搞了好久终于搞出来了,问题是有个别尾节点位置会拉的非常远,如图
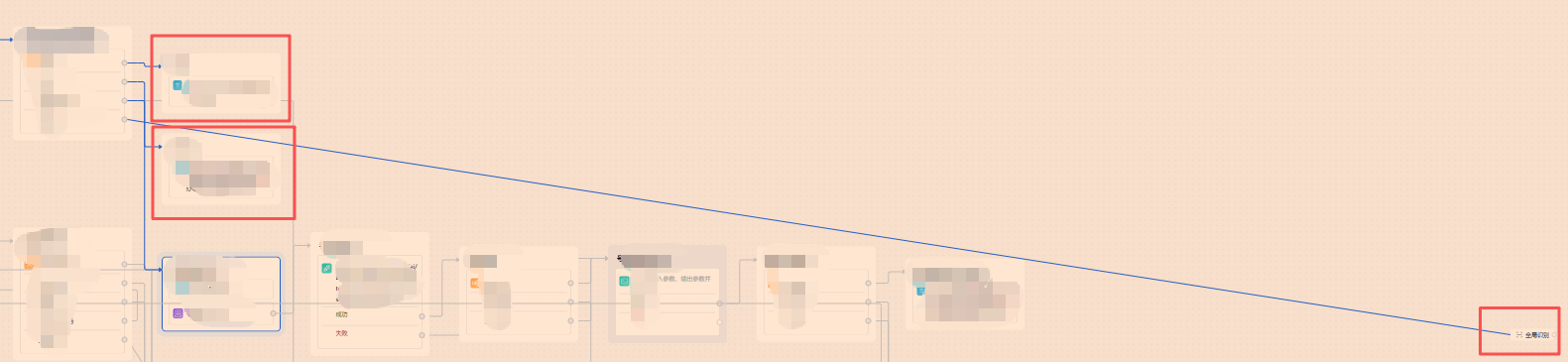
只测1个节点的尾节点都有距离,如图

我又搞了个普通节点做对比,也有问题
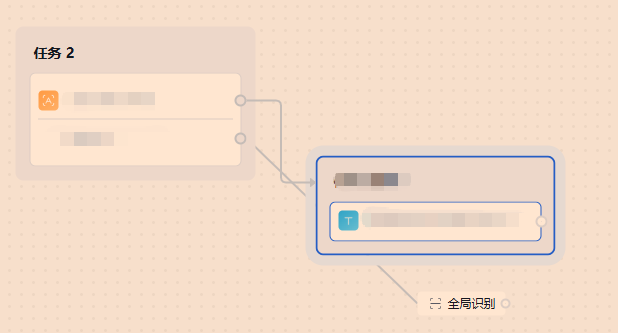
我就不会了,以为是dagre的事儿, 换了elk还是有问题,各种大模型找原因,都不行
我就一个节点一个节点的坐标全都打出来,把整理前和整理后的节点都打出来,发现尾节点的x坐标和普通尾节点的x坐标一致,我都懵了
最后捅咕出来的成功代码
Zhenglijiedian = (): void => {
const originNodes = this.flowInstance?.getNodes()
const edges = this.flowInstance?.getEdges()
//过滤出width不为空的节点
var parentNode = []
const nodes = originNodes.filter(node => {
if(node.parentId){
parentNode.push(node.parentId);
}
return node.width !== undefined && node.width !== null && node.width > 0;
});
console.log("nodes:", nodes)
const dagreGraph = new dagre.graphlib.Graph();
dagreGraph.setDefaultEdgeLabel(() => ({}));
dagreGraph.setGraph({
rankdir: 'LR', // 布局方向,可以是 'TB'(上到下)、'LR'(左到右)、'BT'(下到上)、'RL'(右到左)
align: 'UL', // 对齐方式
nodesep: 40, // 节点之间的水平距离
ranksep: 60, // 节点之间的垂直距离
ranker: 'network-simplex', // 节点排序方式
marginx: 60, // 左边距
marginy: 200 // 上边距
});
const parentNodeLayoutMap = {} as Record<string, Node>
nodes.forEach(node => {
dagreGraph.setNode(node.id, { width: node.width, height: node.height });
if(parentNode.includes(node.id)){
parentNodeLayoutMap[node.id] = node;
}
});
edges.forEach(edge => {
dagreGraph.setEdge(edge.source, edge.target);
});
dagre.layout(dagreGraph);
nodes.map(node => {
const position = dagreGraph.node(node.id);
node.position.x = position.x - node.width / 2
node.position.y = position.y - node.height / 2
if (node.parentId && parentNodeLayoutMap.hasOwnProperty(node.parentId)) {
//如果是有parentId的子节点,减去父节点坐标的位置
node.position.x = node.position.x - parentNodeLayoutMap[node.parentId].position.x;
node.position.y = node.position.y - parentNodeLayoutMap[node.parentId].position.y;
}
});
}解释:多次查大模型的过程中,发现个问题,"全局识别"这个尾节点和其他普通尾节点不同的是他有parentId,大模型说,有parentId的节点算作子节点,他在实际布局时,【坐标是子节点的坐标+父节点的坐标】,一下我就恍然大悟了