1. 多态的基本概念
多态(Polymorphism) = "多种形态",指同一个接口在不同情况下表现出不同的行为。
两种多态类型:
-
编译时多态(静态多态):在编译期间确定具体调用哪个函数
-
运行时多态(动态多态):在运行期间确定具体调用哪个函数
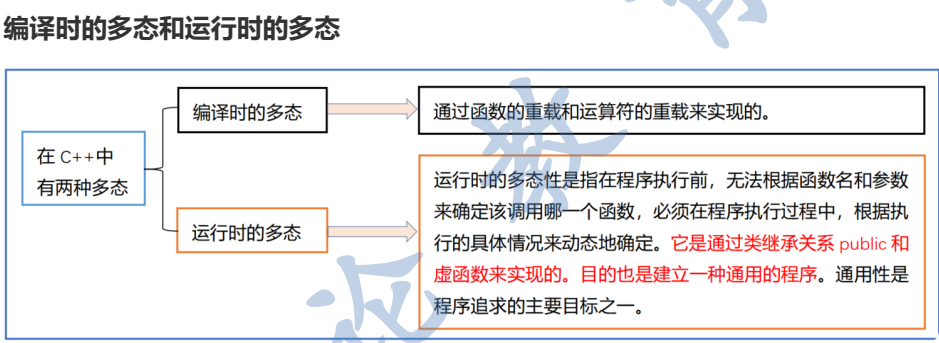
2. 编译时多态(Static Polymorphism)
编译时多态在编译阶段就确定了具体调用的函数,主要通过以下机制实现:
2.1 函数重载(Function Overloading)
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Calculator {
public:
// 函数重载:同名函数,参数列表不同
int add(int a, int b) {
cout << "调用 add(int, int)" << endl;
return a + b;
}
double add(double a, double b) {
cout << "调用 add(double, double)" << endl;
return a + b;
}
int add(int a, int b, int c) {
cout << "调用 add(int, int, int)" << endl;
return a + b + c;
}
string add(const string& a, const string& b) {
cout << "调用 add(string, string)" << endl;
return a + b;
}
};
int main() {
Calculator calc;
cout << calc.add(1, 2) << endl; // 调用 add(int, int)
cout << calc.add(1.5, 2.5) << endl; // 调用 add(double, double)
cout << calc.add(1, 2, 3) << endl; // 调用 add(int, int, int)
cout << calc.add("Hello", "World") << endl; // 调用 add(string, string)
return 0;
}输出:
text
调用 add(int, int)
3
调用 add(double, double)
4
调用 add(int, int, int)
6
调用 add(string, string)
HelloWorld特点:
-
编译时根据参数类型和数量决定调用哪个函数
-
函数名相同,参数列表必须不同
-
返回类型不同不足以构成重载
2.2 运算符重载(Operator Overloading)
cpp
class Complex {
private:
double real, imag;
public:
Complex(double r = 0, double i = 0) : real(r), imag(i) {}
// 运算符重载:编译时确定
Complex operator+(const Complex& other) const {
return Complex(real + other.real, imag + other.imag);
}
Complex operator-(const Complex& other) const {
return Complex(real - other.real, imag - other.imag);
}
void display() const {
cout << real << " + " << imag << "i" << endl;
}
};
int main() {
Complex c1(3.0, 4.0), c2(1.0, 2.0);
Complex c3 = c1 + c2; // 编译时确定调用 operator+
Complex c4 = c1 - c2; // 编译时确定调用 operator-
c3.display(); // 4 + 6i
c4.display(); // 2 + 2i
return 0;
}2.3 模板(Templates)
cpp
// 函数模板 - 编译时实例化
template<typename T>
T max(T a, T b) {
return (a > b) ? a : b;
}
// 类模板 - 编译时实例化
template<typename T>
class Container {
private:
T value;
public:
Container(T v) : value(v) {}
T getValue() const { return value; }
};
int main() {
// 编译时生成具体函数
cout << max(10, 20) << endl; // 生成 max<int>
cout << max(3.14, 2.71) << endl; // 生成 max<double>
cout << max('a', 'z') << endl; // 生成 max<char>
// 编译时生成具体类
Container<int> intContainer(100); // 生成 Container<int>
Container<string> strContainer("Hello"); // 生成 Container<string>
return 0;
}3. 运行时多态(Dynamic Polymorphism)
运行时多态在程序运行期间确定具体调用的函数,主要通过虚函数实现:
3.1 虚函数机制
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
class Animal {
public:
// 虚函数 - 实现运行时多态
virtual void speak() const {
cout << "Animal speaks" << endl;
}
virtual void eat() const {
cout << "Animal eats" << endl;
}
// 虚析构函数 - 重要!
virtual ~Animal() {
cout << "Animal destructor" << endl;
}
};
class Dog : public Animal {
public:
void speak() const override {
cout << "Woof! Woof!" << endl;
}
void eat() const override {
cout << "Dog eats bone" << endl;
}
~Dog() override {
cout << "Dog destructor" << endl;
}
};
class Cat : public Animal {
public:
void speak() const override {
cout << "Meow! Meow!" << endl;
}
void eat() const override {
cout << "Cat eats fish" << endl;
}
~Cat() override {
cout << "Cat destructor" << endl;
}
};
class Bird : public Animal {
public:
void speak() const override {
cout << "Chirp! Chirp!" << endl;
}
void eat() const override {
cout << "Bird eats seeds" << endl;
}
~Bird() override {
cout << "Bird destructor" << endl;
}
};
// 多态函数:接受基类引用,实际调用派生类函数
void animalConcert(const Animal& animal) {
animal.speak(); // 运行时确定调用哪个speak
}
int main() {
vector<unique_ptr<Animal>> animals;
animals.push_back(make_unique<Dog>());
animals.push_back(make_unique<Cat>());
animals.push_back(make_unique<Bird>());
cout << "=== 多态演示 ===" << endl;
for (const auto& animal : animals) {
animal->speak(); // 运行时多态
animal->eat(); // 运行时多态
cout << "---" << endl;
}
cout << "=== 通过基类引用 ===" << endl;
Dog dog;
Cat cat;
Bird bird;
animalConcert(dog); // 输出: Woof! Woof!
animalConcert(cat); // 输出: Meow! Meow!
animalConcert(bird); // 输出: Chirp! Chirp!
return 0;
}输出:
text
=== 多态演示 ===
Woof! Woof!
Dog eats bone
---
Meow! Meow!
Cat eats fish
---
Chirp! Chirp!
Bird eats seeds
---
=== 通过基类引用 ===
Woof! Woof!
Meow! Meow!
Chirp! Chirp!
Dog destructor
Animal destructor
Cat destructor
Animal destructor
Bird destructor
Animal destructor3.2 纯虚函数与抽象类
cpp
// 抽象类 - 包含纯虚函数
class Shape {
public:
// 纯虚函数 - 接口定义
virtual double area() const = 0;
virtual double perimeter() const = 0;
virtual void draw() const = 0;
// 虚析构函数
virtual ~Shape() = default;
};
class Circle : public Shape {
private:
double radius;
public:
Circle(double r) : radius(r) {}
double area() const override {
return 3.14159 * radius * radius;
}
double perimeter() const override {
return 2 * 3.14159 * radius;
}
void draw() const override {
cout << "Drawing Circle with radius " << radius << endl;
}
};
class Rectangle : public Shape {
private:
double width, height;
public:
Rectangle(double w, double h) : width(w), height(h) {}
double area() const override {
return width * height;
}
double perimeter() const override {
return 2 * (width + height);
}
void draw() const override {
cout << "Drawing Rectangle " << width << "x" << height << endl;
}
};
void printShapeInfo(const Shape& shape) {
shape.draw();
cout << "Area: " << shape.area() << ", Perimeter: " << shape.perimeter() << endl;
}
int main() {
Circle circle(5.0);
Rectangle rectangle(4.0, 6.0);
printShapeInfo(circle); // 运行时多态
printShapeInfo(rectangle); // 运行时多态
return 0;
}总结:运行时的多态性: 公有继承 + 虚函数 + (指针或引用调用虚函数)。
4. 两种多态的对比
对比表格:
| 特性 | 编译时多态 | 运行时多态 |
|---|---|---|
| 确定时间 | 编译期间 | 运行期间 |
| 实现机制 | 函数重载、运算符重载、模板 | 虚函数、继承 |
| 性能 | 高效,无运行时开销 | 有轻微性能开销(vtable查找) |
| 灵活性 | 相对较低 | 很高,支持动态绑定 |
| 代码体积 | 可能较大(模板实例化) | 相对较小 |
| 典型应用 | 通用算法、数学运算 | 框架设计、插件系统 |
5.总结
编译时多态:
-
✅ 高性能,无运行时开销
-
✅ 类型安全,编译期检查
-
❌ 灵活性较低
-
❌ 代码可能膨胀(模板)
运行时多态:
-
✅ 高灵活性,支持动态绑定
-
✅ 接口统一,易于扩展
-
❌ 有性能开销(vtable查找)
-
❌ 需要虚析构函数确保安全
选择准则:
-
需要高性能 和类型安全 → 编译时多态
-
需要灵活扩展 和动态行为 → 运行时多态
-
大型框架和系统 → 结合使用两种多态