这个条款揭示了RAII类设计中一个关键但常被忽视的问题:拷贝行为的选择直接影响资源管理的正确性和效率。正确的拷贝语义设计是构建健壮资源管理类的核心。
思维导图:资源管理类拷贝行为的完整体系
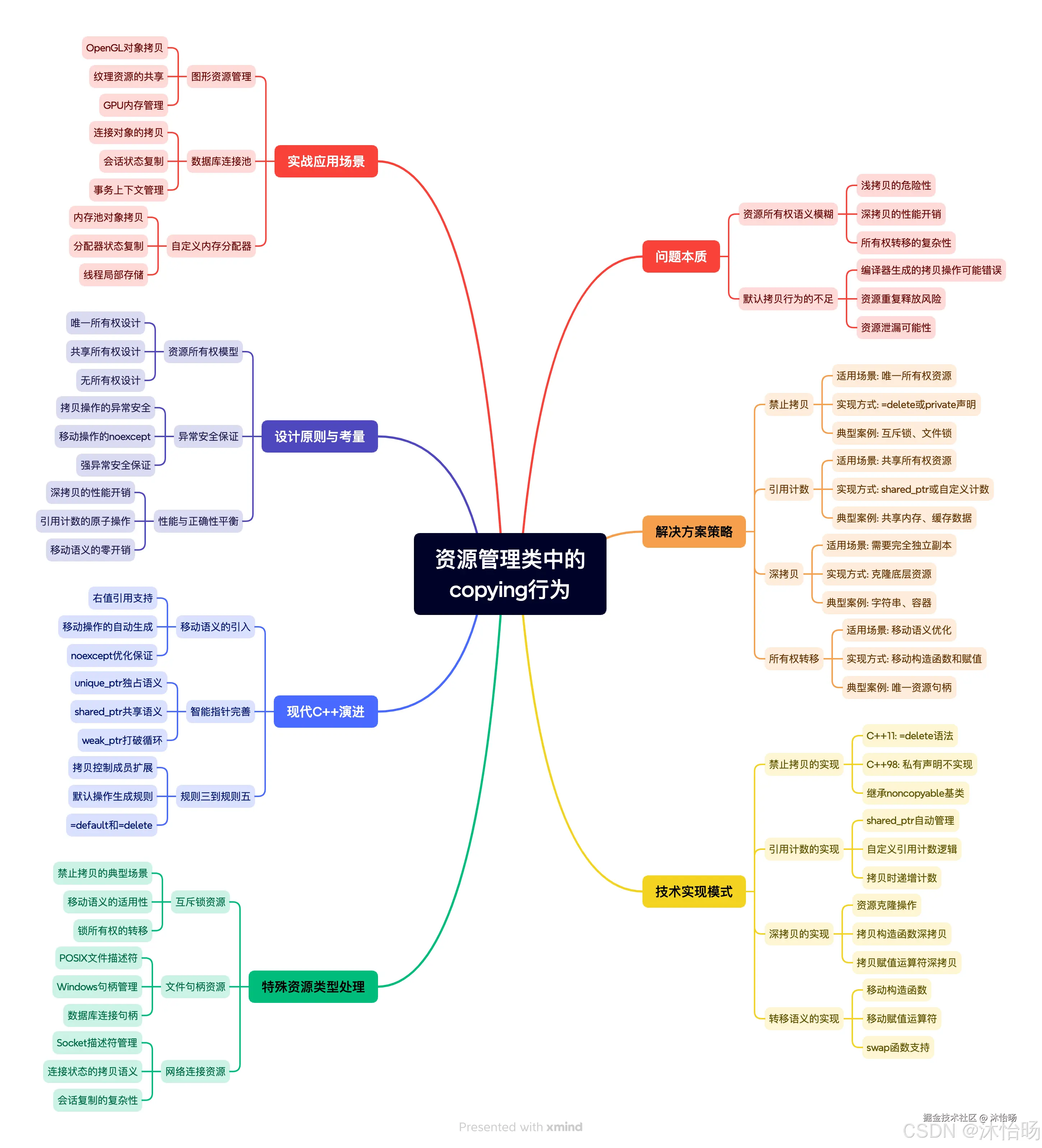
关键洞见与行动指南
必须遵守的核心原则:
- 明确所有权语义:在设计RAII类时首先确定资源的拷贝语义
- 遵循三/五法则:如果需要自定义析构函数,通常需要自定义拷贝/移动操作
- 优先使用移动语义:对于不可拷贝资源,提供移动操作支持所有权转移
- 利用标准库工具 :使用
unique_ptr、shared_ptr等简化资源管理
现代C++开发建议:
- 默认禁止拷贝:除非有明确需求,否则优先禁止拷贝操作
- 提供移动操作:为资源管理类实现移动构造函数和移动赋值运算符
- 使用=delete明确意图 :用
=delete而非私有声明来禁止操作 - 考虑noexcept :移动操作和析构函数应该标记为
noexcept
设计原则总结:
- 单一职责:每个RAII类应该只管理一种资源类型
- 明确语义:拷贝行为应该清晰明确,符合程序员直觉
- 异常安全:确保资源操作在异常情况下仍然安全
- 性能意识:在保证正确性的前提下考虑性能影响
需要警惕的陷阱:
- 默认拷贝的错误:编译器生成的拷贝操作可能不正确
- 浅拷贝的危险:指针成员的浅拷贝导致双重释放
- 循环引用 :
shared_ptr的循环引用导致内存泄漏 - 不完整的移动操作:只实现了部分移动语义
最终建议: 将拷贝行为设计视为RAII类的核心职责。培养"拷贝语义思维"------在设计每个资源管理类时都问自己:"这个资源的拷贝应该是什么语义?禁止拷贝、共享所有权、深拷贝还是转移所有权?" 这种系统性的思考是构建正确资源管理类的关键。
记住:在C++资源管理中,正确的拷贝行为设计不是事后考虑,而是RAII类设计的核心组成部分。 条款14教会我们的不仅是一组技术方案,更是资源管理哲学的具体体现。
深入解析:资源拷贝的核心挑战
1. 问题根源:资源所有权的复杂性
危险的默认拷贝行为:
cpp
class Mutex {
// 互斥锁实现...
};
class Lock {
private:
Mutex* mutexPtr;
public:
explicit Lock(Mutex* pm) : mutexPtr(pm) {
lock(mutexPtr); // 获取资源
}
~Lock() {
unlock(mutexPtr); // 释放资源
}
// 问题:编译器会生成默认的拷贝构造函数和拷贝赋值运算符!
// 这会导致多个Lock对象管理同一个Mutex!
};
void demonstrate_dangerous_copy() {
Mutex m;
{
Lock lock1(&m); // 锁定互斥锁
// 如果允许拷贝...
Lock lock2 = lock1; // 现在有两个对象管理同一个mutex!
// lock2离开作用域时会解锁mutex!
// 但lock1仍然认为它拥有锁!
} // lock1离开作用域时会再次解锁已解锁的mutex - 未定义行为!
}资源重复释放的灾难:
cpp
class BadResourceManager {
private:
int* resource;
public:
BadResourceManager(int value) : resource(new int(value)) {
std::cout << "分配资源: " << resource << std::endl;
}
~BadResourceManager() {
std::cout << "释放资源: " << resource << std::endl;
delete resource; // 假设释放某种资源
}
// 编译器生成的拷贝构造函数会浅拷贝指针!
// 拷贝赋值运算符也会浅拷贝指针!
};
void demonstrate_double_free() {
BadResourceManager obj1(42);
{
BadResourceManager obj2 = obj1; // 浅拷贝 - 两个对象共享同一资源
} // obj2析构,释放资源
// 现在obj1.resource是悬空指针!
std::cout << "obj2已析构,obj1仍持有悬空指针" << std::endl;
} // obj1析构,再次释放同一内存 - 双重释放!解决方案:四种拷贝策略
1. 策略一:禁止拷贝(Prohibit Copying)
适用于唯一所有权资源:
cpp
#include <memory>
class NonCopyableMutexLock {
private:
std::mutex* mutexPtr;
public:
explicit NonCopyableMutexLock(std::mutex* pm) : mutexPtr(pm) {
mutexPtr->lock();
std::cout << "锁定互斥锁" << std::endl;
}
~NonCopyableMutexLock() {
if (mutexPtr) {
mutexPtr->unlock();
std::cout << "解锁互斥锁" << std::endl;
}
}
// C++11: 明确删除拷贝操作
NonCopyableMutexLock(const NonCopyableMutexLock&) = delete;
NonCopyableMutexLock& operator=(const NonCopyableMutexLock&) = delete;
// 允许移动语义(如果需要)
NonCopyableMutexLock(NonCopyableMutexLock&& other) noexcept
: mutexPtr(other.mutexPtr) {
other.mutexPtr = nullptr; // 源对象放弃所有权
}
NonCopyableMutexLock& operator=(NonCopyableMutexLock&& other) noexcept {
if (this != &other) {
// 释放当前资源
if (mutexPtr) {
mutexPtr->unlock();
}
// 接管新资源
mutexPtr = other.mutexPtr;
other.mutexPtr = nullptr;
}
return *this;
}
};
void demonstrate_non_copyable() {
std::mutex mtx;
{
NonCopyableMutexLock lock1(&mtx);
// NonCopyableMutexLock lock2 = lock1; // 错误:拷贝构造函数被删除
NonCopyableMutexLock lock2 = std::move(lock1); // 正确:移动构造
} // 自动解锁
}C++98的禁止拷贝方法:
cpp
class NonCopyableLock_Cpp98 {
private:
std::mutex* mutexPtr;
// 声明为private且不实现 - 禁止拷贝
NonCopyableLock_Cpp98(const NonCopyableLock_Cpp98&);
NonCopyableLock_Cpp98& operator=(const NonCopyableLock_Cpp98&);
public:
explicit NonCopyableLock_Cpp98(std::mutex* pm) : mutexPtr(pm) {
mutexPtr->lock();
}
~NonCopyableLock_Cpp98() {
mutexPtr->unlock();
}
};2. 策略二:引用计数(Reference Counting)
使用shared_ptr的引用计数:
cpp
#include <memory>
class SharedResource {
private:
struct Resource {
int* data;
size_t size;
Resource(size_t s) : size(s) {
data = new int[size];
std::fill(data, data + size, 0);
std::cout << "创建资源,大小: " << size << std::endl;
}
~Resource() {
delete[] data;
std::cout << "销毁资源,大小: " << size << std::endl;
}
};
std::shared_ptr<Resource> resourcePtr;
public:
explicit SharedResource(size_t size)
: resourcePtr(std::make_shared<Resource>(size)) {}
// 使用默认的拷贝构造函数和拷贝赋值运算符 - 共享所有权!
// shared_ptr会自动处理引用计数
// 自定义删除器示例
static void customDeleter(Resource* res) {
std::cout << "使用自定义删除器释放资源" << std::endl;
delete res;
}
void setValue(size_t index, int value) {
if (index < resourcePtr->size) {
resourcePtr->data[index] = value;
}
}
int getValue(size_t index) const {
return (index < resourcePtr->size) ? resourcePtr->data[index] : -1;
}
size_t useCount() const {
return resourcePtr.use_count();
}
void printInfo(const std::string& name) const {
std::cout << name << ": 使用计数=" << useCount()
<< ", 大小=" << resourcePtr->size << std::endl;
}
};
void demonstrate_reference_counting() {
SharedResource res1(10);
res1.setValue(0, 100);
res1.printInfo("res1");
{
SharedResource res2 = res1; // 共享所有权!
res2.setValue(1, 200);
res2.printInfo("res2");
SharedResource res3 = res2; // 再次共享!
res3.printInfo("res3");
std::cout << "res1的值[0]=" << res1.getValue(0)
<< ", [1]=" << res1.getValue(1) << std::endl;
} // res2和res3析构,但资源不会被释放
res1.printInfo("res1 after res2/res3 destruction");
} // res1析构,引用计数归零,资源被释放3. 策略三:深拷贝(Deep Copying)
完全独立的资源副本:
cpp
class DeepCopyResource {
private:
int* data;
size_t size;
std::string name;
// 辅助深拷贝函数
void deepCopyFrom(const DeepCopyResource& other) {
size = other.size;
name = other.name + "_copy";
// 深拷贝数据
data = new int[size];
std::copy(other.data, other.data + size, data);
std::cout << "深拷贝资源: " << name << std::endl;
}
void cleanup() {
if (data) {
delete[] data;
data = nullptr;
std::cout << "清理资源: " << name << std::endl;
}
}
public:
DeepCopyResource(size_t s, const std::string& n)
: size(s), name(n) {
data = new int[size];
std::fill(data, data + size, 0);
std::cout << "创建资源: " << name << std::endl;
}
// 拷贝构造函数 - 深拷贝
DeepCopyResource(const DeepCopyResource& other) {
deepCopyFrom(other);
}
// 拷贝赋值运算符 - 深拷贝
DeepCopyResource& operator=(const DeepCopyResource& other) {
if (this != &other) {
cleanup(); // 释放现有资源
deepCopyFrom(other);
}
return *this;
}
// 移动构造函数
DeepCopyResource(DeepCopyResource&& other) noexcept
: data(other.data), size(other.size), name(std::move(other.name)) {
other.data = nullptr;
other.size = 0;
other.name = "moved";
std::cout << "移动构造资源" << std::endl;
}
// 移动赋值运算符
DeepCopyResource& operator=(DeepCopyResource&& other) noexcept {
if (this != &other) {
cleanup();
data = other.data;
size = other.size;
name = std::move(other.name);
other.data = nullptr;
other.size = 0;
other.name = "moved";
}
return *this;
}
~DeepCopyResource() {
cleanup();
}
void setValue(size_t index, int value) {
if (index < size) {
data[index] = value;
}
}
void printInfo() const {
std::cout << "资源: " << name << ", 大小: " << size;
if (data) {
std::cout << ", 数据指针: " << data;
} else {
std::cout << ", [无数据]";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
};
void demonstrate_deep_copy() {
DeepCopyResource original(5, "原始资源");
original.setValue(0, 42);
std::cout << "=== 深拷贝演示 ===" << std::endl;
DeepCopyResource copy1 = original; // 深拷贝
copy1.setValue(1, 100);
DeepCopyResource copy2(3, "临时资源");
copy2 = original; // 深拷贝赋值
original.printInfo();
copy1.printInfo();
copy2.printInfo();
std::cout << "=== 移动语义演示 ===" << std::endl;
DeepCopyResource moved = std::move(copy1); // 移动构造
original.printInfo();
copy1.printInfo(); // copy1已被移动
moved.printInfo();
}4. 策略四:所有权转移(Transfer Ownership)
移动语义的现代实现:
cpp
#include <utility>
class UniqueFileHandle {
private:
FILE* fileHandle;
std::string filename;
void closeFile() noexcept {
if (fileHandle) {
fclose(fileHandle);
std::cout << "关闭文件: " << filename << std::endl;
fileHandle = nullptr;
}
}
public:
explicit UniqueFileHandle(const std::string& fname,
const std::string& mode = "r")
: filename(fname) {
fileHandle = fopen(fname.c_str(), mode.c_str());
if (fileHandle) {
std::cout << "打开文件: " << filename << std::endl;
} else {
throw std::runtime_error("无法打开文件: " + fname);
}
}
// 禁止拷贝
UniqueFileHandle(const UniqueFileHandle&) = delete;
UniqueFileHandle& operator=(const UniqueFileHandle&) = delete;
// 移动构造函数
UniqueFileHandle(UniqueFileHandle&& other) noexcept
: fileHandle(other.fileHandle), filename(std::move(other.filename)) {
other.fileHandle = nullptr;
other.filename = "moved";
std::cout << "移动构造文件句柄: " << filename << std::endl;
}
// 移动赋值运算符
UniqueFileHandle& operator=(UniqueFileHandle&& other) noexcept {
if (this != &other) {
closeFile(); // 关闭当前文件
fileHandle = other.fileHandle;
filename = std::move(other.filename);
other.fileHandle = nullptr;
other.filename = "moved";
std::cout << "移动赋值文件句柄: " << filename << std::endl;
}
return *this;
}
~UniqueFileHandle() {
closeFile();
}
// 资源访问
bool isValid() const noexcept { return fileHandle != nullptr; }
const std::string& getFilename() const noexcept { return filename; }
void write(const std::string& data) {
if (!fileHandle) {
throw std::logic_error("文件句柄无效");
}
fputs(data.c_str(), fileHandle);
}
std::string readLine() {
if (!fileHandle) {
throw std::logic_error("文件句柄无效");
}
char buffer[256];
if (fgets(buffer, sizeof(buffer), fileHandle)) {
return std::string(buffer);
}
return "";
}
};
void demonstrate_ownership_transfer() {
try {
UniqueFileHandle file1("test1.txt", "w");
file1.write("Hello World\n");
std::cout << "=== 所有权转移前 ===" << std::endl;
std::cout << "file1有效: " << file1.isValid()
<< ", 文件名: " << file1.getFilename() << std::endl;
// 转移所有权
UniqueFileHandle file2 = std::move(file1);
std::cout << "=== 所有权转移后 ===" << std::endl;
std::cout << "file1有效: " << file1.isValid()
<< ", 文件名: " << file1.getFilename() << std::endl;
std::cout << "file2有效: " << file2.isValid()
<< ", 文件名: " << file2.getFilename() << std::endl;
file2.write("第二行内容\n");
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
std::cout << "错误: " << e.what() << std::endl;
}
}实战案例:复杂资源管理设计
案例1:数据库连接池的拷贝策略
cpp
#include <memory>
#include <vector>
#include <mutex>
class DatabaseConnection {
private:
std::string connectionString;
void* nativeHandle;
bool isConnected;
// 禁止拷贝 - 数据库连接应该是唯一的
DatabaseConnection(const DatabaseConnection&) = delete;
DatabaseConnection& operator=(const DatabaseConnection&) = delete;
public:
explicit DatabaseConnection(const std::string& connStr)
: connectionString(connStr), nativeHandle(nullptr), isConnected(false) {
connect();
}
// 移动构造函数
DatabaseConnection(DatabaseConnection&& other) noexcept
: connectionString(std::move(other.connectionString)),
nativeHandle(other.nativeHandle),
isConnected(other.isConnected) {
other.nativeHandle = nullptr;
other.isConnected = false;
}
// 移动赋值运算符
DatabaseConnection& operator=(DatabaseConnection&& other) noexcept {
if (this != &other) {
disconnect();
connectionString = std::move(other.connectionString);
nativeHandle = other.nativeHandle;
isConnected = other.isConnected;
other.nativeHandle = nullptr;
other.isConnected = false;
}
return *this;
}
~DatabaseConnection() {
disconnect();
}
void connect() {
if (!isConnected) {
// 模拟连接操作
nativeHandle = malloc(100); // 模拟分配资源
isConnected = true;
std::cout << "连接数据库: " << connectionString << std::endl;
}
}
void disconnect() {
if (isConnected && nativeHandle) {
free(nativeHandle);
isConnected = false;
std::cout << "断开数据库连接: " << connectionString << std::endl;
}
}
void execute(const std::string& query) {
if (!isConnected) throw std::logic_error("未连接数据库");
std::cout << "执行查询: " << query << " on " << connectionString << std::endl;
}
bool connected() const { return isConnected; }
const std::string& getConnectionString() const { return connectionString; }
};
class ConnectionPool {
private:
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<DatabaseConnection>> connections;
std::mutex poolMutex;
size_t maxSize;
public:
explicit ConnectionPool(size_t maxConnections = 10)
: maxSize(maxConnections) {}
// 禁止拷贝 - 连接池应该是唯一的
ConnectionPool(const ConnectionPool&) = delete;
ConnectionPool& operator=(const ConnectionPool&) = delete;
// 允许移动
ConnectionPool(ConnectionPool&&) = default;
ConnectionPool& operator=(ConnectionPool&&) = default;
std::unique_ptr<DatabaseConnection> acquireConnection(const std::string& connStr) {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(poolMutex);
// 查找可用连接
for (auto it = connections.begin(); it != connections.end(); ++it) {
if ((*it)->getConnectionString() == connStr && (*it)->connected()) {
auto conn = std::move(*it);
connections.erase(it);
std::cout << "从池中获取现有连接" << std::endl;
return conn;
}
}
// 创建新连接
if (connections.size() < maxSize) {
auto newConn = std::make_unique<DatabaseConnection>(connStr);
std::cout << "创建新连接" << std::endl;
return newConn;
}
throw std::runtime_error("连接池已满");
}
void releaseConnection(std::unique_ptr<DatabaseConnection> conn) {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(poolMutex);
if (conn && conn->connected()) {
connections.push_back(std::move(conn));
std::cout << "连接返回到池中,当前大小: " << connections.size() << std::endl;
}
}
size_t size() const {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(poolMutex);
return connections.size();
}
};
void demonstrate_connection_pool() {
ConnectionPool pool(2);
auto conn1 = pool.acquireConnection("server1/db1");
conn1->execute("SELECT * FROM users");
auto conn2 = pool.acquireConnection("server2/db2");
conn2->execute("UPDATE accounts SET balance = 1000");
// 返回连接给池
pool.releaseConnection(std::move(conn1));
pool.releaseConnection(std::move(conn2));
std::cout << "连接池大小: " << pool.size() << std::endl;
// 再次获取连接 - 应该重用现有的
auto conn3 = pool.acquireConnection("server1/db1");
conn3->execute("DELETE FROM logs");
pool.releaseConnection(std::move(conn3));
}案例2:图形API资源管理
cpp
#include <memory>
#include <vector>
class OpenGLTexture {
private:
unsigned int textureID;
int width, height;
std::string filename;
// 禁止拷贝 - OpenGL纹理对象不能直接拷贝
OpenGLTexture(const OpenGLTexture&) = delete;
OpenGLTexture& operator=(const OpenGLTexture&) = delete;
public:
OpenGLTexture(int w, int h, const std::string& name = "")
: width(w), height(h), filename(name) {
// 模拟OpenGL纹理创建
textureID = static_cast<unsigned int>(malloc(1)); // 模拟GL纹理ID
std::cout << "创建OpenGL纹理: ID=" << textureID
<< ", 尺寸=" << width << "x" << height << std::endl;
}
// 移动构造函数
OpenGLTexture(OpenGLTexture&& other) noexcept
: textureID(other.textureID),
width(other.width),
height(other.height),
filename(std::move(other.filename)) {
other.textureID = 0;
other.width = other.height = 0;
other.filename = "moved";
std::cout << "移动纹理: ID=" << textureID << std::endl;
}
// 移动赋值运算符
OpenGLTexture& operator=(OpenGLTexture&& other) noexcept {
if (this != &other) {
// 释放当前纹理
if (textureID != 0) {
free(reinterpret_cast<void*>(textureID)); // 模拟glDeleteTextures
std::cout << "删除纹理: ID=" << textureID << std::endl;
}
textureID = other.textureID;
width = other.width;
height = other.height;
filename = std::move(other.filename);
other.textureID = 0;
other.width = other.height = 0;
other.filename = "moved";
}
return *this;
}
~OpenGLTexture() {
if (textureID != 0) {
free(reinterpret_cast<void*>(textureID)); // 模拟glDeleteTextures
std::cout << "析构纹理: ID=" << textureID << std::endl;
}
}
void bind() const {
if (textureID != 0) {
std::cout << "绑定纹理: ID=" << textureID << std::endl;
}
}
unsigned int getID() const { return textureID; }
std::pair<int, int> getSize() const { return {width, height}; }
const std::string& getFilename() const { return filename; }
};
class TextureManager {
private:
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<OpenGLTexture>> textures;
public:
// 使用默认的拷贝和移动操作
OpenGLTexture* createTexture(int width, int height, const std::string& name) {
auto texture = std::make_unique<OpenGLTexture>(width, height, name);
OpenGLTexture* ptr = texture.get();
textures.push_back(std::move(texture));
return ptr;
}
// 转移纹理所有权到管理器
void addTexture(std::unique_ptr<OpenGLTexture> texture) {
textures.push_back(std::move(texture));
}
// 获取纹理(不转移所有权)
OpenGLTexture* getTexture(size_t index) {
return (index < textures.size()) ? textures[index].get() : nullptr;
}
size_t textureCount() const {
return textures.size();
}
};
void demonstrate_graphics_resource() {
TextureManager manager;
// 创建纹理
auto* tex1 = manager.createTexture(256, 256, "diffuse_map");
auto* tex2 = manager.createTexture(512, 512, "normal_map");
std::cout << "纹理管理器中有 " << manager.textureCount() << " 个纹理" << std::endl;
// 使用纹理
tex1->bind();
tex2->bind();
// 创建独立纹理并转移到管理器
auto independentTexture = std::make_unique<OpenGLTexture>(128, 128, "independent");
manager.addTexture(std::move(independentTexture));
std::cout << "转移后纹理数量: " << manager.textureCount() << std::endl;
// independentTexture现在为空
}