1.Simple(简单模式):

P:生产者,也就是要发送的程序。
C:消费者,消息的接受者。
Queue:消息队列,图中黄色的部分,类似一个邮箱,P可以往里面投敌消息,消费者可以从其中取出消息。
特点:一个生产者P,一个消费者C,消息只能被消费一次,也被称为点对点模式。
2.Work Queue(工作队列):
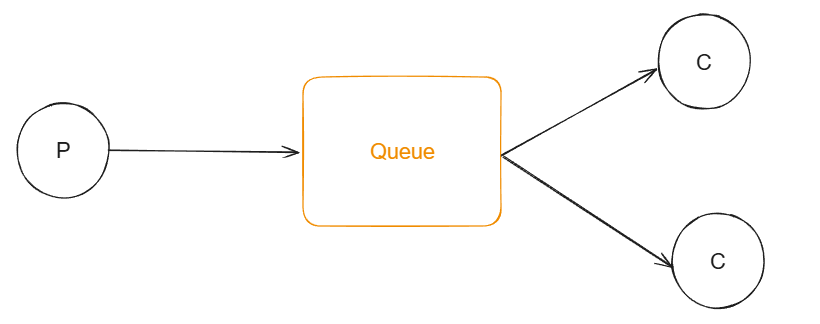
一个生产者P,多个消费者C,在多个消息的情况下,Work Queue会将消息分派给不同的消费者,也就是说每个消费者收到的消息都不同。
特点:消息不会重复,分配给不同的消费者。
交换机有关的工作模式:
在订阅模型中,多了一个交换机角色,过程略有办法。
概念介绍:
交换机(exchange)
作用:生产者将消息发送到Exchange中,然后交换机按照一定规则路由到一个或多个队列中。
RabbitMQ交换机有四种类型:fanout,direct,topic,headers,不同类型有不同的路由策略。
Fanout:广播,将所有消息交给所绑定到交换机的队列(Publish/Subscribe模式)
Direct:定向,把消息定向交给指定的routingKey的队列(Routing模式)
Topic:通配符,把消息交给符合Routing pattern(路由模式)的队列(Topics模式)
headers:headers类型的交换器不依赖于路由键的匹配规则来路由消息,而且也不实用,基本不会用到。
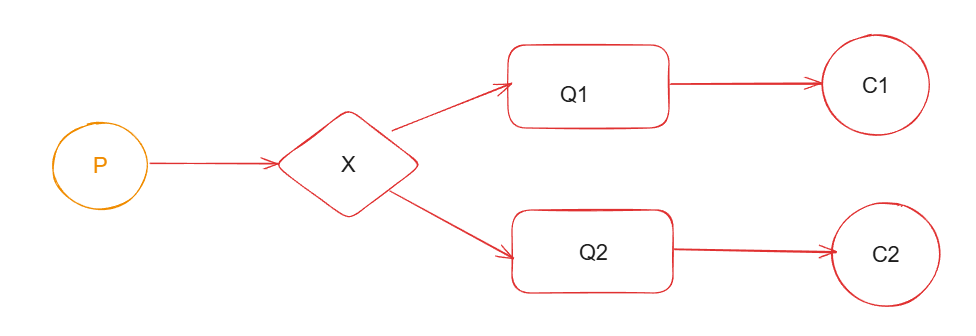
3.Publish/Subscribe(发布/订阅):
一个生产者P,多个消费者,这时就多了一个交换机的角色,每个消费者都能收到相同的消息。生产者发送一条消息,经过交换机转换到多个不同的队列,多个队列有多个不同的消费者。
适合场景:消息需要被多个消费者同时接收的场景,如:实时通知或者广播消息。
4.Routing(路由模式):
路由模式是发布订阅模式的变更,比发布订阅模式基础上,加了一个路由key,发布订阅模式是无条件将所有消息分发给所有消费者,路由模式是Exchange根据RoutingKey的规则,将数据进行匹配后发送给对应的消费者队列。
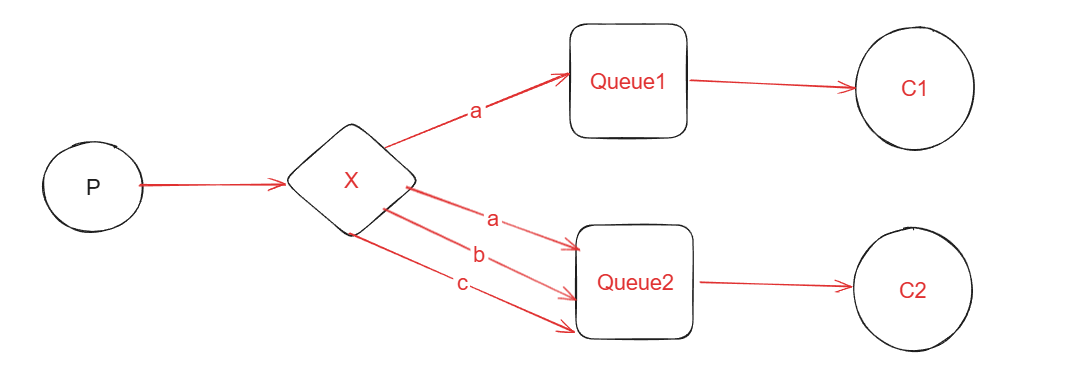
X是交换机,然后根据不同的RoutingKey(a,b,c)发送到对应的队列中。
5.Topics(通配符模式):
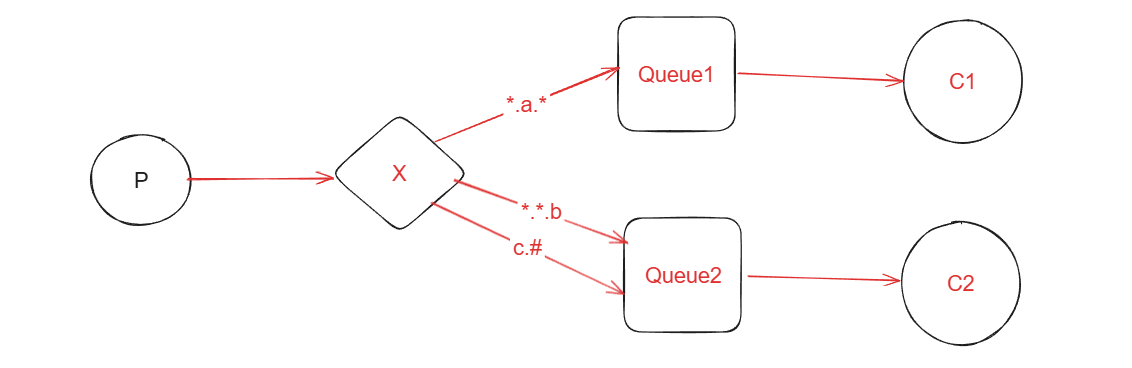
通配符模式是路由模式的升级,在RoutingKey的基础上,增加了通配符的功能,使之更加灵活。
Topic和Routing的基本原理相同,但是匹配的规则不同,Routing是相等匹配,而topics模式是通配符匹配。
*号匹配一个且仅一个单词。
#号匹配0个或者多个单词。
6.RPC(RPC通信):
在RPC通信过程中,没有生产者和消费者,比较像咱们RPC远程调用,大概通过两个队列实现了一个可回调过程。
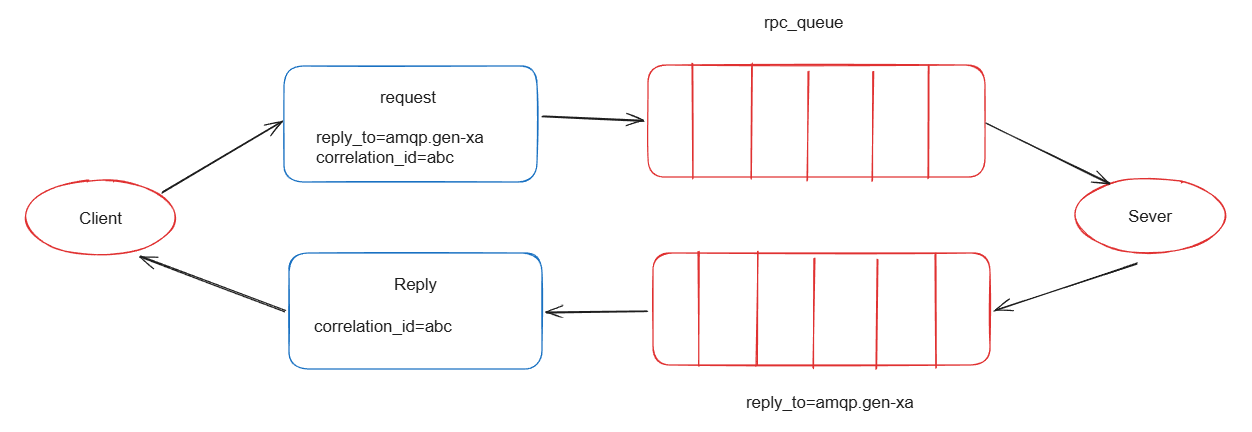
1.客户端发送一个消息到指定的队列,并且在消息属性中设置ReplyTo字段,这个字段指定了一个回到队列,用于接受服务器的响应。
2.服务器就收到消息后,处理请求并响应消息到ReplyTo指定的回调队列中。
3.客户端在回调队列上等待响应消息,一旦接收到响应,客户端会检查消息的correlationId属性,确保是不是自己期望的响应。
7.Publisher Confirm(发布确认):
Publisher Comfirm模式是RabbitMQ提供的一种确保消息可靠发送到RabbitMQ服务器的机制,这种模式下,生产者发送了消息后,可以等待RabbitMQ服务器的确认,以确保消息已经被服务器接受并处理。
1.生产者将channel设置为Confirm模式(通过调用channel.confirmSelect()完成)后,发布每一条消息都会获得一个唯一ID,生产者可以将这些序列号关联起来,追踪消息的状态。
2.当消息被RabbitMQ服务器接收并处理后,服务器会异步的向生产者发送一个确认(ACK)给生产者(包含唯一ID),表示消息已经送达。
工作队列的代码:
1.引入依赖:
java
<dependency>
<groupId>com.rabbitmq</groupId>
<artifactId>amqp-client</artifactId>
<version>5.25.0</version>
</dependency>2.编写生产者代码:
java
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
//创建channel通道
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");//默认值localhost
factory.setPort(5672);//默认值是5672
factory.setUsername("guest");//用户名,默认guest
factory.setPassword("guest");//密码,默认guest
factory.setVirtualHost("Virtual host");//虚拟机的名称
Connection connection=factory.newConnection();
Channel channel=connection.createChannel();
//声明队列,如果没有这样的队列,就会自动生成一个,如果有则不生成。
channel.queueDeclare("hello",true, false, false, null);
//发送消息
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
String message = "Hello RabbitMQ!";
//发送消息,默认交换机是""
channel.basicPublish("","hello",null,message.getBytes());
}
//释放资源
channel.close();
connection.close();
}3.编写消费者代码:
java
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
//创建channel通道
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost("localhost");//默认值localhost
connectionFactory.setPort(5672);//默认值是5672
connectionFactory.setUsername("guest");//用户名,默认guest
connectionFactory.setPassword("guest");//密码,默认guest
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost("Virtual host");//虚拟机的名称
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//声明队列
channel.queueDeclare("hello", true, false, false, null);
//接收消息,并消费
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("接收到消息"+new String(body));
}
};
channel.basicConsume("hello",true,consumer);
}运行结果:
Publish/Subscribe(发布/订阅)代码:
在发布订阅模式中,多了一个Exchange交换机。同时还有将交换机和队列进行关系绑定,以便路由到对应的队列中,给消费者消费。
1.引入依赖:
java
<dependency>
<groupId>com.rabbitmq</groupId>
<artifactId>amqp-client</artifactId>
<version>5.25.0</version>
</dependency>2.生产者代码:
java
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
//建立channel通道
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");//默认值localhost
factory.setPort(5672);//默认值是5672
factory.setUsername("guest");//用户名,默认guest
factory.setPassword("guest");//密码,默认guest
factory.setVirtualHost("Virtual host");//虚拟机的名称
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//声明交换机,因为这里是发布/订阅模式,所以type是BuiltinExchangeType.FANOUT
channel.exchangeDeclare("fanout.exchange",BuiltinExchangeType.FANOUT,true,false,false,null);
//声明队列,这里声明两个队列
channel.queueDeclare("fanout.queue1",true,false,false,null);
channel.queueDeclare("fanout.queue2",true,false,false,null);
//绑定交换机和队列,后面的routinKey是匹配规则,这里的发布订阅模式所以是""
channel.queueBind("fanout.queue1", "fanout.exchange","");
channel.queueBind("fanout.queue2", "fanout.exchange","");
//发送消息
String message = "Hello fanout!!";
channel.basicPublish("fanout.exchange","", null, message.getBytes());
//资源释放
channel.close();
connection.close();
}3.消费者代码:
这里有两个消费者:
消费者1代码:
java
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
//建立channel通道
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");//默认值localhost
factory.setPort(5672);//默认值是5672
factory.setUsername("guest");//用户名,默认guest
factory.setPassword("guest");//密码,默认guest
factory.setVirtualHost("Virtual host");//虚拟机的名称
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//声明队列
channel.queueDeclare("fanout.queue1", true, false, false, null);
//消费队列
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("接收到消息"+new String(body));
}
};
channel.basicConsume("fanout.queue1",true,consumer);
}消费者2代码:
java
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");//默认值localhost
factory.setPort(5672);//默认值是5672
factory.setUsername("guest");//用户名,默认guest
factory.setPassword("guest");//密码,默认guest
factory.setVirtualHost("Virtual host");//虚拟机的名称
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
channel.queueDeclare("fanout.queue2", true, false, false, null);
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("接收到消息"+new String(body));
}
};
channel.basicConsume("fanout.queue2",true,consumer);
}运行结果:
消费者1:
消费者2:
可以看出发布订阅模式中,每个消费者都收到了相同的消息。
Routing(路由模式):
路由模式不同于上面的发布/订阅模式,路由模式的匹配规则不是任意绑定了,而是要指定一个BindingKey的一种。
而且生产者在像Exchange发送消息时,也需要指定消息的RoutingKey。
Exchange不再把消息交给每个绑定的key,而是根据消息的RoutingKey进行判断,只有队列绑定时的BindKey和发送消息的Routingkey完全一致时,才会收到消息。
接下来看代码实现:
1.引入依赖:
java
<dependency>
<groupId>com.rabbitmq</groupId>
<artifactId>amqp-client</artifactId>
<version>5.25.0</version>
</dependency>2.编写生产者代码:
这时交换机类型是DIRECT。

java
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
//建立channel通道
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");//默认值localhost
factory.setPort(5672);//默认值是5672
factory.setUsername("guest");//用户名,默认guest
factory.setPassword("guest");//密码,默认guest
factory.setVirtualHost("Virtual host");//虚拟机的名称
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//创建交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare("direct.exchange", BuiltinExchangeType.DIRECT,true,false,false,null);
//声明队列
channel.queueDeclare("direct.queue1", true, false, false, null);
channel.queueDeclare("direct.queue2", true, false, false, null);
//绑定队列和交换机的关系
channel.queueBind("direct.queue1", "direct.exchange", "a");
channel.queueBind("direct.queue2", "direct.exchange", "a");
channel.queueBind("direct.queue2", "direct.exchange", "b");
channel.queueBind("direct.queue2", "direct.exchange", "c");
//发送消息
String msga="hello a!";
String msgb="hello b!";
String msgc="hello c!";
channel.basicPublish("direct.exchange", "a", null, msga.getBytes());
channel.basicPublish("direct.exchange", "b", null, msgb.getBytes());
channel.basicPublish("direct.exchange", "c", null, msgc.getBytes());
System.out.println("消息发送成功!!!");
//释放资源
channel.close();
connection.close();
}3.编写消费者代码:
消费者1代码:
java
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");//默认值localhost
factory.setPort(5672);//默认值是5672
factory.setUsername("guest");//用户名,默认guest
factory.setPassword("guest");//密码,默认guest
factory.setVirtualHost("Virtual host");//虚拟机的名称
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//接收消息并消费
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("接收到消息"+new String(body));
}
};
channel.basicConsume("direct.queue1",true,consumer);
}消费者2代码:
java
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");//默认值localhost
factory.setPort(5672);//默认值是5672
factory.setUsername("guest");//用户名,默认guest
factory.setPassword("guest");//密码,默认guest
factory.setVirtualHost("Virtual host");//虚拟机的名称
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//接收消息并消费
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("接收到消息"+new String(body));
}
};
channel.basicConsume("direct.queue2",true,consumer);
}运行结果:
消费者1:
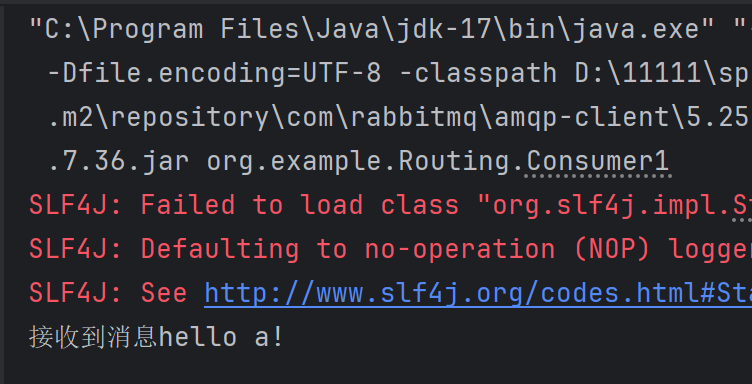
消费者2:
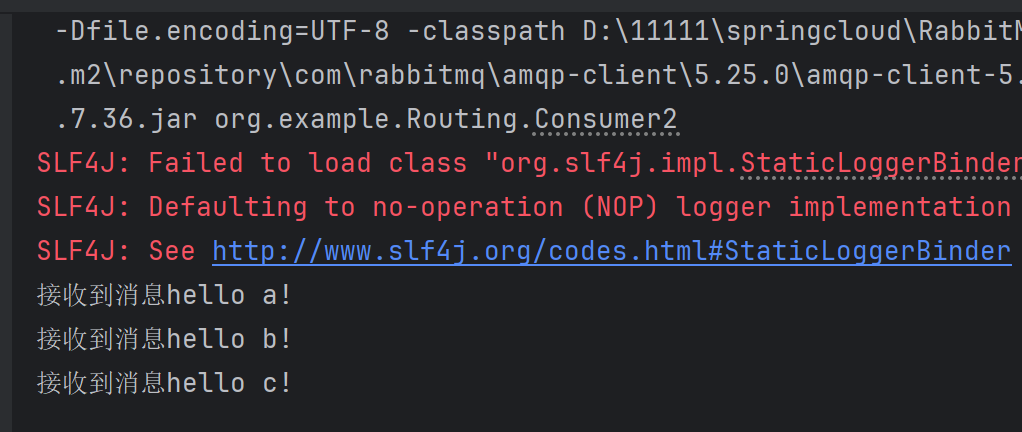
从运行结果可以看出Routing模式的规则。因为发送a消息时,只发送给了对应的消费者1,但发送a,b,c时,发送给了消费者2,因为他们二者和交换机的绑定规则不一样。
Topics(通配符模式):
这里的通配符模式,交换机类型是TOPIC
topic类型的交换机在匹配规则上进行了扩展,BindKey支持通配符匹配,direct类型的交换机的规则是Bindingkey和Routingkey完全匹配。

代码和上面的Routing模式一样,我就只写区别代码,也就是交换机和队列绑定的代码。
java
//声明交换机和队列
channel.exchangeDeclare("topic.exchange", BuiltinExchangeType.TOPIC,true);
channel.queueDeclare("topic.queue1", true, false, false, null);
channel.queueDeclare("topic.queue2", true, false, false, null);
//绑定交换机和队列,这里的绑定规则使用通配符绑定,*表示匹配一个且仅一个单词,#表示匹配0个或多个单词
channel.queueBind("topic.queue1", "topic.exchange", "*.a.*");
channel.queueBind("topic.queue2", "topic.exchange", "*.*.b");
channel.queueBind("topic.queue2", "topic.exchange", "c.#");
//发送消息,此时,也要注明要将消息发送哪一个交换机,并且写明BingingKey,后续根据对应的BingingKey,匹配到对应的队列中
String message = "Hello A!";
channel.basicPublish("topic.exchange", "e.a.f", null, message.getBytes());
String message2 = "Hello B!";
channel.basicPublish("topic.exchange", "ef.a.b", null, message2.getBytes());
String message3 = "Hello C!";
channel.basicPublish("topic.exchange", "c.ef.b", null, message3.getBytes());RPC(RPC通信):
RPC(Remote Procedure Call),即远程过程调用,它是一种通过网络从远程计算机上请求服务,而不需要了解底层网络的技术,类是与Http远程调用。
RabbitMQ实现RPC通信的过程,大概是通过两个队列实现一个可回调的过程。
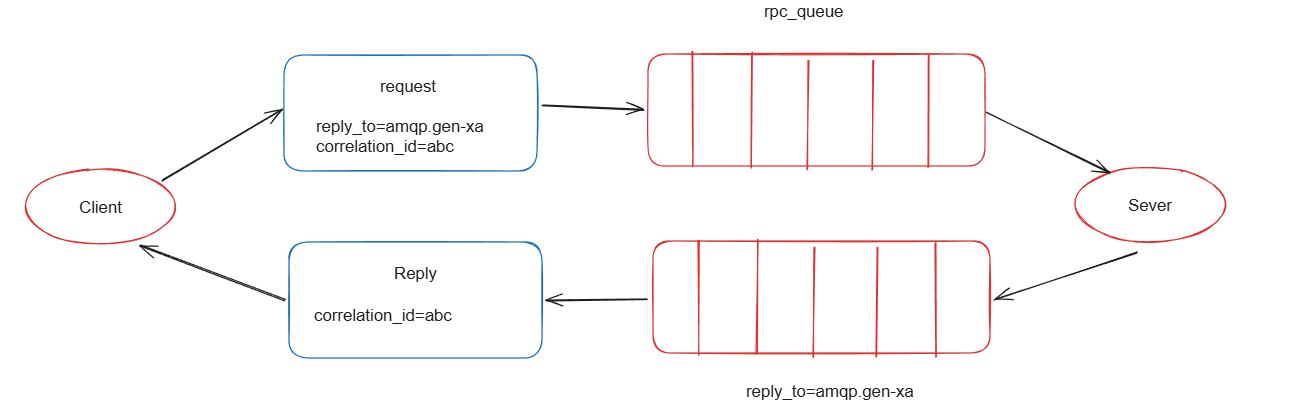
大致流程如下:
1.客户端发送一个消息到一个指定的队列,并在消息属性中设置replyTo字段,这个字段指定了一个回调队列,服务端处理后,会把响应结果发送到这个队里。
2.服务端接收到请求后,处理请求并发送响应消息到replyTo指定的回调队列。
3.客户端在回调队列上等待响应的消息,一旦有消息响应,客户端就会检查消息的correlationId属性,以确保是自己想要的响应。
PRC的代码实现:
1.引入依赖:
java
<dependency>
<groupId>com.rabbitmq</groupId>
<artifactId>amqp-client</artifactId>
<version>5.25.0</version>
</dependency>2.客户端代码:
java
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException, InterruptedException {
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");//默认值localhost
factory.setPort(5672);//默认值是5672
factory.setUsername("guest");//用户名,默认guest
factory.setPassword("guest");//密码,默认guest
factory.setVirtualHost("Virtual host");//虚拟机的名称
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//声明队列
channel.queueDeclare("rpc.queue", true, false, false, null);
//定义回调队列
channel.queueDeclare("rpc.response.queue", true, false, false, null);
String message = "Hello RabbitMQ!";
//本词请求的唯一标志
String correlationId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
//生成发送消息的属性
AMQP.BasicProperties props=new AMQP.BasicProperties().builder()
.correlationId(correlationId)
.replyTo("rpc.response.queue")
.build();
//发送消息
channel.basicPublish("", "rpc.queue", props,message.getBytes());
//阻塞队列,用于储存回调结果
final BlockingQueue<String> queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<String>(1);
//接收服务器的响应
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("接收到回调消息" + new String(body));
//进行标识判断,放到阻塞队列中
if(correlationId.equals(properties.getCorrelationId())){
queue.offer(new String(body));
}
}
};
channel.basicConsume("rpc.response.queue",true,consumer);
//获取回调结果
String result=queue.take();
System.out.println("RPC响应结果+"+result);
}3.服务端代码:
java
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost("localhost");//默认值localhost
factory.setPort(5672);//默认值是5672
factory.setUsername("guest");//用户名,默认guest
factory.setPassword("guest");//密码,默认guest
factory.setVirtualHost("Virtual host");//虚拟机的名称
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//设置同时只能获取一个消息
channel.basicQos(1);
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println(new String(body));
//处理请求,并生成返回
System.out.println("接收到请求!!"+new String(body));
AMQP.BasicProperties props=new AMQP.BasicProperties().builder()
.correlationId(properties.getCorrelationId())
.build();
//回复消息,通知已经收到的请求
channel.basicPublish("", "rpc.response.queue", props, body);
//对消息进行应答
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
};
channel.basicConsume("rpc.queue",false,consumer);
}运行结果:
客户端:
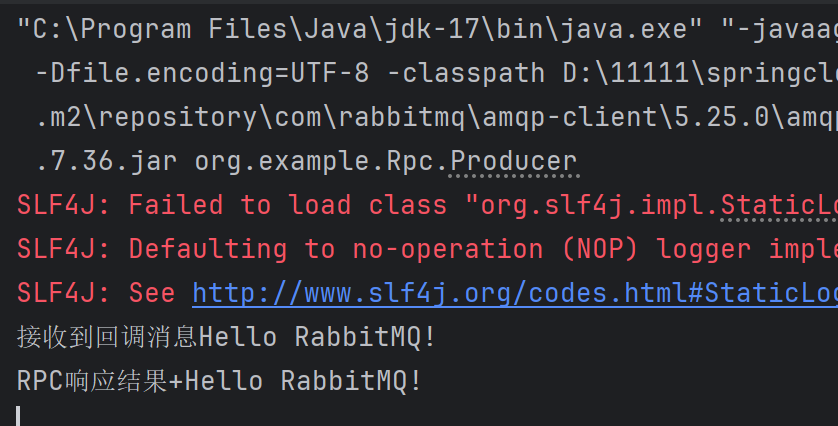
服务端:
可以看出,客户端给服务端成功发送了请求,并成功处理后,服务端还给客户端进行响应请求。
还有一种发布确认模式,在后面的文章会续上。