为什么需要智能指针?
cpp
int div()
{
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
if (b == 0)
throw invalid_argument("除0错误");
return a / b;
}
void Func()
{
//1、如果p1这里new 抛异常会如何?
// 2、如果p2这里new 抛异常会如何?
// 3、如果div调用这里抛异常会如何?
int* p1 = new int;
int* p2 = new int;
cout << div() << endl;
delete p1;
delete p2;
}
int main()
{
try
{
Func();
}
catch (exception& e)
{
cout << e.what() << endl;
}
return 0;
}可能会出现没有delete的问题,导致内存泄漏。
内存泄漏
内存泄漏指因为疏忽或错误造成程序未能释放且已经不再使用的内存的情况。并不是指内存在物理上的消失,而是程序分配某段内存后,因为设计错误,失去了对该段内存的控制,因此造成了内存的浪费。
危害:像操作系统,后台服务这种长期运行的程序出现内存泄漏会导致响应越来越慢,最终卡死。
内存泄漏分类
C/C++程序中一般我们关心两种方面的内存泄漏:
一.堆内存泄漏(Heap leak)
堆内存指的是程序执行中依据须要分配通过malloc / calloc / realloc / new等从堆中分配的一块内存,用完后必须通过调用相应的 free或者delete 删掉。假设程序的设计错误导致这部分内存没有被释放,那么以后这部分空间将无法再被使用,就会产生Heap Leak。
二.系统资源泄漏
指程序使用系统分配的资源,比方套接字、文件描述符、管道等没有使用对应的函数释放掉,导致系统资源的浪费,严重可导致系统效能减少,系统执行不稳定。
如何避免内存泄漏
1.事前预防型:如智能指针等。
2.事后查错型:如内存泄漏检测工具。
智能指针的使用及原理
RAII
RAII(Resource Acquisition Is Initialization)是一种利用对象生命周期来控制程序资源 的简单技术。
在对象构造时获取资源 ,接着控制对资源的访问使之在对象的生命周期内始终有效,最后在对象析构的时候释放资源 。借此,我们实际把管理一份资源的责任托管给了一个对象。这种做法有两大好处:
1.不需要显式的释放资源
2.采用这种方式,对象所需的资源在其生命期内始终保持有效。
cpp
class SmartPtr
{
public:
SmartPtr(T* ptr=nullptr)
:_ptr(ptr)
{ }
~SmartPtr()
{
if (_ptr)
delete _ptr;
}
private:
T* _ptr;
};
int div()
{
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
if (b == 0)
throw invalid_argument("除0错误");
return a / b;
}
void Func()
{
SmartPtr<int> sp1(new int);
SmartPtr<int> sp2(new int);
cout << div() << endl;
}
int main()
{
try
{
Func();
}
catch (exception& e)
{
cout << e.what() << endl;
}
return 0;
}智能指针的原理
上述的SmartPtr还不能将其称为智能指针,因为它还不具有指针的行为。指针可以解引用,也可
以通过->去访问所指空间中的内容,因此:模板类中还得需要将* 、->重载下,才可让其像指针一样去使用。
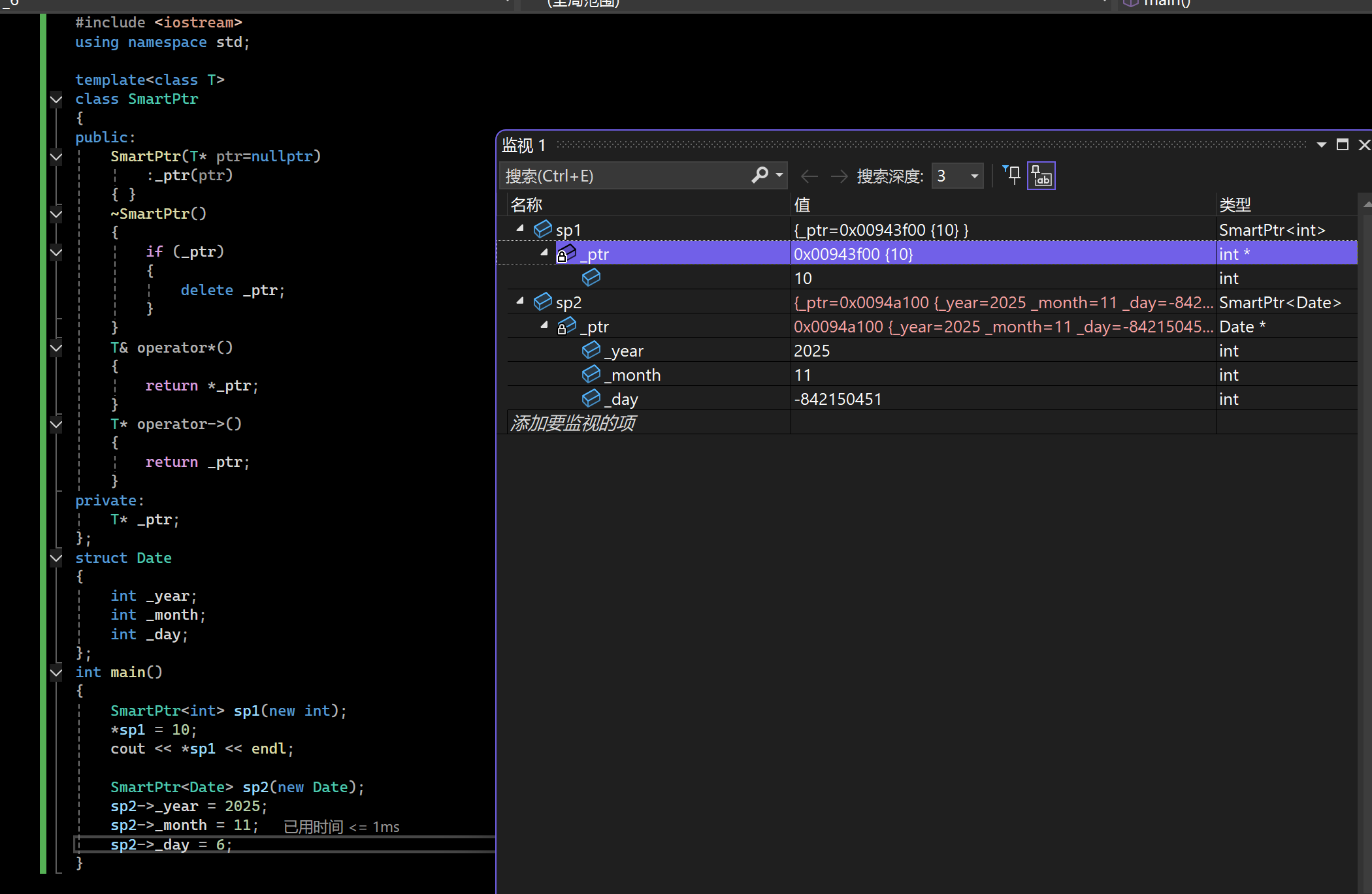
智能指针的原理总结:
1.RAII特性
2.重载operator*和operator->,具有像指针一样的行为。
std::auto_ptr
C++98版本的库中就提供了auto_ptr的智能指针。下面是auto_ptr的使用及问题。
实现原理:管理权转移的思想,下面简化模拟了一份Q::auto_ptr
cpp
namespace Q
{
template<class T>
class auto_ptr
{
public:
auto_ptr(T* ptr)
:_ptr(ptr)
{ }
auto_ptr(auto_ptr<T>& sp)//要修改,前面不能加const!
_ptr(sp._ptr)
{
sp._ptr = nullptr;
}
auto_ptr<T>& operator=(auto_ptr<T>& ap)
{
if (this != &ap)
{
if (_ptr)
{
delete _ptr;
}
_ptr = ap._ptr;
ap._ptr = nullptr;
}
return *this;
}
~auto_ptr()
{
if (_ptr)
{
cout << "~auto_ptr()" << endl;
delete _ptr;
}
}
T& operator*()
{
return *_ptr;
}
T* operator->()
{
return _ptr;
}
private:
T* _ptr;
};
}
/*int main()
{
std::auto_ptr<int> sp1(new int);
std::auto_ptr<int> sp2(sp1);
*sp2 = 6;
*sp1 = 5;//错误!
cout << *sp1 << endl;//错误!
cout << *sp2 << endl;
return 0;
}*/std::unique_ptr
C++11中开始提供靠谱的unique_ptr。
原理:简单粗暴的防拷贝。
cpp
namespace Q
{
template<class T>
class unique_ptr
{
public:
unique_ptr(T* ptr)
:_ptr(ptr)
{
}
~unique_ptr()
{
if (_ptr)
{
cout << "~unique_ptr()" << endl;
delete _ptr;
}
}
T& operator*()
{
return *_ptr;
}
T* operator->()
{
return _ptr;
}
unique_ptr(const unique_ptr<T>& sp)=delete;
unique_ptr<T>& operator=(const unique_ptr<T>& ap)=delete;
private:
T* _ptr;
};
}
int main()
{
Q::unique_ptr<int> p(new int(10));
cout << *p << endl;
}std::shard_ptr
C++11中开始提供更靠谱的并且支持拷贝的shared_ptr。
原理:通过引用计数的方式来实现多个shared_ptr对象之间共享资源。
1.shared_ptr在其内部,给每个资源 都维护了一份计数,用来记录该份资源被几个对象共享。
2.在对象被销毁时(也就是析构函数调用),说明自己不使用该资源了,对象的引用计数减一。
3.如果引用计数是0,说明是最后一个使用该资源的对象,必须释放该资源。
cpp
namespace Q
{
template<class T>
class shared_ptr
{
public:
shared_ptr(T* ptr=nullptr)
:_ptr(ptr)
,_pcount(new int(1))
{ }
~shared_ptr()
{
if (--(*_pcount) == 0)
{
cout << "delete:" << _ptr << endl;
delete _ptr;
delete _pcount;
}
}
T& operator*()
{
return *_ptr;
}
T* operator->()
{
return _ptr;
}
shared_ptr(const shared_ptr<T>& sp)
:_ptr(sp._ptr)
, _pcount(sp._pcount)
{
++(*_pcount);
}
// sp1 = sp5
// sp6 = sp6
// sp4 = sp5
shared_ptr<T>& operator=(const shared_ptr<T>& sp)
{
if (sp._ptr == _ptr)
{
return *this;
}
if (--(*_pcount) == 0)//这一步判断是何意味?
{
delete _ptr;
delete _pcount;
//在当前对象(this)被赋值为另一个 shared_ptr 之前,先减少原来所管理对象的引用计数。
//如果减少后引用计数变为 0,说明没有其它 shared_ptr 再指向这块内存,于是就要释放它
}
_ptr = sp._ptr;
_pcount = sp._pcount;
++(*_pcount);
return *this;
}
int use_count() const
{
return *_pcount;
}
T* get() const
{
return _ptr;
}
private:
T* _ptr;
int* _pcount;
};
template<class T>
class weak_ptr
{
public:
weak_ptr()
:_ptr(nullptr)
{ }
weak_ptr(const shared_ptr<T>& sp)
:_ptr(sp.get())
{ }
weak_ptr<T>& operator=(const shared_ptr<T>& sp)
{
_ptr = sp.get();
return *this;
}
T& operator*()
{
return *_ptr;
}
T* operator->()
{
return _ptr;
}
private:
T* _ptr;
};
}shared_ptr智能指针是线程安全的吗?
是的,引用计数的加减是加锁保护的。但是指向资源不是线程安全的。
std::shared_ptr的循环引用
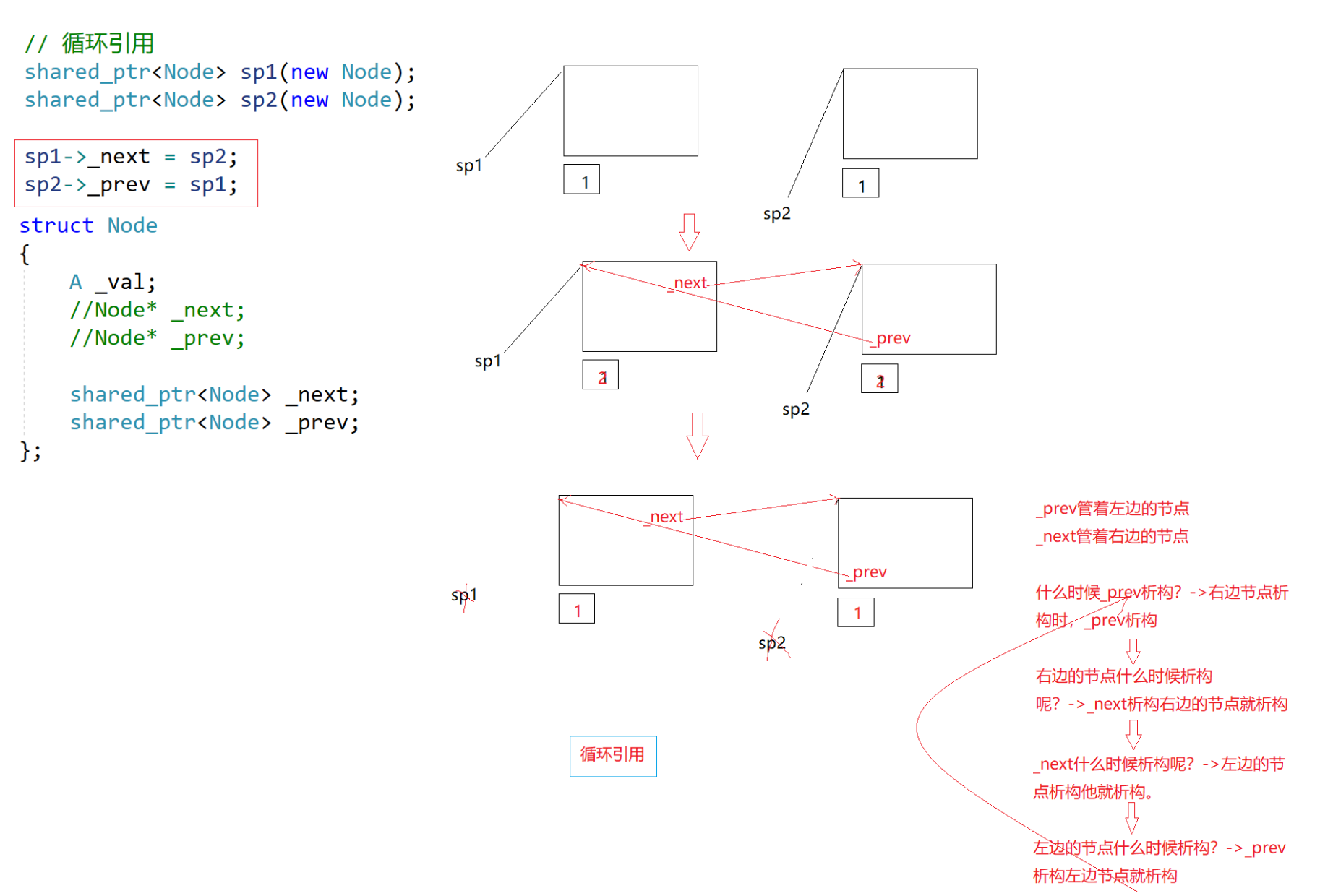
若不是new出来的对象如何通过智能指针管理呢?shared_ptr设计了一个删除器 来解决这
个问题(了解即可)
cpp
class A
{
public:
A(int a = 0)
:_a(a)
{
cout << "A(int a = 0)" << endl;
}
~A()
{
cout << this;
cout << "~A()" << endl;
}
private:
int _a;
};
// 仿函数的删除器
template<class T>
struct FreeFunc {
void operator()(T* ptr)
{
cout << "free:" << ptr << endl;
free(ptr);
}
};
template<class T>
struct DeleteArrayFunc {
void operator()(T* ptr)
{
cout << "delete[]" << ptr << endl;
delete[] ptr;
}
};
int main()
{
FreeFunc<int> freeFunc;
std::shared_ptr<int> sp1((int*)malloc(4), freeFunc);
//或:
std::shared_ptr<int> sp6((int*)malloc(sizeof(int)), FreeFunc<int>());
DeleteArrayFunc<int> deleteArrayFunc;
std::shared_ptr<int> sp2(new int[5], deleteArrayFunc);
std::shared_ptr<A> sp4(new A[10], [](A* p) {delete[] p; });
std::shared_ptr<FILE> sp5(fopen("test.txt", "w"), [](FILE* p)
{fclose(p); });
return 0;
}C++11和boost中智能指针的关系
