上期分享了使用大模型+LangExtract从真实业务场景的复杂文本中提取Key-Value结构的结构化数据,K-V结构相对比较简单,容易理解。
本期将升级难度,从复杂文本中提取表格列表类型数据。
业务需求
依然是上期真实的业务场景:业务方需要给企业的涉害劳动者(工人)创建档案,劳动者的一些基本信息需要从《职业健康检查表》中获取(这个"检查表"是其他体检机构提供的,不是业务方自己的),形成结构化数据并存储下来,然后建立劳动者的个人档案。"检查表"如下图所示(所有信息均已做脱敏处理)
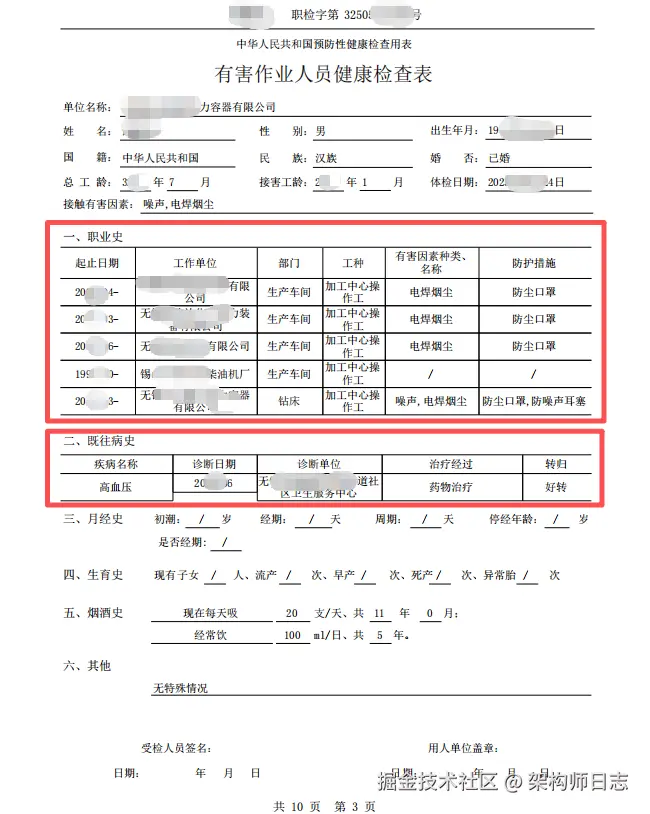
需要提取的内容不但有K-V对结构的数据(上期已给出提取示例,详见:LangExtract实战第二弹,还要提取职业史 和既往病史数据。
从职业史中要提取的信息有以下字段:
- 起止日期
- 工作单位
- 部门
- 工种
- 有害因素种类、名称
- 防护措施
从既往病史中要提取的信息有以下字段:
- 疾病名称
- 诊断日期
- 诊断单位
- 治疗经过
- 转归
从截图中可以看到,职业史 和既往病史 是一个Table,即list数据结构。 而lx.data.Extraction的两个入参extraction_class和extraction_text只支持字符串类型,想要提取如list或者JSON数据结构的数据,就力不从心了。
解决方案
不过不用担心,lx.data.Extraction还有一个参数:attributes,我们可以使用这个参数来帮助提取list数据。
接下来我们看一下github上的源码,点击链接去github查看:
python
@dataclasses.dataclass(init=False)
class Extraction:
"""Represents an extraction extracted from text.
This class encapsulates an extraction's characteristics and its position
within the source text. It can represent a diverse range of information for
NLP information extraction tasks.
Attributes:
extraction_class: The class of the extraction.
extraction_text: The text of the extraction.
char_interval: The character interval of the extraction in the original
text.
alignment_status: The alignment status of the extraction.
extraction_index: The index of the extraction in the list of extractions.
group_index: The index of the group the extraction belongs to.
description: A description of the extraction.
attributes: A list of attributes of the extraction.
token_interval: The token interval of the extraction.
"""
extraction_class: str
extraction_text: str
char_interval: CharInterval | None = None
alignment_status: AlignmentStatus | None = None
extraction_index: int | None = None
group_index: int | None = None
description: str | None = None
attributes: dict[str, str | list[str]] | None = None
_token_interval: tokenizer.TokenInterval | None = dataclasses.field(
default=None, repr=False, compare=False
)可以看到attributes 的描述:A list of attributes of the extraction.
以及attributes 的类型定义:attributes: dict[str, str | list[str]] | None = None,是一个字典类型(dict),其中:
- 键(key) 的类型是
str(字符串) - 值(value) 的类型可以是:
str(字符串)- 或
list[str](字符串列表)
因此我们可以借助attributes属性来提取复杂类型的数据结构,比如list或者json。
处理流程
处理流程依然是文档、图片转成markdown,然后通过LangExtract提取结构化数据。
有了Markdown文档之后,就可以从文档里提取关键信息了。
源码
由于数据涉及敏感信息,原始的PDF我就不上传了。我把通过MinerU转换成的Markdown上传到这里下载(为了避免隐私数据泄露,已做混淆处理),大家可以下载下来,然后运行下面代码。
python
from __future__ import annotations
import textwrap
import langextract as lx
import os
import re
import logging
import re
import ftfy
import json
# # 配置日志:设置为 DEBUG 级别
# logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG)
# # 获取 LangExtract 的 logger
# logger = logging.getLogger("langextract")
# logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
_TRANSLATE = str.maketrans(
{
0x2022: "*",
0x25CF: "*",
0x27A1: "->",
0xF0E0: "->",
0x2192: "->",
0x2190: "<-",
0x00D7: "x",
0x2191: "up",
0x2642: "male",
0x2640: "female",
0x2010: "-",
0x2013: "-",
0x2014: "-",
0x00A0: " ",
}
)
_WS = re.compile(r"[ \t]+")
_BLANKS = re.compile(r"\n\s*\n\s*\n+")
# Structure normalization patterns
_BEGIN = re.compile(r"---\s*BEGIN [^-]+---\n*", re.I)
_END = re.compile(r"\n*---\s*END [^-]+---\s*", re.I)
_HEADER = re.compile(r"\*{3}\s*([^*]+?)\s*\*{3}", re.I)
_BULLET_HDR = re.compile(r"^[ \t]*[\*\u2022\u25CF-]+\s*", re.M)
_ENUM = re.compile(r"^[ \t]*(\d+)[\)\.][ \t]+", re.M)
def sanitize_text(text: str) -> str:
"""Sanitizes Unicode characters and normalizes whitespace.
Applies ftfy text repair, translates problematic Unicode symbols to ASCII
equivalents, normalizes whitespace, and removes excessive blank lines.
Args:
text: The input text to sanitize.
Returns:
Sanitized text with Unicode issues resolved and whitespace normalized.
"""
out = ftfy.fix_text(text, remove_control_chars=True, normalization="NFC")
out = out.translate(_TRANSLATE)
out = _WS.sub(" ", out)
out = out.replace("\r\n", "\n").replace("\r", "\n")
out = _BLANKS.sub("\n\n", out)
return out.strip()
def normalize_structure(text: str) -> str:
"""Normalizes structural elements in radiology reports.
Removes report wrappers, converts asterisk headers to colon format,
removes bullet prefixes, and standardizes enumerations.
Args:
text: The input text to normalize.
Returns:
Text with structural elements normalized for consistent formatting.
"""
text = _BEGIN.sub("", text)
text = _END.sub("", text)
text = _HEADER.sub(lambda m: f"{m.group(1).strip()}:", text)
text = _BULLET_HDR.sub("", text)
text = _ENUM.sub(lambda m: f"{m.group(1)}. ", text)
return text.strip()
def preprocess_report(raw: str) -> str:
"""Preprocesses radiology reports with sanitization and normalization.
Combines Unicode sanitization and structural normalization to prepare
radiology reports for downstream processing. This is the main entry point
for text preprocessing.
Args:
raw: The raw radiology report text.
Returns:
Preprocessed text ready for structured extraction.
"""
return normalize_structure(sanitize_text(raw))
def strip_html_tags(text: str) -> str:
clean = re.sub(r'<[^>]+>', '', text) # 删除所有HTML标签
return clean
# 1. 读取本地 Markdown 文件
with open("readme.md", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
text = f.read()
"""
查找职业史的demo
"""
sales_text = text
sales_text = strip_html_tags(sales_text)
sales_text = preprocess_report(sales_text)
print(sales_text)
prompt = textwrap.dedent("""\
从这份检测报告中提取职业史列表(如果有),则返回职业史列表,列表中的每一个元素包含:
- 起止日期
- 工作单位
- 部门
- 工种
- 有害因素种类、名称
- 防护措施
重要提示:extraction_text 必须取自原文,按照顺序提取字段,如果全部字段都提取到值了,就停止继续提取,避免被覆盖掉。另外,要注意的是,文本有可能包含HTML标签或者unicode字符,移除这些标签或者unicode字符,并且提取的内容里也不应该有HTML标签或者unicode字符。
另外,不需要提取例子中的信息,忽略掉,不要返回。
""")
"""
思考:是否有必要将职业史、既往病史都放在同一个例子中提取出来?
放在一起的好处:一次完成,省算力
分开的好处:单一自责原则,各干各的事情,好维护。
既然是demo,先分开写,然后再考虑合并的,这样有问题方便排查。
"""
examples = [
lx.data.ExampleData(
text="""
# 一、职业史
<table><tr><td>起止日期</td><td>工作单位</td><td>部门</td><td>工种</td><td>有害因素种类、名称</td><td>防护措施</td></tr><tr><td>2000.04-</td><td>无锡南泉压力容器有限公司</td><td>生产车间</td><td>加工中心操作工</td><td>电焊烟尘</td><td>防尘口罩</td></tr><tr><td>2011.03-</td><td>无锡科伦达化工热力装备有限公司</td><td>生产车间</td><td>加工中心操作工</td><td>电焊烟尘</td><td>防尘口罩</td></tr><tr><td>2016.06-</td><td>无锡明燕装备有限公司</td><td>生产车间</td><td>加工中心操作工</td><td>电焊烟尘</td><td>防尘口罩</td></tr><tr><td>1992.10-</td><td>锡山市洛社某柴油机厂</td><td>生产车间</td><td>加工中心操作工</td><td>/</td><td>/</td></tr><tr><td>2024.03-</td><td>无锡汇丰锅炉压力容器有限公司</td><td>钻床</td><td>加工中心操作工</td><td>噪声,电焊烟尘</td><td>防尘口罩,防噪声耳塞</td></tr></table>
""",
extractions=[
lx.data.Extraction(extraction_class="职业史", extraction_text="职业史信息提取",
attributes={
"职业史":[
{"起止日期":"1900.04-", "工作单位":"苏州南泉压力容器有限公司", "部门":"组装车间", "工种":"生产中心操作工", "有害因素种类、名称":"放射、粉尘", "防护措施":"防护口罩"},
{"起止日期":"1911.03-", "工作单位":"苏州科伦达化工热力装备有限公司", "部门":"配货车间", "工种":"生产中心操作工", "有害因素种类、名称":"放射", "防护措施":"防护口罩"},
{"起止日期":"1916.06-", "工作单位":"苏州明燕装备有限公司", "部门":"加工车间", "工种":"生产中心操作工", "有害因素种类、名称":"粉尘", "防护措施":"防护口罩"},
{"起止日期":"1892.10-", "工作单位":"太仓市洛社某柴油机厂", "部门":"组装车间", "工种":"生产中心操作工", "有害因素种类、名称":"噪声", "防护措施":"防护耳塞"},
{"起止日期":"1924.03-", "工作单位":"苏州汇丰锅炉压力容器有限公司", "部门":"冲床", "工种":"生产中心操作工", "有害因素种类、名称":"放射、烟尘", "防护措施":"工业级防护口罩,防护耳塞"}
]
})
]
),
]
"""
这个例子使用qwen/qwen3-30b-a3b模型,还是比较稳定的
"""
model_config = lx.factory.ModelConfig(
model_id="qwen/qwen3-30b-a3b",
provider="OpenAILanguageModel",
provider_kwargs={
"base_url": "https://platform.aitools.cfd/api/v1", # 这里的不能使用下面的后缀,要用base_url
#"model_url": "https://platform.aitools.cfd/api/v1/chat/completions",
# "format_type": lx.data.FormatType.JSON,
"temperature": 0.1,
"api_key": "sk-b891a5d021d4**********af0a781",
"max_workers": 50,
},
)
print(lx.providers.router.list_providers())
model = lx.factory.create_model(
config=model_config,
)
result = lx.extract(
text_or_documents=sales_text,
prompt_description=prompt,
examples=examples,
model=model,
fence_output=True,
use_schema_constraints=False,
# debug=True
extraction_passes=1
)
# 步骤4:处理结果
if result.extractions:
extracted_metadata = {}
extracted_metadata_attributes = {}
for ext in result.extractions:
# 如果 key 已存在就跳过
if ext.extraction_class not in extracted_metadata:
extracted_metadata[ext.extraction_class] = ext.extraction_text
# extracted_metadata_attributes[ext.extraction_class] = ext.attributes
# 用下面的方式,不需要写额外的逻辑了,直接取出
extracted_metadata_attributes[ext.extraction_class] = ext.attributes[ext.extraction_class]
attributes_json = json.dumps(extracted_metadata_attributes, ensure_ascii=False)
print("attributes_json---->" + attributes_json)
else:
print("未能提取出任何信息。")
# 步骤5 (可选): 可视化调试
lx.io.save_annotated_documents([result], output_name="extraction_results.jsonl", output_dir=".")
html_content = lx.visualize("extraction_results.jsonl")
with open("visualization.html","w", encoding="utf-8")as f:
f.write(html_content)上述代码中用到的openai的api_key已经做了脱敏处理,大家可以参考这篇文章的指引免费大模型API,完美兼容OpenAI接口(零门槛,免注册),自行申请api_key。
运行结果
代码运行后打印的JSON数据结果如下:
JSON
{
"职业史": [
{
"起止日期": "2000.05-",
"工作单位": "苏州北海压力容器有限公司",
"部门": "生产车间",
"工种": "加工中心操作工",
"有害因素种类、名称": "电焊烟尘",
"防护措施": "防尘口罩"
},
{
"起止日期": "2011.05-",
"工作单位": "苏州科罗拉多化工热力装备有限公司",
"部门": "生产车间",
"工种": "加工中心操作工",
"有害因素种类、名称": "电焊烟尘",
"防护措施": "防尘口罩"
},
{
"起止日期": "2016.07-",
"工作单位": "苏州黑凤装备有限公司",
"部门": "生产车间",
"工种": "加工中心操作工",
"有害因素种类、名称": "电焊烟尘",
"防护措施": "防尘口罩"
},
{
"起止日期": "1992.08-",
"工作单位": "太长市湖海某柴油机厂",
"部门": "生产车间",
"工种": "加工中心操作工",
"有害因素种类、名称": "",
"防护措施": ""
},
{
"起止日期": "2024.03-",
"工作单位": "苏州龙华飞鸟锅炉压力容器有限公司",
"部门": "钻床",
"工种": "加工中心操作工",
"有害因素种类、名称": "噪声,电焊烟尘",
"防护措施": "防尘口罩,防噪声耳塞"
}
]
}完美搞定!
总结
LangExtract实际上是充分利用了大模型的few-shot(少样本学习和推理能力),只给她一个简单的例子,就可以让他准确识别你的意图并提取出你想要的数据。
另外,LangExtract不仅可以用于从复杂非结构化文本中提取结构化数据,还可以对非结构化数据进行归类、关系识别、打标签等操作,这些在进行高质量数据集建设的时候很有帮助。
本人会不定期将研究成果发布出来,与大家进行交流,共同提高。