文章目录
- 为什么需要用到扫描被注解修饰的类
- PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver扫描文件
- [ASM 读取类注解信息解析](#ASM 读取类注解信息解析)
为什么需要用到扫描被注解修饰的类
我们利用Spring框架或者SpringBoot框架经常会自己写一些注解,来方便自己的业务使用,但是我们如何获取到被注解修饰的类或方法,是一个值得探讨的问题,下面我们会具体分析一些demo来给出路径下某些被注解修饰的类的方案。
demo1
一、核心方案:使用 ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider
这是 Spring 官方提供的扫描类,用来:
1.按包扫描 class;
2.按注解过滤;
3.支持 classpath 路径;
4.返回每个匹配类的 BeanDefinition。
下面的case是我们获取org.apache.dubbo.springboot.demo下的被@Service修饰的类
java
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1️⃣ 创建扫描器
ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider scanner =
new ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider(false); // false 表示不使用默认过滤器
// 2️⃣ 添加注解过滤器(比如扫描 @Service 的类)
scanner.addIncludeFilter(new AnnotationTypeFilter(org.springframework.stereotype.Service.class));
// 可选:也可以加类型过滤器,比如所有实现 MyInterface 的类
// scanner.addIncludeFilter(new AssignableTypeFilter(MyInterface.class));
String name = SayController.class.getPackage().getName();
System.out.println("name = " + name);
// 3️⃣ 扫描指定包路径
String basePackage = "org.apache.dubbo.springboot.demo";
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = scanner.findCandidateComponents(basePackage);
// 4️⃣ 遍历结果
for (BeanDefinition bd : candidates) {
String className = bd.getBeanClassName();
System.out.println("发现被 @Service 修饰的类: " + className);
}
}输出的结果

ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider
ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider 底层执行的流程:
1.扫描PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver#getResources("classpath*:org/apache/dubbo/springboot/demo/**/*.class")
2.扫描出所有 .class 文件;
3.读取字节码(不加载类)→ MetadataReader;
4.判断类上是否包含指定注解;
5.符合条件则返回 ScannedGenericBeanDefinition。
demo2:
使用PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver.class来进行获取路径org.apache.dubbo.springboot.demo下被@RestController注解修饰的类
java
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String basePackage = "org.apache.dubbo.springboot.demo";
String packageSearchPath = "classpath*:" + basePackage.replace('.', '/') + "/**/*.class";
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver resolver = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
Resource[] resources = resolver.getResources(packageSearchPath);
SimpleMetadataReaderFactory readerFactory = new SimpleMetadataReaderFactory();
for (Resource resource : resources) {
MetadataReader metadataReader = readerFactory.getMetadataReader(resource);
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata = metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata();
if (annotationMetadata.hasAnnotation(RestController.class.getName())) {
Map<String, Object> annotationAttributes = annotationMetadata.getAnnotationAttributes(RestController.class.getName());
System.out.println("发现 @RestController 类:" + metadataReader.getClassMetadata().getClassName());
System.out.println("注解@RestController 类的属性:" + annotationAttributes);
}
}
}执行结果

PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver扫描文件
核心PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver.getResource()
java
public Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException {
//校验路径不为null
Assert.notNull(locationPattern, "Location pattern must not be null");
//判断路径的开头是否是classpath*:
if (locationPattern.startsWith("classpath*:")) {
//AntPathMatcher.isPattern()方法是校验路径中是否含有*等字符,true执行findPathMatchingResources()方法,false执行findAllClassPathResources()方法
return this.getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring("classpath*:".length())) ? this.findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern) : this.findAllClassPathResources(locationPattern.substring("classpath*:".length()));
} else {
int prefixEnd = locationPattern.startsWith("war:") ? locationPattern.indexOf("*/") + 1 : locationPattern.indexOf(58) + 1;
return this.getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(prefixEnd)) ? this.findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern) : new Resource[]{this.getResourceLoader().getResource(locationPattern)};
}
}findPathMatchingResources方法
java
protected Resource[] findPathMatchingResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException {
//获取我们的根路径
String rootDirPath = this.determineRootDir(locationPattern);
//将*后面的字段去掉
String subPattern = locationPattern.substring(rootDirPath.length());
//获取目录下的所有的文件 递归走getResource()
Resource[] rootDirResources = this.getResources(rootDirPath);
Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet(16);
for(Resource rootDirResource : rootDirResources) {
rootDirResource = this.resolveRootDirResource(rootDirResource);
URL rootDirUrl = rootDirResource.getURL();
if (equinoxResolveMethod != null && rootDirUrl.getProtocol().startsWith("bundle")) {
URL resolvedUrl = (URL)ReflectionUtils.invokeMethod(equinoxResolveMethod, (Object)null, new Object[]{rootDirUrl});
if (resolvedUrl != null) {
rootDirUrl = resolvedUrl;
}
rootDirResource = new UrlResource(rootDirUrl);
}
if (rootDirUrl.getProtocol().startsWith("vfs")) {
result.addAll(PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver.VfsResourceMatchingDelegate.findMatchingResources(rootDirUrl, subPattern, this.getPathMatcher()));
} else if (!ResourceUtils.isJarURL(rootDirUrl) && !this.isJarResource(rootDirResource)) {
result.addAll(this.doFindPathMatchingFileResources(rootDirResource, subPattern));
} else {
result.addAll(this.doFindPathMatchingJarResources(rootDirResource, rootDirUrl, subPattern));
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Resolved location pattern [" + locationPattern + "] to resources " + result);
}
return (Resource[])result.toArray(new Resource[0]);
}findAllClassPathResources()方法
java
protected Resource[] findAllClassPathResources(String location) throws IOException {
String path = location;
if (location.startsWith("/")) {
path = location.substring(1);
}
//核心点doFindAllClassPathResources()
Set<Resource> result = this.doFindAllClassPathResources(path);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Resolved classpath location [" + location + "] to resources " + result);
}
return (Resource[])result.toArray(new Resource[0]);
}
protected Set<Resource> doFindAllClassPathResources(String path) throws IOException {
//创建一个结果集合
Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet(16);
//DefaultResourceLoade创建,为什么考虑用DefaultResourceLoader?
//JVM 会在以下路径中查找:当前 classpath 目录;所有依赖的 JAR 包;父类加载器的路径(如 AppClassLoader → ExtClassLoader)。这也是为什么即使 com/example/MyService.class 在不同 JAR 中都有,Spring 也能找到多个匹配。
ClassLoader cl = this.getClassLoader();
//获取路径下的所有的类
Enumeration<URL> resourceUrls = cl != null ? cl.getResources(path) : ClassLoader.getSystemResources(path);
//循环遍历获取到的resourceUrls
while(resourceUrls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = (URL)resourceUrls.nextElement();
result.add(this.convertClassLoaderURL(url));
}
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(path)) {
this.addAllClassLoaderJarRoots(cl, result);
}
return result;
}PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver#doFindPathMatchingFileResources()方法
java
protected Set<Resource> doFindPathMatchingFileResources(Resource rootDirResource, String subPattern) throws IOException {
File rootDir;
try {
//获取根路径
rootDir = rootDirResource.getFile().getAbsoluteFile();
} catch (FileNotFoundException ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Cannot search for matching files underneath " + rootDirResource + " in the file system: " + ex.getMessage());
}
return Collections.emptySet();
} catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Failed to resolve " + rootDirResource + " in the file system: " + ex);
}
return Collections.emptySet();
}
//执行核心方法
return this.doFindMatchingFileSystemResources(rootDir, subPattern);
}PathMatchingResourcePatternResource#rerrieveMatchingFiles()方法
java
protected Set<File> retrieveMatchingFiles(File rootDir, String pattern) throws IOException {
//校验路径是否存在
if (!rootDir.exists()) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipping [" + rootDir.getAbsolutePath() + "] because it does not exist");
}
// 不存在直接返回
return Collections.emptySet();
//判断是否是目录
} else if (!rootDir.isDirectory()) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Skipping [" + rootDir.getAbsolutePath() + "] because it does not denote a directory");
}
//不是直接返回
return Collections.emptySet();
//判断目录是否可读
} else if (!rootDir.canRead()) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Skipping search for matching files underneath directory [" + rootDir.getAbsolutePath() + "] because the application is not allowed to read the directory");
}
//不可读直接返回
return Collections.emptySet();
} else {
//重新定义路径
String fullPattern = StringUtils.replace(rootDir.getAbsolutePath(), File.separator, "/");
if (!pattern.startsWith("/")) {
fullPattern = fullPattern + "/";
}
fullPattern = fullPattern + StringUtils.replace(pattern, File.separator, "/");
Set<File> result = new LinkedHashSet(8);
this.doRetrieveMatchingFiles(fullPattern, rootDir, result);
return result;
}
}PathMatchingResourcePatternResource#doRetriveMatchingFiles()方法
java
protected void doRetrieveMatchingFiles(String fullPattern, File dir, Set<File> result) throws IOException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Searching directory [" + dir.getAbsolutePath() + "] for files matching pattern [" + fullPattern + "]");
}
//获取路径下的所有的文件,并进行循环遍历,将匹配到的文件放入集合中,如果是文件夹,继续循环遍历。
for(File content : this.listDirectory(dir)) {
String currPath = StringUtils.replace(content.getAbsolutePath(), File.separator, "/");
if (content.isDirectory() && this.getPathMatcher().matchStart(fullPattern, currPath + "/")) {
if (!content.canRead()) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipping subdirectory [" + dir.getAbsolutePath() + "] because the application is not allowed to read the directory");
}
} else {
//递归继续循环遍历
this.doRetrieveMatchingFiles(fullPattern, content, result);
}
}
//判断是否匹配
if (this.getPathMatcher().match(fullPattern, currPath)) {
result.add(content);
}
}
}
解析二进制文件的类
java
final class SimpleAnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor extends ClassVisitor {
@Nullable
private final ClassLoader classLoader;
private String className = "";
private int access;
@Nullable
private String superClassName;
private String[] interfaceNames = new String[0];
@Nullable
private String enclosingClassName;
private boolean independentInnerClass;
private Set<String> memberClassNames = new LinkedHashSet(4);
private List<MergedAnnotation<?>> annotations = new ArrayList();
private List<SimpleMethodMetadata> annotatedMethods = new ArrayList();
@Nullable
private SimpleAnnotationMetadata metadata;
@Nullable
private Source source;
SimpleAnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
super(17432576);
this.classLoader = classLoader;
}
//获取类名称,接口名称,父类名称
public void visit(int version, int access, String name, String signature, @Nullable String supername, String[] interfaces) {
this.className = this.toClassName(name);
this.access = access;
if (supername != null && !this.isInterface(access)) {
this.superClassName = this.toClassName(supername);
}
this.interfaceNames = new String[interfaces.length];
for(int i = 0; i < interfaces.length; ++i) {
this.interfaceNames[i] = this.toClassName(interfaces[i]);
}
}
public void visitOuterClass(String owner, String name, String desc) {
this.enclosingClassName = this.toClassName(owner);
}
public void visitInnerClass(String name, @Nullable String outerName, String innerName, int access) {
if (outerName != null) {
String className = this.toClassName(name);
String outerClassName = this.toClassName(outerName);
if (this.className.equals(className)) {
this.enclosingClassName = outerClassName;
this.independentInnerClass = (access & 8) != 0;
} else if (this.className.equals(outerClassName)) {
this.memberClassNames.add(className);
}
}
}
//获取类筑基期
@Nullable
public AnnotationVisitor visitAnnotation(String descriptor, boolean visible) {
ClassLoader var10000 = this.classLoader;
Source var10001 = this.getSource();
List var10004 = this.annotations;
var10004.getClass();
return MergedAnnotationReadingVisitor.get(var10000, var10001, descriptor, visible, var10004::add);
}
//获取方法名称
@Nullable
public MethodVisitor visitMethod(int access, String name, String descriptor, String signature, String[] exceptions) {
if (this.isBridge(access)) {
return null;
} else {
ClassLoader var10002 = this.classLoader;
String var10003 = this.className;
List var10007 = this.annotatedMethods;
var10007.getClass();
return new SimpleMethodMetadataReadingVisitor(var10002, var10003, access, name, descriptor, var10007::add);
}
}
//汇总为 SimpleAnnotationMetadata
public void visitEnd() {
String[] memberClassNames = StringUtils.toStringArray(this.memberClassNames);
MethodMetadata[] annotatedMethods = (MethodMetadata[])this.annotatedMethods.toArray(new MethodMetadata[0]);
MergedAnnotations annotations = MergedAnnotations.of(this.annotations);
this.metadata = new SimpleAnnotationMetadata(this.className, this.access, this.enclosingClassName, this.superClassName, this.independentInnerClass, this.interfaceNames, memberClassNames, annotatedMethods, annotations);
}
public SimpleAnnotationMetadata getMetadata() {
Assert.state(this.metadata != null, "AnnotationMetadata not initialized");
return this.metadata;
}
private Source getSource() {
Source source = this.source;
if (source == null) {
source = new Source(this.className);
this.source = source;
}
return source;
}
private String toClassName(String name) {
return ClassUtils.convertResourcePathToClassName(name);
}
private boolean isBridge(int access) {
return (access & 64) != 0;
}
private boolean isInterface(int access) {
return (access & 512) != 0;
}
private static final class Source {
private final String className;
Source(String className) {
this.className = className;
}
public int hashCode() {
return this.className.hashCode();
}
public boolean equals(@Nullable Object obj) {
if (this == obj) {
return true;
} else {
return obj != null && this.getClass() == obj.getClass() ? this.className.equals(((Source)obj).className) : false;
}
}
public String toString() {
return this.className;
}
}
}ASM 读取类注解信息解析
ASM 是一个字节码操作框架(来自 ObjectWeb),它可以在不加载类到 JVM 的情况下,直接解析 .class 文件的二进制结构。
类似于我们平常用 Class.forName("xxx") 是加载 + 解析。ASM 则是 只解析 class 文件内容,不加载类,直接读取文件的二进制流。
Spring 在启动时要扫描大量类(比如 @Component、@Configuration),如果每个类都用反射加载,会极慢且占内存。
于是 Spring 用 ASM 读取 .class 文件里的元数据(如类名、父类、接口、注解、方法名等),而不创建 Class 对象。
ASM获取类加载信息
java
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1 读取 class 文件(这里从 classpath 获取)
InputStream in = SayController.class.getClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream("org/apache/dubbo/springboot/demo/service/SayService.class");
// 2 创建 ASM 的 ClassReader
ClassReader classReader = new ClassReader(in);
// 3 调用 accept() 让 ASM 解析并回调自定义的 ClassVisitor
classReader.accept(new ClassVisitor(Opcodes.ASM9) {
@Override
public void visit(int version, int access, String name,
String signature, String superName, String[] interfaces) {
System.out.println("类名:" + name);
System.out.println("父类:" + superName);
}
@Override
public AnnotationVisitor visitAnnotation(String descriptor, boolean visible) {
System.out.println("类注解:" + descriptor);
return super.visitAnnotation(descriptor, visible);
}
@Override
public MethodVisitor visitMethod(int access, String name,
String descriptor, String signature, String[] exceptions) {
System.out.println("方法名:" + name + " | 描述符:" + descriptor);
return new MethodVisitor(Opcodes.ASM9) {
@Override
public AnnotationVisitor visitAnnotation(String desc, boolean visible) {
System.out.println(" 方法注解:" + desc);
return super.visitAnnotation(desc, visible);
}
};
}
@Override
public void visitEnd() {
System.out.println("=== 解析结束 ===");
}
}, 0);
in.close();
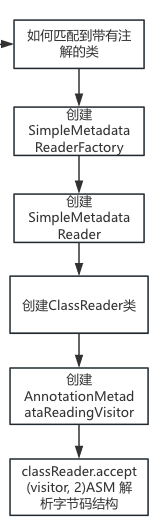
}Spring 中 ASM 的使用路径:
当 Spring 扫描包时(如 @ComponentScan("com.xxx")):
1.SimpleMetadataReader(Resource, ClassLoader) 打开 class 文件的输入流
2.new ClassReader(is) 解析 class 文件字节流
3.AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor visitor = new AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor(classLoader) 创建一个 ASM 的 Visitor
4.classReader.accept(visitor, 2) 让 ASM 开始扫描 class 文件并回调 visitor
5.AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor 收集所有类、方法、注解等元数据
6.最终生成 AnnotationMetadata 对象,供 Spring 上层逻辑(如 BeanDefinitionScanner)使用