文章的目的为了记录使用QT QML开发学习的经历。开发流程和要点有些记忆模糊,赶紧记录,防止忘记。
相关链接:
开源 C++ QT QML 开发(四)复杂控件--Listview
开源 C++ QT QML 开发(五)复杂控件--Gridview
开源 C++ QT QML 开发(十一)通讯--TCP服务器端
开源 C++ QT QML 开发(十二)通讯--TCP客户端
开源 C++ QT QML 开发(十五)通讯--http下载
推荐链接:
开源 C# 快速开发(十六)数据库--sqlserver增删改查
本章节主要内容是:Qt 多线程编程的例子,实现了线程之间的通讯,采用信号槽通讯。
1.代码分析
2.所有源码
3.效果演示
一、代码分析
整体架构
主线程(main) ↔ ThreadController ↔ Worker(后台线程)
↓ ↓
QML界面 信号槽通信
Worker 类详细分析
构造函数 Worker::Worker()
Worker::Worker(QObject *parent)
: QObject(parent)
, m_count(0) // 初始化计数器为0
{
m_timer = new QTimer(this); // 创建定时器,父对象为this
connect(m_timer, &QTimer::timeout, this, &Worker::doWork);
}功能:
初始化数据成员 m_count
创建 QTimer 用于模拟周期性工作
连接定时器超时信号到工作槽函数
关键点:
使用 this 作为父对象,但后续会被 moveToThread(),父子关系会调整
定时器在工作者线程中运行
析构函数 Worker::~Worker()
Worker::~Worker()
{
qDebug() << "Worker: 析构函数被调用";
if (m_timer && m_timer->isActive()) {
m_timer->stop(); // 停止定时器
}
}功能:确保在对象销毁时停止定时器
开始工作 Worker::startWork()
void Worker::startWork()
{
qDebug() << "Worker: 开始工作,线程ID:" << QThread::currentThreadId();
m_count = 0; // 重置计数器
m_timer->start(1000); // 启动1秒间隔的定时器
}调用时机:当收到来自主线程的 startWork 信号时
作用:启动后台工作流程
停止工作 Worker::stopWork()
void Worker::stopWork()
{
if (m_timer->isActive()) {
m_timer->stop(); // 停止定时器
}
qDebug() << "Worker: 停止工作";
}功能:立即停止后台工作
核心工作函数 Worker::doWork()
void Worker::doWork()
{
m_count++;
QString data = QString("后台数据 %1 - 线程ID: %2")
.arg(m_count)
.arg((quintptr)QThread::currentThreadId());
// 发送数据到主线程
emit dataUpdated(data);
qDebug() << "Worker: 发送数据:" << data;
if(m_count >= 10) { // 限制执行10次
stopWork();
emit workFinished(); // 通知工作完成
}
}执行流程:
增加计数器
生成包含线程ID的数据字符串
发射 dataUpdated 信号将数据发送到主线程
检查是否达到执行上限,如果是则停止并通知完成
ThreadController 类详细分析
构造函数 ThreadController::ThreadController()
ThreadController::ThreadController(QObject *parent)
: QObject(parent)
, m_workerThread(nullptr)
, m_worker(nullptr)
, m_isWorking(false)
{
// 1. 创建线程和工作对象
m_workerThread = new QThread(this); // 父对象为this
m_worker = new Worker(); // 无父对象,准备移动到线程
// 2. 关键:将工作者移动到工作线程
m_worker->moveToThread(m_workerThread);
// 3. 建立信号槽连接
connect(m_workerThread, &QThread::finished, m_worker, &QObject::deleteLater);
connect(this, &ThreadController::startWork, m_worker, &Worker::startWork);
connect(this, &ThreadController::stopWork, m_worker, &Worker::stopWork);
connect(m_worker, &Worker::dataUpdated, this, &ThreadController::onDataUpdated);
connect(m_worker, &Worker::workFinished, this, &ThreadController::onWorkFinished);
// 4. 启动线程(此时线程就绪,等待信号)
m_workerThread->start();
qDebug() << "ThreadController: 主线程ID:" << QThread::currentThreadId();
}关键连接分析:
信号源 信号 接收者 槽函数 连接类型
m_workerThread finished m_worker deleteLater 自动
ThreadController startWork Worker startWork 队列
ThreadController stopWork Worker stopWork 队列
Worker dataUpdated ThreadController onDataUpdated 队列
Worker workFinished ThreadController onWorkFinished 队列
重要细节:
moveToThread(m_workerThread) 是核心,它将 Worker 的事件循环转移到新线程
所有跨线程连接自动使用 Qt::QueuedConnection
线程启动后处于等待状态,直到收到开始信号
析构函数 ThreadController::~ThreadController()
ThreadController::~ThreadController()
{
qDebug() << "ThreadController: 析构函数被调用";
if (m_workerThread && m_workerThread->isRunning()) {
// 1. 停止工作
if (m_worker) {
m_worker->stopWork();
}
// 2. 优雅退出
m_workerThread->quit();
m_workerThread->wait(1000); // 等待1秒
// 3. 强制终止(如果优雅退出失败)
if (m_workerThread->isRunning()) {
m_workerThread->terminate();
m_workerThread->wait();
}
}
}资源清理策略:
先尝试停止工作
请求线程退出并等待
超时后强制终止
由于 m_workerThread 的父对象是 this,会自动删除
QML接口函数 ThreadController::start() 和 stop()
void ThreadController::start()
{
if (!m_isWorking) {
setWorking(true); // 更新状态
emit startWork(); // 触发后台线程开始工作
}
}
void ThreadController::stop()
{
if (m_isWorking) {
emit stopWork(); // 触发后台线程停止工作
setWorking(false); // 更新状态
}
}设计模式:
作为 QML 调用的接口
先更新状态再发射信号,确保状态一致性
数据转发函数 ThreadController::onDataUpdated()
void ThreadController::onDataUpdated(const QString &data)
{
// 在主线程中接收数据并转发给QML
qDebug() << "ThreadController: 接收数据 -" << data;
emit newData(data); // 转发到QML
}线程上下文:
在主线程中执行(因为 ThreadController 在主线程)
将从 Worker 线程接收的数据转发给 QML
工作完成处理 ThreadController::onWorkFinished()
void ThreadController::onWorkFinished()
{
qDebug() << "ThreadController: 工作完成";
setWorking(false); // 更新工作状态
}作用:处理 Worker 的自然结束(执行完10次后)
状态管理函数 ThreadController::setWorking()
void ThreadController::setWorking(bool working)
{
if (m_isWorking != working) {
m_isWorking = working;
emit isWorkingChanged(); // 通知QML属性变化
qDebug() << "ThreadController: 工作状态改变为:" << working;
}
}QML集成关键:
通过 emit isWorkingChanged() 通知 QML 属性已更新
QML 的 isWorking 绑定会自动更新
main.cpp 分析
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QGuiApplication app(argc, argv);
// 1. 创建控制器(在主线程)
ThreadController controller;
QQmlApplicationEngine engine;
// 2. 注册为QML上下文属性
engine.rootContext()->setContextProperty("threadController", &controller);
// 3. 加载QML
engine.load(url);
return app.exec();
}重要点:
ThreadController controller 在主线程创建
通过 setContextProperty 暴露给 QML,名称为 threadController
完整执行流程
启动流程
QML点击开始 → threadController.start()
ThreadController → setWorking(true) + emit startWork()
Worker线程 → startWork() 启动定时器
每秒触发 → doWork() 生成数据 → emit dataUpdated()
数据流
Worker线程 → dataUpdated信号 → ThreadController主线程 → newData信号 → QML界面
停止流程
手动停止:
QML停止按钮 → threadController.stop() → emit stopWork() → Worker::stopWork()
自动停止:
Worker::doWork() (第10次) → stopWork() → emit workFinished() → ThreadController::onWorkFinished()
二、所有源码
worker.h文件源码
#ifndef WORKER_H
#define WORKER_H
#include <QObject>
#include <QThread>
#include <QDebug>
#include <QTimer>
class Worker : public QObject
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
explicit Worker(QObject *parent = nullptr);
~Worker();
public slots:
void startWork();
void stopWork();
private slots:
void doWork();
signals:
void dataUpdated(const QString &data);
void workFinished();
private:
QTimer *m_timer;
int m_count;
};
#endif // WORKER_Hworker.cpp文件源码
#include "worker.h"
Worker::Worker(QObject *parent)
: QObject(parent)
, m_count(0)
{
m_timer = new QTimer(this);
connect(m_timer, &QTimer::timeout, this, &Worker::doWork);
}
Worker::~Worker()
{
qDebug() << "Worker: 析构函数被调用";
if (m_timer && m_timer->isActive()) {
m_timer->stop();
}
}
void Worker::startWork()
{
qDebug() << "Worker: 开始工作,线程ID:" << QThread::currentThreadId();
m_count = 0;
m_timer->start(1000); // 每秒触发一次
}
void Worker::stopWork()
{
if (m_timer->isActive()) {
m_timer->stop();
}
qDebug() << "Worker: 停止工作";
}
void Worker::doWork()
{
m_count++;
QString data = QString("后台数据 %1 - 线程ID: %2").arg(m_count).arg((quintptr)QThread::currentThreadId());
// 发送数据到主线程
emit dataUpdated(data);
qDebug() << "Worker: 发送数据:" << data;
if(m_count >= 10) {
stopWork();
emit workFinished();
}
}threadController.h文件源码#ifndef THREADCONTROLLER_H
#define THREADCONTROLLER_H
#include <QObject>
#include <QThread>
#include "worker.h"
class ThreadController : public QObject
{
Q_OBJECT
// 将状态属性暴露给QML
Q_PROPERTY(bool isWorking READ isWorking NOTIFY isWorkingChanged)
public:
explicit ThreadController(QObject *parent = nullptr);
~ThreadController();
// QML可调用的函数
Q_INVOKABLE void start();
Q_INVOKABLE void stop();
bool isWorking() const;
signals:
void startWork();
void stopWork();
void newData(const QString &data);
void isWorkingChanged();
private slots:
void onDataUpdated(const QString &data);
void onWorkFinished();
private:
void setWorking(bool working);
QThread *m_workerThread;
Worker *m_worker;
bool m_isWorking;
};
#endif // THREADCONTROLLER_HthreadController.cpp文件源码
#include "threadcontroller.h"
#include <QDebug>
ThreadController::ThreadController(QObject *parent)
: QObject(parent)
, m_workerThread(nullptr)
, m_worker(nullptr)
, m_isWorking(false)
{
// 创建工作线程和工作者
m_workerThread = new QThread(this);
m_worker = new Worker();
// 将工作者移动到工作线程
m_worker->moveToThread(m_workerThread);
// 连接信号槽 - 使用QueuedConnection确保跨线程安全
connect(m_workerThread, &QThread::finished, m_worker, &QObject::deleteLater);
connect(this, &ThreadController::startWork, m_worker, &Worker::startWork);
connect(this, &ThreadController::stopWork, m_worker, &Worker::stopWork);
connect(m_worker, &Worker::dataUpdated, this, &ThreadController::onDataUpdated);
connect(m_worker, &Worker::workFinished, this, &ThreadController::onWorkFinished);
// 启动线程(但不立即开始工作)
m_workerThread->start();
qDebug() << "ThreadController: 主线程ID:" << QThread::currentThreadId();
}
ThreadController::~ThreadController()
{
qDebug() << "ThreadController: 析构函数被调用";
if (m_workerThread && m_workerThread->isRunning()) {
// 停止工作
if (m_worker) {
m_worker->stopWork();
}
// 退出线程
m_workerThread->quit();
m_workerThread->wait(1000); // 等待1秒
// 如果线程仍然在运行,强制终止
if (m_workerThread->isRunning()) {
m_workerThread->terminate();
m_workerThread->wait();
}
}
}
void ThreadController::start()
{
if (!m_isWorking) {
setWorking(true);
emit startWork();
}
}
void ThreadController::stop()
{
if (m_isWorking) {
emit stopWork();
setWorking(false);
}
}
bool ThreadController::isWorking() const
{
return m_isWorking;
}
void ThreadController::onDataUpdated(const QString &data)
{
// 在主线程中接收数据并转发给QML
qDebug() << "ThreadController: 接收数据 -" << data;
emit newData(data);
}
void ThreadController::onWorkFinished()
{
qDebug() << "ThreadController: 工作完成";
setWorking(false);
}
void ThreadController::setWorking(bool working)
{
if (m_isWorking != working) {
m_isWorking = working;
emit isWorkingChanged();
qDebug() << "ThreadController: 工作状态改变为:" << working;
}
}main.qml文件源码
import QtQuick 2.12
import QtQuick.Window 2.12
import QtQuick.Controls 2.12
import QtQuick.Layouts 1.12
import QtQuick.Dialogs 1.2
ApplicationWindow {
id: window
width: 500
height: 400
visible: true
title: qsTr("Qt QML 多线程示例 - 基于C++实现")
minimumWidth: 400
minimumHeight: 300
ColumnLayout {
anchors.fill: parent
anchors.margins: 20
spacing: 25
// 标题
Text {
Layout.alignment: Qt.AlignHCenter
text: "QML + C++ 多线程演示"
font.bold: true
font.pixelSize: 18
color: "#2c3e50"
}
// 状态显示区域
Rectangle {
Layout.fillWidth: true
Layout.preferredHeight: 80
color: threadController.isWorking ? "#d4edda" : "#f8d7da"
border.color: threadController.isWorking ? "#c3e6cb" : "#f5c6cb"
border.width: 2
radius: 8
RowLayout {
anchors.fill: parent
anchors.margins: 10
// 状态指示器
Rectangle {
Layout.preferredWidth: 20
Layout.preferredHeight: 20
radius: 10
color: threadController.isWorking ? "#28a745" : "#dc3545"
border.color: "#ffffff"
border.width: 2
}
ColumnLayout {
Layout.fillWidth: true
spacing: 5
Text {
text: threadController.isWorking ? "后台线程运行中" : "后台线程已停止"
font.bold: true
font.pixelSize: 16
color: threadController.isWorking ? "#155724" : "#721c24"
}
Text {
text: threadController.isWorking ?
"正在从后台线程接收数据..." :
"点击开始按钮启动后台线程"
font.pixelSize: 12
color: threadController.isWorking ? "#155724" : "#721c24"
}
}
}
}
// 数据显示区域
GroupBox {
Layout.fillWidth: true
Layout.fillHeight: true
title: "后台线程数据接收区"
ScrollView {
anchors.fill: parent
TextArea {
id: dataDisplay
readOnly: true
placeholderText: "等待接收后台线程数据...\n数据将在这里显示"
background: Rectangle {
color: "#f8f9fa"
border.color: "#dee2e6"
radius: 4
}
font.family: "Courier New"
font.pixelSize: 12
selectByMouse: true
}
}
}
// 控制按钮区域
RowLayout {
Layout.alignment: Qt.AlignHCenter
spacing: 20
Button {
text: "开始任务"
enabled: !threadController.isWorking
onClicked: {
dataDisplay.text = "开始接收后台线程数据...\n" +
"================================\n";
threadController.start();
}
background: Rectangle {
color: parent.enabled ? "#28a745" : "#6c757d"
radius: 5
}
contentItem: Text {
text: parent.text
color: "white"
horizontalAlignment: Text.AlignHCenter
verticalAlignment: Text.AlignVCenter
font.bold: true
}
}
Button {
text: "停止任务"
enabled: threadController.isWorking
onClicked: {
threadController.stop();
dataDisplay.text += "================================\n" +
"任务被手动停止\n";
}
background: Rectangle {
color: parent.enabled ? "#dc3545" : "#6c757d"
radius: 5
}
contentItem: Text {
text: parent.text
color: "white"
horizontalAlignment: Text.AlignHCenter
verticalAlignment: Text.AlignVCenter
font.bold: true
}
}
Button {
text: "清空显示"
onClicked: {
dataDisplay.text = "";
}
background: Rectangle {
color: "#17a2b8"
radius: 5
}
contentItem: Text {
text: parent.text
color: "white"
horizontalAlignment: Text.AlignHCenter
verticalAlignment: Text.AlignVCenter
font.bold: true
}
}
}
// 信息提示
Text {
Layout.alignment: Qt.AlignHCenter
text: "提示: 后台线程每秒发送一次数据,发送10次后自动停止"
font.pixelSize: 11
color: "#6c757d"
font.italic: true
}
}
// 连接来自C++的信号
Connections {
target: threadController
onNewData: {
dataDisplay.text += data + "\n";
// 自动滚动到底部
dataDisplay.cursorPosition = dataDisplay.length;
}
}
// 关于对话框
MessageDialog {
id: aboutDialog
title: "关于"
text: "多线程示例\n\n" +
"演示如何使用C++实现后台线程,\n" +
"并通过信号槽与QML主线程通信。\n\n" +
"版本 1.0"
icon: StandardIcon.Information
}
// 菜单栏
menuBar: MenuBar {
Menu {
title: "文件"
MenuItem {
text: "退出"
onTriggered: Qt.quit()
}
}
Menu {
title: "帮助"
MenuItem {
text: "关于"
onTriggered: aboutDialog.open()
}
}
}
}main.cpp文件源码
#include <QGuiApplication>
#include <QQmlApplicationEngine>
#include <QQmlContext>
#include <QDebug>
#include "threadcontroller.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QCoreApplication::setAttribute(Qt::AA_EnableHighDpiScaling);
QGuiApplication app(argc, argv);
// 设置应用程序信息
app.setApplicationName("QML多线程示例");
app.setApplicationVersion("1.0");
app.setOrganizationName("Example Company");
// 创建线程控制器实例
ThreadController controller;
QQmlApplicationEngine engine;
// 将控制器实例注册为QML上下文属性
engine.rootContext()->setContextProperty("threadController", &controller);
// 加载QML文件
const QUrl url(QStringLiteral("qrc:/main.qml"));
QObject::connect(&engine, &QQmlApplicationEngine::objectCreated,
&app, [url](QObject *obj, const QUrl &objUrl) {
if (!obj && url == objUrl) {
qCritical() << "QML加载失败:" << url;
QCoreApplication::exit(-1);
} else {
qDebug() << "QML界面加载成功";
}
}, Qt::QueuedConnection);
engine.load(url);
qDebug() << "应用程序启动完成";
return app.exec();
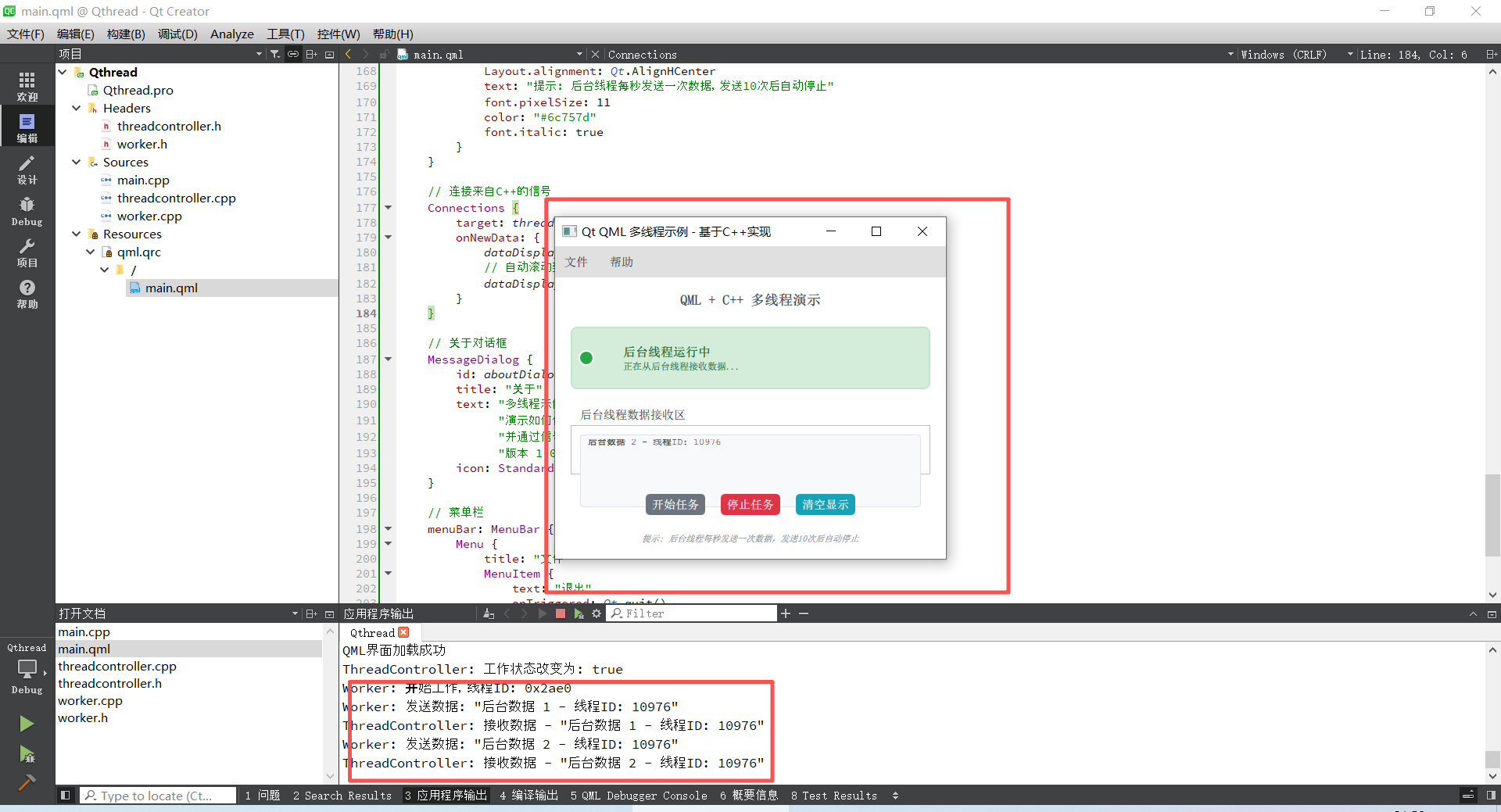
}三、效果演示
开始任务后,线程会发送数据,输出将会打印消息。