目录
[一、初识 ProtoBuf](#一、初识 ProtoBuf)
[1. 序列化概念](#1. 序列化概念)
[2. ProtoBuf 是什么](#2. ProtoBuf 是什么)
[3. ProtoBuf 的使用特点](#3. ProtoBuf 的使用特点)
[二、安装 ProtoBuf](#二、安装 ProtoBuf)
[1、ProtoBuf 在 window 下的安装](#1、ProtoBuf 在 window 下的安装)
[1.1、下载 ProtoBuf 编译器](#1.1、下载 ProtoBuf 编译器)
[2、ProtoBuf 在 Linux 下的安装](#2、ProtoBuf 在 Linux 下的安装)
[2.1、下载 ProtoBuf](#2.1、下载 ProtoBuf)
[2.2、安装 ProtoBuf](#2.2、安装 ProtoBuf)
[步骤1:创建 .proto 文件](#步骤1:创建 .proto 文件)
[指定 proto3 语法](#指定 proto3 语法)
[package 声明符](#package 声明符)
[步骤2:编译 contacts.proto 文件,生成 C++ 文件](#步骤2:编译 contacts.proto 文件,生成 C++ 文件)
[编译 contacts.proto 文件后会生成什么](#编译 contacts.proto 文件后会生成什么)
[四、proto 3 语法详解](#四、proto 3 语法详解)
[1. 字段规则](#1. 字段规则)
[2. 消息类型的定义与使用](#2. 消息类型的定义与使用)
[2.1 定义](#2.1 定义)
[2.2 使用](#2.2 使用)
[2.3 创建通讯录 2.0 版本](#2.3 创建通讯录 2.0 版本)
[2.3.1 通讯录 2.0 的写入实现](#2.3.1 通讯录 2.0 的写入实现)
[2.3.2 通讯录 2.0 的读取实现](#2.3.2 通讯录 2.0 的读取实现)
[3. enum 类型](#3. enum 类型)
[3.1 定义规则](#3.1 定义规则)
[3.2 定义时注意](#3.2 定义时注意)
[3.3 升级通讯录至 2.1 版本](#3.3 升级通讯录至 2.1 版本)
[4. Any 类型](#4. Any 类型)
[4.1 升级通讯录至 2.2 版本](#4.1 升级通讯录至 2.2 版本)
[5. oneof 类型](#5. oneof 类型)
[5.1 升级通讯录至 2.3 版本](#5.1 升级通讯录至 2.3 版本)
[6. map 类型](#6. map 类型)
[6.1 升级通讯录至 2.4 版本](#6.1 升级通讯录至 2.4 版本)
[7. 默认值](#7. 默认值)
[8. 更新消息](#8. 更新消息)
[8.1 更新规则](#8.1 更新规则)
[8.2 保留字段 reserved](#8.2 保留字段 reserved)
[8.2.1 创建通讯录 3.0 版本---验证 错误删除字段 造成的数据损坏](#8.2.1 创建通讯录 3.0 版本---验证 错误删除字段 造成的数据损坏)
[8.3 未知字段](#8.3 未知字段)
[8.3.1 未知字段从哪获取](#8.3.1 未知字段从哪获取)
[MessageLite 类介绍(了解)](#MessageLite 类介绍(了解))
[Message 类介绍(了解)](#Message 类介绍(了解))
[Descriptor 类介绍(了解)](#Descriptor 类介绍(了解))
[Reflection 类介绍(了解)](#Reflection 类介绍(了解))
[UnknownFieldSet 类介绍(重要)](#UnknownFieldSet 类介绍(重要))
[UnknownField 类介绍(重要)](#UnknownField 类介绍(重要))
[8.3.2 升级通讯录 3.1 版本---验证未知字段](#8.3.2 升级通讯录 3.1 版本---验证未知字段)
[8.4 前后兼容性](#8.4 前后兼容性)
[9. 选项 option](#9. 选项 option)
[9.1 选项分类](#9.1 选项分类)
[9.2 常用选项列举](#9.2 常用选项列举)
[9.3 设置自定义选项](#9.3 设置自定义选项)
[六、通讯录 4.0 实现---网络版](#六、通讯录 4.0 实现---网络版)
[1. 环境搭建](#1. 环境搭建)
[2. centos 下编写的注意事项](#2. centos 下编写的注意事项)
[3. 约定双端交互接口](#3. 约定双端交互接口)
[4. 约定双端交互req/resp](#4. 约定双端交互req/resp)
[5. 客户端代码实现](#5. 客户端代码实现)
[6. 服务端代码实现](#6. 服务端代码实现)
[1. 序列化能力对比验证](#1. 序列化能力对比验证)
[2. 总结](#2. 总结)
一、初识 ProtoBuf
1. 序列化概念
序列化和反序列化
序列化:把对象转换为字节序列的过程 称为对象的序列化。
反序列化:把字节序列恢复为对象的过程 称为对象的反序列化。
什么情况下需要序列化
存储数据:当你想把的内存中的对象状态保存到一个文件中或者存到数据库中时。
网络传输:网络直接传输数据,但是无法直接传输对象,所以要在传输前序列化,传输完成后反序列化成对象。例如我们之前学习过 socket 编程中发送与接收数据。
上面两种方式都是面向字节流的形式,由于数据存储/传输转换成不同包数据之间没有明显的区分,往往会出现年包问题,所以需要传输双方预定好协议,protobuffer解决的就是这个环节中的序列化、反序列化问题
如何实现序列化
xml、json、 protobuf
2. ProtoBuf 是什么
我们先来看看官方给出的答案是什么
Protocol buffers are Google's language-neutral, platform-neutral, extensible mechanism for
serializing structured data -- think XML, but smaller, faster, and simpler. You define how you
want your data to be structured once, then you can use special generated source code to
easily write and read your structured data to and from a variety of data streams and using a
variety of languages.
翻译过来的意思就是
Protocol Buffers 是 Google 的一种语言无关、平台无关、可扩展的序列化结构数据的方法,它可用于(数据)通信协议、数据存储等。
Protocol Buffers 类比于 XML,是一种灵活,高效,自动化机制的结构数据序列化方法,但是比
XML 更小、更快、更为简单。
你可以定义数据的结构,然后使用特殊生成的源代码轻松的在各种数据流中使用各种语言进行编写和读取结构数据。你甚至可以更新数据结构,而不破坏由旧数据结构编译的已部署程序。
简单来讲, ProtoBuf(全称为 Protocol Buffer)是让结构数据序列化的方法,其具有以下特点:
• 语言无关、平台无关 :即 ProtoBuf 支持 Java、C++、Python 等多种语言,支持多个平台。
• 高效 :即比 XML 更小、更快、更为简单。
•扩展性、兼容性好:你可以更新数据结构,而不影响和破坏原有的旧程序。
3. ProtoBuf 的使用特点
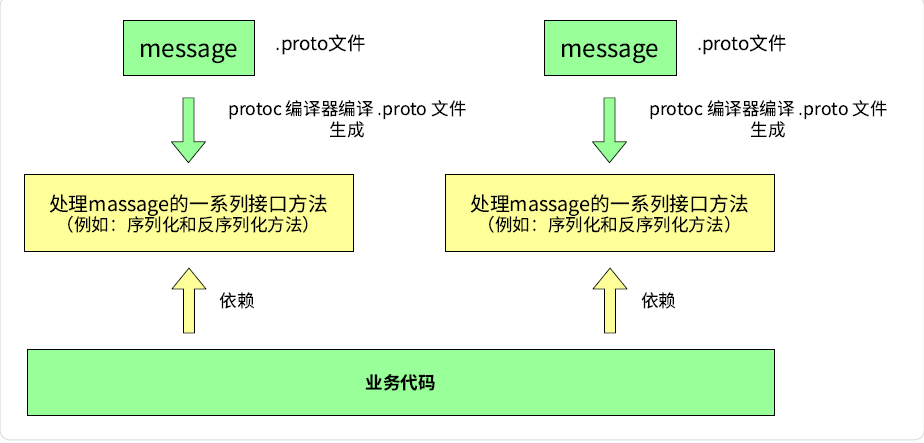
编写 .proto 文件,目的是为了定义结构对象(message)及属性内容。
使用 protoc 编译器编译 .proto 文件,生成一系列接口代码,存放在新生成头文件和源文件中。
依赖生成的接口,将编译生成的头文件包含进我们的代码中,实现对 .proto 文件中定义的字段进行设置和获取的方法 ,和对message 对象进行序列化和反序列化的方法(proto编译器会根据我们定义的结构对象自动生成这些方法)。
总的来说:ProtoBuf 是需要依赖通过编译生成的头文件和源文件来使用的。有了这种代码生成机制,开发人员再也不用吭哧吭哧地编写那些协议解析的代码了(干这种活是典型的吃力不讨好)。
二、安装 ProtoBuf
1、ProtoBuf 在 window 下的安装
1.1、下载 ProtoBuf 编译器
下载地址:https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf/releases
可以不用下载最新版本,文章以 v21.11 为例,具体的下载根据自己电脑情况选择。
下载之后将压缩包解压到本地目录下。解压后的文件内包含 bin、include文件,以及一个
readme.txt。

1.2、配置环境变量
把解压后文件中的bin目录配置到系统环境变量的Path中去
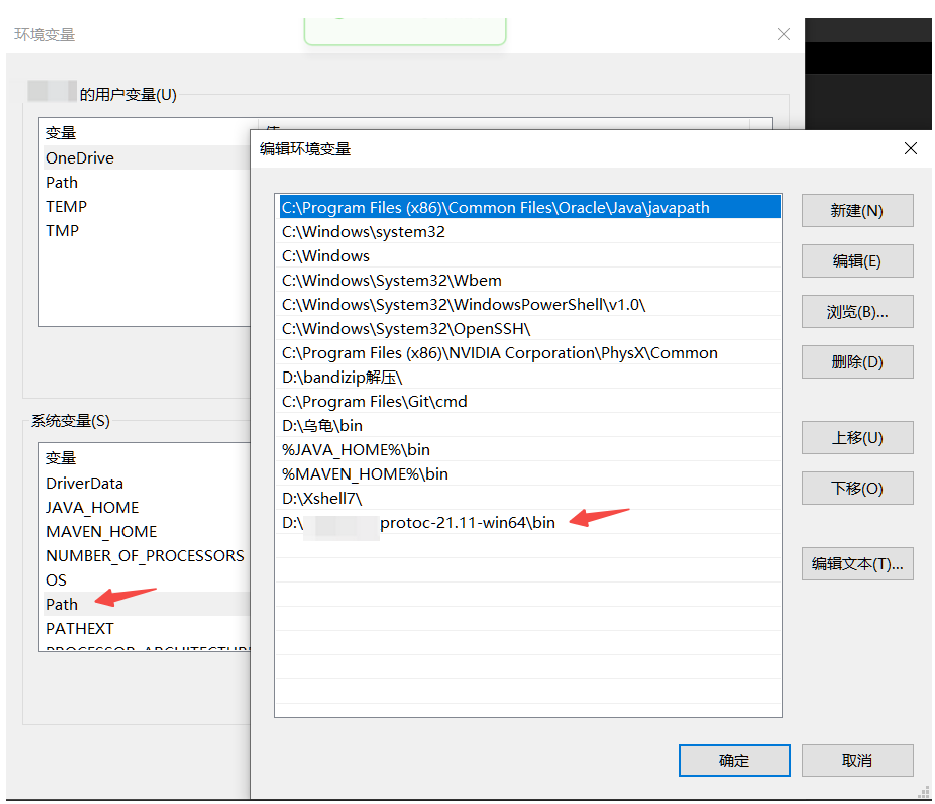
1.3、检查是否配置成功
打开cmd,输入:
protoc --version
查看版本,有显示说明成功

ProtoBuf 安装成功
2、ProtoBuf 在 Linux 下的安装
2.1、下载 ProtoBuf
下载 ProtoBuf 前一定要安装依赖库:autoconf automake libtool curl make g++ unzip
如未安装,安装命令如下:
Ubuntu 用户选择:
bash
sudo apt-get install autoconf automake libtool curl make g++ unzip -yCentOS 用户选择:
bash
sudo yum install autoconf automake libtool curl make gcc-c++ unzipProtoBuf 下载地址:https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf/releases
可以不用下载最新版本,文章以 v21.11 为例,具体的下载根据自己电脑情况选择。
• 如果要在 C++ 下使用 ProtoBuf,可以选择cpp.zip ;
• 如果要在 JAVA 下使用 ProtoBuf,可以选择 java.zip;
• 其他语言选择对应的链接即可。
• 希望支持全部语言,选择 all.zip 。
在这里我们希望支持全部语言,所以选择 protobuf-all-21.11.zip,右键将下载链接复制出来。
下载命令:
wgethttps://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf/releases/download/v21.11/protobuf-all-21.11.zip
下载完成后,解压zip包:
unzip protobuf-all-21.11.zip
解压完成后,会生成 protobuf-21.11 文件,进入文件:
cd protobuf-21.11
内容如下:

2.2、安装 ProtoBuf
进入解压好的文件,执行以下命令:
bash
# 第一步执行autogen.sh,但如果下载的是具体的某一门语言,不需要执行这一步。
./autogen.sh
# 第二步执行configure,有两种执行方式,任选其一即可,如下:
# 1、protobuf默认安装在 /usr/local 目录,lib、bin都是分散的
./configure
# 2、修改安装目录,统一安装在/usr/local/protobuf下
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/protobuf再依次执行
bash
make // 执行15分钟左右
make check // 执行15分钟左右
sudo make install可能会在make check 出现错误,例如:
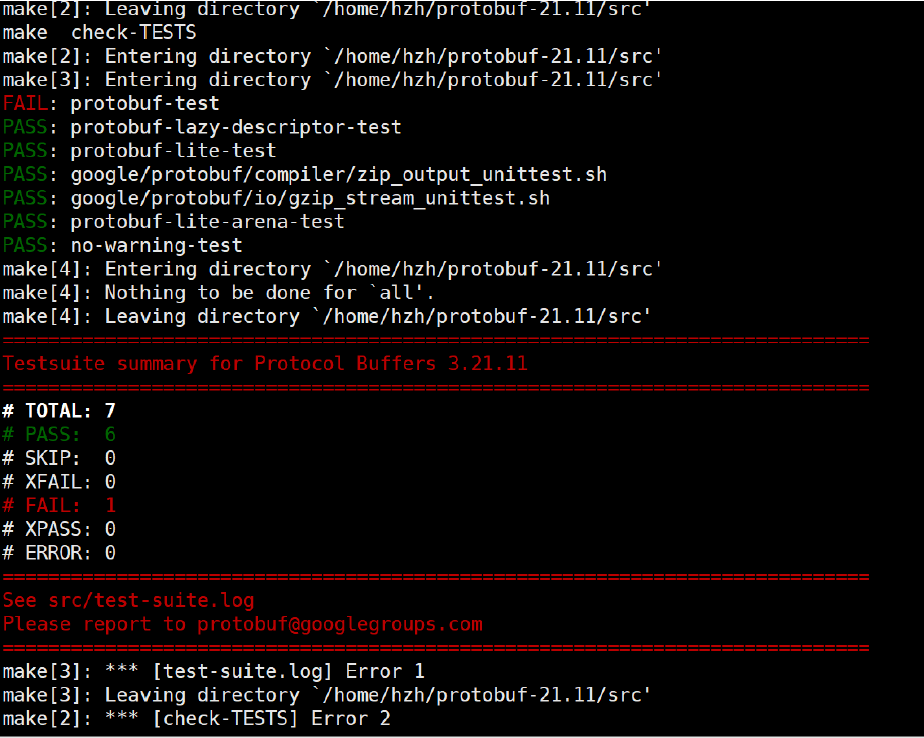
出现以上错误的原因是test的模块里面有非常多的测试用例,这些用例对服务器环境要求特别严格,需要增大下swap分区,具体操作可参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/AlexWang30/article/details/90341172
(建议可以先扩大3G,再执行 make check 。如果还是报错,再扩大到5G重新执行 make
check )
执行 make check 后 ,出现以下内容就可以执行 sudo make install 。
到此,需要你回忆一下在执行configure时,如果当时选择了第一种执行方式,也就是
./configure ,那么到这就可以正常使用protobuf了。如果选择了第二种执行方式,即修改了安装
目录,那么还需要在/etc/profile 中添加一些内容:
bash
sudo vim /etc/profile
# 添加内容如下:
#(动态库搜索路径) 程序加载运行期间查找动态链接库时指定除了系统默认路径之外的其他路径
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/usr/local/protobuf/lib/
#(静态库搜索路径) 程序编译期间查找动态链接库时指定查找共享库的路径
export LIBRARY_PATH=$LIBRARY_PATH:/usr/local/protobuf/lib/
#执行程序搜索路径
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/protobuf/bin/
#c程序头文件搜索路径
export C_INCLUDE_PATH=$C_INCLUDE_PATH:/usr/local/protobuf/include/
#c++程序头文件搜索路径
export CPLUS_INCLUDE_PATH=$CPLUS_INCLUDE_PATH:/usr/local/protobuf/include/
#pkg-config 路径
export PKG_CONFIG_PATH=/usr/local/protobuf/lib/pkgconfig/最后一步,重新执行 /etc/profile 文件:
bash
source /etc/profile2.3、检查是否安装成功
输入 protoc --version 查看版本,有显示说明安装成功。
bash
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/install/protobuf-21.11$ protoc --version
libprotoc 3.21.11ProtoBuf安装成功
三、快速上手
在快速上手中,会编写第一版本的通讯录 1.0。在通讯录 1.0 版本中,将实现:
• 对一个联系人的信息使用 PB 进行序列化,并将结果打印出来。
• 对序列化后的内容使用 PB 进行反序列,解析出联系人信息并打印出来。
• 联系人包含以下信息: 姓名、年龄。
通过通讯录 1.0,我们便能了解使用 ProtoBuf 初步要掌握的内容,以及体验到 ProtoBuf 的完整使用流程。
步骤1:创建 .proto 文件
文件规范
• 创建 .proto 文件时,文件命名 应该使用全小写字母命名,多个字母之间用 _ 连接 。 例如:
lower_snake_case.proto 。
• 书写 .proto 文件代码时,应使用 2 个空格的缩进。
我们为通讯录 1.0 新建文件: contacts.proto
添加注释
向文件添加注释,可使用 // 或者 /* ... */
指定 proto3 语法
Protocol Buffers 语言版本3,简称 proto3,是 .proto 文件最新的语法版本。proto3 简化了 ProtocolBuffers 语言,既易于使用,又可以在更广泛的编程语言中使用。它允许你使用 Java,C++,Python等多种语言生成 protocol buffer 代码。
在 .proto 文件中,要使用 syntax = "proto3"; 来指定文件语法为 proto3,并且必须写在除去注释内容的第一行 。 如果没有指定,编译器会使用proto2语法。
在通讯录 1.0 的 contacts.proto 文件中,可以为文件指定 proto3 语法,内容如下:
bash
syntax = "proto3";package 声明符
package 是一个可选的声明符,能表示 .proto 文件的命名空间 (proto编译器生成对应的方法的外面会根据package生成对应的命名空间),在项目中要有唯一性。它的作用是为了避免我们定义的消息出现冲突。
在通讯录 1.0 的 contacts.proto 文件中,可以声明其命名空间,内容如下:
bash
package contacts;定义消息(message)
消息(message): 要定义的结构化对象,我们可以给这个结构化对象中定义其对应的属性内容
经过proto编译器就可以生成对应处理的方法**,message对象的命名方式推荐采用驼峰命名法** 。
这里再提一下为什么要定义消息?
在网络传输中,我们需要为传输双方定制协议。定制协议说白了就是定义结构体或者结构化数据,
比如,tcp,udp 报文就是结构化的。
再比如将数据持久化存储到数据库时,会将一系列元数据统一用对象组织起来,再进行存储。
所以 ProtoBuf 就是以 message 的方式来支持我们定制协议字段,后期帮助我们形成类和方法来使
用。在通讯录 1.0 中我们就需要为 联系人 定义一个 message。
.proto 文件中定义一个消息类型的格式为:
bash
message 消息类型名{
}
消息类型命名规范:使用驼峰命名法,首字母大写。为 contacts.proto(通讯录 1.0)新增联系人message,内容如下:
bash
syntax = "proto3";
package contacts;
// 定义联系人消息
message PeopleInfo {
}定义消息字段
在 message 中我们可以定义其属性字段,字段定义格式为:字段类型 字段名 = 字段唯一编号;
• 字段名称命名规范:全小写字母,多个字母之间用 _ 连接。
• 字段类型分为:标量数据类型 和 特殊类型(包括枚举、其他消息类型等)。
• 字段唯一编号:用来标识字段,一旦开始使用就不能够再改变,不同字段的编号不能冲突。
该表格展示了定义于消息体中的标量数据类型,以及编译 .proto 文件之后自动生成的类中与之对应的字段类型。在这里展示了与 C++ 语言对应的类型。
| .proto Type | Notes | C++ Type |
|---|---|---|
| double | double | |
| float | float | |
| int32 | 使用变长编码[1]。负数的编码效率较低------若字段可能为负值,应使用 sint32 代替。 | int32 |
| int64 | 使用变长编码[1]。负数的编码效率较低------若字段可 能为负值,应使用 sint64 代替。 | int64 |
| uint32 | 使用变长编码[1]。 | uint32 |
| uint64 | 使用变长编码[1]。 | uint64 |
| sint32 | 使用变长编码[1]。符号整型。负值的编码效率高于 常规的 int32 类型。 | int32 |
| sint64 | 使用变长编码[1]。符号整型。负值的编码效率高于 常规的 int64 类型。 | int64 |
| fixed32 | 定长 4 字节。若值常大于2^28 则会比 uint32 更高 效。 | uint32 |
| fixed64 | 定长 8 字节。若值常大于2^56 则会比 uint64 更高 效。 | uint64 |
| sfixed32 | 定长 4 字节。 | int32 |
| sfixed64 | 定长 8 字节。 | int64 |
| bool | bool | |
| string | 包含 UTF-8 和 ASCII 编码的字符串,长度不能超过 2^32 。 | string |
| bytes | 可包含任意的字节序列但长度不能超过 2^32 。 | string |
1\] 变长编码是指:经过protobuf 编码后,原本4字节或8字节的数可能会被变为其他字节数(比如原本4字节表示的字符串可能变为3字节的空间,但字符本身不会变化)。
更新 contacts.proto (通讯录 1.0),新增姓名、年龄字段:
bash
syntax = "proto3";
package contacts;
message PeopleInfo {
string name = 1;
int32 age = 2;
}在这里还要特别讲解一下字段唯一编号的范围:
**1 ~ 536,870,911 (2^29 - 1) ,其中 19000 ~ 19999 不可用。
19000 ~ 19999 不可用是因为:在 Protobuf 协议的实现中,对这些数进行了预留。**如果非要在.proto文件中使用这些预留标识号,例如将 name 字段的编号设置为19000,编译时就会报警:
bash
// 消息中定义了如下编号,代码会告警:
// Field numbers 19,000 through 19,999 are reserved for the protobuf
implementation
string name = 19000;值得一提的是,范围为 1 ~ 15 的字段编号需要一个字节进行编码, 16 ~ 2047 内的数字需要两个字节进行编码。编码后的字节不仅只包含了编号,还包含了字段类型。所以 1 ~ 15 要用来标记出现非常频繁的字段,要为将来有可能添加的、频繁出现的字段预留一些出来。
步骤2:编译 contacts.proto 文件,生成 C++ 文件
编译命令
编译命令行格式为:

编译 contacts.proto 文件命令如下:
bash
protoc --cpp_out=. contacts.proto编译 contacts.proto 文件后会生成什么
编译 contacts.proto 文件后,会生成所选择语言的代码,我们选择的是C++,所以编译后生成了两个文件: contacts.pb.h contacts.pb.cc 。
对于编译生成的 C++ 代码,包含了以下内容 :
• 对于每个 message ,都会生成一个对应的消息类以这个对于这个类反序列化和序列化的方法。
• 在消息类中,编译器为每个字段提供了获取和设置方法,以及一下其他能够操作字段的方法。
• 编辑器会针对于每个 .proto 文件生成.h 和 .cc 文件,分别用来存放类的声明与类的实现。
contacts.pb.h 部分代码展示
cpp
class PeopleInfo final : public ::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::Message {
public:
using ::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::Message::CopyFrom;
void CopyFrom(const PeopleInfo& from);
using ::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::Message::MergeFrom;
void MergeFrom( const PeopleInfo& from) {
PeopleInfo::MergeImpl(*this, from);
}
static ::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::StringPiece FullMessageName() {
return "PeopleInfo";
}
// string name = 1;
void clear_name();
const std::string& name() const;
template <typename ArgT0 = const std::string&, typename... ArgT>
void set_name(ArgT0&& arg0, ArgT... args);
std::string* mutable_name();
PROTOBUF_NODISCARD std::string* release_name();
void set_allocated_name(std::string* name);
// int32 age = 2;
void clear_age();
int32_t age() const;
void set_age(int32_t value);
};上述的例子中:
• 每个字段都有设置和获取的方法, getter 的名称与小写字段完全相同,setter 方法以 set_ 开头。
• 每个字段都有一个 clear_ 方法,可以将字段重新设置回 empty 状态。
contacts.pb.cc 中的代码就是对类声明方法的一些实现,在这里就不展开了。
到这里有人可能就有疑惑了,那之前提到的序列化和反序列化方法在哪里呢?在消息类的父类
MessageLite 中,提供了读写消息实例的方法,包括序列化方法和反序列化方法。protobuffer的设计中很多的功能是通过继承获得的,这样之后我们就可以通过设置对应的选项来调整所拥有的功能
cpp
class MessageLite
{
public:
// 序列化:
bool SerializeToOstream(ostream *output) const; // 将序列化后数据写入文件
流 bool SerializeToArray(void *data, int size) const;
bool SerializeToString(string *output) const;
// 反序列化:
bool ParseFromIstream(istream *input); // 从流中读取数据,再进行反序列化
动作
bool ParseFromArray(const void *data, int size);
bool ParseFromString(const string &data);
};注意:
• 序列化的结果为二进制字节序列,而非文本格式。
• 以上三种序列化的方法没有本质上的区别,只是序列化后输出的格式不同,可以供不同的应用场景使用。
• 序列化的 API 函数均为const成员函数,因为序列化不会改变类对象的内容, 而是将序列化的结果保存到函数入参指定的地址中。
• 详细 message API 可以参见 完整列表。
步骤3:序列化与反序列化的使用
创建一个测试文件 main.cc,方法中我们实现:
• 对一个联系人的信息使用 PB 进行序列化,并将结果打印出来。
• 对序列化后的内容使用 PB 进行反序列,解析出联系人信息并打印出来。
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "contacts.pb.h" // 引入编译生成的头文件
using namespace std;
int main() {
string people_str;
{
// .proto文件声明的package,通过protoc编译后,会为编译生成的C++代码声明同名的
//命名空间
// 其范围是在.proto 文件中定义的内容
contacts::PeopleInfo people;
people.set_age(20);
people.set_name("张珊");
// 调用序列化方法,将序列化后的二进制序列存入string中
if (!people.SerializeToString(&people_str)) {
cout << "序列化联系人失败." << endl;
}
// 打印序列化结果
cout << "序列化后的 people_str: " << people_str << endl;
}
{
contacts::PeopleInfo people;
// 调用反序列化方法,读取string中存放的二进制序列,并反序列化出对象
if (!people.ParseFromString(people_str)) {
cout << "反序列化出联系人失败." << endl;
}
// 打印结果
cout << "Parse age: " << people.age() << endl;
cout << "Parse name: " << people.name() << endl;
}
}代码书写完成后,编译 main.cc,生成可执行程序 TestProtoBuf :
cpp
g++ main.cc contacts.pb.cc -o TestProtoBuf -std=c++11 -lprotobuf• -lprotobuf:必加,不然会有链接错误,指明需要依赖这个第三方库。
• -std=c++11:必加,使用C++11语法。
执行 TestProtoBuf ,可以看见 people 经过序列化和反序列化后的结果:
bash
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/protobuf$ ./TestProtoBuf
序列化后的 people_str:
张珊
Parse age: 20
Parse name: 张珊由于 ProtoBuf 是把联系人对象序列化成了二进制序列,这里用 string 来作为接收二进制序列的容器。所以在终端打印的时候会有换行等一些乱码显示。
所以相对于 xml 和 JSON 来说,因为被编码成二进制,破解成本增大,ProtoBuf 编码是相对安全的。
四、proto 3 语法详解
在语法详解部分,依旧使用 项目推进 的方式完成讲解。这个部分会对通讯录进行多次升级,使用 2.x表示升级的版本,最终将会升级如下内容:
• 不再打印联系人的序列化结果,而是将通讯录序列化后并写入文件中。
• 从文件中将通讯录解析出来,并进行打印。
• 新增联系人属性,共包括:姓名、年龄、电话信息、地址、其他联系方式、备注。
1. 字段规则
消息的字段可以用下面几种规则来修饰:
• singular :消息中可以包含该字段零次或一次(不超过一次) 。 proto3 语法中,字段默认使用该规则。
• repeated :消息中可以包含该字段任意多次(包括零次),其中重复值的顺序会被保留。可以理解为定义了一个数组。
更新 contacts.proto , PeopleInfo 消息中新增 phone_numbers 字段,表示一个联系人有多个
号码,可将其设置为 repeated,写法如下:
cpp
syntax = "proto3";
package contacts;
message PeopleInfo {
string name = 1;
int32 age = 2;
repeated string phone_numbers = 3;
}2. 消息类型的定义与使用
2.1 定义
在单个 .proto 文件中可以定义多个消息体,且支持定义嵌套类型的消息(任意多层 )。每个消息体中的字段编号可以重新计数 (每一个message对象可以视为一级,message内嵌套的message对象内的字段编号可以和上一级message中字段编号重复,但是一个message中的同一级字段的编号不可重复)。
更新 contacts.proto,我们可以将 phone_number 提取出来,单独成为一个消息:
bash
// -------------------------- 嵌套写法 -------------------------
syntax = "proto3";
package contacts;
message PeopleInfo {
string name = 1;
int32 age = 2;
message Phone {
string number = 1;
}
}
// -------------------------- 非嵌套写法 -------------------------
syntax = "proto3";
package contacts;
message Phone {
string number = 1;
}
message PeopleInfo {
string name = 1;
int32 age = 2;
}2.2 使用
• 消息类型可作为字段类型使用
contacts.proto
bash
syntax = "proto3";
package contacts;
// 联系人
message PeopleInfo {
string name = 1;
int32 age = 2;
message Phone {
string number = 1;
}
repeated Phone phone = 3;
}• 可导入其他 .proto 文件的消息并使用,需要使用import进行导入
例如 Phone 消息定义在 phone.proto 文件中:
cpp
syntax = "proto3";
package phone;
message Phone {
string number = 1;
}contacts.proto 中的 PeopleInfo 使用 Phone 消息:
cpp
syntax = "proto3";
package contacts;
import "phone.proto"; // 使用 import 将 phone.proto 文件导入进来 !!!
message PeopleInfo {
string name = 1;
int32 age = 2;
// 引入的文件声明了package,使用消息时,需要用 '命名空间.消息类型' 格式
repeated phone.Phone phone = 3;
}注:在 proto3 文件中可以导入 proto2 消息类型并使用它们,反之亦然。
2.3 创建通讯录 2.0 版本
通讯录 2.x 的需求是向文件中写入通讯录列表,以上我们只是定义了一个联系人的消息,并不能存放通讯录列表,所以还需要在完善一下 contacts.proto (终版通讯录 2.0):
bash
syntax = "proto3";
package contacts;
// 联系人
message PeopleInfo {
string name = 1; // 姓名
int32 age = 2; // 年龄
message Phone {
string number = 1; // 电话号码
}
repeated Phone phone = 3; // 电话
}
// 通讯录
message Contacts {
repeated PeopleInfo contacts = 1;
}接着进行一次编译:
bash
protoc --cpp_out=. contacts.proto编译后生成的 contacts.pb.h contacts.pb.cc 会将上一次快速上手的生成文件覆盖掉 。
contacts.pb.h 更新的部分代码展示
cpp
// 新增了 PeopleInfo_Phone 类
class PeopleInfo_Phone final : public ::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::Message {
public:
using ::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::Message::CopyFrom;
void CopyFrom(const PeopleInfo_Phone& from);
using ::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::Message::MergeFrom;
void MergeFrom(const PeopleInfo_Phone& from) {
PeopleInfo_Phone::MergeImpl(*this, from);
}
static ::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::StringPiece FullMessageName() {
return "PeopleInfo.Phone";
}
// string number = 1;
void clear_number();
const std::string& number() const;
template <typename ArgT0 = const std::string&, typename... ArgT>
void set_number(ArgT0&& arg0, ArgT... args);
std::string* mutable_number();
PROTOBUF_NODISCARD std::string* release_number();
void set_allocated_number(std::string* number);
};
// 更新了 PeopleInfo 类
class PeopleInfo final : public ::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::Message {
public:
using ::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::Message::CopyFrom;
void CopyFrom(const PeopleInfo& from);
using ::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::Message::MergeFrom;
void MergeFrom(const PeopleInfo& from) {
PeopleInfo::MergeImpl(*this, from);
}
static ::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::StringPiece FullMessageName() {
return "PeopleInfo";
}
typedef PeopleInfo_Phone Phone;
// repeated .PeopleInfo.Phone phone = 3;
int phone_size() const;
void clear_phone();
::PeopleInfo_Phone* mutable_phone(int index);
::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::RepeatedPtrField< ::PeopleInfo_Phone >*
mutable_phone();
const ::PeopleInfo_Phone& phone(int index) const;
::PeopleInfo_Phone* add_phone();
const ::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::RepeatedPtrField< ::PeopleInfo_Phone >&
phone() const;
};
// 新增了 Contacts 类
class Contacts final : public ::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::Message {
public:
using ::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::Message::CopyFrom;
void CopyFrom(const Contacts& from);
using ::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::Message::MergeFrom;
void MergeFrom(const Contacts& from) {
Contacts::MergeImpl(*this, from);
}
static ::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::StringPiece FullMessageName() {
return "Contacts";
}
// repeated .PeopleInfo contacts = 1;
int contacts_size() const;
void clear_contacts();
::PeopleInfo* mutable_contacts(int index);
::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::RepeatedPtrField< ::PeopleInfo >*
mutable_contacts();
const ::PeopleInfo& contacts(int index) const;
::PeopleInfo* add_contacts();
const ::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::RepeatedPtrField< ::PeopleInfo >&
contacts() const;
};上述的例子中:
• 每个字段都有一个 clear_ 方法,可以将字段重新设置回 empty 状态。
• 每个字段都有设置和获取的方法, 获取方法的方法名称与小写字段名称完全相同。但如果是消息类型的字段,其设置方法为 mutable_ 方法,返回值为消息类型的指针,这类方法会为我们开辟好空间,可以直接对这块空间的内容进行修改。
• 对于使用 repeated 修饰的字段,也就是数组类型,pb 为我们提供了 add_ 方法来新增一个值,并且提供了 _size 方法来判断数组存放元素的个数。
2.3.1 通讯录 2.0 的写入实现
write.cc (通讯录 2.0)
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include "contacts.pb.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace contacts;
/**
* 新增联系人
*/
void AddPeopleInfo(PeopleInfo* people_info_ptr)
{
cout << "-------------新增联系人-------------" << endl;
cout << "请输入联系人姓名: ";
string name;
getline(cin, name);
//set_系列的方法用来设置message字段的值
people_info_ptr->set_name(name);
cout << "请输入联系人年龄: ";
int age;
cin >> age;
people_info_ptr->set_age(age);
//清楚cin中\n,避免对下次输入造成影响
//清楚掉\n,清除掉256个字符或者清除掉所有字符但是不满256个
//该方法都会返回
cin.ignore(256, '\n');
for (int i = 1; ; i++) {
cout << "请输入联系人电话" << i << "(只输入回车完成电话新增): ";
string number;
getline(cin, number);
if (number.empty()) {
break;
}
PeopleInfo_Phone* phone = people_info_ptr->add_phone();
phone->set_number(number);
}
cout << "-----------添加联系人成功-----------" << endl;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
// GOOGLE_PROTOBUF_VERIFY_VERSION 宏: 验证没有意外链接到与编译的头文件不兼容的库版
//本。如果检测到版本不匹配,程序将中止。注意,每个.pb.cc 文件在启动时都会自动调用此宏。在使
//用 C++ Protocol Buffer 库之前执行此宏是一种很好的做法,但不是绝对必要的。
GOOGLE_PROTOBUF_VERIFY_VERSION;
if (argc != 2)
{
cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " CONTACTS_FILE" << endl;
return -1;
}
Contacts contacts;
// 先读取已存在的 contacts
fstream input(argv[1], ios::in | ios::binary);
if (!input) {
cout << argv[1] << ": File not found. Creating a new file." << endl;
}
else if (!contacts.ParseFromIstream(&input)) {
cerr << "Failed to parse contacts." << endl;
input.close();
return -1;
}
// 新增一个联系人
AddPeopleInfo(contacts.add_contacts());
// 向磁盘文件写入新的 contacts
fstream output(argv[1], ios::out | ios::trunc | ios::binary);
if (!contacts.SerializeToOstream(&output))//序列化message对象到流的接口
{
cerr << "Failed to write contacts." << endl;
input.close();
output.close();
return -1;
}
input.close();
output.close();
// 在程序结束时调用 ShutdownProtobufLibrary(),为了删除 Protocol Buffer 库分配的所
//有全局对象。对于大多数程序来说这是不必要的,因为该过程无论如何都要退出,并且操作系统将负责
//回收其所有内存。但是,如果你使用了内存泄漏检查程序,该程序需要释放每个最后对象,或者你正在
//编写可以由单个进程多次加载和卸载的库,那么你可能希望强制使用 Protocol Buffers 来清理所有
//内容。
google::protobuf::ShutdownProtobufLibrary();
return 0;
}makefile
bash
write:write.cc contacts.pb.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++11 -lprotobuf
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -f writemake之后,运行 write
bash
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/project/protobuf/contacts$ make
g++ -o write write.cc contacts.pb.cc -std=c++11 -lprotobuf
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/project/protobuf/contacts$ ./write contacts.bin
contacts.bin: File not found. Creating a new file.
-------------新增联系人-------------
请输入联系人姓名: 张三
请输入联系人年龄: 20
请输入联系人电话1(只输入回车完成电话新增): 13111111111
请输入联系人电话2(只输入回车完成电话新增): 15111111111
请输入联系人电话3(只输入回车完成电话新增):
-----------添加联系人成功-----------查看二进制文件
bash
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/project/protobuf/contacts$ hexdump -C contacts.bin
00000000 0a 28 0a 06 e5 bc a0 e4 b8 89 10 14 1a 0d 0a 0b |.(..............|
00000010 31 33 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 1a 0d 0a 0b 31 |13111111111....1|
00000020 35 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 31 |5111111111|
0000002a
解释:
hexdump:是Linux下的一个二进制文件查看工具,它可以将二进制文件转换为ASCII、八进制、
十进制、十六进制格式进行查看。
-C: 表示每个字节显示为16进制和相应的ASCII字符2.3.2 通讯录 2.0 的读取实现
read.cc (通讯录 2.0)
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include "contacts.pb.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace contacts;
/**
* 打印联系人列表
*/
void PrintfContacts(const Contacts& contacts) {
//repeated修饰,可以视作一个数组遍历得到每一个元素
for (int i = 0; i < contacts.contacts_size(); ++i) {
const PeopleInfo& people = contacts.contacts(i);
cout << "------------联系人" << i + 1 << "------------" << endl;
//使用protobuffer相关pb.cc文件中与字段同名的接口,可以获得字段的值
cout << "姓名:" << people.name() << endl;
cout << "年龄:" << people.age() << endl;
int j = 1;
//pb.c文件中也为message对象中嵌套的message对象分配了对应的类型
//命名风格一般是message对象名的组合
for (const PeopleInfo_Phone& phone : people.phone()) {
cout << "电话" << j++ << ": " << phone.number() << endl;
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
GOOGLE_PROTOBUF_VERIFY_VERSION;
if (argc != 2) {
cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << "CONTACTS_FILE" << endl;
return -1;
}
// 以二进制方式读取 contacts
Contacts contacts;
fstream input(argv[1], ios::in | ios::binary);
if (!contacts.ParseFromIstream(&input)) {
cerr << "Failed to parse contacts." << endl;
input.close();
return -1;
}
// 打印 contacts
PrintfContacts(contacts);
input.close();
google::protobuf::ShutdownProtobufLibrary();
return 0;
}makefile
bash
all:write read
write:write.cc contacts.pb.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++11 -lprotobuf
read:read.cc contacts.pb.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++11 -lprotobuf
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -f write readmake 后运行 read
bash
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/project/protobuf/contacts$ make
g++ -o read read.cc contacts.pb.cc -std=c++11 -lprotobuf
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/project/protobuf/contacts$ ./read contacts.bin
------------联系人1------------
姓名:张三
年龄:20
电话1: 13111111111
电话2: 15111111111另一种验证方法--decode
我们可以用 protoc -h 命令来查看 ProtoBuf 为我们提供的所有命令 option。其中 ProtoBuf 提供一个命令选项 --decode ,表示从标准输入中读取给定类型的二进制消息,并将其以文本格式写入标准输出。 消息类型必须在 .proto 文件或导入的文件中定义。
bash
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/project/protobuf/contacts$ protoc --
decode=contacts.Contacts contacts.proto < contacts.bin
contacts {
name: "\345\274\240\344\270\211" // 在这里是将utf-8汉字转为八进制格式输出了
age: 20
phone {
number: "13111111111"
}
phone {
number: "15111111111"
}
}3. enum 类型
3.1 定义规则
语法支持我们定义枚举类型并使用。在.proto文件中枚举类型的书写规范为:
枚举类型名称:
使用驼峰命名法,首字母大写。 例如: MyEnum
常量值名称:
全大写字母,多个字母之间用 _ 连接。例如: ENUM_CONST = 0;
我们可以定义一个名为 PhoneType 的枚举类型,定义如下:
bash
enum PhoneType {
MP = 0; // 移动电话
TEL = 1; // 固定电话
}要注意枚举类型的定义有以下几种规则:
1. 0 值常量必须存在,且要作为第一个元素。这是为了与 proto2 的语义兼容:第一个元素作为默认值,且值为 0。2. 枚举类型可以在消息外定义,也可以在消息体内定义(嵌套)。
3. 枚举的常量值在 32 位整数的范围内。但因负值无效因而不建议使用(与编码规则有关)。
3.2 定义时注意
将两个 '具有相同枚举值名称' 的枚举类型放在单个 .proto 文件下测试时,编译后会报错:某某某常
量已经被定义!所以这里要注意:
• 同级(同层)的枚举类型,各个枚举类型中的常量不能重名。
• 单个 .proto 文件下,最外层枚举类型和嵌套枚举类型,不算同级。
• 多个 .proto 文件下,若一个文件引入了其他文件,且每个文件都未声明 package,每个 proto 文件中的枚举类型都在最外层,算同级。
• 多个 .proto 文件下,若一个文件引入了其他文件,且每个文件都声明了 package,不算同级。
bash
// ---------------------- 情况1:同级枚举类型包含相同枚举值名称--------------------
enum PhoneType {
MP = 0; // 移动电话
TEL = 1; // 固定电话
}
enum PhoneTypeCopy {
MP = 0; // 移动电话 // 编译后报错:MP 已经定义
}
// ---------------------- 情况2:不同级枚举类型包含相同枚举值名称-------------------
-
enum PhoneTypeCopy {
MP = 0; // 移动电话 // 用法正确
}
message Phone {
string number = 1; // 电话号码
enum PhoneType {
MP = 0; // 移动电话
TEL = 1; // 固定电话
}
}
// ---------------------- 情况3:多文件下都未声明package--------------------
// phone1.proto
import "phone1.proto"
enum PhoneType {
MP = 0; // 移动电话 // 编译后报错:MP 已经定义
TEL = 1; // 固定电话
}
// phone2.proto
enum PhoneTypeCopy {
MP = 0; // 移动电话
}
// ---------------------- 情况4:多文件下都声明了package--------------------
// phone1.proto
import "phone1.proto"
package phone1;
enum PhoneType {
MP = 0; // 移动电话 // 用法正确
TEL = 1; // 固定电话
}
// phone2.proto
package phone2;
enum PhoneTypeCopy {
MP = 0; // 移动电话
}3.3 升级通讯录至 2.1 版本
更新 contacts.proto (通讯录 2.1),新增枚举字段并使用,更新内容如下:
bash
syntax = "proto3";
package contacts;
// 联系人
message PeopleInfo {
string name = 1; // 姓名
int32 age = 2; // 年龄
message Phone {
string number = 1; // 电话号码
enum PhoneType {
MP = 0; // 移动电话
TEL = 1; // 固定电话
}
PhoneType type = 2; // 类型
}
repeated Phone phone = 3; // 电话
}
// 通讯录
message Contacts {
repeated PeopleInfo contacts = 1;
}编译
bash
protoc --cpp_out=. contacts.protocontacts.pb.h 更新的部分代码展示:
cpp
// 新生成的 PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType 枚举类
enum PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType : int {
PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType_MP = 0,
PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType_TEL = 1,
PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType_PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType_INT_MIN_SENTINEL_DO_NOT_U
SE_ = std::numeric_limits<int32_t>::min(),
PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType_PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType_INT_MAX_SENTINEL_DO_NOT_U
SE_ = std::numeric_limits<int32_t>::max()
};
// 更新的 PeopleInfo_Phone 类
class PeopleInfo_Phone final : public ::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::Message {
public:
typedef PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType PhoneType;
static inline bool PhoneType_IsValid(int value) {
return PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType_IsValid(value);
}
template<typename T>
static inline const std::string& PhoneType_Name(T enum_t_value) { ... }
static inline bool PhoneType_Parse(
::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::ConstStringParam name, PhoneType* value) {
...
}
// .contacts.PeopleInfo.Phone.PhoneType type = 2;
void clear_type();
::contacts::PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType type() const;
void set_type(::contacts::PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType value);
};上述的代码中:
• 对于在.proto文件中定义的枚举类型,编译生成的代码中会含有与之对应的枚举类型、校验枚举值是否有效的方法 _IsValid、以及获取枚举值名称的方法 _Name。• 对于使用了枚举类型的字段,包含设置和获取字段的方法,已经清空字段的方法clear_。
更新 write.cc (通讯录 2.1)
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include "contacts.pb.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace contacts;
/**
* 新增联系人
*/
void AddPeopleInfo(PeopleInfo* people_info_ptr)
{
cout << "-------------新增联系人-------------" << endl;
cout << "请输入联系人姓名: ";
string name;
getline(cin, name);
people_info_ptr->set_name(name);
cout << "请输入联系人年龄: ";
int age;
cin >> age;
people_info_ptr->set_age(age);
cin.ignore(256, '\n');
for (int i = 1; ; i++) {
cout << "请输入联系人电话" << i << "(只输入回车完成电话新增): ";
string number;
getline(cin, number);
if (number.empty()) {
break;
}
PeopleInfo_Phone* phone = people_info_ptr->add_phone();
phone->set_number(number);
cout << "选择此电话类型 (1、移动电话 2、固定电话) : ";
int type;
cin >> type;
cin.ignore(256, '\n');
switch (type) {
case 1:
phone->set_type(PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType::PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType_MP);
break;
case 2:
phone->set_type(PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType::PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType_TEL);
break;
default:
cout << "非法选择,使用默认值!" << endl;
break;
}
}
cout << "-----------添加联系人成功-----------" << endl;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
GOOGLE_PROTOBUF_VERIFY_VERSION;
if (argc != 2)
{
cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " CONTACTS_FILE" << endl;
return -1;
}
Contacts contacts;
// 先读取已存在的 contacts
fstream input(argv[1], ios::in | ios::binary);
if (!input) {
cout << argv[1] << ": File not found. Creating a new file." << endl;
}
else if (!contacts.ParseFromIstream(&input)) {
cerr << "Failed to parse contacts." << endl;
input.close();
return -1;
}
// 新增一个联系人
AddPeopleInfo(contacts.add_contacts());
// 向磁盘文件写入新的 contacts
fstream output(argv[1], ios::out | ios::trunc | ios::binary);
if (!contacts.SerializeToOstream(&output))
{
cerr << "Failed to write contacts." << endl;
input.close();
output.close();
return -1;
}
input.close();
output.close();
google::protobuf::ShutdownProtobufLibrary();
return 0;
}更新 read.cc (通讯录 2.1)
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include "contacts.pb.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace contacts;
/**
* 打印联系人列表
*/
void PrintfContacts(const Contacts& contacts) {
for (int i = 0; i < contacts.contacts_size(); ++i) {
const PeopleInfo& people = contacts.contacts(i);
cout << "------------联系人" << i + 1 << "------------" << endl;
cout << "姓名:" << people.name() << endl;
cout << "年龄:" << people.age() << endl;
int j = 1;
for (const PeopleInfo_Phone& phone : people.phone()) {
cout << "电话" << j++ << ": " << phone.number();
cout << " (" << phone.PhoneType_Name(phone.type()) << ")" << endl;
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
GOOGLE_PROTOBUF_VERIFY_VERSION;
if (argc != 2) {
cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << "CONTACTS_FILE" << endl;
return -1;
}
// 以二进制方式读取 contacts
Contacts contacts;
fstream input(argv[1], ios::in | ios::binary);
if (!contacts.ParseFromIstream(&input)) {
cerr << "Failed to parse contacts." << endl;
input.close();
return -1;
}
// 打印 contacts
PrintfContacts(contacts);
input.close();
google::protobuf::ShutdownProtobufLibrary();
return 0;
}代码完成后,编译后进行读写验证:
bash
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/project/protobuf/contacts$ ./write contacts.bin
-------------新增联系人-------------
请输入联系人姓名: 李四
请输入联系人年龄: 25
请输入联系人电话1(只输入回车完成电话新增): 12333
选择此电话类型 (1、移动电话 2、固定电话) : 2
请输入联系人电话2(只输入回车完成电话新增):
-----------添加联系人成功-----------
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/project/protobuf/contacts$ ./read contacts.bin
------------联系人1------------
姓名:张三
年龄:20
电话1: 13111111111 (MP) // 这里打印出 MP 是因为未设置该字段,导致用了枚举的第一个
元素作为默认值
电话2: 15111111111 (MP)
------------联系人2------------
姓名:李四
年龄:25
电话1: 12333 (TEL)4. Any 类型
字段还可以声明为Any 类型,可以理解为泛型类型。使用时可以在 Any 中存储任意消息类型。Any 类型的字段也用 repeated 来修饰。
Any 类型是 google 已经帮我们定义好的类型,在安装 ProtoBuf 时,其中的 include 目录下查找所有google 已经定义好的 .proto 文件,所以定义类型,需要使用import引入 any.proto 文件

4.1 升级通讯录至 2.2 版本
通讯录 2.2 版本会新增联系人的地址信息,我们可以使用 any 类型的字段来存储地址信息。
更新 contacts.proto (通讯录 2.2),更新内容如下:
bash
syntax = "proto3";
package contacts;
import "google/protobuf/any.proto"; // 引入 any.proto 文件
// 地址
message Address{
string home_address = 1; // 家庭地址
string unit_address = 2; // 单位地址
}
// 联系人
message PeopleInfo {
string name = 1; // 姓名
int32 age = 2; // 年龄
message Phone {
string number = 1; // 电话号码
enum PhoneType {
MP = 0; // 移动电话
TEL = 1; // 固定电话
}
PhoneType type = 2; // 类型
}
repeated Phone phone = 3; // 电话
google.protobuf.Any data = 4;
}
// 通讯录
message Contacts {
repeated PeopleInfo contacts = 1;
}编译
bash
protoc --cpp_out=. contacts.protocontacts.pb.h 更新的部分代码展示:
cpp
// 新生成的 Address 类
class Address final : public ::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::Message {
public:
using ::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::Message::CopyFrom;
void CopyFrom(const Address& from);
using ::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::Message::MergeFrom;
void MergeFrom(const Address& from) {
Address::MergeImpl(*this, from);
}
// string home_address = 1;
void clear_home_address();
const std::string& home_address() const;
template <typename ArgT0 = const std::string&, typename... ArgT>
void set_home_address(ArgT0&& arg0, ArgT... args);
std::string* mutable_home_address();
PROTOBUF_NODISCARD std::string* release_home_address();
void set_allocated_home_address(std::string* home_address);
// string unit_address = 2;
void clear_unit_address();
const std::string& unit_address() const;
template <typename ArgT0 = const std::string&, typename... ArgT>
void set_unit_address(ArgT0&& arg0, ArgT... args);
std::string* mutable_unit_address();
PROTOBUF_NODISCARD std::string* release_unit_address();
void set_allocated_unit_address(std::string* unit_address);
};
// 更新的 PeopleInfo 类
class PeopleInfo final : public ::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::Message {
public:
// .google.protobuf.Any data = 4;
bool has_data() const;
void clear_data();
const ::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::Any& data() const;
PROTOBUF_NODISCARD::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::Any* release_data();
::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::Any* mutable_data();
void set_allocated_data(::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::Any* data);
};上述的代码中,对于 Any 类型字段:
• 设置和获取:获取方法的方法名称与小写字段名称完全相同。设置方法可以使用 mutable_ 方法,返回值为Any类型的指针,这类方法会为我们开辟好空间,可以直接对这块空间的内容进行修改。
之前讲过,我们可以在 Any 字段中存储任意消息类型,这就要涉及到任意消息类型 和 Any 类型的互转。这部分代码就在 Google为我们写好的头文件 any.pb.h 中。对 any.pb.h 部分代码展示:
cpp
class PROTOBUF_EXPORT Any final : public ::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::Message {
bool PackFrom(const ::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::Message& message) {
...
}
bool UnpackTo(::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::Message* message) const {
...
}
template<typename T> bool Is() const {
return _impl_._any_metadata_.Is<T>();
}
};
解释:
使用 PackFrom() 方法可以将任意消息类型转为 Any 类型。
使用 UnpackTo() 方法可以将 Any 类型转回之前设置的任意消息类型。
使用 Is() 方法可以用来判断存放的消息类型是否为 typename T。更新 write.cc (通讯录 2.2)
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include "contacts.pb.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace contacts;
/**
* 新增联系人
*/
void AddPeopleInfo(PeopleInfo* people_info_ptr)
{
cout << "-------------新增联系人-------------" << endl;
cout << "请输入联系人姓名: ";
string name;
getline(cin, name);
people_info_ptr->set_name(name);
cout << "请输入联系人年龄: ";
int age;
cin >> age;
people_info_ptr->set_age(age);
cin.ignore(256, '\n');
for (int i = 1; ; i++) {
cout << "请输入联系人电话" << i << "(只输入回车完成电话新增): ";
string number;
getline(cin, number);
if (number.empty()) {
break;
}
PeopleInfo_Phone* phone = people_info_ptr->add_phone();
phone->set_number(number);
cout << "选择此电话类型 (1、移动电话 2、固定电话) : ";
int type;
cin >> type;
cin.ignore(256, '\n');
switch (type) {
case 1:
phone -> set_type(PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType::PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType_MP);
break;
case 2:
phone -> set_type(PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType::PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType_TEL);
break;
default:
cout << "非法选择,使用默认值!" << endl;
break;
}
}
Address address;
cout << "请输入联系人家庭地址: ";
string home_address;
getline(cin, home_address);
address.set_home_address(home_address);
cout << "请输入联系人单位地址: ";
string unit_address;
getline(cin, unit_address);
address.set_unit_address(unit_address);
google::protobuf::Any* data = people_info_ptr->mutable_data();
data->PackFrom(address);
cout << "-----------添加联系人成功-----------" << endl;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
...
}更新 read.cc (通讯录 2.2)
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include "contacts.pb.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace contacts;
/**
* 打印联系人列表
*/
void PrintfContacts(const Contacts& contacts) {
for (int i = 0; i < contacts.contacts_size(); ++i) {
const PeopleInfo& people = contacts.contacts(i);
cout << "------------联系人" << i + 1 << "------------" << endl;
cout << "姓名:" << people.name() << endl;
cout << "年龄:" << people.age() << endl;
int j = 1;
for (const PeopleInfo_Phone& phone : people.phone()) {
cout << "电话" << j++ << ": " << phone.number();
cout << " (" << phone.PhoneType_Name(phone.type()) << ")" << endl;
}
if (people.has_data() && people.data().Is<Address>()) {
Address address;
people.data().UnpackTo(&address);
if (!address.home_address().empty()) {
cout << "家庭地址:" << address.home_address() << endl;
}
if (!address.unit_address().empty()) {
cout << "单位地址:" << address.unit_address() << endl;
}
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
...
}代码编写完成后,编译后进行读写:
cpp
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/project/protobuf/contacts$ ./write contacts.bin
-------------新增联系人-------------
请输入联系人姓名: 王五
请输入联系人年龄: 49
请输入联系人电话1(只输入回车完成电话新增): 642
选择此电话类型 (1、移动电话 2、固定电话) : 2
请输入联系人电话2(只输入回车完成电话新增):
请输入联系人家庭地址: 陕西省西安市
请输入联系人单位地址: 陕西省西安市
-----------添加联系人成功-----------
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/project/protobuf/contacts$ ./read contacts.bin
# 此处省略前两个添加的联系人
------------联系人3------------
姓名:王五
年龄:49
电话1: 642 (TEL)
家庭地址:陕西省西安市
单位地址:陕西省西安市5. oneof 类型
如果消息中有很多可选字段, 并且将来不管我们如何设置,只会保留最后一个设置的字段, 那么就可以使用 oneof 加强这个行为,也能有节约内存的效果。
5.1 升级通讯录至 2.3 版本
通讯录 2.3 版本想新增联系人的其他联系方式,比如qq或者微信号二选一,我们就可以使用 oneof 字段来加强多选一这个行为。oneof 字段定义的格式为: oneof 字段名 { 字段1; 字段2; ... }
更新 contacts.proto (通讯录 2.3),更新内容如下:
bash
syntax = "proto3";
package contacts;
import "google/protobuf/any.proto"; // 引入 any.proto 文件
// 地址
message Address{
string home_address = 1; // 家庭地址
string unit_address = 2; // 单位地址
}
// 联系人
message PeopleInfo {
string name = 1; // 姓名
int32 age = 2; // 年龄
message Phone {
string number = 1; // 电话号码
enum PhoneType {
MP = 0; // 移动电话
TEL = 1; // 固定电话
}
PhoneType type = 2; // 类型
}
repeated Phone phone = 3; // 电话
google.protobuf.Any data = 4;
oneof other_contact { // 其他联系方式:多选一
string qq = 5;
string weixin = 6;
}
}
// 通讯录
message Contacts {
repeated PeopleInfo contacts = 1;
}注意:
• 可选字段中的字段编号,不能与非可选字段的编号冲突。• 不能在 oneof 中使用 repeated 字段。
• 将来在设置 oneof 字段中值时,如果将 oneof 中的字段设置多个,那么只会保留最后一次设置的成员,之前设置的 oneof 成员会自动清除。
编译
bash
protoc --cpp_out=. contacts.protocontacts.pb.h 更新的部分代码展示:
cpp
// 更新的 PeopleInfo 类
class PeopleInfo final : public ::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::Message {
enum OtherContactCase {
kQq = 5,
kWeixin = 6,
OTHER_CONTACT_NOT_SET = 0,
};
// string qq = 5;
bool has_qq() const;
void clear_qq();
const std::string& qq() const;
template <typename ArgT0 = const std::string&, typename... ArgT>
void set_qq(ArgT0&& arg0, ArgT... args);
std::string* mutable_qq();
PROTOBUF_NODISCARD std::string* release_qq();
void set_allocated_qq(std::string* qq);
// string weixin = 6;
bool has_weixin() const;
void clear_weixin();
const std::string& weixin() const;
template <typename ArgT0 = const std::string&, typename... ArgT>
void set_weixin(ArgT0&& arg0, ArgT... args);
std::string* mutable_weixin();
PROTOBUF_NODISCARD std::string* release_weixin();
void set_allocated_weixin(std::string* weixin);
void clear_other_contact();
OtherContactCase other_contact_case() const;
};上述的代码中,对于 oneof 字段:
• 会将 oneof 中的多个字段定义为一个枚举类型。• 设置和获取:对 oneof 内的字段进行常规的设置和获取即可,但要注意只能设置一个。如果设置多个,那么只会保留最后一次设置的成员。
• 清空oneof字段:clear_ 方法
• 获取当前设置了哪个字段:_case 方法
更新 write.cc (通讯录 2.3),更新内容如下:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include "contacts.pb.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace contacts;
/**
* 新增联系人
*/
void AddPeopleInfo(PeopleInfo* people_info_ptr)
{
cout << "-------------新增联系人-------------" << endl;
cout << "请输入联系人姓名: ";
string name;
getline(cin, name);
people_info_ptr->set_name(name);
cout << "请输入联系人年龄: ";
int age;
cin >> age;
people_info_ptr->set_age(age);
cin.ignore(256, '\n');
for (int i = 1; ; i++) {
cout << "请输入联系人电话" << i << "(只输入回车完成电话新增): ";
string number;
getline(cin, number);
if (number.empty()) {
break;
}
PeopleInfo_Phone* phone = people_info_ptr->add_phone();
phone->set_number(number);
cout << "选择此电话类型 (1、移动电话 2、固定电话) : ";
int type;
cin >> type;
cin.ignore(256, '\n');
switch (type) {
case 1:
phone-> set_type(PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType::PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType_MP);
break;
case 2:
phone-> set_type(PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType::PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType_TEL);
break;
default:
cout << "非法选择,使用默认值!" << endl;
break;
}
}
Address address;
cout << "请输入联系人家庭地址: ";
string home_address;
getline(cin, home_address);
address.set_home_address(home_address);
cout << "请输入联系人单位地址: ";
string unit_address;
getline(cin, unit_address);
address.set_unit_address(unit_address);
google::protobuf::Any* data = people_info_ptr->mutable_data();
data->PackFrom(address);
cout << "选择添加一个其他联系方式 (1、qq号 2、微信号) : ";
int other_contact;
cin >> other_contact;
cin.ignore(256, '\n');
if (1 == other_contact) {
cout << "请输入qq号: ";
string qq;
getline(cin, qq);
people_info_ptr->set_qq(qq);
}
else if (2 == other_contact) {
cout << "请输入微信号: ";
string weixin;
getline(cin, weixin);
people_info_ptr->set_weixin(weixin);
}
else {
cout << "非法选择,该项设置失败!" << endl;
}
cout << "-----------添加联系人成功-----------" << endl;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
...
}更新 read.cc (通讯录 2.3),更新内容如下:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include "contacts.pb.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace contacts;
/**
* 打印联系人列表
*/
void PrintfContacts(const Contacts& contacts) {
for (int i = 0; i < contacts.contacts_size(); ++i) {
const PeopleInfo& people = contacts.contacts(i);
cout << "------------联系人" << i + 1 << "------------" << endl;
cout << "姓名:" << people.name() << endl;
cout << "年龄:" << people.age() << endl;
int j = 1;
for (const PeopleInfo_Phone& phone : people.phone()) {
cout << "电话" << j++ << ": " << phone.number();
cout << " (" << phone.PhoneType_Name(phone.type()) << ")" << endl;
}
if (people.has_data() && people.data().Is<Address>()) {
Address address;
people.data().UnpackTo(&address);
if (!address.home_address().empty()) {
cout << "家庭地址:" << address.home_address() << endl;
}
if (!address.unit_address().empty()) {
cout << "单位地址:" << address.unit_address() << endl;
}
}
/* if (people.has_qq()) {
} else if (people.has_weixin()) {
} */
switch (people.other_contact_case()) {
case PeopleInfo::OtherContactCase::kQq:
cout << "qq号: " << people.qq() << endl;
break;
case PeopleInfo::OtherContactCase::kWeixin:
cout << "微信号: " << people.weixin() << endl;
break;
case PeopleInfo::OtherContactCase::OTHER_CONTACT_NOT_SET:
break;
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
...
}代码编写完成后,编译后进行读写:
bash
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/project/protobuf/contacts$ ./write contacts.bin
-------------新增联系人-------------
请输入联系人姓名: 郭六
请输入联系人年龄: 38
请输入联系人电话1(只输入回车完成电话新增): 171
选择此电话类型 (1、移动电话 2、固定电话) : 1
请输入联系人电话2(只输入回车完成电话新增):
请输入联系人家庭地址: 北京市
请输入联系人单位地址: 北京市
选择添加一个其他联系方式 (1、qq号 2、微信号) : 2
请输入微信号: guo_liu
-----------添加联系人成功-----------
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/project/protobuf/contacts$ ./read contacts.bin
# 此处省略前三个添加的联系人
------------联系人4------------
姓名:郭六
年龄:38
电话1: 171 (MP)
家庭地址:北京市
单位地址:北京市
微信号: guo_liu6. map 类型
语法支持创建一个关联映射字段,也就是可以使用 map 类型去声明字段类型,格式为:
map<key_type, value_type> map_field = N;
要注意的是:• key_type 是除了 float 和 bytes 类型以外的任意标量类型。 value_type 可以是任意类型。
• map 字段不可以用 repeated 修饰
• map 中存入的元素是无序的
6.1 升级通讯录至 2.4 版本
最后,通讯录 2.4 版本想新增联系人的备注信息,我们可以使用 map 类型的字段来存储备注信息。更新 contacts.proto (通讯录 2.4),更新内容如下:
bash
syntax = "proto3";
package contacts;
import "google/protobuf/any.proto"; // 引入 any.proto 文件
// 地址
message Address{
string home_address = 1; // 家庭地址
string unit_address = 2; // 单位地址
}
// 联系人
message PeopleInfo {
string name = 1; // 姓名
int32 age = 2; // 年龄
message Phone {
string number = 1; // 电话号码
enum PhoneType {
MP = 0; // 移动电话
TEL = 1; // 固定电话
}
PhoneType type = 2; // 类型
}
repeated Phone phone = 3; // 电话
google.protobuf.Any data = 4;
oneof other_contact { // 其他联系方式:多选一
string qq = 5;
string weixin = 6;
}
map<string, string> remark = 7; // 备注
}
// 通讯录
message Contacts {
repeated PeopleInfo contacts = 1;
}编译
bash
protoc --cpp_out=. contacts.protocontacts.pb.h 更新的部分代码展示:
cpp
// 更新的 PeopleInfo 类
class PeopleInfo final : public ::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::Message {
// map<string, string> remark = 7;
int remark_size() const;
void clear_remark();
const ::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::Map< std::string, std::string >&
remark() const;
::PROTOBUF_NAMESPACE_ID::Map< std::string, std::string >*
mutable_remark();
};上述的代码中,对于Map类型的字段:
• 清空map: clear_ 方法• 设置和获取:获取方法的方法名称与小写字段名称完全相同。设置方法为 mutable_ 方法,返回值为Map类型的指针,这类方法会为我们开辟好空间,可以直接对这块空间的内容进行修改。
更新 write.cc (通讯录 2.4),更新内容如下:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include "contacts.pb.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace contacts;
/**
* 新增联系人
*/
void AddPeopleInfo(PeopleInfo* people_info_ptr)
{
cout << "-------------新增联系人-------------" << endl;
cout << "请输入联系人姓名: ";
string name;
getline(cin, name);
people_info_ptr->set_name(name);
cout << "请输入联系人年龄: ";
int age;
cin >> age;
people_info_ptr->set_age(age);
cin.ignore(256, '\n');
for (int i = 1; ; i++) {
cout << "请输入联系人电话" << i << "(只输入回车完成电话新增): ";
string number;
getline(cin, number);
if (number.empty()) {
break;
}
PeopleInfo_Phone* phone = people_info_ptr->add_phone();
phone->set_number(number);
cout << "选择此电话类型 (1、移动电话 2、固定电话) : ";
int type;
cin >> type;
cin.ignore(256, '\n');
switch (type) {
case 1:
phone-> set_type(PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType::PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType_MP);
break;
case 2:
phone-> set_type(PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType::PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType_TEL);
break;
default:
cout << "非法选择,使用默认值!" << endl;
break;
}
}
Address address;
cout << "请输入联系人家庭地址: ";
string home_address;
getline(cin, home_address);
address.set_home_address(home_address);
cout << "请输入联系人单位地址: ";
string unit_address;
getline(cin, unit_address);
address.set_unit_address(unit_address);
google::protobuf::Any* data = people_info_ptr->mutable_data();
data->PackFrom(address);
cout << "选择添加一个其他联系方式 (1、qq号 2、微信号) : ";
int other_contact;
cin >> other_contact;
cin.ignore(256, '\n');
if (1 == other_contact) {
cout << "请输入qq号: ";
string qq;
getline(cin, qq);
people_info_ptr->set_qq(qq);
}
else if (2 == other_contact) {
cout << "请输入微信号: ";
string weixin;
getline(cin, weixin);
people_info_ptr->set_weixin(weixin);
}
else {
cout << "非法选择,该项设置失败!" << endl;
}
for (int i = 1; ; i++) {
cout << "请输入备注" << i << "标题 (只输入回车完成备注新增): ";
string remark_key;
getline(cin, remark_key);
if (remark_key.empty()) {
break;
}
cout << "请输入备注" << i << "内容: ";
string remark_value;
getline(cin, remark_value);
people_info_ptr->mutable_remark()->insert({ remark_key, remark_value });
}
cout << "-----------添加联系人成功-----------" << endl;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
...
}更新 read.cc (通讯录 2.4),更新内容如下:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include "contacts.pb.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace contacts;
/**
* 打印联系人列表
*/
void PrintfContacts(const Contacts& contacts) {
for (int i = 0; i < contacts.contacts_size(); ++i) {
const PeopleInfo& people = contacts.contacts(i);
cout << "------------联系人" << i + 1 << "------------" << endl;
cout << "姓名:" << people.name() << endl;
cout << "年龄:" << people.age() << endl;
int j = 1;
for (const PeopleInfo_Phone& phone : people.phone()) {
cout << "电话" << j++ << ": " << phone.number();
cout << " (" << phone.PhoneType_Name(phone.type()) << ")" << endl;
}
if (people.has_data() && people.data().Is<Address>()) {
Address address;
people.data().UnpackTo(&address);
if (!address.home_address().empty()) {
cout << "家庭地址:" << address.home_address() << endl;
}
if (!address.unit_address().empty()) {
cout << "单位地址:" << address.unit_address() << endl;
}
}
/* if (people.has_qq()) {
} else if (people.has_weixin()) {
} */
switch (people.other_contact_case()) {
case PeopleInfo::OtherContactCase::kQq:
cout << "qq号: " << people.qq() << endl;
break;
case PeopleInfo::OtherContactCase::kWeixin:
cout << "微信号: " << people.weixin() << endl;
break;
case PeopleInfo::OtherContactCase::OTHER_CONTACT_NOT_SET:
break;
}
if (people.remark_size()) {
cout << "备注信息: " << endl;
}
for (auto it = people.remark().cbegin(); it != people.remark().cend();
++it) {
cout << " " << it->first << ": " << it->second << endl;
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
...
}代码编写完成后,编译后进行读写:
bash
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/project/protobuf/contacts$ ./write contacts.bin
-------------新增联系人-------------
请输入联系人姓名: 胡七
请输入联系人年龄: 28
请输入联系人电话1(只输入回车完成电话新增): 110
选择此电话类型 (1、移动电话 2、固定电话) : 2
请输入联系人电话2(只输入回车完成电话新增):
请输入联系人家庭地址: 海南海口
请输入联系人单位地址: 海南海口
选择添加一个其他联系方式 (1、qq号 2、微信号) : 1
请输入qq号: 123123123
请输入备注1标题 (只输入回车完成备注新增): 日程
请输入备注1内容: 10月1一起出去玩
请输入备注2标题 (只输入回车完成备注新增):
-----------添加联系人成功-----------
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/project/protobuf/contacts$ ./read contacts.bin
# 此处省略前四个添加的联系人
------------联系人5------------
姓名:胡七
年龄:28
电话1: 110 (TEL)
家庭地址:海南海口
单位地址:海南海口
qq号: 123123123
备注信息:
日程: 10月1一起出去玩到此,我们对通讯录 2.x 要求的任务全部完成。在这个过程中我们将通讯录升级到了 2.4 版本,同时对ProtoBuf 的使用也进一步熟练了,并且也掌握了 ProtoBuf 的 proto3 语法支持的大部分类型及其使用,但只是正常使用还是完全不够的。通过接下来的学习,我们就能更进一步了解到 ProtoBuf 深入的内容。
7. 默认值
反序列化消息时,如果被反序列化的二进制序列中不包含某个字段,反序列化对象中相应字段时,就会设置为该字段的默认值。不同的类型对应的默认值不同:
• 对于字符串,默认值为空字符串。
• 对于字节,默认值为空字节。
• 对于布尔值,默认值为 false。
• 对于数值类型,默认值为 0,浮点数默认0.0。
• 对于枚举,默认值是第一个定义的枚举值, 必须为 0。
• 对于消息字段,未设置该字段。它的取值是依赖于语言。
• 对于设置了 repeated 的字段的默认值是空的( 通常是相应语言的一个空列表 )。
• **对于消息字段、oneof字段和any字段,C++ 和 Java 语言中都有 has_ 方法来检测当前字段是否被设置,**这有利于我们来区分当前字段的值是否是故意这样设置的。
• 对于标量数据,在proto3语法下,没有生成has_方法来检测当前字段是否被设置,对于标量数据来说,需要判断的情况主要就是0是否是设置过的,但是不管0这个数是人为还是默认的都是满足我们使用需要的,所以判断其实没有太大的意义。
8. 更新消息
8.1 更新规则
如果现有的消息类型已经不再满足我们的需求,例如需要扩展一个字段,在不破坏任何现有代码的情况下更新消息类型非常简单。遵循如下规则即可:
• 禁止修改任何已有字段的字段编号。
• 若是移除老字段,要保证不再使用移除字段的字段编号。正确的做法是保留字段编号
(reserved),以确保该编号将不能被重复使用。不建议直接删除或注释掉字段。• int32, uint32, int64, uint64 和 bool 是完全兼容的。可以从这些类型中的一个改为另一个,而不破坏前后兼容性。若解析出来的数值与相应的类型不匹配,会采用与 C++ 一致的处理方案(例如,若将 64 位整数当做 32 位进行读取,它将被截断为 32 位)。
• sint32 和 sint64 相互兼容但不与其他的整型兼容。
• string 和 bytes 在合法 UTF-8 字节前提下也是兼容的。
• bytes 包含消息编码版本的情况下,嵌套消息与 bytes 也是兼容的。
• fixed32 与 sfixed32 兼容, fixed64 与 sfixed64兼容。
• enum 与 int32,uint32, int64 和 uint64 兼容(注意若值不匹配会被截断)。但要注意当反序列化消息时会根据语言采用不同的处理方案:例如,未识别的 proto3 枚举类型会被保存在消息中,但是当消息反序列化时如何表示是依赖于编程语言的。整型字段总是会保持其的值。
•oneof:
◦ 将一个单独的值更改为 新 oneof 类型成员之一是安全和二进制兼容的。
◦ 若确定没有代码一次性设置多个值那么将多个字段移入一个新 oneof 类型也是可行的。
◦ 将任何字段移入已存在的 oneof 类型是不安全的。
8.2 保留字段 reserved
如果通过删除 或 注释掉 字段来更新消息类型,未来的用户在添加新字段时,有可能会使用以前已经存在,但已经被删除或注释掉的字段编号 。将来使用该 .proto 的旧版本时的程序会引发很多问题:数据损坏、隐私错误等等。
确保不会发生这种情况的一种方法是:使用 reserved 将指定字段的编号或名称设置为保留项 。当我们再使用这些编号或名称时,protocol buffer 的编译器将会警告这些编号或名称不可用。
举个例子:
bash
message Message {
// 设置保留项
reserved 100, 101, 200 to 299;
reserved "field3", "field4";
// 注意:不要在一行 reserved 声明中同时声明字段编号和名称。
// reserved 102, "field5";
// 设置保留项之后,下面代码会告警
int32 field1 = 100; //告警:Field 'field1' uses reserved number 100
int32 field2 = 101; //告警:Field 'field2' uses reserved number 101
int32 field3 = 102; //告警:Field name 'field3' is reserved
int32 field4 = 103; //告警:Field name 'field4' is reserved
}8.2.1 创建通讯录 3.0 版本---验证 错误删除字段 造成的数据损坏
现模拟有两个服务,他们各自使用一份通讯录 .proto 文件,内容约定好了是一模一样的。
服务1(service):负责序列化通讯录对象,并写入文件中。
服务2(client):负责读取文件中的数据,解析并打印出来。
一段时间后,service 更新了自己的 .proto 文件,更新内容为:删除了某个字段,并新增了一个字段,新增的字段使用了被删除字段的字段编号。并将新的序列化对象写进了文件。
但 client 并没有更新自己的 .proto 文件。根据结论,可能会出现数据损坏的现象,接下来就让我们来验证下这个结论。
新建两个目录:service、client。分别存放两个服务的代码。
service 目录下新增 contacts.proto (通讯录 3.0)
bash
syntax = "proto3";
package s_contacts;
// 联系人
message PeopleInfo {
string name = 1; // 姓名
int32 age = 2; // 年龄
message Phone {
string number = 1; // 电话号码
}
repeated Phone phone = 3; // 电话
}
// 通讯录
message Contacts {
repeated PeopleInfo contacts = 1;
}client 目录下新增 contacts.proto (通讯录 3.0)
bash
syntax = "proto3";
package c_contacts;
// 联系人
message PeopleInfo {
string name = 1; // 姓名
int32 age = 2; // 年龄
message Phone {
string number = 1; // 电话号码
}
repeated Phone phone = 3; // 电话
}
// 通讯录
message Contacts {
repeated PeopleInfo contacts = 1;
}分别对两个文件进行编译,可自行操作。
继续对 service 目录下新增 service.cc (通讯录 3.0),负责向文件中写通讯录消息,内容如下:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include "contacts.pb.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace s_contacts;
/**
* 新增联系人
*/
void AddPeopleInfo(PeopleInfo* people_info_ptr)
{
cout << "-------------新增联系人-------------" << endl;
cout << "请输入联系人姓名: ";
string name;
getline(cin, name);
people_info_ptr->set_name(name);
cout << "请输入联系人年龄: ";
int age;
cin >> age;
people_info_ptr->set_age(age);
cin.ignore(256, '\n');
for (int i = 1; ; i++) {
cout << "请输入联系人电话" << i << "(只输入回车完成电话新增): ";
string number;
getline(cin, number);
if (number.empty()) {
break;
}
PeopleInfo_Phone* phone = people_info_ptr->add_phone();
phone->set_number(number);
}
cout << "-----------添加联系人成功-----------" << endl;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
GOOGLE_PROTOBUF_VERIFY_VERSION;
if (argc != 2)
{
cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " CONTACTS_FILE" << endl;
return -1;
}
Contacts contacts;
// 先读取已存在的 contacts
fstream input(argv[1], ios::in | ios::binary);
if (!input) {
cout << argv[1] << ": File not found. Creating a new file." << endl;
}
else if (!contacts.ParseFromIstream(&input)) {
cerr << "Failed to parse contacts." << endl;
input.close();
return -1;
}
// 新增一个联系人
AddPeopleInfo(contacts.add_contacts());
// 向磁盘文件写入新的 contacts
fstream output(argv[1], ios::out | ios::trunc | ios::binary);
if (!contacts.SerializeToOstream(&output))
{
cerr << "Failed to write contacts." << endl;
input.close();
output.close();
return -1;
}
input.close();
output.close();
google::protobuf::ShutdownProtobufLibrary();
return 0;
}service 目录下新增 makefile
bash
service:service.cc contacts.pb.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++11 -lprotobuf
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -f serviceclient 目录下新增 client.cc (通讯录 3.0),负责向读出文件中的通讯录消息,内容如下:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include "contacts.pb.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace c_contacts;
/**
* 打印联系人列表
*/
void PrintfContacts(const Contacts& contacts) {
for (int i = 0; i < contacts.contacts_size(); ++i) {
const PeopleInfo& people = contacts.contacts(i);
cout << "------------联系人" << i + 1 << "------------" << endl;
cout << "姓名:" << people.name() << endl;
cout << "年龄:" << people.age() << endl;
int j = 1;
for (const PeopleInfo_Phone& phone : people.phone()) {
cout << "电话" << j++ << ": " << phone.number() << endl;
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
GOOGLE_PROTOBUF_VERIFY_VERSION;
if (argc != 2) {
cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << "CONTACTS_FILE" << endl;
return -1;
}
// 以二进制方式读取 contacts
Contacts contacts;
fstream input(argv[1], ios::in | ios::binary);
if (!contacts.ParseFromIstream(&input)) {
cerr << "Failed to parse contacts." << endl;
input.close();
return -1;
}
// 打印 contacts
PrintfContacts(contacts);
input.close();
google::protobuf::ShutdownProtobufLibrary();
return 0;
}client 目录下新增 makefile
bash
client:client.cc contacts.pb.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++11 -lprotobuf
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -f client代码编写完成后,进行一次读写(读写前的编译过程省略,自行操作)。
bash
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/project/protobuf/update/service$ ./service
../contacts.bin
../contacts.bin: File not found. Creating a new file.
-------------新增联系人-------------
请输入联系人姓名: 张珊
请输入联系人年龄: 34
请输入联系人电话1(只输入回车完成电话新增): 131
请输入联系人电话2(只输入回车完成电话新增):
-----------添加联系人成功-----------
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/project/protobuf/update/client$ ./client ../contacts.bin
------------联系人1------------
姓名:张珊
年龄:34
电话1: 131确认无误后,对 service 目录下的 contacts.proto 文件进行更新:删除 age 字段,新增 birthday 字
段,新增的字段使用被删除字段的字段编号。
更新后的 contacts.proto(通讯录 3.0)内容如下:
bash
syntax = "proto3";
package s_contacts;
// 联系人
message PeopleInfo {
string name = 1; // 姓名
// 删除年龄字段
// int32 age = 2; // 年龄
int32 birthday = 2; // 生日
message Phone {
string number = 1; // 电话号码
}
repeated Phone phone = 3; // 电话
}
// 通讯录
message Contacts {
repeated PeopleInfo contacts = 1;
}编译文件 .proto 后,还需要更新一下对应的 service.cc(通讯录 3.0):
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include "contacts.pb.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace s_contacts;
/**
* 新增联系人
*/
void AddPeopleInfo(PeopleInfo* people_info_ptr)
{
cout << "-------------新增联系人-------------" << endl;
cout << "请输入联系人姓名: ";
string name;
getline(cin, name);
people_info_ptr->set_name(name);
/*cout << "请输入联系人年龄: ";
int age;
cin >> age;
people_info_ptr->set_age(age);
cin.ignore(256, '\n'); */
cout << "请输入联系人生日: ";
int birthday;
cin >> birthday;
people_info_ptr->set_birthday(birthday);
cin.ignore(256, '\n');
for (int i = 1; ; i++) {
cout << "请输入联系人电话" << i << "(只输入回车完成电话新增): ";
string number;
getline(cin, number);
if (number.empty()) {
break;
}
PeopleInfo_Phone* phone = people_info_ptr->add_phone();
phone->set_number(number);
}
cout << "-----------添加联系人成功-----------" << endl;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { ... }我们对 client 相关的代码保持原样,不进行更新。
再进行一次读写(对 service.cc 编译过程省略,自行操作)。
cpp
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/project/protobuf/update/service$ ./service
../contacts.bin
-------------新增联系人-------------
请输入联系人姓名: 李四
请输入联系人生日: 1221
请输入联系人电话1(只输入回车完成电话新增): 151
请输入联系人电话2(只输入回车完成电话新增):
-----------添加联系人成功-----------
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/project/protobuf/update/client$ ./client ../contacts.bin
------------联系人1------------
姓名:张珊
年龄:34
电话1: 131
------------联系人2------------
姓名:李四
年龄:1221
电话1: 151这时问题便出现了,我们发现输入的生日,在反序列化时,被设置到了使用了相同字段编号的年龄
上!!所以得出结论:若是移除老字段,要保证不再使用移除字段的字段编号,不建议直接删除或注释掉字段。
那么正确的做法是保留字段编号(reserved),以确保该编号将不能被重复使用。
正确 service 目录下的 contacts.proto 写法如下(终版通讯录 3.0)。
bash
syntax = "proto3";
package s_contacts;
// 联系人
message PeopleInfo {
reserved 2;
string name = 1; // 姓名
int32 birthday = 4; // 生日
message Phone {
string number = 1; // 电话号码
}
repeated Phone phone = 3; // 电话
}
// 通讯录
message Contacts {
repeated PeopleInfo contacts = 1;
}编译 .proto 文件后,还需要重新编译下 service.cc,让 service 程序保持使用新生成的 pb C++文件。
cpp
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/project/protobuf/update/service$ ./service
../contacts.bin
-------------新增联系人-------------
请输入联系人姓名: 王五
请输入联系人生日: 1112
请输入联系人电话1(只输入回车完成电话新增): 110
请输入联系人电话2(只输入回车完成电话新增):
-----------添加联系人成功-----------
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/project/protobuf/update/client$ ./client ../contacts.bin
------------联系人1------------
姓名:张珊
年龄:34
电话1: 131
------------联系人2------------
姓名:李四
年龄:1221
电话1: 151
------------联系人3------------
姓名:王五
年龄:0
电话1: 110根据实验结果,发现 '王五' 的年龄为 0,这是由于新增时未设置年龄,通过 client 程序反序列化
时,给年龄字段设置了默认值 0。这个结果显然是我们想看到的。
还要解释一下 '李四' 的年龄依旧使用了之前设置的生日字段 '1221',这是因为在新增 '李四'
的时候,生日字段的字段编号依旧为 2,并且已经被序列化到文件中了。最后再读取的时候,字段编号依旧为 2。
还要再说一下的是:因为使用了 reserved 关键字,ProtoBuf在编译阶段就拒绝了我们使用已经保留的字段编号。到此实验结束,也印证了我们的结论。
根据以上的例子,有的人可能还有一个疑问:如果使用了 reserved 2 了,那么 service 给 '王
五' 设置的生日 '1112',client 就没法读到了吗? 答案是可以的。继续学习下面的未知字段即可揭
晓答案。
8.3 未知字段
在通讯录 3.0 版本中,我们向 service 目录下的 contacts.proto 新增了'生日'字段,但对于 client 相
关的代码并没有任何改动。验证后发现 新代码序列化的消息(service)也可以被旧代码(client)解析。并且这里要说的是,新增的 '生日'字段在旧程序(client)中其实并没有丢失,而是会作为旧程序的未知字段。
• 未知字段:解析结构良好的 protocol buffer 已序列化数据中的未识别字段的表示方式。例如,当旧程序解析带有新字段的数据时,这些新字段就会成为旧程序的未知字段。
• 本来,proto3 在解析消息时总是会丢弃未知字段,但在 3.5 版本中重新引入了对未知字段的保留机制。所以在 3.5 或更高版本中,未知字段在反序列化时会被保留,同时也会包含在序列化的结果中。
8.3.1 未知字段从哪获取
了解相关类关系图
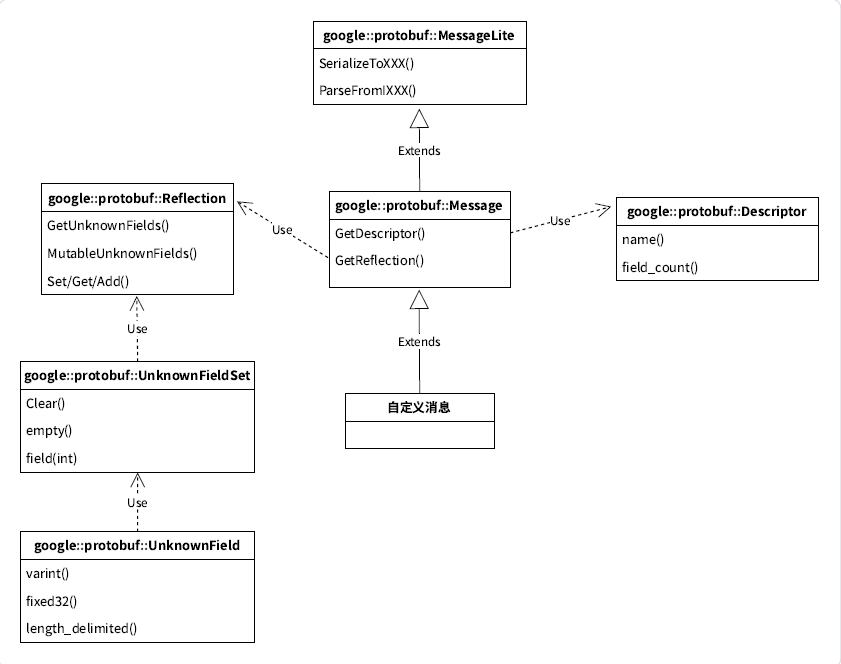
MessageLite 类介绍(了解)
• MessageLite 从名字看是轻量级的 message,仅仅提供序列化、反序列化功能。
• 类定义在 google 提供的 message_lite.h 中。
Message 类介绍(了解)
• 我们自定义的message类,都是继承自Message。
• Message 最重要的两个接口 GetDescriptor/GetReflection,可以获取该类型对应的Descriptor对象指针 和 Reflection 对象指针。
• 类定义在 google 提供的 message.h 中。
bash
//google::protobuf::Message 部分代码展示
const Descriptor* GetDescriptor() const;
const Reflection* GetReflection() const;Descriptor 类介绍(了解)
• Descriptor:是对message类型定义的描述,包括message的名字、所有字段的描述、原始的proto文件内容等。
• 类定义在 google 提供的 descriptor.h 中。
cpp
// 部分代码展示
class PROTOBUF_EXPORT Descriptor : private internal::SymbolBase {
string& name() const
int field_count() const;
const FieldDescriptor* field(int index) const;
const FieldDescriptor* FindFieldByNumber(int number) const;
const FieldDescriptor* FindFieldByName(const std::string& name) const;
const FieldDescriptor* FindFieldByLowercaseName(
const std::string& lowercase_name) const;
const FieldDescriptor* FindFieldByCamelcaseName(
const std::string& camelcase_name) const;
int enum_type_count() const;
const EnumDescriptor* enum_type(int index) const;
const EnumDescriptor* FindEnumTypeByName(const std::string& name) const;
const EnumValueDescriptor* FindEnumValueByName(const std::string& name)
const;
}Reflection 类介绍(了解)
• Reflection接口类,主要提供了动态读写消息字段的接口,对消息对象的自动读写主要通过该类完成。
• 提供方法来动态访问/修改message中的字段,对每种类型,Reflection都提供了一个单独的接口用于读写字段对应的值。
◦ 针对所有不同的field类型FieldDescriptor::TYPE_* ,需要使用不同的Get*()/Set*
()/Add*() 接口;
◦ repeated类型需要使用 GetRepeated*()/SetRepeated*() 接口,不可以和非repeated
类型接口混用;
◦ message对象只可以被由它自身的reflection(message.GetReflection()) 来操
作; • 类中还包含了访问/修改未知字段的方法。
• 类定义在 google 提供的 message.h 中。
cpp
// 部分代码展示
class PROTOBUF_EXPORT Reflection final {
const UnknownFieldSet& GetUnknownFields(const Message& message) const;
UnknownFieldSet* MutableUnknownFields(Message* message) const;
bool HasField(const Message& message, const FieldDescriptor* field) const;
int FieldSize(const Message& message, const FieldDescriptor* field) const;
void ClearField(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field) const;
bool HasOneof(const Message& message,
const OneofDescriptor* oneof_descriptor) const;
void ClearOneof(Message* message,
const OneofDescriptor* oneof_descriptor) const;
const FieldDescriptor* GetOneofFieldDescriptor(
const Message& message, const OneofDescriptor* oneof_descriptor) const;
// Singular field getters ------------------------------------------
// These get the value of a non-repeated field. They return the default
// value for fields that aren't set.
int32_t GetInt32(const Message& message, const FieldDescriptor* field) const;
int64_t GetInt64(const Message& message, const FieldDescriptor* field) const;
uint32_t GetUInt32(const Message& message,
const FieldDescriptor* field) const;
uint64_t GetUInt64(const Message& message,
const FieldDescriptor* field) const;
float GetFloat(const Message& message, const FieldDescriptor* field) const;
double GetDouble(const Message& message, const FieldDescriptor* field) const;
bool GetBool(const Message& message, const FieldDescriptor* field) const;
std::string GetString(const Message& message,
const FieldDescriptor* field) const;
const EnumValueDescriptor* GetEnum(const Message& message,
const FieldDescriptor* field) const;
int GetEnumValue(const Message& message, const FieldDescriptor* field) const;
const Message& GetMessage(const Message& message,
const FieldDescriptor* field,
MessageFactory* factory = nullptr) const;
// Singular field mutators -----------------------------------------
// These mutate the value of a non-repeated field.
void SetInt32(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int32_t value) const;
void SetInt64(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int64_t value) const;
void SetUInt32(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
uint32_t value) const;
void SetUInt64(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
uint64_t value) const;
void SetFloat(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
float value) const;
void SetDouble(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
double value) const;
void SetBool(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
bool value) const;
void SetString(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
std::string value) const;
void SetEnum(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
const EnumValueDescriptor* value) const;
void SetEnumValue(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int value) const;
Message* MutableMessage(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
MessageFactory* factory = nullptr) const;
PROTOBUF_NODISCARD Message* ReleaseMessage(
Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
MessageFactory* factory = nullptr) const;
// Repeated field getters ------------------------------------------
// These get the value of one element of a repeated field.
int32_t GetRepeatedInt32(const Message& message, const FieldDescriptor*
field,
int index) const;
int64_t GetRepeatedInt64(const Message& message, const FieldDescriptor*
field,
int index) const;
uint32_t GetRepeatedUInt32(const Message& message,
const FieldDescriptor* field, int index) const;
uint64_t GetRepeatedUInt64(const Message& message,
const FieldDescriptor* field, int index) const;
float GetRepeatedFloat(const Message& message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index) const;
double GetRepeatedDouble(const Message& message, const FieldDescriptor*
field,
int index) const;
bool GetRepeatedBool(const Message& message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index) const;
std::string GetRepeatedString(const Message& message,
const FieldDescriptor* field, int index) const;
const EnumValueDescriptor* GetRepeatedEnum(const Message& message,
const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index) const;
int GetRepeatedEnumValue(const Message& message, const FieldDescriptor*
field,
int index) const;
const Message& GetRepeatedMessage(const Message& message,
const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index) const;
const std::string& GetRepeatedStringReference(const Message& message,
const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index,
std::string* scratch) const;
// Repeated field mutators -----------------------------------------
// These mutate the value of one element of a repeated field.
void SetRepeatedInt32(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index, int32_t value) const;
void SetRepeatedInt64(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index, int64_t value) const;
void SetRepeatedUInt32(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index, uint32_t value) const;
void SetRepeatedUInt64(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index, uint64_t value) const;
void SetRepeatedFloat(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index, float value) const;
void SetRepeatedDouble(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index, double value) const;
void SetRepeatedBool(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index, bool value) const;
void SetRepeatedString(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index, std::string value) const;
void SetRepeatedEnum(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index, const EnumValueDescriptor* value) const;
void SetRepeatedEnumValue(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index, int value) const;
Message* MutableRepeatedMessage(Message* message,
const FieldDescriptor* field,
int index) const;
// Repeated field adders -------------------------------------------
// These add an element to a repeated field.
void AddInt32(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int32_t value) const;
void AddInt64(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int64_t value) const;
void AddUInt32(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
uint32_t value) const;
void AddUInt64(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
uint64_t value) const;
void AddFloat(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
float value) const;
void AddDouble(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
double value) const;
void AddBool(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
bool value) const;
void AddString(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
std::string value) const;
void AddEnum(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
const EnumValueDescriptor* value) const;
void AddEnumValue(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
int value) const;
Message* AddMessage(Message* message, const FieldDescriptor* field,
MessageFactory* factory = nullptr) const;
const FieldDescriptor* FindKnownExtensionByName(
const std::string& name) const;
const FieldDescriptor* FindKnownExtensionByNumber(int number) const;
bool SupportsUnknownEnumValues() const;
};UnknownFieldSet 类介绍(重要)
• UnknownFieldSet 包含在分析消息时遇到但未由其类型定义的所有字段。
• 若要将 UnknownFieldSet 附加到任何消息,请调用 Reflection::GetUnknownFields()。
• 类定义在 unknown_field_set.h 中。
cpp
class PROTOBUF_EXPORT UnknownFieldSet {
inline void Clear();
void ClearAndFreeMemory();
inline bool empty() const;
inline int field_count() const;
inline const UnknownField& field(int index) const;
inline UnknownField* mutable_field(int index);
// Adding fields ---------------------------------------------------
void AddVarint(int number, uint64_t value);
void AddFixed32(int number, uint32_t value);
void AddFixed64(int number, uint64_t value);
void AddLengthDelimited(int number, const std::string& value);
std::string* AddLengthDelimited(int number);
UnknownFieldSet* AddGroup(int number);
// Parsing helpers -------------------------------------------------
// These work exactly like the similarly-named methods of Message.
bool MergeFromCodedStream(io::CodedInputStream* input);
bool ParseFromCodedStream(io::CodedInputStream* input);
bool ParseFromZeroCopyStream(io::ZeroCopyInputStream* input);
bool ParseFromArray(const void* data, int size);
inline bool ParseFromString(const std::string& data) {
return ParseFromArray(data.data(), static_cast<int>(data.size()));
}
// Serialization.
bool SerializeToString(std::string* output) const;
bool SerializeToCodedStream(io::CodedOutputStream* output) const;
static const UnknownFieldSet& default_instance();
};UnknownField 类介绍(重要)
• 表示未知字段集中的一个字段。
• 类定义在 unknown_field_set.h 中。
cpp
class PROTOBUF_EXPORT UnknownField {
public:
enum Type {
TYPE_VARINT,
TYPE_FIXED32,
TYPE_FIXED64,
TYPE_LENGTH_DELIMITED,
TYPE_GROUP
};
inline int number() const;
inline Type type() const;
// Accessors -------------------------------------------------------
// Each method works only for UnknownFields of the corresponding type.
inline uint64_t varint() const;
inline uint32_t fixed32() const;
inline uint64_t fixed64() const;
inline const std::string& length_delimited() const;
inline const UnknownFieldSet& group() const;
inline void set_varint(uint64_t value);
inline void set_fixed32(uint32_t value);
inline void set_fixed64(uint64_t value);
inline void set_length_delimited(const std::string& value);
inline std::string* mutable_length_delimited();
inline UnknownFieldSet* mutable_group();
};8.3.2 升级通讯录 3.1 版本---验证未知字段
更新 client.cc (通讯录 3.1),在这个版本中,需要打印出未知字段的内容。更新的代码如下:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <google/protobuf/unknown_field_set.h>
#include "contacts.pb.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace c_contacts;
using namespace google::protobuf;
/**
* 打印联系人列表
*/
void PrintfContacts(const Contacts& contacts) {
for (int i = 0; i < contacts.contacts_size(); ++i) {
const PeopleInfo& people = contacts.contacts(i);
cout << "------------联系人" << i + 1 << "------------" << endl;
cout << "姓名:" << people.name() << endl;
cout << "年龄:" << people.age() << endl;
int j = 1;
for (const PeopleInfo_Phone& phone : people.phone()) {
cout << "电话" << j++ << ": " << phone.number() << endl;
}
// 打印未知字段
const Reflection* reflection = PeopleInfo::GetReflection();
const UnknownFieldSet& unknowSet = reflection->GetUnknownFields(people);
for (int j = 0; j < unknowSet.field_count(); j++) {
const UnknownField& unknow_field = unknowSet.field(j);
cout << "未知字段" << j + 1 << ":"
<< " 字段编号: " << unknow_field.number()
<< " 类型: " << unknow_field.type();
switch (unknow_field.type()) {
case UnknownField::Type::TYPE_VARINT:
cout << " 值: " << unknow_field.varint() << endl;
break;
case UnknownField::Type::TYPE_LENGTH_DELIMITED:
cout << " 值: " << unknow_field.length_delimited() << endl;
break;
}
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
GOOGLE_PROTOBUF_VERIFY_VERSION;
if (argc != 2) {
cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << "CONTACTS_FILE" << endl;
return -1;
}
// 以二进制方式读取 contacts
Contacts contacts;
fstream input(argv[1], ios::in | ios::binary);
if (!contacts.ParseFromIstream(&input)) {
cerr << "Failed to parse contacts." << endl;
input.close();
return -1;
}
// 打印 contacts
PrintfContacts(contacts);
input.close();
google::protobuf::ShutdownProtobufLibrary();
return 0;
}其他文件均不用做任何修改,重新编译 client.cc,进行一次读操作可得如下结果:
bash
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/project/protobuf/update/client$ ./client ../contacts.bin
------------联系人1------------
姓名:张珊
年龄:34
电话1: 131
------------联系人2------------
姓名:李四
年龄:1221
电话1: 151
------------联系人3------------
姓名:王五
年龄:0
电话1: 110
未知字段1: 字段编号: 4 类型: 0 值: 1112
类型为何为 0 ?在介绍 UnknownField 类中讲到了类中包含了未知字段的几种类型:
enum Type {
TYPE_VARINT,
TYPE_FIXED32,
TYPE_FIXED64,
TYPE_LENGTH_DELIMITED,
TYPE_GROUP
};
类型为 0,即为 TYPE_VARINT。8.4 前后兼容性
根据上述的例子可以得出,pb是具有向前兼容的。为了叙述方便,把增加了"生日"属性的 service
称为"新模块";未做变动的 client 称为 "老模块"。
• 向前兼容:老模块能够正确识别新模块生成或发出的协议。这时新增加的"生日"属性会被当作未知字段(pb 3.5版本及之后)。
• 向后兼容:新模块也能够正确识别老模块生成或发出的协议。
前后兼容的作用:当我们维护一个很庞大的分布式系统时,由于你无法同时 升级所有 模块,为了保证在升级过程中,整个系统能够尽可能不受影响,就需要尽量保证通讯协议的"向后兼容"或"向前兼容"。
9. 选项 option
.proto 文件中可以声明许多选项,使用 option 标注。选项能影响 proto 编译器的某些处理方式。
9.1 选项分类
选项的完整列表在google/protobuf/descriptor.proto中定义。部分代码:
bash
syntax = "proto2"; // descriptor.proto 使用 proto2 语法版本
message FileOptions { ... } // 文件选项 定义在 FileOptions 消息中
message MessageOptions { ... } // 消息类型选项 定义在 MessageOptions 消息中
message FieldOptions { ... } // 消息字段选项 定义在 FieldOptions 消息中
message OneofOptions { ... } // oneof字段选项 定义在 OneofOptions 消息中
message EnumOptions { ... } // 枚举类型选项 定义在 EnumOptions 消息中
message EnumValueOptions { .. } // 枚举值选项 定义在 EnumValueOptions 消息中
message ServiceOptions { ... } // 服务选项 定义在 ServiceOptions 消息中
message MethodOptions { ... } // 服务方法选项 定义在 MethodOptions 消息中
...由此可见,选项分为文件级、消息级、字段级等等, 但并没有一种选项能作用于所有的类型。
9.2 常用选项列举
• optimize_for : 该选项为文件选项**,可以设置 protoc 编译器的优化级别** ,分别为 SPEED 、
CODE_SIZE 、LITE_RUNTIME 。受该选项影响,设置不同的优化级别,编译 .proto 文件后生成的代码内容不同。◦ SPEED : protoc 编译器将生成的代码是高度优化的,代码运行效率高,但是由此生成的代码编译后会占用更多的空间 。SPEED 是默认选项。
◦ CODE_SIZE : proto 编译器将生成最少的类,会占用更少的空间,是依赖基于反射的代码来实现序列化、反序列化和各种其他操作 。但和SPEED 恰恰相反,它的代码运行效率较低。这种方式适合用在包含大量的.proto文件,但并不盲目追求速度的应用中。
◦ LITE_RUNTIME :生成的代码执行效率高,同时生成代码编译后的所占用的空间也是非常少 。这是以牺牲Protocol Buffer提供的反射功能为代价的,仅仅提供 encoding+序列化 功能,所以我们在链接 BP 库时仅需链接libprotobuf-lite,而非libprotobuf。这种模式通常用于资源有限的平台,例如移动手机平台中。
bash
option optimize_for = LITE_RUNTIME;• allow_alias : 允许将相同的常量值分配给不同的枚举常量,用来定义别名。该选项为枚举选项。举个例子:
bash
enum PhoneType {
option allow_alias = true;
MP = 0;
TEL = 1;
LANDLINE = 1; // 若不加 option allow_alias = true; 这一行会编译报错
}9.3 设置自定义选项
ProtoBuf 允许自定义选项并使用。该功能大部分场景用不到,在这里不拓展讲解。
有兴趣可以参考:https://developers.google.cn/protocol-buffers/docs/proto?hl=zhcn#customoptions
六、通讯录 4.0 实现---网络版
Protobuf 还常用于通讯协议、服务端数据交换场景。那么在这个示例中,我们将实现一个网络版本的通讯录,模拟实现客户端与服务端的交互,通过 Protobuf 来实现各端之间的协议序列化。
需求如下:
• 客户端可以选择对通讯录进行以下操作:
◦ 新增一个联系人
◦ 删除一个联系人
◦ 查询通讯录列表
◦ 查询一个联系人的详细信息
• 服务端提供 增 删 查 能力,并需要持久化通讯录。
• 客户端、服务端间的交互数据使用 Protobuf 来完成。
1. 环境搭建
Httplib 库:cpp-httplib 是个开源的库,是一个c++封装的http库,使用这个库可以在linux、
windows平台下完成http客户端、http服务端的搭建。使用起来非常方便,只需要包含头文件
httplib.h 即可。编译程序时,需要带上 -lpthread 选项。
源码库地址:https://github.com/yhirose/cpp-httplib
2. centos 下编写的注意事项
如果使用 centOS 环境,yum源带的 g++ 最新版本是4.8.5,发布于2015年,年代久远。编译该项目会出现异常。将 gcc/g++ 升级为更高版本可解决问题。
bash
# 升级参考:https://juejin.cn/post/6844903873111392263
# 安装gcc 8版本
yum install -y devtoolset-8-gcc devtoolset-8-gcc-c++
# 启用版本
source /opt/rh/devtoolset-8/enable
# 查看版本已经变成gcc 8.3.1
gcc -v3. 约定双端交互接口
新增一个联系人:
bash
[请求]
Post /contacts/add AddContactRequest
Content-Type: application/protobuf
[响应]
AddContactResponse
Content-Type: application/protobuf删除一个联系人:
bash
[请求]
Post /contacts/del DelContactRequest
Content-Type: application/protobuf
[响应]
DelContactResponse
Content-Type: application/protobuf查询通讯录列表:
bash
[请求]
GET /contacts/find-all
[响应]
FindAllContactsResponse
Content-Type: application/protobuf查询一个联系人的详细信息:
bash
[请求]
Post /contacts/find-one FindOneContactRequest
Content-Type: application/protobuf
[响应]
FindOneContactResponse
Content-Type: application/protobuf4. 约定双端交互req/resp
base_response.proto
bash
syntax = "proto3";
package base_response;
message BaseResponse {
bool success = 1; // 返回结果
string error_desc = 2; // 错误描述
}add_contact_request.proto
bash
syntax = "proto3";
package add_contact_req;
// 新增联系人 req
message AddContactRequest {
string name = 1; // 姓名
int32 age = 2; // 年龄
message Phone {
string number = 1; // 电话号码
enum PhoneType {
MP = 0; // 移动电话
TEL = 1; // 固定电话
}
PhoneType type = 2; // 类型
}
repeated Phone phone = 3; // 电话
map<string, string> remark = 4; // 备注
}add_contact_response.proto
bash
syntax = "proto3";
package add_contact_resp;
import "base_response.proto"; // 引入base_response
message AddContactResponse {
base_response.BaseResponse base_resp = 1;
string uid = 2;
}del_contact_request.proto
bash
syntax = "proto3";
package del_contact_req;
// 删除一个联系人 req
message DelContactRequest {
string uid = 1; // 联系人ID
}del_contact_response.proto
bash
syntax = "proto3";
package del_contact_resp;
import "base_response.proto"; // 引入base_response
// 删除一个联系人 resp
message DelContactResponse {
base_response.BaseResponse base_resp = 1;
string uid = 2;
}find_one_contact_request.proto
bash
syntax = "proto3";
package find_one_contact_req;
// 查询一个联系人 req
message FindOneContactRequest {
string uid = 1; // 联系人ID
}find_one_contact_response.proto
bash
syntax = "proto3";
package find_one_contact_resp;
import "base_response.proto"; // 引入base_response
// 查询一个联系人 resp
message FindOneContactResponse {
base_response.BaseResponse base_resp = 1;
string uid = 2; // 联系人ID
string name = 3; // 姓名
int32 age = 4; // 年龄
message Phone {
string number = 1; // 电话号码
enum PhoneType {
MP = 0; // 移动电话
TEL = 1; // 固定电话
}
PhoneType type = 2; // 类型
}
repeated Phone phone = 5; // 电话
map<string, string> remark = 6; // 备注
}find_all_contacts_response.proto
bash
syntax = "proto3";
package find_all_contacts_resp;
import "base_response.proto"; // 引入base_response
// 联系人摘要信息
message PeopleInfo {
string uid = 1; // 联系人ID
string name = 2; // 姓名
}
// 查询所有联系人 resp
message FindAllContactsResponse {
base_response.BaseResponse base_resp = 1;
repeated PeopleInfo contacts = 2;
}5. 客户端代码实现
cpp
void menu() {
std::cout << "-----------------------------------------------------" <<
std::endl
<< "--------------- 请选择对通讯录的操作 ----------------" <<
std::endl
<< "------------------ 1、新增联系人 --------------------" <<
std::endl
<< "------------------ 2、删除联系人 --------------------" <<
std::endl
<< "------------------ 3、查看联系人列表 ----------------" <<
std::endl
<< "------------------ 4、查看联系人详细信息 ------------" <<
std::endl
<< "------------------ 0、退出 --------------------------" <<
std::endl
<< "-----------------------------------------------------" <<
std::endl;
}
int main() {
enum OPERATE { ADD = 1, DEL, FIND_ALL, FIND_ONE };
ContactsServer contactsServer;
while (true) {
menu();
std::cout << "---> 请选择:";
int choose;
std::cin >> choose;
std::cin.ignore(256, '\n');
try {
switch (choose) {
case OPERATE::ADD:
contactsServer.addContact();
break;
case OPERATE::DEL:
contactsServer.delContact();
break;
case OPERATE::FIND_ALL:
contactsServer.findContacts();
break;
case OPERATE::FIND_ONE:
contactsServer.findContact();
break;
case 0:
std::cout << "---> 程序已退出" << std::endl;
return 0;
default:
std::cout << "---> 无此选项,请重新选择!" << std::endl;
break;
}
}
catch (const ContactException& e) {
std::cerr << "---> 操作通讯录时发现异常!!!" << std::endl
<< "---> 异常信息:" << e.what() << std::endl;
}
catch (const std::exception& e) {
std::cerr << "---> 操作通讯录时发现异常!!!" << std::endl
<< "---> 异常信息:" << e.what() << std::endl;
}
}
}ContactException.h:定义异常类
cpp
// 自定义异常类
class ContactException
{
private:
std::string message;
public:
ContactException(std::string str = "A problem") : message{str} {}
std::string what() const { return message; }
};ContactsServer.h:客户端通讯录服务定义
cpp
class ContactsServer
{
public:
void addContact();
void delContact();
void findContacts();
void findContact();
private:
void buildAddContactRequest(add_contact_req::AddContactRequest* req);
void
printFindOneContactResponse(find_one_contact_resp::FindOneContactResponse&
resp);
void
printFindAllContactsResponse(find_all_contacts_resp::FindAllContactsResponse&
resp);
};ContactsServer.cc:客户端通讯录服务实现
cpp
#define CONTACTS_IP "43.138.218.166"
#define CONTACTS_PORT 8123
void ContactsServer::addContact() {
httplib::Client cli(CONTACTS_IP, CONTACTS_PORT);
// 构建 request 请求
add_contact_req::AddContactRequest req;
buildAddContactRequest(&req);
// 序列化 request
std::string req_str;
if (!req.SerializeToString(&req_str)) {
throw ContactException("AddContactRequest序列化失败!");
}
// 发起 post 请求
auto res = cli.Post("/contacts/add", req_str, "application/protobuf");
if (!res) {
std::string err_desc;
err_desc.append("/contacts/add 链接错误!错误信息:")
.append(httplib::to_string(res.error()));
throw ContactException(err_desc);
}
// 反序列化 response
add_contact_resp::AddContactResponse resp;
bool parse = resp.ParseFromString(res->body);
// 处理异常
if (res->status != 200 && !parse) {
std::string err_desc;
err_desc.append("post '/contacts/add/' 失败:")
.append(std::to_string(res->status))
.append("(").append(res->reason)
.append(")");
throw ContactException(err_desc);
}
else if (res->status != 200) {
// 处理服务异常
std::string err_desc;
err_desc.append("post '/contacts/add/' 失败 ")
.append(std::to_string(res->status))
.append("(").append(res->reason)
.append(") 错误原因:")
.append(resp.base_resp().error_desc());
throw ContactException(err_desc);
}
else if (!resp.base_resp().success()) {
// 处理结果异常
std::string err_desc;
err_desc.append("post '/contacts/add/' 结果异常:")
.append("异常原因:")
.append(resp.base_resp().error_desc());
throw ContactException(err_desc);
}
// 正常返回,打印结果
std::cout << "---> 新增联系人成功,联系人ID:" << resp.uid() << std::endl;
}
void ContactsServer::delContact() {
httplib::Client cli(CONTACTS_IP, CONTACTS_PORT);
// 构建 request 请求
del_contact_req::DelContactRequest req;
std::cout << "请输入要删除的联系人id: ";
std::string uid;
getline(std::cin, uid);
req.set_uid(uid);
// 序列化 request
std::string req_str;
if (!req.SerializeToString(&req_str)) {
throw ContactException("DelContactRequest序列化失败!");
}
// 发起 post 请求
auto res = cli.Post("/contacts/del", req_str, "application/protobuf");
if (!res) {
std::string err_desc;
err_desc.append("/contacts/del 链接错误!错误信息:")
.append(httplib::to_string(res.error()));
throw ContactException(err_desc);
}
// 反序列化 response
del_contact_resp::DelContactResponse resp;
bool parse = resp.ParseFromString(res->body);
// 处理异常
if (res->status != 200 && !parse) {
std::string err_desc;
err_desc.append("post '/contacts/del' 失败:")
.append(std::to_string(res->status))
.append("(").append(res->reason)
.append(")");
throw ContactException(err_desc);
}
else if (res->status != 200) {
std::string err_desc;
err_desc.append("post '/contacts/del' 失败 ")
.append(std::to_string(res->status))
.append("(").append(res->reason)
.append(") 错误原因:")
.append(resp.base_resp().error_desc());
throw ContactException(err_desc);
}
else if (!resp.base_resp().success()) {
// 结果异常
std::string err_desc;
err_desc.append("post '/contacts/del' 结果异常:")
.append("异常原因:")
.append(resp.base_resp().error_desc());
throw ContactException(err_desc);
}
// 正常返回,打印结果
std::cout << "---> 成功删除联系人,被删除的联系人ID为:" << resp.uid() <<
std::endl;
}
void ContactsServer::findContacts() {
httplib::Client cli(CONTACTS_IP, CONTACTS_PORT);
// 发起 get 请求
auto res = cli.Get("/contacts/find-all");
if (!res) {
std::string err_desc;
err_desc.append("/contacts/find-all 链接错误!错误信息:")
.append(httplib::to_string(res.error()));
throw ContactException(err_desc);
}
// 反序列化 response
find_all_contacts_resp::FindAllContactsResponse resp;
bool parse = resp.ParseFromString(res->body);
// 处理异常
if (res->status != 200 && !parse) {
std::string err_desc;
err_desc.append("get '/contacts/find-all' 失败:")
.append(std::to_string(res->status))
.append("(").append(res->reason)
.append(")");
throw ContactException(err_desc);
}
else if (res->status != 200) {
// 服务端异常
std::string err_desc;
err_desc.append("post '/contacts/find-all' 失败 ")
.append(std::to_string(res->status))
.append("(").append(res->reason)
.append(") 错误原因:")
.append(resp.base_resp().error_desc());
throw ContactException(err_desc);
}
else if (!resp.base_resp().success()) {
// 结果异常
std::string err_desc;
err_desc.append("post '/contacts/find-all' 结果异常:")
.append("异常原因:")
.append(resp.base_resp().error_desc());
throw ContactException(err_desc);
}
// 正常返回,打印结果
printFindAllContactsResponse(resp);
}
void ContactsServer::findContact() {
httplib::Client cli(CONTACTS_IP, CONTACTS_PORT);
// 构建 request 请求
find_one_contact_req::FindOneContactRequest req;
std::cout << "请输入要查询的联系人id: ";
std::string uid;
getline(std::cin, uid);
req.set_uid(uid);
// 序列化 request
std::string req_str;
if (!req.SerializeToString(&req_str)) {
throw ContactException("FindOneContactRequest序列化失败!");
}
// 发起 post 请求
auto res = cli.Post("/contacts/find-one", req_str, "application/protobuf");
if (!res) {
std::string err_desc;
err_desc.append("/contacts/find-one 链接错误!错误信息:")
.append(httplib::to_string(res.error()));
throw ContactException(err_desc);
}
// 反序列化 response
find_one_contact_resp::FindOneContactResponse resp;
bool parse = resp.ParseFromString(res->body);
// 处理异常
if (res->status != 200 && !parse) {
std::string err_desc;
err_desc.append("post '/contacts/find-one' 失败:")
.append(std::to_string(res->status))
.append("(").append(res->reason)
.append(")");
throw ContactException(err_desc);
}
else if (res->status != 200) {
std::string err_desc;
err_desc.append("post '/contacts/find-one' 失败 ")
.append(std::to_string(res->status))
.append("(").append(res->reason)
.append(") 错误原因:")
.append(resp.base_resp().error_desc());
throw ContactException(err_desc);
}
else if (!resp.base_resp().success()) {
// 结果异常
std::string err_desc;
err_desc.append("post '/contacts/find-one' 结果异常:")
.append("异常原因:")
.append(resp.base_resp().error_desc());
throw ContactException(err_desc);
}
// 正常返回,打印结果
std::cout << "---> 查询到联系人ID为:" << resp.uid() << " 的信息:" <<
std::endl;
printFindOneContactResponse(resp);
}
void ContactsServer::printFindAllContactsResponse(
find_all_contacts_resp::FindAllContactsResponse& resp) {
if (0 == resp.contacts_size()) {
std::cout << "还未添加任何联系人" << std::endl;
return;
}
for (auto contact : resp.contacts()) {
std::cout << "联系人姓名: " << contact.name() << " 联系人ID:" <<
contact.uid() << std::endl;
}
}
void
ContactsServer::buildAddContactRequest(add_contact_req::AddContactRequest* req)
{
std::cout << "请输入联系人姓名: ";
std::string name;
getline(std::cin, name);
req->set_name(name);
std::cout << "请输入联系人年龄: ";
int age;
std::cin >> age;
req->set_age(age);
std::cin.ignore(256, '\n');
for (int i = 1; ; i++) {
std::cout << "请输入联系人电话" << i << "(只输入回车完成电话新增): ";
std::string number;
getline(std::cin, number);
if (number.empty()) {
break;
}
add_contact_req::AddContactRequest_Phone* phone = req->add_phone();
phone->set_number(number);
std::cout << "选择此电话类型 (1、移动电话 2、固定电话) : ";
int type;
std::cin >> type;
std::cin.ignore(256, '\n');
switch (type) {
case 1:
phone->set_type(
add_contact_req::AddContactRequest_Phone_PhoneType::AddContactRequest_Phone_Pho
neType_MP);
break;
case 2:
phone->set_type(
add_contact_req::AddContactRequest_Phone_PhoneType::AddContactRequest_Phone_Pho
neType_TEL);
break;
default:
std::cout << "----非法选择,使用默认值!" << std::endl;
break;
}
}
for (int i = 1; ; i++) {
std::cout << "请输入备注" << i << "标题 (只输入回车完成备注新增): ";
std::string remark_key;
getline(std::cin, remark_key);
if (remark_key.empty()) {
break;
}
std::cout << "请输入备注" << i << "内容: ";
std::string remark_value;
getline(std::cin, remark_value);
req->mutable_remark()->insert({ remark_key, remark_value });
}
}
void ContactsServer::printFindOneContactResponse(
find_one_contact_resp::FindOneContactResponse&
resp) {
std::cout << "姓名:" << resp.name() << std::endl;
std::cout << "年龄:" << resp.age() << std::endl;
for (auto& phone : resp.phone()) {
int j = 1;
std::cout << "电话" << j++ << ": " << phone.number();
std::cout << " (" << phone.PhoneType_Name(phone.type()) << ")" <<
std::endl;
}
if (resp.remark_size()) {
std::cout << "备注信息: " << std::endl;
}
for (auto it = resp.remark().cbegin(); it != resp.remark().cend(); ++it) {
std::cout << " " << it->first << ": " << it->second << std::endl;
}
}客户端完整代码:
https://gitee.com/hyb91/protobuf/tree/master/http_contacts_by_protobuf/linux_client
6. 服务端代码实现
服务端存储通讯录结构定义:contacts.proto
bash
syntax = "proto3";
package contacts;
// 联系人
message PeopleInfo {
string uid = 1; // 联系人ID
string name = 2; // 姓名
int32 age = 3; // 年龄
message Phone {
string number = 1; // 电话号码
enum PhoneType {
MP = 0; // 移动电话
TEL = 1; // 固定电话
}
PhoneType type = 2; // 类型
}
repeated Phone phone = 4; // 电话
map<string, string> remark = 5; // 备注
}
// 通讯录
message Contacts {
map<string, PeopleInfo> contacts = 1;
}
cpp
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::cerr;
using namespace httplib;
int main() {
cout << "---> 服务启动..." << endl;
Server srv; // 创建服务端对象
ContactsServer contactsServer;
srv.Post("/contacts/add", [contactsServer](const Request& req, Response&
res) {
add_contact_req::AddContactRequest request;
add_contact_resp::AddContactResponse response;
try {
// 反序列化 request
if (!request.ParseFromString(req.body)) {
throw ContactException("Parse AddContactRequest error!");
}
// 新增联系人
contactsServer.add(request, &response);
// 序列化 resp
std::string response_str;
if (!response.SerializeToString(&response_str)) {
throw ContactException("Serialize AddContactResponse error");
}
res.body = response_str;
res.set_header("Content-Type", "application/protobuf");
res.status = 200;
}
catch (ContactException& e) {
cerr << "---> /contacts/add 发现异常!!!" << endl
<< "---> 异常信息:" << e.what() << endl;
res.status = 500;
base_response::BaseResponse* baseResponse =
response.mutable_base_resp();
baseResponse->set_success(false);
baseResponse->set_error_desc(e.what());
std::string response_str;
if (response.SerializeToString(&response_str)) {
res.body = response_str;
res.set_header("Content-Type", "application/protobuf");
}
}
});
srv.Post("/contacts/del", [contactsServer](const Request& req, Response&
res) {
del_contact_req::DelContactRequest request;
del_contact_resp::DelContactResponse response;
try {
// 反序列化 request
if (!request.ParseFromString(req.body)) {
throw ContactException("Parse DelContactRequest error!");
}
// 删除联系人
contactsServer.del(request, &response);
// 序列化 response
std::string response_str;
if (!response.SerializeToString(&response_str)) {
throw ContactException("Serialize DelContactResponse error");
}
res.body = response_str;
res.set_header("Content-Type", "application/protobuf");
res.status = 200;
}
catch (ContactException& e) {
cerr << "---> /contacts/del 发现异常!!!" << endl
<< "---> 异常信息:" << e.what() << endl;
res.status = 500;
base_response::BaseResponse* baseResponse =
response.mutable_base_resp();
baseResponse->set_success(false);
baseResponse->set_error_desc(e.what());
std::string response_str;
if (response.SerializeToString(&response_str)) {
res.body = response_str;
res.set_header("Content-Type", "application/protobuf");
}
}
});
srv.Post("/contacts/find-one", [contactsServer](const Request& req,
Response& res) {
find_one_contact_req::FindOneContactRequest request;
find_one_contact_resp::FindOneContactResponse response;
try {
// 反序列化 request
if (!request.ParseFromString(req.body)) {
throw ContactException("Parse FindOneContactRequest error!");
}
// 查询联系人详细信息
contactsServer.findOne(request, &response);
// 序列化 response
std::string response_str;
if (!response.SerializeToString(&response_str)) {
throw ContactException("Serialize FindOneContactResponse
error");
}
res.body = response_str;
res.set_header("Content-Type", "application/protobuf");
res.status = 200;
}
catch (ContactException& e) {
cerr << "---> /contacts/find-one 发现异常!!!" << endl
<< "---> 异常信息:" << e.what() << endl;
res.status = 500;
base_response::BaseResponse* baseResponse =
response.mutable_base_resp();
baseResponse->set_success(false);
baseResponse->set_error_desc(e.what());
std::string response_str;
if (response.SerializeToString(&response_str)) {
res.body = response_str;
res.set_header("Content-Type", "application/protobuf");
}
}
});
srv.Get("/contacts/find-all", [contactsServer](const Request& req,
Response& res) {
find_all_contacts_resp::FindAllContactsResponse response;
try {
// 查询所有联系人
contactsServer.findAll(&response);
// 序列化 response
std::string response_str;
if (!response.SerializeToString(&response_str)) {
throw ContactException("Serialize FindAllContactsResponse
error");
}
res.body = response_str;
res.set_header("Content-Type", "application/protobuf");
res.status = 200;
}
catch (ContactException& e) {
cerr << "---> /contacts/find-all 发现异常!!!" << endl
<< "---> 异常信息:" << e.what() << endl;
res.status = 500;
base_response::BaseResponse* baseResponse =
response.mutable_base_resp();
baseResponse->set_success(false);
baseResponse->set_error_desc(e.what());
std::string response_str;
if (response.SerializeToString(&response_str)) {
res.body = response_str;
res.set_header("Content-Type", "application/protobuf");
}
}
});
srv.listen("0.0.0.0", 8123);
}ContactException.h:定义异常类
cpp
// 自定义异常类
class ContactException
{
private:
std::string message;
public:
ContactException(std::string str = "A problem") : message{ str } {}
std::string what() const { return message; }
};ContactsServer.h:通讯录服务定义
cpp
using namespace httplib;
class ContactsServer {
public:
ContactsMapper contactsMapper;
public:
void add(add_contact_req::AddContactRequest& request,
add_contact_resp::AddContactResponse* response) const;
void del(del_contact_req::DelContactRequest& request,
del_contact_resp::DelContactResponse* response) const;
void findOne(find_one_contact_req::FindOneContactRequest request,
find_one_contact_resp::FindOneContactResponse* response)
const;
void findAll(find_all_contacts_resp::FindAllContactsResponse* rsp) const;
private:
void printAddContactRequest(add_contact_req::AddContactRequest& request)
const;
void buildPeopleInfo(contacts::PeopleInfo* people,
add_contact_req::AddContactRequest& request) const;
void buildFindOneContactResponse(const contacts::PeopleInfo& people,
find_one_contact_resp::FindOneContactResponse* response) const;
void buildFindAllContactsResponse(contacts::Contacts& contacts,
find_all_contacts_resp::FindAllContactsResponse* rsp) const;
};ContactsServer.cc:通讯录服务实现
cpp
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
void ContactsServer::add(add_contact_req::AddContactRequest& request,
add_contact_resp::AddContactResponse* response) const
{
// 打印日志
printAddContactRequest(request);
// 先读取已存在的 contacts
contacts::Contacts contacts;
contactsMapper.selectContacts(&contacts);
// 转换为存入文件的消息对象
google::protobuf::Map<std::string, contacts::PeopleInfo>* map_contacts =
contacts.mutable_contacts();
contacts::PeopleInfo people;
buildPeopleInfo(&people, request);
map_contacts->insert({ people.uid(), people });
// 向磁盘文件写入新的 contacts
contactsMapper.insertContacts(contacts);
response->set_uid(people.uid());
response->mutable_base_resp()->set_success(true);
// 打印日志
cout << "---> (ContactsServer::add) Success to write contacts." << endl;
}
void ContactsServer::del(del_contact_req::DelContactRequest& request,
del_contact_resp::DelContactResponse* response) const
{
// 打印日志
cout << "---> (ContactsServer::del) DelContactRequest: uid: " <<
request.uid() << endl;
// 先读取已存在的 contacts
contacts::Contacts contacts;
contactsMapper.selectContacts(&contacts);
// 不含uid直接返回
if (contacts.contacts().find(request.uid()) == contacts.contacts().end())
{
cout << "---> (ContactsServer::del) not find uid: " << request.uid()
<< endl;
response->set_uid(request.uid());
response->mutable_base_resp()->set_success(false);
response->mutable_base_resp()->set_error_desc("not find uid");
return;
}
// 删除用户
contacts.mutable_contacts()->erase(request.uid());
// 向磁盘文件写入新的 contacts
contactsMapper.insertContacts(contacts);
// 构造resp
response->set_uid(request.uid());
response->mutable_base_resp()->set_success(true);
// 打印日志
cout << "---> (ContactsServer::del) Success to del contact, uid: " <<
request.uid() << endl;
}
void ContactsServer::findOne(find_one_contact_req::FindOneContactRequest
request,
find_one_contact_resp::FindOneContactResponse*
response) const {
// 打印日志
cout << "---> (ContactsServer::findOne) FindOneContactRequest: uid: " <<
request.uid() << endl;
// 获取通讯录
contacts::Contacts contacts;
contactsMapper.selectContacts(&contacts);
// 转换resp消息对象
const google::protobuf::Map<std::string, contacts::PeopleInfo>&
map_contacts = contacts.contacts();
auto it = map_contacts.find(request.uid());
// 查找的联系人不存在
if (it == map_contacts.end()) {
cout << "---> (ContactsServer::findOne) not find uid: " <<
request.uid() << endl;
response->mutable_base_resp()->set_success(false);
response->mutable_base_resp()->set_error_desc("uid not exist");
return;
}
// 构建resp
buildFindOneContactResponse(it->second, response);
// 打印日志
cout << "---> (ContactsServer::findOne) find uid: " << request.uid() <<
endl;
}
void ContactsServer::findAll(find_all_contacts_resp::FindAllContactsResponse*
rsp) const {
// 打印日志
cout << "---> (ContactsServer::findAll) " << endl;
// 获取通讯录
contacts::Contacts contacts;
contactsMapper.selectContacts(&contacts);
// 转换resp消息对象
buildFindAllContactsResponse(contacts, rsp);
}
void ContactsServer::buildFindAllContactsResponse(contacts::Contacts&
contacts,
find_all_contacts_resp::FindAllContactsResponse* rsp) const {
if (nullptr == rsp) {
return;
}
rsp->mutable_base_resp()->set_success(true);
for (auto it = contacts.contacts().cbegin(); it !=
contacts.contacts().cend(); ++it) {
find_all_contacts_resp::PeopleInfo* people = rsp->add_contacts();
people->set_uid(it->first);
people->set_name(it->second.name());
}
}
void ContactsServer::buildFindOneContactResponse(const contacts::PeopleInfo&
people,
find_one_contact_resp::FindOneContactResponse* response) const {
if (nullptr == response) {
return;
}
response->mutable_base_resp()->set_success(true);
response->set_uid(people.uid());
response->set_name(people.name());
response->set_age(people.age());
for (auto& phone : people.phone()) {
find_one_contact_resp::FindOneContactResponse_Phone* resp_phone =
response->add_phone();
resp_phone->set_number(phone.number());
switch (phone.type()) {
case
contacts::PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType::PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType_MP:resp_phone->set_type(find_one_contact_resp::FindOneContactResponse_Phone_PhoneType::FindOneContactResponse_Phone_PhoneType_MP);
break;
case
contacts::PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType::PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType_TEL:resp_phone->set_type(find_one_contact_resp::FindOneContactResponse_Phone_PhoneType::FindOneContactResponse_Phone_PhoneType_TEL);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
Utils::map_copy(response->mutable_remark(), people.remark());
}
void
ContactsServer::printAddContactRequest(add_contact_req::AddContactRequest&
request) const {
cout << "---> (ContactsServer::add) AddContactRequest:" << endl;
cout << "姓名:" << request.name() << endl;
cout << "年龄:" << request.age() << endl;
for (auto& phone : request.phone()) {
int j = 1;
cout << "电话" << j++ << ": " << phone.number();
cout << " (" << phone.PhoneType_Name(phone.type()) << ")" << endl;
}
if (request.remark_size()) {
cout << "备注信息: " << endl;
}
for (auto it = request.remark().cbegin(); it != request.remark().cend();
++it) {
cout << " " << it->first << ": " << it->second << endl;
}
}
void ContactsServer::buildPeopleInfo(contacts::PeopleInfo* people,
add_contact_req::AddContactRequest& request) const {
std::string uid = Utils::generate_hex(10);
people->set_uid(uid);
people->set_name(request.name());
people->set_age(request.age());
for (auto& phone : request.phone()) {
contacts::PeopleInfo_Phone* peo_phone = people->add_phone();
peo_phone->set_number(phone.number());
switch (phone.type()) {
case
add_contact_req::AddContactRequest_Phone_PhoneType::AddContactRequest_Phone_PhoneType_MP:
peo_phone->set_type(contacts::PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType::PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType_MP);
break;
case
add_contact_req::AddContactRequest_Phone_PhoneType::AddContactRequest_Phone_Pho
neType_TEL :
peo_phone->set_type(contacts::PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType::PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType_TEL);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
Utils::map_copy(people->mutable_remark(), request.remark());
}Utils.h :定义工具类
cpp
#include <sstream>
#include <random>
#include <google/protobuf/map.h>
class Utils
{
public:
static unsigned int random_char() {
// 用于随机数引擎获得随机种子
std::random_device rd;
// mt19937是c++11新特性,它是一种随机数算法,用法与rand()函数类似,但是mt19937
具有速度快,周期长的特点
// 作用是生成伪随机数
std::mt19937 gen(rd());
// 随机生成一个整数i 范围[0, 255]
std::uniform_int_distribution<> dis(0, 255);
return dis(gen);
}
// 生成 UUID (通用唯一标识符)
static std::string generate_hex(const unsigned int len) {
std::stringstream ss;
// 生成 len 个16进制随机数,将其拼接而成
for (auto i = 0; i < len; i++) {
const auto rc = random_char();
std::stringstream hexstream;
hexstream << std::hex << rc;
auto hex = hexstream.str();
ss << (hex.length() < 2 ? '0' + hex : hex);
}
return ss.str();
}
static void map_copy(google::protobuf::Map<std::string, std::string>*
target,
const google::protobuf::Map<std::string,
std::string>& source) {
if (nullptr == target) {
std::cout << "map_copy warning, target is nullptr!" << std::endl;
return;
}
for (auto it = source.cbegin(); it != source.cend(); ++it) {
target->insert({ it->first, it->second });
}
}
};ContactsMapper.h:持久化存储通讯录方法定义
cpp
class ContactsMapper{
public:
void selectContacts(contacts::Contacts* contacts) const;
void insertContacts(contacts::Contacts& contacts) const;
};ContactsMapper.cc:持久化存储通讯录方法实现
注:本应该存入数据库中,在这里为了简化流程,将通讯录存入本地文件
cpp
#define TEXT_NAME "contacts.bin"
using std::ios;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
// 本应该存入数据库中,在这里为了简化流程,将通讯录存入本地文件
void ContactsMapper::selectContacts(contacts::Contacts* contacts) const {
std::fstream input(TEXT_NAME, ios::in | ios::binary);
if (!input) {
cout << "---> (ContactsMapper::selectContacts) " << TEXT_NAME << ":
File not found.Creating a new file." << endl;
}
else if (!contacts->ParseFromIstream(&input)) {
input.close();
throw ContactException("(ContactsMapper::selectContacts) Failed to
parse contacts.");
}
input.close();
}
void ContactsMapper::insertContacts(contacts::Contacts& contacts) const {
std::fstream output(TEXT_NAME, ios::out | ios::trunc | ios::binary);
if (!contacts.SerializeToOstream(&output)) {
output.close();
throw ContactException("(ContactsMapper::insertContacts) Failed to
write contacts.");
}
output.close();
}服务端完整代码:
https://gitee.com/hyb91/protobuf/tree/master/http_contacts_by_protobuf/linux_service
七、总结
1. 序列化能力对比验证
在这里让我们分别使用 PB 与 JSON 的序列化与反序列化能力, 对值完全相同的一份结构化数据进行不同次数的性能测试。
为了可读性,下面这一份文本使用 JSON 格式展示了需要被进行测试的结构化数据内容:
bash
{
"age": 20,
"name": "张珊",
"phone": [
{
"number": "110112119",
"type": 0
},
{
"number": "110112119",
"type": 0
},
{
"number": "110112119",
"type": 0
},
{
"number": "110112119",
"type": 0
},
{
"number": "110112119",
"type": 0
}
],
"qq": "95991122",
"address": {
"home_address": "陕西省西安市长安区",
"unit_address": "陕西省西安市雁塔区"
},
"remark": {
"key1": "value1",
"key2": "value2",
"key3": "value3",
"key4": "value4",
"key5": "value5"
}
}开始进行测试代码编写,我们在新的目录下新建 contacts.proto文件,内容如下:
bash
syntax = "proto3";
package compare_serialization;
import "google/protobuf/any.proto"; // 引入 any.proto 文件
// 地址
message Address{
string home_address = 1; // 家庭地址
string unit_address = 2; // 单位地址
}
// 联系人
message PeopleInfo {
string name = 1; // 姓名
int32 age = 2; // 年龄
message Phone {
string number = 1; // 电话号码
enum PhoneType {
MP = 0; // 移动电话
TEL = 1; // 固定电话
}
PhoneType type = 2; // 类型
}
repeated Phone phone = 3; // 电话
google.protobuf.Any data = 4;
oneof other_contact { // 其他联系方式:多选一
string qq = 5;
string weixin = 6;
}
map<string, string> remark = 7; // 备注
}使用 protoc 命令编译文件后,新建性能测试文件 compare.cc,我们分别对相同的结构化数据进行
100 、1000 、10000 、100000 次的序列化与反序列化,分别获取其耗时与序列化后的大小。
内容如下:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <jsoncpp/json/json.h>
#include "contacts.pb.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace compare_serialization;
using namespace google::protobuf;
#define TEST_COUNT 100
void createPeopleInfoFromPb(PeopleInfo* people_info_ptr);
void createPeopleInfoFromJson(Json::Value& root);
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
struct timeval t_start, t_end;
double time_used;
int count;
string pb_str, json_str;
// ------------------------------Protobuf 序列化------------------------------
------
{
PeopleInfo pb_people;
createPeopleInfoFromPb(&pb_people);
count = TEST_COUNT;
gettimeofday(&t_start, NULL);
// 序列化count次
while ((count--) > 0) {
pb_people.SerializeToString(&pb_str);
}
gettimeofday(&t_end, NULL);
time_used = 1000000 * (t_end.tv_sec - t_start.tv_sec) + t_end.tv_usec -
t_start.tv_usec;
cout << TEST_COUNT << "次 [pb序列化]耗时:" << time_used / 1000 << "ms."
<< " 序列化后的大小:" << pb_str.length() << endl;
}
// ------------------------------Protobuf 反序列化----------------------------
--------
{
PeopleInfo pb_people;
count = TEST_COUNT;
gettimeofday(&t_start, NULL);
// 反序列化count次
while ((count--) > 0) {
pb_people.ParseFromString(pb_str);
}
gettimeofday(&t_end, NULL);
time_used = 1000000 * (t_end.tv_sec - t_start.tv_sec) + t_end.tv_usec -
t_start.tv_usec;
cout << TEST_COUNT << "次 [pb反序列化]耗时:" << time_used / 1000 << "ms."
<< endl;
}
// ------------------------------JSON 序列化----------------------------------
--
{
Json::Value json_people;
createPeopleInfoFromJson(json_people);
Json::StreamWriterBuilder builder;
count = TEST_COUNT;
gettimeofday(&t_start, NULL);
// 序列化count次
while ((count--) > 0) {
json_str = Json::writeString(builder, json_people);
}
gettimeofday(&t_end, NULL);
// 打印序列化结果
// cout << "json: " << endl << json_str << endl;
time_used = 1000000 * (t_end.tv_sec - t_start.tv_sec) + t_end.tv_usec -
t_start.tv_usec;
cout << TEST_COUNT << "次 [json序列化]耗时:" << time_used / 1000 << "ms."
<< " 序列化后的大小:" << json_str.length() << endl;
}
// ------------------------------JSON 反序列化--------------------------------
----
{
Json::CharReaderBuilder builder;
unique_ptr<Json::CharReader> reader(builder.newCharReader());
Json::Value json_people;
count = TEST_COUNT;
gettimeofday(&t_start, NULL);
// 反序列化count次
while ((count--) > 0) {
reader->parse(json_str.c_str(), json_str.c_str() + json_str.length(),
&json_people, nullptr);
}
gettimeofday(&t_end, NULL);
time_used = 1000000 * (t_end.tv_sec - t_start.tv_sec) + t_end.tv_usec -
t_start.tv_usec;
cout << TEST_COUNT << "次 [json反序列化]耗时:" << time_used / 1000 << "ms."
<< endl;
}
return 0;
}
/**
* 构造pb对象
*/
void createPeopleInfoFromPb(PeopleInfo* people_info_ptr)
{
people_info_ptr->set_name("张珊");
people_info_ptr->set_age(20);
people_info_ptr->set_qq("95991122");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
PeopleInfo_Phone* phone = people_info_ptr->add_phone();
phone->set_number("110112119");
phone->set_type(PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType::PeopleInfo_Phone_PhoneType_MP);
}
Address address;
address.set_home_address("陕西省西安市长安区");
address.set_unit_address("陕西省西安市雁塔区");
google::protobuf::Any* data = people_info_ptr->mutable_data();
data->PackFrom(address);
people_info_ptr->mutable_remark()->insert({ "key1", "value1" });
people_info_ptr->mutable_remark()->insert({ "key2", "value2" });
people_info_ptr->mutable_remark()->insert({ "key3", "value3" });
people_info_ptr->mutable_remark()->insert({ "key4", "value4" });
people_info_ptr->mutable_remark()->insert({ "key5", "value5" });
}
/**
* 构造json对象
*/
void createPeopleInfoFromJson(Json::Value& root) {
root["name"] = "张珊";
root["age"] = 20;
root["qq"] = "95991122";
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
Json::Value phone;
phone["number"] = "110112119";
phone["type"] = 0;
root["phone"].append(phone);
}
Json::Value address;
address["home_address"] = "陕西省西安市长安区";
address["unit_address"] = "陕西省西安市雁塔区";
root["address"] = address;
Json::Value remark;
remark["key1"] = "value1";
remark["key2"] = "value2";
remark["key3"] = "value3";
remark["key4"] = "value4";
remark["key5"] = "value5";
root["remark"] = remark;
}Makefile
bash
compare:compare.cc contacts.pb.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++11 -lprotobuf -ljsoncpp
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -f compare测试结果如下:
bash
100次 [pb序列化]耗时:0.342ms. 序列化后的大小:278
100次 [pb反序列化]耗时:0.435ms.
100次 [json序列化]耗时:1.306ms. 序列化后的大小:567
100次 [json反序列化]耗时:0.926ms.
1000次 [pb序列化]耗时:3.59ms. 序列化后的大小:278
1000次 [pb反序列化]耗时:5.069ms.
1000次 [json序列化]耗时:11.582ms. 序列化后的大小:567
1000次 [json反序列化]耗时:9.289ms.
10000次 [pb序列化]耗时:34.386ms. 序列化后的大小:278
10000次 [pb反序列化]耗时:45.96ms.
10000次 [json序列化]耗时:115.76ms. 序列化后的大小:567
10000次 [json反序列化]耗时:91.046ms.
100000次 [pb序列化]耗时:349.937ms. 序列化后的大小:278
100000次 [pb反序列化]耗时:428.366ms.
100000次 [json序列化]耗时:1150.54ms. 序列化后的大小:567
100000次 [json反序列化]耗时:904.58ms.由实验结果可粗略得:
• 编解码性能:ProtoBuf 的编码解码性能,比 JSON 高出 2-4 倍。
• 内存占用:ProtoBuf 的内存278,而JSON到达567,ProtoBuf的内存占用只有JSON的1/2。
注:以上结论的数据只是根据该项实验得出。因为受不同的字段类型、字段个数等影响,测出的数据会有所差异。
该实验有很多可待优化的地方。但其实这种粗略的测试,也能看出来 ProtoBuf 的优势。
2. 总结
| 序列化协议 | 通用性 | 格式 | 可读性 | 序列化大 小 | 序列化性能 | 适用场景 |
| JSON | 通用 (json、 xml已成为多种 行业标准的编 写工具) | 文本格式 | 好 | 轻量(使 用键值对 方式,压 缩了一定 的数据空 间) | 中 | web项目。因为浏览 器对于json数据支持 非常好,有很多内建 的函数支持。 |
| XML | 通用 | 文本格式 | 好 | 重量(数 据冗余, 因为需要 成对的闭 合标签) | 低 | XML 作为一种扩展标 记语言,衍生出了 HTML、RDF/RDFS, 它强调数据结构化的 能力和可读性。 |
| ProtoBuf | 独立 (Protobuf只 是Google公司 内部的工具) | 二进制格式 | 差(只能 反序列化 后得到真 正可读的 数据) | 轻量(比 JSON更轻 量,传输 起来带宽 和速度会 有优化) | 高 | 适合高性能,对响应 速度有要求的数据传 输场景。Protobuf比 XML、JSON 更小、 更快。 |
|---|
小结:
- XML、JSON、ProtoBuf 都具有数据结构化和数据序列化的能力
。
XML、JSON 更注重数据结构化,关注可读性和语义表达能力 。ProtoBuf 更注重数据序列化,关注效率、空间、速度,可读性差,语义表达能力不足,为保证极致的效率,会舍弃一部分元信息。
ProtoBuf 的应用场景更为明确,XML、JSON 的应用场景更为丰富。