结合响应式编程思想,深入理解Netty的高性能网络编程架构
1. Reactor模式基础
1.1 Reactor核心概念
Reactor模式是一种事件驱动的设计模式,专门用于处理多个客户端并发请求。其核心思想是将请求分发与业务处理分离。
业务处理层 Reactor核心组件 Handler 处理器 Handler 处理器 Handler 处理器 Reactor Acceptor 接收器 Dispatcher 分发器 客户端请求
Reactor模式三大核心角色:
| 角色 | 职责 | 对应现实比喻 |
|---|---|---|
| Reactor | 事件监听和分发 | 公司前台总机 |
| Acceptor | 接收新连接 | 接待员 |
| Handler | 处理具体业务 | 各部门专员 |
1.2 Reactor线程模型演进
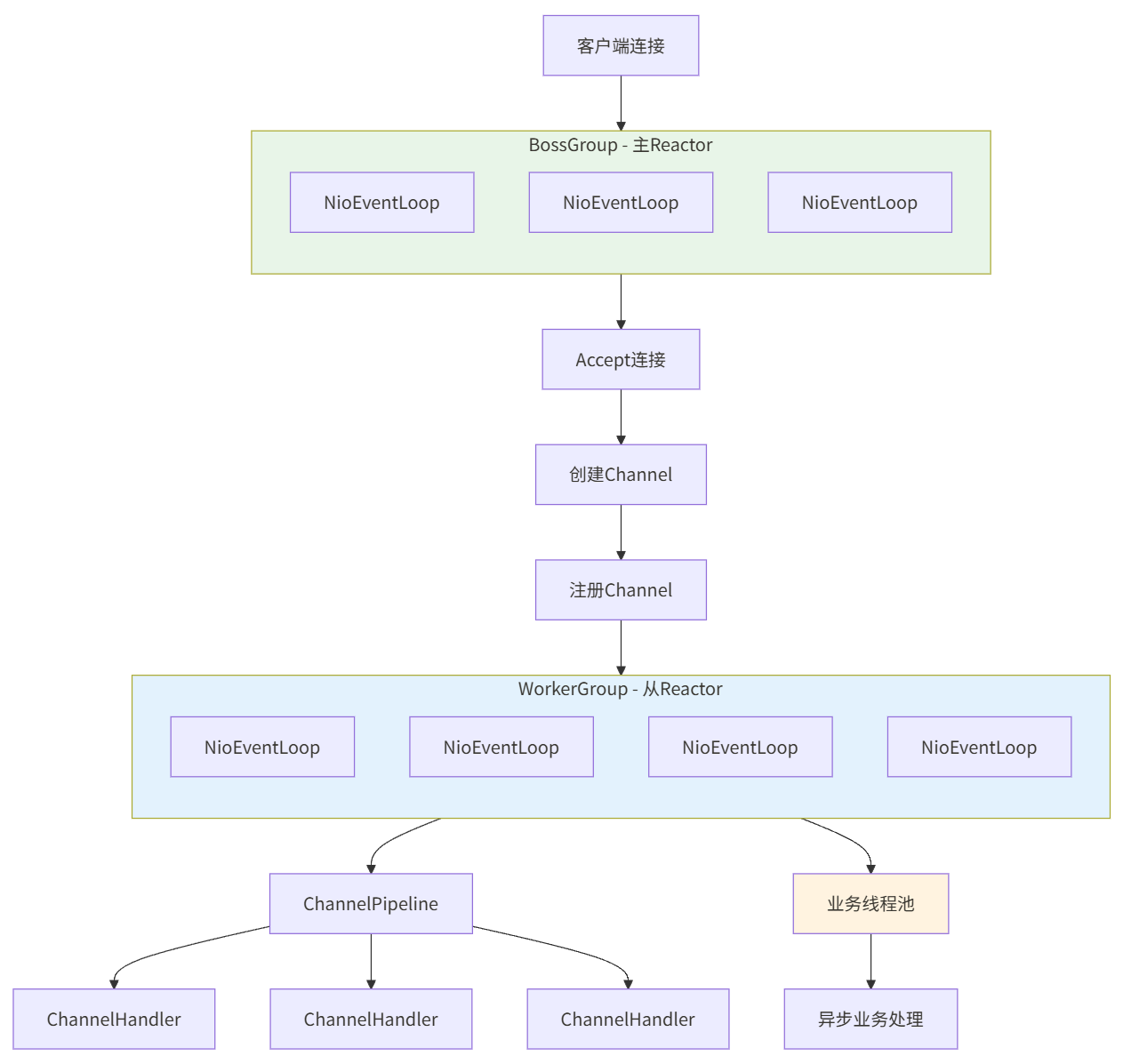
2.2 Netty核心组件关系
<<interface>> EventLoopGroup +next() : EventLoop +register(Channel) : ChannelFuture <<interface>> EventLoop +parent() : EventLoopGroup +register(Channel) : ChannelFuture +execute(Runnable) : void <<interface>> Channel +pipeline() : ChannelPipeline +eventLoop() : EventLoop +write(Object) : ChannelFuture <<interface>> ChannelPipeline +addLast(Handler...) : ChannelPipeline +fireChannelRead(Object) : ChannelPipeline +write(Object) : ChannelFuture <<interface>> ChannelHandler +channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext, Object) +exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext, Throwable) <<interface>> ChannelHandlerContext +channel() : Channel +handler() : ChannelHandler +write(Object) : ChannelFuture +fireChannelRead(Object) : ChannelHandlerContext
3. Netty核心源码解析
3.1 EventLoop事件循环机制
java
/**
* Netty事件循环核心逻辑
*/
public class NioEventLoop extends SingleThreadEventLoop {
// 核心选择器,用于监听IO事件
private Selector selector;
private SelectorProvider provider;
@Override
protected void run() {
for (;;) {
try {
try {
// 1. 计算下一个定时任务的等待时间
int strategy = selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(
selectNowSupplier, hasTasks());
switch (strategy) {
case SelectStrategy.CONTINUE:
continue;
case SelectStrategy.SELECT:
// 2. 执行select操作,等待IO事件
strategy = selector.select(timeoutMillis);
break;
default:
// fallthrough
}
// 3. 处理IO事件和任务
processSelectedKeys();
} finally {
// 4. 确保执行所有 scheduled 任务
runAllTasks();
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleLoopException(t);
}
}
}
private void processSelectedKeys() {
if (selectedKeys != null) {
processSelectedKeysOptimized();
} else {
processSelectedKeysPlain(selector.selectedKeys());
}
}
private void processSelectedKeysOptimized() {
for (int i = 0; i < selectedKeys.size; ++i) {
final SelectionKey k = selectedKeys.keys[i];
selectedKeys.keys[i] = null;
final Object a = k.attachment();
//jdk8
if (a instanceof AbstractNioChannel) {
// 处理Channel的IO事件
processSelectedKey(k, (AbstractNioChannel) a);
}
//jdk17以上
if (a instanceof AbstractNioChannel b) {
// 处理Channel的IO事件
processSelectedKey(k, b);
}
}
}
}3.2 ChannelPipeline责任链模式
java
/**
* ChannelPipeline实现 - 责任链模式
*/
public class DefaultChannelPipeline implements ChannelPipeline {
// 责任链的头尾节点
final AbstractChannelHandlerContext head;
final AbstractChannelHandlerContext tail;
@Override
public ChannelPipeline addLast(String name, ChannelHandler handler) {
return addLast(null, name, handler);
}
private ChannelPipeline addLast(EventExecutorGroup group, String name,
ChannelHandler handler) {
final AbstractChannelHandlerContext newCtx;
synchronized (this) {
// 1. 检查重复性
checkMultiplicity(handler);
// 2. 创建新的Handler上下文
newCtx = newContext(group, filterName(name, handler), handler);
// 3. 添加到链表尾部
addLast0(newCtx);
}
// 4. 回调Handler添加事件
callHandlerAdded0(newCtx);
return this;
}
private void addLast0(AbstractChannelHandlerContext newCtx) {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext prev = tail.prev;
newCtx.prev = prev;
newCtx.next = tail;
prev.next = newCtx;
tail.prev = newCtx;
}
// 事件传播 - 入站事件
@Override
public ChannelPipeline fireChannelRead(Object msg) {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext.invokeChannelRead(head, msg);
return this;
}
// 事件传播 - 出站事件
@Override
public ChannelFuture write(Object msg) {
return tail.write(msg);
}
}
/**
* Handler上下文 - 维护Handler链表关系
*/
abstract class AbstractChannelHandlerContext implements ChannelHandlerContext {
volatile AbstractChannelHandlerContext next;
volatile AbstractChannelHandlerContext prev;
// 入站事件传播
static void invokeChannelRead(final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next,
Object msg) {
final Object m = msg;
// 执行下一个Handler的channelRead方法
next.invokeChannelRead(m);
}
private void invokeChannelRead(Object msg) {
if (invokeHandler()) {
try {
// 调用具体Handler的业务逻辑
((ChannelInboundHandler) handler()).channelRead(this, msg);
} catch (Throwable t) {
notifyHandlerException(t);
}
} else {
// 继续传播
fireChannelRead(msg);
}
}
}4. 响应式编程在Netty中的体现
4.1 异步回调与Future/Promise模式
Client ChannelHandler ChannelPipeline ChannelFuture EventLoop 调用write()发送数据 传播write事件 提交写任务到EventLoop 执行实际的IO写操作 设置操作结果 回调Listener(如果注册了) 整个过程完全异步 调用立即返回Future Client ChannelHandler ChannelPipeline ChannelFuture EventLoop
java
/**
* Future/Promise模式在Netty中的应用
*/
public class FuturePromiseExample {
public void demonstrateAsync() {
Channel channel = ...;
// 1. 写入消息并立即返回Future
ChannelFuture future = channel.write("Hello World");
// 2. 添加监听器,在操作完成时回调
future.addListener(new GenericFutureListener<ChannelFuture>() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
if (future.isSuccess()) {
System.out.println("写入成功");
} else {
System.out.println("写入失败: " + future.cause());
}
}
});
// 3. 可以继续执行其他逻辑,无需等待写入完成
doOtherWork();
}
/**
* Promise模式 - 手动控制异步操作结果
*/
public void demonstratePromise() {
EventLoop eventLoop = ...;
// 创建Promise
DefaultPromise<String> promise = new DefaultPromise<>(eventLoop);
// 异步执行任务
eventLoop.execute(() -> {
try {
// 模拟耗时操作
Thread.sleep(1000);
// 设置成功结果
promise.setSuccess("操作完成");
} catch (Exception e) {
// 设置失败结果
promise.setFailure(e);
}
});
// 添加完成监听
promise.addListener(future -> {
if (future.isSuccess()) {
System.out.println("结果: " + future.get());
}
});
}
}4.2 响应式数据流处理
java
/**
* 基于Netty的响应式数据流处理
*/
public class ReactiveStreamHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
// 背压支持
private volatile ChannelHandlerContext ctx;
private volatile Subscription subscription;
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
this.ctx = ctx;
// 开启读取自动背压
ctx.channel().config().setAutoRead(true);
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
// 响应式处理数据流
handleMessageReactive(msg)
.subscribe(new Subscriber<Object>() {
@Override
public void onSubscribe(Subscription s) {
subscription = s;
// 请求第一个数据项
s.request(1);
}
@Override
public void onNext(Object processedMsg) {
// 处理完成,继续管道传播
ctx.fireChannelRead(processedMsg);
// 请求下一个数据项
subscription.request(1);
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable t) {
ctx.fireExceptionCaught(t);
}
@Override
public void onComplete() {
// 流处理完成
}
});
}
/**
* 响应式消息处理
*/
private Flowable<Object> handleMessageReactive(Object msg) {
return Flowable.just(msg)
.map(this::decodeMessage)
.filter(this::validateMessage)
.flatMap(this::processMessageAsync)
.onErrorResumeNext(this::handleError);
}
private Object decodeMessage(Object rawMsg) {
// 解码逻辑
return rawMsg;
}
private boolean validateMessage(Object msg) {
// 验证逻辑
return true;
}
private Flowable<Object> processMessageAsync(Object msg) {
return Flowable.fromFuture(
ctx.executor().submit(() -> intensiveProcessing(msg))
);
}
private Flowable<Object> handleError(Throwable error) {
// 错误处理逻辑
return Flowable.error(error);
}
private Object intensiveProcessing(Object msg) {
// 密集型处理逻辑
return msg;
}
}5. Netty完整示例:Echo服务器
java
/**
* 基于Netty的Echo服务器 - 展示完整架构
*/
public class NettyEchoServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1. 创建线程组
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1); // 主Reactor
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); // 从Reactor
try {
// 2. 创建服务器启动引导
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) // 通道类型
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 100) // 连接队列大小
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO)) // 主Handler
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
// 3. 配置管道责任链
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
// 添加Handler到责任链
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder());
pipeline.addLast("business", new EchoServerHandler());
pipeline.addLast("exception", new ExceptionHandler());
}
});
// 4. 绑定端口并启动
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(8080).sync();
System.out.println("Echo服务器启动在端口 8080");
// 5. 等待服务器通道关闭
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
// 6. 优雅关闭
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
/**
* 业务处理器 - 实现Echo逻辑
*/
class EchoServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
// 响应式处理:接收消息并原样返回
String received = (String) msg;
System.out.println("服务器收到: " + received);
// 异步写回 - 立即返回ChannelFuture
ChannelFuture future = ctx.writeAndFlush("Echo: " + received + "\n");
// 添加完成监听器
future.addListener(f -> {
if (f.isSuccess()) {
System.out.println("消息回显成功");
} else {
System.out.println("消息回显失败: " + f.cause());
}
});
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
// 读取完成,强制刷新缓冲区
ctx.flush();
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
// 异常处理
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
/**
* 异常处理器
*/
class ExceptionHandler extends ChannelDuplexHandler {
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
System.err.println("处理异常: " + cause.getMessage());
ctx.close();
}
}6. 性能优化与最佳实践
6.1 内存管理优化
java
/**
* Netty内存管理最佳实践
*/
public class MemoryOptimizationExample {
public void demonstrateMemoryManagement() {
// 1. 使用池化的ByteBuf分配器
ByteBufAllocator allocator = new PooledByteBufAllocator();
ByteBuf buffer = allocator.buffer(1024);
try {
// 2. 写入数据
buffer.writeBytes("Hello".getBytes());
// 3. 使用retain/release管理引用计数
ByteBuf retained = buffer.retain();
// 异步处理...
processBufferAsync(retained);
} finally {
// 4. 释放缓冲区
if (buffer.refCnt() > 0) {
buffer.release();
}
}
}
private void processBufferAsync(ByteBuf buffer) {
// 在异步处理完成后释放
try {
// 处理逻辑...
} finally {
buffer.release();
}
}
/**
* 使用CompositeByteBuf减少内存复制
*/
public void demonstrateCompositeBuffer() {
CompositeByteBuf composite = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.compositeBuffer();
ByteBuf header = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer();
header.writeBytes("Header".getBytes());
ByteBuf body = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer();
body.writeBytes("Body".getBytes());
// 组合缓冲区,避免数据复制
composite.addComponents(true, header, body);
// 使用组合缓冲区...
System.out.println(composite.readableBytes());
composite.release();
}
}7. 总结
7.1 Netty架构核心要点
-
Reactor模式实现
- 主从Reactor线程模型
- 事件驱动的异步处理
- 高效的IO多路复用
-
响应式编程思想
- 异步回调机制
- Future/Promise模式
- 背压支持的数据流
-
责任链设计模式
- ChannelPipeline处理器链
- 灵活的业务逻辑组装
- 清晰的责任分离
7.2 性能优势来源
零拷贝技术 高性能 内存池化 无锁化设计 事件驱动 异步非阻塞
Netty的成功在于它巧妙地将Reactor模式 、响应式编程思想 和Java NIO技术相结合,构建了一个既高性能又易于使用的网络编程框架。理解这些底层原理对于构建高并发、低延迟的网络应用至关重要。