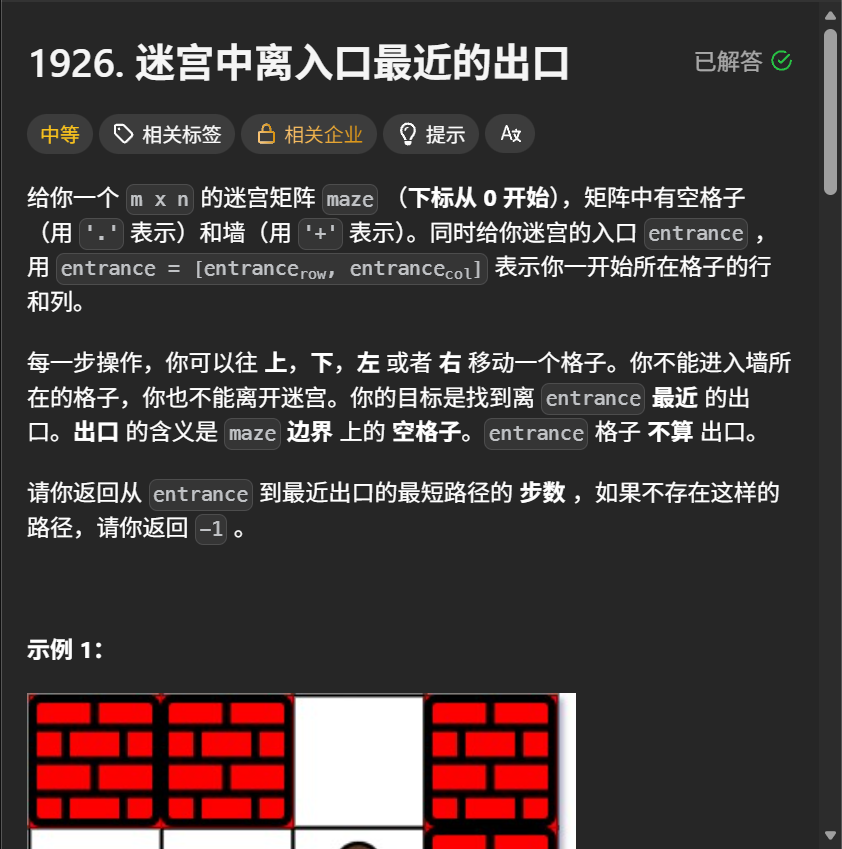
单源bfs,从一个固定的点开始向外遍历找到一个离自己最近的点,而当他向外遍历时,第一次碰到了满足要求的点,那么这时这一条路就是最近的,对应到这道题就是从entrance遍历到边界的最近的出口,而为什么第一次bfs到他就是最近的?
可以这样理解,每一次bfs就相当于从这个点开始向外的每个点都走了一步,这样就走出了不同的路径,让后当有个点路径第一次走到了出口,那么他就时最近的,因为每一条路径的权值都是相同的
bfs的实现
将固定源储存在一个队列中,以这个点为原点开始向四周遍历,记为第一层,四周遍历的点又储存在队列中,记为第二层的节点,当吧第一层的所有节点出完,点第二层的节点也遍历完了,这时队列中的全是第二层的节点了,这就完成了一层的bfs,重复这个过程,直到队列为空,那么就完成了层序遍历
java
int[] dx = {0, 0, -1, 1};
int[] dy = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
public int nearestExit(char[][] maze, int[] entrance) {
int m = maze.length;
int n = maze[0].length;
boolean[][] check = new boolean[m][n];
List<int[]> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add(new int[]{entrance[0], entrance[1]});
check[entrance[0]][entrance[1]] = true;
int times = 0;
while (!list.isEmpty()) {
times++;
int size = list.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
int[] arr = list.remove(0);
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
int yy = arr[0] + dy[j];
int xx = arr[1] + dx[j];
if (yy < 0 || yy == m || xx < 0 || xx == n || check[yy][xx] || maze[yy][xx] == '+') continue;
if (yy == 0 || yy == m - 1 || xx == 0 || xx == n - 1) {
return times;
}
check[yy][xx] = true;
list.add(new int[]{yy, xx});
}
}
}
return -1;
}类似的题还有
最小基因变化 单词接龙 diff 为高尔夫砍树