首先,本次项目采用typescript+ai-sdk+nestjs框架搭建,我们给出项目的总体结构,大致如下图所示:
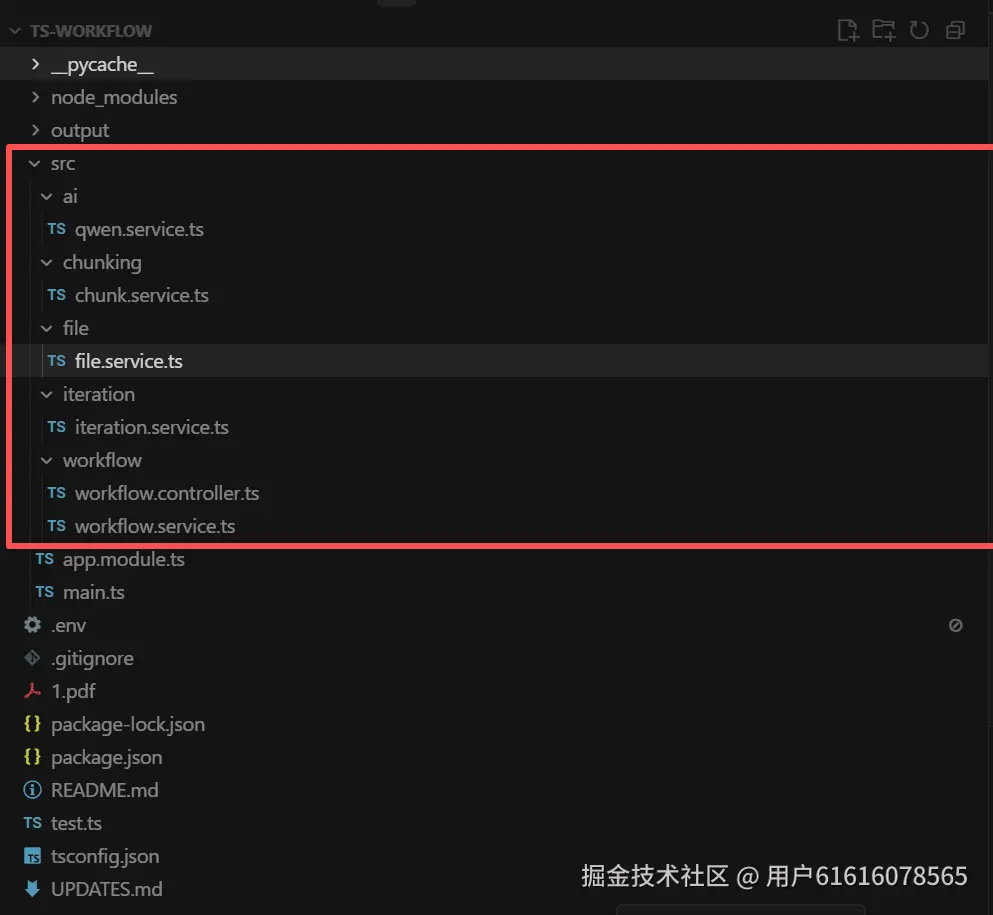
其中,首先创建package.json文件,文件内容为:
{
"name": "workflow-chunking",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "Document chunking and processing workflow based on Dify iteration mechanism",
"scripts": {
"start": "ts-node src/main.ts",
"build": "tsc",
"test": "ts-node test.ts"
},
"dependencies": {
"@nestjs/common": "^10.3.0",
"@nestjs/core": "^10.3.0",
"@nestjs/platform-express": "^10.3.0",
"@nestjs/config": "^3.1.1",
"reflect-metadata": "^0.2.1",
"rxjs": "^7.8.1",
"ai": "^3.0.0",
"@ai-sdk/openai": "^0.0.66",
"pdf-parse": "^1.1.1",
"p-limit": "^5.0.0",
"axios": "^1.6.0"
},
"devDependencies": {
"@types/node": "^20.11.0",
"typescript": "^5.3.3",
"ts-node": "^10.9.2"
}
}对应的tsconfig.json文件如下所示:
{
"compilerOptions": {
"module": "commonjs",
"target": "ES2021",
"lib": ["ES2021"],
"declaration": true,
"outDir": "./dist",
"rootDir": "./src",
"strict": true,
"esModuleInterop": true,
"skipLibCheck": true,
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true,
"experimentalDecorators": true,
"emitDecoratorMetadata": true,
"resolveJsonModule": true
},
"include": ["src/**/*"],
"exclude": ["node_modules", "dist"]
}之后我们创建一个.env文件,存放大模型的api-key,本次数据清洗使用的大模型是qwen-max,因此设置对应的api,如下图所示:
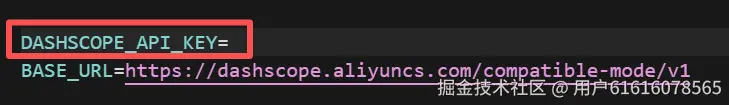 之后我们输入:
之后我们输入:
pnpm install下载json文件中所对应的包,之后构造我们的项目主要文件,首先是大模型服务qwen.service.ts文件,主要内容为给大模型的提示词以及模型相关配置,代码如下:
import
import { generateText } from 'ai';
import { createOpenAI } from '@ai-sdk/openai';
/**
* 千问大模型服务 - 使用ai-sdk调用千问API
*/
@Injectable()
export class QwenService {
private readonly qwen;
private readonly prompt: string;
constructor() {
// 配置千问大模型
this.qwen = createOpenAI({
apiKey: process.env.DASHSCOPE_API_KEY || '',
baseURL: 'https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1',
});
// 从prompt.md加载的提示词
this.prompt = `你是一位专业的数据清洗与段落拆分工程师。
任务:处理单条文本内容并生成JSON格式输出(只包含一个segment_01),将文本按"句子/子句"进行子段拆分,粒度适中(避免拆到词语级)。仅输出 text 与 tags,tags 内放子段字符串;若同时存在"章标题"和"条标题",须将二者合并为一个首个子段(如"第二章保险合同 第十条")。
<文本内容>:
{{context}}
处理规则:
一、数据清洗(重要)
1. 过滤噪声内容:
- 页码标记:如"---1---"、"---2---"、"第1页"等
- 页眉页脚:重复出现的文档标题、作者信息等
- 空白行和无效数据
- 乱码字符
- 版权声明、广告信息
2. 提取纯净的正文内容
3. 保持有效文本的原文不变(不改写、不增删)
二、子段拆分(替代关键词提取)
1. 拆分单位:句子/子句级,不要细到词语
2. 拆分依据:中文标点(。!?;:、)、换行和明显的语义停顿
3. 粒度控制:单个子段建议约20--80个汉字;过短子段应与相邻合并;过长子段可在自然停顿处分割
4. 保序:子段顺序必须与原文一致,覆盖全部正文且不重叠、不遗漏
5. 不得改写文本;子段必须是原文的连续片段
6. 若清洗后的正文整体较短(如不足20个汉字),则 tags 仅包含一个元素,等于 text 本身
7. 标题合并:若检测到"章标题"(如"第二章保险合同")与"条标题"(如"第十条")均存在,则在 tags 中放置一个合并后的首个子段,格式为"{章标题} {条标题}";正文内容另行拆分为后续子段,不重复包含标题文本。若仅存在其中之一,则该标题作为一个独立子段置于首位。
三、输出字段
1. segment_01.text:清洗后的完整正文(不改写)
2. segment_01.tags:子段数组(按顺序,字符串数组),每个元素是一个子段原文
输出格式(单条内容):
示例:
{
"segment_01": {
"text": "第二章保险合同\n第十条 保险合同是投保人与保险人约定保险权利义务关系的协议。",
"tags": [
"第二章保险合同 第十条",
"保险合同是投保人与保险人约定保险权利义务关系的协议。"
]
}
}
【关键要求 - 必须遵守】
1. 输入是单条内容,输出也必须是单条(只有segment_01)
2. text字段:必须过滤掉页码、页眉页脚、乱码、空白行等噪声;只保留纯净正文;不要改写正文内容
3. tags:覆盖正文全部内容;顺序一致;不重叠;每个子段是原文连续片段;若正文整体较短可仅包含一个等于 text 的元素;若存在"章+条",首个子段必须为"{章标题} {条标题}",正文另行拆分
4. 只输出规定字段(text, tags),不要添加其它键
5. 只输出纯JSON对象,不要任何额外说明文字
6. 不要使用markdown代码块标记(如\`\`\`json)
7. 不要输出"好的"、"以下是"、"根据要求"等话语
8. 输出必须能被JSON.parse()直接解析
现在开始处理,只输出JSON:`;
}
/**
* 从文本中提取JSON对象
*/
private extractJSON(text: string): string {
// 移除可能的markdown代码块标记
text = text.replace(/```json\s*/g, '').replace(/```\s*/g, '');
// 尝试找到第一个{和最后一个}
const firstBrace = text.indexOf('{');
const lastBrace = text.lastIndexOf('}');
if (firstBrace === -1 || lastBrace === -1 || firstBrace >= lastBrace) {
throw new Error('无法在响应中找到有效的JSON对象');
}
// 提取JSON部分
const jsonStr = text.substring(firstBrace, lastBrace + 1);
// 验证是否为有效JSON
try {
JSON.parse(jsonStr);
return jsonStr;
} catch (error) {
console.error('提取的JSON无效:', jsonStr.substring(0, 200));
throw new Error('提取的JSON格式无效');
}
}
/**
* 调用千问大模型处理文本段落
*/
async processSegment(context: string): Promise<string> {
try {
const { text } = await generateText({
model: this.qwen('qwen-max-latest'),
prompt: this.prompt.replace('{{context}}', context),
temperature: 0.7,
maxTokens: 4000,
});
// 提取并验证JSON
const cleanJSON = this.extractJSON(text);
return cleanJSON;
} catch (error) {
console.error('千问API调用失败:', error);
throw error;
}
}
}设置完提示词之后进入我们的主要分块代码chunk.service.ts文件,该代码文件主要进行条例类文档的分块,输入一个条例类pdf文件,例如法律法规,学生守则等,pdf中有着明确的第几章第几条的规范,该代码会将该pdf按照每一条进行切分,并在每一条的前面加入章节与条例信息,代码如下所示:
import
import * as fs from 'fs/promises';
import pdfParse from 'pdf-parse';
@Injectable()
export class ChunkService {
// 文档的层次化模式匹配
private readonly BULLET_PATTERN = [
[
/^第[零一二三四五六七八九十百0-9]+(分?编|部分)/,
/^第[零一二三四五六七八九十百0-9]+章/,
/^第[零一二三四五六七八九十百0-9]+节/,
/^第[零一二三四五六七八九十百0-9]+条/,
/^[\((][零一二三四五六七八九十百]+[\))]/,
],
[
/^第[0-9]+章/,
/^第[0-9]+节/,
/^[0-9]{1,2}[\. 、]/,
/^[0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9]{1,2}[^a-zA-Z/%~-]/,
/^[0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9]{1,2}/,
/^[0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9]{1,2}\.[0-9]{1,2}/,
],
[
/^第[零一二三四五六七八九十百0-9]+章/,
/^第[零一二三四五六七八九十百0-9]+节/,
/^[零一二三四五六七八九十百]+[ 、]/,
/^[\((][零一二三四五六七八九十百]+[\))]/,
/^[\((][0-9]{1,2}[\))]/,
],
[
/^PART (ONE|TWO|THREE|FOUR|FIVE|SIX|SEVEN|EIGHT|NINE|TEN)/,
/^Chapter (I+V?|VI*|XI|IX|X)/,
/^Section [0-9]+/,
/^Article [0-9]+/,
],
];
/**
* 判断是否不是有效的项目符号
*/
private notBullet(line: string): boolean {
const patterns = [/^0$/, /^[0-9]+ +[0-9~个只-]/, /^[0-9]+\.{2,}/];
return patterns.some((p) => p.test(line));
}
/**
* 识别文档使用的项目符号类别
*/
private bulletsCategory(sections: string[]): number {
const hits = new Array(this.BULLET_PATTERN.length).fill(0);
for (let i = 0; i < this.BULLET_PATTERN.length; i++) {
const patternGroup = this.BULLET_PATTERN[i];
for (const section of sections) {
for (const pattern of patternGroup) {
if (pattern.test(section) && !this.notBullet(section)) {
hits[i]++;
break;
}
}
}
}
let maxHits = 0;
let result = -1;
for (let i = 0; i < hits.length; i++) {
if (hits[i] > maxHits) {
result = i;
maxHits = hits[i];
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* 判断文本是否包含中文
*/
private isChinese(text: string): boolean {
if (!text) return false;
const chineseCount = (text.match(/[\u4e00-\u9fff]/g) || []).length;
return chineseCount / text.length > 0.2;
}
/**
* 计算token数量
*/
private numTokensFromString(text: string): number {
if (this.isChinese(text)) {
const chineseChars = (text.match(/[\u4e00-\u9fff]/g) || []).length;
const englishWords = (text.match(/[a-zA-Z]+/g) || []).length;
return chineseChars + englishWords;
} else {
return text.split(/\s+/).length;
}
}
/**
* 细粒度分块算法 - 每条法律条文单独成块,并携带章节信息
*/
private hierarchicalMerge(
bulletType: number,
sections: string[],
depth: number = 5,
): string[][] {
if (!sections.length || bulletType < 0) {
return this.simpleChunk(sections);
}
// 过滤空白和无效内容
const filteredSections = sections.filter(
(text) => text && text.split('@')[0].trim().length > 1 && !/^[0-9]+$/.test(text.split('@')[0].trim()),
);
// 为每个段落分配层级
const sectionLevels: number[] = new Array(filteredSections.length).fill(-1);
for (let i = 0; i < filteredSections.length; i++) {
const text = filteredSections[i];
for (let level = 0; level < this.BULLET_PATTERN[bulletType].length; level++) {
if (this.BULLET_PATTERN[bulletType][level].test(text.trim())) {
sectionLevels[i] = level;
break;
}
}
}
// 细粒度分块:每个"条"级别的内容单独成块,只携带章信息
const chunks: string[][] = [];
let currentChapter = ''; // 当前章标题
let currentArticleChunk: string[] = []; // 当前条的内容
for (let i = 0; i < filteredSections.length; i++) {
const level = sectionLevels[i];
const text = filteredSections[i];
// 判断是否是"章"级别(可能带标题,如"第一章总则")
const chapterMatch = text.trim().match(/^(第[零一二三四五六七八九十百0-9]+(分?编|部分|章)[^\n]*)/);
const isChapter = !!chapterMatch;
// 判断是否是"节"级别(节单独作为一个chunk)
const sectionMatch = text.trim().match(/^(第[零一二三四五六七八九十百0-9]+节[^\n]*)/);
const isSection = !!sectionMatch;
// 判断是否是"条"级别
const isArticleLevel = level === 3 || /^第[零一二三四五六七八九十百0-9]+条/.test(text.trim());
if (isChapter) {
// 遇到新章,保存之前的条
if (currentArticleChunk.length > 0) {
const chunkContent = this.buildChunkWithChapter(currentChapter, currentArticleChunk);
chunks.push(chunkContent);
currentArticleChunk = [];
}
// 更新章标题
currentChapter = chapterMatch![1].trim();
} else if (isSection) {
// 遇到新节,保存之前的条,但不生成节标题的chunk
if (currentArticleChunk.length > 0) {
const chunkContent = this.buildChunkWithChapter(currentChapter, currentArticleChunk);
chunks.push(chunkContent);
currentArticleChunk = [];
}
// 节标题直接跳过,不生成单独的chunk
} else if (isArticleLevel) {
// 遇到新的条,保存之前的条
if (currentArticleChunk.length > 0) {
const chunkContent = this.buildChunkWithChapter(currentChapter, currentArticleChunk);
chunks.push(chunkContent);
}
// 开始新的条
currentArticleChunk = [text];
} else {
// 普通内容
if (currentArticleChunk.length > 0) {
currentArticleChunk.push(text);
}
}
}
// 添加最后一个chunk
if (currentArticleChunk.length > 0) {
const chunkContent = this.buildChunkWithChapter(currentChapter, currentArticleChunk);
chunks.push(chunkContent);
}
return chunks.filter((c) => c.length > 0);
}
/**
* 构建带章信息的chunk(不包含节)
*/
private buildChunkWithChapter(chapter: string, content: string[]): string[] {
if (chapter) {
return [chapter, ...content];
}
return content;
}
/**
* 简单分块策略 - 用于没有明显层级结构的文档
* 按段落数量分块,每3-5个段落一块
*/
private simpleChunk(sections: string[]): string[][] {
const chunks: string[][] = [];
let currentChunk: string[] = [];
const maxParagraphs = 5; // 每个chunk最多5个段落
for (const section of sections) {
currentChunk.push(section);
if (currentChunk.length >= maxParagraphs) {
chunks.push([...currentChunk]);
currentChunk = [];
}
}
if (currentChunk.length > 0) {
chunks.push(currentChunk);
}
return chunks;
}
/**
* 移除目录部分
*/
private removeContentsTable(sections: string[]): void {
let i = 0;
while (i < sections.length) {
const text = sections[i].trim();
if (!/^(contents|目录|目次|table of contents|致谢|acknowledge)$/i.test(text.replace(/[ \u3000]+/g, ''))) {
i++;
continue;
}
sections.splice(i, 1);
if (i >= sections.length) break;
let removedCount = 0;
while (i < sections.length && removedCount < 100) {
const line = sections[i].trim();
// 检测目录条目特征:包含页码、省略号、或特定格式
const isTableOfContentsLine =
line.length < 50 && (
/[\.。]{2,}/.test(line) || // 包含多个点(省略号)
/\d+\s*$/.test(line) || // 以数字结尾(页码)
/第[零一二三四五六七八九十百0-9]+[章节条]/g.test(line) // 章节标题
);
if (isTableOfContentsLine) {
sections.splice(i, 1);
removedCount++;
} else {
// 遇到正文内容,停止删除
break;
}
if (i >= sections.length) break;
}
}
}
/**
* 对纯文本进行法律文档切分
*/
async chunkText(text: string): Promise<{ result: string[] }> {
// 按行分割
let sections = text
.split('\n')
.map((s) => s.trim())
.filter((s) => s);
if (!sections.length) {
return { result: [] };
}
// 移除目录
this.removeContentsTable(sections);
// 识别项目符号类型
const bulletType = this.bulletsCategory(sections);
// 层次化合并
const chunks = this.hierarchicalMerge(bulletType, sections, 5);
if (!chunks.length) {
return { result: [] };
}
// 转换为字符串列表
const resultSegments = chunks.map((chunk) => chunk.join('\n'));
return { result: resultSegments };
}
/**
* 从PDF文件提取文本
*/
async extractTextFromPdf(filePath: string): Promise<string> {
const dataBuffer = await fs.readFile(filePath);
const data = await pdfParse(dataBuffer);
// 清洗PDF文本中的不必要换行
return this.cleanPdfText(data.text);
}
/**
* 清洗PDF文本,合并不必要的换行
*/
private cleanPdfText(text: string): string {
// 将文本按行分割
const lines = text.split('\n');
const cleanedLines: string[] = [];
for (let i = 0; i < lines.length; i++) {
const currentLine = lines[i].trim();
// 跳过空行
if (!currentLine) {
cleanedLines.push('');
continue;
}
// 判断是否是标题行(章节条等)
const isTitleLine = /^(第[零一二三四五六七八九十百0-9]+(分?编|部分|章|节|条)|---\d+---)/.test(currentLine);
// 如果是标题行,单独成行
if (isTitleLine) {
cleanedLines.push(currentLine);
} else {
// 判断当前行是否应该与上一行合并
const lastLine = cleanedLines[cleanedLines.length - 1];
const lastLineIsTitleOrEmpty = !lastLine ||
lastLine.trim() === '' ||
/^(第[零一二三四五六七八九十百0-9]+(分?编|部分|章|节|条)|---\d+---)/.test(lastLine);
if (lastLineIsTitleOrEmpty) {
// 上一行是标题或空行,开始新行
cleanedLines.push(currentLine);
} else {
// 合并到上一行(不管上一行是否以句号结尾)
cleanedLines[cleanedLines.length - 1] = lastLine + currentLine;
}
}
}
return cleanedLines.join('\n');
}
/**
* 对文件进行文档切分
*/
async chunkFile(filePath: string): Promise<{ result: string[] }> {
let text: string;
if (filePath.toLowerCase().endsWith('.pdf')) {
text = await this.extractTextFromPdf(filePath);
} else {
text = await fs.readFile(filePath, 'utf-8');
}
if (!text.trim()) {
return { result: [] };
}
const result = await this.chunkText(text);
console.log(`文档分割完成: 共生成 ${result.result.length} 个段落`);
return result;
}
}之后这些信息会传给大模型进行处理,转为我们需要的格式,将每一条信息的原文作为text,为了防止原文过长,将原文分为子段tag,tag的内容便是将原段落拆解后的内容,每个tag中都包含第几章第几条的信息。
之后创建文件生成与合并文件file.service.ts,该文件主要负责将大模型处理后的json格式文件写为md文件,并在不同text之间生成####分隔符,不同tag之间生成@@@分隔符,之后合并这些文件,生成一个完整的txt文件,该代码文件的主要内容如下:
typescript
import { Injectable } from '@nestjs/common';
import * as fs from 'fs/promises';
import * as path from 'path';
/**
* 文件服务 - 负责文件的生成和合并
*/
@Injectable()
export class FileService {
private readonly outputDir = path.join(process.cwd(), 'output');
constructor() {
this.ensureOutputDir();
}
/**
* 确保输出目录存在
*/
private async ensureOutputDir(): Promise<void> {
try {
await fs.mkdir(this.outputDir, { recursive: true });
} catch (error) {
console.error('创建输出目录失败:', error);
}
}
/**
* 生成单个MD文件
*/
async generateMdFile(content: string, index: number): Promise<string> {
const filePath = path.join(this.outputDir, `part${index}.md`);
// 验证content是否为有效JSON
try {
JSON.parse(content);
} catch (error) {
console.error(`part${index}.md 的内容不是有效的JSON,尝试修复...`);
console.error('原始内容前200字符:', content.substring(0, 200));
}
// 移除管道符号(如generate.py中的处理)
const cleanContent = content.replace(/\|/g, '');
await fs.writeFile(filePath, cleanContent, 'utf-8');
return `文件 part${index}.md 生成完毕`;
}
/**
* 合并所有MD文件为TXT文件
*/
async integrateMdFiles(outputFileName: string): Promise<string> {
const outputPath = path.join(this.outputDir, `${outputFileName}_combine.txt`);
// 获取所有part*.md文件
const files = await fs.readdir(this.outputDir);
const mdFiles = files
.filter((f) => f.toLowerCase().startsWith('part') && f.endsWith('.md'))
.sort((a, b) => {
const numA = parseInt(a.match(/\d+/)?.[0] || '0');
const numB = parseInt(b.match(/\d+/)?.[0] || '0');
return numA - numB;
});
const outputLines: string[] = [];
for (const file of mdFiles) {
const filePath = path.join(this.outputDir, file);
const content = await fs.readFile(filePath, 'utf-8');
try {
const data = JSON.parse(content);
// 遍历所有segment
for (const segment of Object.values(data)) {
const seg = segment as any;
// 写入text内容
if (seg.text) {
outputLines.push(seg.text);
}
// 写入 @@@tags(在同一行)
if (seg.tags && Array.isArray(seg.tags)) {
outputLines.push('@@@' + seg.tags.join('@@@'));
} else {
outputLines.push('@@@');
}
// 写入####分隔行
outputLines.push('####\n');
}
} catch (error) {
console.error(`解析文件 ${file} 失败:`, error);
console.error(`文件内容前500字符:\n${content.substring(0, 500)}`);
throw new Error(`文件 ${file} 的JSON格式无效,请检查大模型输出`);
}
}
await fs.writeFile(outputPath, outputLines.join('\n'), 'utf-8');
return '标注文件生成完毕!';
}
/**
* 清理输出目录中的临时文件
*/
async cleanupTempFiles(): Promise<void> {
const files = await fs.readdir(this.outputDir);
const mdFiles = files.filter((f) => f.toLowerCase().startsWith('part') && f.endsWith('.md'));
for (const file of mdFiles) {
await fs.unlink(path.join(this.outputDir, file));
}
}
}之后便是迭代器的代码,为了并行的执行任务提升效率,创建iteration.service.ts文件,内容如下:
import
import pLimit from 'p-limit';
/*
* 支持并行处理和错误处理
*/
@Injectable()
export class IterationService {
/**
* 并行处理迭代任务
* @param items 待处理的项目列表
* @param processor 处理函数
* @param parallelNums 并行数量,默认10
*/
async runParallel<T, R>(
items: T[],
processor: (item: T, index: number) => Promise<R>,
parallelNums: number = 10,
): Promise<R[]> {
if (!items || items.length === 0) {
return [];
}
// 使用p-limit控制并发数量
const limit = pLimit(parallelNums);
// 创建所有任务
const tasks = items.map((item, index) =>
limit(async () => {
try {
console.log(`开始处理第 ${index + 1}/${items.length} 个任务`);
const result = await processor(item, index);
console.log(`完成处理第 ${index + 1}/${items.length} 个任务`);
return result;
} catch (error) {
console.error(`处理第 ${index + 1} 个任务时出错:`, error);
throw error;
}
}),
);
// 等待所有任务完成
return Promise.all(tasks);
}
/**
* 串行处理迭代任务
* @param items 待处理的项目列表
* @param processor 处理函数
*/
async runSequential<T, R>(items: T[], processor: (item: T, index: number) => Promise<R>): Promise<R[]> {
if (!items || items.length === 0) {
return [];
}
const results: R[] = [];
for (let index = 0; index < items.length; index++) {
try {
console.log(`开始处理第 ${index + 1}/${items.length} 个任务`);
const result = await processor(items[index], index);
results.push(result);
console.log(`完成处理第 ${index + 1}/${items.length} 个任务`);
} catch (error) {
console.error(`处理第 ${index + 1} 个任务时出错:`, error);
throw error;
}
}
return results;
}
/**
* 运行迭代任务(自动选择并行或串行)
* @param items 待处理的项目列表
* @param processor 处理函数
* @param isParallel 是否并行,默认true
* @param parallelNums 并行数量,默认10
*/
async run<T, R>(
items: T[],
processor: (item: T, index: number) => Promise<R>,
isParallel: boolean = true,
parallelNums: number = 10,
): Promise<R[]> {
if (isParallel) {
return this.runParallel(items, processor, parallelNums);
} else {
return this.runSequential(items, processor);
}
}
}之后便是形成一个工作流,代码分为工作流控制器与工作流服务,首先创建workflow.controller.ts文件,内容如下:
typescript
import { Controller, Post, Body } from '@nestjs/common';
import { WorkflowService } from './workflow.service';
/**
* 工作流控制器
*/
@Controller('workflow')
export class WorkflowController {
constructor(private readonly workflowService: WorkflowService) {}
/**
* 处理文档的API端点
*/
@Post('process')
async processDocument(
@Body()
body: {
pdfPath: string;
outputFileName?: string;
parallelNums?: number;
},
) {
const { pdfPath, outputFileName = 'output', parallelNums = 10 } = body;
try {
const result = await this.workflowService.processDocument(pdfPath, outputFileName, parallelNums);
return {
success: true,
message: result,
};
} catch (error: any) {
return {
success: false,
error: error.message,
};
}
}
}工作流服务workflow.service.ts文件内容如下:
import
import { ChunkService } from '../chunking/chunk.service';
import { QwenService } from '../ai/qwen.service';
import { IterationService } from '../iteration/iteration.service';
import { FileService } from '../file/file.service';
/**
* 工作流服务 - 整合所有步骤的主要服务
*/
@Injectable()
export class WorkflowService {
constructor(
private readonly chunkService: ChunkService,
private readonly qwenService: QwenService,
private readonly iterationService: IterationService,
private readonly fileService: FileService,
) {}
/**
* 执行完整的文档处理工作流
* @param pdfPath PDF文件路径
* @param outputFileName 输出文件名
* @param parallelNums 并行数量,默认10
*/
async processDocument(pdfPath: string, outputFileName: string = 'output', parallelNums: number = 10): Promise<string> {
console.log('=== 开始文档处理工作流 ===');
// 步骤1: 使用chunk.py算法分割文档
console.log('\n步骤1: 分割PDF文档...');
const chunkResult = await this.chunkService.chunkFile(pdfPath);
const segments = chunkResult.result;
if (!segments || segments.length === 0) {
throw new Error('文档分割失败,没有生成任何段落');
}
console.log(`文档分割完成,共生成 ${segments.length} 个段落\n`);
// 步骤2: 使用迭代并行模式处理每个段落
console.log(`步骤2: 使用大模型处理段落(并行度: ${parallelNums})...`);
await this.iterationService.runParallel(
segments,
async (segment: string, index: number) => {
// 2.1: 调用千问大模型处理
const llmResult = await this.qwenService.processSegment(segment);
// 2.2: 生成MD文件
await this.fileService.generateMdFile(llmResult, index);
return llmResult;
},
parallelNums,
);
console.log('所有段落处理完成\n');
// 步骤3: 合并所有MD文件为TXT文件
console.log('步骤3: 合并生成最终文件...');
const integrateResult = await this.fileService.integrateMdFiles(outputFileName);
console.log(integrateResult);
// 步骤4: 清理临时文件
console.log('\n步骤4: 清理临时文件...');
await this.fileService.cleanupTempFiles();
console.log('临时文件清理完成');
console.log('\n=== 文档处理工作流完成 ===');
return `处理完成!共处理 ${segments.length} 个段落,输出文件: ${outputFileName}_combine.txt`;
}
}主体服务已经搭建完毕,之后便是简单的app.module.ts文件与main.ts文件,app.module.ts文件主要内容如下:
import
import { ConfigModule } from '@nestjs/config';
import { ChunkService } from './chunking/chunk.service';
import { QwenService } from './ai/qwen.service';
import { IterationService } from './iteration/iteration.service';
import { FileService } from './file/file.service';
import { WorkflowService } from './workflow/workflow.service';
import { WorkflowController } from './workflow/workflow.controller';
@Module({
imports: [
ConfigModule.forRoot({
isGlobal: true, // 使配置在整个应用中全局可用
envFilePath: '.env', // 指定.env文件路径
}),
],
controllers: [WorkflowController],
providers: [ChunkService, QwenService, IterationService, FileService, WorkflowService],
})
export class AppModule {}服务启动文件main.ts主要内容如下:
import
import { AppModule } from './app.module';
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
// 启用CORS
app.enableCors();
const port = process.env.PORT || 3000;
await app.listen(port);
console.log(`应用程序运行在: http://localhost:${port}`);
console.log(`API端点: POST http://localhost:${port}/workflow/process`);
console.log(`
请求体示例:
{
"pdfPath": "/path/to/your/document.pdf",
"outputFileName": "output",
"parallelNums": 10
}
`);
}
bootstrap();至此,所有服务搭建完毕,可以启动main.ts进行测试,首先确保下载了ts-node或者其它ts环境输入,这里使用该指令进行测试:
css
ts-node src/main.ts当输出以下信息时,证明启动成功,服务启动在本机的3000端口
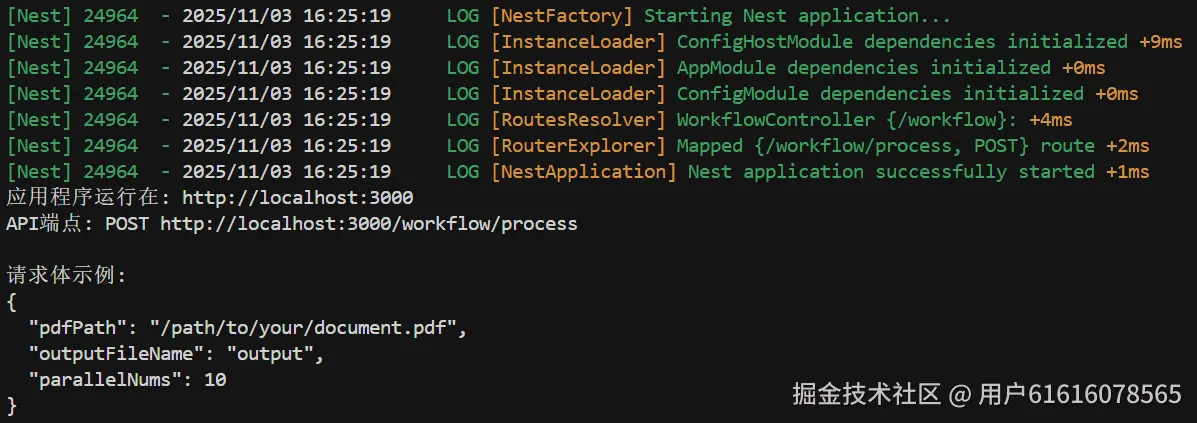 接下来,我们使用一个post请求来进行测试,在根目录编辑一个测试脚本test.ts,内容如下:
接下来,我们使用一个post请求来进行测试,在根目录编辑一个测试脚本test.ts,内容如下:
import
import * as path from 'path';
/**
* 测试脚本 - 调用文档处理工作流API
*/
const API_URL = 'http://localhost:3000/workflow/process';
interface WorkflowRequest {
pdfPath: string;
outputFileName?: string;
parallelNums?: number;
}
interface WorkflowResponse {
success: boolean;
message?: string;
error?: string;
}
/**
* 发送工作流处理请求
*/
async function testWorkflow(pdfPath: string, outputFileName: string = 'output', parallelNums: number = 10) {
console.log('=== 测试文档处理工作流 ===\n');
console.log(`PDF路径: ${pdfPath}`);
console.log(`输出文件名: ${outputFileName}`);
console.log(`并行数量: ${parallelNums}`);
console.log('\n发送请求...\n');
try {
const requestData: WorkflowRequest = {
pdfPath,
outputFileName,
parallelNums,
};
const response = await axios.post<WorkflowResponse>(API_URL, requestData, {
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
timeout: 600000, // 10分钟超时
});
console.log('响应状态:', response.status);
console.log('响应数据:', JSON.stringify(response.data, null, 2));
if (response.data.success) {
console.log('\n处理成功!');
console.log(`${response.data.message}`);
console.log(`\n输出文件位置: output/${outputFileName}_combine.txt`);
} else {
console.log('\n处理失败!');
console.log(`错误: ${response.data.error}`);
}
} catch (error: any) {
console.error('\n请求失败!');
if (error.response) {
// 服务器响应了错误状态码
console.error('状态码:', error.response.status);
console.error('响应数据:', error.response.data);
} else if (error.request) {
// 请求已发送但没有收到响应
console.error('无法连接到服务器,请确保服务已启动 (npm start)');
} else {
// 其他错误
console.error('错误信息:', error.message);
}
}
}
/**
* 主函数
*/
async function main() {
// 从命令行参数获取PDF路径,或使用默认路径
const args = process.argv.slice(2);
if (args.length === 0) {
console.log('使用方法:');
console.log(' npm run test [PDF路径] [输出文件名] [并行数量]');
console.log('\n示例:');
console.log(' npm run test ./sample.pdf');
console.log(' npm run test ./sample.pdf output 10');
console.log(' npm run test "C:\\Documents\\test.pdf" result 5');
console.log('\n或者使用默认测试路径:');
console.log(' npm run test\n');
}
const pdfPath = args[0] || './1.pdf';
const outputFileName = args[1] || 'output';
const parallelNums = args[2] ? parseInt(args[2]) : 10;
// 检查服务器是否运行
try {
await axios.get('http://localhost:3000', { timeout: 3000 });
} catch (error) {
console.error('警告: 无法连接到服务器 (http://localhost:3000)');
console.error('请先启动服务: npm start\n');
}
await testWorkflow(pdfPath, outputFileName, parallelNums);
}
// 运行主函数
main().catch((error) => {
console.error('脚本执行失败:', error);
process.exit(1);
});启动该脚本,命令行会出现以下信息,证明大模型正在处理数据:
 之后会出现output文件夹,逐渐产生md文件,最后会合并为txt文件,大致如下图所示:
之后会出现output文件夹,逐渐产生md文件,最后会合并为txt文件,大致如下图所示:
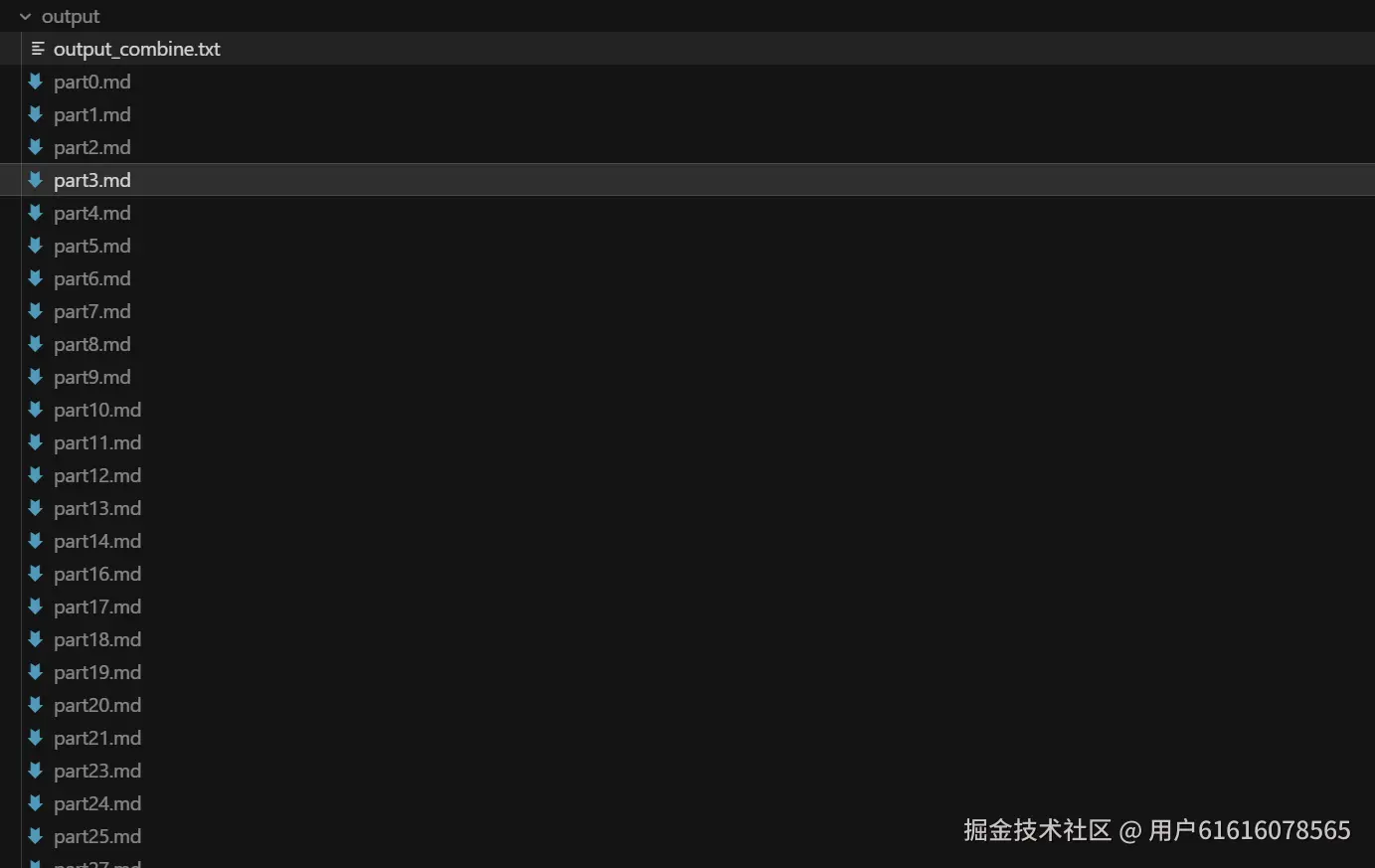
生成的数据每个段落之间用####符号表示,每个段落的子段用@@@表示,在后续构建RAG索引时可以进行父子索引构建,以此平衡召回率与精确率。