C语言需要掌握的基础知识点之图
图是一种非常重要的非线性数据结构,由顶点的集合和顶点之间边的集合组成。以下是C语言中图的详细介绍和实现。
图的基本概念
图的定义
顶点(Vertex):图的基本单元
边(Edge):顶点之间的连接
有向图:边有方向
无向图:边没有方向
权重图:边带有权值
图的表示方法
邻接矩阵
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <limits.h>
#define MAX_VERTICES 100
#define INF INT_MAX // 表示无穷大
typedef struct Graph {
int numVertices;
int adjacencyMatrix[MAX_VERTICES][MAX_VERTICES];
} Graph;
// 初始化图
Graph* createGraph(int vertices) {
Graph* graph = (Graph*)malloc(sizeof(Graph));
graph->numVertices = vertices;
// 初始化邻接矩阵
for(int i = 0; i < vertices; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < vertices; j++) {
if(i == j)
graph->adjacencyMatrix[i][j] = 0; // 对角线为0
else
graph->adjacencyMatrix[i][j] = INF; // 初始为无穷大
}
}
return graph;
}
// 添加边(无向图)
void addEdgeUndirected(Graph* graph, int src, int dest, int weight) {
graph->adjacencyMatrix[src][dest] = weight;
graph->adjacencyMatrix[dest][src] = weight;
}
// 添加边(有向图)
void addEdgeDirected(Graph* graph, int src, int dest, int weight) {
graph->adjacencyMatrix[src][dest] = weight;
}
// 打印邻接矩阵
void printGraph(Graph* graph) {
printf("邻接矩阵:\n");
for(int i = 0; i < graph->numVertices; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < graph->numVertices; j++) {
if(graph->adjacencyMatrix[i][j] == INF)
printf("INF ");
else
printf("%3d ", graph->adjacencyMatrix[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}邻接表
c
// 邻接表节点
typedef struct AdjListNode {
int dest;
int weight;
struct AdjListNode* next;
} AdjListNode;
// 邻接表
typedef struct AdjList {
AdjListNode* head;
} AdjList;
// 图结构(邻接表)
typedef struct GraphList {
int numVertices;
AdjList* array;
} GraphList;
// 创建邻接表节点
AdjListNode* createAdjListNode(int dest, int weight) {
AdjListNode* newNode = (AdjListNode*)malloc(sizeof(AdjListNode));
newNode->dest = dest;
newNode->weight = weight;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
// 创建图(邻接表)
GraphList* createGraphList(int vertices) {
GraphList* graph = (GraphList*)malloc(sizeof(GraphList));
graph->numVertices = vertices;
graph->array = (AdjList*)malloc(vertices * sizeof(AdjList));
for(int i = 0; i < vertices; i++) {
graph->array[i].head = NULL;
}
return graph;
}
// 添加边(无向图-邻接表)
void addEdgeListUndirected(GraphList* graph, int src, int dest, int weight) {
// 添加从src到dest的边
AdjListNode* newNode = createAdjListNode(dest, weight);
newNode->next = graph->array[src].head;
graph->array[src].head = newNode;
// 添加从dest到src的边
newNode = createAdjListNode(src, weight);
newNode->next = graph->array[dest].head;
graph->array[dest].head = newNode;
}
// 添加边(有向图-邻接表)
void addEdgeListDirected(GraphList* graph, int src, int dest, int weight) {
AdjListNode* newNode = createAdjListNode(dest, weight);
newNode->next = graph->array[src].head;
graph->array[src].head = newNode;
}
// 打印邻接表
void printGraphList(GraphList* graph) {
printf("邻接表:\n");
for(int i = 0; i < graph->numVertices; i++) {
AdjListNode* temp = graph->array[i].head;
printf("顶点 %d: ", i);
while(temp) {
printf("-> %d(w:%d) ", temp->dest, temp->weight);
temp = temp->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
}图的遍历算法
深度优先搜索(DFS)
c
// DFS递归实现(邻接矩阵)
void DFS_Matrix(Graph* graph, int vertex, int visited[]) {
visited[vertex] = 1;
printf("%d ", vertex);
for(int i = 0; i < graph->numVertices; i++) {
if(graph->adjacencyMatrix[vertex][i] != INF && !visited[i]) {
DFS_Matrix(graph, i, visited);
}
}
}
void DFSTraversal(Graph* graph, int startVertex) {
int visited[MAX_VERTICES] = {0};
printf("DFS遍历: ");
DFS_Matrix(graph, startVertex, visited);
printf("\n");
}广度优先搜索(BFS)
c
// 队列实现
typedef struct Queue {
int items[MAX_VERTICES];
int front;
int rear;
} Queue;
Queue* createQueue() {
Queue* q = (Queue*)malloc(sizeof(Queue));
q->front = -1;
q->rear = -1;
return q;
}
int isEmpty(Queue* q) {
return q->rear == -1;
}
void enqueue(Queue* q, int value) {
if(q->rear == MAX_VERTICES - 1)
printf("队列已满\n");
else {
if(q->front == -1)
q->front = 0;
q->rear++;
q->items[q->rear] = value;
}
}
int dequeue(Queue* q) {
int item;
if(isEmpty(q)) {
printf("队列为空\n");
item = -1;
} else {
item = q->items[q->front];
q->front++;
if(q->front > q->rear) {
q->front = q->rear = -1;
}
}
return item;
}
// BFS遍历(邻接矩阵)
void BFS_Matrix(Graph* graph, int startVertex) {
int visited[MAX_VERTICES] = {0};
Queue* q = createQueue();
visited[startVertex] = 1;
enqueue(q, startVertex);
printf("BFS遍历: ");
while(!isEmpty(q)) {
int currentVertex = dequeue(q);
printf("%d ", currentVertex);
for(int i = 0; i < graph->numVertices; i++) {
if(graph->adjacencyMatrix[currentVertex][i] != INF && !visited[i]) {
visited[i] = 1;
enqueue(q, i);
}
}
}
printf("\n");
}图的最小生成树算法
Prim算法
c
// Prim算法求最小生成树
void primMST(Graph* graph) {
int parent[MAX_VERTICES]; // 存储MST
int key[MAX_VERTICES]; // 权值数组
int mstSet[MAX_VERTICES]; // 标记顶点是否在MST中
// 初始化
for(int i = 0; i < graph->numVertices; i++) {
key[i] = INF;
mstSet[i] = 0;
}
key[0] = 0; // 从第一个顶点开始
parent[0] = -1; // 第一个顶点是根节点
for(int count = 0; count < graph->numVertices - 1; count++) {
// 选择最小权值的顶点
int min = INF, minIndex;
for(int v = 0; v < graph->numVertices; v++) {
if(!mstSet[v] && key[v] < min) {
min = key[v];
minIndex = v;
}
}
int u = minIndex;
mstSet[u] = 1;
// 更新相邻顶点的权值
for(int v = 0; v < graph->numVertices; v++) {
if(graph->adjacencyMatrix[u][v] != INF && !mstSet[v] &&
graph->adjacencyMatrix[u][v] < key[v]) {
parent[v] = u;
key[v] = graph->adjacencyMatrix[u][v];
}
}
}
// 打印MST
printf("Prim算法 - 最小生成树:\n");
for(int i = 1; i < graph->numVertices; i++) {
printf("%d - %d : %d\n", parent[i], i, graph->adjacencyMatrix[i][parent[i]]);
}
}Kruskal算法
c
// 边的结构体
typedef struct Edge {
int src, dest, weight;
} Edge;
// 并查集结构
typedef struct Subset {
int parent;
int rank;
} Subset;
// 查找根节点
int find(Subset subsets[], int i) {
if(subsets[i].parent != i)
subsets[i].parent = find(subsets, subsets[i].parent);
return subsets[i].parent;
}
// 合并两个集合
void unionSets(Subset subsets[], int x, int y) {
int rootX = find(subsets, x);
int rootY = find(subsets, y);
if(subsets[rootX].rank < subsets[rootY].rank)
subsets[rootX].parent = rootY;
else if(subsets[rootX].rank > subsets[rootY].rank)
subsets[rootY].parent = rootX;
else {
subsets[rootY].parent = rootX;
subsets[rootX].rank++;
}
}
// 比较函数(用于排序)
int compareEdges(const void* a, const void* b) {
Edge* edge1 = (Edge*)a;
Edge* edge2 = (Edge*)b;
return edge1->weight - edge2->weight;
}
// Kruskal算法
void kruskalMST(Graph* graph) {
int V = graph->numVertices;
Edge result[V]; // 存储MST结果
int e = 0; // 结果数组的索引
int i = 0; // 排序后边的索引
// 获取所有边
Edge* edges = (Edge*)malloc(V * V * sizeof(Edge));
int edgeCount = 0;
for(int u = 0; u < V; u++) {
for(int v = u + 1; v < V; v++) {
if(graph->adjacencyMatrix[u][v] != INF) {
edges[edgeCount].src = u;
edges[edgeCount].dest = v;
edges[edgeCount].weight = graph->adjacencyMatrix[u][v];
edgeCount++;
}
}
}
// 按权值排序
qsort(edges, edgeCount, sizeof(Edge), compareEdges);
// 分配内存给并查集
Subset* subsets = (Subset*)malloc(V * sizeof(Subset));
// 初始化并查集
for(int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
subsets[v].parent = v;
subsets[v].rank = 0;
}
// 处理每条边
while(e < V - 1 && i < edgeCount) {
Edge nextEdge = edges[i++];
int x = find(subsets, nextEdge.src);
int y = find(subsets, nextEdge.dest);
// 如果不形成环,加入MST
if(x != y) {
result[e++] = nextEdge;
unionSets(subsets, x, y);
}
}
// 打印MST
printf("Kruskal算法 - 最小生成树:\n");
int minimumCost = 0;
for(i = 0; i < e; i++) {
printf("%d - %d : %d\n", result[i].src, result[i].dest, result[i].weight);
minimumCost += result[i].weight;
}
printf("最小生成树总权值: %d\n", minimumCost);
free(edges);
free(subsets);
}最短路径算法
Dijkstra算法
c
// Dijkstra算法求单源最短路径
void dijkstra(Graph* graph, int src) {
int dist[MAX_VERTICES]; // 最短距离数组
int visited[MAX_VERTICES]; // 已访问标记
// 初始化
for(int i = 0; i < graph->numVertices; i++) {
dist[i] = INF;
visited[i] = 0;
}
dist[src] = 0;
for(int count = 0; count < graph->numVertices - 1; count++) {
// 选择最小距离的顶点
int min = INF, minIndex;
for(int v = 0; v < graph->numVertices; v++) {
if(!visited[v] && dist[v] <= min) {
min = dist[v];
minIndex = v;
}
}
int u = minIndex;
visited[u] = 1;
// 更新相邻顶点的距离
for(int v = 0; v < graph->numVertices; v++) {
if(!visited[v] && graph->adjacencyMatrix[u][v] != INF &&
dist[u] != INF && dist[u] + graph->adjacencyMatrix[u][v] < dist[v]) {
dist[v] = dist[u] + graph->adjacencyMatrix[u][v];
}
}
}
// 打印最短路径
printf("Dijkstra算法 - 从顶点%d到各顶点的最短距离:\n", src);
for(int i = 0; i < graph->numVertices; i++) {
if(dist[i] == INF)
printf("到顶点%d: 不可达\n", i);
else
printf("到顶点%d: %d\n", i, dist[i]);
}
}Floyd-Warshall算法
c
// Floyd-Warshall算法求所有顶点对最短路径
void floydWarshall(Graph* graph) {
int dist[MAX_VERTICES][MAX_VERTICES];
int V = graph->numVertices;
// 初始化距离矩阵
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < V; j++) {
dist[i][j] = graph->adjacencyMatrix[i][j];
}
}
// Floyd-Warshall算法核心
for(int k = 0; k < V; k++) {
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < V; j++) {
if(dist[i][k] != INF && dist[k][j] != INF &&
dist[i][k] + dist[k][j] < dist[i][j]) {
dist[i][j] = dist[i][k] + dist[k][j];
}
}
}
}
// 打印结果
printf("Floyd-Warshall算法 - 所有顶点对最短距离:\n");
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < V; j++) {
if(dist[i][j] == INF)
printf("INF ");
else
printf("%3d ", dist[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}拓扑排序
c
// 拓扑排序(邻接表)
void topologicalSortUtil(GraphList* graph, int v, int visited[], int stack[], int* top) {
visited[v] = 1;
AdjListNode* temp = graph->array[v].head;
while(temp != NULL) {
int adjVertex = temp->dest;
if(!visited[adjVertex]) {
topologicalSortUtil(graph, adjVertex, visited, stack, top);
}
temp = temp->next;
}
stack[++(*top)] = v;
}
void topologicalSort(GraphList* graph) {
int stack[MAX_VERTICES];
int top = -1;
int visited[MAX_VERTICES] = {0};
for(int i = 0; i < graph->numVertices; i++) {
if(!visited[i]) {
topologicalSortUtil(graph, i, visited, stack, &top);
}
}
printf("拓扑排序: ");
while(top >= 0) {
printf("%d ", stack[top--]);
}
printf("\n");
}完整示例程序
c
int main() {
int V = 5; // 顶点数
// 创建图(邻接矩阵)
Graph* graph = createGraph(V);
// 添加边(无向图)
addEdgeUndirected(graph, 0, 1, 2);
addEdgeUndirected(graph, 0, 3, 6);
addEdgeUndirected(graph, 1, 2, 3);
addEdgeUndirected(graph, 1, 3, 8);
addEdgeUndirected(graph, 1, 4, 5);
addEdgeUndirected(graph, 2, 4, 7);
addEdgeUndirected(graph, 3, 4, 9);
// 打印图
printGraph(graph);
// 图遍历
DFSTraversal(graph, 0);
BFS_Matrix(graph, 0);
// 最小生成树
primMST(graph);
kruskalMST(graph);
// 最短路径
dijkstra(graph, 0);
floydWarshall(graph);
// 创建有向图进行拓扑排序
GraphList* graphList = createGraphList(6);
addEdgeListDirected(graphList, 5, 2, 1);
addEdgeListDirected(graphList, 5, 0, 1);
addEdgeListDirected(graphList, 4, 0, 1);
addEdgeListDirected(graphList, 4, 1, 1);
addEdgeListDirected(graphList, 2, 3, 1);
addEdgeListDirected(graphList, 3, 1, 1);
printGraphList(graphList);
topologicalSort(graphList);
// 释放内存
free(graph);
return 0;
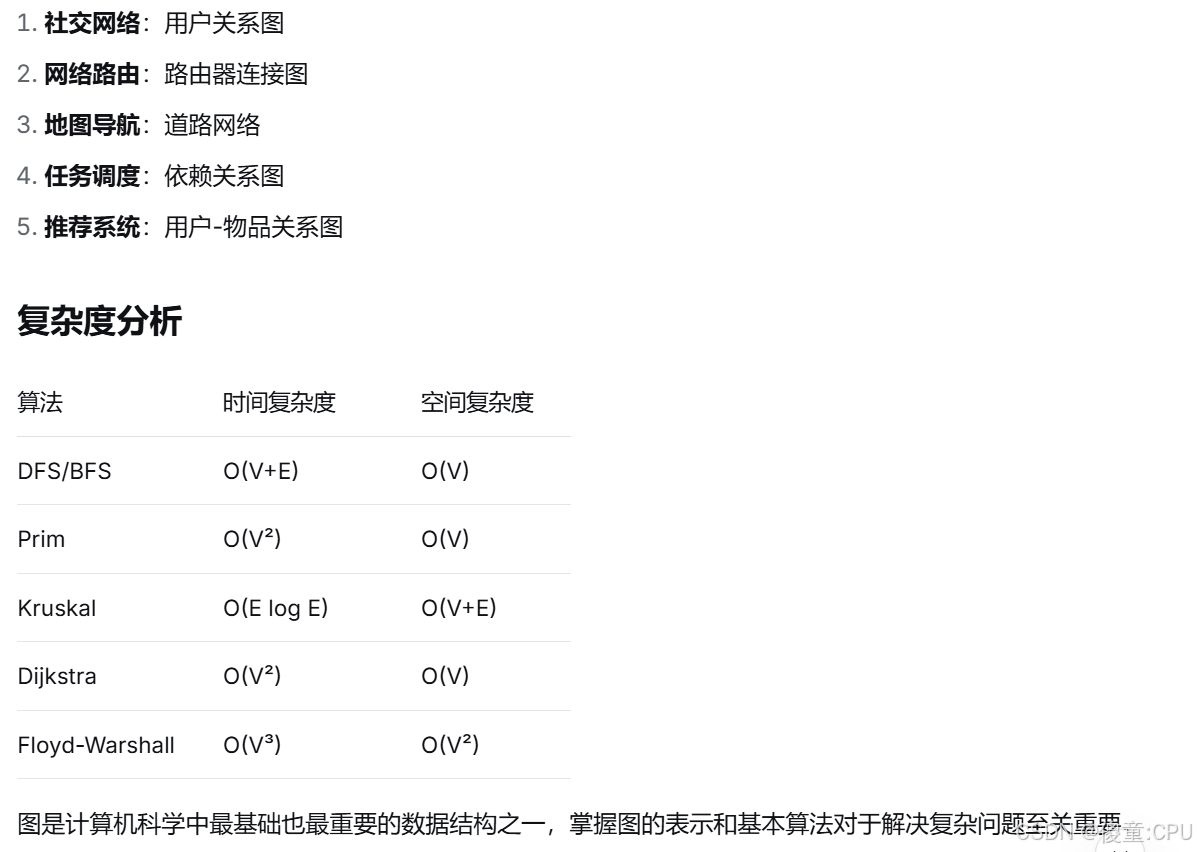
}图的应用场景