上一篇文章已经介绍了使用Apache Shiro权限认证框架实现动态授权功能。
Spring Boot整合Apache Shiro权限认证框架(应用篇)![]() https://blog.csdn.net/2501_92713943/article/details/152666246这篇文章介绍的是Apache Shiro的最佳实践,可直接用于项目。
https://blog.csdn.net/2501_92713943/article/details/152666246这篇文章介绍的是Apache Shiro的最佳实践,可直接用于项目。
目录
getAvailableAuthorizationCache()
对于刚接触Apache Shiro的同学来说,可以会觉得很好奇:
上一篇文章并没有涉及到密码比较,怎么就知道密码是对的还是错的呢?
登录认证流程
这就需要了解一下Apache Shiro的登录认证流程了:
1、对于普通的登录认证,用户会在登录页面输入账号(用户名、手机号、邮箱等)和密码;
2、在后端会得到用户输入的登录信息(账号+密码),调用Subject.login()方法登录;
Subject
org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject是一个接口,它有一个实现类DelegatingSubject
DelegatingSubject
在DelegatingSubject重写的login()方法中,调用了SecurityManager的login()方法。
login()
java
Subject subject = securityManager.login(this, token);SecurityManager
SecurityManager也是一个接口,其默认实现类是DefaultSecurityManager。
DefaultSecurityManager
然后让我们看看这个实现类里的login()方法的代码:
java
public Subject login(Subject subject, AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
AuthenticationInfo info;
try {
info = authenticate(token);
} catch (AuthenticationException ae) {
try {
onFailedLogin(token, ae, subject);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info("onFailedLogin method threw an " +
"exception. Logging and propagating original AuthenticationException.", e);
}
}
throw ae; // propagate
}
Subject loggedIn = createSubject(token, info, subject);
onSuccessfulLogin(token, info, loggedIn);
return loggedIn;
}首先会通过调用authenticate()方法得到AuthenticationInfo对象。
Authenticator
在authenticate()方法中调用了Authenticator接口的authenticate()方法。
authenticate()
java
public AuthenticationInfo authenticate(AuthenticationToken token)
throws AuthenticationException {
return this.authenticator.authenticate(token);
}AbstractAuthenticator
查看Authenticator接口的抽象实现类AbstractAuthenticator的authenticate()方法。
java
public final AuthenticationInfo authenticate(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
if (token == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Method argument (authentication token) cannot be null.");
}
log.trace("Authentication attempt received for token [{}]", token);
AuthenticationInfo info;
try {
info = doAuthenticate(token);
if (info == null) {
String msg = "No account information found for authentication token [" + token + "] by this " +
"Authenticator instance. Please check that it is configured correctly.";
throw new AuthenticationException(msg);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
AuthenticationException ae = null;
if (t instanceof AuthenticationException) {
ae = (AuthenticationException) t;
}
if (ae == null) {
//Exception thrown was not an expected AuthenticationException. Therefore it is probably a little more
//severe or unexpected. So, wrap in an AuthenticationException, log to warn, and propagate:
String msg = "Authentication failed for token submission [" + token + "]. Possible unexpected " +
"error? (Typical or expected login exceptions should extend from AuthenticationException).";
ae = new AuthenticationException(msg, t);
if (log.isWarnEnabled())
log.warn(msg, t);
}
try {
notifyFailure(token, ae);
} catch (Throwable t2) {
if (log.isWarnEnabled()) {
String msg = "Unable to send notification for failed authentication attempt - listener error?. " +
"Please check your AuthenticationListener implementation(s). Logging sending exception " +
"and propagating original AuthenticationException instead...";
log.warn(msg, t2);
}
}
throw ae;
}
log.debug("Authentication successful for token [{}]. Returned account [{}]", token, info);
notifySuccess(token, info);
return info;
}doAuthenticate()
在这个方法里通过doAuthenticate()方法获取AuthenticationInfo对象。
java
protected abstract AuthenticationInfo doAuthenticate(AuthenticationToken token)
throws AuthenticationException;ModularRealmAuthenticator
由于AbstractAuthenticator的authenticate()方法是抽象方法,定位到其派生类ModularRealmAuthenticator。
获取所有Realm,如果只有一个Realm,调用doSingleRealmAuthentication()方法。
java
protected AuthenticationInfo doAuthenticate(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken)
throws AuthenticationException {
assertRealmsConfigured();
Collection<Realm> realms = getRealms();
if (realms.size() == 1) {
return doSingleRealmAuthentication(realms.iterator().next(), authenticationToken);
} else {
return doMultiRealmAuthentication(realms, authenticationToken);
}
}Realm
doSingleRealmAuthentication()
在doSingleRealmAuthentication()方法中最终调用了Realm的getAuthenticationInfo()方法。
java
AuthenticationInfo info = realm.getAuthenticationInfo(token);AuthenticatingRealm
Realm是一个接口,定位到其派生类AuthenticatingRealm重写的getAuthenticationInfo()方法。
getAuthenticationInfo()
java
public final AuthenticationInfo getAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token)
throws AuthenticationException {
// 从缓存中获取AuthenticationInfo
AuthenticationInfo info = getCachedAuthenticationInfo(token);
if (info == null) {
// otherwise not cached, perform the lookup:
info = doGetAuthenticationInfo(token);
log.debug("Looked up AuthenticationInfo [{}] from doGetAuthenticationInfo", info);
if (token != null && info != null) {
cacheAuthenticationInfoIfPossible(token, info);
}
} else {
log.debug("Using cached authentication info [{}] to perform credentials matching.", info);
}
if (info != null) {
assertCredentialsMatch(token, info);
} else {
log.debug("No AuthenticationInfo found for submitted AuthenticationToken [{}]. Returning null.", token);
}
return info;
}先从缓存中获取AuthenticationInfo对象,如果缓存中没有,则通过doGetAuthenticationInfo()方法获取。
java
protected abstract AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException;其实就是调用了我们提供的UsernameRealm重写的getAuthenticationInfo()方法,这个方法返回的就是用于认证的信息。AuthorizingRealm是AuthenticatingRealm的一个派生类。
java
public class UsernameRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {assertCredentialsMatch()
在这里方法中完成了密码的匹配,通过调用CredentialsMatcher的doCredentialsMatch()方法。
java
protected void assertCredentialsMatch(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info)
throws AuthenticationException {
CredentialsMatcher cm = getCredentialsMatcher();
if (cm != null) {
if (!cm.doCredentialsMatch(token, info)) {
//not successful - throw an exception to indicate this:
String msg = "Submitted credentials for token [" + token + "] did not match the expected credentials.";
throw new IncorrectCredentialsException(msg);
}
} else {
throw new AuthenticationException("A CredentialsMatcher must be configured in order to verify " +
"credentials during authentication. If you do not wish for credentials to be examined, you " +
"can configure an " + AllowAllCredentialsMatcher.class.getName() + " instance.");
}
}CredentialsMatcher
CredentialsMatcher是一个接口,定位到其派生类重写的doCredentialsMatch()方法。
SimpleCredentialsMatcher
doCredentialsMatch()
在doCredentialsMatch()方法中调用了equals()方法。
java
public boolean doCredentialsMatch(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info) {
Object tokenCredentials = getCredentials(token);
Object accountCredentials = getCredentials(info);
return equals(tokenCredentials, accountCredentials);
}equals()
在这个方法中,首先判断比较的两个密码是不是字节,一般来说都是字符串,所以执行else分支的通过Object的equals()方法简单比较两个对象的值是否相等。
java
protected boolean equals(Object tokenCredentials, Object accountCredentials) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Performing credentials equality check for tokenCredentials of type [" +
tokenCredentials.getClass().getName() + " and accountCredentials of type [" +
accountCredentials.getClass().getName() + "]");
}
if (isByteSource(tokenCredentials) && isByteSource(accountCredentials)) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Both credentials arguments can be easily converted to byte arrays. Performing " +
"array equals comparison");
}
byte[] tokenBytes = toBytes(tokenCredentials);
byte[] accountBytes = toBytes(accountCredentials);
return MessageDigest.isEqual(tokenBytes, accountBytes);
} else {
// 比较两个字符串的内容是否相等
return accountCredentials.equals(tokenCredentials);
}
}DefaultSecurityManager
好了,获取AuthenticationInfo对象的方法已经看完了,回到刚开始的DefaultSecurityManager的login()方法。
java
Subject loggedIn = createSubject(token, info, subject);
onSuccessfulLogin(token, info, loggedIn);
return loggedIn;createSubject()
第一行代码是创建Subject对象
java
protected Subject createSubject(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info, Subject existing) {
SubjectContext context = createSubjectContext();
context.setAuthenticated(true);
context.setAuthenticationToken(token);
context.setAuthenticationInfo(info);
if (existing != null) {
context.setSubject(existing);
}
return createSubject(context);
}onSuccessfulLogin()
继续看onSuccessfulLogin()方法。
java
protected void onSuccessfulLogin(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info, Subject subject) {
rememberMeSuccessfulLogin(token, info, subject);
}继续调用rememberMeSuccessfulLogin()方法,在这里调用了RememberMeManager的onSuccessfulLogin()方法。
java
protected void rememberMeSuccessfulLogin(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info, Subject subject) {
RememberMeManager rmm = getRememberMeManager();
if (rmm != null) {
try {
rmm.onSuccessfulLogin(subject, token, info);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (log.isWarnEnabled()) {
String msg = "Delegate RememberMeManager instance of type [" + rmm.getClass().getName() +
"] threw an exception during onSuccessfulLogin. RememberMe services will not be " +
"performed for account [" + info + "].";
log.warn(msg, e);
}
}
} else {
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("This " + getClass().getName() + " instance does not have a " +
"[" + RememberMeManager.class.getName() + "] instance configured. RememberMe services " +
"will not be performed for account [" + info + "].");
}
}
}RememberMeManager
RememberMeManager是一个接口,定位到其派生类AbstractRememberMeManager重写的onSuccessfulLogin()方法。
AbstractRememberMeManager
onSuccessfulLogin()
java
public void onSuccessfulLogin(Subject subject, AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info) {
// always clear any previous identity:
forgetIdentity(subject);
// now save the new identity:
if (isRememberMe(token)) {
rememberIdentity(subject, token, info);
} else {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("AuthenticationToken did not indicate RememberMe is requested. " +
"RememberMe functionality will not be executed for corresponding account.");
}
}
}rememberIdentity()
方法名翻译过来是"记住身份",很显然应该是跟会话有关。
java
public void rememberIdentity(Subject subject, AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo authcInfo) {
PrincipalCollection principals = getIdentityToRemember(subject, authcInfo);
rememberIdentity(subject, principals);
}传参继续调用重载的rememberIdentity()方法。
java
protected void rememberIdentity(Subject subject, PrincipalCollection accountPrincipals) {
byte[] bytes = convertPrincipalsToBytes(accountPrincipals);
rememberSerializedIdentity(subject, bytes);
}rememberSerializedIdentity()
java
protected abstract void rememberSerializedIdentity(Subject subject, byte[] serialized);CookieRememberMeManager
由于AbsreactRememberMeManager的rememberSerializedIdentity()方法是抽象的,定位带其派生类重写的rememberSerializedIdentity()方法。
rememberSerializedIdentity()
很显然,就是设置返回给浏览器的Cooklie值。
java
protected void rememberSerializedIdentity(Subject subject, byte[] serialized) {
if (!WebUtils.isHttp(subject)) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
String msg = "Subject argument is not an HTTP-aware instance. This is required to obtain a servlet " +
"request and response in order to set the rememberMe cookie. Returning immediately and " +
"ignoring rememberMe operation.";
log.debug(msg);
}
return;
}
HttpServletRequest request = WebUtils.getHttpRequest(subject);
HttpServletResponse response = WebUtils.getHttpResponse(subject);
//base 64 encode it and store as a cookie:
String base64 = Base64.encodeToString(serialized);
Cookie template = getCookie(); //the class attribute is really a template for the outgoing cookies
Cookie cookie = new SimpleCookie(template);
cookie.setValue(base64);
cookie.saveTo(request, response);
}权限缓存问题
上面章节已经详细地深入源码介绍了Apache Shiro的登录认证流程。
接下来,有一个比较大的问题需要处理一下,每次访问API接口的时候,发现都会去查询一次用户的权限(查询角色+查询权限),用户的角色和权限通常是不会变更的,可以对权限进行缓存。
可以在UsernameRealm的doGetAuthorizationInfo()方法中增加缓存的代码。
但是,查看源代码之后会发现,Apache Shiro提供了一个缓存机制。
权限缓存源码
AuthorizingRealm
getAuthorizationInfo()
在UsernameRealm的超类中调用了我们重写的doGetAuthorizationInfo()方法
java
protected AuthorizationInfo getAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
if (principals == null) {
return null;
}
AuthorizationInfo info = null;
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("Retrieving AuthorizationInfo for principals [" + principals + "]");
}
// 获取可用的授权信息缓存缓存类
Cache<Object, AuthorizationInfo> cache = getAvailableAuthorizationCache();
if (cache != null) { // 缓存可用
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("Attempting to retrieve the AuthorizationInfo from cache.");
}
// 获取缓存key
Object key = getAuthorizationCacheKey(principals);
// 通过key从缓存中获取值
info = cache.get(key);
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
if (info == null) {
log.trace("No AuthorizationInfo found in cache for principals [" + principals + "]");
} else {
log.trace("AuthorizationInfo found in cache for principals [" + principals + "]");
}
}
}
if (info == null) { // 没有命中缓存
// 调用doGetAuthorizationInfo()方法获取授权信息
info = doGetAuthorizationInfo(principals);
// 缓存可用,并且获取到了授权信息
if (info != null && cache != null) {
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("Caching authorization info for principals: [" + principals + "].");
}
// 将授权信息存入缓存中
Object key = getAuthorizationCacheKey(principals);
cache.put(key, info);
}
}
return info;
}
/**
* 获取缓存key
*/
protected Object getAuthorizationCacheKey(PrincipalCollection principals) {
return principals;
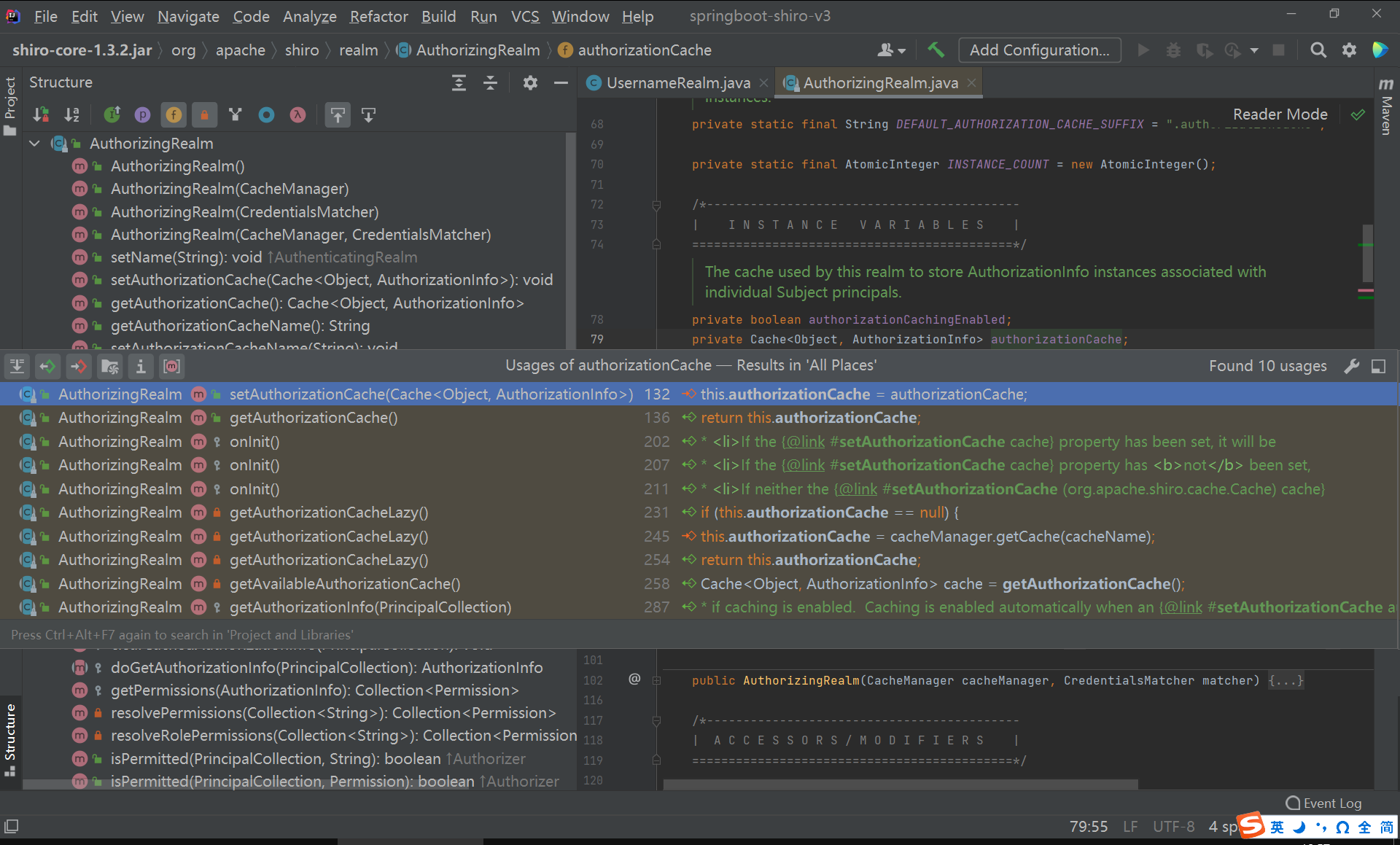
}getAvailableAuthorizationCache()
继续深入探究如何获取可用的授权缓存。
java
private Cache<Object, AuthorizationInfo> getAvailableAuthorizationCache() {
Cache<Object, AuthorizationInfo> cache = getAuthorizationCache();
if (cache == null && isAuthorizationCachingEnabled()) {
cache = getAuthorizationCacheLazy();
}
return cache;
}getAuthorizationCache()
getAuthorizationCache()方法直接返回了当前类的成员变量。
java
public Cache<Object, AuthorizationInfo> getAuthorizationCache() {
return this.authorizationCache;
}发现只有一个set方法可以设置缓存类。
创建授权缓存类
根据上面的信息,我们可以创建一个自定义的授权缓存类。
可以将授权信息缓存到Map中,但是当登录的用户多了之后,Map中的数据会越来越大,甚至可能导致内存溢出。
因此,使用Redis作为缓存更合适,虽然没有内存中的Map快,也有每秒十万左右的并发。
pom.xml
添加Spring Boot整合Redis的依赖。
XML
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>RedisUtils.java
创建redis包,在redis包下创建RedisUtils接口。
java
package cn.edu.sgu.www.shiro.redis;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @author 沐雨橙风ιε
* @version 1.0
*/
public interface RedisUtils {
/**
* 获取key的值:get key
* @param key redis的key
* @return key的值
*/
String get(String key);
/**
* 一次性根据多个key获取多个值
* @param keys key列表
* @return List<String>
*/
List<String> multiGet(Set<String> keys);
/**
* 根据pattern批量获取key
* @param pattern String
* @return Set<String> 所有key的列表
*/
Set<String> keys(String pattern);
/**
* 设置key:set key value
* @param key redis的key
* @param value key的值
*/
void set(String key, String value);
/**
* 设置key:set key value ex timeout = set key value + expire key timeout
* @param key redis的key
* @param value key的值
* @param timeout 过期时间
* @param timeUnit 时间单位
*/
void set(String key, String value, long timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit);
/**
* 删除key:del key
* @param key redis的key
*/
void delete(String key);
/**
* 根据pattern删除key:del keys pattern
* @param pattern String
*/
void deleteByPattern(String pattern);
/**
* 让key自增:incrby key
* @param key redis的key
* @return 自增后的值
*/
Long incrBy(String key);
/**
* 判断key是否存在
* @param key redis的key
* @return key存在则返回true,否则返回false
*/
Boolean hasKey(String key);
/**
* 设置key的过期时间:expire key seconds
* @param key redis的key
* @param timeout 过期时间
* @param timeUnit 时间单位
*/
void expire(String key, long timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit);
}StringRedisUtils.java
创建RedisUtils接口的实现类。
java
package cn.edu.sgu.www.shiro.redis;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* 封装了StringRedisTemplate的redis工具类
* @author 沐雨橙风ιε
* @version 1.0
*/
@Component
public class StringRedisUtils implements RedisUtils {
private final StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@Autowired
public StringRedisUtils(StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate) {
this.stringRedisTemplate = stringRedisTemplate;
}
@Override
public String get(String key) {
return getValueOperations().get(key);
}
@Override
public List<String> multiGet(Set<String> keys) {
return getValueOperations().multiGet(keys);
}
@Override
public Set<String> keys(String pattern) {
return stringRedisTemplate.keys(pattern);
}
@Override
public void set(String key, String value) {
getValueOperations().set(key, value);
}
@Override
public void set(String key, String value, long timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit) {
getValueOperations().set(key, value, timeout, timeUnit);
}
@Override
public void delete(String key) {
stringRedisTemplate.delete(key);
}
@Override
public void deleteByPattern(String pattern) {
Set<String> keys = stringRedisTemplate.keys(pattern);
if (keys != null && !keys.isEmpty()) {
stringRedisTemplate.delete(keys);
}
}
@Override
public Long incrBy(String key) {
return getValueOperations().increment(key);
}
@Override
public Boolean hasKey(String key) {
return stringRedisTemplate.hasKey(key);
}
@Override
public void expire(String key, long timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit) {
stringRedisTemplate.expire(key, timeout, timeUnit);
}
/**
* 获取ValueOperations对象
* @return ValueOperations<String, String>
*/
private ValueOperations<String, String> getValueOperations() {
return stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue();
}
}RedisCache.java
创建一个Cache<Object, AuthorizationInfo>的派生类。
至于为什么是Cache<Object, AuthorizationInfo>类型的,因为set方法需要这个类型。
java
package cn.edu.sgu.www.shiro.support;
import cn.edu.sgu.www.shiro.consts.RedisKeyPrefixes;
import cn.edu.sgu.www.shiro.redis.RedisUtils;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.SimpleAuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.cache.Cache;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* @author 沐雨橙风ιε
* @version 1.0
*/
@Component
public class RedisCache implements Cache<Object, AuthorizationInfo> {
private final RedisUtils redisUtils;
@Autowired
public RedisCache(RedisUtils redisUtils) {
this.redisUtils = redisUtils;
}
@Override
public SimpleAuthorizationInfo get(Object key) {
String value = redisUtils.get(key.toString());
return JSON.parseObject(value, SimpleAuthorizationInfo.class);
}
@Override
public AuthorizationInfo put(Object key, AuthorizationInfo value) {
redisUtils.set(key.toString(), JSON.toJSONString(value));
return value;
}
@Override
public SimpleAuthorizationInfo remove(Object key) {
redisUtils.delete(key.toString());
return null;
}
@Override
public void clear() {
redisUtils.deleteByPattern(RedisKeyPrefixes.PREFIX_SHIRO_PERMISSIONS + "*");
}
@Override
public int size() {
return keys().size();
}
@Override
public Set<Object> keys() {
Set<String> keys = redisUtils.keys(RedisKeyPrefixes.PREFIX_SHIRO_PERMISSIONS + "*");
Stream<String> stream = keys.stream();
return stream.map(new Function<String, Object>() {
@Override
public Object apply(String key) {
return key;
}
}).collect(Collectors.toSet());
}
@Override
public Collection<AuthorizationInfo> values() {
Set<Object> keys = keys();
Stream<Object> stream = keys.stream();
List<String> list = redisUtils.multiGet(stream.map(new Function<Object, String>() {
@Override
public String apply(Object key) {
return key.toString();
}
}).collect(Collectors.toSet()));
return list.stream().map(new Function<Object, SimpleAuthorizationInfo>() {
@Override
public SimpleAuthorizationInfo apply(Object value) {
return JSON.parseObject(value.toString(), SimpleAuthorizationInfo.class);
}
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}ShiroConfig
因为要设置授权缓存的管理器,需要修改UsernameRealm的Bean定义方式。
java
@Bean
public UsernameRealm usernameRealm(RedisCache redisCache) {
UsernameRealm usernameRealm = new UsernameRealm();
usernameRealm.setAuthorizationCache(redisCache);
return usernameRealm;
}RedisKeyPrefixes.java
java
package cn.edu.sgu.www.shiro.consts;
/**
* Redis的key前缀的常量接口
* @author 沐雨橙风ιε
* @version 1.0
*/
public interface RedisKeyPrefixes {
/**
* 应用名,所有key的统一前缀
* 在所有key之前加上应用名,方便Redis的数据管理
* 不同应用的key会通过前缀区分,做到数据隔离的效果
*/
String PREFIX_BASE = "springboot-shiro:";
/**
* Apache Shiro角色权限缓存的key前缀
*/
String PREFIX_SHIRO_PERMISSIONS = PREFIX_BASE + "shiro:permissions:";
}UsernameRealm.java
删除类上的@Component注解,重写getAuthorizationCacheKey()方法,使用前缀+用户ID作为key
java
package cn.edu.sgu.www.shiro.support;
import cn.edu.sgu.www.shiro.consts.ErrorMessages;
import cn.edu.sgu.www.shiro.consts.RedisKeyPrefixes;
import cn.edu.sgu.www.shiro.entity.User;
import cn.edu.sgu.www.shiro.mapper.RolePermissionMapper;
import cn.edu.sgu.www.shiro.mapper.UserMapper;
import cn.edu.sgu.www.shiro.mapper.UserRoleMapper;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.*;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.SimpleAuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author 沐雨橙风ιε
* @version 1.0
*/
public class UsernameRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Autowired
private UserRoleMapper userRoleMapper;
@Autowired
private RolePermissionMapper rolePermissionMapper;
/**
* 获取认证信息
*/
@Override
public AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {
// 获取登录时提交的token
UsernamePasswordToken token = (UsernamePasswordToken) authenticationToken;
// 得到用户名
String username = token.getUsername();
// 根据用户名查询用户信息
User user = userMapper.selectByUsername(username);
// 查询结果为空,则说明用户不存在
if (user == null) {
throw new AuthenticationException(ErrorMessages.loginFail);
} else if (user.isDisabled()) { // 账号被封禁,抛出异常
throw new AuthenticationException("登录失败,账号状态异常!");
}
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user, user.getPassword(), "usernameRealm");
}
/**
* 获取授权信息
*/
@Override
public AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
SimpleAuthorizationInfo authorizationInfo = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
// 得到用户ID
User user = (User) principals.getPrimaryPrincipal();
String userId = user.getId();
// 查询用户的角色列表
List<String> roleList = userRoleMapper.selectUserRoles(userId);
if (!roleList.isEmpty()) {
authorizationInfo.setRoles(new HashSet<>(roleList));
Set<String> stringPermissions = new HashSet<>();
for (String roleId : roleList) {
// 查询角色的权限列表
List<String> permissions = rolePermissionMapper.selectRolePermissions(roleId);
if (!permissions.isEmpty()) {
stringPermissions.addAll(permissions);
}
}
if (!stringPermissions.isEmpty()) {
authorizationInfo.setStringPermissions(stringPermissions);
}
}
return authorizationInfo;
}
/**
* 配置授权缓存的key
* @param principals PrincipalCollection
*/
@Override
public String getAuthorizationCacheKey(PrincipalCollection principals) {
User user = (User) principals.getPrimaryPrincipal();
return RedisKeyPrefixes.PREFIX_SHIRO_PERMISSIONS + user.getId();
}
}至此,授权缓存的问题就解决了。
密码安全问题
现在另外一个不容忽视的隐患是密码的安全问题,登录密码是直接明文存储在数据库的,对于这类高度敏感的信息,一般会采取加密的方式保证数据的安全性。
像密码这类信息,使用不可逆的加密方式会更合理,否则,安全问题依然存在。
这也就是为什么大部分APP忘记密码之后要求重置密码,应用本身也不知道你当时设置的密码是多少。
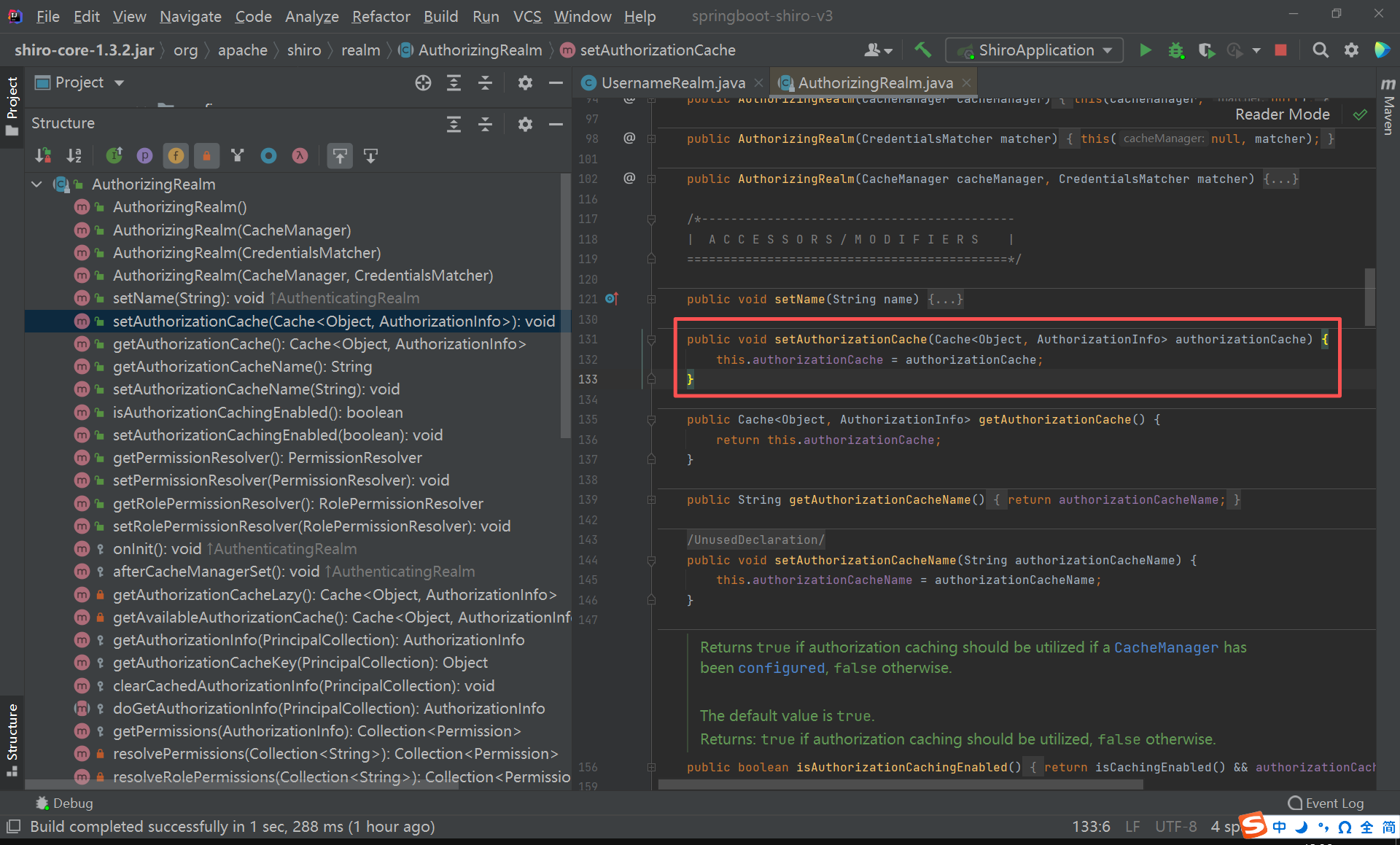
为了解决这个问题,需要查看前面AuthenticatingRealm的assertCredentialsMatch()方法。
java
CredentialsMatcher cm = getCredentialsMatcher();getCredentialsMatcher()方法也是返回一个当前类的成员变量。
java
public CredentialsMatcher getCredentialsMatcher() {
return credentialsMatcher;
}很显然,这里也能通过set方法设置这个密码匹配器。
创建密码匹配器
既然可以直接通过set方法设置这个密码匹配器,那么,我们就可以自定义验证密码的逻辑。
也就可以实现对密码的加密处理了,而不是原来的简单比较字符串内容。
PasswordEncoder.java
创建自己的密码加密器,使用MD5加密算法。
java
package cn.edu.sgu.www.shiro.support;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.util.DigestUtils;
import java.util.UUID;
/**
* 密码加密器
* @author 沐雨橙风ιε
* @version 1.0
*/
@Slf4j
public class PasswordEncoder {
/**
* 对用户提供的密码进行加密
* @param password 用户提供的密码
* @return 加密后的密码
*/
public static String encode(String password) {
// 生成随机盐
String salt = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-", "");
String encodedPassword = password;
encodedPassword = DigestUtils.md5DigestAsHex(
(salt + encodedPassword + salt + salt + encodedPassword + salt + salt + salt).getBytes()
);
return salt + encodedPassword;
}
/**
* 匹配密码
* @param password 用户提供的密码
* @param encodedPassword 加密后的密码
* @return 密码匹配返回true,否则返回false
*/
public static boolean matches(String password, String encodedPassword) {
String salt = null;
try {
// 获取盐
salt = encodedPassword.substring(0, 32);
} catch (StringIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
log.debug("密码格式错误:password = {}", encodedPassword);
e.printStackTrace();
}
String newPassword = password;
newPassword = DigestUtils.md5DigestAsHex(
(salt + newPassword + salt + salt + newPassword + salt + salt + salt).getBytes()
);
newPassword = salt + newPassword;
return newPassword.equals(encodedPassword);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String password = "mhxy1218";
System.out.println(encode(password));
}
}PasswordMatcher.java
创建自定义的密码匹配器,通过调用密码加密器的matches()方法匹配密码。
java
package cn.edu.sgu.www.shiro.support;
import cn.edu.sgu.www.shiro.consts.ErrorMessages;
import cn.edu.sgu.www.shiro.entity.User;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.credential.CredentialsMatcher;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* Apache Shiro密码匹配器
* @author 沐雨橙风ιε
* @version 1.0
*/
@Component
public class PasswordMatcher implements CredentialsMatcher {
@Override
public boolean doCredentialsMatch(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken, AuthenticationInfo authenticationInfo) {
// 得到用户输入的密码
UsernamePasswordToken token = (UsernamePasswordToken) authenticationToken;
String password = new String(token.getPassword());
// 得到数据库密码
PrincipalCollection principals = authenticationInfo.getPrincipals();
User user = (User) principals.getPrimaryPrincipal();
String encodedPassword = user.getPassword();
// 匹配密码
if (!PasswordEncoder.matches(password, encodedPassword)) {
throw new AuthenticationException(ErrorMessages.loginFail);
}
return true;
}
}ShiroConfig.java
设置密码匹配器到Realm中。
java
@Bean
public UsernameRealm usernameRealm(PasswordMatcher passwordMatcher, RedisCache redisCache) {
UsernameRealm usernameRealm = new UsernameRealm();
usernameRealm.setAuthorizationCache(redisCache);
usernameRealm.setCredentialsMatcher(passwordMatcher);
return usernameRealm;
}修改用户登录密码
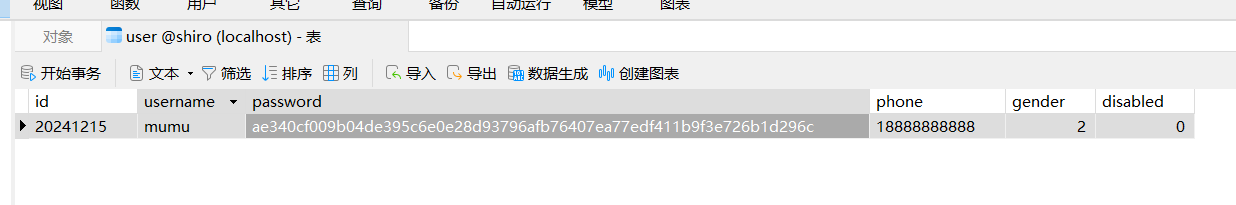
运行PasswordEncoder的main()方法,生成通过密码加密器加密得到的密码,然后替换数据库中的用户登录密码。
自定义未授权逻辑
当访问未授权的资源时,Apache Shiro的过滤器会拦截请求,并返回401状态码。
通常,我们需要定义自己的处理逻辑,比如返回一个比较个性化的提示。
指定处理路径
Apache Shiro支持未授权时重定向到指定的URL,可以在Controller接口中处理未授权,返回包装后的响应数据。
ShiroConfig.java
java
/**
* 配置Shiro过滤器工厂
*/
@Bean
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean shiroFilter(DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager) {
ShiroFilterFactoryBean shiroFilterFactoryBean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
// 注册安全管理器
shiroFilterFactoryBean.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
/*
* 设置登录页面的地址
* 当用户访问认证资源的时候,如果用户没有登录,那么就会跳转到该属性指定的页面
*/
shiroFilterFactoryBean.setLoginUrl("/login.html");
/*
* 设置访问未授权资源时重定向的地址
* 当用户访问需要指定权限才能访问的资源时,如果用户没有此权限,那么就会重定向到指定的页面
*/
shiroFilterFactoryBean.setUnauthorizedUrl("/user/unauthorized");
// 定义资源访问规则
Map<String, String> filterChainDefinitionMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
/*
* 过滤器说明
* anon:不需要认证就可以访问的资源
* authc:需要登录认证才能访问的资源
* perms:需要指定权限才能访问的资源
*/
// 需要登录认证才能访问的资源
filterChainDefinitionMap.put("/", "authc");
filterChainDefinitionMap.put("/index.html", "authc");
// 查询所有权限
List<Permission> permissions = permissionMapper.selectPermissions();
// 需要指定权限才能访问的资源
for (Permission permission : permissions) {
if (permission.getAnonymity() == 0) {
filterChainDefinitionMap.put(permission.getUrl(), "perms[" + permission.getValue() + "]");
} else {
filterChainDefinitionMap.put(permission.getUrl(), "anon");
}
}
shiroFilterFactoryBean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(filterChainDefinitionMap);
return shiroFilterFactoryBean;
}UserController.java
java
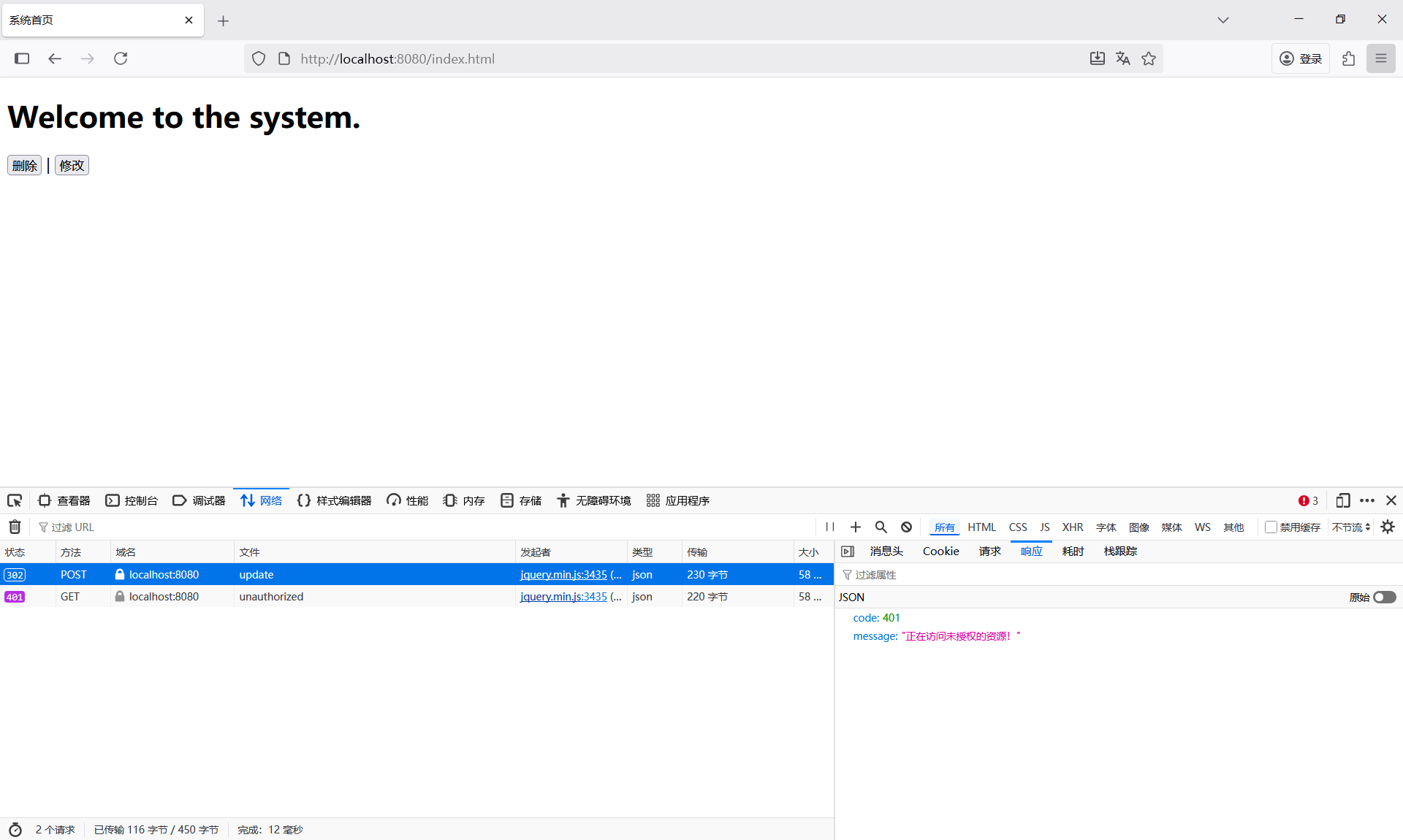
@RequestMapping(path = "/unauthorized", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public JsonResult<Void> unauthorized() {
throw new GlobalException(ResponseCode.UNAUTHORIZED, "正在访问未授权的资源!");
}取消修改用户的权限,删除Redis中的权限缓存。
点击修改按钮,可以看到响应内容确实是UserController.unauthorized()方法的返回值。
自定义过滤器
除了指定未授权的处理路径,还可以通过滤器处理未授权的访问。
Shiro是通过PermissionsAuthorizationFilter这个过滤器处理授权访问资源的请求的,可以重写这个过滤器,然后覆盖设置到perms过滤器链中。
PermsFilter.java
java
package cn.edu.sgu.www.shiro.support;
import cn.edu.sgu.www.shiro.restful.JsonResult;
import cn.edu.sgu.www.shiro.restful.ResponseCode;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.shiro.web.filter.authz.PermissionsAuthorizationFilter;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.ServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
/**
* 定义PermsFilter过滤器(覆盖shiro的perms过滤器)
* @author 沐雨橙风ιε
* @version 1.0
*/
@Slf4j
public class PermsFilter extends PermissionsAuthorizationFilter {
@Override
public boolean isAccessAllowed(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse resp, Object mappedValue) throws IOException {
boolean accessAllowed = super.isAccessAllowed(req, resp, mappedValue);
if (!accessAllowed) {
// 获取request对象
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
// 得到请求地址
String requestURI = request.getRequestURI();
String errorMessage = "正在访问未授权的资源:" + requestURI;
log.debug(errorMessage);
ResponseCode responseCode = ResponseCode.UNAUTHORIZED;
// 获取response对象
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) resp;
response.setStatus(responseCode.getValue());
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=UTF-8");
// 构建返回对象
JsonResult<Void> jsonResult = JsonResult.error(responseCode, errorMessage);
try (PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter()) {
writer.write(JSON.toJSONString(jsonResult));
}
}
return true;
}
}ShiroConfig.java
将PermsFilter设置到Shiro的过滤器链中,覆盖原来名字为perms的过滤器。
java
// 添加自定义过滤器
Map<String, Filter> filters = shiroFilterFactoryBean.getFilters();
filters.put("perms", new PermsFilter());
shiroFilterFactoryBean.setFilters(filters);