out.println("car run...");
}
}Framework
java
package com.example.ioc.demos.ioc.v2;
public class Framework {
private Bottom bottom;
public Framework(Bottom bottom) {
this.bottom = bottom;
System.out.println("Framework init...");
}
}Bottom
java
package com.example.ioc.demos.ioc.v2;
public class Bottom {
private Tire tire;
private int price;
public Bottom(Tire tire,int price) {
this.tire = tire;
this.price = price;
System.out.println("Bottom init..." + ",price: " + price);
}
}Tire
java
package com.example.ioc.demos.ioc.v2;
public class Tire {
private int size;
public String color;
public Tire(int size,String color){
this.size = size;
this.color = color;
System.out.println("tire init..." + size + " + color: " + color);
}
}Spring 帮我们管理对象:
1.告诉Spring,帮我们管理哪些对象(存)
2.知道如何取出来这些对象(取)
DI
- IoC是一种控制反转(把你的权力交给别人来行使,达到你要的结果)的思想,有很多种方式可以实现IoC,这里使用DI来实现IoC

- 什么是依赖注入?
DI是依赖注入,比如第一个类依赖于第二个类,那么可以把第二个类注入到第一个类中
下面这个图,就是依赖注入的具体实现:

总结
- 对上面内容的总结:
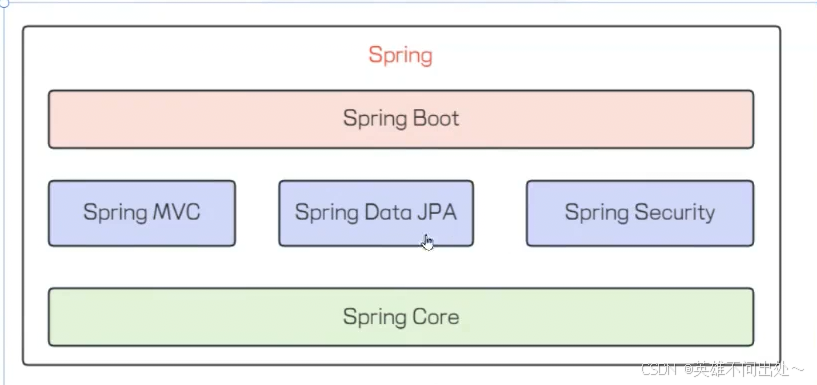
Spring包括了Spring家族
Spring中有Spring Core,Spring Framework等
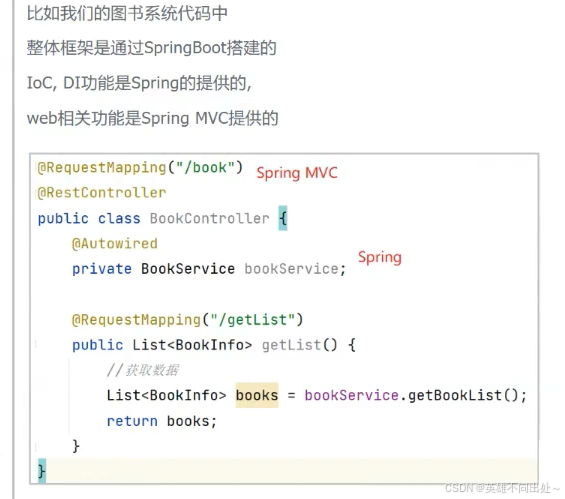
(1) Spring,SpringMVC,SpringBoot区别?
Spring是一个管理对象的容器,Spring是包含众多工具的IoC容器,Spring存的是对象,对象这个词,在Spring的范围内,称为bean
SpringMVC是Spring下的一个web框架,使用SpringBoot可以更加快速的创建Spring
(2) 什么是IoC?
IoC是控制权的反转,将控制权交给别人(控制反转)
优点:
1.解耦 ,使各个模块之间的影响要小
2.对象的资源可以共享
IoC是思想,DI是一种实现方式
IoC:依赖对象的创建的控制权交给Spring来管理(存)
DI:依赖注入,DI就是把依赖对象取出来,并赋给对象的属性(取)
DI就是使用注解进行依赖注入
(3) 软件的设计原则:高内聚,低耦合
高内聚:一个模块内部的关系要紧密
低耦合:各个模块之间的影响要小
(4) 以前的Spring问题:配置多且繁琐,现在有了SpringBoot帮我们配置文件
DI详解
- IoC就是用来存的,IoC共有两种注解类型可以实现:
context也叫做容器
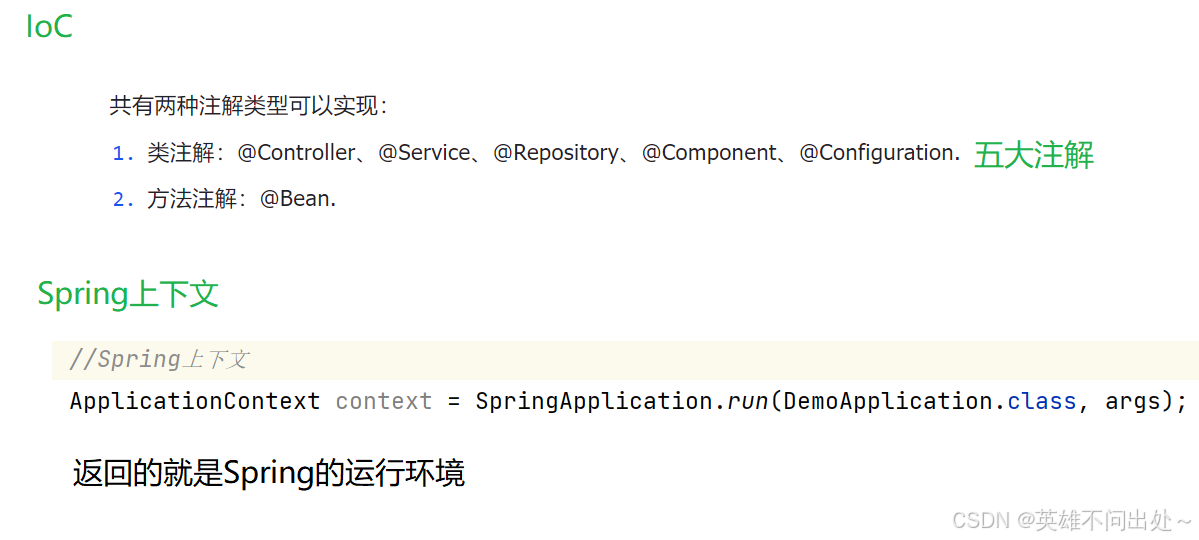
类注解可以把这些类存入容器中,可以使用容器来使用这些类
- 有三种方法可以获取存入容器中的对象:
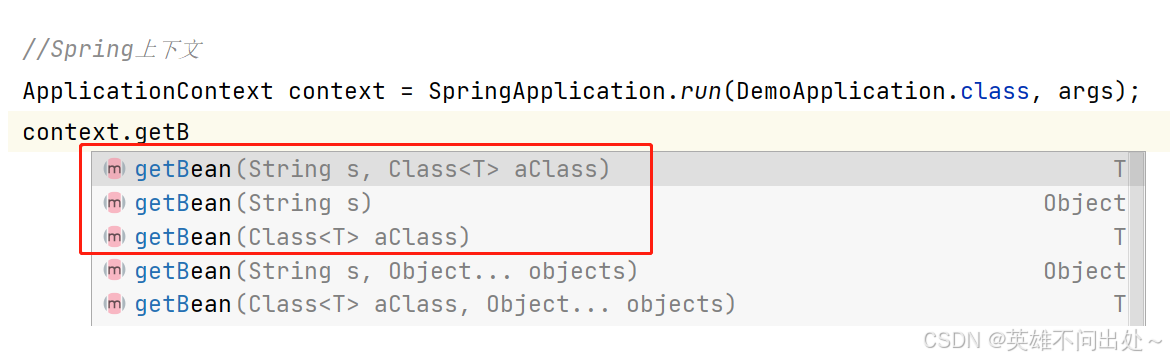
@Controller(表现层存储)
@Controller:Spring用来存储类,然后取出来获取类的对象
- @Controller注解:
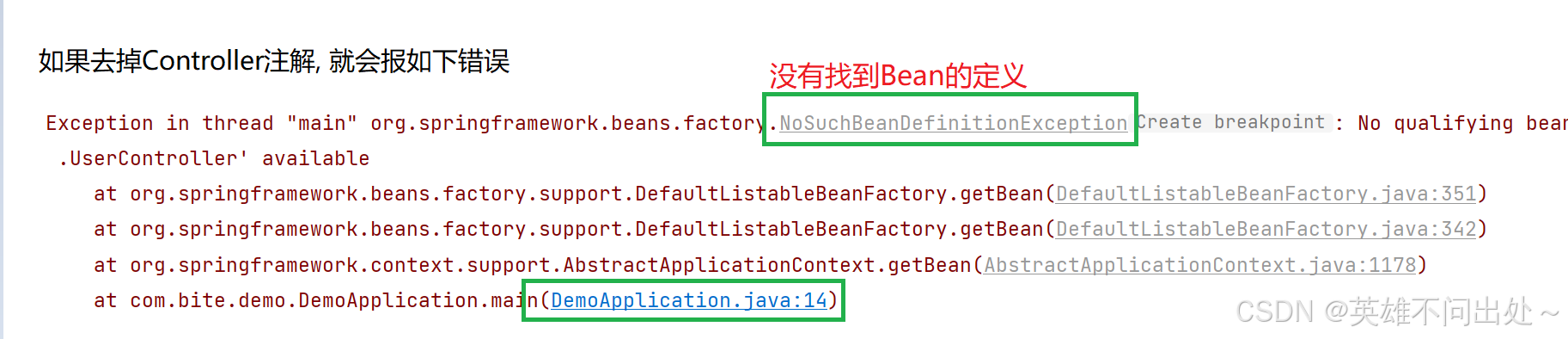
IocApplication.java
java
package com.example.ioc;
import com.example.ioc.demos.controller.UserController;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
// 启动类
@SpringBootApplication
public class IocApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 这条代码帮我们返回了一个容器
// Spring上下文
ApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(IocApplication.class, args);
UserController bean = context.getBean(UserController.class);
bean.doController();
}
}UserController.java
java
package com.example.ioc.demos.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@Controller
public class UserController {
public void doController(){
System.out.println("doController...");
}
}Spring存对象时,名称是唯一的
@Service(业务逻辑存储)
@Service:Spring用来存储类,然后取出来获取类的对象
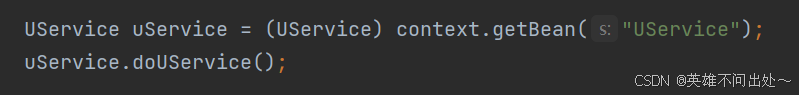
- 三种获取bean的方式,还有一种特殊情况(如果类名的前两个字母都大写,那么获取bean的名称就是类名,不用更改名称)
Spring中文文档
java
package com.example.ioc;
import com.example.ioc.demos.controller.UserController;
import com.example.ioc.demos.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
// 启动类
@SpringBootApplication
public class IocApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 这条代码帮我们返回了一个容器
// Spring上下文
// 从context中获取bean
ApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(IocApplication.class, args);
UserController bean = context.getBean(UserController.class);
bean.doController();
// 1.根据类名来获取bean
UserService bean1 = context.getBean(UserService.class);
bean1.doService();
// 2. 根据名称来获取bean,名称是类名,但是是使用小驼峰的方式来命名
// 要进行类型的转换,因为getBean是Object类型的
UserService bean2 = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
bean2.doService();
// 3. 根据名称和类名拿到bean,可能根据类名拿到多个对象
UserService userServiece = context.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
userServiece.doService();
}
}bean内部的实现方法:
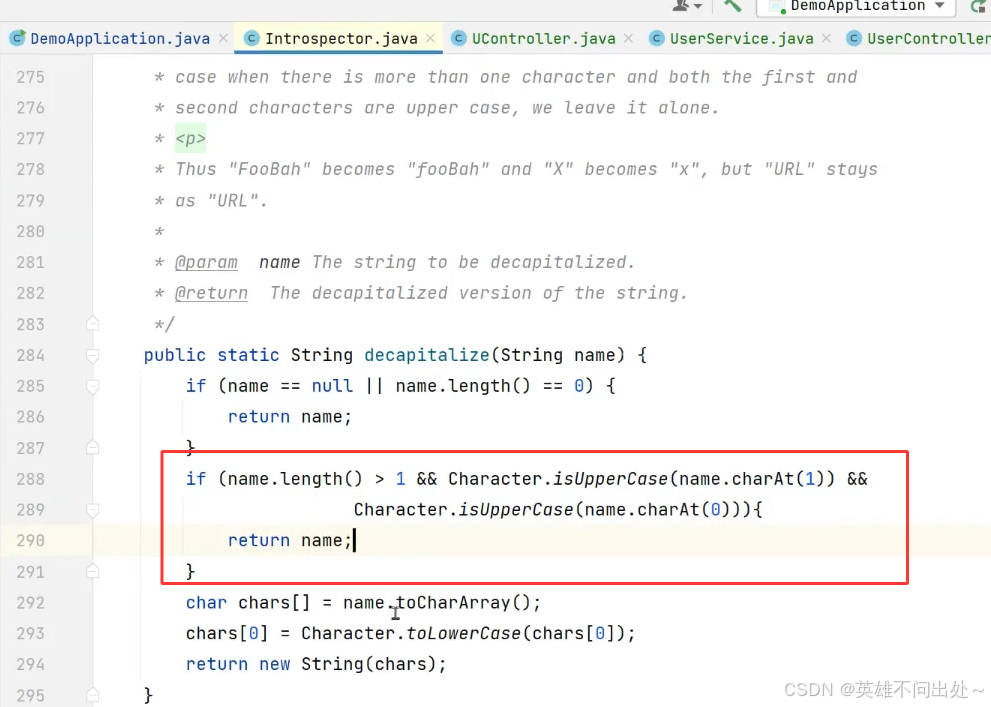
一个经典的面试题:

@Repository(仓库存储)
持久层,存在数据库中的
格式化的快捷键:ctrl + alt + l(小写的L)
IocApplication.java
java
// Repository
UserRepository repository = context.getBean(UserRepository.class);
repository.doRepository();UserRepository.java
java
package com.example.ioc.demos.repo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class UserRepository {
public void doRepository(){
System.out.println("do Repository...");
}
}@Component(组件存储)
IocApplication.java
java
// Component
UserComponent userComponent = context.getBean(UserComponent.class);
userComponent.doComponent();UserComponent.java
java
package com.example.ioc.demos.component;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class UserComponent {
public void doComponent(){
System.out.println("doComponent");
}
}@Configuration(配置存储)
-
Spring会帮我们配置大多数很普遍遇到的配置,但是小众的配置不会帮我们配置,所以引入了@Configuration
-
为什么要这么多的注解?
可以更好地识别和管理

-
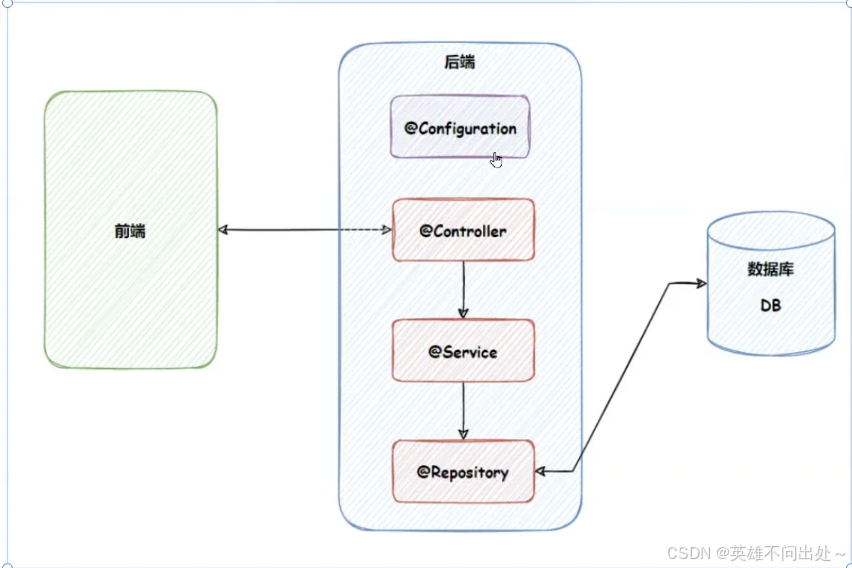
程序的应用分层,调用流程如下:
-
如果想要被外界(网络)访问到,只能使用Controller
-
几个注解之间的关系:
