使用仓颉开发一个简单的http服务
linux下安装仓颉
sh
tar xvg cangjie-sdk-linux-x64-1.0.1.tar.gz等待完成后
执行
sh
source cangjie/envsetup.sh验证
sh
cjc -v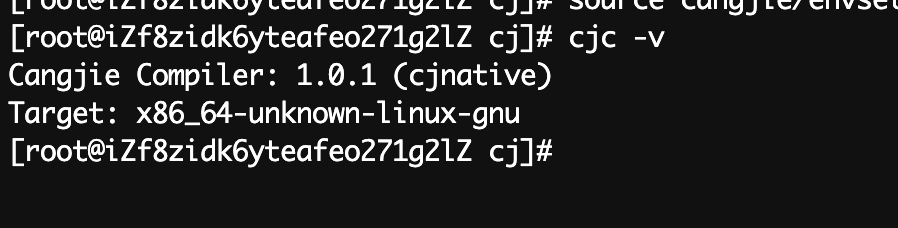
新建项目
新建一个文件夹,初始化cjpm项目
sh
cjpm init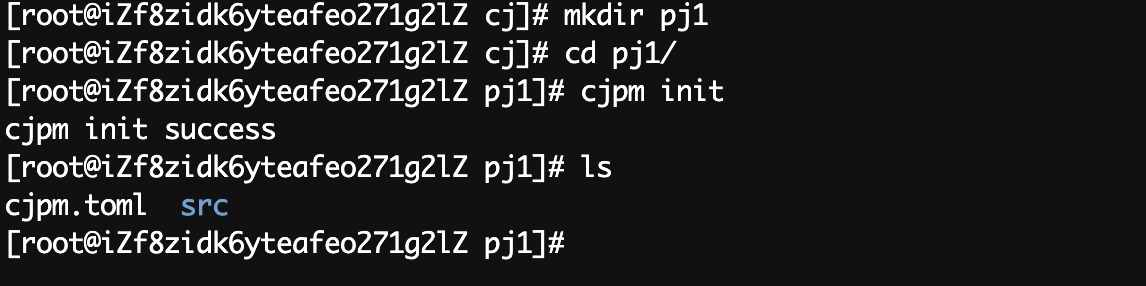
和我们之前在windows的是一样的。
运行一下
sh
cjpm run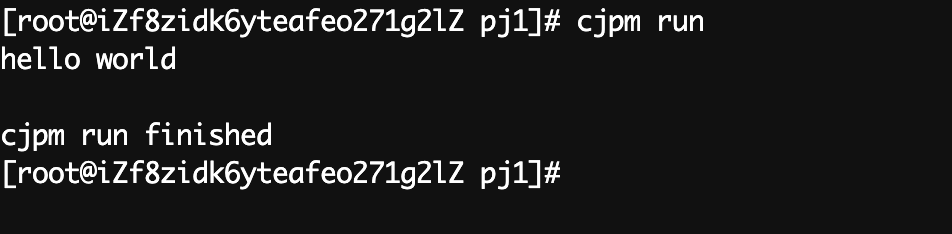
构建一下
sh
cjpm build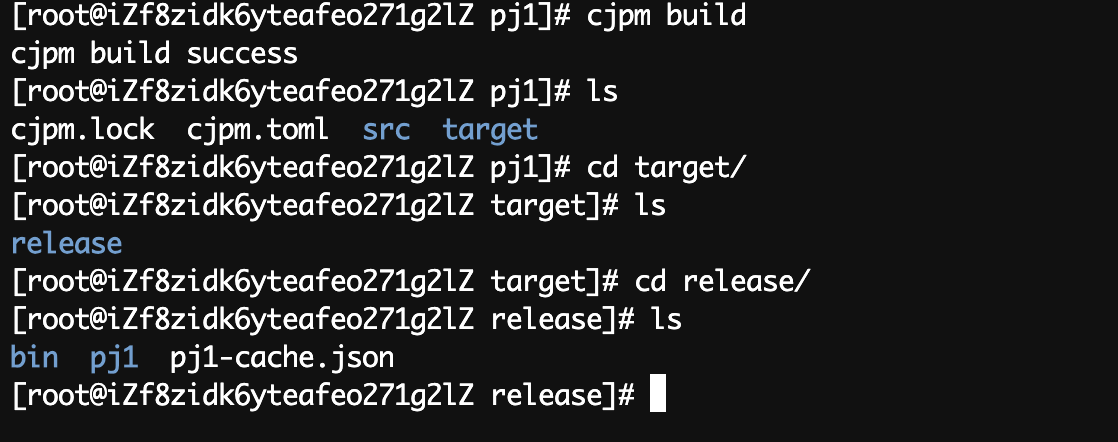
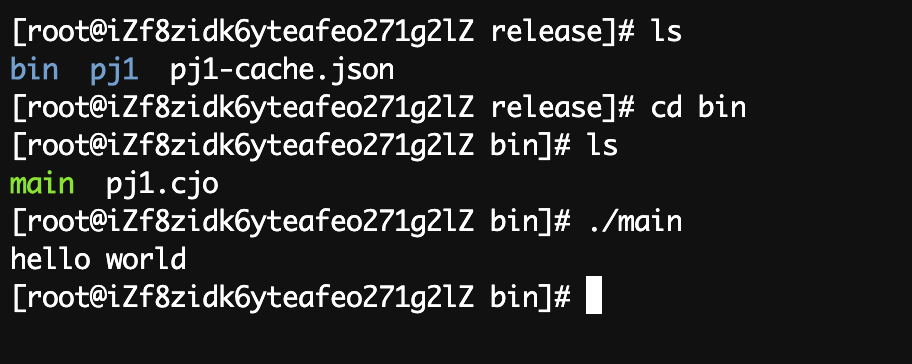
那么构建完成后,如何运行呢?
进入bin目录下。看到有一个可执行文件,main。执行它。
引入stdx
下载构建好的stdx
https://gitcode.com/Cangjie/cangjie-stdx-bin/releases?isLogin=1
根据你的型号选择,如果你不知道,可以执行cjc -v
比如我的
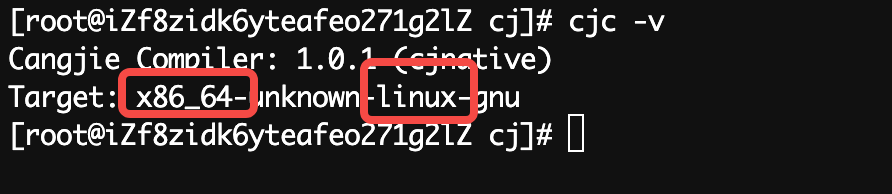

下载完成后,解压。
在cjpm.toml引入使用。
stdx使用文档
这里的target.后面的就是你执行cjc -v 获取到的。如上。
"${CANGJIE_STDX_PATH}"换成你的stdx的解压路径。
js
[target.x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu]
[target.x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu.bin-dependencies]
path-option = ["${CANGJIE_STDX_PATH}"]比如我的
js
[package]
cjc-version = "1.0.1"
name = "pj1"
description = "nothing here"
version = "1.0.0"
target-dir = ""
src-dir = ""
output-type = "executable"
compile-option = ""
override-compile-option = ""
link-option = ""
package-configuration = {}
[dependencies]
[target.x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu]
[target.x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu.bin-dependencies]
path-option = ["/www/cj/pj1/linux_x86_64_llvm/dynamic/stdx"]编写代码
js
package pj1
import stdx.net.http.*
import stdx.log.*
// 1. 构建 Server 实例
let server = ServerBuilder()
.addr("127.0.0.1")
.port(3000)
.build()
func startServer(): Unit {
// 2. 注册请求处理逻辑
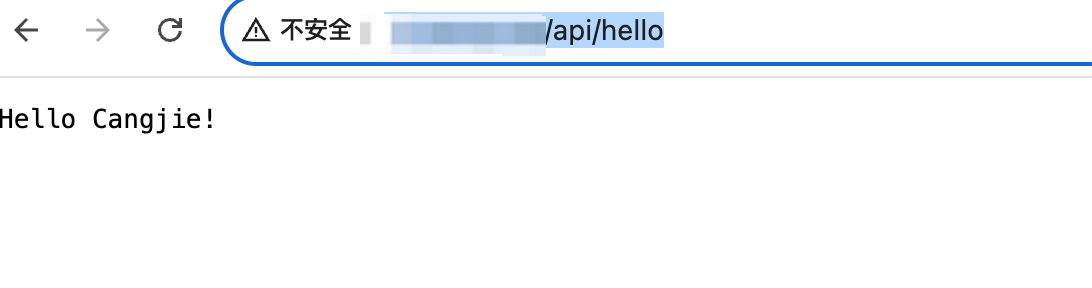
server.distributor.register("/hello", {httpContext =>
httpContext.responseBuilder.body("Hello Cangjie!")
})
server.logger.level = LogLevel.OFF
// 3. 启动服务
server.serve()
}
main () {
spawn {
startServer()
}
sleep(Duration.second)
// 主线程无限休眠,不退出(进程保持存活,服务器持续监听)
while (true) {
sleep(Duration.second * 3600) // 每小时醒一次,继续循环
}
}测试请求
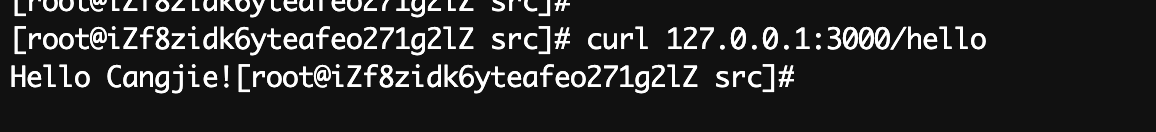
改造
src下新增目录
scr/controller/
新增文件
src/controller/user.cj
增加controller/user.cj
js
package pj1.controller
import stdx.net.http.*
public func UserController (distributor:HttpRequestDistributor) {
distributor.register("user", {httpContext =>
let request = httpContext.request
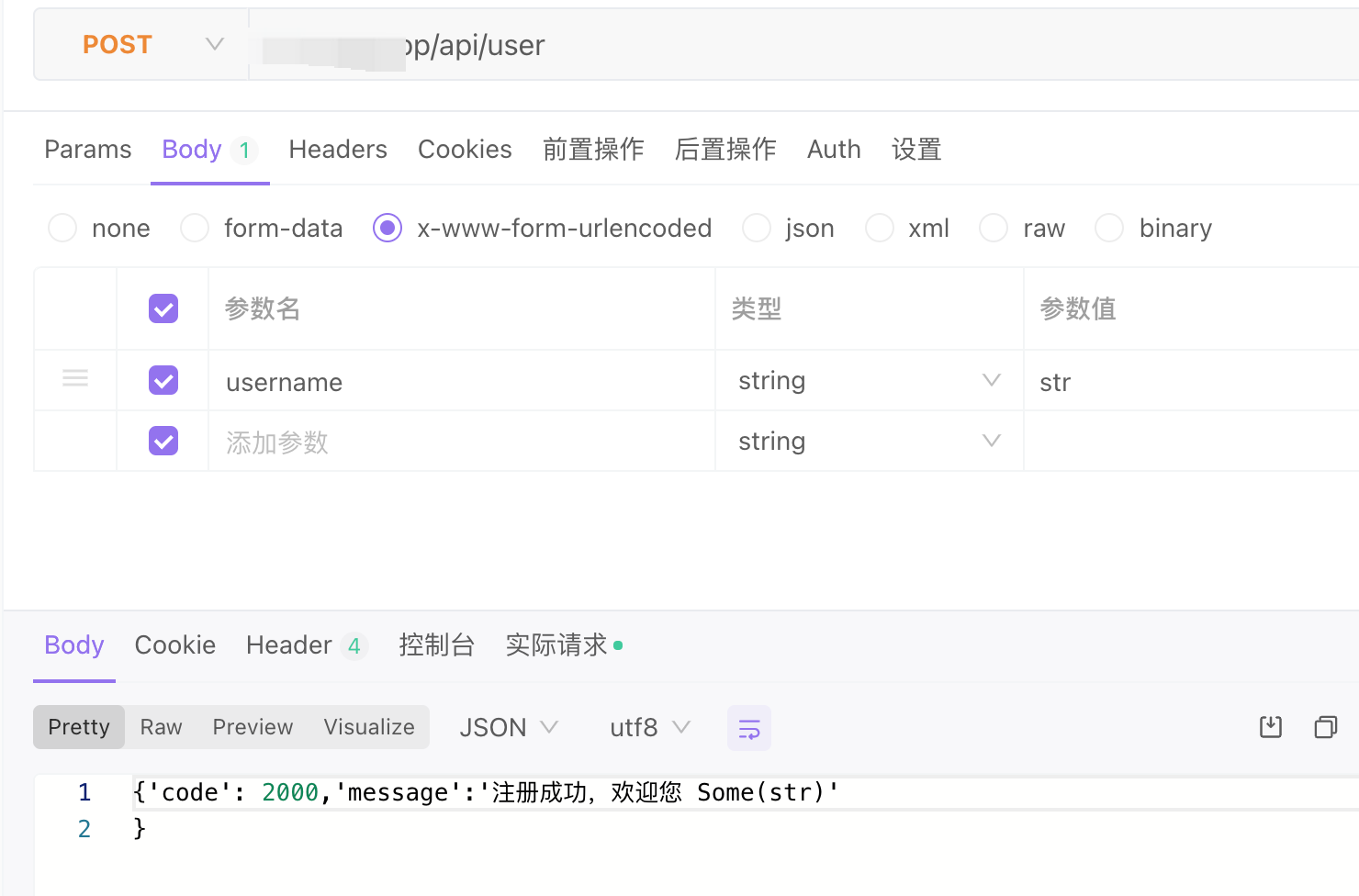
let username = request.form.get("username")
httpContext.responseBuilder.body("{'code':2000,'message':'注册成功,欢迎您 ${username}'}")
})
}在main.cj中使用
js
package pj1
import stdx.net.http.*
import stdx.log.*
import pj1.controller as Controller
// 1. 构建 Server 实例
let server = ServerBuilder()
.addr("0.0.0.0")
.port(3000)
.build()
func startServer(): Unit {
Controller.UserController(server.distributor);
// 2. 注册请求处理逻辑
server.distributor.register("/hello", {httpContext =>
httpContext.responseBuilder.body("Hello Cangjie!")
})
server.logger.level = LogLevel.OFF
// 3. 启动服务
server.serve()
}
main () {
spawn {
startServer()
}
sleep(Duration.second)
// 主线程无限休眠,不退出(进程保持存活,服务器持续监听)
while (true) {
sleep(Duration.second * 3600) // 每小时醒一次,继续循环
}
}启动
cjpm run
请求
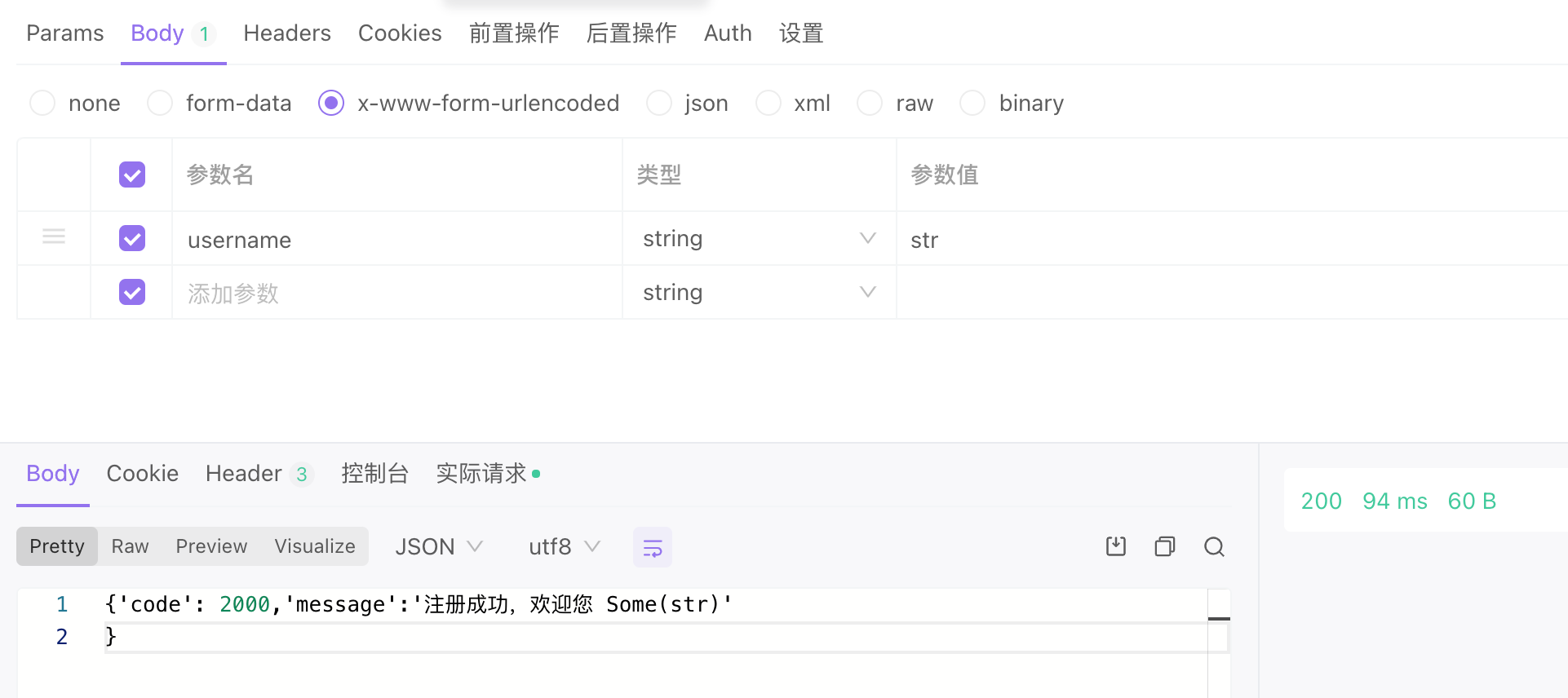
构建
cjpm build

在 target/release/bin/目录下
新增脚本 start.sh
sh
#!/bin/bash
# 配置区:修改为你的目标执行文件路径
TARGET_EXEC="./main" # 要运行的文件(绝对路径或相对路径)
LOG_FILE="./process.log" # 程序输出日志
PID_FILE="./process.pid" # 进程PID记录文件
# 检查进程是否运行
is_running() {
if [ -f "$PID_FILE" ]; then
local pid=$(cat "$PID_FILE")
# 检查PID对应的进程是否存在
if ps -p "$pid" > /dev/null 2>&1; then
return 0 # 运行中
else
rm -f "$PID_FILE" # PID文件存在但进程已死,清理文件
fi
fi
return 1 # 未运行
}
# 启动进程(后台运行)
start_process() {
if is_running; then
echo "程序已在运行中(PID: $(cat "$PID_FILE"))"
return 0
fi
# 后台启动程序,重定向输出到日志,记录PID
nohup "$TARGET_EXEC" > "$LOG_FILE" 2>&1 &
local pid=$! # 获取后台进程PID
echo "$pid" > "$PID_FILE"
echo "程序已启动(PID: $pid),日志文件: $LOG_FILE"
}
# 停止进程(强制终止)
stop_process() {
if ! is_running; then
echo "程序未在运行"
return 0
fi
local pid=$(cat "$PID_FILE")
kill "$pid" # 发送终止信号
# 等待进程退出(最多等5秒)
for i in {1..5}; do
if ! ps -p "$pid" > /dev/null 2>&1; then
rm -f "$PID_FILE"
echo "程序已停止(PID: $pid)"
return 0
fi
sleep 1
done
# 如果5秒后仍未退出,强制杀死
kill -9 "$pid"
rm -f "$PID_FILE"
echo "程序已强制停止(PID: $pid)"
}
# 暂停进程(发送暂停信号)
pause_process() {
if ! is_running; then
echo "程序未在运行"
return 0
fi
local pid=$(cat "$PID_FILE")
# 发送暂停信号(SIGSTOP)
kill -19 "$pid"
echo "程序已暂停(PID: $pid)"
}
# 恢复进程(发送继续信号)
resume_process() {
if ! is_running; then
echo "程序未在运行"
return 0
fi
local pid=$(cat "$PID_FILE")
# 发送继续信号(SIGCONT)
kill -18 "$pid"
echo "程序已恢复运行(PID: $pid)"
}
# 重启进程(先停止再启动)
restart_process() {
echo "正在重启程序..."
stop_process
start_process
}
# 查看进程状态
status_process() {
if is_running; then
local pid=$(cat "$PID_FILE")
# 检查进程是否处于暂停状态
local state=$(ps -p "$pid" -o state --no-headers)
if [ "$state" = "T" ]; then
echo "程序状态:暂停中(PID: $pid)"
else
echo "程序状态:运行中(PID: $pid)"
fi
else
echo "程序状态:未运行"
fi
}
# 帮助信息
show_help() {
echo "用法: $0 [命令]"
echo "命令列表:"
echo " start - 启动程序(后台运行)"
echo " stop - 停止程序"
echo " restart - 重启程序"
echo " pause - 暂停程序"
echo " resume - 恢复暂停的程序"
echo " status - 查看程序状态"
echo " help - 显示帮助信息"
}
# 解析参数
case "$1" in
start)
start_process
;;
stop)
stop_process
;;
restart)
restart_process
;;
pause)
pause_process
;;
resume)
resume_process
;;
status)
status_process
;;
help)
show_help
;;
*)
echo "未知命令: $1"
show_help
exit 1
;;
esac执行
sh
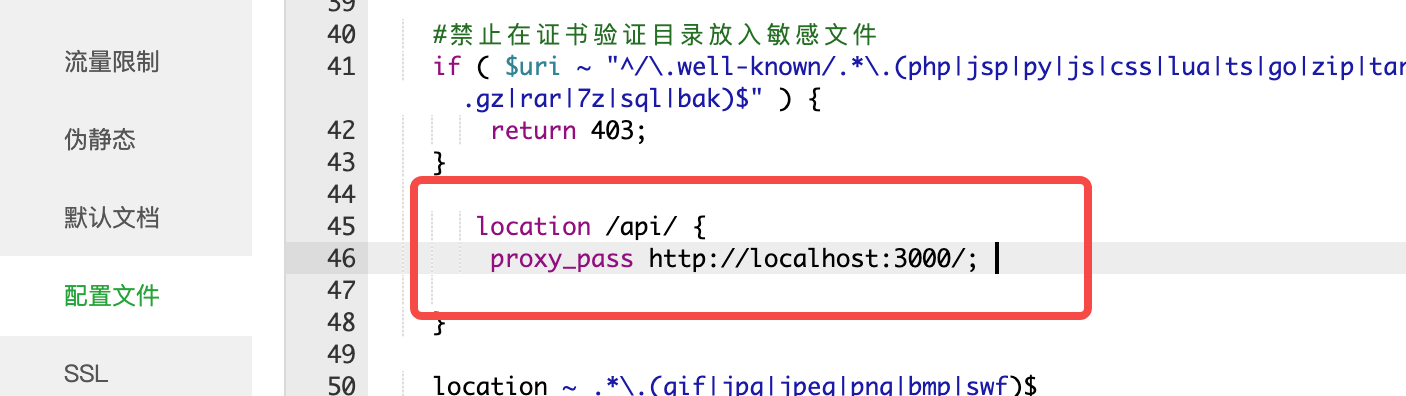
./start.sh startnginx代理
简单配置