作者:来自 Elastic Enrico Zimuel 及 Florian Bernd
学习如何使用 Microsoft Agent Framework 与 Elasticsearch 构建智能代理应用,从 Elasticsearch 客户端库中使用 ES|QL 提取电商数据。
Elasticsearch 原生集成了业界领先的生成式 AI 工具和提供商。查看我们的网络研讨会,了解如何超越 RAG 基础,或使用 Elastic 向量数据库构建可用于生产的应用。
要为你的用例构建最佳搜索解决方案,请立即开始免费云试用或在本地机器上体验 Elastic。
在本文中,我们将介绍如何使用 Microsoft Agent Framework 与 Elasticsearch 在 Python 和 .NET 中构建一个简单的智能代理应用。
我们将展示如何使用 ES|QL 语言和 Elasticsearch 客户端库轻松构建一个用于从 Elasticsearch 中提取业务知识的代理。
Microsoft Agent Framework
Microsoft Agent Framework 是一个在 2025 年 10 月 1 日发布的新库。
它是一个多语言框架,用于构建、编排和部署 AI 代理,支持 Python 和 .NET。该框架提供从简单聊天代理到使用基于图的编排实现的复杂多代理工作流的完整功能。
使用 Agent Framework,你只需几行代码就能创建一个代理。下面是在 Python 中构建一个关于 Elasticsearch 的俳句的简单代理示例:
python
``
1. # pip install agent-framework --pre
2. # Use `az login` to authenticate with Azure CLI
3. import os
4. import asyncio
5. from agent_framework.azure import AzureOpenAIResponsesClient
6. from azure.identity import AzureCliCredential
9. async def main():
10. # Initialize a chat agent with Azure OpenAI Responses
11. # configuration can be set via environment variables
12. # or they can be passed in directly to the AzureOpenAIResponsesClient constructor
13. agent = AzureOpenAIResponsesClient(
14. credential=AzureCliCredential(),
15. ).create_agent(
16. ,
17. instructions="You are an upbeat assistant that writes beautifully.",
18. )
20. print(await agent.run("Write a haiku about Elasticsearch."))
22. if __name__ == "__main__":
23. asyncio.run(main())
``AI写代码在 Python 示例中,我们使用 AzureOpenAIResponseClient 类创建了 HaikuBot 代理。我们通过 run() 函数执行该代理,并传入用户的问题 "Write a haiku about Elasticsearch"。
下面是在 .NET 中的相同示例:
less
`
1. // dotnet add package Microsoft.Agents.AI.OpenAI --prerelease
2. using System;
3. using OpenAI;
5. // Replace the <apikey> with your OpenAI API key.
6. var agent = new OpenAIClient("<apikey>")
7. .GetOpenAIResponseClient("gpt-4o-mini")
8. .CreateAIAgent(name: "HaikuBot", instructions: "You are an upbeat assistant that writes beautifully.");
10. Console.WriteLine(await agent.RunAsync("Write a haiku about Elasticsearch."));
`AI写代码在 .NET 示例中,我们使用了 OpenAIClient 类,并通过 CreateAIAgent() 方法创建了代理。我们可以使用 RunAsync() 方法运行该代理,并传入与 Python 示例中相同的用户问题。
安装示例数据
在本文中,我们使用了一个来自电商网站的示例数据集。要安装此数据集,需要在示例中运行一个 Elasticsearch 实例。你可以使用 Elastic Cloud,或者直接在电脑上安装 Elasticsearch,使用以下命令:
sql
`curl -fsSL https://elastic.co/start-local | sh`AI写代码这将安装最新版本的 Elasticsearch 和 Kibana。
安装完成后,你可以使用用户名 elastic 和由 start-local 脚本生成的密码(存储在 .env 文件中)登录 Kibana。
你可以在 Kibana 中安装可用的电商订单数据集。该数据集包含一个名为 kibana_sample_data_ecommerce 的索引,其中包含来自某电商网站的 4,675 条订单信息。每个订单包含以下信息:
-
客户信息(姓名、ID、出生日期、邮箱等)
-
订单日期
-
订单 ID
-
产品(包含价格、数量、ID、类别、折扣等的产品列表)
-
SKU
-
总价(不含税、含税)
-
总数量
-
地理信息(城市、国家、大洲、位置、区域)
要安装示例数据,请在 Kibana 中打开 Integrations 页面(在顶部搜索栏中搜索 "Integration "),然后安装 "Sample Data "。
更多详细信息请参阅文档:
www.elastic.co/docs/explor...
构建一个 Elasticsearch 代理
我们希望使用 Microsoft 的框架创建一个能够与 Elasticsearch 通信以搜索特定索引的代理。我们可以使用 Elasticsearch 客户端库(例如 Python 和 .NET)并构建自定义工具。这些库通过为多种语言提供符合语言习惯的接口,简化了 Elasticsearch 的使用。
例如,我们可能想知道是否有人在电商网站上购买了某样商品。这个目标可以通过多种方式实现。例如,我们可以使用 ES|QL 语言并执行以下查询:
sql
`
1. FROM kibana_sample_data_ecommerce
2. | WHERE MATCH(customer_full_name,"Name Surname", {"operator": "AND"})
`AI写代码或者使用邮箱地址搜索客户:
ini
`
1. FROM kibana_sample_data_ecommerce
2. | WHERE email == "name@domain.com"
`AI写代码另一个我们可能感兴趣的例子是按地理位置(例如城市名称)查看电商网站的收入:
sql
`
1. FROM kibana_sample_data_ecommerce
2. | STATS revenue = SUM(taxful_total_price) BY geoip.city_name
3. | SORT revenue DESC
`AI写代码该查询将返回一个包含城市名称和总收入的表,如图 1 所示。我们可以看到,纽约是产生收入最多的城市。
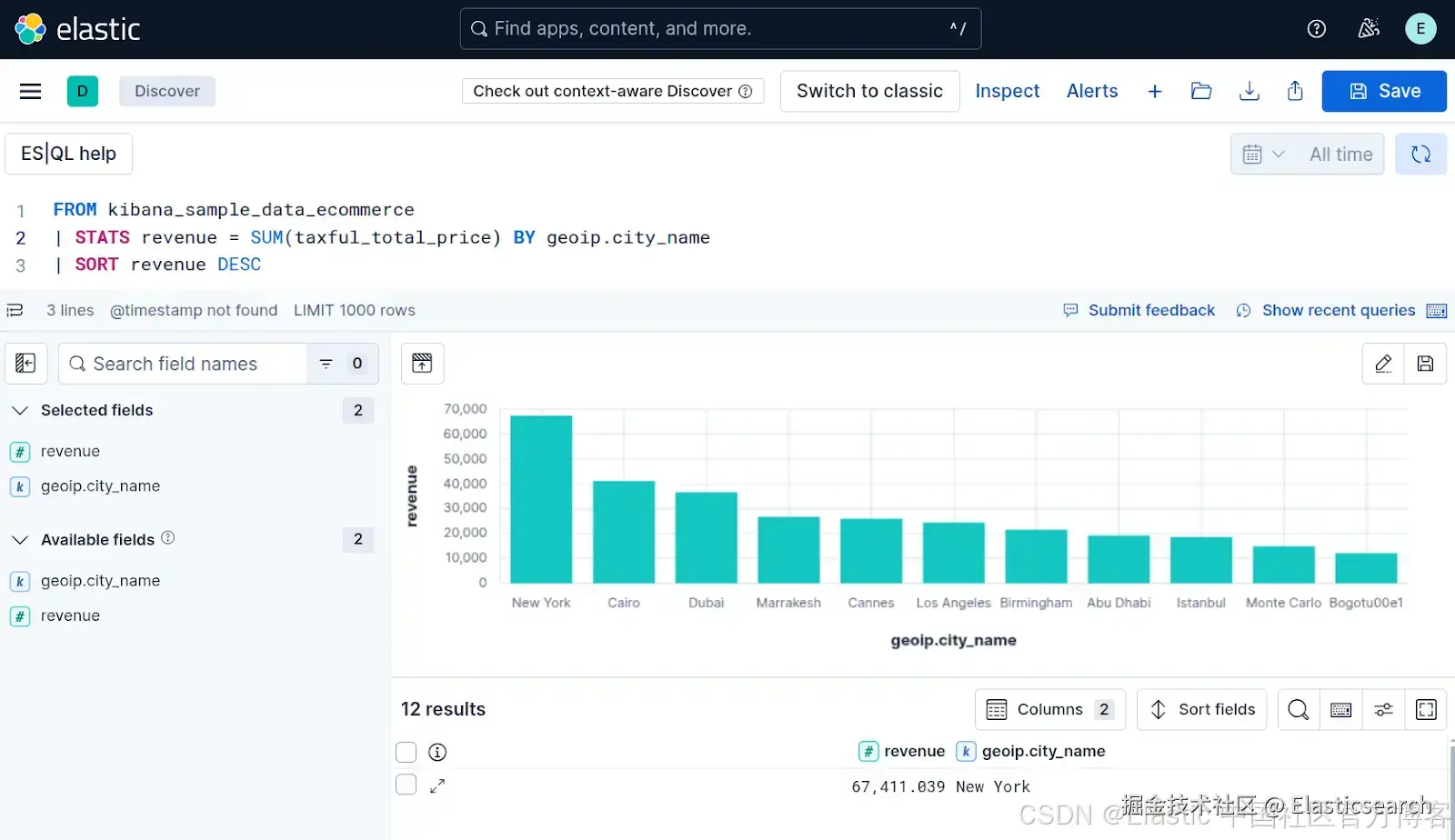 Figure 1: ES|QL console in Kibana
Figure 1: ES|QL console in Kibana
我们可以使用 Microsoft Agent Framework 将这些查询集成到不同的函数工具中。
代理架构
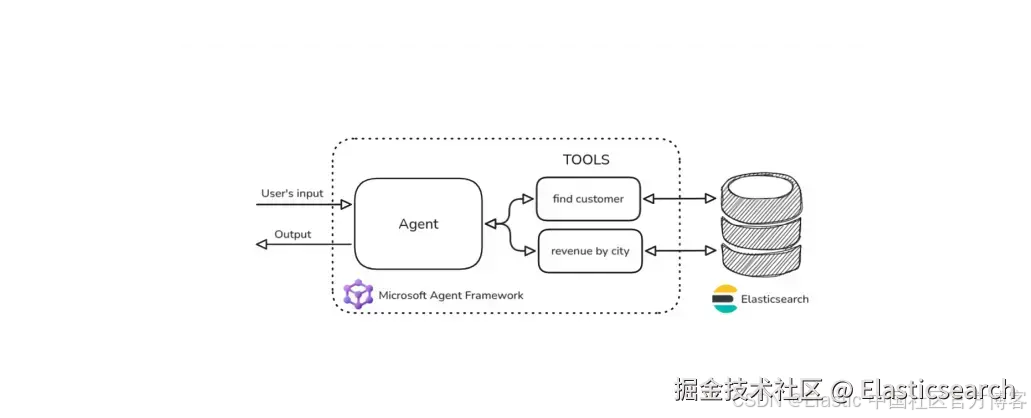
我们将构建一个简单的代理应用,包含几个函数工具,用于从 Elasticsearch 中的 kibana_sample_data_ecommerce 索引检索信息(图 2)。
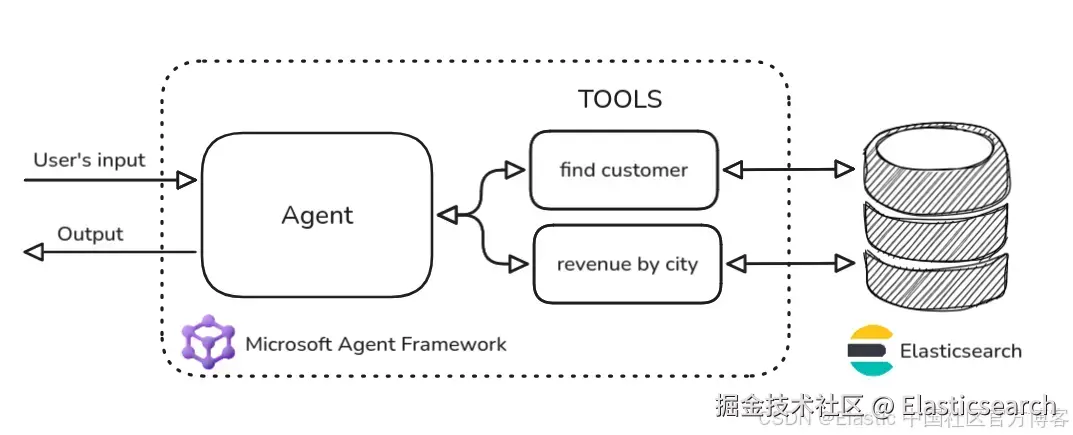 Figure 2: Diagram architecture of the Agentic application with Elasticsearch
Figure 2: Diagram architecture of the Agentic application with Elasticsearch
在构建智能代理 AI 应用时,非常重要的一点是描述 LLM 应调用的工具和参数。
在我们的示例中,我们将定义以下工具:
-
查找客户,通过姓名。此函数的描述可以是 "获取指定姓名的客户信息"。
-
获取订单收入,按城市分组。此函数的描述可以是 "按城市获取总收入"。
这些描述是 LLM 用于识别函数调用的关键信息。
函数调用(也称工具调用)是 LLM 的一种涌现特性,也是开发智能代理 AI 应用的核心理念。关于函数调用的更多信息,我们建议阅读 Ashish Tiwari 的《OpenAI function calling with Elasticsearch》文章。
我们还需要提供与函数调用相关的参数描述。
对于第一个工具,我们需要指定客户姓名,以及一个用于限制搜索结果的参数。这个参数用于避免执行可能返回成千上万条 Elasticsearch 文档的高成本查询。
第二个工具不需要任何参数,因为我们希望对完整数据集进行分组。按城市聚合查询的限制可以固定(例如 100)。
Python 示例
我们使用 ElasticsearchTools 类中创建的两个工具构建了代理,如下:
python
`
1. class ElasticsearchTools:
2. # ...
3. def find_customer(
4. self,
5. name: Annotated[str, Field(description="The name of the customer to find.")],
6. limit: Annotated[int, Field(description="The maximum number of results to return.", default=10)]
7. ) -> str:
8. """Get the customer information for a given name."""
9. query = f"
10. FROM kibana_sample_data_ecommerce
11. | WHERE MATCH(customer_full_name,"{name}", {{"operator": "AND"}})
12. | LIMIT {limit}"
13. response = self.client.esql.query(query=query)
14. print(f"-- DEBUG - Tool: find_customer, ES|QL query: ",query)
15. if response['documents_found'] == 0:
16. return "No customer found."
17. return f"Found {response['documents_found']} customer(s) with name {name}:\n {response['values']}"
19. def revenue_by_cities(self) -> str:
20. """Get the total revenue grouped by city."""
21. query = f"
22. FROM kibana_sample_data_ecommerce
23. | STATS revenue = SUM(taxful_total_price) BY geoip.city_name
24. | SORT revenue DESC
25. | LIMIT 1000"
26. response = self.client.esql.query(query=query)
27. print(f"-- DEBUG - Tool: revenue_by_cities, ES|QL query: ", query)
29. if response['documents_found'] == 0:
30. return "No revenue found grouped by city."
31. return f"Total revenue grouped by cities:\n {response['values']}"
`AI写代码如你在函数工具中所见,我们使用了 Elasticsearch Python 客户端来执行 ES|QL 查询。在 find_customer() 函数中,我们在查询中使用了两个命名参数:{name} 和 {limit}。
这些参数与函数描述一起,由 LLM 管理,LLM 需要理解:
-
如果用户的输入需要执行 find_customer(),使用函数本身的描述。
-
如何根据参数描述提取 {name} 和 {limit} 参数以调用 find_customer() 函数。
我们还在代码中添加了一些调试打印,以确认 LLM 识别了执行工具的需求。
使用 ElasticsearchTools 类,我们在 simple_agent_tools.py 脚本中构建了一个简单的代理。代码的相关部分在 main() 函数中:
python
`
1. async def main() -> None:
2. tools = ElasticsearchTools()
3. agent = AzureOpenAIResponsesClient(credential=AzureCliCredential()).create_agent(
4. instructions="You are a helpful assistant for an ecommerce backend application.",
5. tools=[tools.find_customer, tools.revenue_by_cities],
6. )
8. # Example 1: Simple query to find a customer
9. query = "Is Eddie Underwood our customer? If so, what is his email?"
10. print(f"User: {query}")
11. result = await agent.run(query)
12. print(f"Result: {result}\n")
14. # Example 2: More complex query with limit
15. query = "List all customers with the last name 'Smith'. Limit to 5 results."
16. print(f"User: {query}")
17. result = await agent.run(query)
18. print(f"Result: {result}\n")
20. # Example 3: What are the first three city with more revenue?
21. query = "What are the first three cities with more revenue?"
22. print(f"User: {query}")
23. result = await agent.run(query)
24. print(f"Result: {result}\n")
`AI写代码在这里,我们为代理指定了指令 "You are a helpful assistant for an ecommerce backend application",并将两个工具 find_customer 和 revenue_by_cities 附加到代理上。
如果我们执行 main() 函数,对于问题 "Is Eddie Underwood our customer? If so, what is his email?",将得到如下输出:
sql
`
1. User: Is Eddie Underwood our customer? If so, what is his email?
2. -- DEBUG - Tool: find_customer, ES|QL query:
3. FROM kibana_sample_data_ecommerce
4. | WHERE MATCH(customer_full_name,"Eddie Underwood", {"operator": "AND"})
5. | LIMIT 1
7. Result: Yes, Eddie Underwood is one of our customers. His email address is eddie@underwood-family.zzz.
`AI写代码有趣的是,LLM 从问题中识别出了 limit 参数的值为 1,因为我们指定了完整姓名进行查找。
这是第二个问题的输出:List all customers with the last name 'Smith'. Limit to 5 results. - 列出所有姓 "Smith" 的客户,限制为 5 条结果。
markdown
`
1. User: List all customers with the last name 'Smith'. Limit to 5 results.
2. -- DEBUG - Tool: find_customer, ES|QL query:
3. FROM kibana_sample_data_ecommerce
4. | WHERE MATCH(customer_full_name,"Smith", {"operator": "AND"})
5. | LIMIT 5
7. Result: Here are 5 customers with the last name "Smith":
9. 1. **Jackson Smith**
10. - Email: jackson@smith-family.zzz
11. - Location: Los Angeles, California, USA
13. 2. **Abigail Smith**
14. - Email: abigail@smith-family.zzz
15. - Location: Birmingham, UK
17. 3. **Abd Smith**
18. - Email: abd@smith-family.zzz
19. - Location: Cairo, Egypt
21. 4. **Oliver Smith**
22. - Email: oliver@smith-family.zzz
23. - Location: Europe (Exact location unknown), UK
25. 5. **Tariq Smith**
26. - Email: tariq@smith-family.zzz
27. - Location: Istanbul, Turkey
`AI写代码在这个示例中,limit 参数在用户查询中是隐含的,因为我们指定了 "Limit to 5 results"。无论如何,很有趣的是 LLM 可以从 ES|QL 结果中提取并总结前 5 个客户的上下文,也就是在 find_customer() 函数中 response['values'] 返回的表格结构。
最后,这是第三个问题的输出:
sql
`
1. User: What are the first three cities with more revenue?
2. -- DEBUG - Tool: revenue_by_cities, ES|QL query:
3. FROM kibana_sample_data_ecommerce
4. | STATS revenue = SUM(taxful_total_price) BY geoip.city_name
5. | SORT revenue DESC
6. | LIMIT 1000
8. Result: The top three cities generating the highest revenue are:
10. 1. **New York** with $67,411.04
11. 2. **Cairo** with $41,095.38
12. 3. **Dubai** with $36,586.71
`AI写代码在这里,LLM 不需要构建参数,因为 revenue_by_cities() 函数不需要任何参数。不过,也值得一提的是,LLM 可以对从 ES|QL 查询返回的原始表格执行复杂的知识提取和处理。
.NET 示例
.NET 示例展示了一个稍微高级一些的案例。我们创建了一个 "main" 代理,该代理被指示用德语回答所有问题,并将专门的 "e-commerce" 代理注册为函数工具。完整示例可在此处查看。
第一步,我们实现 ECommerceQuery 类,为 "e-commerce" 代理提供函数工具。这些方法的功能与 Python 示例中的相应函数相同。
请注意,我们返回原始 JsonElement 对象以保持示例简单。在大多数情况下,用户会希望为检索到的数据创建一个专门的模型。Agent Framework 会在将信息传递给 LLM 之前自动处理数据类型的序列化。
csharp
`
1. internal sealed class ECommerceQuery
2. {
3. private readonly ElasticsearchClient _client;
5. public ECommerceQuery(IElasticsearchClientSettings settings)
6. {
7. ArgumentNullException.ThrowIfNull(settings);
9. this._client = new ElasticsearchClient(settings);
10. }
12. [Description("Get the customer information for a given name.")]
13. public async Task<IEnumerable<JsonElement>> QueryCustomersAsync(
14. [Description("The name of the customer to find.")]
15. string name,
16. [Description("The maximum number of results to return.")]
17. int limit = 10)
18. {
19. IEnumerable<JsonElement> response = await this._client.Esql
20. .QueryAsObjectsAsync<JsonElement>(x => x
21. .Params(
22. name,
23. limit
24. )
25. .Query("""
26. FROM kibana_sample_data_ecommerce
27. | WHERE MATCH(customer_full_name, ?1, {"operator": "AND"})
28. | LIMIT ?2
29. """
30. )
31. )
32. .ConfigureAwait(false);
34. Console.WriteLine($"-- DEBUG - Tool: QueryCustomersAsync, ES|QL query parameters: name = {name}, limit = {limit}");
36. return response;
37. }
39. [Description("Get the total revenue grouped by city.")]
40. public async Task<IEnumerable<JsonElement>> QueryRevenueAsync()
41. {
42. IEnumerable<JsonElement> response = await this._client.Esql
43. .QueryAsObjectsAsync<JsonElement>(x => x
44. .Query("""
45. FROM kibana_sample_data_ecommerce
46. | STATS revenue = SUM(taxful_total_price) BY geoip.city_name
47. | SORT revenue DESC
48. | LIMIT 1000
49. """)
50. )
51. .ConfigureAwait(false);
53. Console.WriteLine("-- DEBUG - Tool: QueryRevenueAsync");
55. return response;
56. }
57. }
`AI写代码收起代码块在我们的主程序中,我们实例化了 ECommerceQuery 并创建了 "ecommerce" 代理:
less
`
1. var eCommercePlugin =
2. new ECommerceQuery(
3. new ElasticsearchClientSettings(new SingleNodePool(new Uri(esEndpoint)))
4. .Authentication(new ApiKey(esKey))
5. .EnableDebugMode()
6. );
8. // Create the ecommerce agent and register the Elasticsearch tools.
9. var ecommerceAgent = new AzureOpenAIClient(
10. new Uri(oaiEndpoint),
11. new ApiKeyCredential(oaiKey))
12. .GetChatClient(oaiDeploymentName)
13. .CreateAIAgent(
14. instructions: "You are a helpful assistant for an ecommerce backend application.",
15. name: "ECommerceAgent",
16. description: "An agent that answers questions about orders in an ecommerce system.",
17. tools:
18. [
19. AIFunctionFactory.Create(eCommercePlugin.QueryCustomersAsync),
20. AIFunctionFactory.Create(eCommercePlugin.QueryRevenueAsync)
21. ]
22. );
`AI写代码在第二步中,我们创建了 "main" 代理,并将 "ecommerce" 代理注册为函数工具:
less
`
1. var agent = new AzureOpenAIClient(
2. new Uri(oaiEndpoint),
3. new ApiKeyCredential(oaiKey))
4. .GetChatClient(oaiDeploymentName)
5. .CreateAIAgent("You are a helpful assistant who responds in German.", tools: [ecommerceAgent.AsAIFunction()]);
`AI写代码最后,我们提出了与 Python 示例中相同的问题:
arduino
`
1. Console.WriteLine(await agent.RunAsync("Is Eddie Underwood our customer? If so, what is his email?"));
2. Console.WriteLine(await agent.RunAsync("List all customers with the last name 'Smith'. Limit to 5 results."));
3. Console.WriteLine(await agent.RunAsync("What are the first three cities with the highest revenue?"));
`AI写代码我们可以看到几乎相同的答案,但用德语表示。这表明 "main" 代理正确地将 "ecommerce" 代理作为函数工具调用。
结论
在本文中,我们演示了如何使用 Microsoft 的 Agent Framework 和 Elasticsearch 构建一个简单的智能代理应用。通过创建自定义工具,可以实现从 Elasticsearch 检索知识的特定逻辑。我们使用 ES|QL 语言构建带参数的查询,这些参数可以由 LLM 管理。这种方法允许我们将执行限制在某些类型的查询上。通过对工具及其参数的详细描述,我们可以引导 LLM 正确解释查询并提取适当的上下文。
Microsoft 的 Agent Framework 帮助开发者构建高效的智能代理应用,而 Elasticsearch 作为战略合作伙伴,提供了多种上下文提取方法。我们相信 Elasticsearch 可以成为新兴的上下文工程方法的关键组成部分,这种方法补充了应用开发的智能代理范式。
你可以在 GitHub 上找到本文示例的完整代码,仓库地址如下:
github.com/elastic/age...