目录
- 前言
- 一、list的介绍
- 二、list的使用
-
- [1. 构造函数和拷贝构造函数](#1. 构造函数和拷贝构造函数)
- [2. 析构函数](#2. 析构函数)
- [3. 赋值运算符重载operator=](#3. 赋值运算符重载operator=)
- [4. 迭代器begin/end、rbegin/rend](#4. 迭代器begin/end、rbegin/rend)
- [5. empty/size](#5. empty/size)
- [6. front/back](#6. front/back)
- [7. assign](#7. assign)
- [8. push_front/pop_front/push_back/pop_back](#8. push_front/pop_front/push_back/pop_back)
- [9. insert/erase](#9. insert/erase)
- [10. swap/clear](#10. swap/clear)
- 11.resize
- 12.reverse
- [13. sort](#13. sort)
- [14. merge](#14. merge)
- [15. unique](#15. unique)
- [16. remove](#16. remove)
- [17. splice](#17. splice)
- 三、完整代码
前言
前面介绍了【C++】STL容器--vector的模拟实现详情请点击,本文将学习另一个STL容器--list,本文主要讲解list的使用
一、list的介绍
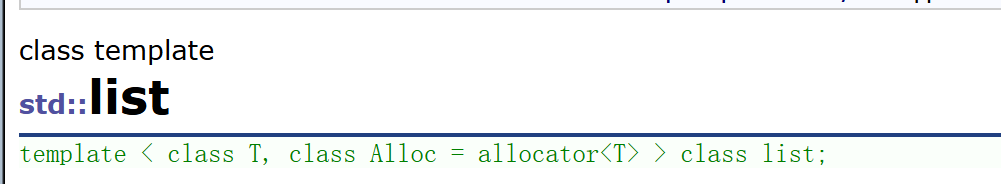
- list 是标准模板库(STL)中的一个容器,它实现了一个双向链表
- 支持在任意位置快速插入和删除元素,但不支持快速随机访问
二、list的使用
1. 构造函数和拷贝构造函数
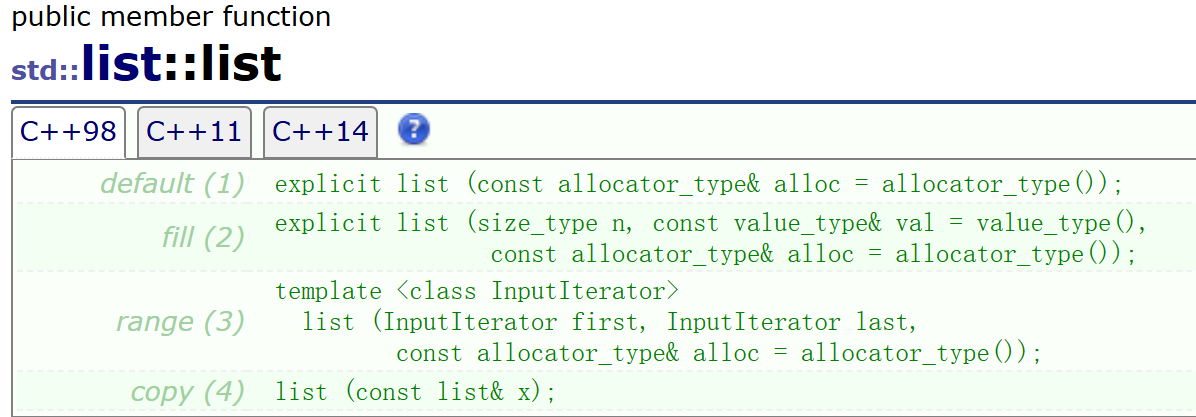
- 构造函数有全缺省的构造,缺省值allocator_type()是空间配置器,避免频繁向堆上申请空间,提高效率,默认不传参即可
- 还可以使用n个值进行初始化
- 构造函数还可以使用迭代器进行初始化,迭代器可以是list类型也可以是其他类型
cpp
void test_list1()
{
list<int> lt1;
list<int> lt2(5, 4);
list<int> lt3(lt2.begin(), lt2.end());
vector<int> v(4, 7);
list<int> lt4(v.begin() + 1, v.end() - 1);
list<int> lt5(lt4);
}2. 析构函数
析构函数在list生命周期结束后自动调用完成资源清理工作

3. 赋值运算符重载operator=
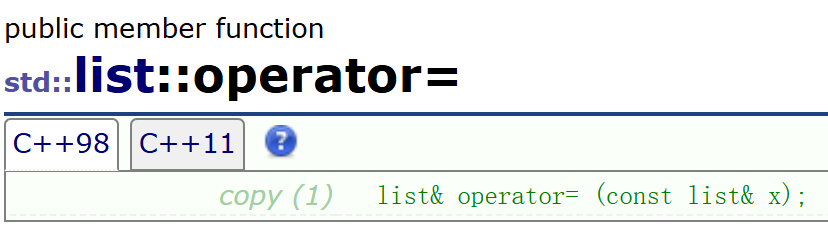
- 注意使用赋值运算符时,list对象已经创建,否则就会调用拷贝构造函数
cpp
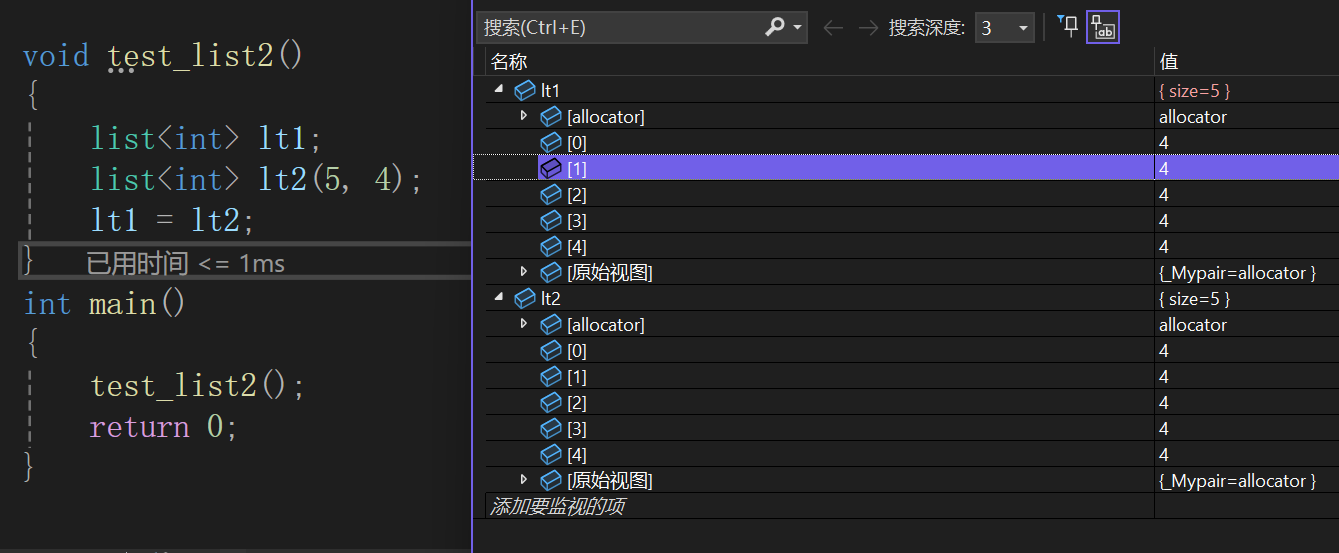
void test_list2()
{
list<int> lt1;
list<int> lt2(5, 4);
lt1 = lt2;
}
4. 迭代器begin/end、rbegin/rend
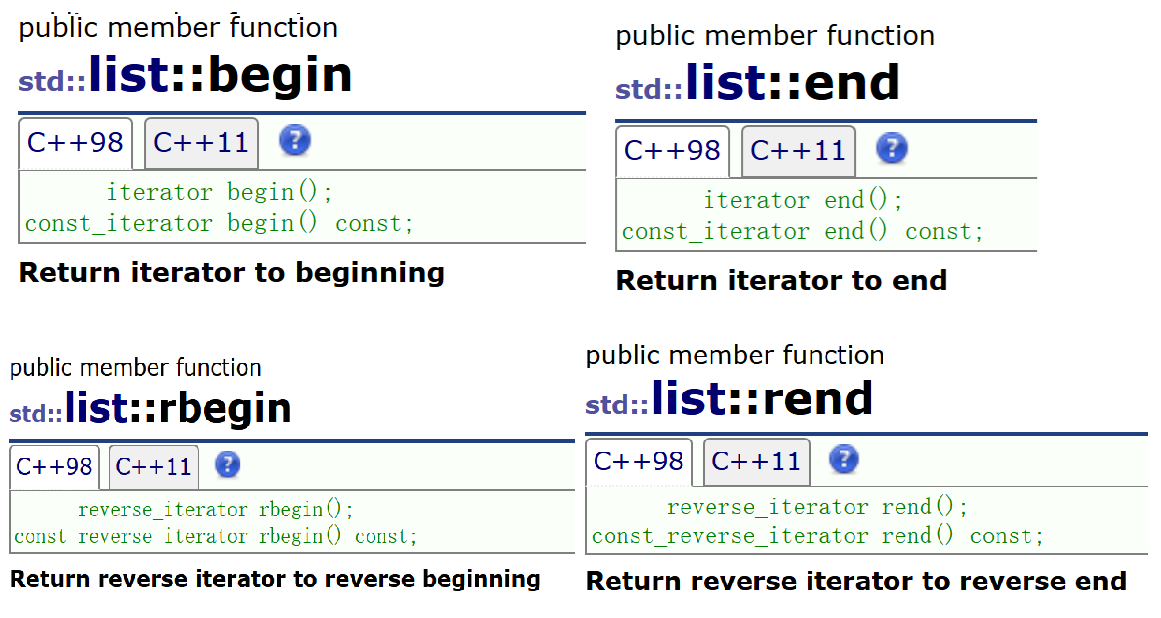
- begin/end、rbegin/rend都是获得开头或结尾位置的迭代器
cpp
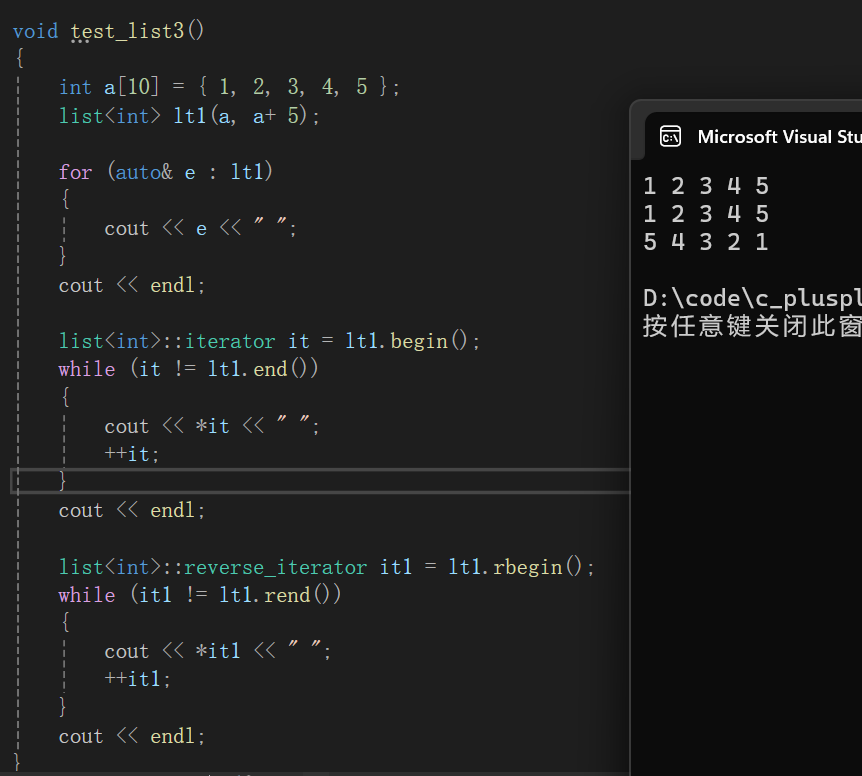
void test_list3()
{
int a[10] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
list<int> lt1(a, a+ 5);
for (auto& e : lt1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
list<int>::iterator it = lt1.begin();
while (it != lt1.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
list<int>::reverse_iterator it1 = lt1.rbegin();
while (it1 != lt1.rend())
{
cout << *it1 << " ";
++it1;
}
cout << endl;
}
5. empty/size
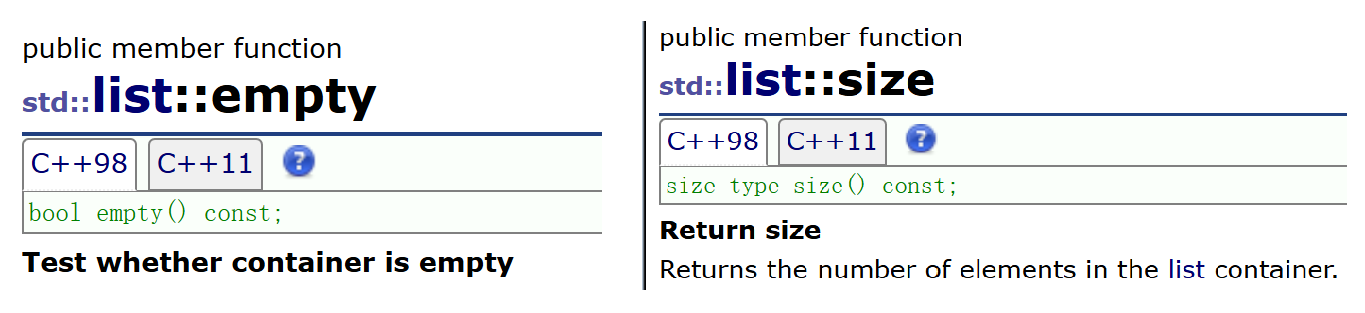
- empty:判断list是否为空
- size:返回有效数据个数
cpp
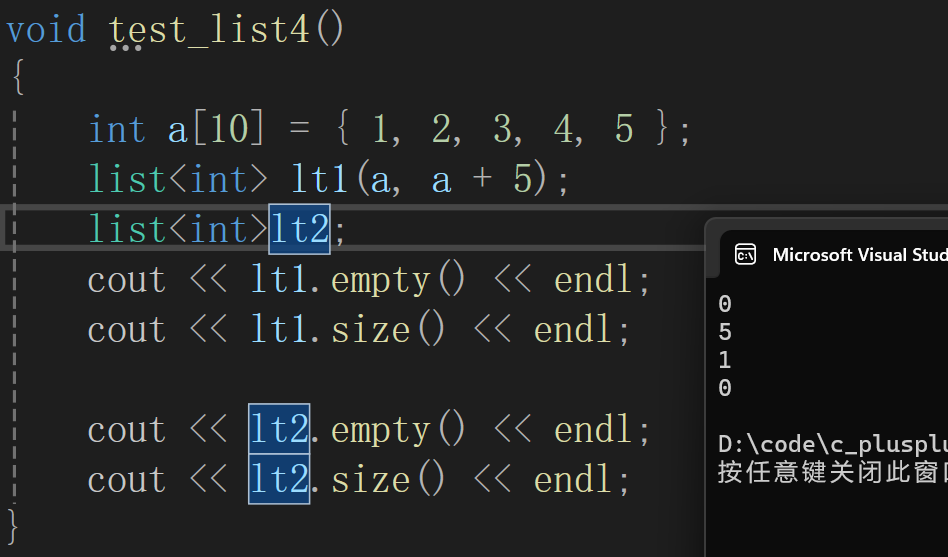
void test_list4()
{
int a[10] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
list<int> lt1(a, a + 5);
list<int>lt2;
cout << lt1.empty() << endl;
cout << lt1.size() << endl;
cout << lt2.empty() << endl;
cout << lt2.size() << endl;
}
6. front/back

front/back返回list第一个位置/最后一个位置数据的引用,可以访问和修改
7. assign

assin会将数据全部清空,再重新传入你需要的数据
cpp
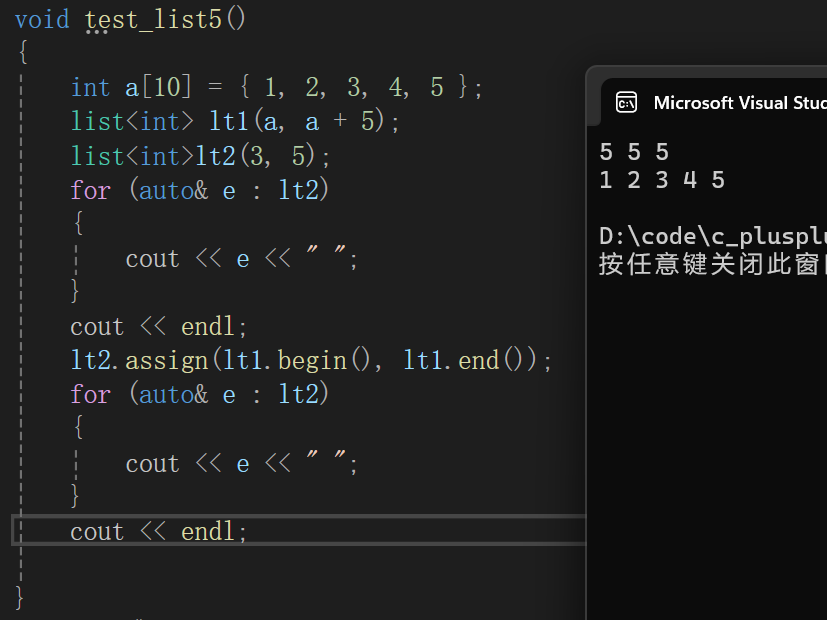
void test_list5()
{
int a[10] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
list<int> lt1(a, a + 5);
list<int>lt2(3, 5);
for (auto& e : lt2)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt2.assign(lt1.begin(), lt1.end());
for (auto& e : lt2)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
8. push_front/pop_front/push_back/pop_back
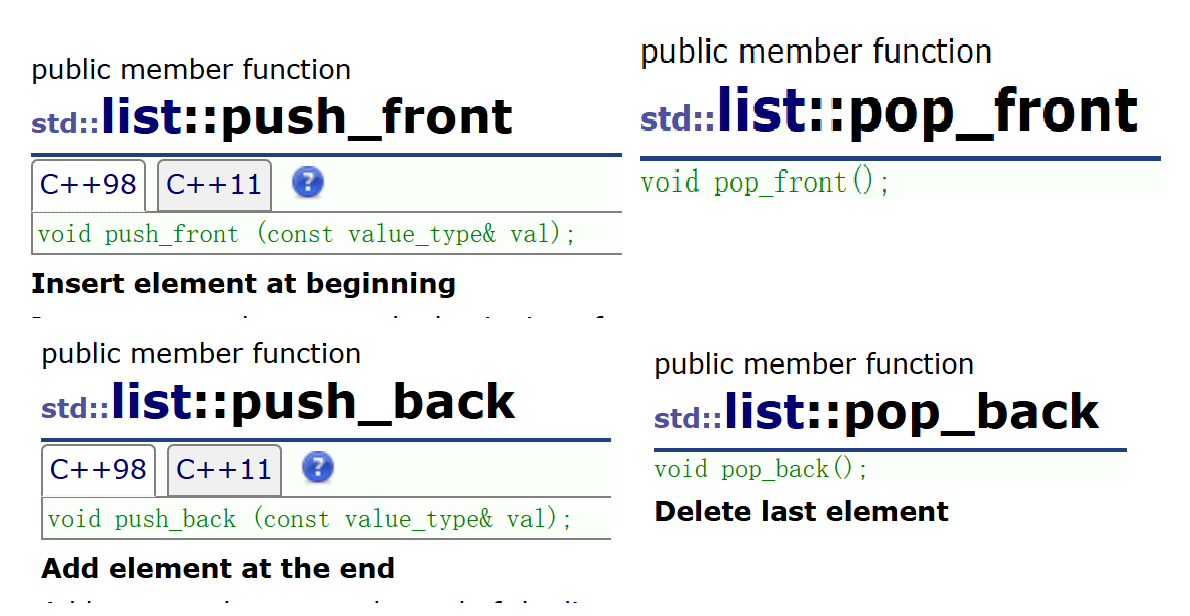
push_front/pop_front/push_back/pop_back分别是头插、头删、尾插、尾删
cpp
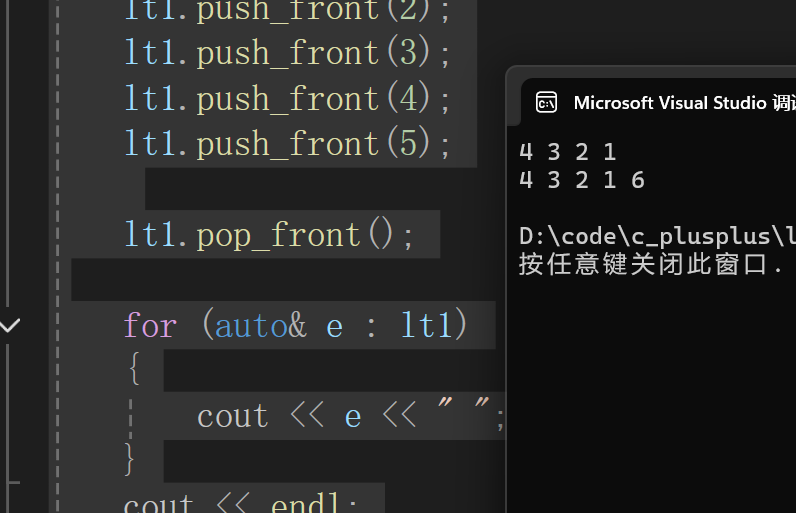
void test_list6()
{
list<int> lt1;
lt1.push_front(1);
lt1.push_front(2);
lt1.push_front(3);
lt1.push_front(4);
lt1.push_front(5);
lt1.pop_front();
for (auto& e : lt1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt1.push_back(6);
lt1.push_back(7);
lt1.pop_back();
for (auto& e : lt1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
9. insert/erase
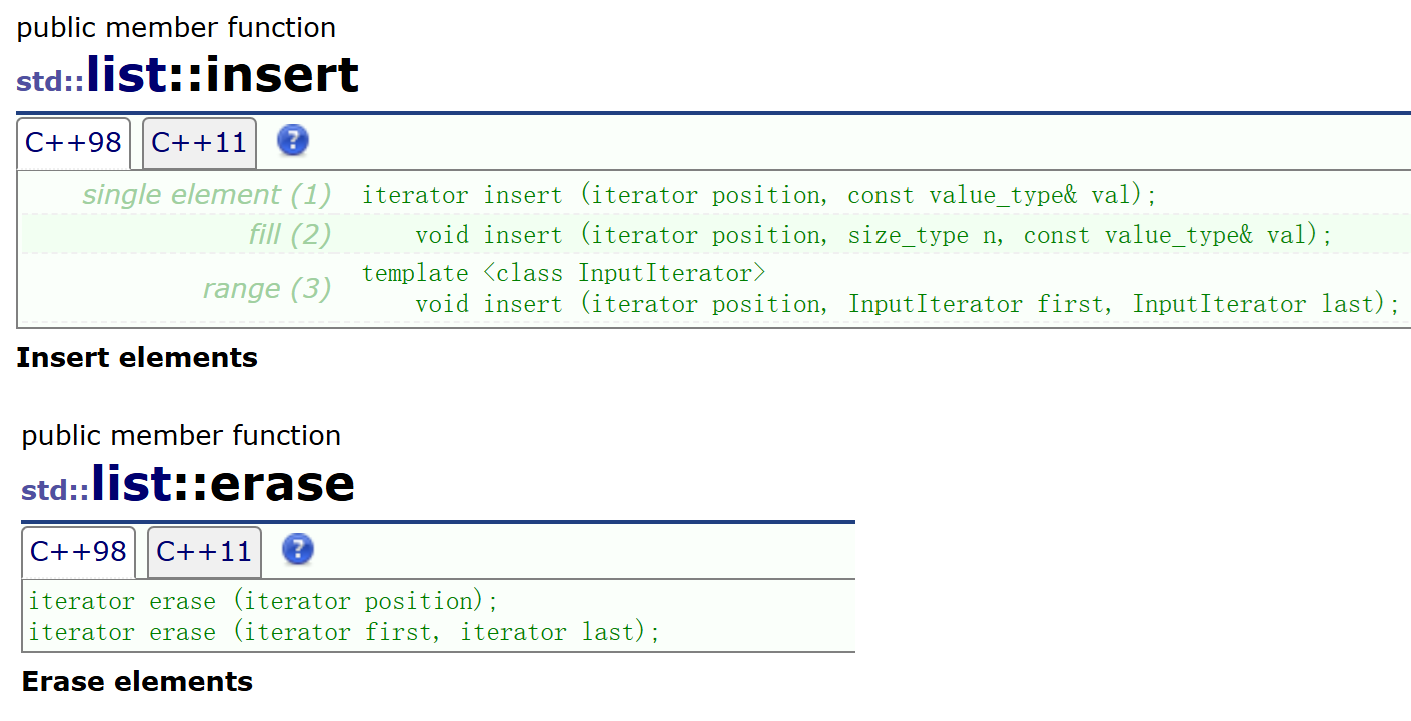
- list的insert不涉及迭代器失效问题,因为list的插入和删除是对链表节点做处理,并不会涉及异地扩容问题,但是erase会涉及迭代器失效问题,erase进行删除就是释放迭代器指向的节点,并改变节点之间的连接关系,节点被释放,那么再访问这个节点就会报错
- insert再迭代器位置插入一个值,并返回插入元素的迭代器;insert在迭代器位置插入n个值;insert在迭代器位置插入一段迭代区间
- insert在中间某个位置插入,需要使用循环迭代到那个位置再插入
- erase会返回一个迭代器,这个返回的迭代器是删除节点的下一个节点的迭代器,如果后续还要进行操作,可以接收这个返回值
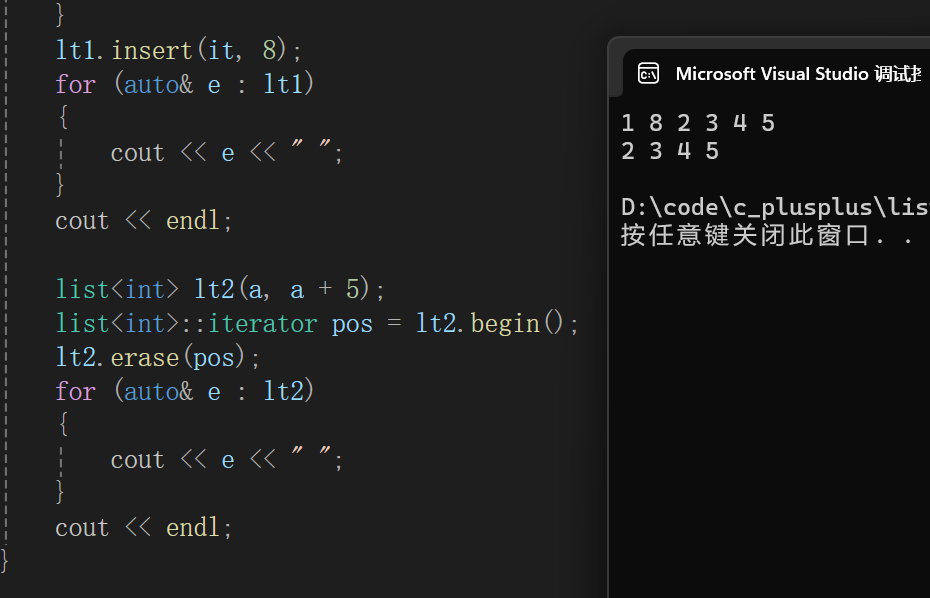
cpp
void test_list7()
{
int a[10] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
list<int> lt1(a, a + 5);
list<int>::iterator it = lt1.begin();
int ret = 1;
while (ret--)
{
it++;
}
lt1.insert(it, 8);
for (auto& e : lt1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
list<int> lt2(a, a + 5);
list<int>::iterator pos = lt2.begin();
lt2.erase(pos);
for (auto& e : lt2)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
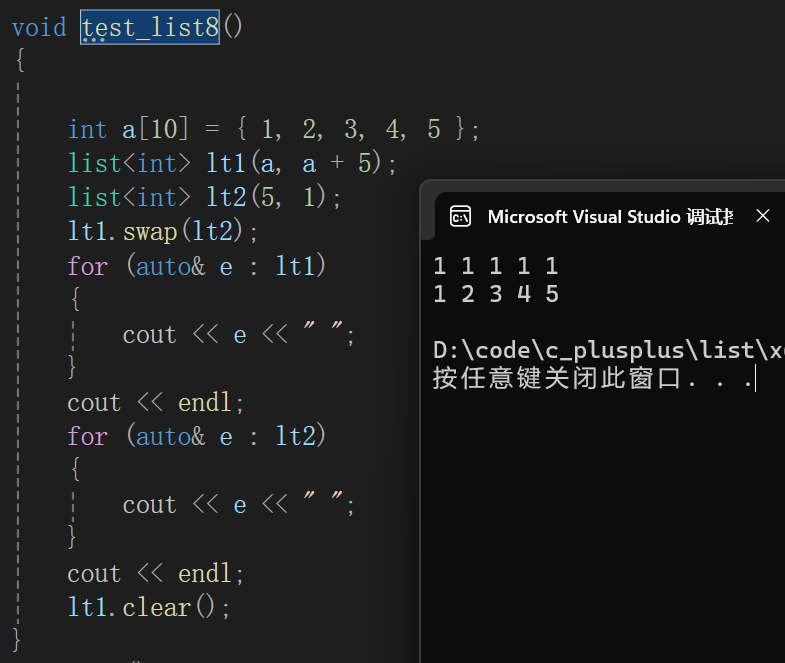
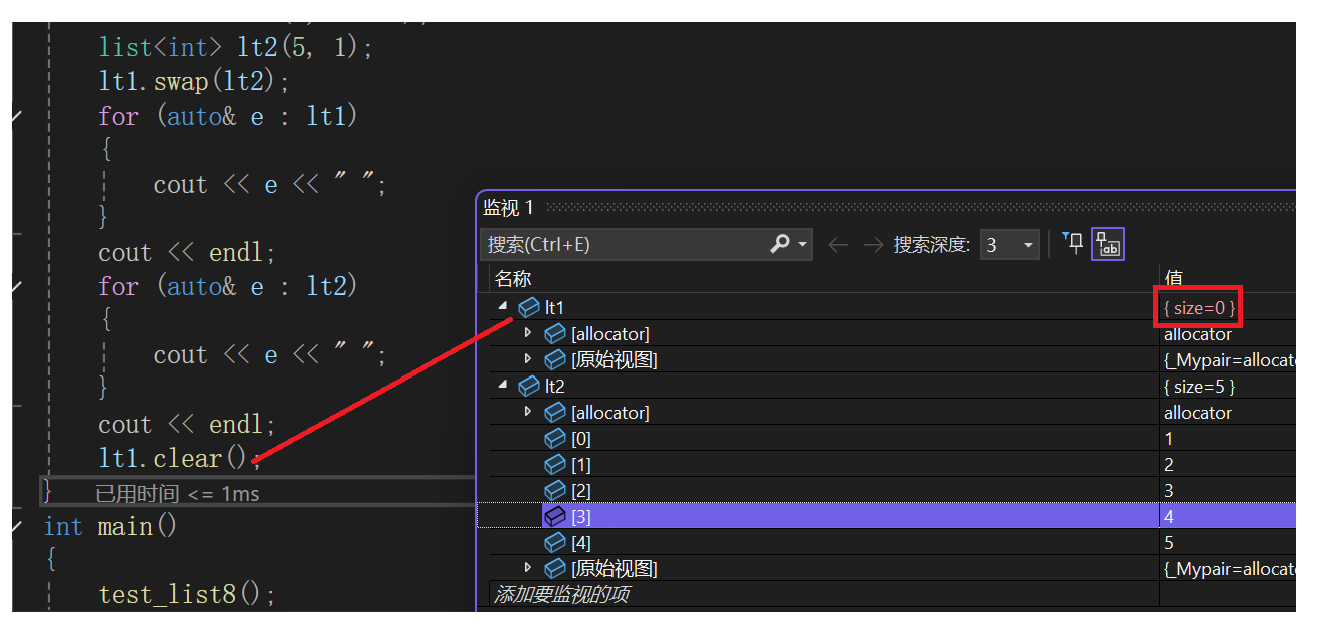
10. swap/clear
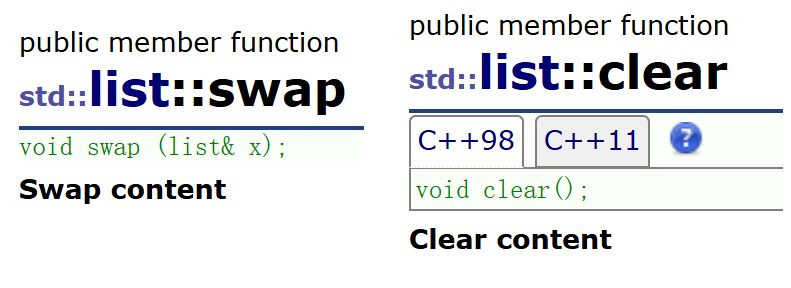
- swap交换两个list对象数据
- clear清除list数据
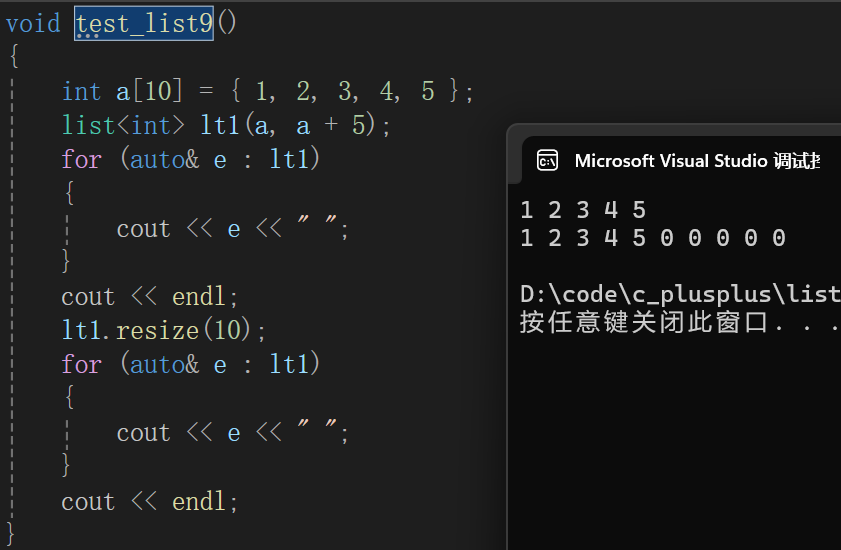
11.resize
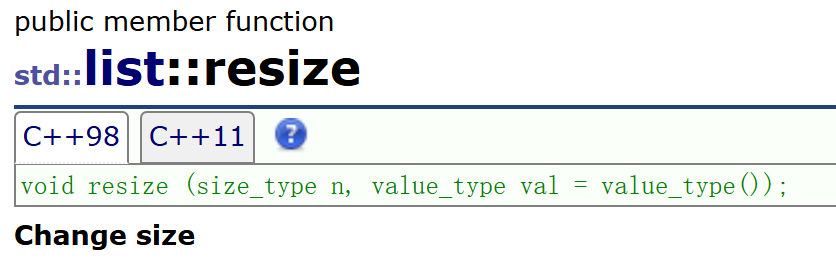
- resize用于改变list的有效数据个数,当n小于当前list有效数据个数,会删除多余节点数据,当小于有效数据个数,会在list后面尾插val
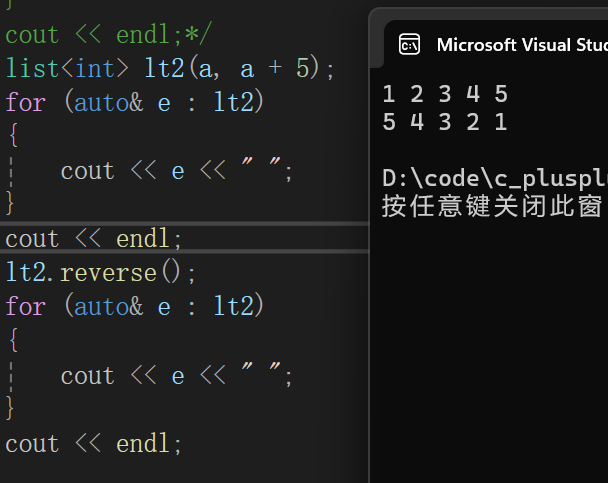
12.reverse

对list数据进行逆置操作
13. sort
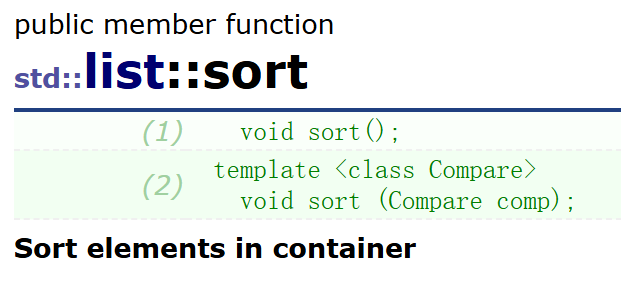
- list的sort排序底层使用的是归并排序的非递归方式,虽然算法库中也有sort,但是它只支持随机访问的迭代器:vector、string等,不支持list双向迭代器排序
迭代器分为
- 单向迭代器:仅支持++/*
- 双向迭代器:支持++/--/*
- 随机访问迭代器:支持++/--/+/-/*/[]
- 数据量大时我们将数据存储在vector中进行排序,再copy到list中,这样比直接在list中排序效率更高
14. merge
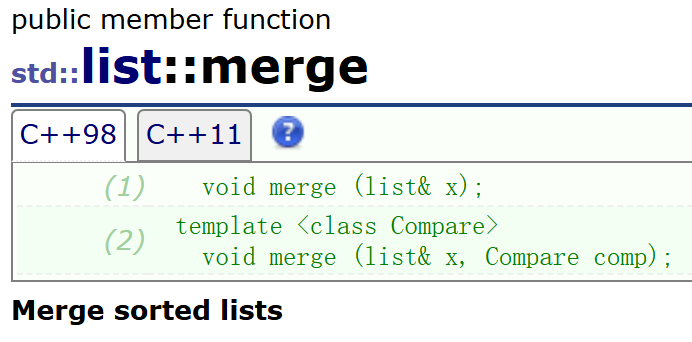
- merge:将一个list对象 x 的数据归并到另一个list对象上(归并的前提是两个list对象数据必须是有序的)
- 归并后,x有效数据为0
cpp
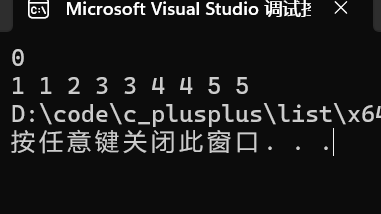
void test_list10()
{
int a[10] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
list<int> lt1(a, a + 5);
list<int> lt2;
lt2.push_back(3);
lt2.push_back(1);
lt2.push_back(4);
lt2.push_back(5);
lt1.sort();
lt2.sort();
lt2.merge(lt1);
cout << lt1.size();
cout << endl;
for (auto& e : lt2)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
}
15. unique

- unique:去重操作
cpp
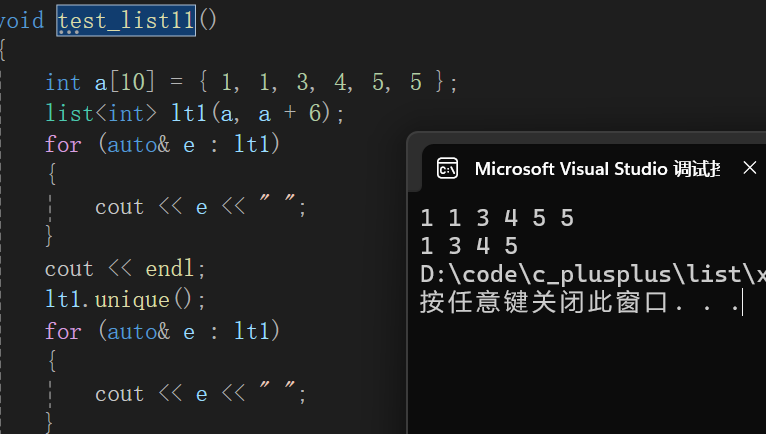
void test_list11()
{
int a[10] = { 1, 1, 3, 4, 5, 5 };
list<int> lt1(a, a + 6);
for (auto& e : lt1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt1.unique();
for (auto& e : lt1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
}
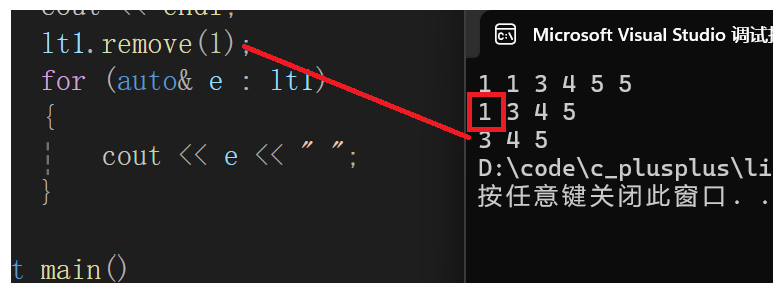
16. remove

- remove:移除数据为val的节点
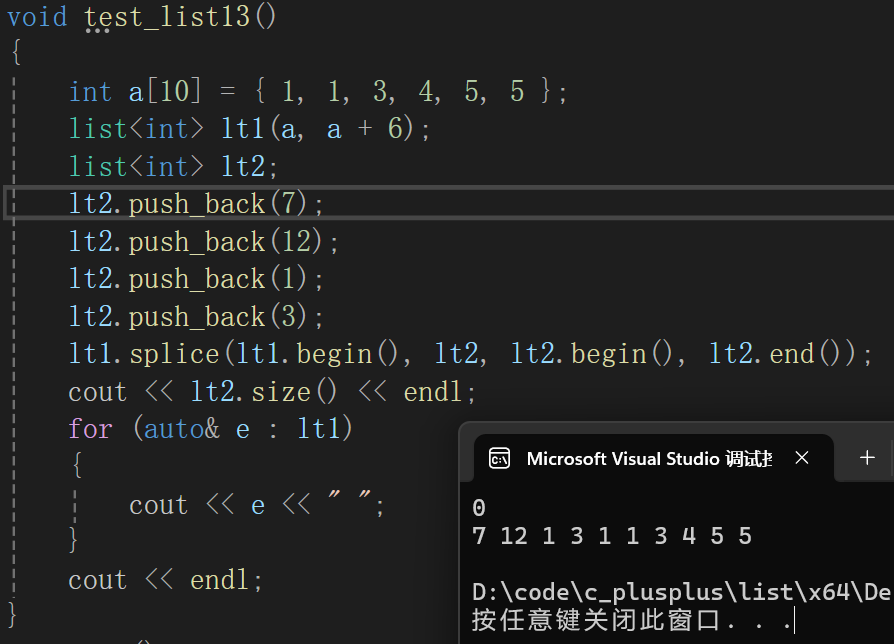
17. splice
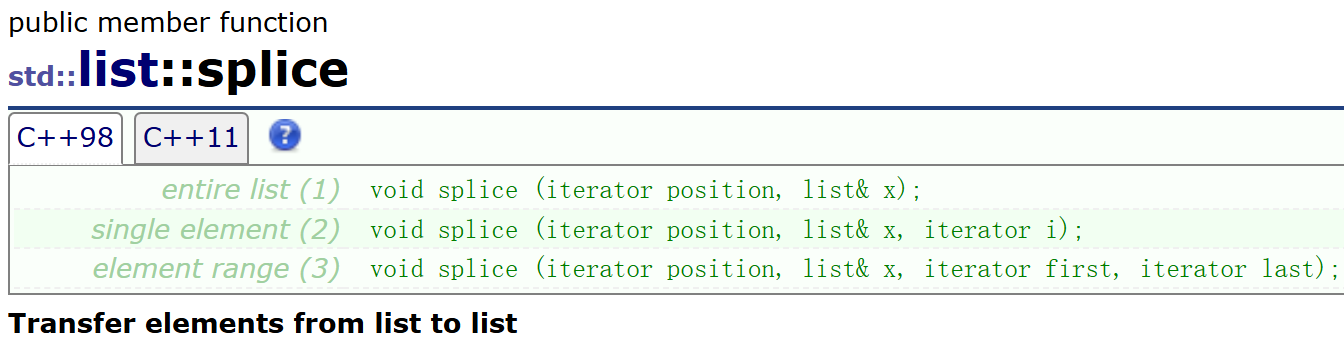
- splice:将list对象x链接到另一个list对象上,x中链接的节点就不在x上了
- 将x全部节点连接到pos位置
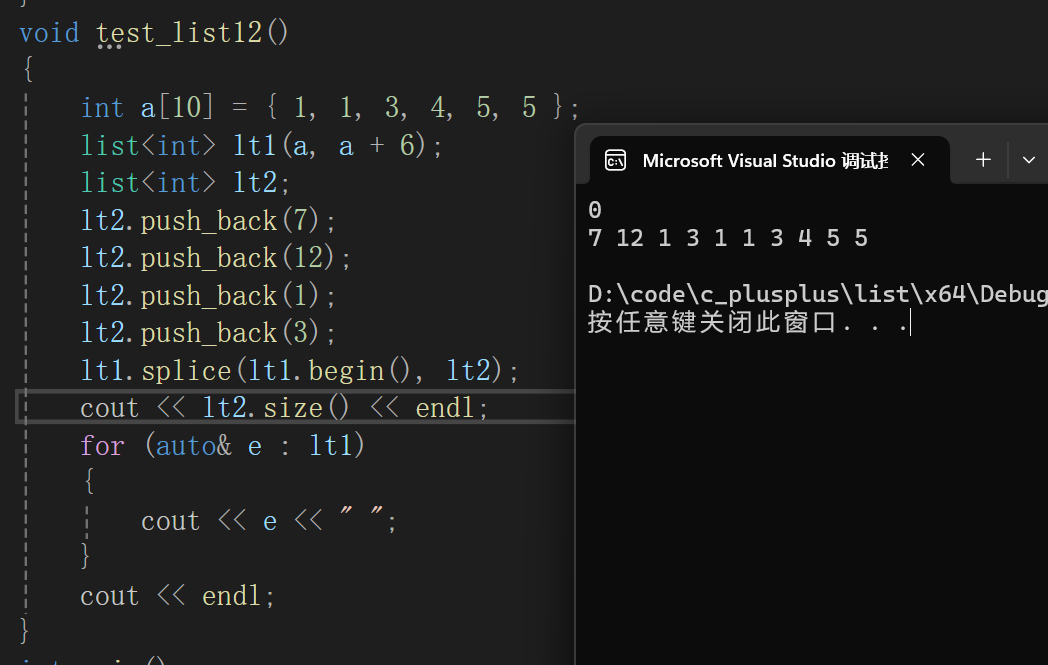
- 将list对象x中迭代器i的节点链接到pos位置
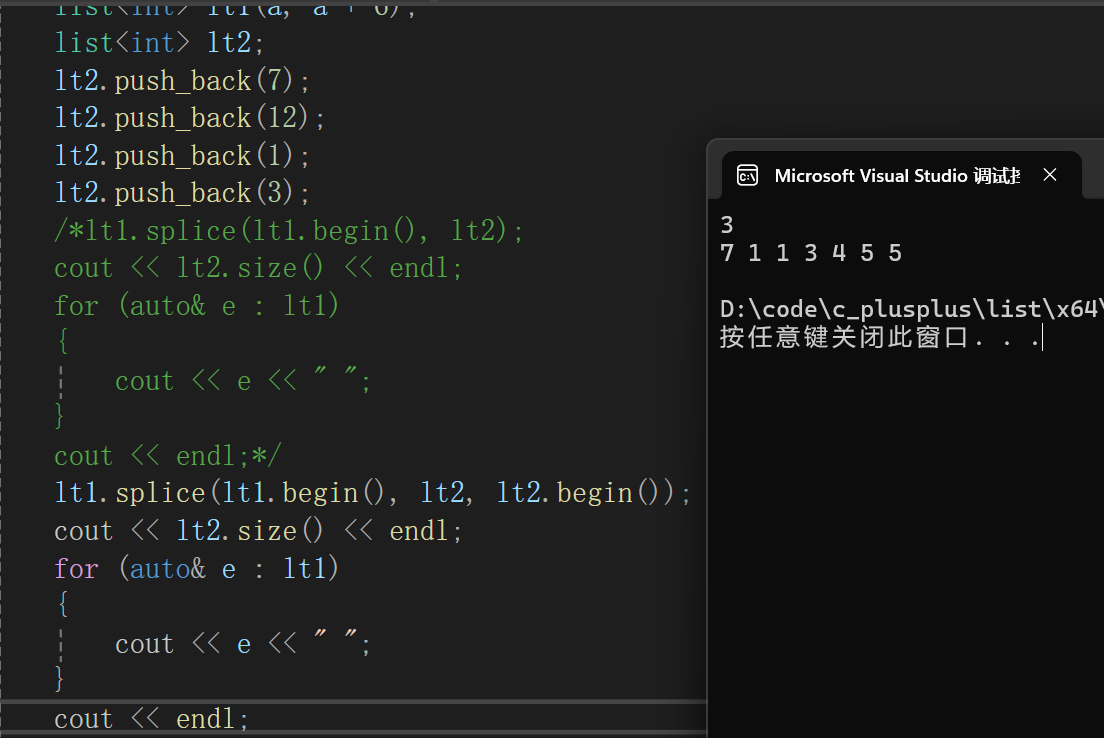
- 将一个list对象x的某个迭代器区间的节点链接到pos位置
cpp
void test_list13()
{
int a[10] = { 1, 1, 3, 4, 5, 5 };
list<int> lt1(a, a + 6);
list<int> lt2;
lt2.push_back(7);
lt2.push_back(12);
lt2.push_back(1);
lt2.push_back(3);
lt1.splice(lt1.begin(), lt2, lt2.begin(), lt2.end());
cout << lt2.size() << endl;
for (auto& e : lt1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}