Konva.js 多维表格系统
基于 Konva.js 实现的高性能「多维表格系统」,支持大规模渲染、分组管理、筛选与排序等复杂功能,旨在构建类似腾讯文档 / 飞书多维表格的交互体验。
目录
一、项目概述
本项目使用 Konva.js 实现一个高性能的二维/多维表格系统,支持:
- 大规模表格渲染(行列可达数百万级)
- 按分组管理的数据展示
- 多维度筛选与排序
- 支持图片、文本、状态标签等多类型单元格
- 响应式布局与虚拟滚动优化
该系统适用于「任务管理」「资源调度」「项目需求规划」等复杂表格场景。
二、功能清单
| 功能模块 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 表格渲染 | 基于 Konva Layer + Group 分层渲染,实现单元格、边框、背景高效绘制 |
| 分组管理 | 支持按分类分组显示,组可展开/折叠 |
| 筛选功能 | 支持多列字段条件过滤(文本、数值、状态) |
| 排序功能 | 支持单列与多列排序逻辑 |
| 单元格类型 | 文本、图片、状态标签、自定义渲染器 |
| 交互操作 | 选中、框选、多选、悬浮提示、滚动同步 |
| 虚拟滚动优化 | 仅渲染视口内元素,提升渲染性能 |
| 动态布局 | 自适应行高、列宽及容器尺寸变化 |
| 批量更新机制 | 使用 requestAnimationFrame 实现批量绘制,避免重复渲染 |
三、核心架构设计
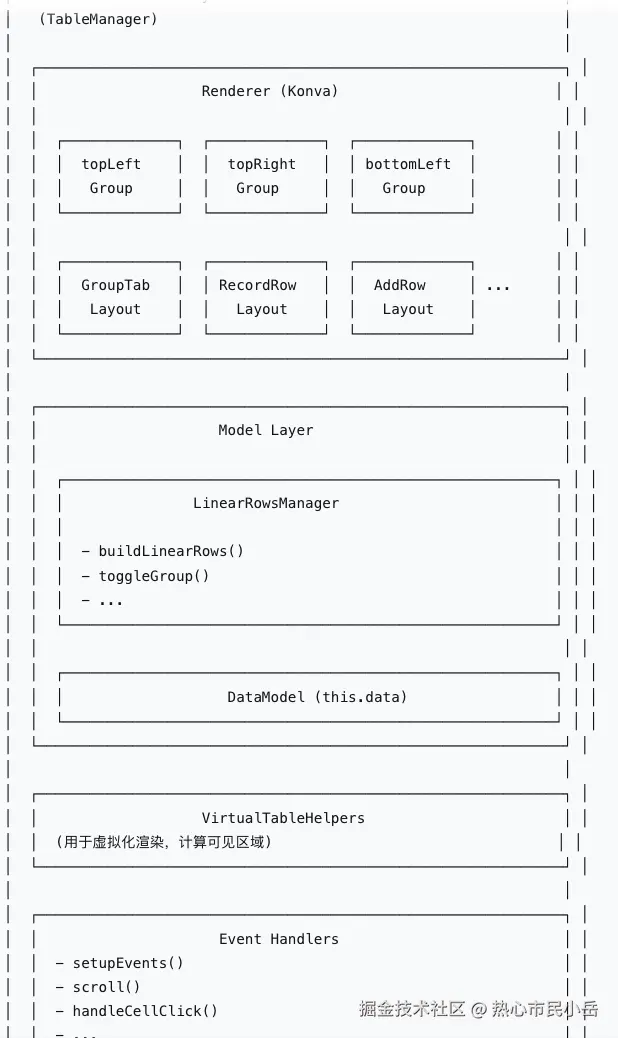
markdown
## 🎯 主控制器
- **table**
- 图层系统
- `backgroundLayer` - 背景层
- `bodyLayer` - 主体层
- `featureLayer` - 特性层
- 分组系统
- `topLeft Group` - 左上冻结区域
- `topRight Group` - 右上冻结区域
- `bottomLeft Group` - 左下冻结区域
- `bottomRight Group` - 右下冻结区域
- 数据管理
- **LinearRowsManager**
- `linearRows: ILinearRow[]` - 线性行数据
- `buildLinearRows()` - 构建行数据
- `toggleGroup()` - 切换分组状态
- 布局系统
- **CellLayout** (抽象基类)
- `GroupTabLayout` - 分组行布局
- `RecordRowLayout` - 数据行布局
- `AddRowLayout` - 添加行布局
- `BlankRowLayout` - 空白行布局
- `headerLayout` - 表头布局
- 工具类
- **VirtualTableHelpers**
- `getItemMetadata()` - 获取项目元数据
- `findNearestItem()` - 查找最近项目
- `...` - 其他辅助方法
- 事件处理
- `setupEvents()` - 初始化事件
- `scroll()` - 滚动处理
- `handleCellClick()` - 单元格点击
- `...` - 其他事件四、模块说明
1. Renderer 模块
负责表格的可视化渲染逻辑:
- 使用
Konva.Layer管理背景层、内容层、交互层 - 每一行或一组单元格使用
Konva.Group表示 - 支持增量渲染与批量更新
- 通过矩阵坐标快速定位渲染区域
2. Model 模块
- 提供数据源抽象
- 支持筛选、排序、分组聚合与动态更新
- 通过观察者模式与渲染层同步数据变更
3. Controller 模块
- 监听用户输入事件(鼠标、滚动、拖拽)
- 控制渲染队列与更新节奏
- 管理当前选中状态与焦点单元格
- 与 Model 层进行数据同步
五、关键机制
1. 分组渲染(Group Rendering)
- 每个分组独立使用一个
Konva.Group - 折叠后仅渲染组头
- 展开时批量加载子节点
- 支持懒加载以优化性能
2. 虚拟滚动(Virtual Scrolling)
- 计算可视区域内应渲染的行列
- 减少内存占用与重绘次数
- 支持横向与纵向滚动同步
3. 批量绘制(Batch Draw)
ts
private _waitingForDraw = false;
private animQueue: Function[] = [];
public batchDraw() {
if (!this._waitingForDraw) {
this._waitingForDraw = true;
requestAnimationFrame(() => {
this.animQueue.forEach(fn => fn());
this.animQueue = [];
this._waitingForDraw = false;
});
}
}六、实现过程
1. konva.js实现一个简单的表格绘制 但是这样太过于简单了 如果行列数量巨大且需要扩展显示 卡顿的比较严重。
js
// 绘制表格
for (let row = 0; row < 10; row++) {
for (let col = 0; col < 10; col++) {
// 创建每个单元格
const rect = new Konva.Rect({
x: col * cellSize,
y: row * cellSize,
width: cellSize,
height: cellSize,
fill: 'lightgrey',
stroke: 'black',
strokeWidth: 1
});
// 将矩形添加到图层
layer.add(rect);
}
}2.使用辅助类 VirtualTableHelpers 这个类中提供了一系列的函数,如下图。通过offsetY和offsetX 以及 rowHeight colWidth 我们可以计算出当前可视区域 应该渲染哪些row 和 column。
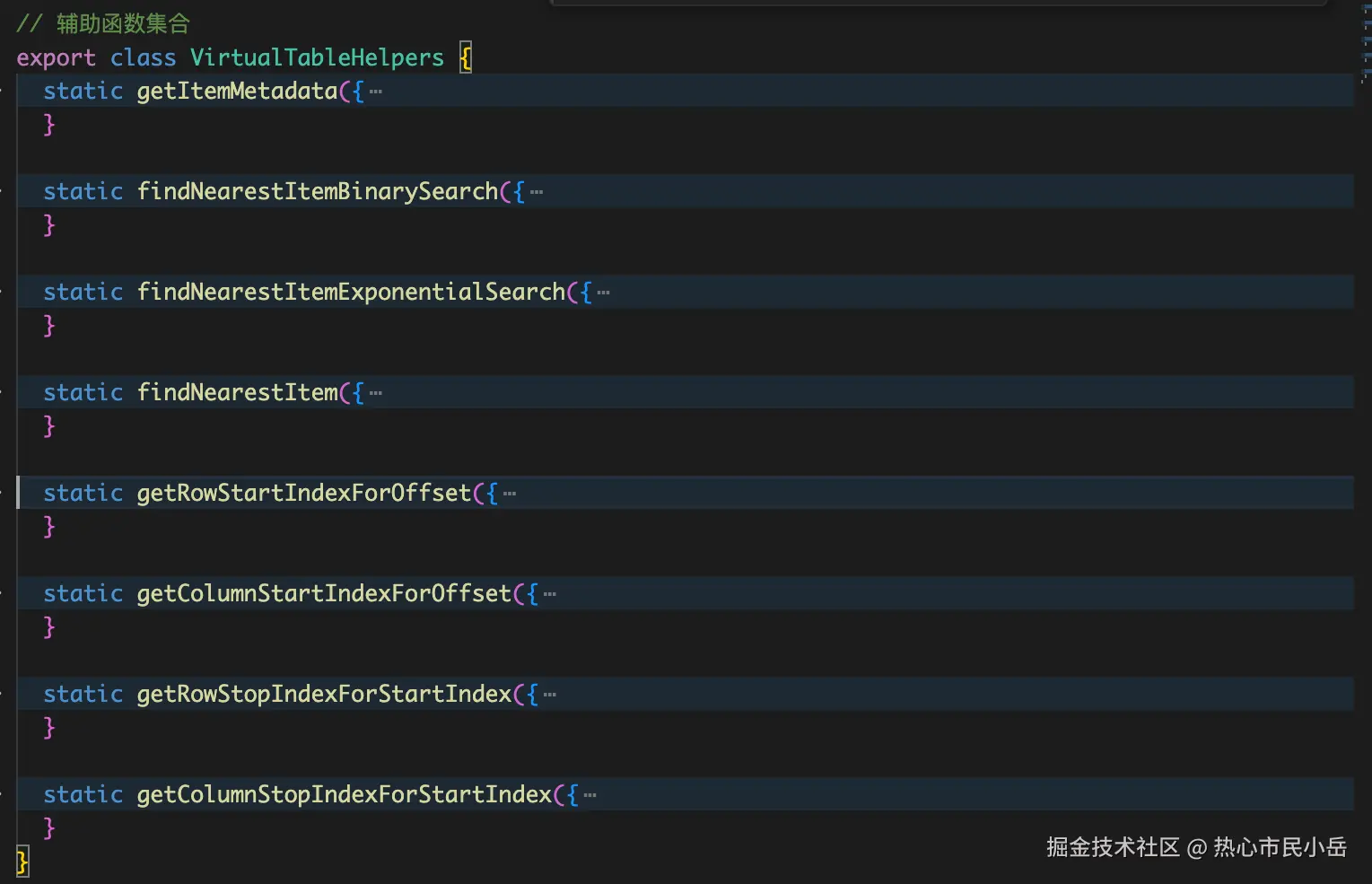
js
getVisibleRowRange(frozenRowsHeight: number): { start: number; end: number } {
const rowCount = this.linearRowsManager.getRowCount();
const viewportHeight = this.visibleHeight - frozenRowsHeight - this.scrollBarSize;
// 使用二分查找找到起始行(O(log n))
const startRow = VirtualTableHelpers.getRowStartIndexForOffset({
itemType: "row",
rowHeight: this.getRowHeight,
columnWidth: this.getColumnWidth,
rowCount: rowCount,
columnCount: this.cols,
instanceProps: this.instanceProps,
offset: this.scrollY
});
// 基于起始行计算结束行(增量计算)
const endRow = VirtualTableHelpers.getRowStopIndexForStartIndex({
startIndex: Math.max(this.frozenRows, startRow),
rowCount: rowCount,
rowHeight: this.getRowHeight,
columnWidth: this.getColumnWidth,
scrollTop: this.scrollY,
containerHeight: viewportHeight,
instanceProps: this.instanceProps
});
// 添加缓冲区(预渲染上下各 2 行)
const buffer = 2;
return {
start: Math.max(this.frozenRows, startRow - buffer),
end: Math.min(rowCount - 1, endRow + buffer)
};
}
getVisibleColRange(frozenColsWidth: number): { start: number; end: number } {
const viewportWidth = this.visibleWidth - frozenColsWidth - this.scrollBarSize;
const startCol = VirtualTableHelpers.getColumnStartIndexForOffset({
itemType: "column",
rowHeight: this.getRowHeight,
columnWidth: this.getColumnWidth,
rowCount: this.rows,
columnCount: this.cols,
instanceProps: this.instanceProps,
offset: this.scrollX
});
const endCol = VirtualTableHelpers.getColumnStopIndexForStartIndex({
startIndex: Math.max(this.frozenCols, startCol),
rowHeight: this.getRowHeight,
columnWidth: this.getColumnWidth,
instanceProps: this.instanceProps,
containerWidth: viewportWidth,
scrollLeft: this.scrollX,
columnCount: this.cols
});
const buffer = 2;
return {
start: Math.max(this.frozenCols, startCol - buffer),
end: Math.min(this.cols - 1, endCol + buffer)
};
}
// 渲染一下即可看到效果
// 渲染单元格 - 从 leftPadding 开始
for (let row = visibleRows.start; row <= visibleRows.end; row++) {
const height = this.getRowHeight(row);
if (currentY + height >= frozenRowsHeight &&
currentY <= this.visibleHeight - this.scrollBarSize) {
let currentX = this.leftPadding;
for (let col = 0; col < this.frozenCols; col++) {
const width = this.getColumnWidth(col);
const cell = this.createCell(row, col, currentX, currentY, width, height);
this.groups.bottomLeft.add(cell);
currentX += width;
}
}
currentY += height;
}
}填充一点数据即可 到这里一个高性能的表格也就成了 但是我们是要实现多维表格 还有段距离。
3. 画布分层 以及 兼容冻结行列。( 相对有点难度 )
- 使用 bodyLayer更新不那么频繁且渲染成本较高, 渲染 静态表格数据。 使用featureLayer渲染 用户选区,横纵滚动条,高亮等等用户交互。
- 为什么这样做 : bodyLayer更新不那么频繁且渲染成本较高,featureLayer更新渲染非常频繁,bodyLayer不受影响。
- 我们定义一个
Canvas类专门处理画布,首先创建画布
js
setupLayers() {
this.backgroundLayer = new Konva.Layer({ name: 'backgroundLayer' });
this.bodyLayer = new Konva.Layer({ name: 'bodyLayer' });
this.featureLayer = new Konva.Layer({ name: 'featureLayer' });
this.stage.add(this.backgroundLayer, this.bodyLayer, this.featureLayer);
}-
接下来就是处理冻结行列,冻结行列我计划分成四块区域 | 或者说四个组 来渲染,如图,区域 | 组可以使用layer | group来划分,这里我采用konva.group来划分,因为官网说了不建议过多的layer。
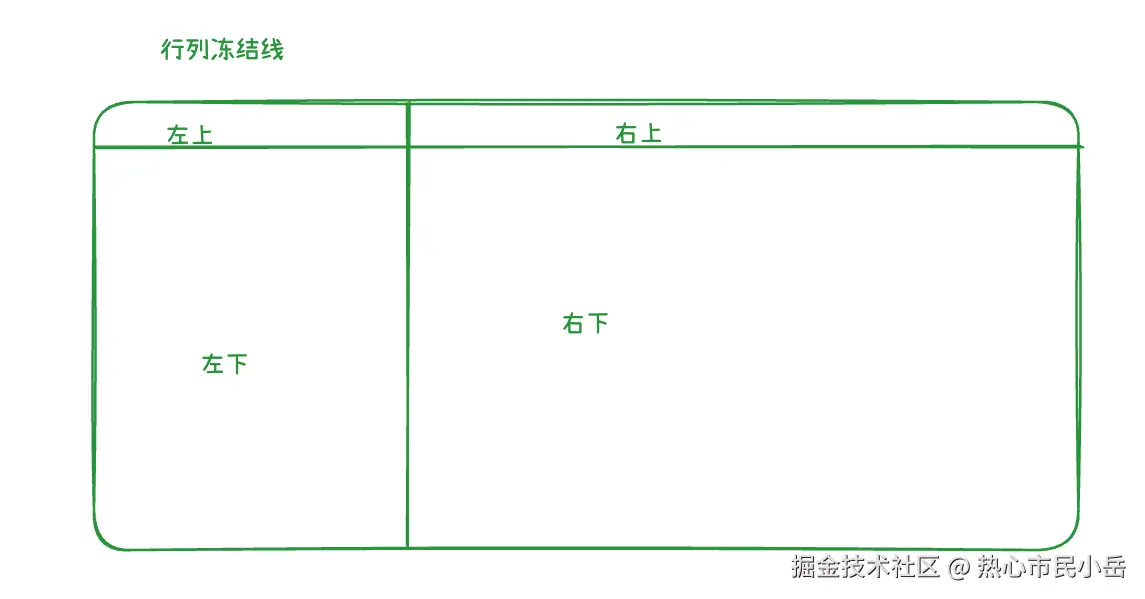
-
固定行冻结为一列 列假设设置成4列 计算出冻结区域 这样我们就为每一个group确定了应有的宽高,拖动行列滚动条的时候 就只需要更新 右下角的group就可以了,也需要重新计算bottomRight可视区域内的行列起始行列,为什么不需要处理其他三个区域呢 因为冻结不能冻结超出屏幕以外的行列。
js
// 创建四个分组
this.groups = {
topLeft: new Konva.Group(),
topRight: new Konva.Group(),
bottomLeft: new Konva.Group(),
bottomRight: new Konva.Group(),
};
this.bodyLayer.add(...Object.values(this.groups))
裁剪一下实现冻结的效果
setClipping() {
const frozenColsWidth = this.core.getFrozenColsWidth() + 1;
const frozenRowsHeight = this.core.getFrozenRowsHeight();
// 为每个Group设置裁剪
this.groups.topRight.clipFunc((ctx) => {
ctx.rect(
frozenColsWidth,
0,
this.visibleWidth - frozenColsWidth,
frozenRowsHeight
);
});
this.groups.bottomLeft.clipFunc((ctx) => {
ctx.rect(
0,
frozenRowsHeight,
frozenColsWidth,
this.visibleHeight - frozenRowsHeight
);
});
this.groups.bottomRight.clipFunc((ctx) => {
ctx.rect(
frozenColsWidth,
frozenRowsHeight,
this.visibleWidth - frozenColsWidth,
this.visibleHeight - frozenRowsHeight
);
});
}- 滚动条不需要在讲解了 在之前实现
腾讯文档甘特图时已说过实现。定义一个HorizontalBarScrollbar类来测试一下 , 创建滚动条 , 并且注册dragmove事件 更新offsetX从而来确定 显示的行列以及 offsetX渲染起点。测试结果
js
createScrollBars() {
const { canvas } = this;
// 创建滚动条背景和滑块
this.hScrollBg = new Konva.Rect({
fill: "#f0f0f0",
stroke: "#e0e0e0",
strokeWidth: 1,
});
this.hScrollThumb = new Konva.Rect({
fill: "#cccecf",
cornerRadius: 4,
draggable: true,
});
// 添加到主图层
canvas.bodyLayer.add(this.hScrollBg, this.hScrollThumb);
this.setupScrollBarEvents();
}
public setupScrollBarEvents() {
let isDraggingHScroll = false;
// 水平滚动条事件
this.hScrollThumb.on("mousedown touchstart", () => {
isDraggingHScroll = true;
});
this.hScrollThumb.on("dragmove touchmove", () => {
if (isDraggingHScroll) {
const frozenColsWidth = this.core.getFrozenColsWidth();
const scrollableWidth =
this.canvas.visibleWidth - frozenColsWidth - this.config.scrollBarSize;
const thumbWidth = this.hScrollThumb.width();
let thumbX = this.hScrollThumb.x();
thumbX = Math.max(
frozenColsWidth,
Math.min(thumbX, frozenColsWidth + scrollableWidth - thumbWidth)
);
this.hScrollThumb.x(thumbX);
this.hScrollThumb.y(this.canvas.visibleHeight - this.config.scrollBarSize + 1); // 固定Y坐标
if (scrollableWidth > thumbWidth) {
const scrollRatio =
(thumbX - frozenColsWidth) / (scrollableWidth - thumbWidth);
this.scrollX = scrollRatio * this.maxScrollX;
this.core.render.batchDraw();
}
}
});
this.canvas.stage.on("mouseup touchend", () => {
isDraggingHScroll = false;
// isDraggingVScroll = false;
});
- 这里有两个小点需要注意一下
-
- dragmove的时候我们只需要更新 groupRight 内的行列即可 不需要针对整个画布, 优化渲染。
-
- dragmove会频繁调用render去更新 groupRight内容, 这里需要优化一下
- 通过
requestAnimationFrame和队列机制将多个绘制请求合并,确保在同一帧内只执行一次实际的绘制操作,从而避免了不必要的多次渲染,提升了性能
js
private _waitingForDraw = false;
private animQueue = [] as Array<Function>;
public batchDraw() {
if (!this._waitingForDraw) {
this._waitingForDraw = true;
this.requestAnimFrame(() => {
this.render();
this._waitingForDraw = false;
});
}
return this;
}
private requestAnimFrame(callback: Function) {
this.animQueue.push(callback);
if (this.animQueue.length === 1) {
req(() => {
const queue = this.animQueue;
this.animQueue = [];
queue.forEach(function (cb) {
cb();
});
});
}
}
render() {
this.renderContent();
this.core.updateScrollBars();
}4.分组的实现 ( 难点 )
1.前期准备
- 先来调研一下腾讯文档的 我们就光靠这个效果需要分析出如何实现分组的效果
- 经过苦思冥想, 想出来两套方案。最终我选择了第二种,因为我对于第二种的思路好打开一点
js
定义好嵌套数据格式
1 通过每一个嵌套数据,一组一组的渲染,对于需要结合可视区域渲染来说 稍有难度。
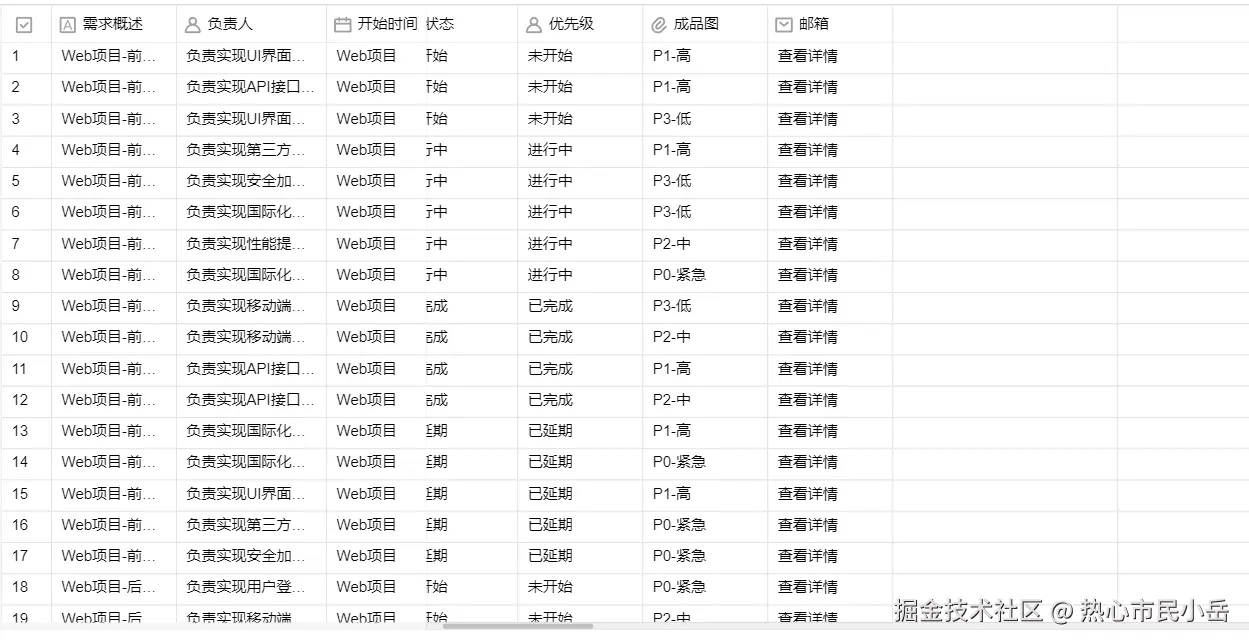
2.不要被嵌套给影响 还是一行一行的渲染 ,分组头我也按照行来渲染 只不过需要控制行缩进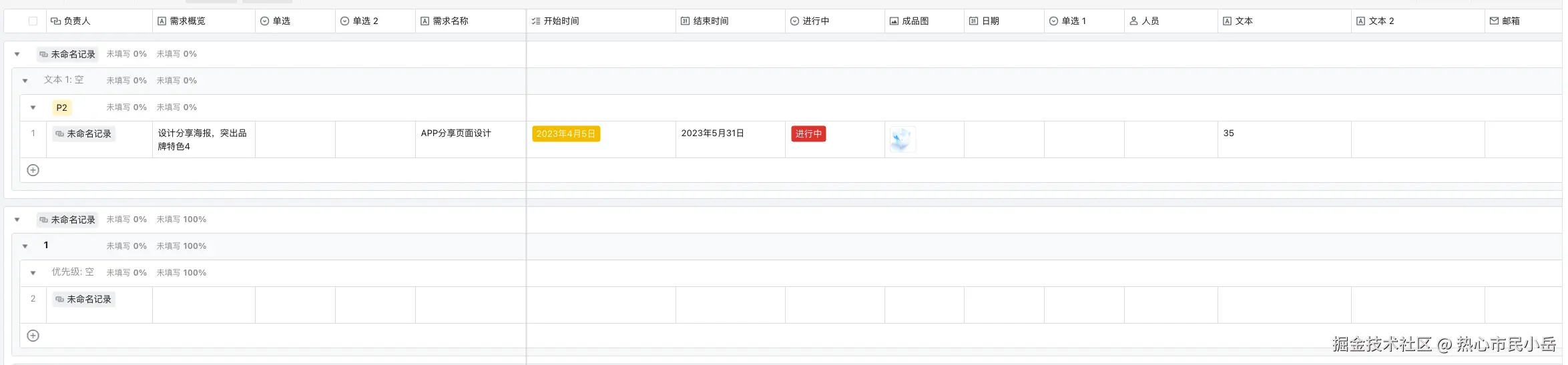
一组一组的渲染的效果 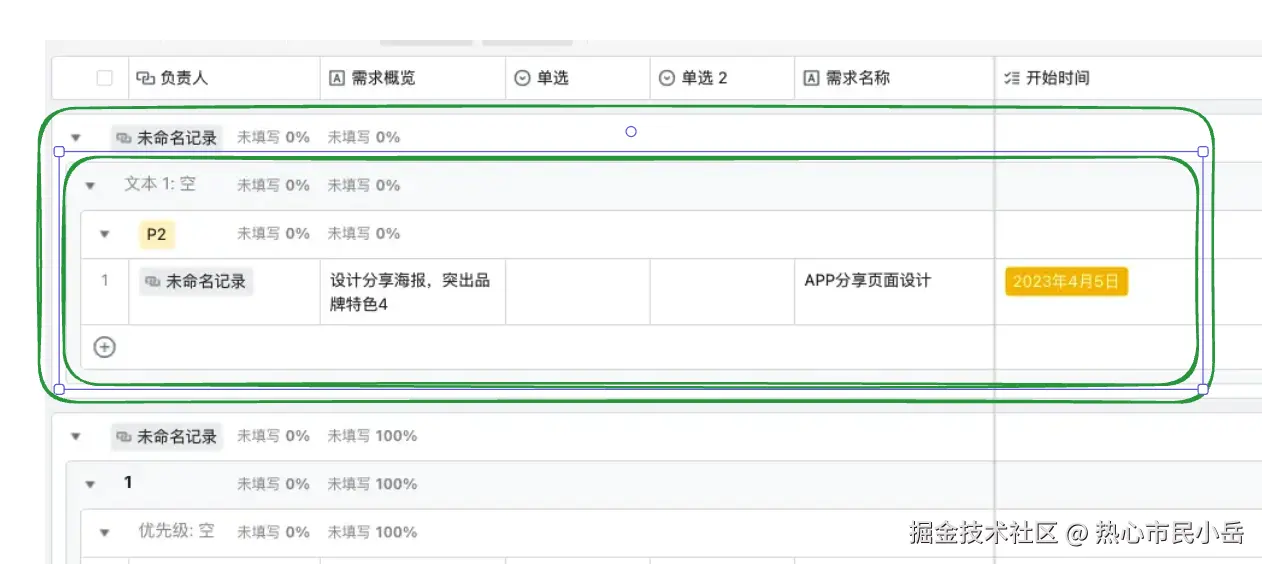
一行一行的渲染 ( 我在使用这种的方案实现的时候 没有经过太多的困难 => 比较推荐) 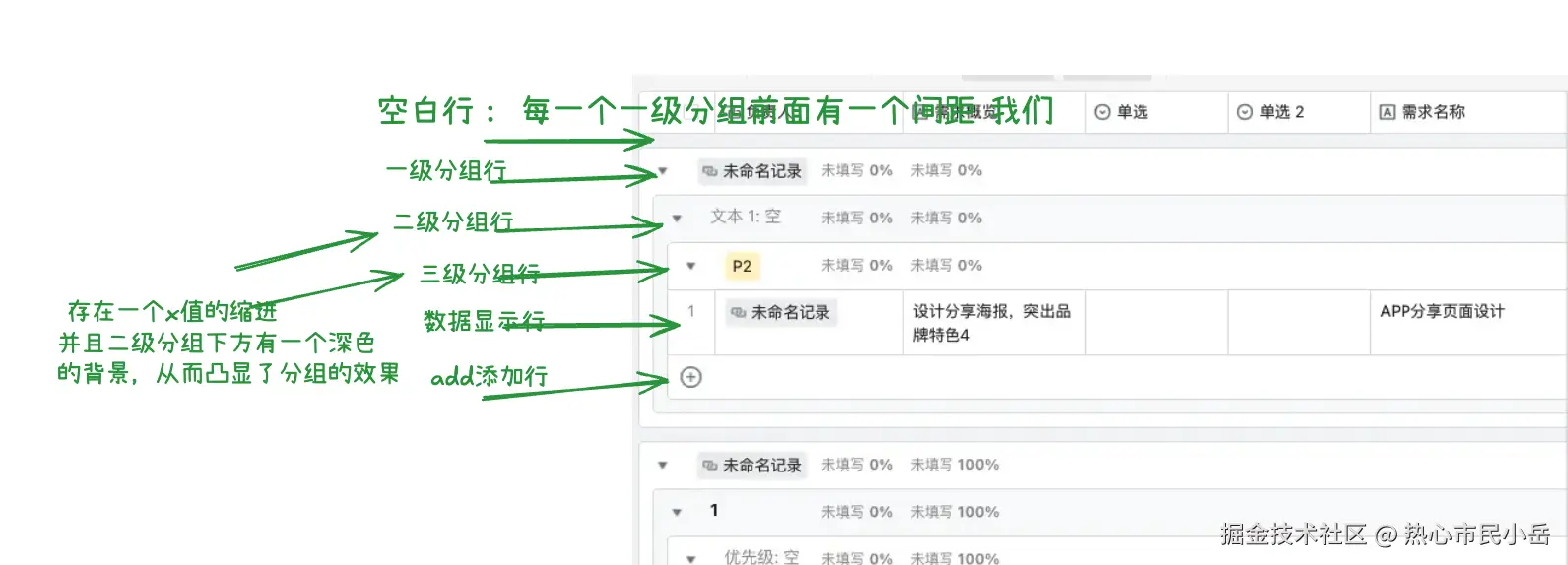
2.定义处理分组的类
ini
先定义行存在哪些类型
export enum CellType {
Record = 'Record',
GroupTab = 'GroupTab',
AddRow = 'AddRow',
BlankRow = 'BlankRow',
Header = 'Header'
}
// 处理分组的类
export class LinearRowsManager {
private linearRows: ILinearRow[] = [];
private rawData: any[][] = [];
private groupConfig: { field: string; enabled: boolean } = { field: '', enabled: false };
private groupStates = new Map<string, boolean>(); // 保存分组展开状态
constructor(data: any[][]) {
this.rawData = data;
}
// 支持多级分组的构建方法
buildLinearRows(groupFields?: string[]): ILinearRow[] {
this.linearRows = [];
this.groupConfig = {
fields: groupFields || [],
enabled: !!(groupFields && groupFields.length > 0)
};
// 表头行(始终存在)
this.linearRows.push({
type: CellType.Header,
recordId: 'header-row',
depth: 0,
dataIndex: 0,
displayIndex: 0
} as ILinearRowHeader);
if (!this.groupConfig.enabled) {
// 无分组:直接映射所有数据行
for (let i = 1; i < this.rawData.length; i++) {
this.linearRows.push({
type: CellType.Record,
recordId: `record-${i}`,
depth: 0,
dataIndex: i,
displayIndex: i
} as ILinearRowRecord);
}
} else {
// 多级分组:递归构建分组树
this.buildMultiLevelGroups();
}
return this.linearRows;
}class中还定义了一些其他方法
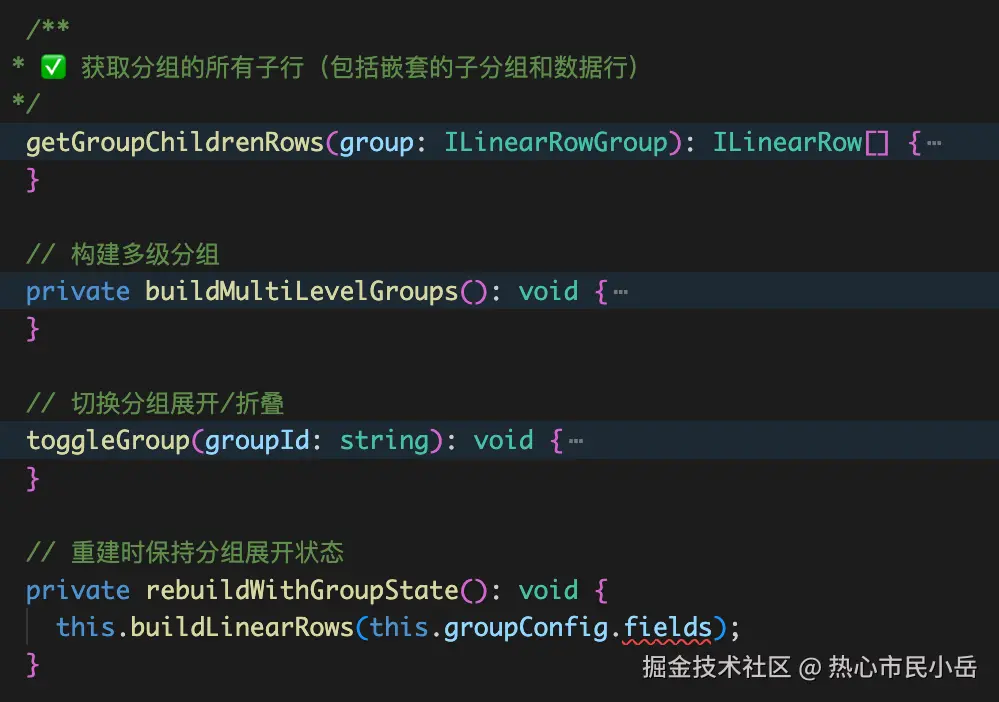
经过分组class的处理 我们的数据变成了这样 我们在render中处理的时候就不要处理行列数据了 直接拿这个分组生成的数据来渲染。
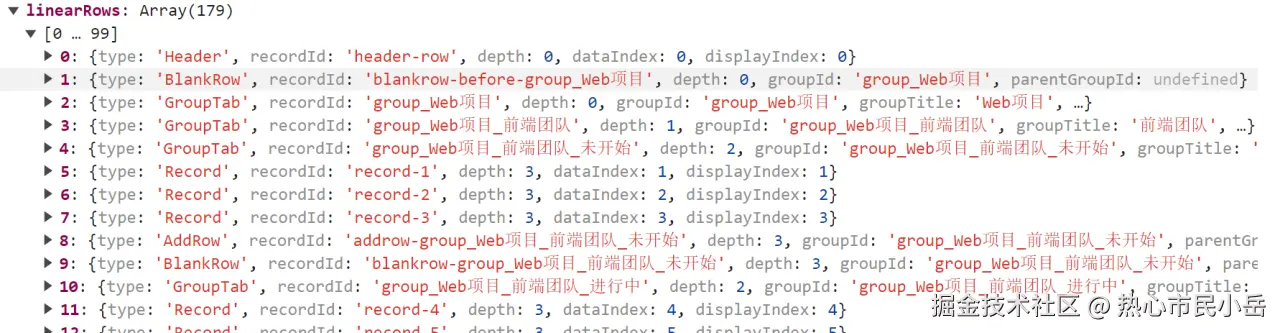
在render中开启分组 this.enableMultiLevelGrouping(['负责人', '开始时间', '状态']); 看下 groupRight如何渲染的, 核心思维就是要生成 createCell
js
//
renderBottomRight() {
console.time('renderBottomRight');
const frozenColsWidth = this.getFrozenColsWidth();
const frozenRowsHeight = this.getFrozenRowsHeight();
const visibleRows = this.getVisibleRowRange(frozenRowsHeight);
if (visibleRows.start > visibleRows.end) {
console.timeEnd('renderBottomRight');
return;
}
const visibleCols = this.getVisibleColRange(frozenColsWidth);
if (visibleCols.start > visibleCols.end) {
console.timeEnd('renderBottomRight');
return;
}
// 先绘制背景
this.renderLevel1GroupBackgrounds(visibleRows, frozenColsWidth, frozenRowsHeight, 'bottomRight');
this.renderLevel2GroupBackgrounds(visibleRows, frozenColsWidth, frozenRowsHeight, 'bottomRight');
const colPositions = this.preCalculateColPositions(visibleCols, frozenColsWidth);
let currentY = frozenRowsHeight - this.scrollY;
for (let row = this.frozenRows; row < visibleRows.start; row++) {
currentY += this.getRowHeight(row);
}
for (let row = visibleRows.start; row <= visibleRows.end; row++) {
const height = this.getRowHeight(row);
for (let i = 0, col = visibleCols.start; col <= visibleCols.end; col++, i++) {
const width = this.getColumnWidth(col);
const x = colPositions[i];
const cell = this.createCell(row, col, x, currentY, width, height);
this.groups.bottomRight.add(cell);
}
currentY += height;
}
console.timeEnd('renderBottomRight');
}设定一个createCell函数 你要返回一个正确的 cell group出来,需要处理 枚举的五种类型的渲染方式。 五种类型的渲染方式各有不同 我们可以通过布局思想来定义一下,分别处理渲染。
js
export enum CellType {
Record = 'Record',
GroupTab = 'GroupTab',
AddRow = 'AddRow',
BlankRow = 'BlankRow',
Header = 'Header'
}先定义一个基类
js
export abstract class CellLayout {
protected ctx: CanvasRenderingContext2D;
protected x: number = 0;
protected y: number = 0;
protected width: number = 0;
protected height: number = 0;
setPosition(x: number, y: number, width: number, height: number) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
abstract render(row: ILinearRow, col: number, isFirstCol: boolean, isLastCol: boolean): Konva.Group;
}后续五种行布局也需要定义出来
以分组行布局来举例。 主要是处理分组行的缩进 以及折叠的事件 后续还要扩展 统计之类的功能。
js
class GroupTabLayout extends CellLayout {
render(row: ILinearRow, col: number, isFirstCol: boolean, isLastCol: boolean): Konva.Group {
const group = new Konva.Group({ x: this.x, y: this.y });
const groupRow = row as ILinearRowGroup;
const depth = row.depth;
const bgColor = this.getGroupBackground(depth);
const indentOffset = depth * 20; // 根据层级缩进
if (isFirstCol) {
// 第一列:展开/折叠图标和分组标题
const bgRect = new Konva.Rect({
x: indentOffset,
y: 0,
width: this.width - indentOffset,
height: this.height,
fill: bgColor,
stroke: '#e0e0e0',
strokeWidth: 0.5
});
// 只有非最后一层的分组才显示展开/折叠图标
const showExpandIcon = groupRow.children && groupRow.children.some(child =>
child.type === CellType.GroupTab
);
const icon = new Konva.Text({
x: indentOffset + 15,
y: this.height / 2,
text: showExpandIcon ? (groupRow.expanded ? '▼' : '▶') : '',
fontSize: 8,
fill: '#4a5568',
listening: showExpandIcon
});
const titleText = new Konva.Text({
x: indentOffset + (showExpandIcon ? 30 : 15),
y: this.height / 2 - 5,
text: `${groupRow.groupTitle} (${groupRow.recordCount})`,
fontSize: 8,
fill: '#2d3748',
fontWeight: 'bold'
});
if (showExpandIcon) {
bgRect.on('click', () => {
bgRect.fire('toggleGroup', { groupId: groupRow.groupId });
});
icon.on('click', () => {
icon.fire('toggleGroup', { groupId: groupRow.groupId });
});
}
group.add(bgRect, icon, titleText);
} else if (col === 1) {
// 第二列:分组字段信息
const bgRect = new Konva.Rect({
width: this.width,
height: this.height,
fill: bgColor,
stroke: '#e0e0e0',
strokeWidth: 0.5
});
const fieldLabel = new Konva.Text({
x: 10,
y: 6,
text: `${this.getGroupFieldLabel(depth)}: ${groupRow.groupField}`,
fontSize: 7,
fill: '#718096'
});
const valueLabel = new Konva.Text({
x: 10,
y: this.height / 2 + 2,
text: groupRow.groupTitle,
fontSize: 13,
fontWeight: 'bold',
fill: '#2d3748'
});
group.add(bgRect, fieldLabel);
} else {
// 其他列:空背景
const bgRect = new Konva.Rect({
width: this.width,
height: this.height,
fill: bgColor,
stroke: '#e0e0e0',
strokeWidth: 0.5
});
group.add(bgRect);
}
return group;
}
private getGroupBackground(depth: number): string {
// const colors = ['#f7fafc', '#edf2f7', '#e2e8f0', '#cbd5e0'];
const colors = ['#FFF', '#F5F5F5', '#FFF', '#cbd5e0'];
return colors[Math.min(depth, colors.length - 1)];
}
private getGroupFieldLabel(depth: number): string {
const labels = ['一级分组', '二级分组', '三级分组'];
return labels[Math.min(depth, labels.length - 1)] || '分组';
}
}全部定义好了 全部在 render类中实例化
js
this.linearRowsManager = new LinearRowsManager(this.data);
this.linearRowsManager.buildLinearRows(); // 初始无分组
// 初始化布局渲染器
this.groupTabLayout = new GroupTabLayout();
this.recordRowLayout = new RecordRowLayout(
this.data,
this.colsConfig
);
this.addRowLayout = new AddRowLayout();
this.blankRowLayout = new BlankRowLayout();
this.headerLayout = new headerLayout(this.iconManager, this.columns);正确处理后 生成单元格
js
createCell(rowIndex: number, col: number, x: number, y: number, width: number, height: number): Konva.Group {
const row = this.linearRowsManager.getRow(rowIndex);
if (!row) return new Konva.Group();
const isFirstCol = col === 0;
const headerRow = rowIndex === 0;
const isLastCol = col === this.cols - 1;
let layout: CellLayout;
switch (row.type) {
case CellType.GroupTab:
layout = this.groupTabLayout;
break;
case CellType.AddRow:
layout = this.addRowLayout;
break;
case CellType.BlankRow:
layout = this.blankRowLayout;
break;
case CellType.Header:
layout = this.headerLayout;
break;
case CellType.Record:
layout = this.recordRowLayout;
break;
default:
layout = this.recordRowLayout;
break;
}
layout.setPosition(x, y, width, height);
const cellGroup = layout.render(row, col, isFirstCol, isLastCol);
// 监听分组折叠事件
if (row.type === CellType.GroupTab) {
cellGroup.on('toggleGroup', (e: any) => {
this.linearRowsManager.toggleGroup(e.groupId);
this.render();
});
}
// 监听 AddRow 点击事件
if (row.type === CellType.AddRow) {
cellGroup.on('addRow', (e: any) => {
this.handleAddRow(e.groupId);
});
}
return cellGroup;
}来看下渲染结果 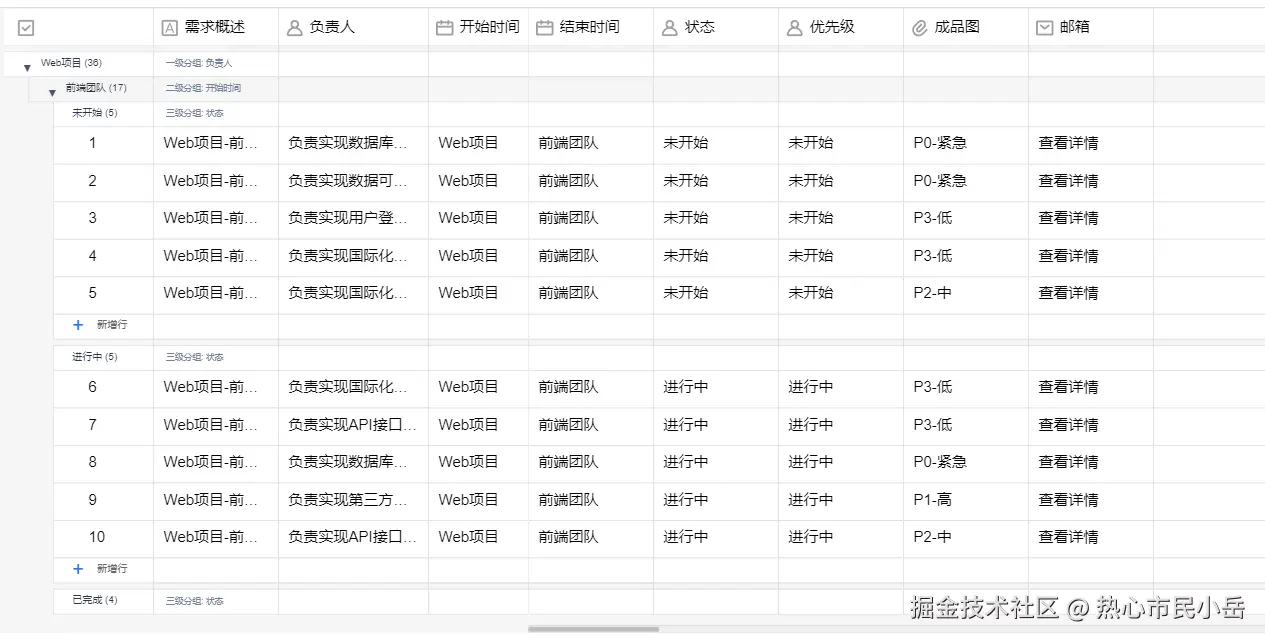
七、性能优化
- cell单元格的值: 可能会在公式 引用之类的大数据量计算,这里我使用web worker。
- 数据统计和筛选,排序,查找这些使用 异步分片来实现。
- 多维表格中的 icon及image的缓存与复用等等...
example:在单元格渲染时计算复杂计算时 使用web worker来计算 然后textNode.text(result)实现单个单元格更新
js
// cacl(40)
if (textContext && textContext.includes('cacl')) {
this.alloyWorker.cookie.exportStaion(Math.random() * 10 >= 5 ? 40 : 39).then((result) => {
const groups = this.groups.bottomRight.find(`#${row}-${col}`) as Group[];
if (groups.length) {
const textNode = groups[0].children[1] as Konva.Text;
textNode.text(result);
}
})
textContext = '计算中...';
}统计之类的使用异步分片 ,可以动态控制fps的变化 来控制处理数据量 。
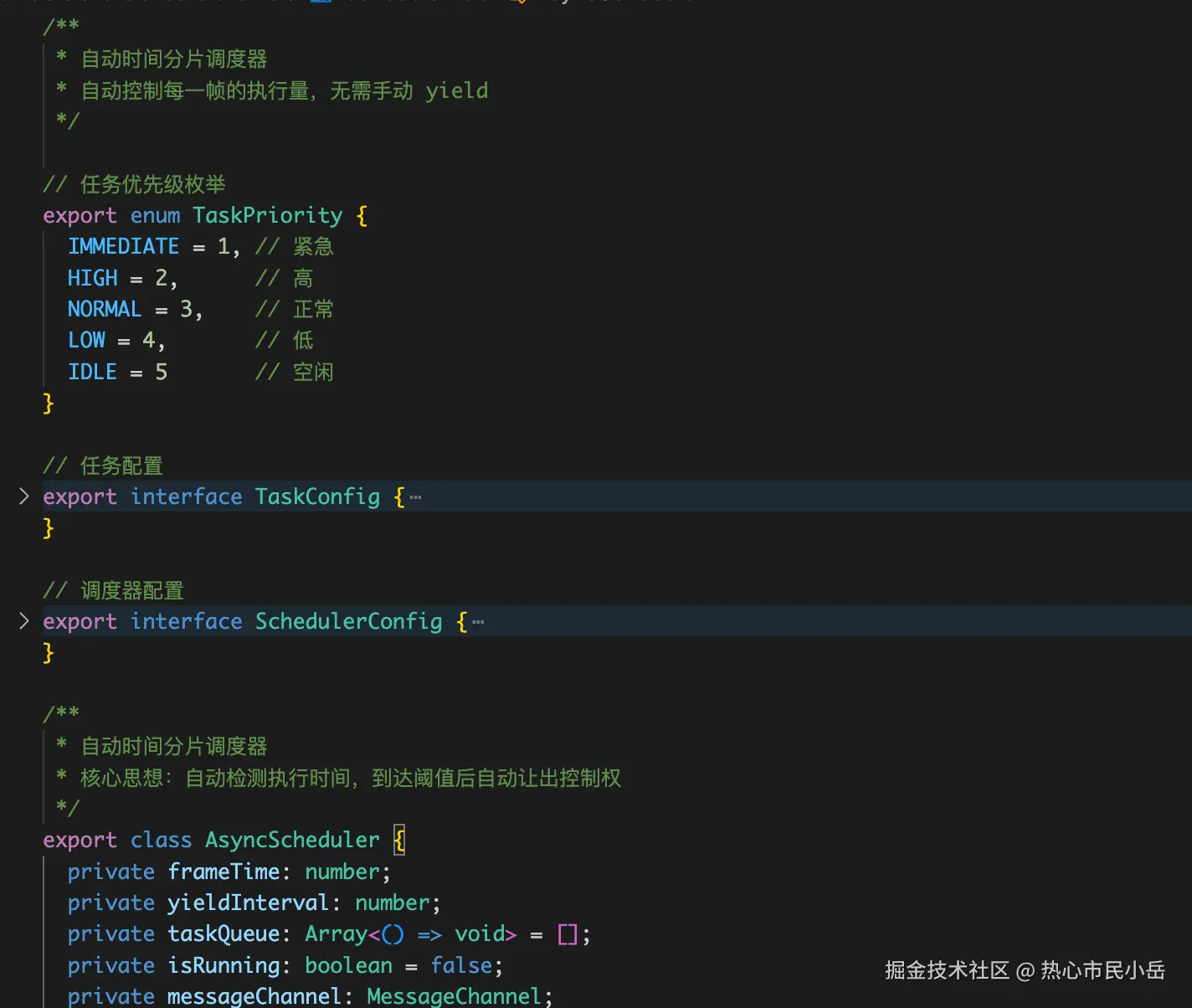
八扩展性
还有很多需要继续去实现和扩展,高亮 选区 列类型生成不同的单元格 等等...
再举个扩展的例子:用户选区

实现起来也很简单
js
export class SelectionNodeManager {
public topRect: Konva.Rect;
public rightRect: Konva.Rect;
public bottomRect: Konva.Rect;
public leftRect: Konva.Rect;
public selectionBorder: Konva.Rect;
public activeCellBorder: Konva.Rect;
constructor() {
const fillConfig = {
fill: "rgba(0, 123, 255, 0.1)",
visible: false,
listening: false,
};
this.topRect = new Konva.Rect(fillConfig);
this.rightRect = new Konva.Rect(fillConfig);
this.bottomRect = new Konva.Rect(fillConfig);
this.leftRect = new Konva.Rect(fillConfig);
this.selectionBorder = new ThinBorderRect({
fill: "transparent",
stroke: "#1e6fff",
strokeWidth: 1,
visible: false,
listening: false,
}) as any;
this.activeCellBorder = new Konva.Rect({
fill: "transparent",
stroke: "#1e6fff",
strokeWidth: 2,
visible: false,
listening: false,
});
}
update({
selectionX,
selectionY,
selectionWidth,
selectionHeight,
activeCellX,
activeCellY,
activeCellWidth,
activeCellHeight
}) {
// 计算相对位置
const relX = activeCellX - selectionX;
const relY = activeCellY - selectionY;
// 1. 上方区域
this.topRect.setAttrs({
x: selectionX,
y: selectionY,
width: selectionWidth,
height: relY,
visible: relY > 0
});
// 2. 右侧区域
const rightWidth = selectionWidth - (relX + activeCellWidth);
this.rightRect.setAttrs({
x: activeCellX + activeCellWidth,
y: activeCellY,
width: rightWidth,
height: activeCellHeight,
visible: rightWidth > 0
});
// 3. 下方区域
const bottomHeight = selectionHeight - (relY + activeCellHeight);
this.bottomRect.setAttrs({
x: selectionX,
y: activeCellY + activeCellHeight,
width: selectionWidth,
height: bottomHeight,
visible: bottomHeight > 0
});
// 4. 左侧区域
this.leftRect.setAttrs({
x: selectionX,
y: activeCellY,
width: relX,
height: activeCellHeight,
visible: relX > 0
});
// 5. 整体边框
this.selectionBorder.setAttrs({
x: selectionX,
y: selectionY,
width: selectionWidth,
height: selectionHeight,
visible: true
});
// 6. 活动单元格边框
this.activeCellBorder.setAttrs({
x: activeCellX + 1,
y: activeCellY + 1,
width: activeCellWidth - 1,
height: activeCellHeight - 1,
visible: true
});
}
hide() {
this.topRect.visible(false);
this.rightRect.visible(false);
this.bottomRect.visible(false);
this.leftRect.visible(false);
this.selectionBorder.visible(false);
this.activeCellBorder.visible(false);
}
}生成选区节点 监听事件并且更新选区即可。还有一个边界就不细说了

九.结语
存在疑问的可以留言,还有许多功能需要开发 打磨,有进展了再发文章。 这篇文章主要帮大家打开思路, 一步一步的解决一个困难功能的实现。