一. 伙伴系统中分配page
cond_accept_memory(zone, order); 3349 3350 mark = wmark_pages(zone, alloc_flags & ALLOC_WMARK_MASK); 3351 trace_android_vh_get_page_wmark(alloc_flags, &mark); 3352 if (!zone_watermark_fast(zone, order, mark, 3353 ac->highest_zoneidx, alloc_flags, 3354 gfp_mask)) { 3355 int ret; 3356 3357 if (cond_accept_memory(zone, order)) 3358 goto try_this_zone;
cs
/*
3271 * get_page_from_freelist goes through the zonelist trying to allocate
3272 * a page.
3273 */
3274 static struct page *
3275 get_page_from_freelist(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order, int alloc_flags,
3276 const struct alloc_context *ac)
3277 {
3278 struct zoneref *z;
3279 struct zone *zone;
3280 struct pglist_data *last_pgdat = NULL;
3281 bool last_pgdat_dirty_ok = false;
3282 bool no_fallback;
3283
3284 retry:
3285 /*
3286 * Scan zonelist, looking for a zone with enough free.
3287 * See also cpuset_node_allowed() comment in kernel/cgroup/cpuset.c.
3288 */
3289 no_fallback = alloc_flags & ALLOC_NOFRAGMENT;
3290 z = ac->preferred_zoneref;
3291 for_next_zone_zonelist_nodemask(zone, z, ac->highest_zoneidx,
3292 ac->nodemask) {
3293 struct page *page;
3294 unsigned long mark;
3295
3296 if (!zone_is_suitable(zone, order))
3297 continue;
3298
3299 if (cpusets_enabled() &&
3300 (alloc_flags & ALLOC_CPUSET) &&
3301 !__cpuset_zone_allowed(zone, gfp_mask))
3302 continue;
3303 /*
3304 * When allocating a page cache page for writing, we
3305 * want to get it from a node that is within its dirty
3306 * limit, such that no single node holds more than its
3307 * proportional share of globally allowed dirty pages.
3308 * The dirty limits take into account the node's
3309 * lowmem reserves and high watermark so that kswapd
3310 * should be able to balance it without having to
3311 * write pages from its LRU list.
3312 *
3313 * XXX: For now, allow allocations to potentially
3314 * exceed the per-node dirty limit in the slowpath
3315 * (spread_dirty_pages unset) before going into reclaim,
3316 * which is important when on a NUMA setup the allowed
3317 * nodes are together not big enough to reach the
3318 * global limit. The proper fix for these situations
3319 * will require awareness of nodes in the
3320 * dirty-throttling and the flusher threads.
3321 */
3322 if (ac->spread_dirty_pages) {
3323 if (last_pgdat != zone->zone_pgdat) {
3324 last_pgdat = zone->zone_pgdat;
3325 last_pgdat_dirty_ok = node_dirty_ok(zone->zone_pgdat);
3326 }
3327
3328 if (!last_pgdat_dirty_ok)
3329 continue;
3330 }
3331
3332 if (no_fallback && nr_online_nodes > 1 &&
3333 zone != ac->preferred_zoneref->zone) {
3334 int local_nid;
3335
3336 /*
3337 * If moving to a remote node, retry but allow
3338 * fragmenting fallbacks. Locality is more important
3339 * than fragmentation avoidance.
3340 */
3341 local_nid = zone_to_nid(ac->preferred_zoneref->zone);
3342 if (zone_to_nid(zone) != local_nid) {
3343 alloc_flags &= ~ALLOC_NOFRAGMENT;
3344 goto retry;
3345 }
3346 }
3347
3348 cond_accept_memory(zone, order);
3349
3350 mark = wmark_pages(zone, alloc_flags & ALLOC_WMARK_MASK);
3351 trace_android_vh_get_page_wmark(alloc_flags, &mark);
3352 if (!zone_watermark_fast(zone, order, mark,
3353 ac->highest_zoneidx, alloc_flags,
3354 gfp_mask)) {
3355 int ret;
3356
3357 if (cond_accept_memory(zone, order))
3358 goto try_this_zone;
3359
3360 #ifdef CONFIG_DEFERRED_STRUCT_PAGE_INIT
3361 /*
3362 * Watermark failed for this zone, but see if we can
3363 * grow this zone if it contains deferred pages.
3364 */
3365 if (deferred_pages_enabled()) {
3366 if (_deferred_grow_zone(zone, order))
3367 goto try_this_zone;
3368 }
3369 #endif
3370 /* Checked here to keep the fast path fast */
3371 BUILD_BUG_ON(ALLOC_NO_WATERMARKS < NR_WMARK);
3372 if (alloc_flags & ALLOC_NO_WATERMARKS)
3373 goto try_this_zone;
3374
3375 if (!node_reclaim_enabled() ||
3376 !zone_allows_reclaim(ac->preferred_zoneref->zone, zone))
3377 continue;
3378
3379 ret = node_reclaim(zone->zone_pgdat, gfp_mask, order);
3380 switch (ret) {
3381 case NODE_RECLAIM_NOSCAN:
3382 /* did not scan */
3383 continue;
3384 case NODE_RECLAIM_FULL:
3385 /* scanned but unreclaimable */
3386 continue;
3387 default:
3388 /* did we reclaim enough */
3389 if (zone_watermark_ok(zone, order, mark,
3390 ac->highest_zoneidx, alloc_flags))
3391 goto try_this_zone;
3392
3393 continue;
3394 }
3395 }
3396
3397 try_this_zone:
3398 page = rmqueue(ac->preferred_zoneref->zone, zone, order,
3399 gfp_mask, alloc_flags, ac->migratetype);
3400 if (page) {
3401 prep_new_page(page, order, gfp_mask, alloc_flags);
3402
3403 /*
3404 * If this is a high-order atomic allocation then check
3405 * if the pageblock should be reserved for the future
3406 */
3407 if (unlikely(alloc_flags & ALLOC_HIGHATOMIC))
3408 reserve_highatomic_pageblock(page, zone);
3409
3410 return page;
3411 } else {
3412 if (cond_accept_memory(zone, order))
3413 goto try_this_zone;
3414
3415 #ifdef CONFIG_DEFERRED_STRUCT_PAGE_INIT
3416 /* Try again if zone has deferred pages */
3417 if (deferred_pages_enabled()) {
3418 if (_deferred_grow_zone(zone, order))
3419 goto try_this_zone;
3420 }
3421 #endif
3422 }
3423 }
3424
3425 /*
3426 * It's possible on a UMA machine to get through all zones that are
3427 * fragmented. If avoiding fragmentation, reset and try again.
3428 */
3429 if (no_fallback) {
3430 alloc_flags &= ~ALLOC_NOFRAGMENT;
3431 goto retry;
3432 }
3433
3434 return NULL;
3435 }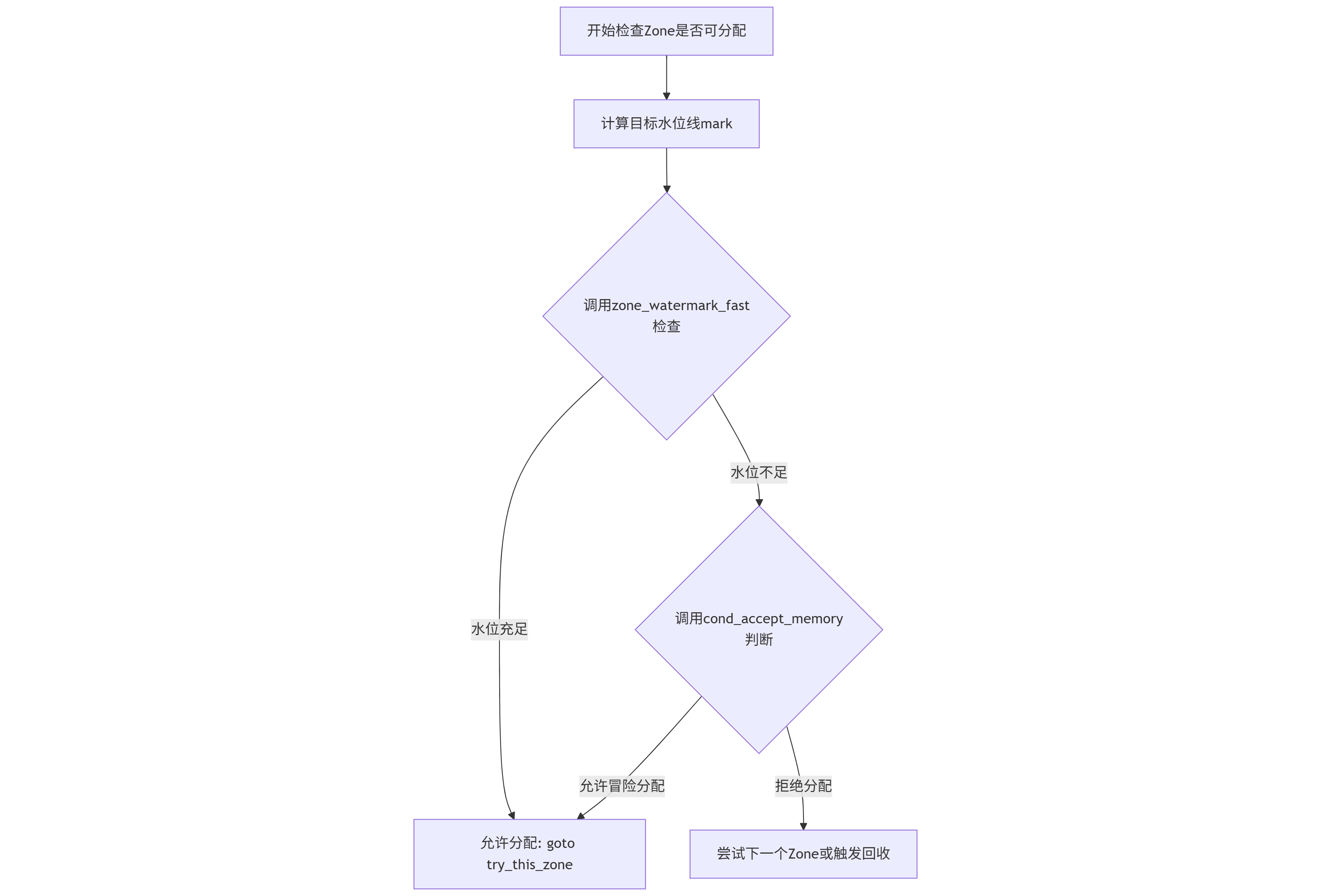
下面我们详细解读图中的关键环节。
⚙️ 代码逻辑详解
1. 计算目标水位线 (mark = wmark_pages(...))
这行代码根据分配标志位 alloc_flags 中的水印掩码 (ALLOC_WMARK_MASK),确定本次分配应该以哪条水位线作为标准
。
ALLOC_WMARK_LOW: 使用低水位线 (WMARK_LOW)。这是最常见 的选择,表示允许内核在内存尚有合理余量时进行分配,并可能唤醒kswapd进行后台回收。ALLOC_WMARK_MIN: 使用最低水位线 (WMARK_MIN)。这通常在内存压力较大、需要进行直接回收时使用,意味着分配请求很紧急。ALLOC_WMARK_HIGH: 使用高水位线 (WMARK_HIGH)。这是最保守的策略,通常用于不允许失败的高优先级分配。
2. 快速水位线检查 (zone_watermark_fast)
这是核心检查函数,它快速判断指定 Zone 的当前空闲页数是否足以满足本次 order 的分配请求,并且不低于 mark 水位线
。其内部会考虑 lowmem_reserve 等预留内存。如果返回 true,表示该 Zone 内存充足,可以直接分配。
3. 条件接受内存的决策 (cond_accept_memory)
当 zone_watermark_fast 检查失败(返回 false)时,表示该 Zone 的空闲内存低于要求的水位线,通常意味着分配应失败或需要触发回收。cond_accept_memory 函数在此刻充当一个"安全阀"或"风险评估器"
。 它的作用是:在内存明显不足的情况下,判断是否可以冒险进行一次分配。
- 若
cond_accept_memory(zone, order)返回true,则代码跳转到try_this_zone标签,允许内核冒险尝试从该 Zone 进行分配。 - 若返回
false,则流程继续,可能导致分配器尝试下一个优先级更低的 Zone,或者进入慢速路径触发直接内存回收。
💡 核心设计思想
这段代码体现了 Linux 内核内存分配在效率 和安全之间的精细权衡:
- 效率优先 :首先尝试最快速的
zone_watermark_fast检查,力求在常规情况下以最小开销完成分配。 - 安全兜底 :当快速检查提示内存不足时,不立即失败,而是通过
cond_accept_memory进行二次评估。这防止了在内存压力"临界点"附近过于保守而导致不必要的分配失败或回收操作,提升了系统的鲁棒性。
🔍 实际应用场景
你可以将 /proc/zoneinfo 中某个 Zone 的 free 数值与它的 min, low, high 水位线进行对比。当 free 低于 low 但 cond_accept_memory 可能允许分配时,正是这套机制在起作用,它试图在内存压力下尽可能维持系统的分配能力。
二. zone 中水位的计算
cs
static void __setup_per_zone_wmarks(void)
5934 {
5935 unsigned long pages_min = min_free_kbytes >> (PAGE_SHIFT - 10);
5936 unsigned long lowmem_pages = 0;
5937 struct zone *zone;
5938 unsigned long flags;
5939
5940 /* Calculate total number of pages below ZONE_HIGHMEM */
5941 for_each_zone(zone) {
5942 if (zone_idx(zone) <= ZONE_NORMAL)
5943 lowmem_pages += zone_managed_pages(zone);
5944 }
5945
5946 for_each_zone(zone) {
5947 u64 tmp;
5948
5949 spin_lock_irqsave(&zone->lock, flags);
5950 tmp = (u64)pages_min * zone_managed_pages(zone);
5951 do_div(tmp, lowmem_pages);
5952 if (zone_idx(zone) > ZONE_NORMAL) {
5953 /*
5954 * __GFP_HIGH and PF_MEMALLOC allocations usually don't
5955 * need pages from zones above ZONE_NORMAL, so cap
5956 * pages_min to a small value here.
5957 *
5958 * The WMARK_HIGH-WMARK_LOW and (WMARK_LOW-WMARK_MIN)
5959 * deltas control async page reclaim, and so should
5960 * not be capped for highmem and movable zones.
5961 */
5962 unsigned long min_pages;
5963
5964 min_pages = zone_managed_pages(zone) / 1024;
5965 min_pages = clamp(min_pages, SWAP_CLUSTER_MAX, 128UL);
5966 zone->_watermark[WMARK_MIN] = min_pages;
5967 } else {
5968 /*
5969 * If it's a lowmem zone, reserve a number of pages
5970 * proportionate to the zone's size.
5971 */
5972 zone->_watermark[WMARK_MIN] = tmp;
5973 }
5974
5975 /*
5976 * Set the kswapd watermarks distance according to the
5977 * scale factor in proportion to available memory, but
5978 * ensure a minimum size on small systems.
5979 */
5980 tmp = max_t(u64, tmp >> 2,
5981 mult_frac(zone_managed_pages(zone),
5982 watermark_scale_factor, 10000));
5983
5984 zone->watermark_boost = 0;
5985 zone->_watermark[WMARK_LOW] = min_wmark_pages(zone) + tmp;
5986 zone->_watermark[WMARK_HIGH] = low_wmark_pages(zone) + tmp;
5987 zone->_watermark[WMARK_PROMO] = high_wmark_pages(zone) + tmp;
5988
5989 spin_unlock_irqrestore(&zone->lock, flags);
5990 }
5991
5992 /* update totalreserve_pages */
5993 calculate_totalreserve_pages();
5994 }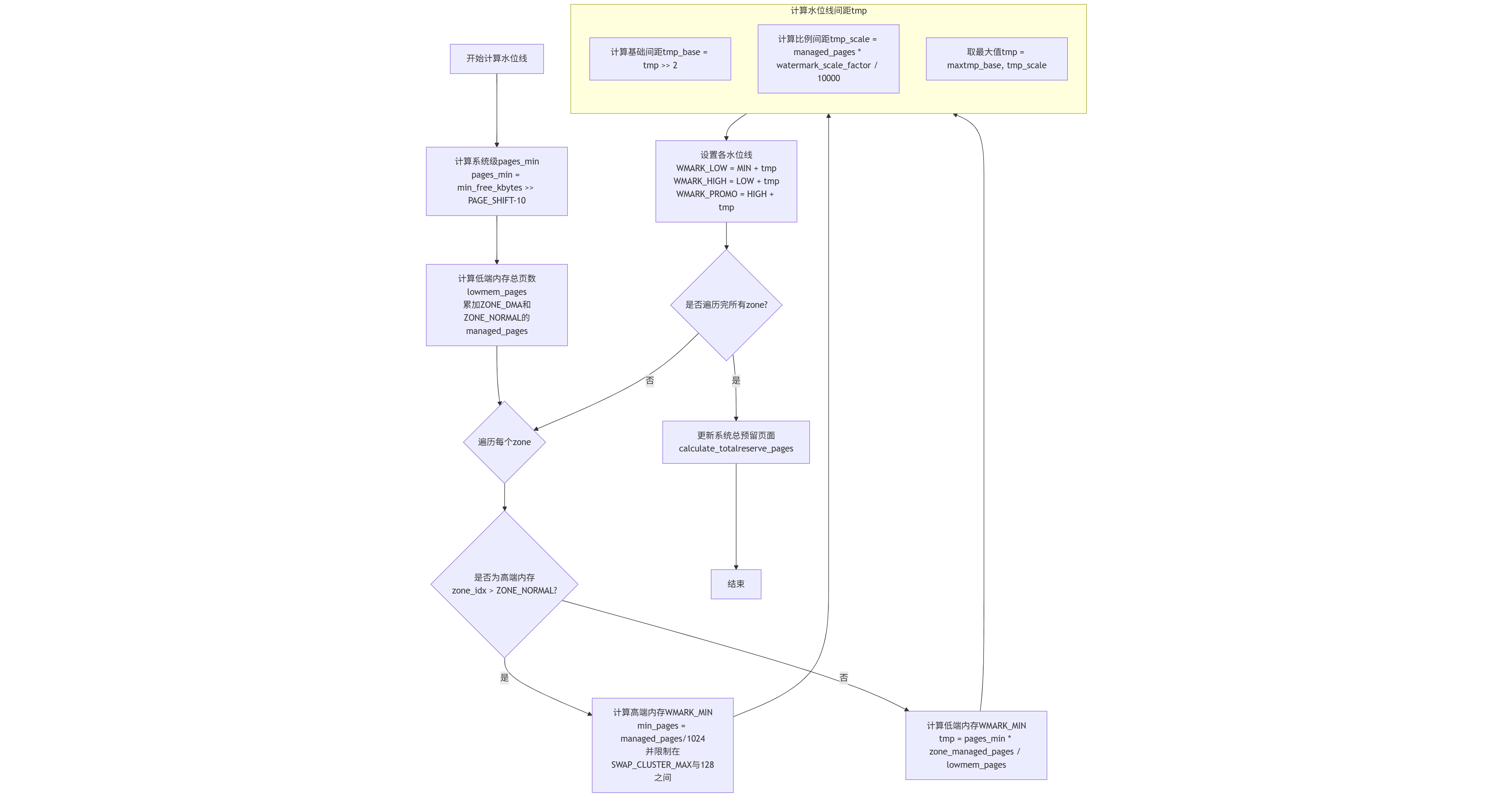
⚙️ 关键步骤详解
结合流程图,我们再来深入看看代码中的几个关键计算环节:
-
系统级基础值计算 (
pages_min):pages_min = min_free_kbytes >> (PAGE_SHIFT - 10);- 这行代码将全局参数
min_free_kbytes(单位为KB)转换为页数pages_min(单位为页)。因为PAGE_SHIFT通常为12(对应4KB页大小),所以PAGE_SHIFT - 10等于2,即右移2位相当于除以4,将KB单位换算成页数。
-
低端内存总页数 (
lowmem_pages):- 代码累加所有
ZONE_DMA和ZONE_NORMAL的managed_pages。这里lowmem_pages特指低端内存的总页数,用于后续按比例分配预留内存。在64位系统中,这通常代表了所有非高端内存区域。
- 代码累加所有
-
分区域计算
WMARK_MIN(最低水位线):- 对于低端内存 Zone (如 DMA、DMA32、Normal):
WMARK_MIN按该 Zone 的内存占比计算。即tmp = (u64)pages_min * zone_managed_pages(zone); do_div(tmp, lowmem_pages);。这确保了每个低端内存区域承担的"最低保障"与其大小成正比。 - 对于高端内存 Zone (HighMem):计算方式不同。
min_pages = zone_managed_pages(zone) / 1024;并限制在SWAP_CLUSTER_MAX和128页之间。这是因为许多内核分配请求无法使用高端内存,因此无需为其保留大量最低保障内存。
- 对于低端内存 Zone (如 DMA、DMA32、Normal):
-
计算水位线间距 (
tmp) 并设置WMARK_LOW和WMARK_HIGH:- 这是较新内核版本(引入
watermark_scale_factor后)的逻辑。tmp取两个值的最大值:tmp >> 2(即pages_min的四分之一)和mult_frac(zone_managed_pages(zone), watermark_scale_factor, 10000)(即该 Zone 总页数乘以缩放因子)。 - 最终,
WMARK_LOW = WMARK_MIN + tmp,WMARK_HIGH = WMARK_LOW + tmp。这使得水位线间距能够根据内存总量动态调整,在大内存机器上间距更大,kswapd 回收更平缓。
- 这是较新内核版本(引入
💡 核心设计思想
这段代码体现了 Linux 内核内存管理的几个关键设计原则:
- 按需分摊 :系统预留内存 (
min_free_kbytes) 按比例分摊到各个 Zone,而不是简单平均。 - 区别对待 :对低端内存和高端内存的
WMARK_MIN采用不同计算策略,符合它们在内核中的实际用途和重要性。 - 动态适应性 :通过
watermark_scale_factor,水位线间距能够随系统总内存大小线性缩放。这在大内存系统上非常重要,避免了 kswapd 过于频繁地被唤醒。
🔍 如何验证与调整
- 查看结果 :使用
cat /proc/zoneinfo命令,查看每个 Zone 的min、low、high等字段的值(单位为页)。 - 调整参数 :你可以通过修改
/proc/sys/vm/min_free_kbytes来直接影响基础预留内存量。通过修改/proc/sys/vm/watermark_scale_factor(如默认是10)来调整水位线间距。增大它会让 kswapd 更早启动、更晚停止,适用于内存压力较大的场景。