一、什么是多态
多态(Polymorphism) 是面向对象程序设计中最重要的特征之一。 它指的是:
"同一个接口,表现出不同的行为"。
也就是说,同样的函数调用语句,在不同对象上会表现出不同的执行结果。
多态的作用
用于解决在继承关系中,基类与派生类存在同名函数时,调用哪个函数的问题。
例如,当你用基类指针或引用操作派生类对象时, 系统会根据实际对象的类型来决定调用哪个函数。
多态的使用场景
-
使用 基类指针 指向 派生类对象
cppBase* p = new Derived(); p->func(); -
使用 基类引用 引用 派生类对象
cppvoid call(Base& obj) { obj.func(); } Derived d; call(d);
二、形成多态的三个条件
| 条件 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ① 有继承关系 | 基类 → 派生类 |
| ② 函数原型相同 | 返回类型、函数名、参数列表都相同 |
③ 基类函数前有 virtual 关键字 |
子类是否写 virtual 无影响,但父类必须有 |
注意:virtual 只在函数声明处出现,在定义实现时不能再次写。
三、虚函数与动态绑定
静态绑定 vs 动态绑定
-
静态绑定(Static Binding): 在编译阶段确定调用哪个函数(如非虚函数、普通对象调用)。
-
动态绑定(Dynamic Binding): 在运行时根据对象的真实类型决定调用哪个函数(即虚函数机制)。
示例:静态绑定与动态绑定对比
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Point {
public:
Point(double i, double j) : x(i), y(j) {}
double Area() const { return 0.0; } // 非虚函数(静态绑定)
private:
double x, y;
};
class Rectangle : public Point {
public:
Rectangle(double i, double j, double w, double h) : Point(i, j), w(w), h(h) {}
double Area() const { return w * h; } // 覆盖函数
private:
double w, h;
};
void fun(Point &s) {
cout << "Area=" << s.Area() << endl;
}
int main() {
Rectangle rec(3.0, 5.2, 15.0, 25.0);
fun(rec);
}输出:
cpp
Area=0这是静态绑定,fun() 的参数类型是 Point&,所以调用的是 Point::Area()。
改进:加上虚函数实现动态绑定
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Point {
public:
Point(double i, double j) : x(i), y(j) {}
virtual double Area() const { return 0.0; } // 虚函数
private:
double x, y;
};
class Rectangle : public Point {
public:
Rectangle(double i, double j, double w, double h) : Point(i, j), w(w), h(h) {}
double Area() const override { return w * h; } // 重写(覆盖)
private:
double w, h;
};
void fun(Point &s) {
cout << "Area=" << s.Area() << endl;
}
int main() {
Rectangle rec(3.0, 5.2, 15.0, 25.0);
fun(rec);
}输出:
cpp
Area=375调用了派生类的 Rectangle::Area()。 动态绑定通过虚函数表(vtable)在运行时确定实际调用的函数。
四、虚函数表(Virtual Table)机制解析
虚表(vtable)
-
虚表是编译器为含虚函数的类自动生成的函数指针数组;
-
数组中的每个元素存放虚函数的入口地址;
-
类中有虚函数 → 编译器自动添加一个隐藏的 虚表指针(vptr);
-
通常
vptr是类对象内存中的第一个成员。

五、虚析构函数
为什么需要虚析构函数?
当通过 基类指针删除派生类对象 时:
cpp
Base* p = new Derived();
delete p; // 只会调用 Base::~Base()如果基类析构函数不是虚函数,就会造成派生类资源泄漏。
解决办法:
cpp
virtual ~Base() { ... }构造函数不能是虚函数,但析构函数可以(且经常需要)。
六、抽象类与纯虚函数
定义
带有至少一个 纯虚函数 的类称为 抽象类。
cpp
class Shape {
public:
virtual double Area() = 0; // 纯虚函数
};-
抽象类不能创建对象;
-
只能作为基类,被派生类继承并实现纯虚函数。
示例:抽象类实现多态
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Shape {
public:
virtual void draw() = 0; // 纯虚函数
};
class Circle : public Shape {
public:
void draw() override { cout << "Drawing Circle" << endl; }
};
class Rectangle : public Shape {
public:
void draw() override { cout << "Drawing Rectangle" << endl; }
};
void render(Shape* s) {
s->draw();
}
int main() {
Circle c;
Rectangle r;
render(&c);
render(&r);
}输出:
cpp
Drawing Circle
Drawing Rectangle七、运算符重载与多态的联系
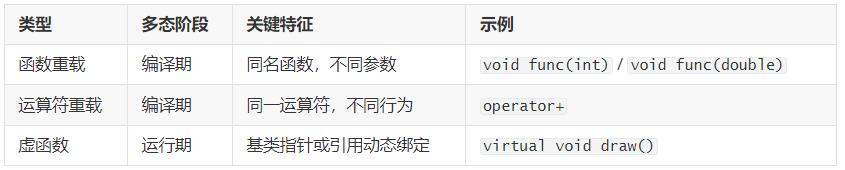
在 C++ 中,函数重载、运算符重载、虚函数 都体现了多态的思想:
-
函数重载:编译期多态(静态绑定);
-
虚函数:运行期多态(动态绑定);
-
运算符重载:通过"同一符号 → 不同类型行为"实现多态。
示例:运算符重载实现复数加减
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Complex {
public:
Complex(double r=0.0, double i=0.0) : real(r), imag(i) {}
Complex operator+(Complex c2) {
return Complex(real + c2.real, imag + c2.imag);
}
Complex operator-(Complex c2) {
return Complex(real - c2.real, imag - c2.imag);
}
void display() const {
cout << "(" << real << "," << imag << ")" << endl;
}
private:
double real, imag;
};
int main() {
Complex c1(5, 4), c2(2, 10), c3;
cout << "c1="; c1.display();
cout << "c2="; c2.display();
c3 = c1 - c2;
cout << "c3=c1-c2="; c3.display();
c3 = c1 + c2;
cout << "c3=c1+c2="; c3.display();
}输出:
cpp
c1=(5,4)
c2=(2,10)
c3=c1-c2=(3,-6)
c3=c1+c2=(7,14)运算符重载是"编译期多态"的体现。
八、总结与对比
多态的核心意义:
让"接口与实现分离",通过统一的接口实现灵活可扩展的运行行为。
三要素:
-
基于继承;
-
相同函数原型;
-
virtual关键字启用动态绑定。