这个条款揭示了RAII设计中的一个关键权衡:如何在保持资源安全封装的同时,提供与现有API的兼容性。正确的原始资源访问设计是构建实用资源管理类的关键。
思维导图:原始资源访问的完整体系
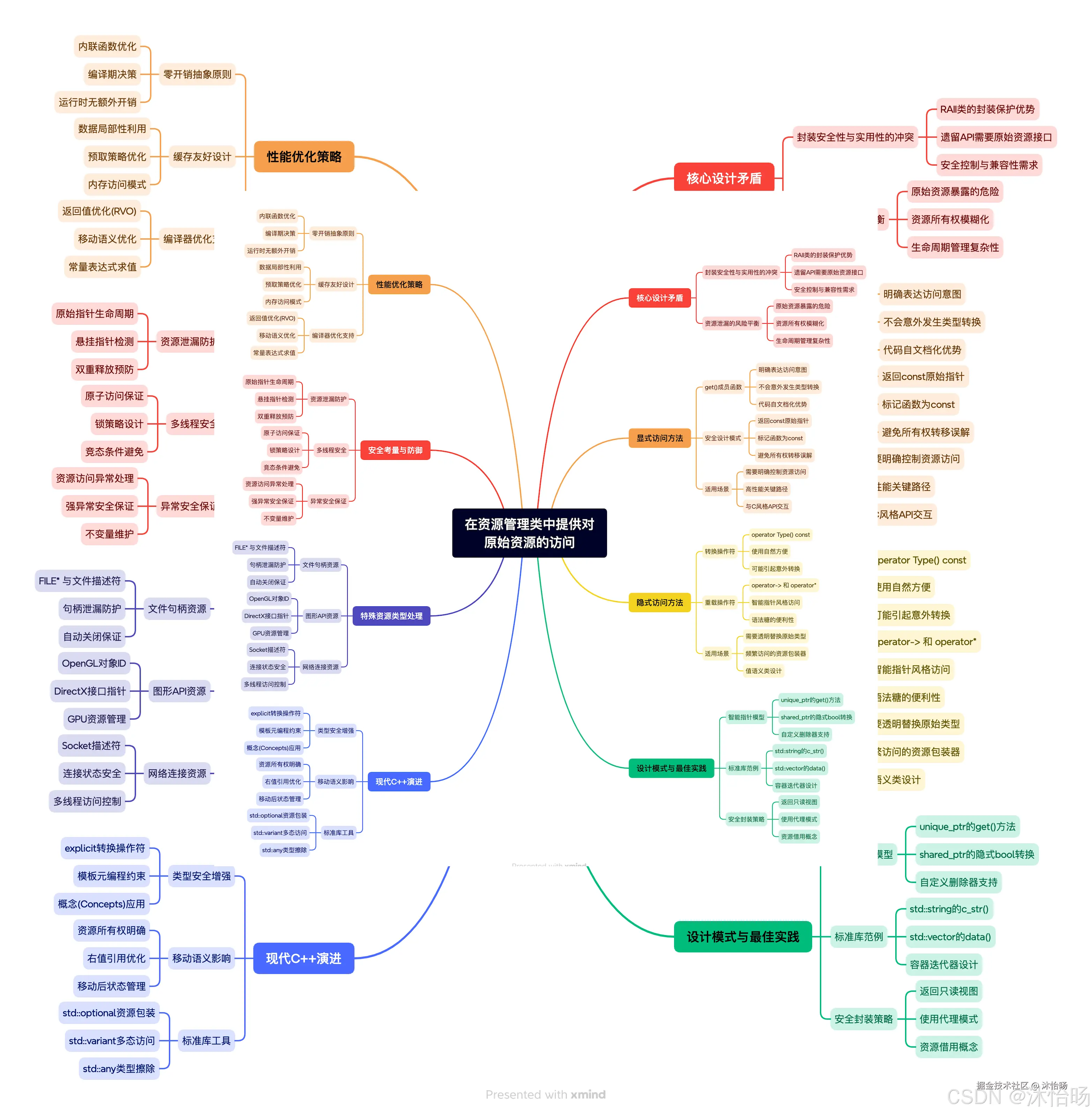
关键洞见与行动指南
必须遵守的核心原则:
- 提供原始资源访问:RAII类必须提供某种方式访问其管理的原始资源
- 明确设计选择:在显式访问和隐式访问之间做出明确的设计决策
- 保持安全性:原始资源访问不应破坏RAII类的资源安全保证
- 文档化访问语义:清晰说明资源访问的所有权和生命周期含义
现代C++开发建议:
- 优先使用显式访问 :默认提供
get()方法,明确表达访问意图 - 谨慎使用隐式转换:只在确实需要自然语法时提供隐式转换
- 使用explicit转换操作符:C++11的显式转换提供安全性和便利性的平衡
- 遵循标准库模式 :参考
std::unique_ptr、std::shared_ptr的设计
设计原则总结:
- 最小惊讶原则:资源访问行为应该符合程序员直觉
- 明确性优先:在安全性和便利性冲突时,优先选择安全性
- 一致性:在整个代码库中使用统一的资源访问模式
- 文档化:清晰记录资源访问的语义和约束
需要警惕的陷阱:
- 意外的资源泄漏:原始资源指针被误用导致资源泄漏
- 悬挂指针:RAII对象销毁后原始资源指针变成悬空指针
- 所有权混淆:调用者误以为获得了资源所有权
- 隐式转换的意外:意外的类型转换导致难以发现的bug
最终建议: 将原始资源访问视为RAII类设计的必要组成部分。培养"访问权限思维"------在设计每个资源管理类时都问自己:"这个类需要提供什么样的原始资源访问?显式还是隐式?如何保证访问的安全性?" 这种系统性的思考是构建实用且安全资源管理类的关键。
记住:在C++资源管理中,封装不是禁止访问,而是控制访问。 条款15教会我们的不仅是一组技术方案,更是封装哲学在实践中的平衡艺术。
深入解析:封装与兼容性的核心矛盾
1. 问题根源:RAII封装与遗留API的冲突
典型的资源管理类设计:
cpp
class Font {
private:
HFONT fontHandle; // 原始字体句柄
public:
explicit Font(const std::string& fontName, int size) {
// 创建字体资源
fontHandle = CreateFont(
size, 0, 0, 0, FW_NORMAL,
FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, DEFAULT_CHARSET,
OUT_DEFAULT_PRECIS, CLIP_DEFAULT_PRECIS,
DEFAULT_QUALITY, DEFAULT_PITCH,
fontName.c_str()
);
if (!fontHandle) {
throw std::runtime_error("无法创建字体: " + fontName);
}
std::cout << "创建字体: " << fontName << std::endl;
}
~Font() {
if (fontHandle) {
DeleteObject(fontHandle);
std::cout << "销毁字体" << std::endl;
}
}
// 问题:没有提供访问原始句柄的方法!
// 但很多Windows API需要HFONT参数...
};
void demonstrate_encapsulation_problem() {
Font myFont("Arial", 12);
// 假设我们需要调用这个Windows API:
// BOOL SelectObject(HDC hdc, HGDIOBJ hgdiobj);
// 但我们无法获取fontHandle来传递给SelectObject!
// HDC hdc = GetDC(NULL);
// SelectObject(hdc, myFont); // 错误:无法转换Font到HGDIOBJ
// 我们需要一种安全的方式来访问原始资源!
}与C风格API的兼容性问题:
cpp
// C风格的文件操作API
void legacyFileOperation(FILE* file) {
if (file) {
fputs("Hello from legacy API\n", file);
}
}
class ModernFile {
private:
std::FILE* file_;
std::string filename_;
public:
explicit ModernFile(const std::string& filename, const std::string& mode = "r")
: filename_(filename) {
file_ = std::fopen(filename.c_str(), mode.c_str());
if (!file_) {
throw std::runtime_error("无法打开文件: " + filename);
}
}
~ModernFile() {
if (file_) {
std::fclose(file_);
}
}
// 问题:如何让legacyFileOperation使用我们的ModernFile?
// legacyFileOperation(file_); // file_是private!
};解决方案:显式与隐式访问方法
1. 显式访问:get()成员函数
安全且明确的原始资源访问:
cpp
class SafeFont {
private:
HFONT fontHandle;
public:
explicit SafeFont(const std::string& fontName, int size) {
fontHandle = CreateFont(
size, 0, 0, 0, FW_NORMAL,
FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, DEFAULT_CHARSET,
OUT_DEFAULT_PRECIS, CLIP_DEFAULT_PRECIS,
DEFAULT_QUALITY, DEFAULT_PITCH,
fontName.c_str()
);
if (!fontHandle) {
throw std::runtime_error("无法创建字体: " + fontName);
}
}
~SafeFont() {
if (fontHandle) {
DeleteObject(fontHandle);
}
}
// 显式访问方法 - 安全且明确
HFONT get() const noexcept {
return fontHandle;
}
// 禁止拷贝(移动语义实现省略以简化示例)
SafeFont(const SafeFont&) = delete;
SafeFont& operator=(const SafeFont&) = delete;
};
void demonstrate_explicit_access() {
SafeFont font("Times New Roman", 14);
HDC hdc = GetDC(NULL);
// 显式调用get() - 明确表达访问原始资源的意图
SelectObject(hdc, font.get());
// 使用原始资源...
ReleaseDC(NULL, hdc);
// 优点:代码清晰表明我们在访问原始资源
// 缺点:需要显式调用get()
}现代文件类的显式访问设计:
cpp
class ExplicitFile {
private:
std::FILE* file_;
std::string filename_;
public:
explicit ExplicitFile(const std::string& filename, const std::string& mode = "r")
: filename_(filename) {
file_ = std::fopen(filename.c_str(), mode.c_str());
if (!file_) {
throw std::runtime_error("无法打开文件: " + filename);
}
}
~ExplicitFile() {
if (file_) {
std::fclose(file_);
}
}
// 显式访问原始FILE*
std::FILE* get() const noexcept {
return file_;
}
// 显式访问文件名
const std::string& filename() const noexcept {
return filename_;
}
// 显式判断有效性
bool is_open() const noexcept {
return file_ != nullptr;
}
// 现代C++:禁止拷贝,允许移动
ExplicitFile(const ExplicitFile&) = delete;
ExplicitFile& operator=(const ExplicitFile&) = delete;
ExplicitFile(ExplicitFile&& other) noexcept
: file_(other.file_), filename_(std::move(other.filename_)) {
other.file_ = nullptr;
}
ExplicitFile& operator=(ExplicitFile&& other) noexcept {
if (this != &other) {
if (file_) std::fclose(file_);
file_ = other.file_;
filename_ = std::move(other.filename_);
other.file_ = nullptr;
}
return *this;
}
};
void demonstrate_explicit_file_usage() {
ExplicitFile file("data.txt", "w");
// 与C风格API交互
legacyFileOperation(file.get()); // 显式访问
// 优点:明确表达意图,不会意外转换
// 缺点:需要显式调用get()
}2. 隐式访问:转换操作符
自然的类型转换接口:
cpp
class ImplicitFont {
private:
HFONT fontHandle;
public:
explicit ImplicitFont(const std::string& fontName, int size) {
fontHandle = CreateFont(
size, 0, 0, 0, FW_NORMAL,
FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, DEFAULT_CHARSET,
OUT_DEFAULT_PRECIS, CLIP_DEFAULT_PRECIS,
DEFAULT_QUALITY, DEFAULT_PITCH,
fontName.c_str()
);
if (!fontHandle) {
throw std::runtime_error("无法创建字体: " + fontName);
}
}
~ImplicitFont() {
if (fontHandle) {
DeleteObject(fontHandle);
}
}
// 隐式转换操作符 - 使用更方便但可能危险
operator HFONT() const noexcept {
return fontHandle;
}
// 也可以提供显式get()作为备选
HFONT get() const noexcept {
return fontHandle;
}
};
void demonstrate_implicit_access() {
ImplicitFont font("Courier New", 10);
HDC hdc = GetDC(NULL);
// 隐式转换 - 更自然的语法
SelectObject(hdc, font); // 自动调用operator HFONT()
ReleaseDC(NULL, hdc);
// 优点:使用方便,语法自然
// 缺点:可能发生意外的类型转换
}智能指针风格的隐式访问:
cpp
class SmartFile {
private:
std::FILE* file_;
std::string filename_;
public:
explicit SmartFile(const std::string& filename, const std::string& mode = "r")
: filename_(filename) {
file_ = std::fopen(filename.c_str(), mode.c_str());
if (!file_) {
throw std::runtime_error("无法打开文件: " + filename);
}
}
~SmartFile() {
if (file_) {
std::fclose(file_);
}
}
// 智能指针风格的访问 - operator->
std::FILE* operator->() const {
if (!file_) {
throw std::logic_error("文件未打开");
}
return file_;
}
// 解引用操作符 - operator*
std::FILE& operator*() const {
if (!file_) {
throw std::logic_error("文件未打开");
}
return *file_;
}
// 隐式bool转换(用于条件检查)
explicit operator bool() const noexcept {
return file_ != nullptr;
}
// 显式get()仍然提供
std::FILE* get() const noexcept {
return file_;
}
};
void demonstrate_smart_pointer_style() {
SmartFile file("config.txt", "r");
if (file) { // 使用operator bool()
// 使用operator->访问成员函数风格
char buffer[256];
file->fgets(buffer, sizeof(buffer));
// 使用operator*获得引用
std::rewind(*file);
// 仍然可以使用get()进行显式访问
legacyFileOperation(file.get());
}
}现代C++的安全增强
1. 显式转换操作符
C++11的显式转换安全:
cpp
class ExplicitConversionFont {
private:
HFONT fontHandle;
public:
explicit ExplicitConversionFont(const std::string& fontName, int size) {
fontHandle = CreateFont(
size, 0, 0, 0, FW_NORMAL,
FALSE, FALSE, FALSE, DEFAULT_CHARSET,
OUT_DEFAULT_PRECIS, CLIP_DEFAULT_PRECIS,
DEFAULT_QUALITY, DEFAULT_PITCH,
fontName.c_str()
);
if (!fontHandle) {
throw std::runtime_error("无法创建字体: " + fontName);
}
}
~ExplicitConversionFont() {
if (fontHandle) {
DeleteObject(fontHandle);
}
}
// C++11: 显式转换操作符 - 防止意外转换
explicit operator HFONT() const noexcept {
return fontHandle;
}
// 传统的get()方法仍然提供
HFONT get() const noexcept {
return fontHandle;
}
};
void demonstrate_explicit_conversion() {
ExplicitConversionFont font("Verdana", 16);
HDC hdc = GetDC(NULL);
// 必须显式转换 - 更安全!
SelectObject(hdc, static_cast<HFONT>(font));
// SelectObject(hdc, font); // 错误:不能隐式转换!
ReleaseDC(NULL, hdc);
// 显式转换提供了隐式访问的便利性,同时减少了意外转换的风险
}2. 模板化的安全访问
编译期安全检查:
cpp
#include <type_traits>
template<typename ResourceType>
class TypedResource {
private:
ResourceType resource_;
std::string resource_name_;
// 静态断言确保资源类型是指针或句柄
static_assert(std::is_pointer<ResourceType>::value ||
std::is_integral<ResourceType>::value,
"ResourceType必须是指针或整型句柄");
public:
explicit TypedResource(ResourceType resource, const std::string& name = "")
: resource_(resource), resource_name_(name) {}
~TypedResource() = default;
// 安全的显式访问
ResourceType get() const noexcept {
return resource_;
}
// 显式bool转换
explicit operator bool() const noexcept {
return resource_ != ResourceType{};
}
const std::string& name() const noexcept {
return resource_name_;
}
// 禁止拷贝,允许移动
TypedResource(const TypedResource&) = delete;
TypedResource& operator=(const TypedResource&) = delete;
TypedResource(TypedResource&& other) noexcept
: resource_(other.resource_), resource_name_(std::move(other.resource_name_)) {
other.resource_ = ResourceType{};
}
TypedResource& operator=(TypedResource&& other) noexcept {
if (this != &other) {
resource_ = other.resource_;
resource_name_ = std::move(other.resource_name_);
other.resource_ = ResourceType{};
}
return *this;
}
};
// 特化版本提供特定资源的语义
using FileHandle = TypedResource<std::FILE*>;
using SocketHandle = TypedResource<int>; // Unix socket descriptor
using WindowHandle = TypedResource<HWND>;
void demonstrate_typed_resource() {
// 编译期类型安全
FileHandle file(stdout, "标准输出");
if (file) {
fprintf(file.get(), "通过类型化资源访问\n");
}
// 明确的资源语义,编译期检查
}实战案例:复杂资源管理设计
案例1:数据库连接的安全访问
cpp
#include <memory>
#include <sql.h>
#include <sqlext.h>
class DatabaseConnection {
private:
SQLHENV environment_;
SQLHDBC connection_;
std::string connection_string_;
bool connected_;
void safeCleanup() noexcept {
if (connected_ && connection_) {
SQLDisconnect(connection_);
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_DBC, connection_);
connected_ = false;
}
if (environment_) {
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV, environment_);
}
}
public:
explicit DatabaseConnection(const std::string& connStr)
: environment_(nullptr), connection_(nullptr),
connection_string_(connStr), connected_(false) {
// 初始化ODBC环境
if (SQLAllocHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV, SQL_NULL_HANDLE, &environment_) != SQL_SUCCESS) {
throw std::runtime_error("无法分配ODBC环境");
}
if (SQLSetEnvAttr(environment_, SQL_ATTR_ODBC_VERSION,
(SQLPOINTER)SQL_OV_ODBC3, 0) != SQL_SUCCESS) {
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV, environment_);
throw std::runtime_error("无法设置ODBC版本");
}
// 分配连接句柄
if (SQLAllocHandle(SQL_HANDLE_DBC, environment_, &connection_) != SQL_SUCCESS) {
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV, environment_);
throw std::runtime_error("无法分配连接句柄");
}
// 建立连接
SQLCHAR connStrOut[1024];
SQLSMALLINT connStrOutLength;
SQLRETURN ret = SQLDriverConnect(
connection_, nullptr,
(SQLCHAR*)connection_string_.c_str(), SQL_NTS,
connStrOut, sizeof(connStrOut), &connStrOutLength,
SQL_DRIVER_COMPLETE
);
if (ret != SQL_SUCCESS && ret != SQL_SUCCESS_WITH_INFO) {
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_DBC, connection_);
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_ENV, environment_);
throw std::runtime_error("数据库连接失败");
}
connected_ = true;
std::cout << "数据库连接成功: " << connection_string_ << std::endl;
}
~DatabaseConnection() {
safeCleanup();
}
// 显式访问原始连接句柄
SQLHDBC get() const noexcept {
return connection_;
}
// 隐式转换到连接句柄
operator SQLHDBC() const noexcept {
return connection_;
}
// 获取连接信息
const std::string& connectionString() const noexcept {
return connection_string_;
}
bool isConnected() const noexcept {
return connected_;
}
// 执行SQL语句的便捷方法
void execute(const std::string& sql) {
SQLHSTMT statement;
if (SQLAllocHandle(SQL_HANDLE_STMT, connection_, &statement) != SQL_SUCCESS) {
throw std::runtime_error("无法分配语句句柄");
}
// RAII包装语句句柄
struct StatementDeleter {
void operator()(SQLHSTMT stmt) const {
SQLFreeHandle(SQL_HANDLE_STMT, stmt);
}
};
std::unique_ptr<std::remove_pointer_t<SQLHSTMT>, StatementDeleter> stmtGuard(statement);
if (SQLExecDirect(statement, (SQLCHAR*)sql.c_str(), SQL_NTS) != SQL_SUCCESS) {
throw std::runtime_error("SQL执行失败: " + sql);
}
std::cout << "执行SQL: " << sql << std::endl;
}
// 禁止拷贝
DatabaseConnection(const DatabaseConnection&) = delete;
DatabaseConnection& operator=(const DatabaseConnection&) = delete;
// 允许移动
DatabaseConnection(DatabaseConnection&& other) noexcept
: environment_(other.environment_),
connection_(other.connection_),
connection_string_(std::move(other.connection_string_)),
connected_(other.connected_) {
other.environment_ = nullptr;
other.connection_ = nullptr;
other.connected_ = false;
}
DatabaseConnection& operator=(DatabaseConnection&& other) noexcept {
if (this != &other) {
safeCleanup();
environment_ = other.environment_;
connection_ = other.connection_;
connection_string_ = std::move(other.connection_string_);
connected_ = other.connected_;
other.environment_ = nullptr;
other.connection_ = nullptr;
other.connected_ = false;
}
return *this;
}
};
void demonstrate_database_access() {
try {
DatabaseConnection conn("DSN=MyDatabase;UID=user;PWD=pass");
// 使用显式访问
SQLHDBC rawConnection = conn.get();
// 可以传递给需要原始连接句柄的ODBC API
// 使用隐式转换
// 某些API可能直接接受SQLHDBC,这时隐式转换更方便
// 使用高级接口
conn.execute("CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS Test (ID INT, Name VARCHAR(50))");
conn.execute("INSERT INTO Test VALUES (1, 'Example')");
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
std::cout << "数据库错误: " << e.what() << std::endl;
}
}案例2:OpenGL资源管理
cpp
#include <vector>
#include <stdexcept>
class OpenGLTexture {
private:
unsigned int textureID_;
int width_, height_;
std::string name_;
void generateTexture() {
glGenTextures(1, &textureID_);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureID_);
// 设置纹理参数
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
// 分配纹理内存
std::vector<unsigned char> emptyData(width_ * height_ * 4, 0);
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGBA, width_, height_, 0,
GL_RGBA, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, emptyData.data());
std::cout << "创建OpenGL纹理: ID=" << textureID_
<< " " << width_ << "x" << height_ << std::endl;
}
public:
OpenGLTexture(int width, int height, const std::string& name = "")
: width_(width), height_(height), name_(name) {
generateTexture();
}
~OpenGLTexture() {
if (textureID_ != 0) {
glDeleteTextures(1, &textureID_);
std::cout << "删除OpenGL纹理: ID=" << textureID_ << std::endl;
}
}
// 显式访问纹理ID
unsigned int id() const noexcept {
return textureID_;
}
// 隐式转换到纹理ID
operator unsigned int() const noexcept {
return textureID_;
}
// 绑定纹理的便捷方法
void bind() const {
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureID_);
}
// 设置纹理数据
void setData(const std::vector<unsigned char>& data, GLenum format = GL_RGBA) {
if (data.size() != static_cast<size_t>(width_ * height_ * 4)) {
throw std::invalid_argument("纹理数据大小不匹配");
}
bind();
glTexSubImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, 0, 0, width_, height_,
format, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, data.data());
}
// 获取纹理信息
std::pair<int, int> size() const noexcept {
return {width_, height_};
}
const std::string& name() const noexcept {
return name_;
}
// 移动语义支持
OpenGLTexture(OpenGLTexture&& other) noexcept
: textureID_(other.textureID_),
width_(other.width_),
height_(other.height_),
name_(std::move(other.name_)) {
other.textureID_ = 0;
other.width_ = other.height_ = 0;
}
OpenGLTexture& operator=(OpenGLTexture&& other) noexcept {
if (this != &other) {
if (textureID_ != 0) {
glDeleteTextures(1, &textureID_);
}
textureID_ = other.textureID_;
width_ = other.width_;
height_ = other.height_;
name_ = std::move(other.name_);
other.textureID_ = 0;
other.width_ = other.height_ = 0;
}
return *this;
}
// 禁止拷贝
OpenGLTexture(const OpenGLTexture&) = delete;
OpenGLTexture& operator=(const OpenGLTexture&) = delete;
};
class TextureManager {
private:
std::vector<OpenGLTexture> textures_;
public:
OpenGLTexture& createTexture(int width, int height, const std::string& name = "") {
textures_.emplace_back(width, height, name);
return textures_.back();
}
OpenGLTexture* findTexture(const std::string& name) {
for (auto& texture : textures_) {
if (texture.name() == name) {
return &texture;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
// 允许直接传递纹理ID给OpenGL API
void useTexture(const OpenGLTexture& texture) {
// 利用隐式转换
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture); // 自动转换为unsigned int
}
void useTextureById(unsigned int textureId) {
// 显式使用纹理ID
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureId);
}
};
void demonstrate_opengl_textures() {
TextureManager manager;
// 创建纹理
auto& diffuseMap = manager.createTexture(256, 256, "diffuse_map");
auto& normalMap = manager.createTexture(128, 128, "normal_map");
// 使用隐式转换访问
manager.useTexture(diffuseMap); // 方便!
// 使用显式访问
unsigned int textureId = normalMap.id();
manager.useTextureById(textureId); // 明确!
// 与需要纹理ID的OpenGL API交互
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, diffuseMap); // 隐式转换
// 或者显式访问
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE1);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, normalMap.id()); // 显式访问
}