本项目基于 TensorFlow 构建了一个生成对抗网络(GAN),用于生成逼真的糖尿病视网膜病变(DR)图像。该 GAN 包含一个基于残差网络(ResNet)的生成器(Generator)和判别器(Discriminator)。
1. 数据集
- 来源:Kaggle 糖尿病视网膜病变数据集
- 结构:
Go
/diabetic-retinopathy/
0/ -> 健康眼(无病变)
1/ -> 轻度糖尿病视网膜病变(mild DR)
2/ -> 中度糖尿病视网膜病变(moderate DR)
3/ -> 重度糖尿病视网膜病变(severe DR)
4/ -> 增殖性糖尿病视网膜病变(proliferative DR)- 划分比例:60% 训练集、20% 验证集、20% 测试集
- 变量:训练集路径(train_paths)、训练集标签(train_labels)、验证集路径(val_paths)、验证集标签(val_labels)、测试集路径(test_paths)、测试集标签(test_labels)
- 图像预处理:调整尺寸为 128×128×3(宽 × 高 × 通道数),并归一化至 [-1, 1] 区间
2. Preprocessing
Go
def load_image(image_path):
img = tf.io.read_file(image_path)
img = tf.image.decode_jpeg(img, channels=3)
img = tf.image.resize(img, IMG_SIZE)
img = (tf.cast(img, tf.float32) - 127.5) / 127.5
return img
train_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(train_paths)
train_dataset = train_dataset.map(load_image, num_parallel_calls=tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
train_dataset = train_dataset.shuffle(BUFFER_SIZE).batch(BATCH_SIZE).prefetch(tf.data.AUTOTUNE)3. GAN 架构
-
生成器(ResNet 风格) 输入随机噪声向量(噪声维度 NOISE_DIM = 100),通过转置卷积(Conv2DTranspose)+ 批归一化(BatchNorm)+ 带泄漏的 ReLU 激活函数(LeakyReLU)进行上采样,最终使用 tanh 激活函数输出 128×128×3 的图像。代码定义:
generator = make_generator_model() -
判别器(ResNet 风格) 输入 128×128×3 的图像,通过残差块(Residual Blocks)+ 平均池化(AveragePooling2D)进行下采样,最终使用 sigmoid 激活函数输出单个值(表示图像为真实 / 伪造的概率)。代码定义:
discriminator = build_discriminator(img_shape=(128,128,3))
4. 损失函数与优化器
Go
cross_entropy = tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True)
generator_optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(1e-4, beta_1=0.5)
discriminator_optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(1e-4, beta_1=0.5)5. Training Step
@tf.function
def train_step(images):
noise = tf.random.normal([BATCH_SIZE, NOISE_DIM])
with tf.GradientTape() as gen_tape, tf.GradientTape() as disc_tape:
generated_images = generator(noise, training=True)
real_output = discriminator(images, training=True)
fake_output = discriminator(generated_images, training=True)
gen_loss = cross_entropy(tf.ones_like(fake_output), fake_output)
real_loss = cross_entropy(tf.ones_like(real_output), real_output)
fake_loss = cross_entropy(tf.zeros_like(fake_output), fake_output)
disc_loss = (real_loss + fake_loss) / 2
gradients_of_generator = gen_tape.gradient(gen_loss, generator.trainable_variables)
gradients_of_discriminator = disc_tape.gradient(disc_loss, discriminator.trainable_variables)
generator_optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients_of_generator, generator.trainable_variables))
discriminator_optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients_of_discriminator, discriminator.trainable_variables))
return gen_loss, disc_loss6. Training Loop
seed = tf.random.normal([NUM_EXAMPLES, NOISE_DIM])
for epoch in range(1, EPOCHS + 1):
for image_batch in train_dataset:
gen_loss, disc_loss = train_step(image_batch)
print(f"Epoch {epoch}, Generator Loss: {gen_loss:.4f}, Discriminator Loss: {disc_loss:.4f}")
generate_and_save_images(generator, epoch, seed)7. Visualization
-
Generated images: after each epoch
-
Discriminator confidence: green = real, red = fake
preds = discriminator(fake_images, training=False).numpy()
pred_value = preds[i][0]
color = 'green' if pred_value > 0.5 else 'red'
8. Testing / Evaluation
- GANs do not have "accuracy" like classifiers
- Check visual quality of generated images
- Discriminator confidence (0--1) for generated images
- Optionally compute FID (Fréchet Inception Distance) for quantitative evaluation
Note: You can adjust IMG_SIZE, BATCH_SIZE, and NOISE_DIM according to GPU capacity.
Go
Needed Library¶
import os ,glob
import random
import warnings
import numpy as np # linear algebra
import pandas as pd # data processing
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from PIL import Image
from IPython.display import Image
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
from tensorflow.keras.models import Model
from sklearn.utils import shuffle
from tensorflow.keras import layers
from tensorflow.keras.utils import plot_model
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, GlobalAveragePooling2D, Dropout
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing import image
print("Library Called ")
2025-10-18 20:03:31.002983: E external/local_xla/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_fft.cc:477] Unable to register cuFFT factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuFFT when one has already been registered
WARNING: All log messages before absl::InitializeLog() is called are written to STDERR
E0000 00:00:1760817811.235525 37 cuda_dnn.cc:8310] Unable to register cuDNN factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuDNN when one has already been registered
E0000 00:00:1760817811.301397 37 cuda_blas.cc:1418] Unable to register cuBLAS factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuBLAS when one has already been registered
Library Called
Split Data & Create Class
# Path of Data File
path='/kaggle/input/diabetic-retinopathy'
if not os.path.exists(path):
print("Dataset folder not found at:", path)
print("Download and extract the Kaggle dataset to that path.")
raise SystemExit(1)
#discover classes and image paths
class_dirs = sorted([d for d in os.listdir(path) if os.path.isdir(os.path.join(path, d))])
if not class_dirs:
print("No class subfolders found. Expect: data/diabetic_retinopathy/<class>/*.jpg")
raise SystemExit(1)
print("Found classes:", class_dirs)
# List after split (images , Labels)
image_paths = []
labels = []
for idx, cls in enumerate(class_dirs):
files = glob.glob(os.path.join(path, cls, "*"))
files = [f for f in files if os.path.splitext(f)[1].lower() in (".jpg", ".jpeg", ".png")]
for f in files:
image_paths.append(f)
labels.append(idx)
print("Total images:", len(image_paths))
if len(image_paths) == 0:
print("No images found - check paths.")
raise SystemExit(1)
#Combination and Random distribution
combined=list(zip(image_paths,labels))
random.seed(42)
random.shuffle(combined)
image_paths,labels = zip(*combined)
image_paths=list(image_paths)
labels=list(labels)
n =len(image_paths)
# ٍSplitting Fractions
train_frac = 0.60
val_frac = 0.20
n_train = int(n* train_frac)
n_val = int(n*val_frac)
n_test = n - n_train - n_val
train_paths = image_paths[:n_train]
train_labels =labels[:n_train]
val_paths = image_paths[n_train:n_train+n_val]
val_labels = labels[n_train:n_train+n_val]
test_paths = image_paths[n_train+n_val:]
test_labels = labels[n_train+n_val:]
print("Split sizes -> train:", len(train_paths), "val:", len(val_paths), "test:", len(test_paths))
dist = pd.DataFrame({
"train": pd.Series(train_labels).value_counts().sort_index(),
"val": pd.Series(val_labels).value_counts().sort_index(),
"test": pd.Series(test_labels).value_counts().sort_index()
}).fillna(0).astype(int)
print("\nClass distribution (by index):\n", dist)
Found classes: ['Healthy', 'Mild DR', 'Moderate DR', 'Proliferate DR', 'Severe DR']
Total images: 2750
Split sizes -> train: 1650 val: 550 test: 550
Class distribution (by index):
train val test
0 594 200 206
1 212 77 81
2 547 183 170
3 181 55 54
4 116 35 39
Parameters Gan Model
# Parameters
BUFFER_SIZE = 60000
BATCH_SIZE = 128
NOISE_DIM = 100
# Hyperparameters
LATENT_DIM = 100
EPOCHS = 80
NUM_EXAMPLES = 16
IMG_SIZE = (128, 128)
Convert them into a TensorFlow dataset
def load_image(image_path):
img = tf.io.read_file(image_path)
img = tf.image.decode_jpeg(img, channels=3)
img = tf.image.resize(img, IMG_SIZE)
img = (tf.cast(img, tf.float32) - 127.5) / 127.5 # Normalize [-1,1]
return img
Building PipeLine
# Build tf.data pipeline correctly
train_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(train_paths)
train_dataset = train_dataset.map(load_image, num_parallel_calls=tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
train_dataset = train_dataset.shuffle(BUFFER_SIZE).batch(BATCH_SIZE).prefetch(tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
val_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(val_paths)
val_dataset = val_dataset.map(load_image, num_parallel_calls=tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
val_dataset = val_dataset.batch(BATCH_SIZE).prefetch(tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
test_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(test_paths)
test_dataset = test_dataset.map(load_image, num_parallel_calls=tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
test_dataset = test_dataset.batch(BATCH_SIZE)
I0000 00:00:1760817824.458397 37 gpu_device.cc:2022] Created device /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:0 with 13942 MB memory: -> device: 0, name: Tesla T4, pci bus id: 0000:00:04.0, compute capability: 7.5
I0000 00:00:1760817824.459131 37 gpu_device.cc:2022] Created device /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:1 with 13942 MB memory: -> device: 1, name: Tesla T4, pci bus id: 0000:00:05.0, compute capability: 7.5
for images in train_dataset.take(1): # take one batch
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
for i in range(9):
ax = plt.subplot(3, 3, i + 1)
plt.imshow((images[i] * 127.5 + 127.5).numpy().astype("uint8"))
plt.axis("off")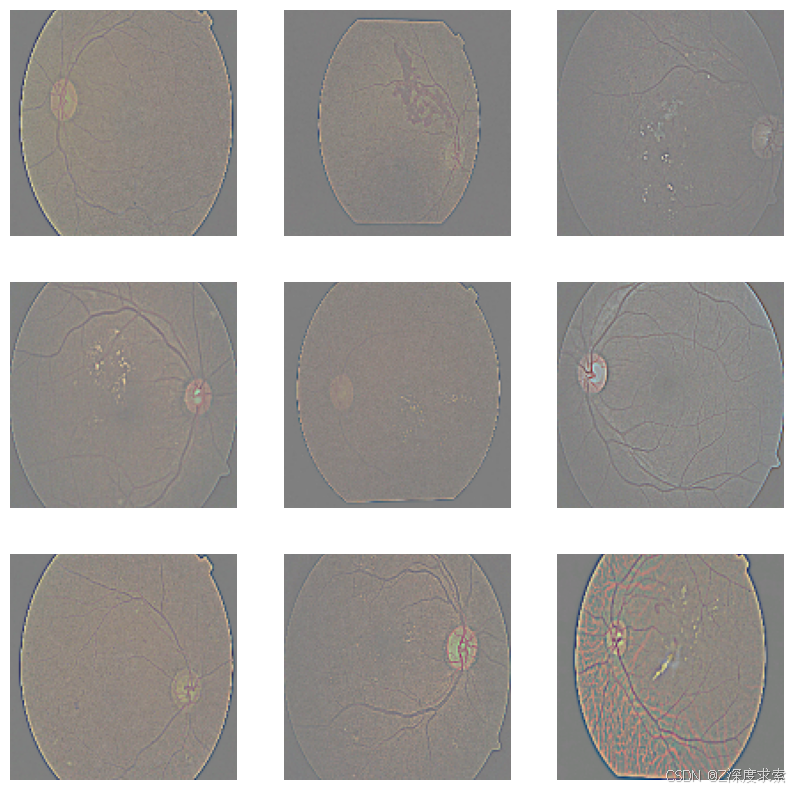
构建生成器 ¶
构建生成器有两种方案(基于残差网络(ResNet)或从零搭建生成器),两者的差异如下表所示:
| 概念 | DCGAN 生成器(你的代码) | 基于 ResNet 的生成器(我的代码) |
|---|---|---|
| 架构类型 | 转置卷积层(Conv2DTranspose)的顺序堆叠 | 带跳跃连接(skip connections)的残差块(Residual blocks) |
| 数据流 | 简单的上采样卷积堆叠 | 每个块学习残差特征,并与输入相加反馈 |
| 跳跃连接 | ❌ 无跳跃连接(朴素架构) | ✅ 采用 x + F (x) 结构,保障梯度流动 |
| 梯度流动 | 训练过程中可能出现梯度消失或梯度爆炸(处理复杂数据时稳定性较差) | 稳定性更强(梯度可通过跳跃连接 "shortcut" 传递) |
| 图像质量 | 在简单数据集(如 MNIST、CIFAR)上表现良好 | 更适用于高分辨率或复杂图像(如视网膜图像) |
| 训练稳定性 | 中等;可能需要调整学习率 | 更高;通常收敛更平滑 |
| 模型灵活性 | 易于实现;参数量更少 | 性能更强,但模型稍厚重 |
| 适用场景 | 适用于小型、低分辨率数据集训练 | 适用于医疗图像、高真实感图像或高分辨率数据集训练 |
Go
Frist Build The Block¶
def residual_block(x, filters):
shortcut = x
x = layers.Conv2D(filters, kernel_size=3, padding='same')(x)
x = layers.BatchNormalization()(x)
x = layers.ReLU()(x)
x = layers.Conv2D(filters, kernel_size=3, padding='same')(x)
x = layers.BatchNormalization()(x)
x = layers.add([shortcut, x])
x = layers.ReLU()(x)
return x
Sec Build The Generator (Takes Noise Paramter)
def build_generator(noise_dim):
inputs = layers.Input(shape=(noise_dim,))
x = layers.Dense(8 * 8 * 256, use_bias=False)(inputs)
x = layers.Reshape((8, 8, 256))(x)
x = layers.ReLU()(x)
# Residual blocks
for _ in range(3):
x = residual_block(x, 256)
# Upsampling layers
x = layers.Conv2DTranspose(128, 4, strides=2, padding='same')(x)
x = layers.ReLU()(x)
x = layers.Conv2DTranspose(64, 4, strides=2, padding='same')(x)
x = layers.ReLU()(x)
x = layers.Conv2DTranspose(32, 4, strides=2, padding='same')(x)
x = layers.ReLU()(x)
# Output
outputs = layers.Conv2D(3, (7,7), padding='same', activation='tanh')(x)
return Model(inputs, outputs, name="generator")
generator = build_generator(NOISE_DIM)
generator.summary()
Model: "generator"┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓
┃ Layer (type) ┃ Output Shape ┃ Param # ┃ Connected to ┃
┡━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┩
│ input_layer │ (None, 100) │ 0 │ - │
│ (InputLayer) │ │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ dense (Dense) │ (None, 16384) │ 1,638,400 │ input_layer[0][0] │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ reshape (Reshape) │ (None, 8, 8, 256) │ 0 │ dense[0][0] │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ re_lu (ReLU) │ (None, 8, 8, 256) │ 0 │ reshape[0][0] │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ conv2d (Conv2D) │ (None, 8, 8, 256) │ 590,080 │ re_lu[0][0] │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ batch_normalization │ (None, 8, 8, 256) │ 1,024 │ conv2d[0][0] │
│ (BatchNormalizatio… │ │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ re_lu_1 (ReLU) │ (None, 8, 8, 256) │ 0 │ batch_normalizat… │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ conv2d_1 (Conv2D) │ (None, 8, 8, 256) │ 590,080 │ re_lu_1[0][0] │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ batch_normalizatio… │ (None, 8, 8, 256) │ 1,024 │ conv2d_1[0][0] │
│ (BatchNormalizatio… │ │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ add (Add) │ (None, 8, 8, 256) │ 0 │ re_lu[0][0], │
│ │ │ │ batch_normalizat… │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ re_lu_2 (ReLU) │ (None, 8, 8, 256) │ 0 │ add[0][0] │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ conv2d_2 (Conv2D) │ (None, 8, 8, 256) │ 590,080 │ re_lu_2[0][0] │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ batch_normalizatio… │ (None, 8, 8, 256) │ 1,024 │ conv2d_2[0][0] │
│ (BatchNormalizatio… │ │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ re_lu_3 (ReLU) │ (None, 8, 8, 256) │ 0 │ batch_normalizat… │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ conv2d_3 (Conv2D) │ (None, 8, 8, 256) │ 590,080 │ re_lu_3[0][0] │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ batch_normalizatio… │ (None, 8, 8, 256) │ 1,024 │ conv2d_3[0][0] │
│ (BatchNormalizatio… │ │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ add_1 (Add) │ (None, 8, 8, 256) │ 0 │ re_lu_2[0][0], │
│ │ │ │ batch_normalizat… │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ re_lu_4 (ReLU) │ (None, 8, 8, 256) │ 0 │ add_1[0][0] │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ conv2d_4 (Conv2D) │ (None, 8, 8, 256) │ 590,080 │ re_lu_4[0][0] │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ batch_normalizatio… │ (None, 8, 8, 256) │ 1,024 │ conv2d_4[0][0] │
│ (BatchNormalizatio… │ │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ re_lu_5 (ReLU) │ (None, 8, 8, 256) │ 0 │ batch_normalizat… │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ conv2d_5 (Conv2D) │ (None, 8, 8, 256) │ 590,080 │ re_lu_5[0][0] │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ batch_normalizatio… │ (None, 8, 8, 256) │ 1,024 │ conv2d_5[0][0] │
│ (BatchNormalizatio… │ │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ add_2 (Add) │ (None, 8, 8, 256) │ 0 │ re_lu_4[0][0], │
│ │ │ │ batch_normalizat… │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ re_lu_6 (ReLU) │ (None, 8, 8, 256) │ 0 │ add_2[0][0] │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ conv2d_transpose │ (None, 16, 16, │ 524,416 │ re_lu_6[0][0] │
│ (Conv2DTranspose) │ 128) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ re_lu_7 (ReLU) │ (None, 16, 16, │ 0 │ conv2d_transpose… │
│ │ 128) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ conv2d_transpose_1 │ (None, 32, 32, │ 131,136 │ re_lu_7[0][0] │
│ (Conv2DTranspose) │ 64) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ re_lu_8 (ReLU) │ (None, 32, 32, │ 0 │ conv2d_transpose… │
│ │ 64) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ conv2d_transpose_2 │ (None, 64, 64, │ 32,800 │ re_lu_8[0][0] │
│ (Conv2DTranspose) │ 32) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ re_lu_9 (ReLU) │ (None, 64, 64, │ 0 │ conv2d_transpose… │
│ │ 32) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ conv2d_6 (Conv2D) │ (None, 64, 64, 3) │ 4,707 │ re_lu_9[0][0] │
└─────────────────────┴───────────────────┴────────────┴───────────────────┘
Go
Total params: 5,878,083 (22.42 MB)
Trainable params: 5,875,011 (22.41 MB)
Non-trainable params: 3,072 (12.00 KB)🧱Build the Discriminator
Go
def residual_block(x, filters, downsample=False):
shortcut = x
# First convolution
x = layers.Conv2D(filters, (3, 3), padding='same')(x)
x = layers.BatchNormalization()(x)
x = layers.LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(x)
# Second convolution
x = layers.Conv2D(filters, (3, 3), padding='same')(x)
x = layers.BatchNormalization()(x)
# Optionally downsample
if downsample:
x = layers.AveragePooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2))(x)
shortcut = layers.Conv2D(filters, (1, 1), padding='same')(shortcut)
shortcut = layers.AveragePooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2))(shortcut)
# Add skip connection
x = layers.add([x, shortcut])
x = layers.LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(x)
return x
def build_discriminator(img_shape=(128, 128, 3)):
inp = layers.Input(shape=img_shape)
x = layers.Conv2D(64, (7,7), strides=2, padding='same')(inp)
x = layers.LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(x)
# Residual blocks with downsampling
for filters in [64, 128, 256]:
x = residual_block(x, filters, downsample=True)
x = layers.GlobalAveragePooling2D()(x)
x = layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')(x)
model = tf.keras.Model(inp, x, name="Discriminator")
return model
discriminator = build_discriminator()
discriminator.summary()/usr/local/lib/python3.11/dist-packages/keras/src/layers/activations/leaky_relu.py:41: UserWarning: Argument `alpha` is deprecated. Use `negative_slope` instead.
warnings.warn(Model: "Discriminator"┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓
┃ Layer (type) ┃ Output Shape ┃ Param # ┃ Connected to ┃
┡━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┩
│ input_layer_1 │ (None, 128, 128, │ 0 │ - │
│ (InputLayer) │ 3) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ conv2d_7 (Conv2D) │ (None, 64, 64, │ 9,472 │ input_layer_1[0]… │
│ │ 64) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ leaky_re_lu │ (None, 64, 64, │ 0 │ conv2d_7[0][0] │
│ (LeakyReLU) │ 64) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ conv2d_8 (Conv2D) │ (None, 64, 64, │ 36,928 │ leaky_re_lu[0][0] │
│ │ 64) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ batch_normalizatio… │ (None, 64, 64, │ 256 │ conv2d_8[0][0] │
│ (BatchNormalizatio… │ 64) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ leaky_re_lu_1 │ (None, 64, 64, │ 0 │ batch_normalizat… │
│ (LeakyReLU) │ 64) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ conv2d_9 (Conv2D) │ (None, 64, 64, │ 36,928 │ leaky_re_lu_1[0]… │
│ │ 64) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ batch_normalizatio… │ (None, 64, 64, │ 256 │ conv2d_9[0][0] │
│ (BatchNormalizatio… │ 64) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ conv2d_10 (Conv2D) │ (None, 64, 64, │ 4,160 │ leaky_re_lu[0][0] │
│ │ 64) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ average_pooling2d │ (None, 32, 32, │ 0 │ batch_normalizat… │
│ (AveragePooling2D) │ 64) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ average_pooling2d_1 │ (None, 32, 32, │ 0 │ conv2d_10[0][0] │
│ (AveragePooling2D) │ 64) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ add_3 (Add) │ (None, 32, 32, │ 0 │ average_pooling2… │
│ │ 64) │ │ average_pooling2… │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ leaky_re_lu_2 │ (None, 32, 32, │ 0 │ add_3[0][0] │
│ (LeakyReLU) │ 64) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ conv2d_11 (Conv2D) │ (None, 32, 32, │ 73,856 │ leaky_re_lu_2[0]… │
│ │ 128) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ batch_normalizatio… │ (None, 32, 32, │ 512 │ conv2d_11[0][0] │
│ (BatchNormalizatio… │ 128) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ leaky_re_lu_3 │ (None, 32, 32, │ 0 │ batch_normalizat… │
│ (LeakyReLU) │ 128) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ conv2d_12 (Conv2D) │ (None, 32, 32, │ 147,584 │ leaky_re_lu_3[0]… │
│ │ 128) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ batch_normalizatio… │ (None, 32, 32, │ 512 │ conv2d_12[0][0] │
│ (BatchNormalizatio… │ 128) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ conv2d_13 (Conv2D) │ (None, 32, 32, │ 8,320 │ leaky_re_lu_2[0]… │
│ │ 128) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ average_pooling2d_2 │ (None, 16, 16, │ 0 │ batch_normalizat… │
│ (AveragePooling2D) │ 128) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ average_pooling2d_3 │ (None, 16, 16, │ 0 │ conv2d_13[0][0] │
│ (AveragePooling2D) │ 128) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ add_4 (Add) │ (None, 16, 16, │ 0 │ average_pooling2… │
│ │ 128) │ │ average_pooling2… │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ leaky_re_lu_4 │ (None, 16, 16, │ 0 │ add_4[0][0] │
│ (LeakyReLU) │ 128) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ conv2d_14 (Conv2D) │ (None, 16, 16, │ 295,168 │ leaky_re_lu_4[0]… │
│ │ 256) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ batch_normalizatio… │ (None, 16, 16, │ 1,024 │ conv2d_14[0][0] │
│ (BatchNormalizatio… │ 256) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ leaky_re_lu_5 │ (None, 16, 16, │ 0 │ batch_normalizat… │
│ (LeakyReLU) │ 256) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ conv2d_15 (Conv2D) │ (None, 16, 16, │ 590,080 │ leaky_re_lu_5[0]… │
│ │ 256) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ batch_normalizatio… │ (None, 16, 16, │ 1,024 │ conv2d_15[0][0] │
│ (BatchNormalizatio… │ 256) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ conv2d_16 (Conv2D) │ (None, 16, 16, │ 33,024 │ leaky_re_lu_4[0]… │
│ │ 256) │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ average_pooling2d_4 │ (None, 8, 8, 256) │ 0 │ batch_normalizat… │
│ (AveragePooling2D) │ │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ average_pooling2d_5 │ (None, 8, 8, 256) │ 0 │ conv2d_16[0][0] │
│ (AveragePooling2D) │ │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ add_5 (Add) │ (None, 8, 8, 256) │ 0 │ average_pooling2… │
│ │ │ │ average_pooling2… │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ leaky_re_lu_6 │ (None, 8, 8, 256) │ 0 │ add_5[0][0] │
│ (LeakyReLU) │ │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ global_average_poo… │ (None, 256) │ 0 │ leaky_re_lu_6[0]… │
│ (GlobalAveragePool… │ │ │ │
├─────────────────────┼───────────────────┼────────────┼───────────────────┤
│ dense_1 (Dense) │ (None, 1) │ 257 │ global_average_p… │
└─────────────────────┴───────────────────┴────────────┴───────────────────┘ Total params: 1,239,361 (4.73 MB) Trainable params: 1,237,569 (4.72 MB) Non-trainable params: 1,792 (7.00 KB)
Go
Define Loss and Optimizers¶
cross_entropy = tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True)
generator_optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(1e-4) # => for generator
discriminator_optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(1e-4) # => for Discriminator
Show Random Samples from Your Training Data
train_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(train_paths)
train_dataset = train_dataset.map(load_image, num_parallel_calls=tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
train_dataset = train_dataset.shuffle(BUFFER_SIZE).batch(BATCH_SIZE)
# Take one batch from dataset
for image_batch in train_dataset.take(1):
sample_images = image_batch[:16] # first 16 images
break
# Denormalize from [-1,1] → [0,1] for display
sample_images = (sample_images + 1) / 2.0
# Plot them
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
for i in range(16):
plt.subplot(4, 4, i + 1)
plt.imshow(sample_images[i])
plt.axis("off")
plt.suptitle("Random Samples from Training Data", fontsize=14)
plt.show()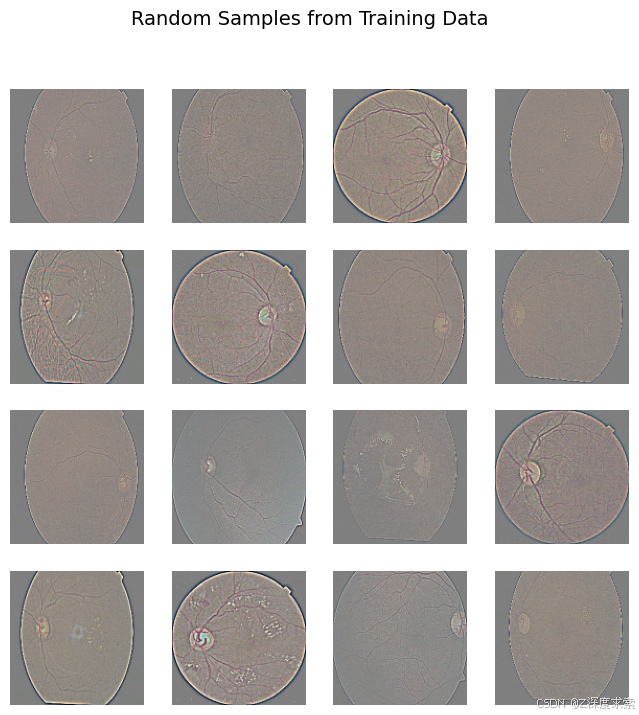
Go
Generator visualizie¶
# visualize your generator
plot_model(
generator,
to_file="generator_model.png", # will save as an image in Kaggle output
show_shapes=True, # show layer input/output shapes
show_layer_names=True, # show layer names
expand_nested=True, # expand residual blocks
dpi=96
)
Image(filename='generator_model.png')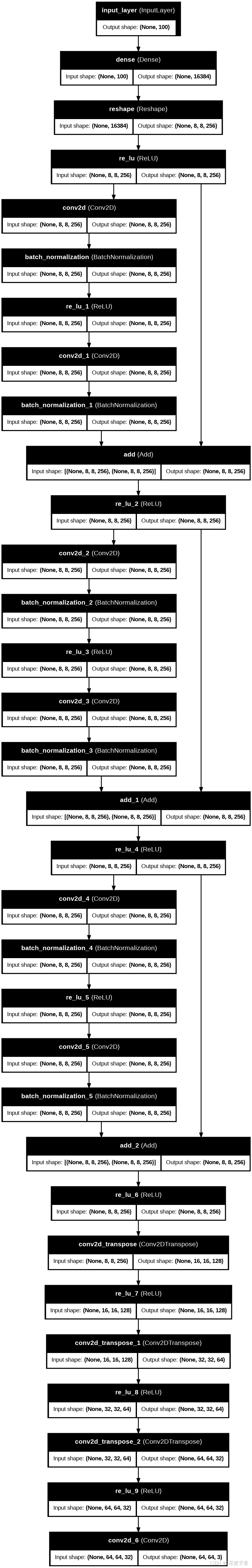
solve the problem¶
noise = tf.random.normal([1, 100])
generated_image = generator(noise, training=False)
print(generated_image.shape)I0000 00:00:1760817835.976041 37 cuda_dnn.cc:529] Loaded cuDNN version 90300(1, 64, 64, 3)layers.Conv2DTranspose(3, (5,5), strides=(2,2), padding='same', activation='tanh')<Conv2DTranspose name=conv2d_transpose_3, built=False>This version outputs (128, 128, 3) --- perfect for your discriminator
Go
def make_generator_model():
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
layers.Dense(8*8*512, use_bias=False, input_shape=(100,)),
layers.BatchNormalization(),
layers.LeakyReLU(),
layers.Reshape((8, 8, 512)),
layers.Conv2DTranspose(256, (5,5), strides=(2,2), padding='same', use_bias=False),
layers.BatchNormalization(),
layers.LeakyReLU(), # 16x16
layers.Conv2DTranspose(128, (5,5), strides=(2,2), padding='same', use_bias=False),
layers.BatchNormalization(),
layers.LeakyReLU(), # 32x32
layers.Conv2DTranspose(64, (5,5), strides=(2,2), padding='same', use_bias=False),
layers.BatchNormalization(),
layers.LeakyReLU(), # 64x64
# 👇 ADD ONE MORE UPSAMPLING TO REACH 128x128
layers.Conv2DTranspose(32, (5,5), strides=(2,2), padding='same', use_bias=False),
layers.BatchNormalization(),
layers.LeakyReLU(), # 128x128
layers.Conv2DTranspose(3, (5,5), strides=(1,1), padding='same', use_bias=False, activation='tanh')
])
return model
# check again the output
generator = make_generator_model()
noise = tf.random.normal([1, 100])
print(generator(noise).shape)/usr/local/lib/python3.11/dist-packages/keras/src/layers/core/dense.py:87: UserWarning: Do not pass an `input_shape`/`input_dim` argument to a layer. When using Sequential models, prefer using an `Input(shape)` object as the first layer in the model instead.
super().__init__(activity_regularizer=activity_regularizer, **kwargs)(1, 128, 128, 3)Build The Gans model¶
# Loss and optimizers
cross_entropy = tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True)
generator_optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(1e-4, beta_1=0.5)
discriminator_optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(1e-4, beta_1=0.5)🧠 Define the Training Step
Go
@tf.function
def train_step(images):
noise = tf.random.normal([BATCH_SIZE, NOISE_DIM])
with tf.GradientTape() as gen_tape, tf.GradientTape() as disc_tape:
generated_images = generator(noise, training=True)
real_output = discriminator(images, training=True)
fake_output = discriminator(generated_images, training=True)
# Losses
gen_loss = cross_entropy(tf.ones_like(fake_output), fake_output)
real_loss = cross_entropy(tf.ones_like(real_output), real_output)
fake_loss = cross_entropy(tf.zeros_like(fake_output), fake_output)
disc_loss = (real_loss + fake_loss) / 2
# Compute gradients
gradients_of_generator = gen_tape.gradient(gen_loss, generator.trainable_variables)
gradients_of_discriminator = disc_tape.gradient(disc_loss, discriminator.trainable_variables)
# Apply updates
generator_optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients_of_generator, generator.trainable_variables))
discriminator_optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients_of_discriminator, discriminator.trainable_variables))
return gen_loss, disc_lossDefine Function to Visualize Results
python
def generate_and_save_images(model, epoch, test_input):
predictions = model(test_input, training=False)
predictions = (predictions + 1) / 2.0 # back to [0,1]
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(4,4))
for i in range(predictions.shape[0]):
plt.subplot(4, 4, i+1)
plt.imshow(predictions[i])
plt.axis('off')
plt.suptitle(f"Epoch {epoch}")
plt.show()🧪 The Training Loop
python
seed = tf.random.normal([NUM_EXAMPLES, NOISE_DIM])
from tqdm import tqdm # => to display epochs when training
for epoch in range(1, EPOCHS + 1):
for image_batch in tqdm(train_dataset, desc=f"Epoch {epoch}/{EPOCHS}"):
gen_loss, disc_loss = train_step(image_batch)
print(f"Epoch {epoch}, Generator Loss: {gen_loss:.4f}, Discriminator Loss: {disc_loss:.4f}")
generate_and_save_images(generator, epoch, seed)/dist-packages/keras/src/backend/tensorflow/nn.py:780: UserWarning: "`binary_crossentropy` received `from_logits=True`, but the `output` argument was produced by a Sigmoid activation and thus does not represent logits. Was this intended?
output, from_logits = _get_logits(
Epoch 1/80: 100%|██████████| 13/13 [00:40<00:00, 3.15s/it]Epoch 1, Generator Loss: 0.8707, Discriminator Loss: 0.4276Epoch 78/80: 100%|██████████| 13/13 [00:14<00:00, 1.11s/it]Epoch 78, Generator Loss: 3.5214, Discriminator Loss: 0.0547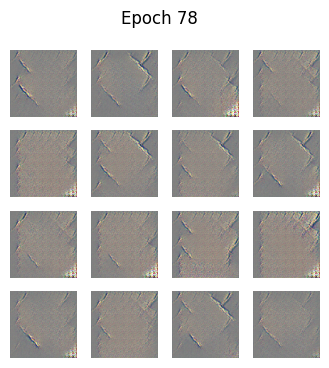
Epoch 79/80: 100%|██████████| 13/13 [00:14<00:00, 1.11s/it]Epoch 79, Generator Loss: 5.3691, Discriminator Loss: 0.0091
Epoch 80/80: 100%|██████████| 13/13 [00:14<00:00, 1.11s/it]Epoch 80, Generator Loss: 3.7142, Discriminator Loss: 0.0200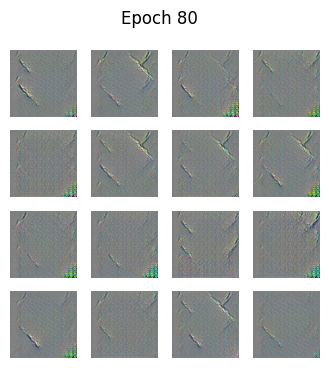
🎯 Why there's no "accuracy" in GANs
在生成对抗网络(GAN)中,包含两个核心模型:¶
- 生成器(G):尝试生成看似真实的伪造图像。
- 判别器(D):尝试区分图像的真实与伪造。
它们以对抗方式进行训练:
- 当生成器成功欺骗判别器时,生成器会进一步优化。
- 当判别器能准确识别伪造图像时,判别器会持续改进。
因此,训练过程中不追踪准确率,而是关注损失值:
- 生成器损失(gen_loss):衡量生成器欺骗判别器的效果。
- 判别器损失(disc_loss):衡量判别器区分真实与伪造图像的能力。
若随着训练推进,两个损失值均趋于稳定(未出现发散),则说明训练有效。
python
# Generate noise
noise = tf.random.normal([16, NOISE_DIM])
# Generate fake images
generated_images = generator(noise, training=False)
# Plot them
plt.figure(figsize=(4, 4))
for i in range(generated_images.shape[0]):
plt.subplot(4, 4, i + 1)
plt.imshow((generated_images[i] * 127.5 + 127.5).numpy().astype("uint8"))
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()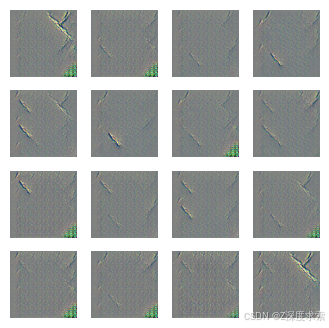
python
# Generate fake images
noise = tf.random.normal([100, NOISE_DIM])
fake_images = generator(noise, training=False)
# Discriminator output for generated images
predictions = discriminator(fake_images, training=False)
# Check how "real" the discriminator thinks they are
mean_pred = tf.reduce_mean(predictions).numpy()
print(f"Average discriminator confidence (real=1, fake=0): {mean_pred:.3f}")
Average discriminator confidence (real=1, fake=0): 0.007
save model
generator.save('generator_model.h5')
discriminator.save('discriminator_model.h5')
Call CNN Model
from tensorflow.keras.models import load_model
classifier = load_model('/kaggle/input/cnn/keras/default/1/improved_dr_cnn.h5')
The next step Analysis and interpretation 🔍
N_SAMPLES = 500 # increase if you want
noise = tf.random.normal([N_SAMPLES, NOISE_DIM])
generated_images = generator(noise, training=False)
# recove the image to the real size
generated_images = (generated_images + 1) / 2.0
preds = classifier.predict(generated_images)
pred_labels = np.argmax(preds, axis=1)
16/16 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 1s 28ms/step
class_names = ['Healthy', 'Mild DR', 'Moderate DR','Proliferate DR', 'Severe DR']
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 12))
for i in range(16):
plt.subplot(4, 4, i + 1)
plt.imshow(generated_images[i])
plt.title(class_names[pred_labels[i]])
plt.axis("off")
plt.suptitle("Predicted Classes for GAN Generated Images", fontsize=16)
plt.show()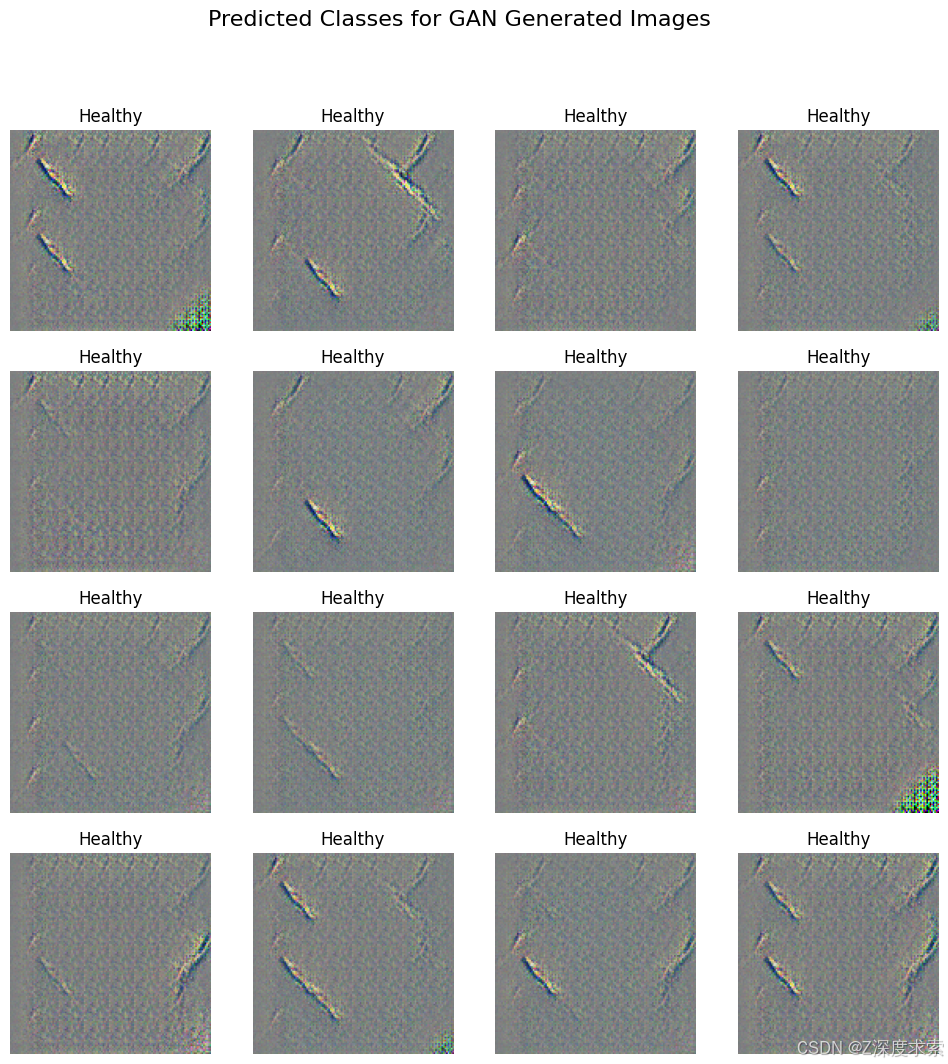
18/18 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 1s 39ms/step
precision recall f1-score support
Healthy 0.80 0.97 0.87 200
Mild DR 0.55 0.21 0.30 77
Moderate DR 0.53 0.81 0.64 183
Proliferate DR 0.00 0.00 0.00 55
Severe DR 0.00 0.00 0.00 35
accuracy 0.65 550
macro avg 0.38 0.40 0.36 550
weighted avg 0.54 0.65 0.57 550
Confusion matrix:
[[194 2 4 0 0]
[ 7 16 54 0 0]
[ 27 8 148 0 0]
[ 9 3 43 0 0]
[ 7 0 28 0 0]]/usr/local/lib/python3.11/dist-packages/sklearn/metrics/_classification.py:1344: UndefinedMetricWarning: Precision and F-score are ill-defined and being set to 0.0 in labels with no predicted samples. Use `zero_division` parameter to control this behavior.
_warn_prf(average, modifier, msg_start, len(result))
/usr/local/lib/python3.11/dist-packages/sklearn/metrics/_classification.py:1344: UndefinedMetricWarning: Precision and F-score are ill-defined and being set to 0.0 in labels with no predicted samples. Use `zero_division` parameter to control this behavior.
_warn_prf(average, modifier, msg_start, len(result))
/usr/local/lib/python3.11/dist-packages/sklearn/metrics/_classification.py:1344: UndefinedMetricWarning: Precision and F-score are ill-defined and being set to 0.0 in labels with no predicted samples. Use `zero_division` parameter to control this behavior.
_warn_prf(average, modifier, msg_start, len(result))