前言
之前实现过定时器,不过当时采用红黑树,使用C/C++中的set 实现,看了下开源代码,发现使用multimap来实现,故写一点心得体会
一、定时器架构设计哲学
1.1 定时器的双重构成要素
定时器系统由 容器结构 和 驱动方式 两个核心要素构成:
- 容器结构:用于存储和管理定时任务的数据结构
- 驱动方式:触发和执行定时任务的机制
1.2、主流定时器容器对比
| 容器类型 | 数据结构 | 时间复杂度 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 红黑树 | 平衡二叉搜索树 | 插入/删除: O(log n),获取最小: O(1) | 需要精确时间管理的复杂系统 |
| 最小堆 | 完全二叉树 | 插入/删除: O(log n),获取最小: O(1) | 简单定时任务,性能要求高 |
| 时间轮 | 哈希表+链表 | 插入/删除: O(1),触发: O(n) | 大量短时定时任务 |
1.3、红黑树在C++中的实现选择
结合之前的定时器实现,可知道,在C++中,STL提供了四个红黑树容器,分别是set,multiset,map和multimap。
- map<key, value>: 以key存触发时间,value存任务,可以实现一个简单的定时器,当存在多个相同触发时间的任务时,map处理起来会比较麻烦。
- set:可以以一个自定义结构作为key值进行存储,并且按触发时间进行排序,也可以处理多个相同触发时间的任务。
c++
// 方案1:map - 简单但不完善
std::map<time_t, TimerTask> timers;
// 缺陷:相同触发时间的任务会被覆盖
// 方案2:set + 自定义结构 - 完整但复杂
struct TimerNode {
time_t expire; // 过期时间
uint64_t id; // 唯一标识符(解决时间冲突)
bool operator<(const TimerNode& other) const {
return expire < other.expire ||
(expire == other.expire && id < other.id);
}
};
std::set<TimerNode> timers;
// 方案3:multimap - TrinityCore的选择
std::multimap<uint64_t, BasicEvent*> events;
// 优势:天然支持相同触发时间的多个任务- multimap<key, value>: 在之前认为使用
multimap麻烦,不如使用set或者最小堆来实现定时器,但看了部分开源项目后,发现其实multimap是实现定时器的一个不错的选择。 - multiset: 同样可以以一个自定义结构作为key值进行存储,并且按触发时间进行排序,也可以处理多个相同触发时间的任务。
个人认为,mutilset和multimap的比较:
| 容器 | multimap | multiset |
|---|---|---|
| 性能 | 都是红黑树,持平 | 持平 |
| 维护 | 简单直观,易于维护 | 不易于维护 |
| 使用场景 | 简单场景 | 复杂场景 |
二、TrinityCore中的定时器
在TrinityCore中,使用multimap封装实现了两种类型的定时器,分别是EventProcessor和TaskScheduler
2.1、EventProcessor:对象专属定时器
设计理念:每个游戏对象拥有独立的定时器系统,管理对象相关的延迟行为。
核心状态机设计
c++
class BasicEvent {
enum class AbortState : uint8 {
STATE_RUNNING, // 运行中
STATE_ABORT_SCHEDULED, // 计划中止
STATE_ABORTED // 已中止
};
// 状态流转:RUNNING → ABORT_SCHEDULED → ABORTED
};现代化Lambda支持
c++
// 传统继承方式
class SpellCastEvent : public BasicEvent {
bool Execute(uint64 e_time, uint32 p_time) override {
player->CastSpell(spellId);
return true;
}
};
// 现代Lambda方式(推荐)
eventProcessor.AddEventAtOffset([player, spellId]() {
player->CastSpell(spellId);
}, 1500ms);2.2、EventProcessor在PVP战场中的实际应用
(代码较长,就画大致流程图):
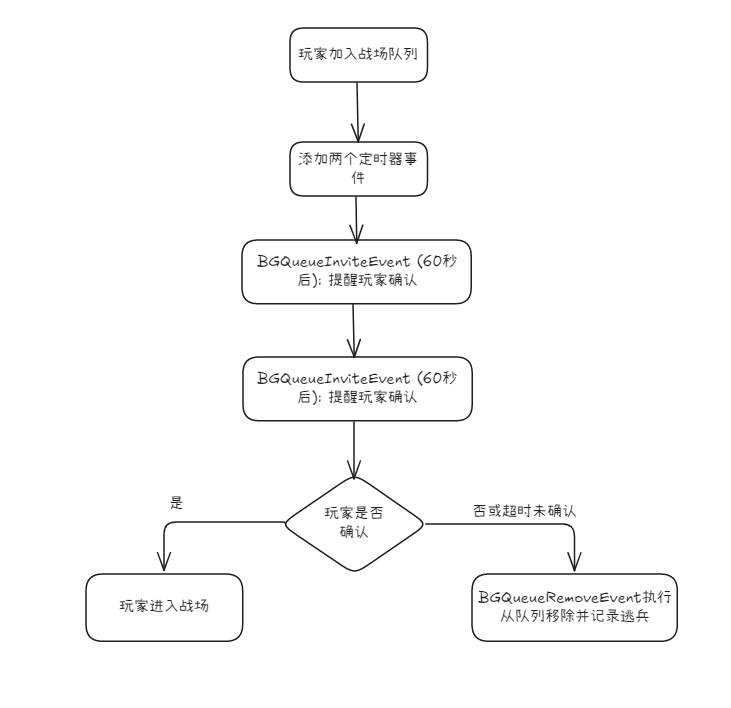
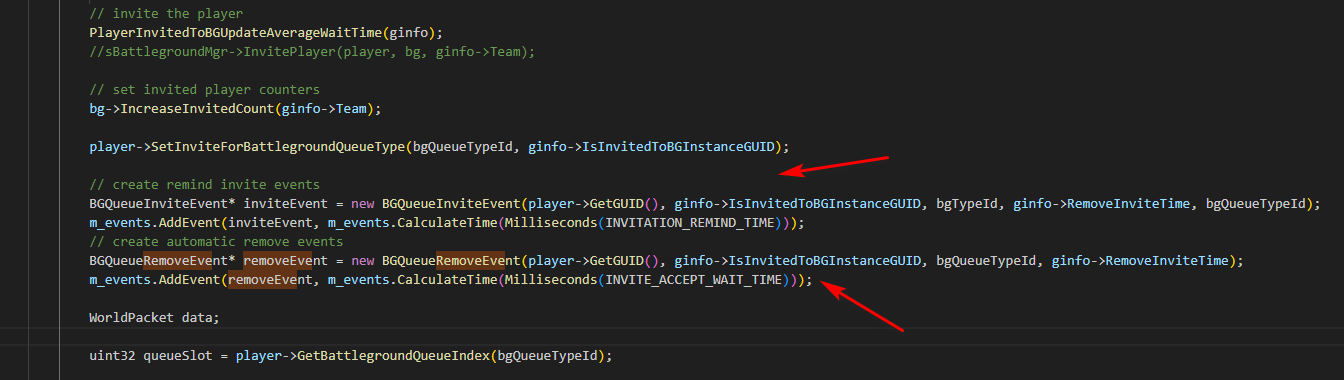
2.3、高性能网络集成: EventProcessor与epoll的结合
看了下网络部分代码,发现TrinityCore中,主要采用select来实现网络IO,并没使用epoll,猜想可能是考虑到兼容与跨平台的原因。
c++
/*
* epoll_wait函数原型
* @parameter epfd: epoll实例的文件描述符
* @parameter events: 事件数组,存放就绪的事件
* @parameter maxevents: 事件数组的最大长度
* @parameter timeout: 超时时间,单位毫秒---相当于内置了一个定时器
*/
int epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event * events, int maxevents, int timeout)就用最后一个参数结合EventProcessor来看看能实现什么效果:
核心点 :
c++
int32_t EventProcessor::NextExecTime() {
if (m_events.empty()) return -1; // 无限等待
auto nextTime = m_events.begin()->first;
if (nextTime > m_time) {
return nextTime - m_time; // 精确超时时间
}
return 0; // 立即执行
}和传统方案进行对比:
c++
// 传统方案:固定频率轮询(资源浪费)
void TraditionalLoop() {
while (running) {
epoll_wait(epfd, events, 64, 10); // 固定10ms超时
ProcessNetwork();
CheckAllTimers(); // 总是检查所有定时器
}
}
// 现代方案:智能超时(高效节能)
void ModernLoop() {
while (running) {
// 动态计算下一个定时器到期时间
int timeout = eventProcessor.NextExecTime();
epoll_wait(epfd, events, 64, timeout);
ProcessNetwork();
eventProcessor.Update(timeDiff); // 只处理到期事件
}
}2.4、完整代码
c++
#ifndef __EVENTPROCESSOR_H
#define __EVENTPROCESSOR_H
#include <map>
#include <type_traits>
#include <chrono>
class EventProcessor;
template<typename T>
using remove_cvref_t = std::remove_cv_t<std::remove_reference_t<T>>;
using Milliseconds = std::chrono::milliseconds;
class BasicEvent
{
friend class EventProcessor;
enum class AbortState : uint8_t
{
STATE_RUNNING, // 正在运行中
STATE_ABORT_SCHEDULED, // 计划终止
STATE_ABORTED // 已终止
};
public:
BasicEvent():m_abortState(AbortState::STATE_RUNNING), m_addTime(0), m_execTime(0) {}
virtual ~BasicEvent(){} // 析构函数,用于执行事件删除时的操作
virtual bool Execute(uint64_t /*e_time*/, uint32_t /*p_time*/) { return true; } // 当事件被触发时执行该方法
virtual bool IsDeletable() const {return true;} // 该事件可以被安全删除
virtual void Abort(uint64_t /*e_time*/) {} // 当事件被终止时执行该方法
void ScheduleAbort(); // 在下一个更新周期终止事件
private:
void SetAborted();
bool IsRunning() const {return (m_abortState == AbortState::STATE_RUNNING);}
bool IsAbortScheduled() const {return (m_abortState == AbortState::STATE_ABORT_SCHEDULED);}
bool IsAborted() const {return (m_abortState == AbortState::STATE_ABORTED);}
uint64_t m_addTime; // 时间戳,事件被添加到队列的时间
uint64_t m_execTime; // 计划执行时间
AbortState m_abortState; // 事件终止状态
};
template<typename T>
class LambdaBasicEvent : public BasicEvent
{
public:
LambdaBasicEvent(T&& callback) : BasicEvent(), _callback(std::move(callback)) { }
bool Execute(uint64_t, uint32_t) override
{
_callback();
return true;
}
private:
T _callback;
};
//用lambda进行包装
template<typename T>
using is_lambda_event = std::enable_if_t<!std::is_base_of_v<BasicEvent, std::remove_pointer_t<remove_cvref_t<T>>>>;
class EventProcessor
{
public:
EventProcessor():m_time(0) {} // 构造函数
virtual ~EventProcessor(); // 析构函数,用于执行事件删除时的操作
void Update(uint32_t p_time); // 更新时间戳并处理所有到期的事件
void KillAllEvents(bool force = false); // 终止所有事件
void AddEvent(BasicEvent* event, Milliseconds e_time, bool set_addtime = true); // 向队列中添加一个新事件
template<typename T>
is_lambda_event<T> AddEvent(T&& event, Milliseconds e_time, bool set_addtime = true) {
AddEvent(new LambdaBasicEvent<T>(std::move(event)), e_time, set_addtime);
}
void AddEventAtOffset(BasicEvent* event, Milliseconds offset) {AddEvent(event, CalculateTime(offset));}
template<typename T>
is_lambda_event<T> AddEventAtOffset(T&& event, Milliseconds offset) { AddEventAtOffset(new LambdaBasicEvent<T>(std::move(event)), offset); }
void ModifyEventTime(BasicEvent* event, Milliseconds newTime);
Milliseconds CalculateTime(Milliseconds t_offset) const { return Milliseconds(m_time) + t_offset; }
int32_t NextExecTime() { // 返回下一个事件执行时间
std::multimap<uint64_t, BasicEvent*>::iterator itr;
if ((itr = m_events.begin()) != m_events.end()) {
if (itr->first > m_time) {
return itr->first - m_time;
}
return 0;
}
return -1;
}
protected:
uint64_t m_time;
std::multimap<uint64_t, BasicEvent*> m_events; // 存储容器
};
#endif
c++
#include "EventProcessor.h"
using namespace std::chrono_literals;
void BasicEvent::ScheduleAbort()
{
m_abortState = AbortState::STATE_ABORT_SCHEDULED;
}
void BasicEvent::SetAborted()
{
m_abortState = AbortState::STATE_ABORTED;
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
EventProcessor::~EventProcessor()
{
KillAllEvents(true);
}
void EventProcessor::Update(uint32_t p_time)
{
m_time += p_time; // 更新时间
std::multimap<uint64_t, BasicEvent*>::iterator i; // 迭代器i用于遍历事件队列
while (((i = m_events.begin()) != m_events.end()) && i->first <= m_time){
BasicEvent* event = i->second; // 获取并移除事件队列中的第一个事件
m_events.erase(i); // 从事件队列中删除该事件
if (event->IsRunning()){
if (event->Execute(m_time, p_time)){ // 如果事件正在运行,则执行它
delete event; // 完全销毁事件(如果它没有被重新添加)
}
continue; // 永远执行
}
if (event->IsAbortScheduled()){ // 如果事件计划终止
event->Abort(m_time); // 终止事件
event->SetAborted(); // 将事件标记为已终止
}
if (event->IsDeletable()){ // 如果事件可以被安全删除
delete event; // 销毁事件
continue; // 永远执行
}
AddEvent(event, CalculateTime(1ms), false); // 将事件重新添加到队列中,以便在下一个更新周期检查
}
}
void EventProcessor::KillAllEvents(bool force)
{
for (auto itr = m_events.begin(); itr != m_events.end();){ // 遍历事件队列
if (!itr->second->IsAborted()){ // 如果事件没有被终止
itr->second->SetAborted(); // 将事件标记为已终止
itr->second->Abort(m_time); // 终止事件
}
if(!force && !itr->second->IsDeletable()){ // 如果不是强制删除,并且事件不可被安全删除
++itr; // 继续下一个迭代
continue;
}
delete itr->second; // 销毁事件
if (force)
++itr; // 在强制模式下清除整个容器
else
itr = m_events.erase(itr); // 非强制模式时从队列中移除该
}
if(force){
m_events.clear();
}
}
void EventProcessor::AddEvent(BasicEvent* event, Milliseconds e_time, bool set_addtime)
{
if (set_addtime) // 如果需要设置添加时间
event->m_addTime = m_time; // 设置事件添加时间为当前时间
event->m_execTime = e_time.count(); // 设置执行时间
m_events.insert(std::pair<uint64_t, BasicEvent*>(e_time.count(), event)); // 将事件插入到队列中,按执行时间排序
}
void EventProcessor::ModifyEventTime(BasicEvent* event, Milliseconds newTime)
{
for(auto itr = m_events.begin(); itr != m_events.end(); ++itr){ // 遍历事件队列
if (itr->second != event) // 如果当前迭代的事件不是要修改时间的事件,则继续下一个迭代
continue;
event->m_execTime = newTime.count(); // 设置新执行时间
m_events.erase(itr); // 从队列中移除该事件
m_events.insert(std::pair<uint64_t, BasicEvent*>(newTime.count(), event)); // 将事件重新插入到队列中,按新执行时间排序
break;
}
}
c++
#include <chrono>
#include <cstdint>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <memory>
#include <iostream>
#include "EventProcessor.h"
using namespace std::chrono_literals;
std::chrono::steady_clock::time_point appStartTime;
inline uint32_t getMSTime() {
using namespace std::chrono;
return uint32_t(duration_cast<milliseconds>(steady_clock::now()-appStartTime).count());
}
inline uint32_t getMSTimeDiff(uint32_t oldMSTime, uint32_t newMSTime) {
if (oldMSTime > newMSTime)
return (0xffffffff-oldMSTime)+ newMSTime;
else
return newMSTime - oldMSTime;
}
class TestEvent : public BasicEvent {
public:
TestEvent() : BasicEvent() {}
bool Execute(uint64_t /*e_time*/, uint32_t /*p_time*/) override {
std::cout << "Execute TestEvent:" << getMSTime() << std::endl;
return true;
}
};
int main()
{
int epfd = epoll_create(1);
std::unique_ptr<EventProcessor> evproc = std::make_unique<EventProcessor>();
evproc->AddEventAtOffset([](){
std::cout << "lambda execute timer." << getMSTime() << std::endl;
}, 100ms);
evproc->AddEventAtOffset(new TestEvent(), 1s);
appStartTime = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
epoll_event evs[64] = {0};
uint32_t realCurrTime = 0, realPrevTime = 0;
while (true) {
int n = epoll_wait(epfd, evs, 64, evproc->NextExecTime());
for (int i=0; i<n; i++);
realCurrTime = getMSTime();
uint32_t diff = getMSTimeDiff(realPrevTime, realCurrTime);
evproc->Update(diff);
realPrevTime = realCurrTime;
}
return 0;
}
//g++ EventProcessor.cpp main.cpp -o event -I./ -std=c++17