蓝桥杯通关秘籍(一):算法基础篇:基础算法(上)
文章目录
- 蓝桥杯通关秘籍(一):算法基础篇:基础算法(上)
- 一、模拟
-
- [1.1 多项式输出](#1.1 多项式输出)
- [1.2 蛇形⽅阵](#1.2 蛇形⽅阵)
- [1.3 字符串的展开](#1.3 字符串的展开)
- 二、高精度
-
- [2.1 ⾼精度加法](#2.1 ⾼精度加法)
- [2.2 ⾼精度减法](#2.2 ⾼精度减法)
- [2.3 ⾼精度乘法](#2.3 ⾼精度乘法)
- [2.4 ⾼精度除法](#2.4 ⾼精度除法)
- 三、枚举
- [3.1 普通枚举](#3.1 普通枚举)
-
- [3.1.1 铺地毯](#3.1.1 铺地毯)
- [3.1.2 回⽂⽇期](#3.1.2 回⽂⽇期)
- [3.1.3 扫雷](#3.1.3 扫雷)
- [3.2 ⼆进制枚举](#3.2 ⼆进制枚举)
-
- [3.2.1 ⼦集](#3.2.1 ⼦集)
- [3.2.2 费解的开关](#3.2.2 费解的开关)
- [3.2.3 Even Parity](#3.2.3 Even Parity)
- 四、前缀和
-
- [4.1 ⼀维前缀和](#4.1 ⼀维前缀和)
- [4.2 最⼤⼦段和](#4.2 最⼤⼦段和)
- [4.3 ⼆维前缀和](#4.3 ⼆维前缀和)
- [4.4 激光炸弹](#4.4 激光炸弹)
- 五、差分
-
- [5.1 ⼀维差分](#5.1 ⼀维差分)
- [5.2 海底⾼铁](#5.2 海底⾼铁)
- [5.3 ⼆维差分](#5.3 ⼆维差分)
- [5.4 地毯](#5.4 地毯)
- 六、双指针
-
- [6.1 唯⼀的雪花](#6.1 唯⼀的雪花)
- [6.2 逛画展](#6.2 逛画展)
- [6.3 字符串](#6.3 字符串)
- [6.4 丢⼿绢](#6.4 丢⼿绢)
- 七、二分算法
- [7.1 ⼆分查找](#7.1 ⼆分查找)
-
- [7.1.1 ⽜可乐和魔法封印](#7.1.1 ⽜可乐和魔法封印)
- [7.1.2 A-B 数对](#7.1.2 A-B 数对)
- [7.1.3 烦恼的⾼考志愿](#7.1.3 烦恼的⾼考志愿)
- [7.2 ⼆分答案](#7.2 ⼆分答案)
-
- [7.2.1 ⽊材加⼯](#7.2.1 ⽊材加⼯)
- [7.2.2 砍树](#7.2.2 砍树)
- [7.2.3 跳⽯头](#7.2.3 跳⽯头)
- 整体源代码
一、模拟
1.1 多项式输出

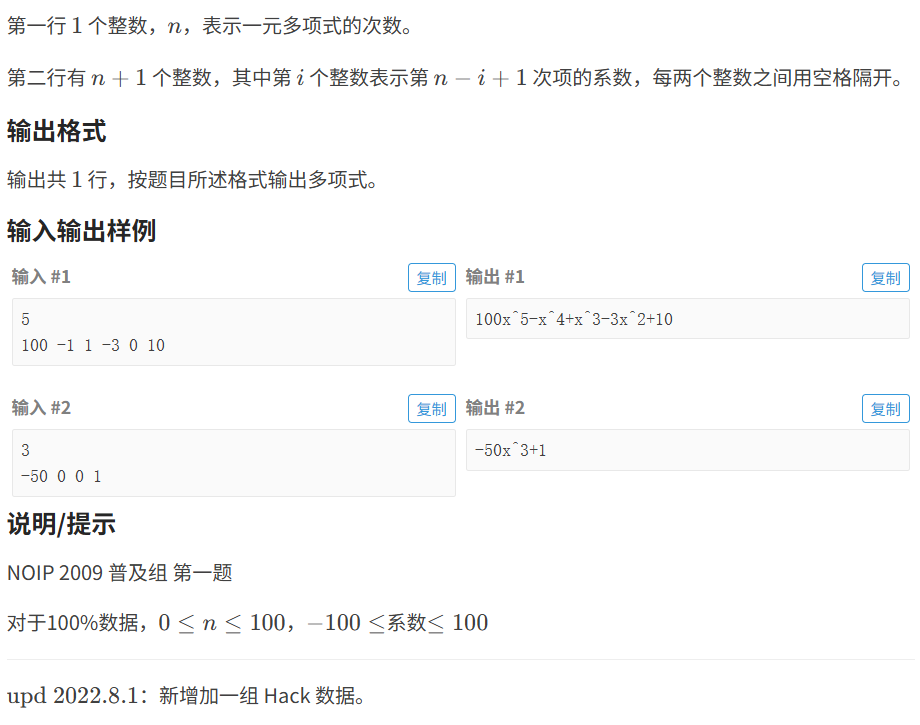

代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n; cin >> n;
// 循环次数
for (int i = n; i >= 0; i--)
{
int a; cin >> a;
if (a == 0) continue; // 处理系数为 0 的情况
// 1. 符号
if (a < 0) cout << '-';
else
{
if (i != n) cout << '+';
}
// 2. 数字
a = abs(a);
if (a != 1 || (a == 1 && i == 0)) cout << a;
// 3. 次数
if (i == 0) continue;
else if (i == 1) cout << 'x';
else cout << "x^" << i;
}
return 0;
}1.2 蛇形⽅阵
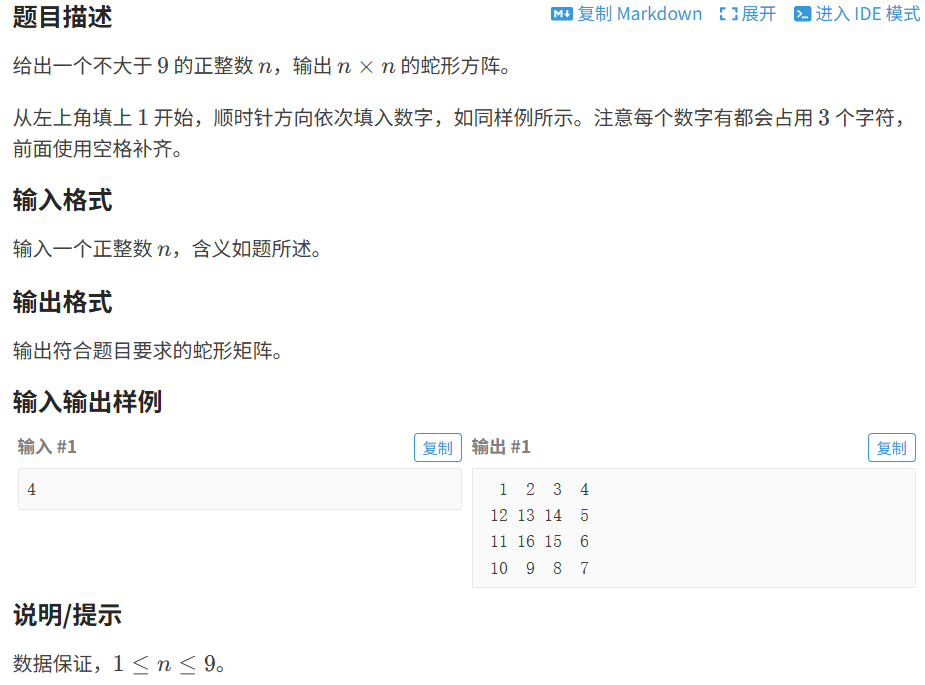

代码如下(示例):
c
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int dx[4] = { 0 , 1 , 0 , -1 };
int dy[4] = { 1 , 0 ,-1 , 0 };
const int N = 15;
int arr[N][N];
int main()
{
int n; cin >> n;
int cnt = 1;
int pos = 0;
int x = 1, y = 1;
while (cnt <= n * n)
{
arr[x][y] = cnt;
int a = x + dx[pos], b = y + dy[pos];
if (a < 1 || a > n || b < 1 || b > n || arr[a][b])
{
pos = (pos + 1) % 4;
a = x + dx[pos], b = y + dy[pos];
}
x = a, y = b;
cnt++;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
printf("%3d", arr[i][j]);
}
puts("");
}
}1.3 字符串的展开

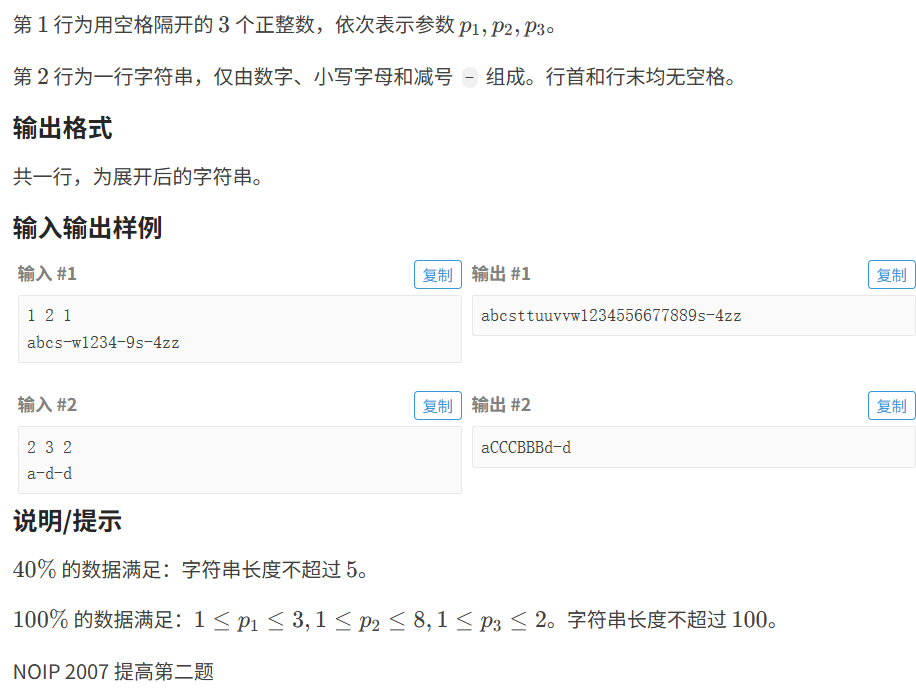
代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int p1, p2, p3, n;
string s;
string ret;
// 判断是否是数字字符
bool isdig(char ch)
{
return ch >= '0' && ch <= '9';
}
// 判断是否是⼩写字⺟
bool islet(char ch)
{
return ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z';
}
// 把 [left, right] 之间的字符展开
// left, right 这两个字符是不做处理
void add(char left, char right)
{
string t;
// 遍历中间的字符
for (char ch = left + 1; ch < right; ch++)
{
char tmp = ch;
// 处理 p1
if (p1 == 2 && islet(tmp)) tmp -= 32; // ⼩写变⼤写
else if (p1 == 3) tmp = '*'; // 变成星号
// 处理 p2
for (int i = 0; i < p2; i++)
{
t += tmp;
}
}
// 处理 p3
if (p3 == 2) reverse(t.begin(), t.end());
ret += t;
}
int main()
{
cin >> p1 >> p2 >> p3 >> s;
n = s.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
char ch = s[i];
if (s[i] != '-' || i == 0 || i == n - 1) ret += ch;
else
{
char left = s[i - 1], right = s[i + 1];
// 判断是否展开
if (isdig(left) && isdig(right) && right > left ||
islet(left) && islet(right) && right > left)
{
// 展开
add(left, right);
}
else
{
ret += ch;
}
}
}
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}二、高精度

2.1 ⾼精度加法
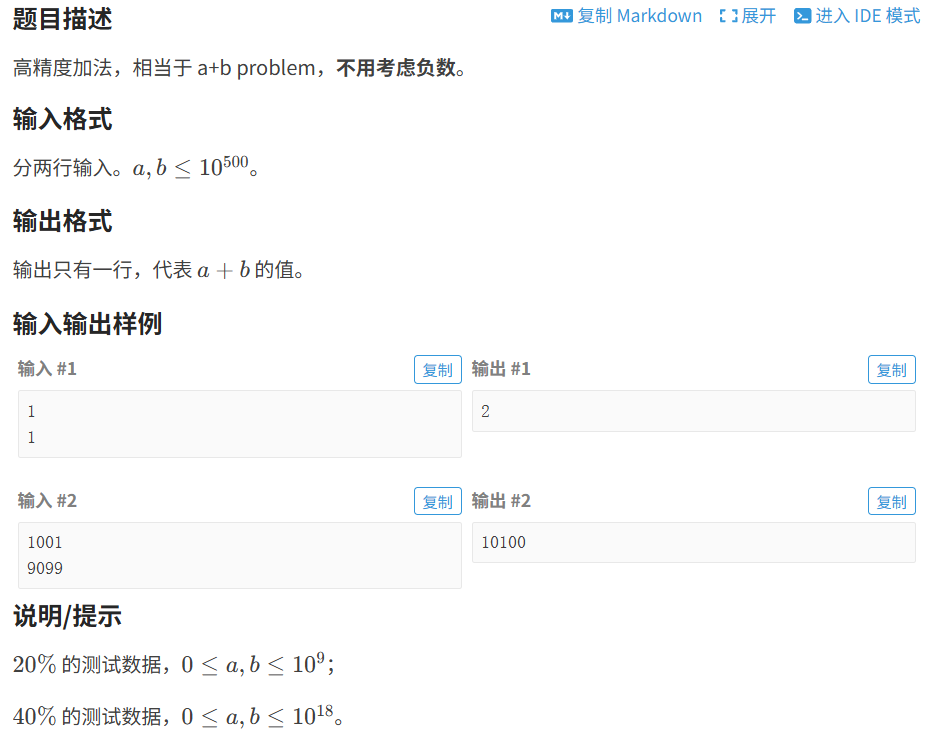

代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int a[N], b[N], c[N];
int la, lb, lc;
// ⾼精度加法的模版 - c = a + b;
void add(int c[], int a[], int b[])
{
for (int i = 0; i < lc; i++)
{
c[i] += a[i] + b[i]; // 对应位相加,再加上进位
c[i + 1] += c[i] / 10; // 处理进位
c[i] %= 10; // 处理余数
}
if (c[lc]) lc++;
}
int main()
{
string x, y; cin >> x >> y;
// 1. 拆分每⼀位,逆序放在数组中
la = x.size(); lb = y.size(); lc = max(la, lb);
for (int i = 0; i < la; i++) a[la - 1 - i] = x[i] - '0';
for (int i = 0; i < lb; i++) b[lb - 1 - i] = y[i] - '0';
// 2. 模拟加法的过程
add(c, a, b); // c = a + b
// 输出结果
for (int i = lc - 1; i >= 0; i--) cout << c[i];
return 0;
}2.2 ⾼精度减法
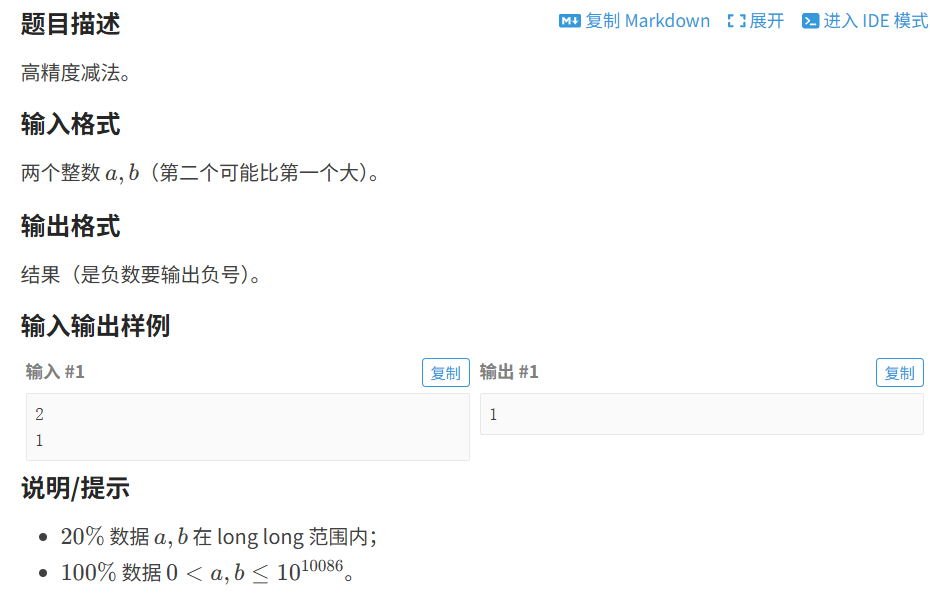

代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int a[N], b[N], c[N];
int la, lb, lc;
// ⽐⼤⼩
bool cmp(string& x, string& y)
{
// 先⽐较⻓度
if (x.size() != y.size()) return x.size() < y.size();
// 再按照 字典序 的⽅式⽐较
return x < y;
}
// ⾼精度减法的模板 - c = a - b
void sub(int c[], int a[], int b[])
{
for (int i = 0; i < lc; i++)
{
c[i] += a[i] - b[i]; // 对应位相减,然后处理借位
if (c[i] < 0)
{
c[i + 1] -= 1; // 借位
c[i] += 10;
}
}
// 处理前导零
while (lc > 1 && c[lc - 1] == 0) lc--;
}
int main()
{
string x, y; cin >> x >> y;
// ⽐⼤⼩
if (cmp(x, y))
{
swap(x, y);
cout << '-';
}
// 1. 拆分每⼀位,然后逆序放在数组中
la = x.size(); lb = y.size(); lc = max(la, lb);
for (int i = 0; i < la; i++) a[la - i - 1] = x[i] - '0';
for (int i = 0; i < lb; i++) b[lb - i - 1] = y[i] - '0';
// 2. 模拟减法的过程
sub(c, a, b); // c = a - b
// 输出结果
for (int i = lc - 1; i >= 0; i--) cout << c[i];
return 0;
}2.3 ⾼精度乘法
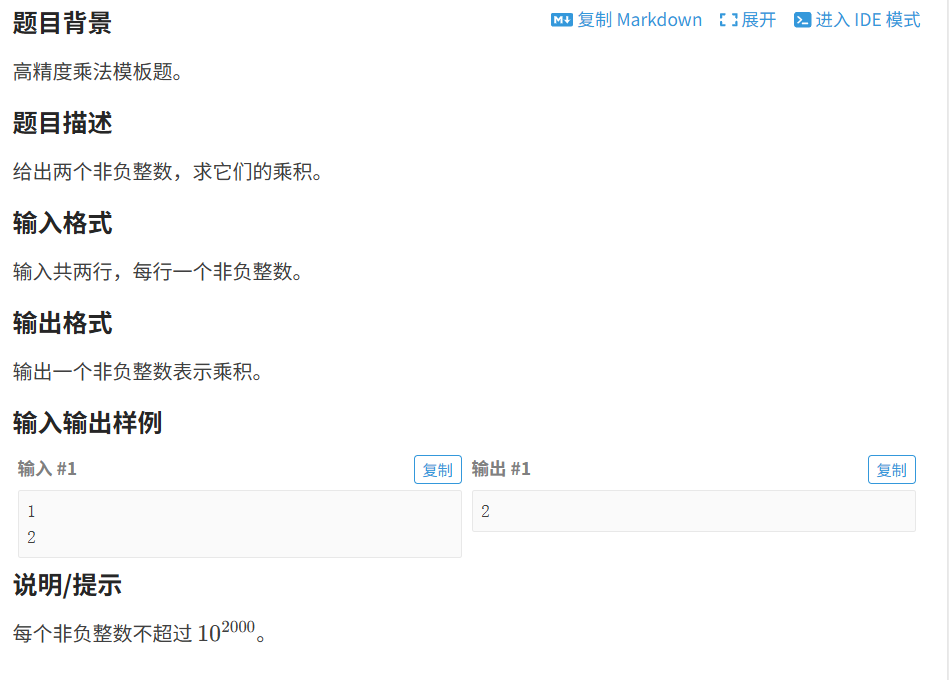
代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int a[N], b[N], c[N];
int la, lb, lc;
// ⾼精度乘法的模版 - c = a * b
void mul(int c[], int a[], int b[])
{
// ⽆进位相乘,然后相加
for (int i = 0; i < la; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < lb; j++)
{
c[i + j] += a[i] * b[j];
}
}
// 处理进位
for (int i = 0; i < lc; i++)
{
c[i + 1] += c[i] / 10;
c[i] %= 10;
}
// 处理前导零
while (lc > 1 && c[lc - 1] == 0) lc--;
}
int main()
{
string x, y; cin >> x >> y;
// 1. 拆分每⼀位,逆序放在数组中
la = x.size(); lb = y.size(); lc = la + lb;
for (int i = 0; i < la; i++) a[la - 1 - i] = x[i] - '0';
for (int i = 0; i < lb; i++) b[lb - 1 - i] = y[i] - '0';
// 2. 模拟乘法的过程
mul(c, a, b); // c = a * b
// 输出结果
for (int i = lc - 1; i >= 0; i--) cout << c[i];
return 0;
}2.4 ⾼精度除法
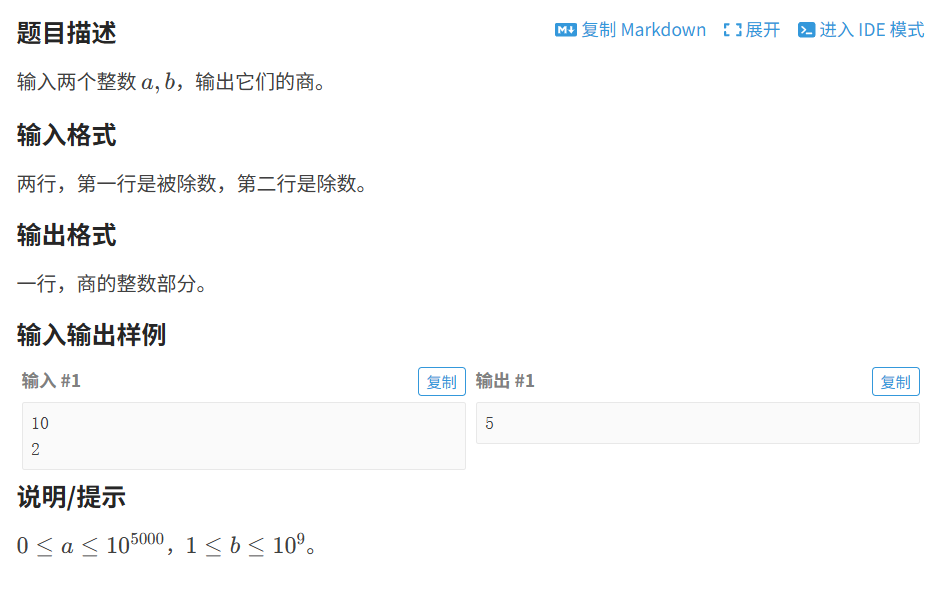
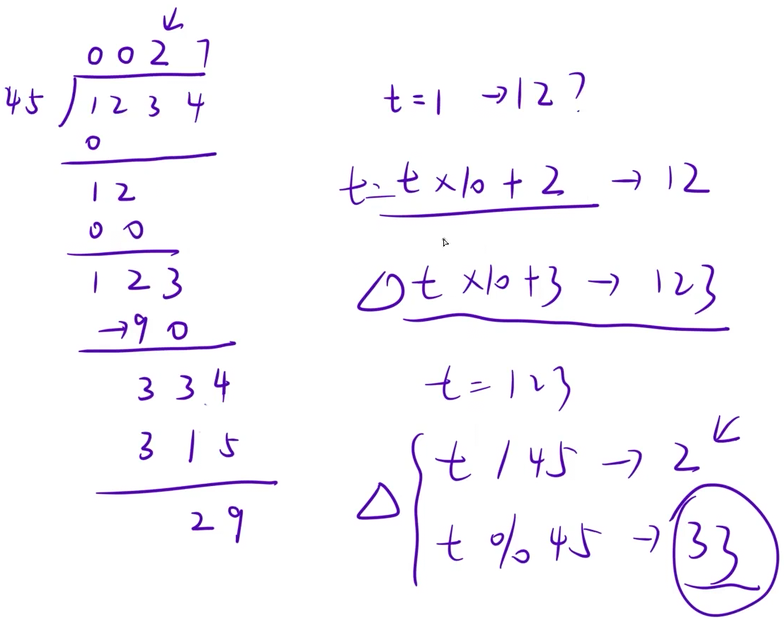
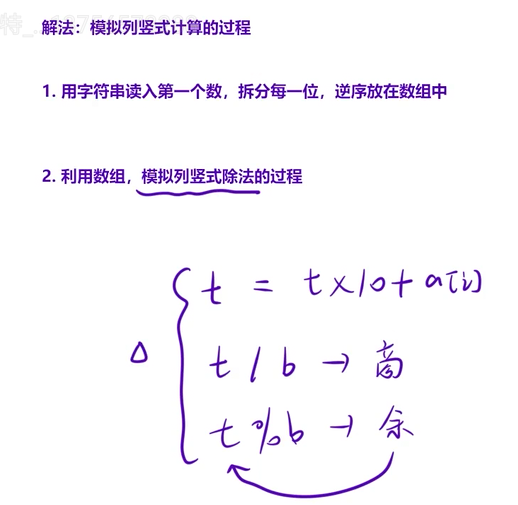
代码如下(示例):
c
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
typedef long long LL;
int a[N], b, c[N];
int la, lc;
// ⾼精度除法的模板 - c = a / b (⾼精度 / 低精度)
void sub(int c[], int a[], int b)
{
LL t = 0; // 标记每次除完之后的余数
for (int i = la - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
// 计算当前的被除数
t = t * 10 + a[i];
c[i] = t / b;
t %= b;
}
// 处理前导 0
while (lc > 1 && c[lc - 1] == 0) lc--;
}
int main()
{
string x; cin >> x >> b;
la = x.size();
for (int i = 0; i < la; i++) a[la - 1 - i] = x[i] - '0';
// 模拟除法的过程
lc = la;
sub(c, a, b); // c = a / b
for (int i = lc - 1; i >= 0; i--) cout << c[i];
return 0;
}三、枚举

3.1 普通枚举
3.1.1 铺地毯

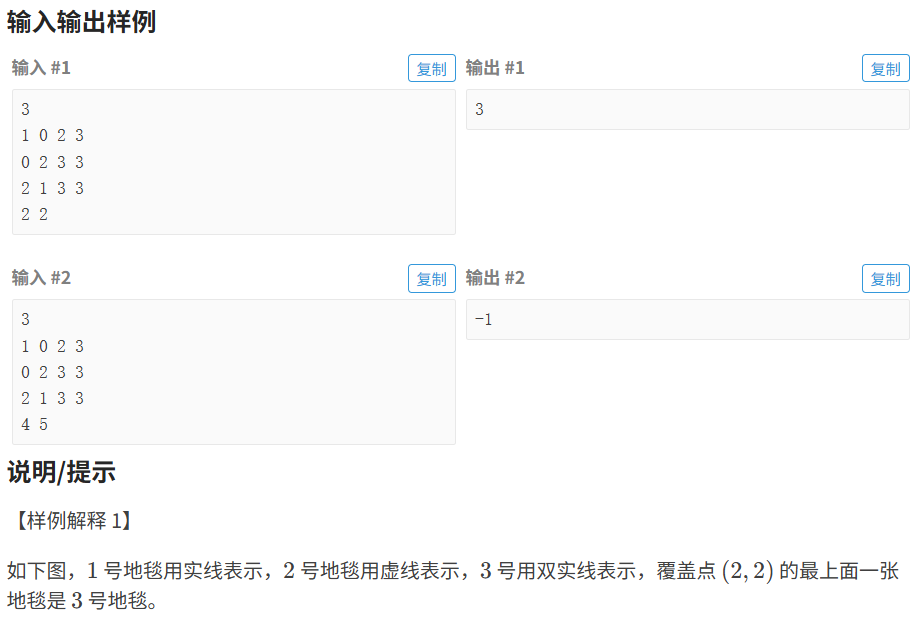
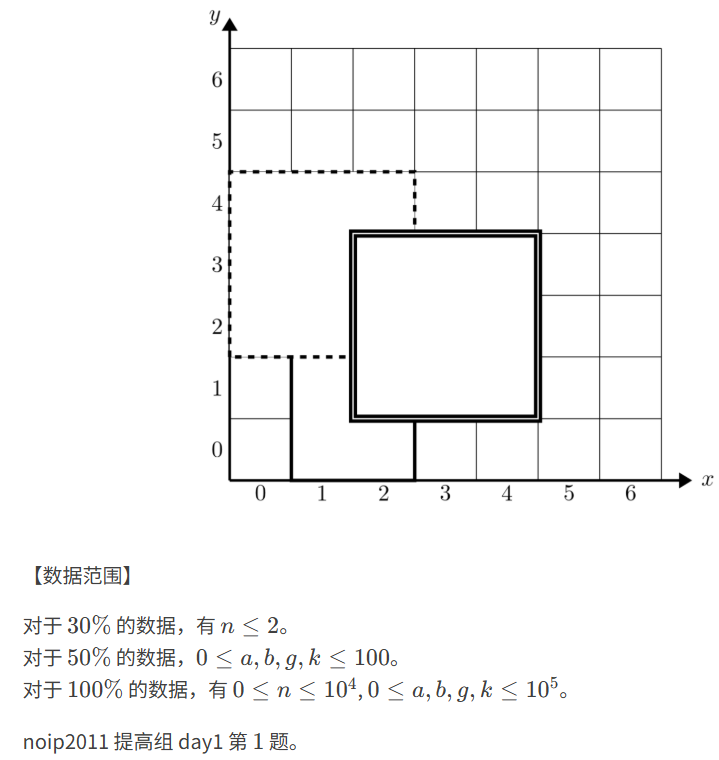

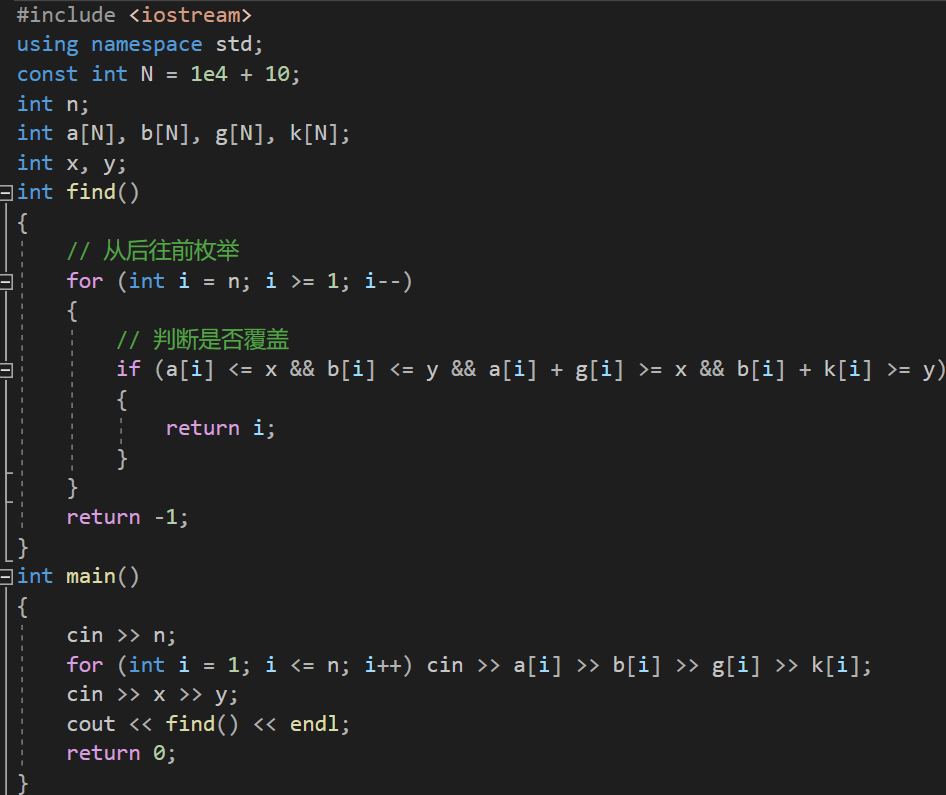
代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e4 + 10;
int n;
int a[N], b[N], g[N], k[N];
int x, y;
int find()
{
// 从后往前枚举
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--)
{
// 判断是否覆盖
if (a[i] <= x && b[i] <= y && a[i] + g[i] >= x && b[i] + k[i] >= y)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i] >> b[i] >> g[i] >> k[i];
cin >> x >> y;
cout << find() << endl;
return 0;
}3.1.2 回⽂⽇期

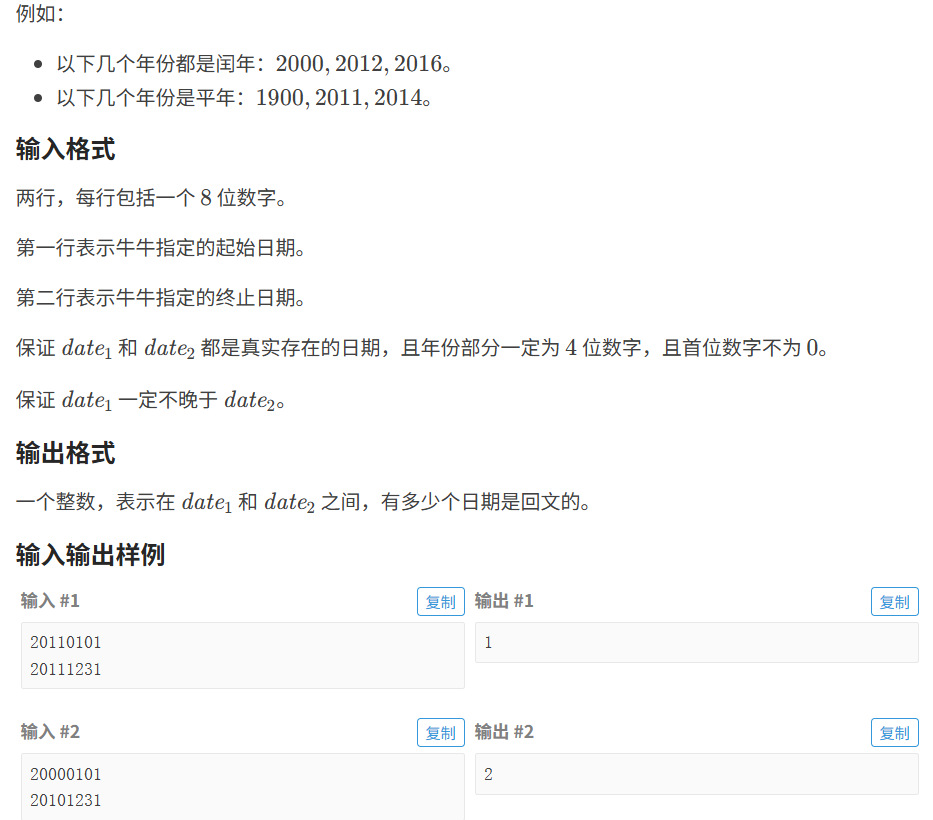

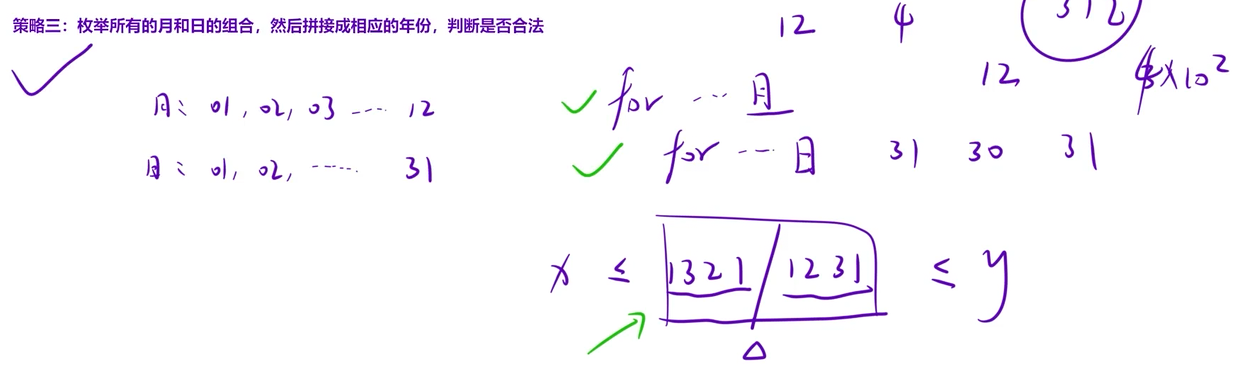
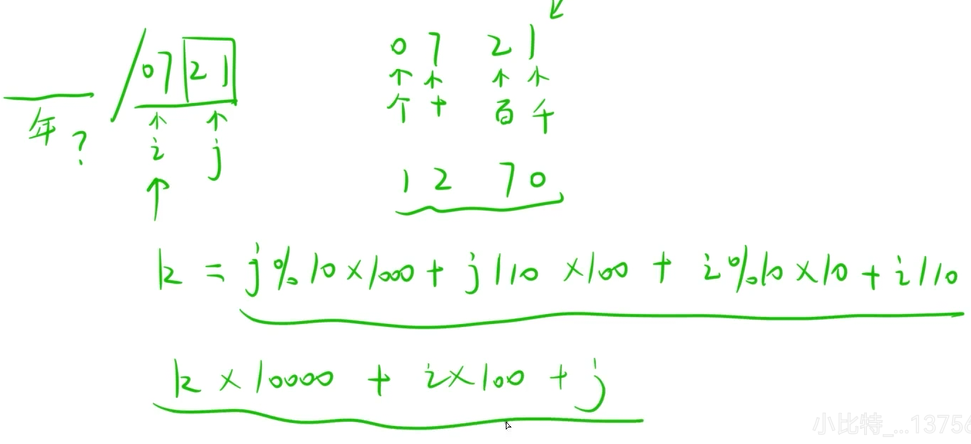
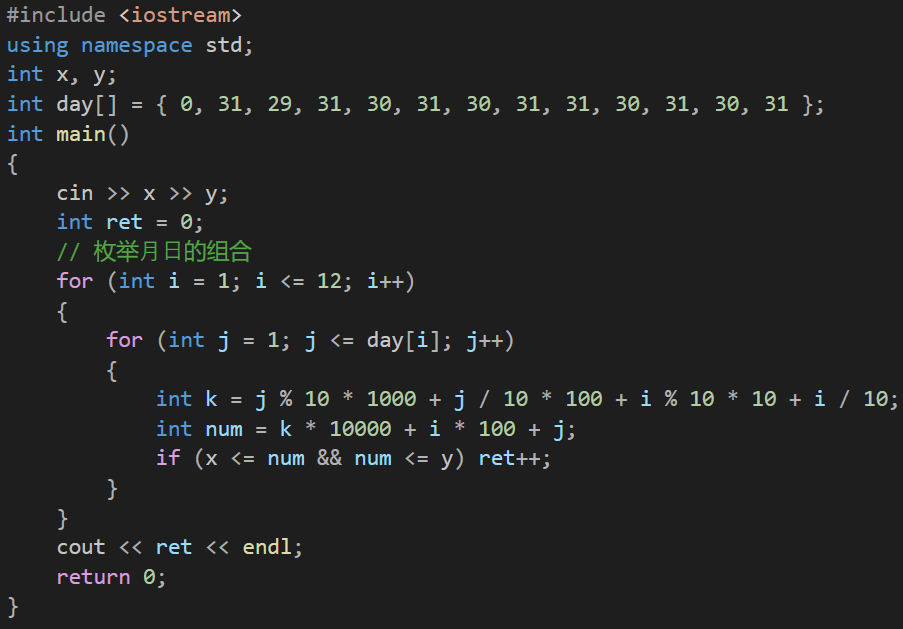
代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int x, y;
int day[] = { 0, 31, 29, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };
int main()
{
cin >> x >> y;
int ret = 0;
// 枚举⽉⽇的组合
for (int i = 1; i <= 12; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= day[i]; j++)
{
int k = j % 10 * 1000 + j / 10 * 100 + i % 10 * 10 + i / 10;
int num = k * 10000 + i * 100 + j;
if (x <= num && num <= y) ret++;
}
}
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}3.1.3 扫雷

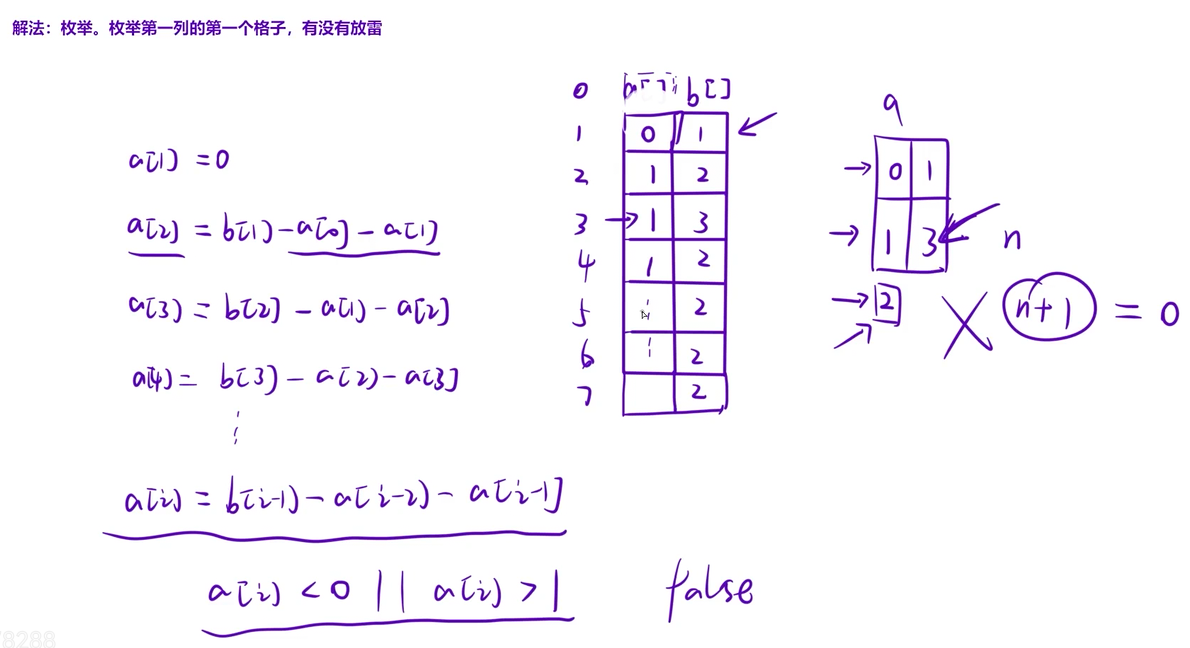
代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e4 + 10;
int n;
int a[N], b[N];
// 不放地雷
int check1()
{
a[1] = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n + 1; i++)
{
a[i] = b[i - 1] - a[i - 1] - a[i - 2];
if (a[i] < 0 || a[i] > 1) return 0;
}
if (a[n + 1] == 0) return 1;
else return 0;
}
int check2()
{
a[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n + 1; i++)
{
a[i] = b[i - 1] - a[i - 1] - a[i - 2];
if (a[i] < 0 || a[i] > 1) return 0;
}
if (a[n + 1] == 0) return 1;
else return 0;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> b[i];
int ret = 0;
ret += check1(); // a[1] 不放地雷
ret += check2(); // a[1] 放地雷
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}3.2 ⼆进制枚举

3.2.1 ⼦集


代码如下(示例):
c
class Solution
{
public:
vector<vector<int>> subsets(vector<int>& nums)
{
vector<vector<int>> ret;
int n = nums.size();
// 枚举所有的状态
for (int st = 0; st < (1 << n); st++)
{
// 根据 st 的状态,还原出要选的数
vector<int> tmp; // 从当前选的⼦集
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if ((st >> i) & 1) tmp.push_back(nums[i]);
}
ret.push_back(tmp);
}
return ret;
}
};3.2.2 费解的开关
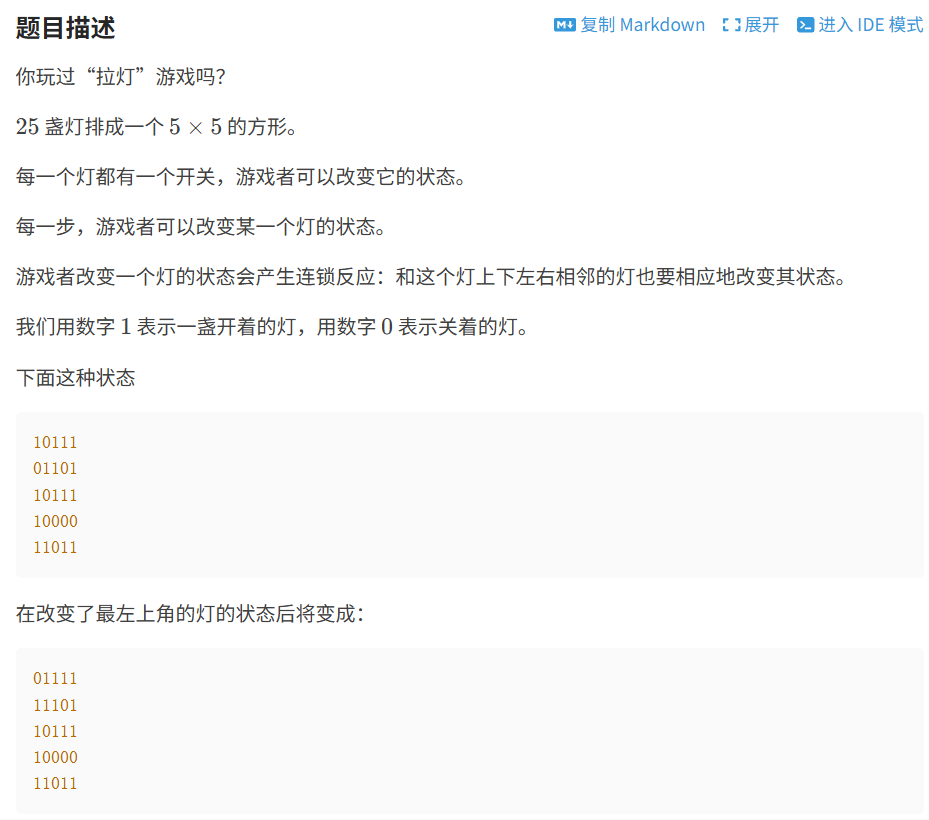

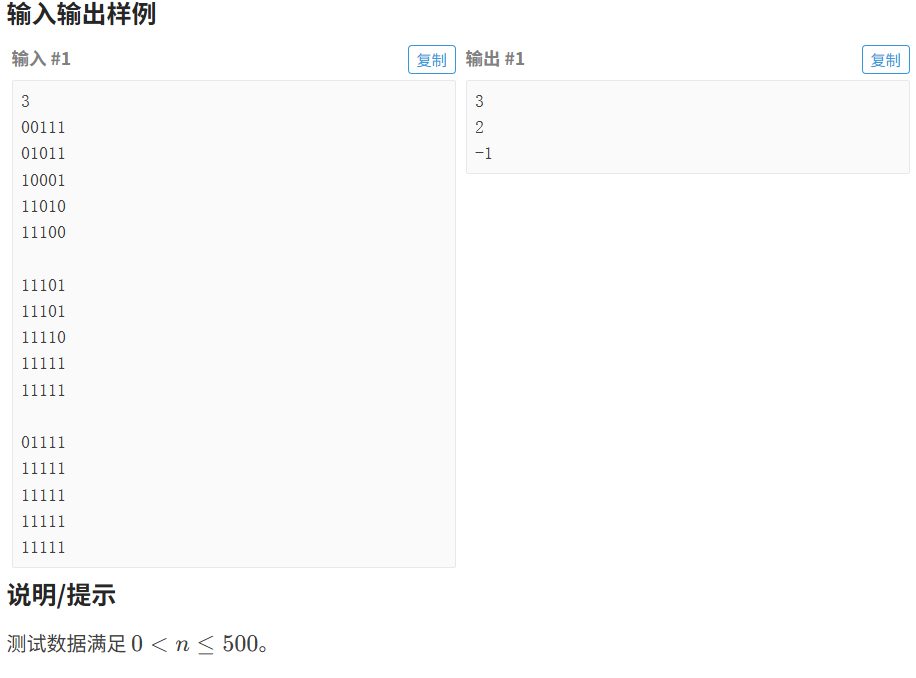


代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10;
int n = 5;
int a[N]; // ⽤⼆进制表⽰,来存储灯的状态
int t[N]; // 备份 a 数组
// 计算 x 的⼆进制表⽰中⼀共有多少个 1
int calc(int x)
{
int cnt = 0;
while (x)
{
cnt++;
x &= x - 1;
}
return cnt;
}
int main()
{
int T; cin >> T;
while (T--)
{
// 多组测试时,⼀定要注意清空之前的数据
memset(a, 0, sizeof a);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
char ch; cin >> ch;
// 存成相反的
if (ch == '0') a[i] |= 1 << j;
}
}
int ret = 0x3f3f3f3f; // 统计所有合法的按法中的最⼩值
// 枚举第⼀⾏所有的按法
for (int st = 0; st < (1 << n); st++)
{
memcpy(t, a, sizeof a);
int push = st; // 当前⾏的按法
int cnt = 0; // 统计当前按法下⼀共按了多少次
// 依次计算后续⾏的结果以及按法
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cnt += calc(push);
// 修改当前⾏被按的结果
t[i] = t[i] ^ push ^ (push << 1) ^ (push >> 1);
t[i] &= (1 << n) - 1; // 清空影响
// 修改下⼀⾏的状态
t[i + 1] ^= push;
// 下⼀⾏的按法
push = t[i];
}
if (t[n - 1] == 0) ret = min(ret, cnt);
}
if (ret > 6) cout << -1 << endl;
else cout << ret << endl;
}
return 0;
}3.2.3 Even Parity

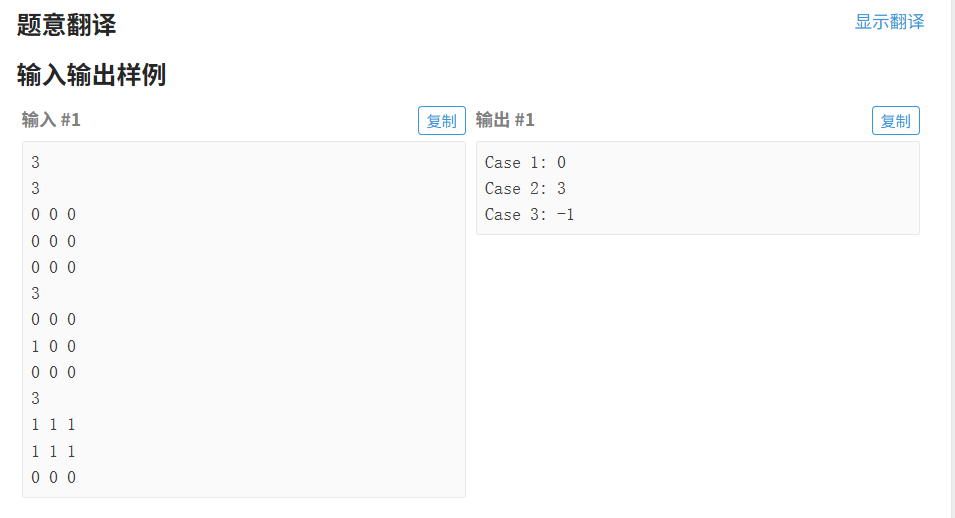

代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 20;
int n;
int a[N]; // ⽤⼆进制存储状态
int t[N]; // 备份
// 判断 x->y 是否合法
// 返回 -1,表⽰不合法
// 其余的数,表⽰合法,并且表⽰ 0->1 的次数
int calc(int x, int y)
{
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (((x >> i) & 1) == 0 && ((y >> i) & 1) == 1) sum++;
if (((x >> i) & 1) == 1 && ((y >> i) & 1) == 0) return -1;
}
return sum;
}
int solve()
{
int ret = 0x3f3f3f3f; // 记录最⼩的改变次数
// 枚举第⼀⾏的最终状态
for (int st = 0; st < (1 << n); st++)
{
memcpy(t, a, sizeof a);
int change = st;
int cnt = 0; // 统计 0->1 的次数
bool flag = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
// 先判断 change 是否合法
int c = calc(t[i], change);
if (c == -1)
{
flag = 0;
break;
}
cnt += c; // 累加次数
// 当前⾏的最终状态
t[i] = change;
// 计算下⼀⾏的最终状态
change = t[i - 1] ^ (t[i] << 1) ^ (t[i] >> 1);
change &= (1 << n) - 1;
}
if (flag) ret = min(ret, cnt);
}
if (ret == 0x3f3f3f3f) return -1;
else return ret;
}
int main()
{
int T; cin >> T;
for (int k = 1; k <= T; k++)
{
// 多组测试数据,记得清空
memset(a, 0, sizeof a);
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) // 避免越界访问
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
int x; cin >> x;
if (x) a[i] |= 1 << j;
}
}
printf("Case %d: %d\n", k, solve());
}
return 0;
}四、前缀和
4.1 ⼀维前缀和
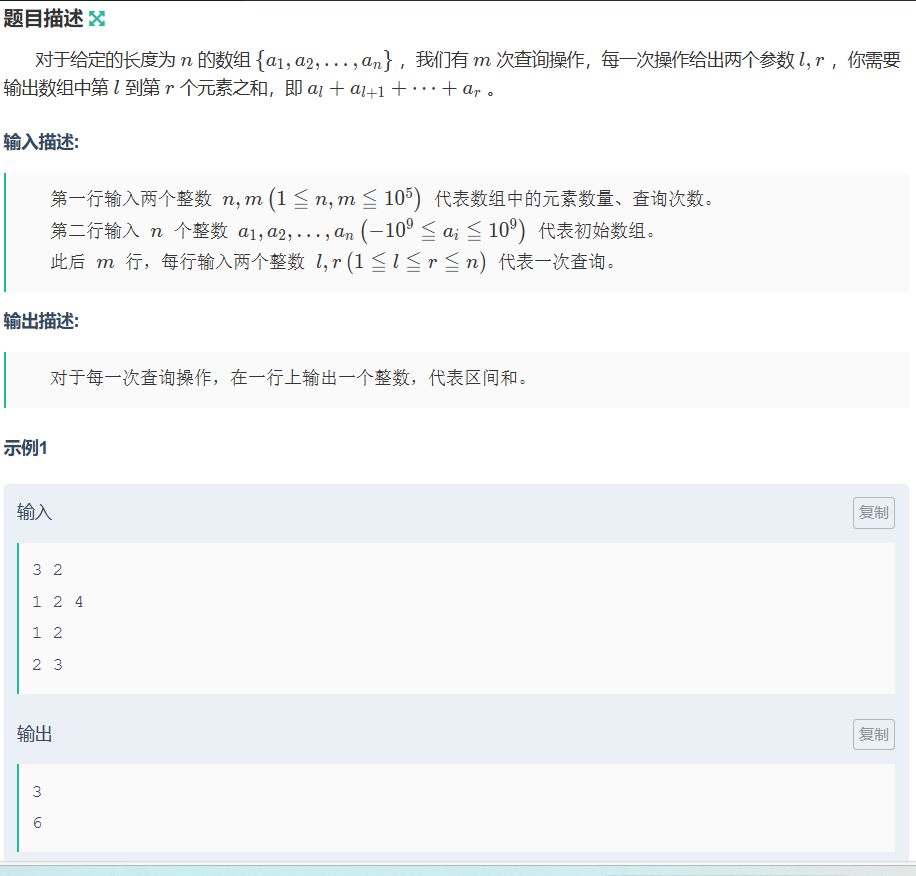

代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n, q;
LL a[N];
LL f[N]; // 前缀和数组
int main()
{
cin >> n >> q;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
// 处理前缀和数组
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
f[i] = f[i - 1] + a[i];
}
// 处理 q 次询问
while (q--)
{
int l, r; cin >> l >> r;
cout << f[r] - f[l - 1] << endl;
}
return 0;
}4.2 最⼤⼦段和
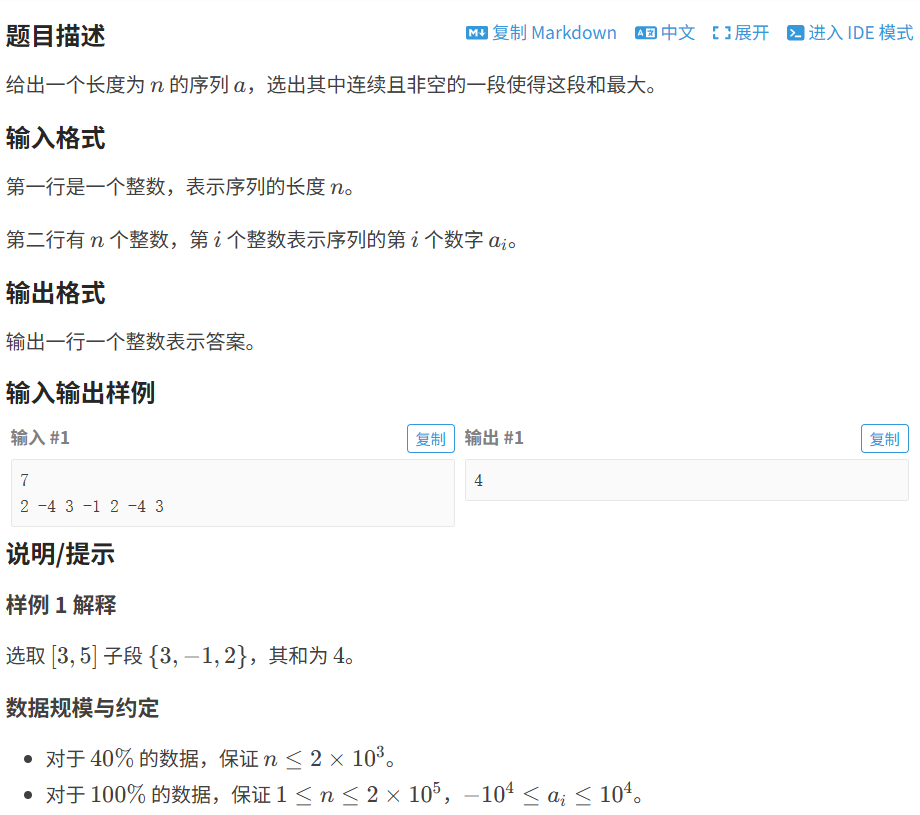

代码如下(示例):
c
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int n, x;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int f[N];
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> x;
f[i] = f[i - 1] + x;
}
int ret = -0x3f3f3f3f;
int prevmin = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
ret = max(ret, f[i] - prevmin);
prevmin = min(prevmin, f[i]);
}
cout << ret << endl;
}4.3 ⼆维前缀和

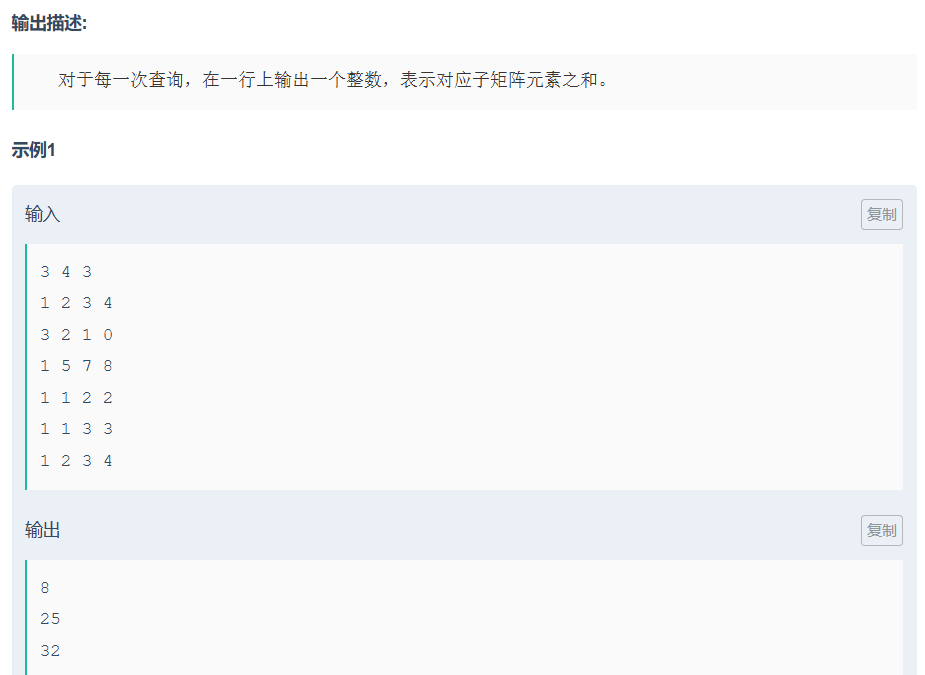
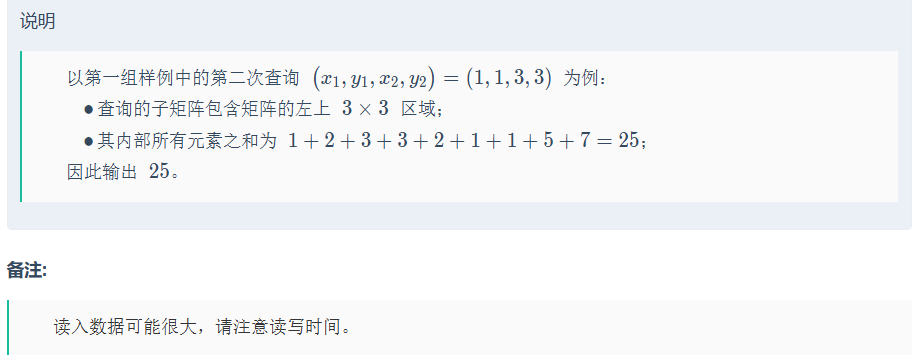
两个公式即可!
代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1010;
int n, m, q;
LL f[N][N];
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m >> q;
// 预处理前缀和矩阵
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
LL x; cin >> x;
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j] + f[i][j - 1] - f[i - 1][j - 1] + x;
}
}
// 处理 q 次查询
while (q--)
{
int x1, y1, x2, y2; cin >> x1 >> y1 >> x2 >> y2;
cout << f[x2][y2] - f[x1 - 1][y2] - f[x2][y1 - 1] + f[x1 - 1][y1 - 1]
<< endl;
}
return 0;
}4.4 激光炸弹
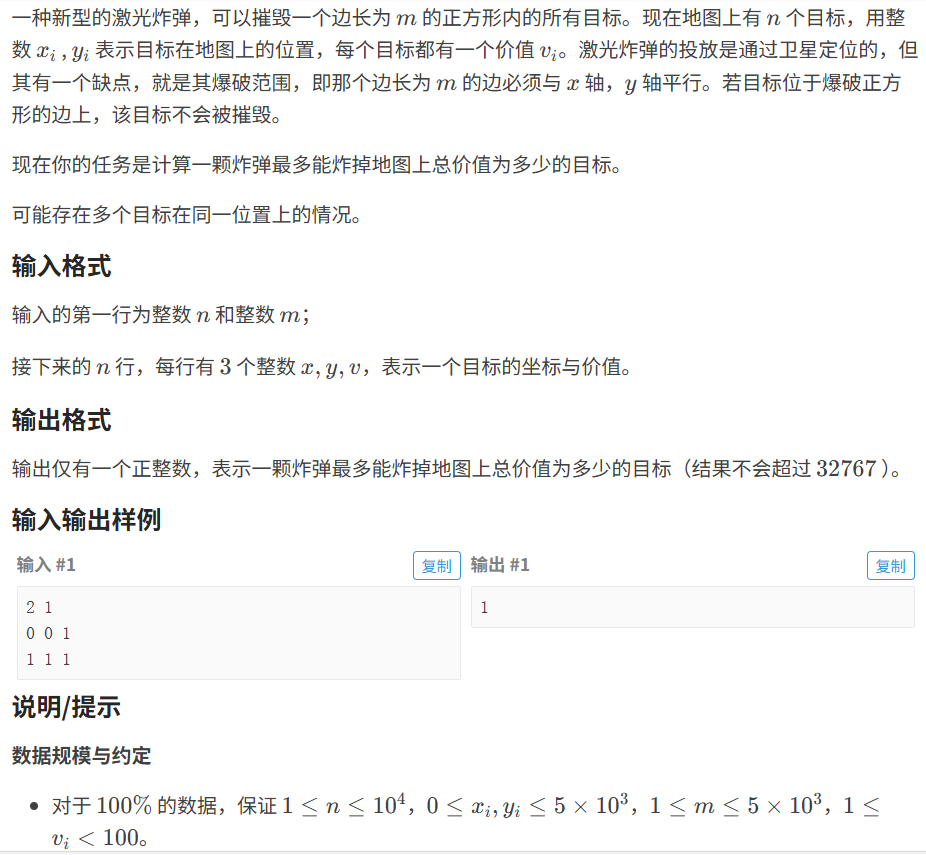

代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5010;
int n, m;
int a[N][N];
int f[N][N]; // 前缀和矩阵
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
while (n--)
{
int x, y, v; cin >> x >> y >> v;
x++, y++; // 下标从 1 开始计数
a[x][y] += v; // 同⼀个位置有可能有多个⽬标
}
n = 5001;
// 预处理前缀和矩阵
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j] + f[i][j - 1] - f[i - 1][j - 1] + a[i][j];
}
}
int ret = 0;
m = min(m, n); // 如果 m 很⼤,相当于就是把整个区域全部摧毁
// 枚举所有边⻓为 m 的正⽅形
for (int x2 = m; x2 <= n; x2++)
{
for (int y2 = m; y2 <= n; y2++)
{
int x1 = x2 - m + 1, y1 = y2 - m + 1;
ret = max(ret, f[x2][y2] - f[x1 - 1][y2] - f[x2][y1 - 1] + f[x1 -
1][y1 - 1]);
}
}
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}五、差分

5.1 ⼀维差分

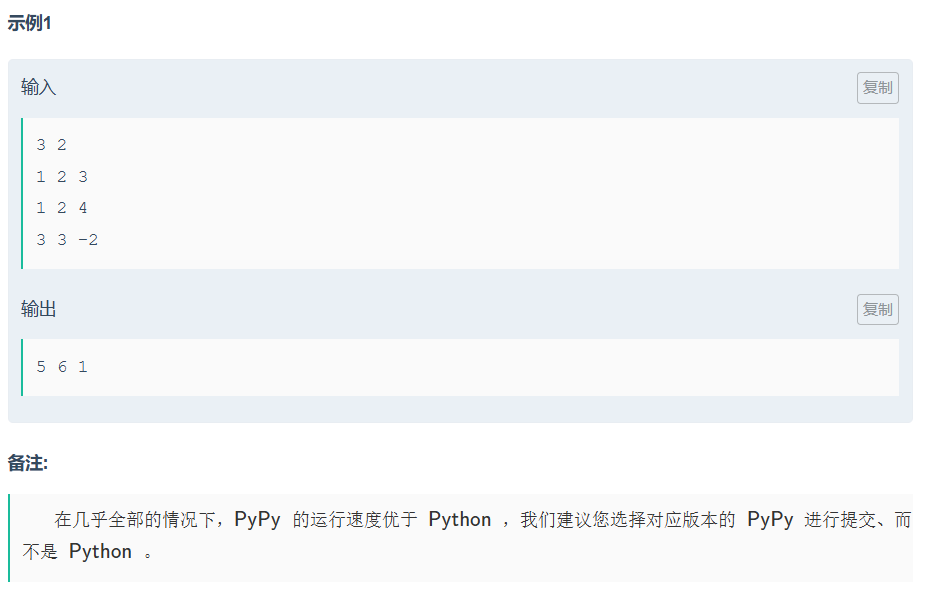
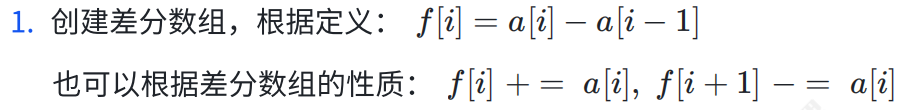
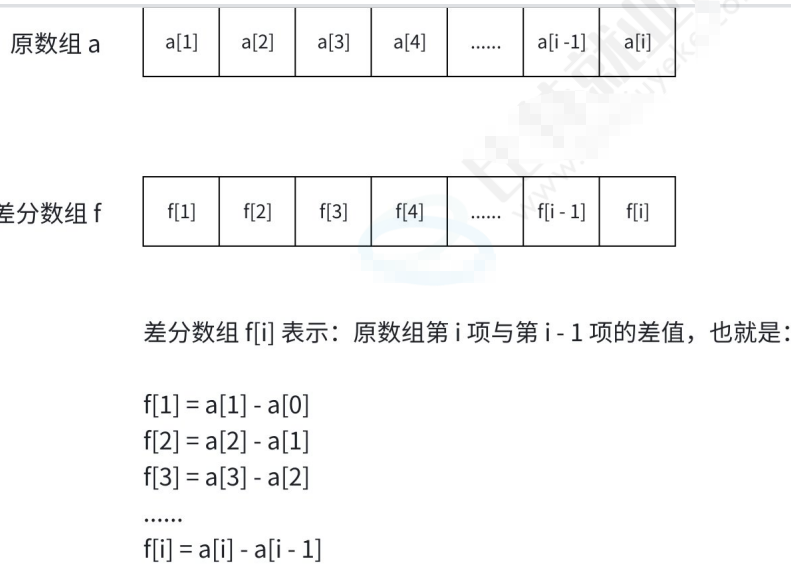

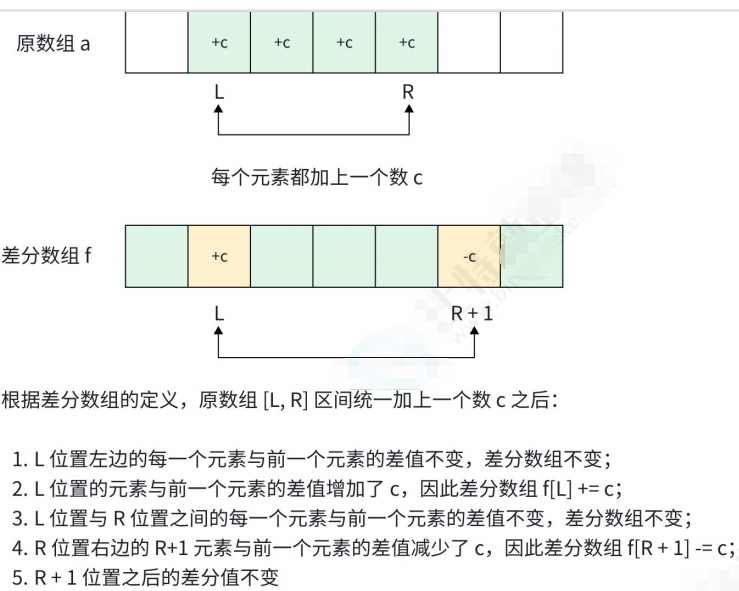

代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n, m;
LL f[N]; // 差分数组
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
// 利⽤差分数组的性质,创建差分数组
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
LL x; cin >> x;
f[i] += x;
f[i + 1] -= x;
}
// 处理 m 次修改操作
while (m--)
{
LL l, r, k; cin >> l >> r >> k;
f[l] += k; f[r + 1] -= k;
}
// 还原出原始的数组
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
f[i] = f[i - 1] + f[i];
cout << f[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}5.2 海底⾼铁



代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n, m;
LL f[N]; // 差分数组
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
// x->y
int x; cin >> x;
for (int i = 2; i <= m; i++)
{
int y; cin >> y;
// x -> y
if (x > y)
{
f[y]++;
f[x]--;
}
else
{
f[x]++;
f[y]--;
}
x = y;
}
// 利⽤差分数组,还原出原数组
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) f[i] += f[i - 1];
// 直接求结果
LL ret = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
LL a, b, c; cin >> a >> b >> c;
ret += min(a * f[i], c + b * f[i]);
}
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}5.3 ⼆维差分

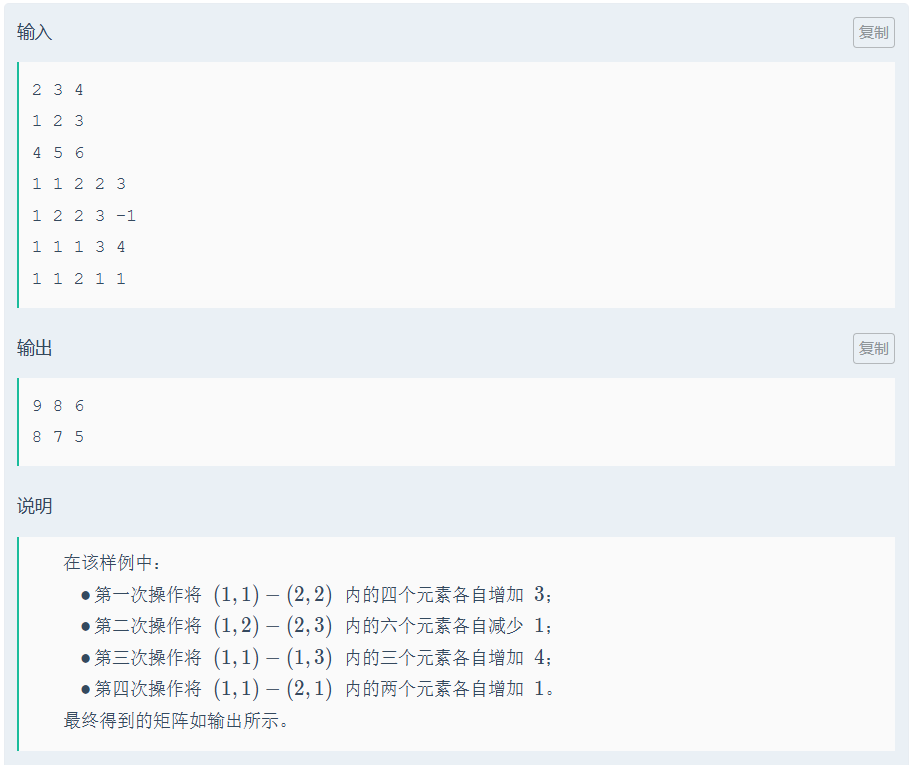

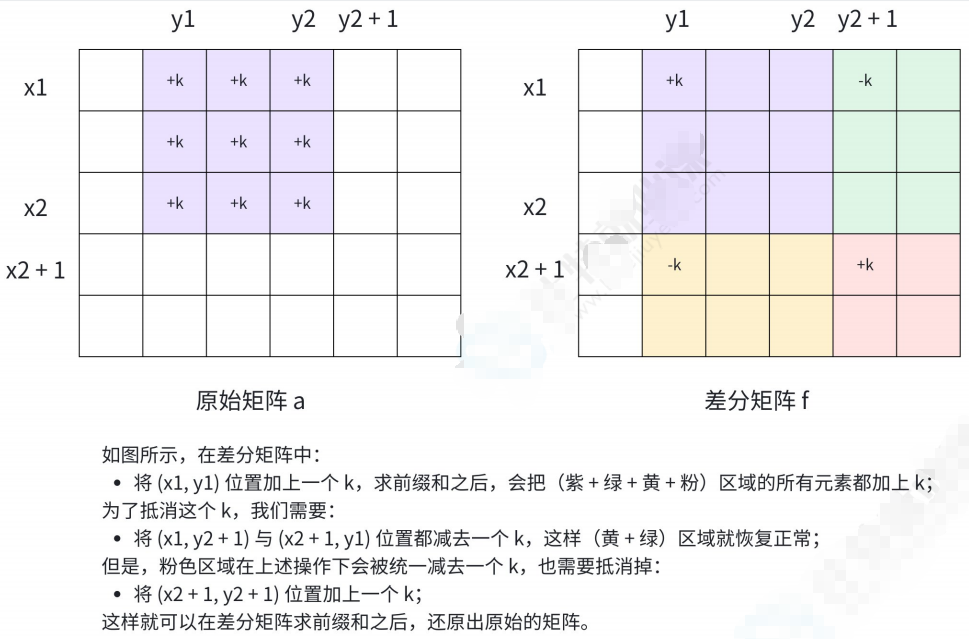

代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1010;
int n, m, q;
LL f[N][N]; // 差分矩阵
// 差分矩阵的性质
void insert(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, LL k)
{
f[x1][y1] += k; f[x1][y2 + 1] -= k; f[x2 + 1][y1] -= k; f[x2 + 1][y2 + 1]
+= k;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m >> q;
// 预处理差分矩阵
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
LL x; cin >> x;
// [i, j]为左上⻆,[i, j]为右下⻆的矩阵,统⼀加上 x
insert(i, j, i, j, x);
}
}
// 处理 q 次修改操作
while (q--)
{
LL x1, y1, x2, y2, k; cin >> x1 >> y1 >> x2 >> y2 >> k;
insert(x1, y1, x2, y2, k);
}
// 利⽤前缀和还原出修改之后的数组
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j] + f[i][j - 1] - f[i - 1][j - 1] + f[i][j];
cout << f[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}5.4 地毯
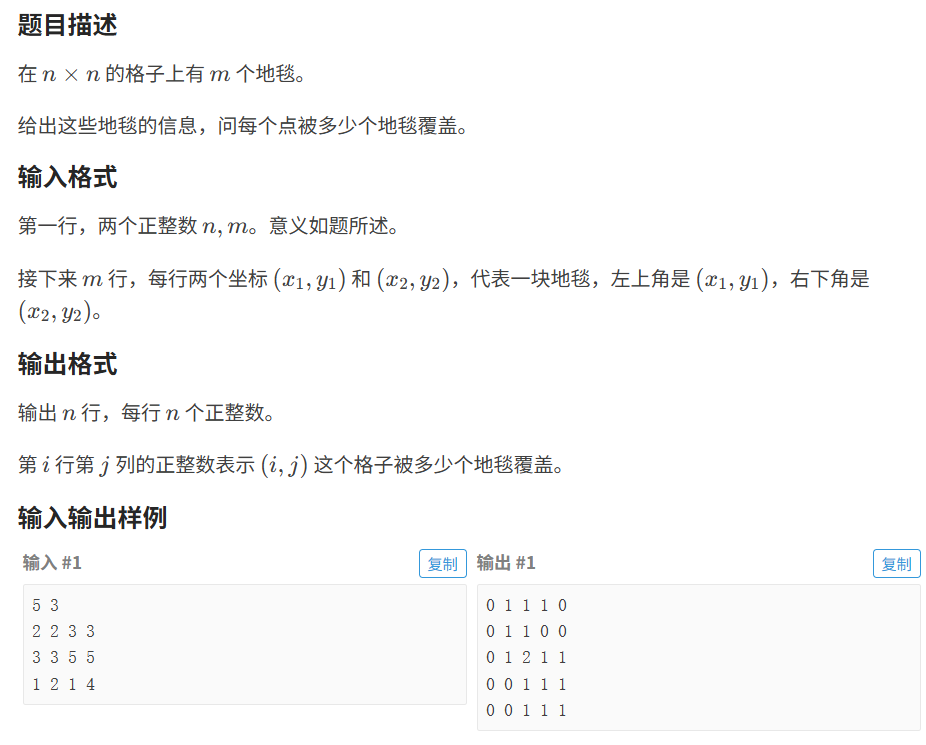
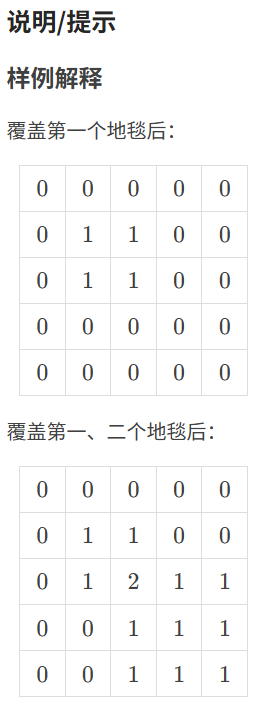
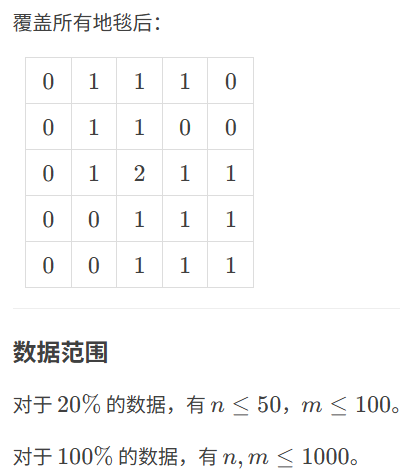
代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
int n, m;
int f[N][N]; // 差分矩阵
// 差分数组的性质
void insert(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int k)
{
f[x1][y1] += k; f[x1][y2 + 1] -= k; f[x2 + 1][y1] -= k; f[x2 + 1][y2 + 1]
+= k;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
// 构建差分数组
while (m--)
{
int x1, y1, x2, y2; cin >> x1 >> y1 >> x2 >> y2;
insert(x1, y1, x2, y2, 1);
}
// 利⽤前缀和还原修改之后的数组
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j] + f[i][j - 1] - f[i - 1][j - 1] + f[i][j];
cout << f[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}六、双指针

6.1 唯⼀的雪花
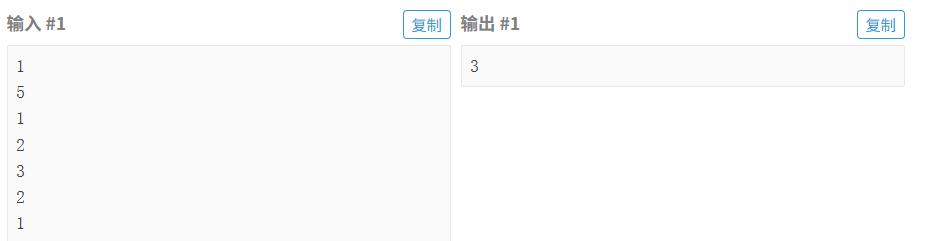
滑动窗口 + 哈希表!
代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int n;
int a[N];
int main()
{
int T; cin >> T;
while (T--)
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
// 初始化
int left = 1, right = 1, ret = 0;
unordered_map<int, int> mp; // 维护窗⼝内所有元素出现的次数
while (right <= n)
{
// 进窗⼝
mp[a[right]]++;
// 判断
while (mp[a[right]] > 1)
{
// 出窗⼝
mp[a[left]]--;
left++;
}
// 窗⼝合法,更新结果
ret = max(ret, right - left + 1);
right++;
}
cout << ret << endl;
}
return 0;
}6.2 逛画展

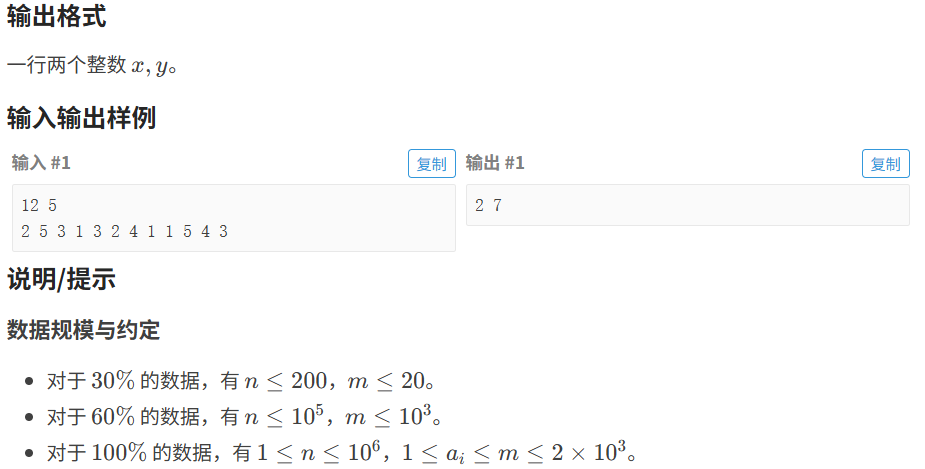

代码如下(示例):
c
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 10, M = 2e3 + 10;
int n, m;
int a[N];
int kind; // 窗⼝内有效元素的个数
int mp[N]; // 统计窗⼝内每个元素出现的次数
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
int left = 1, right = 1;
int ret = n, begin = 1;
while (right <= n)
{
// 进窗⼝
if (mp[a[right]]++ == 0) kind++;
// 判断
while (kind == m)
{
// 更新结果
int len = right - left + 1;
if (len < ret)
{
ret = len;
begin = left;
}
// 出窗⼝
if (mp[a[left]]-- == 1) kind--;
left++;
}
right++;
}
cout << begin << " " << begin + ret - 1 << endl;
return 0;
}6.3 字符串
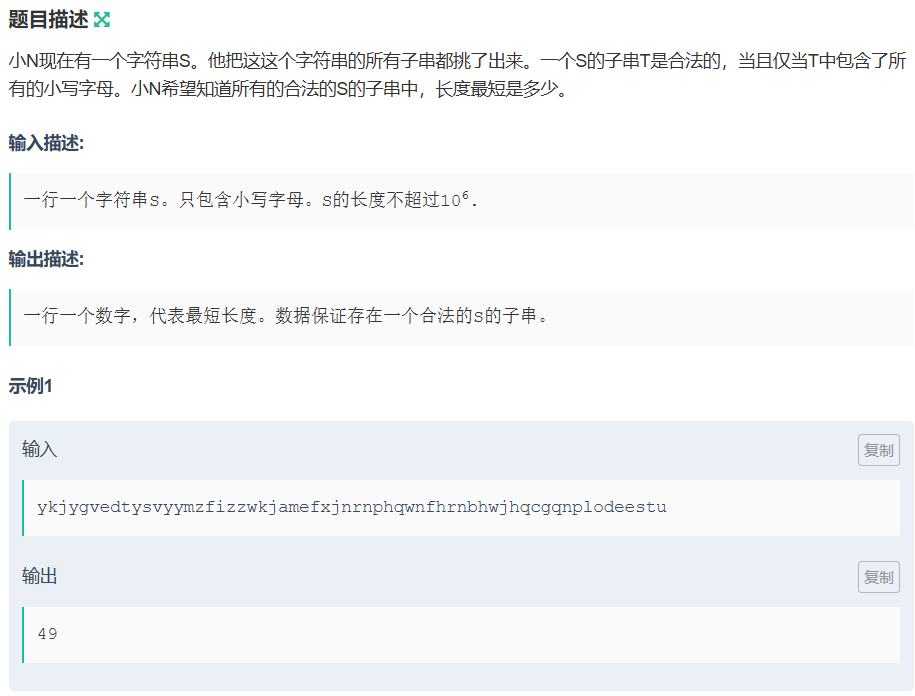
代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
string s;
int mp[26]; // 统计每个⼩写字符出现的次数
int kind; // 窗⼝内⼩写字符的种类
int main()
{
cin >> s;
int n = s.size();
int ret = n;
// 初始化
for (int left = 0, right = 0; right < n; right++)
{
// 进窗⼝
if (mp[s[right] - 'a']++ == 0) kind++;
// 判断
while (kind == 26)
{
// 更新结果
ret = min(ret, right - left + 1);
// 出窗⼝
if (mp[s[left] - 'a']-- == 1) kind--;
left++;
}
}
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}6.4 丢⼿绢

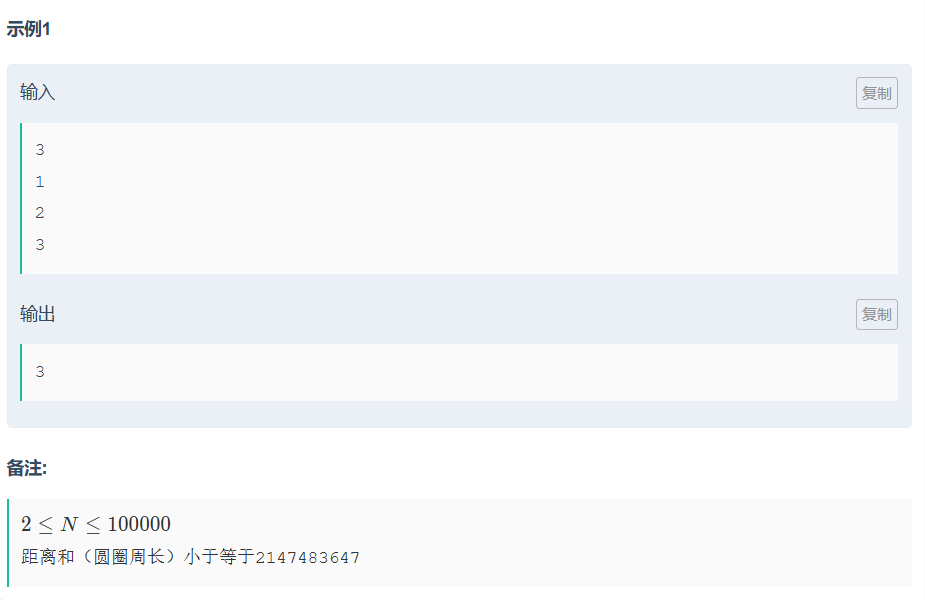


代码如下(示例):
c
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n;
LL a[N];
int main()
{
cin >> n;
LL sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
sum += a[i];
}
int left = 1, right = 1;
LL k = 0;
LL ret = 0;
while (right <= n)
{
k += a[right];
while (2 * k >= sum)
{
// ⽤ sum - k 来更新结果
ret = max(ret, sum - k);
k -= a[left++];
}
// ⽤ k 来更新结果
ret = max(ret, k);
right++;
}
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}七、二分算法

模板题

代码如下(示例):
c
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> searchRange(vector<int>& nums, int target)
{
if(nums.size() == 0) return {-1,-1};
int left = 0 , right = nums.size() - 1;
// 先判断左端点
int begin = 0;
while(left < right)
{
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if(nums[mid] < target) left = mid + 1;
else right = mid;
}
if(nums[left] != target) return {-1 , -1};
else begin = left;
// 再判断右端点
left = 0 , right = nums.size() - 1;
while(left < right)
{
int mid = left + (right - left + 1) / 2;
if(nums[mid] <= target) left = mid;
else right = mid -1;
}
return {begin , right};
}
};7.1 ⼆分查找
7.1.1 ⽜可乐和魔法封印

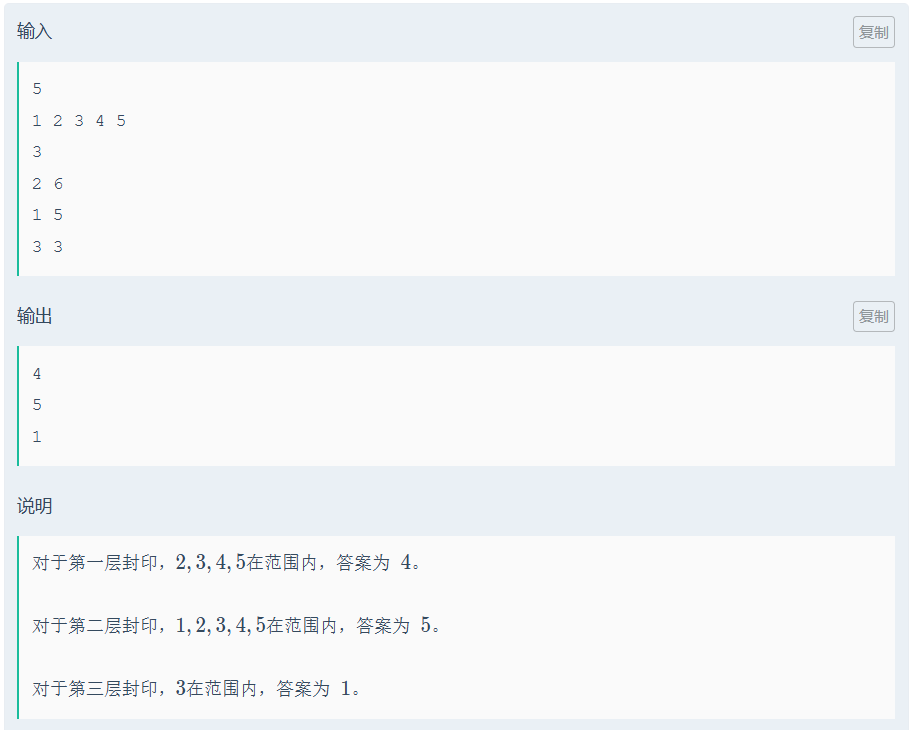
代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n;
int a[N];
int binary_search(int x, int y)
{
// ⼤于等于 x 的最⼩元素
int left = 1, right = n;
while (left < right)
{
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if (a[mid] >= x) right = mid;
else left = mid + 1;
}
if (a[left] < x) return 0;
int tmp = left;
// ⼩于等于 y 的最⼤元素
left = 1, right = n;
while (left < right)
{
int mid = (left + right + 1) / 2;
if (a[mid] <= y) left = mid;
else right = mid - 1;
}
if (a[left] > y) return 0;
return left - tmp + 1;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
int Q; cin >> Q;
while (Q--)
{
int x, y; cin >> x >> y;
cout << binary_search(x, y) << endl;
}
return 0;
}7.1.2 A-B 数对
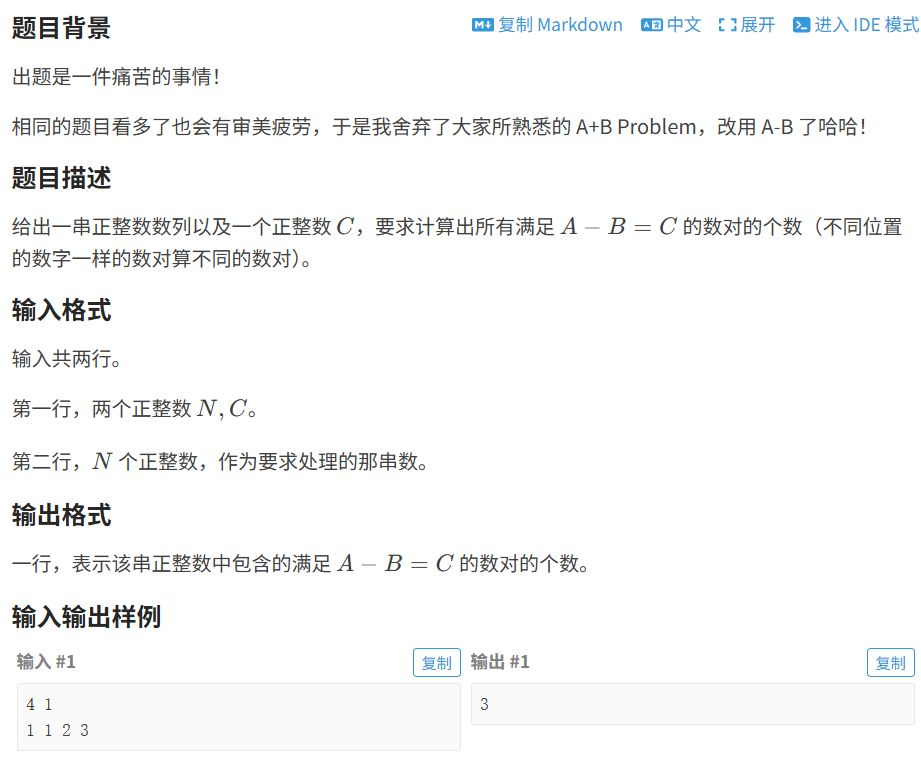
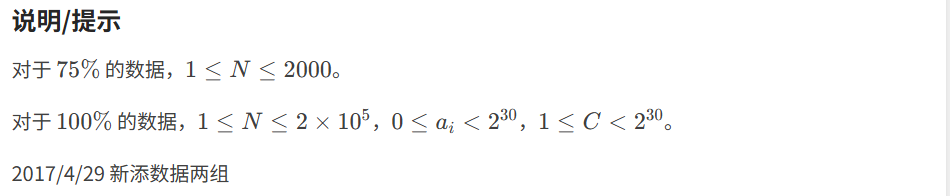


代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
LL n, c;
LL a[N];
int main()
{
cin >> n >> c;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n);
LL ret = 0;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
// a[i]
LL b = a[i] - c;
ret += upper_bound(a + 1, a + i, b) - lower_bound(a + 1, a + i, b);
}
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}7.1.3 烦恼的⾼考志愿
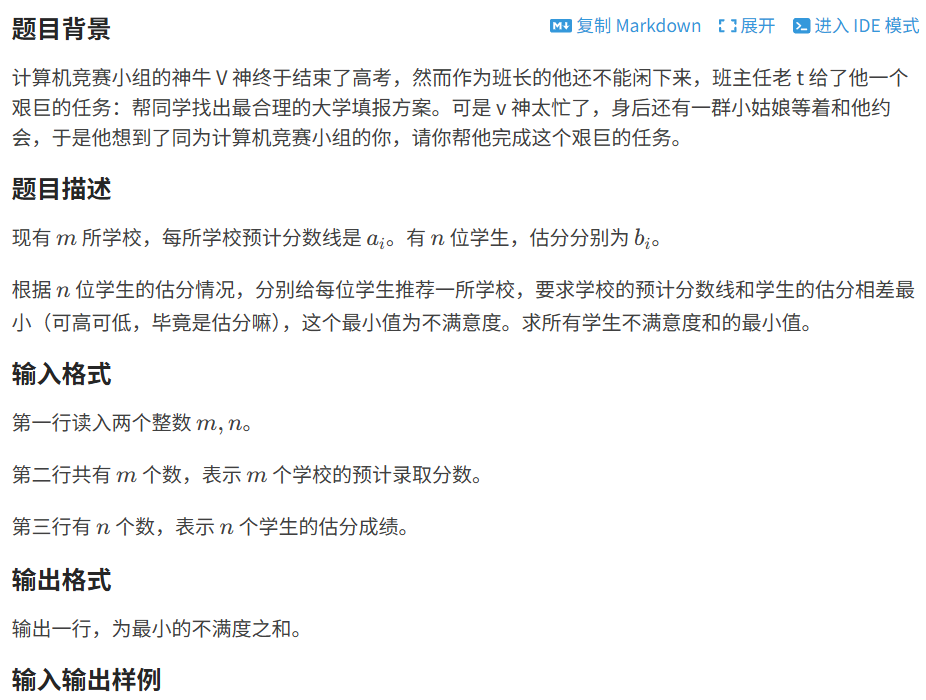


代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n, m;
LL a[N];
int find(LL x)
{
int left = 1, right = m;
while (left < right)
{
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if (a[mid] >= x) right = mid;
else left = mid + 1;
}
return left;
}
int main()
{
cin >> m >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) cin >> a[i];
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + m);
// 加上左右护法
a[0] = -1e7 + 10;
LL ret = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
LL b; cin >> b;
int pos = find(b);
ret += min(abs(a[pos] - b), abs(a[pos - 1] - b));
}
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}7.2 ⼆分答案

7.2.1 ⽊材加⼯



代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
LL n, k;
LL a[N];
// 当切割⻓度为 x 的时候,最多能切出来多少段
LL calc(LL x)
{
LL cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cnt += a[i] / x;
}
return cnt;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> k;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
LL left = 0, right = 1e8;
while (left < right)
{
LL mid = (left + right + 1) / 2;
if (calc(mid) >= k) left = mid;
else right = mid - 1;
}
cout << left << endl;
return 0;
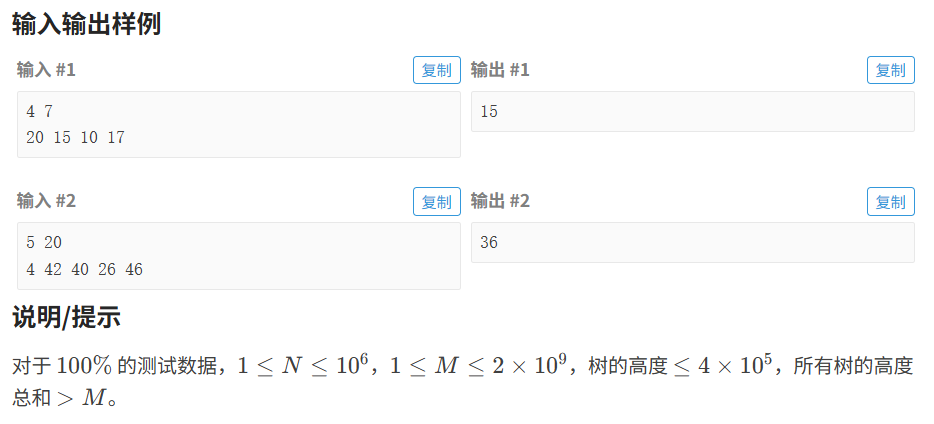
}7.2.2 砍树


代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
LL n, m;
LL a[N];
// 当伐⽊机的⾼度为 x 时,所能获得的⽊材
LL calc(LL x)
{
LL ret = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (a[i] > x) ret += a[i] - x;
}
return ret;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
LL left = 1, right = 2e9;
while (left < right)
{
LL mid = (left + right + 1) / 2;
if (calc(mid) >= m) left = mid;
else right = mid - 1;
}
cout << left << endl;
return 0;
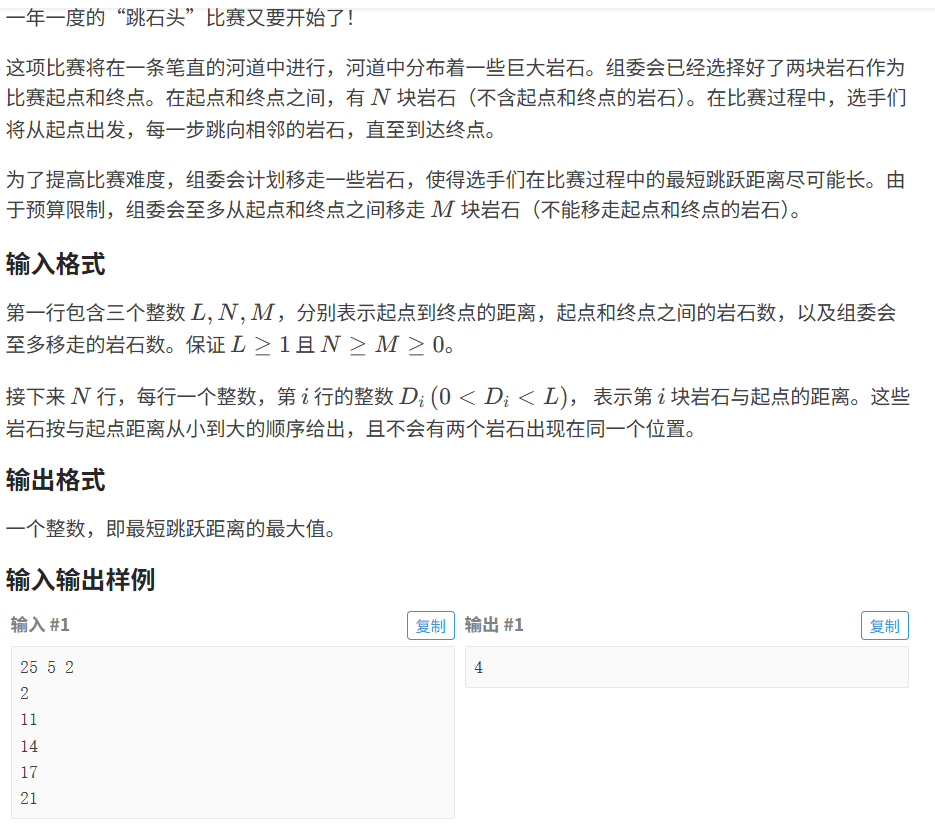
}7.2.3 跳⽯头


代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 5e4 + 10;
LL l, n, m;
LL a[N];
// 当最短跳跃距离为 x 时,移⾛的岩⽯数⽬
LL calc(LL x)
{
LL ret = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
int j = i + 1;
while (j <= n && a[j] - a[i] < x) j++;
ret += j - i - 1;
i = j - 1;
}
return ret;
}
int main()
{
cin >> l >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
a[n + 1] = l;
n++;
LL left = 1, right = l;
while (left < right)
{
LL mid = (left + right + 1) / 2;
if (calc(mid) <= m) left = mid;
else right = mid - 1;
}
cout << left << endl;
return 0;
}整体源代码
代码如下(示例):
c
//#include <iostream>
//#include <cmath>
//using namespace std;
//int main()
//{
// int n; cin >> n;
// // 循环次数
// for (int i = n; i >= 0; i--)
// {
// int a; cin >> a;
// if (a == 0) continue; // 处理系数为 0 的情况
// // 1. 符号
// if (a < 0) cout << '-';
// else
// {
// if (i != n) cout << '+';
// }
// // 2. 数字
// a = abs(a);
// if (a != 1 || (a == 1 && i == 0)) cout << a;
// // 3. 次数
// if (i == 0) continue;
// else if (i == 1) cout << 'x';
// else cout << "x^" << i;
// }
// return 0;
//}
//#include<iostream>
//using namespace std;
//
//int dx[4] = { 0 , 1 , 0 , -1 };
//int dy[4] = { 1 , 0 ,-1 , 0 };
//const int N = 15;
//int arr[N][N];
//
//int main()
//{
// int n; cin >> n;
// int cnt = 1;
// int pos = 0;
// int x = 1, y = 1;
// while (cnt <= n * n)
// {
// arr[x][y] = cnt;
// int a = x + dx[pos], b = y + dy[pos];
// if (a < 1 || a > n || b < 1 || b > n || arr[a][b])
// {
// pos = (pos + 1) % 4;
// a = x + dx[pos], b = y + dy[pos];
// }
// x = a, y = b;
// cnt++;
// }
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
// {
// for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
// {
// printf("%3d", arr[i][j]);
// }
// puts("");
// }
//}
//#include <iostream>
//#include<string>
//#include <algorithm>
//using namespace std;
//int p1, p2, p3, n;
//string s;
//string ret;
//// 判断是否是数字字符
//bool isdig(char ch)
//{
// return ch >= '0' && ch <= '9';
//}
//// 判断是否是⼩写字⺟
//bool islet(char ch)
//{
// return ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z';
//}
//// 把 [left, right] 之间的字符展开
//// left, right 这两个字符是不做处理
//void add(char left, char right)
//{
// string t;
// // 遍历中间的字符
// for (char ch = left + 1; ch < right; ch++)
// {
// char tmp = ch;
// // 处理 p1
// if (p1 == 2 && islet(tmp)) tmp -= 32; // ⼩写变⼤写
// else if (p1 == 3) tmp = '*'; // 变成星号
// // 处理 p2
// for (int i = 0; i < p2; i++)
// {
// t += tmp;
// }
// }
// // 处理 p3
// if (p3 == 2) reverse(t.begin(), t.end());
// ret += t;
//}
//int main()
//{
// cin >> p1 >> p2 >> p3 >> s;
// n = s.size();
// for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
// {
// char ch = s[i];
// if (s[i] != '-' || i == 0 || i == n - 1) ret += ch;
// else
// {
// char left = s[i - 1], right = s[i + 1];
// // 判断是否展开
// if (isdig(left) && isdig(right) && right > left ||
// islet(left) && islet(right) && right > left)
// {
// // 展开
// add(left, right);
// }
// else
// {
// ret += ch;
// }
// }
// }
// cout << ret << endl;
// return 0;
//}
//#include<iostream>
//#include<string>
//using namespace std;
//const int N = 1e6 + 10;
//int a[N], b[N], c[N];
//int la, lb, lc;
//string x, y;
//
//void add(int a[], int b[], int c[])
//{
// for (int i = 0; i < lc; i++)
// {
// c[i] += a[i] + b[i];
// c[i + 1] += c[i] / 10;
// c[i] %= 10;
// }
// if (c[lc]) lc++;
//}
//int main()
//{
// cin >> x >> y;
// la = x.size(), lb = y.size(), lc = max(la, lb);
// for (int i = 0; i < la; i++) a[la - 1 - i] = x[i] - '0';
// for (int i = 0; i < lb; i++) b[lb - 1 - i] = y[i] - '0';
// add(c, a, b);
// for (int i = lc - 1; i >= 0; i--) cout << c[i];
//}
//#include <iostream>
//using namespace std;
//const int N = 1e6 + 10;
//int a[N], b[N], c[N];
//int la, lb, lc;
//// ⾼精度加法的模版 - c = a + b;
//void add(int c[], int a[], int b[])
//{
// for (int i = 0; i < lc; i++)
// {
// c[i] += a[i] + b[i]; // 对应位相加,再加上进位
// c[i + 1] += c[i] / 10; // 处理进位
// c[i] %= 10; // 处理余数
// }
// if (c[lc]) lc++;
//}
//int main()
//{
// string x, y; cin >> x >> y;
// // 1. 拆分每⼀位,逆序放在数组中
// la = x.size(); lb = y.size(); lc = max(la, lb);
// for (int i = 0; i < la; i++) a[la - 1 - i] = x[i] - '0';
// for (int i = 0; i < lb; i++) b[lb - 1 - i] = y[i] - '0';
// // 2. 模拟加法的过程
// add(c, a, b); // c = a + b
// // 输出结果
// for (int i = lc - 1; i >= 0; i--) cout << c[i];
// return 0;
//}
//#include <iostream>
//using namespace std;
//const int N = 1e6 + 10;
//int a[N], b[N], c[N];
//int la, lb, lc;
//// ⽐⼤⼩
//bool cmp(string& x, string& y)
//{
// // 先⽐较⻓度
// if (x.size() != y.size()) return x.size() < y.size();
// // 再按照 字典序 的⽅式⽐较
// return x < y;
//}
//// ⾼精度减法的模板 - c = a - b
//void sub(int c[], int a[], int b[])
//{
// for (int i = 0; i < lc; i++)
// {
// c[i] += a[i] - b[i]; // 对应位相减,然后处理借位
// if (c[i] < 0)
// {
// c[i + 1] -= 1; // 借位
// c[i] += 10;
// }
// }
// // 处理前导零
// while (lc > 1 && c[lc - 1] == 0) lc--;
//}
//int main()
//{
// string x, y; cin >> x >> y;
// // ⽐⼤⼩
// if (cmp(x, y))
// {
// swap(x, y);
// cout << '-';
// }
// // 1. 拆分每⼀位,然后逆序放在数组中
// la = x.size(); lb = y.size(); lc = max(la, lb);
// for (int i = 0; i < la; i++) a[la - i - 1] = x[i] - '0';
// for (int i = 0; i < lb; i++) b[lb - i - 1] = y[i] - '0';
// // 2. 模拟减法的过程
// sub(c, a, b); // c = a - b
// // 输出结果
// for (int i = lc - 1; i >= 0; i--) cout << c[i];
// return 0;
//}
//#include <iostream>
//using namespace std;
//const int N = 1e6 + 10;
//int a[N], b[N], c[N];
//int la, lb, lc;
//// ⾼精度乘法的模版 - c = a * b
//void mul(int c[], int a[], int b[])
//{
// // ⽆进位相乘,然后相加
// for (int i = 0; i < la; i++)
// {
// for (int j = 0; j < lb; j++)
// {
// c[i + j] += a[i] * b[j];
// }
// }
// // 处理进位
// for (int i = 0; i < lc; i++)
// {
// c[i + 1] += c[i] / 10;
// c[i] %= 10;
// }
// // 处理前导零
// while (lc > 1 && c[lc - 1] == 0) lc--;
//}
//int main()
//{
// string x, y; cin >> x >> y;
// // 1. 拆分每⼀位,逆序放在数组中
// la = x.size(); lb = y.size(); lc = la + lb;
// for (int i = 0; i < la; i++) a[la - 1 - i] = x[i] - '0';
// for (int i = 0; i < lb; i++) b[lb - 1 - i] = y[i] - '0';
// // 2. 模拟乘法的过程
// mul(c, a, b); // c = a * b
// // 输出结果
// for (int i = lc - 1; i >= 0; i--) cout << c[i];
// return 0;
//}
//#include<iostream>
//using namespace std;
//const int N = 1e6 + 10;
//typedef long long LL;
//int a[N], b, c[N];
//int la, lc;
//// ⾼精度除法的模板 - c = a / b (⾼精度 / 低精度)
//void sub(int c[], int a[], int b)
//{
// LL t = 0; // 标记每次除完之后的余数
// for (int i = la - 1; i >= 0; i--)
// {
// // 计算当前的被除数
// t = t * 10 + a[i];
// c[i] = t / b;
// t %= b;
// }
// // 处理前导 0
// while (lc > 1 && c[lc - 1] == 0) lc--;
//}
//int main()
//{
// string x; cin >> x >> b;
// la = x.size();
// for (int i = 0; i < la; i++) a[la - 1 - i] = x[i] - '0';
// // 模拟除法的过程
// lc = la;
// sub(c, a, b); // c = a / b
// for (int i = lc - 1; i >= 0; i--) cout << c[i];
// return 0;
//}
//#include<iostream>
//using namespace std;
//int n;
//const int N = 5;
//int a[N], b[N], c[N], d[N];
//int x, y;
//
//int find()
//{
// for (int i = n; i >=1 ; i--)
// {
// if (a[i] <= x && b[i] <= y && a[i] + c[i] >= x && b[i] + d[i] >= y)
// {
// return i;
// }
// return -1;
// }
//}
//int main()
//{
// cin >> n;
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i] >> b[i] >> c[i] >> d[i];
// cin >> x >> y;
// cout << find() << endl;
//}
//#include <iostream>
//using namespace std;
//const int N = 1e4 + 10;
//int n;
//int a[N], b[N], g[N], k[N];
//int x, y;
//int find()
//{
// // 从后往前枚举
// for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--)
// {
// // 判断是否覆盖
// if (a[i] <= x && b[i] <= y && a[i] + g[i] >= x && b[i] + k[i] >= y)
// {
// return i;
// }
// }
// return -1;
//}
//int main()
//{
// cin >> n;
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i] >> b[i] >> g[i] >> k[i];
// cin >> x >> y;
// cout << find() << endl;
// return 0;
//}
//#include <iostream>
//using namespace std;
//int x, y;
//int day[] = { 0, 31, 29, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };
//int main()
//{
// cin >> x >> y;
// int ret = 0;
// // 枚举⽉⽇的组合
// for (int i = 1; i <= 12; i++)
// {
// for (int j = 1; j <= day[i]; j++)
// {
// int k = j % 10 * 1000 + j / 10 * 100 + i % 10 * 10 + i / 10;
// int num = k * 10000 + i * 100 + j;
// if (x <= num && num <= y) ret++;
// }
// }
// cout << ret << endl;
// return 0;
//}
//#include <iostream>
//using namespace std;
//const int N = 1e4 + 10;
//int n;
//int a[N], b[N];
//// 不放地雷
//int check1()
//{
// a[1] = 0;
// for (int i = 2; i <= n + 1; i++)
// {
// a[i] = b[i - 1] - a[i - 1] - a[i - 2];
// if (a[i] < 0 || a[i] > 1) return 0;
// }
// if (a[n + 1] == 0) return 1;
// else return 0;
//}
//int check2()
//{
// a[1] = 1;
// for (int i = 2; i <= n + 1; i++)
// {
// a[i] = b[i - 1] - a[i - 1] - a[i - 2];
// if (a[i] < 0 || a[i] > 1) return 0;
// }
// if (a[n + 1] == 0) return 1;
// else return 0;
//}
//int main()
//{
// cin >> n;
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> b[i];
// int ret = 0;
// ret += check1(); // a[1] 不放地雷
// ret += check2(); // a[1] 放地雷
// cout << ret << endl;
// return 0;
//}
//class Solution
//{
//public:
// vector<vector<int>> subsets(vector<int>& nums)
// {
// vector<vector<int>> ret;
// int n = nums.size();
// // 枚举所有的状态
// for (int st = 0; st < (1 << n); st++)
// {
// // 根据 st 的状态,还原出要选的数
// vector<int> tmp; // 从当前选的⼦集
// for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
// {
// if ((st >> i) & 1) tmp.push_back(nums[i]);
// }
// ret.push_back(tmp);
// }
// return ret;
// }
//};
//#include <iostream>
//#include <cstring>
//using namespace std;
//const int N = 10;
//int n = 5;
//int a[N]; // ⽤⼆进制表⽰,来存储灯的状态
//int t[N]; // 备份 a 数组
//// 计算 x 的⼆进制表⽰中⼀共有多少个 1
//int calc(int x)
//{
// int cnt = 0;
// while (x)
// {
// cnt++;
// x &= x - 1;
// }
// return cnt;
//}
//int main()
//{
// int T; cin >> T;
// while (T--)
// {
// // 多组测试时,⼀定要注意清空之前的数据
// memset(a, 0, sizeof a);
// for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
// {
// for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
// {
// char ch; cin >> ch;
// // 存成相反的
// if (ch == '0') a[i] |= 1 << j;
// }
// }
// int ret = 0x3f3f3f3f; // 统计所有合法的按法中的最⼩值
// // 枚举第⼀⾏所有的按法
// for (int st = 0; st < (1 << n); st++)
// {
// memcpy(t, a, sizeof a);
// int push = st; // 当前⾏的按法
// int cnt = 0; // 统计当前按法下⼀共按了多少次
// // 依次计算后续⾏的结果以及按法
// for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
// {
// cnt += calc(push);
// // 修改当前⾏被按的结果
// t[i] = t[i] ^ push ^ (push << 1) ^ (push >> 1);
// t[i] &= (1 << n) - 1; // 清空影响
// // 修改下⼀⾏的状态
// t[i + 1] ^= push;
// // 下⼀⾏的按法
// push = t[i];
// }
// if (t[n - 1] == 0) ret = min(ret, cnt);
// }
// if (ret > 6) cout << -1 << endl;
// else cout << ret << endl;
// }
// return 0;
//}
//#include <iostream>
//#include <cstring>
//using namespace std;
//const int N = 20;
//int n;
//int a[N]; // ⽤⼆进制存储状态
//int t[N]; // 备份
//// 判断 x->y 是否合法
//// 返回 -1,表⽰不合法
//// 其余的数,表⽰合法,并且表⽰ 0->1 的次数
//int calc(int x, int y)
//{
// int sum = 0;
// for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
// {
// if (((x >> i) & 1) == 0 && ((y >> i) & 1) == 1) sum++;
// if (((x >> i) & 1) == 1 && ((y >> i) & 1) == 0) return -1;
// }
// return sum;
//}
//int solve()
//{
// int ret = 0x3f3f3f3f; // 记录最⼩的改变次数
// // 枚举第⼀⾏的最终状态
// for (int st = 0; st < (1 << n); st++)
// {
// memcpy(t, a, sizeof a);
// int change = st;
// int cnt = 0; // 统计 0->1 的次数
// bool flag = 1;
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
// {
// // 先判断 change 是否合法
// int c = calc(t[i], change);
// if (c == -1)
// {
// flag = 0;
// break;
// }
// cnt += c; // 累加次数
// // 当前⾏的最终状态
// t[i] = change;
// // 计算下⼀⾏的最终状态
// change = t[i - 1] ^ (t[i] << 1) ^ (t[i] >> 1);
// change &= (1 << n) - 1;
// }
// if (flag) ret = min(ret, cnt);
// }
// if (ret == 0x3f3f3f3f) return -1;
// else return ret;
//}
//int main()
//{
// int T; cin >> T;
// for (int k = 1; k <= T; k++)
// {
// // 多组测试数据,记得清空
// memset(a, 0, sizeof a);
// cin >> n;
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) // 避免越界访问
// {
// for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
// {
// int x; cin >> x;
// if (x) a[i] |= 1 << j;
// }
// }
// printf("Case %d: %d\n", k, solve());
// }
// return 0;
//}
//#include <iostream>
//using namespace std;
//typedef long long LL;
//const int N = 1e5 + 10;
//int n, q;
//LL a[N];
//LL f[N]; // 前缀和数组
//int main()
//{
// cin >> n >> q;
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
// // 处理前缀和数组
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
// {
// f[i] = f[i - 1] + a[i];
// }
// // 处理 q 次询问
// while (q--)
// {
// int l, r; cin >> l >> r;
// cout << f[r] - f[l - 1] << endl;
// }
// return 0;
//}
//#include<iostream>
//using namespace std;
//int n, x;
//const int N = 2e5 + 10;
//int f[N];
//
//int main()
//{
// cin >> n;
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
// {
// cin >> x;
// f[i] = f[i - 1] + x;
// }
// int ret = -0x3f3f3f3f;
// int prevmin = 0;
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
// {
// ret = max(ret, f[i] - prevmin);
// prevmin = min(prevmin, f[i]);
// }
// cout << ret << endl;
// }
//#include <iostream>
//using namespace std;
//typedef long long LL;
//const int N = 1010;
//int n, m, q;
//LL f[N][N];
//int main()
//{
// cin >> n >> m >> q;
// // 预处理前缀和矩阵
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
// {
// for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
// {
// LL x; cin >> x;
// f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j] + f[i][j - 1] - f[i - 1][j - 1] + x;
// }
// }
// // 处理 q 次查询
// while (q--)
// {
// int x1, y1, x2, y2; cin >> x1 >> y1 >> x2 >> y2;
// cout << f[x2][y2] - f[x1 - 1][y2] - f[x2][y1 - 1] + f[x1 - 1][y1 - 1]
// << endl;
// }
// return 0;
//}
//#include <iostream>
//using namespace std;
//const int N = 5010;
//int n, m;
//int a[N][N];
//int f[N][N]; // 前缀和矩阵
//int main()
//{
// cin >> n >> m;
// while (n--)
// {
// int x, y, v; cin >> x >> y >> v;
// x++, y++; // 下标从 1 开始计数
// a[x][y] += v; // 同⼀个位置有可能有多个⽬标
// }
// n = 5001;
// // 预处理前缀和矩阵
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
// {
// for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
// {
// f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j] + f[i][j - 1] - f[i - 1][j - 1] + a[i][j];
// }
// }
// int ret = 0;
// m = min(m, n); // 如果 m 很⼤,相当于就是把整个区域全部摧毁
// // 枚举所有边⻓为 m 的正⽅形
// for (int x2 = m; x2 <= n; x2++)
// {
// for (int y2 = m; y2 <= n; y2++)
// {
// int x1 = x2 - m + 1, y1 = y2 - m + 1;
// ret = max(ret, f[x2][y2] - f[x1 - 1][y2] - f[x2][y1 - 1] + f[x1 -
// 1][y1 - 1]);
// }
// }
// cout << ret << endl;
// return 0;
//}
//#include <iostream>
//using namespace std;
//typedef long long LL;
//const int N = 1e5 + 10;
//int n, m;
//LL f[N]; // 差分数组
//int main()
//{
// cin >> n >> m;
// // 利⽤差分数组的性质,创建差分数组
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
// {
// LL x; cin >> x;
// f[i] += x;
// f[i + 1] -= x;
// }
// // 处理 m 次修改操作
// while (m--)
// {
// LL l, r, k; cin >> l >> r >> k;
// f[l] += k; f[r + 1] -= k;
// }
// // 还原出原始的数组
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
// {
// f[i] = f[i - 1] + f[i];
// cout << f[i] << " ";
// }
// return 0;
//}
//#include <iostream>
//using namespace std;
//typedef long long LL;
//const int N = 1e5 + 10;
//int n, m;
//LL f[N]; // 差分数组
//int main()
//{
// cin >> n >> m;
// // x->y
// int x; cin >> x;
// for (int i = 2; i <= m; i++)
// {
// int y; cin >> y;
// // x -> y
// if (x > y)
// {
// f[y]++;
// f[x]--;
// }
// else
// {
// f[x]++;
// f[y]--;
// }
// x = y;
// }
// // 利⽤差分数组,还原出原数组
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) f[i] += f[i - 1];
// // 直接求结果
// LL ret = 0;
// for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
// {
// LL a, b, c; cin >> a >> b >> c;
// ret += min(a * f[i], c + b * f[i]);
// }
// cout << ret << endl;
// return 0;
//}
//#include <iostream>
//using namespace std;
//typedef long long LL;
//const int N = 1010;
//int n, m, q;
//LL f[N][N]; // 差分矩阵
//// 差分矩阵的性质
//void insert(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, LL k)
//{
// f[x1][y1] += k; f[x1][y2 + 1] -= k; f[x2 + 1][y1] -= k; f[x2 + 1][y2 + 1]
// += k;
//}
//int main()
//{
// cin >> n >> m >> q;
// // 预处理差分矩阵
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
// {
// for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
// {
// LL x; cin >> x;
// // [i, j]为左上⻆,[i, j]为右下⻆的矩阵,统⼀加上 x
// insert(i, j, i, j, x);
// }
// }
// // 处理 q 次修改操作
// while (q--)
// {
// LL x1, y1, x2, y2, k; cin >> x1 >> y1 >> x2 >> y2 >> k;
// insert(x1, y1, x2, y2, k);
// }
// // 利⽤前缀和还原出修改之后的数组
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
// {
// for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
// {
// f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j] + f[i][j - 1] - f[i - 1][j - 1] + f[i][j];
// cout << f[i][j] << " ";
// }
// cout << endl;
// }
// return 0;
//}
//#include <iostream>
//using namespace std;
//const int N = 1010;
//int n, m;
//int f[N][N]; // 差分矩阵
//// 差分数组的性质
//void insert(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int k)
//{
// f[x1][y1] += k; f[x1][y2 + 1] -= k; f[x2 + 1][y1] -= k; f[x2 + 1][y2 + 1]
// += k;
//}
//int main()
//{
// cin >> n >> m;
// // 构建差分数组
// while (m--)
// {
// int x1, y1, x2, y2; cin >> x1 >> y1 >> x2 >> y2;
// insert(x1, y1, x2, y2, 1);
// }
// // 利⽤前缀和还原修改之后的数组
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
// {
// for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
// {
// f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j] + f[i][j - 1] - f[i - 1][j - 1] + f[i][j];
// cout << f[i][j] << " ";
// }
// cout << endl;
// }
// return 0;
//}
//#include <iostream>
//#include <unordered_map>
//using namespace std;
//const int N = 1e6 + 10;
//int n;
//int a[N];
//int main()
//{
// int T; cin >> T;
// while (T--)
// {
// cin >> n;
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
// // 初始化
// int left = 1, right = 1, ret = 0;
// unordered_map<int, int> mp; // 维护窗⼝内所有元素出现的次数
// while (right <= n)
// {
// // 进窗⼝
// mp[a[right]]++;
// // 判断
// while (mp[a[right]] > 1)
// {
// // 出窗⼝
// mp[a[left]]--;
// left++;
// }
// // 窗⼝合法,更新结果
// ret = max(ret, right - left + 1);
// right++;
// }
// cout << ret << endl;
// }
// return 0;
//}
//#include<iostream>
//using namespace std;
//const int N = 1e6 + 10, M = 2e3 + 10;
//int n, m;
//int a[N];
//int kind; // 窗⼝内有效元素的个数
//int mp[N]; // 统计窗⼝内每个元素出现的次数
//int main()
//{
// cin >> n >> m;
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
// int left = 1, right = 1;
// int ret = n, begin = 1;
// while (right <= n)
// {
// // 进窗⼝
// if (mp[a[right]]++ == 0) kind++;
// // 判断
// while (kind == m)
// {
// // 更新结果
// int len = right - left + 1;
// if (len < ret)
// {
// ret = len;
// begin = left;
// }
// // 出窗⼝
// if (mp[a[left]]-- == 1) kind--;
// left++;
// }
// right++;
// }
// cout << begin << " " << begin + ret - 1 << endl;
// return 0;
//}
//#include <iostream>
//using namespace std;
//string s;
//int mp[26]; // 统计每个⼩写字符出现的次数
//int kind; // 窗⼝内⼩写字符的种类
//int main()
//{
// cin >> s;
// int n = s.size();
// int ret = n;
// // 初始化
// for (int left = 0, right = 0; right < n; right++)
// {
// // 进窗⼝
// if (mp[s[right] - 'a']++ == 0) kind++;
// // 判断
// while (kind == 26)
// {
// // 更新结果
// ret = min(ret, right - left + 1);
// // 出窗⼝
// if (mp[s[left] - 'a']-- == 1) kind--;
// left++;
// }
// }
// cout << ret << endl;
// return 0;
//}
//#include<iostream>
//using namespace std;
//typedef long long LL;
//const int N = 1e5 + 10;
//int n;
//LL a[N];
//int main()
//{
// cin >> n;
// LL sum = 0;
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
// {
// cin >> a[i];
// sum += a[i];
// }
// int left = 1, right = 1;
// LL k = 0;
// LL ret = 0;
// while (right <= n)
// {
// k += a[right];
// while (2 * k >= sum)
// {
// // ⽤ sum - k 来更新结果
// ret = max(ret, sum - k);
// k -= a[left++];
// }
// // ⽤ k 来更新结果
// ret = max(ret, k);
// right++;
// }
// cout << ret << endl;
// return 0;
//}
//#include <iostream>
//using namespace std;
//const int N = 1e5 + 10;
//int n;
//int a[N];
//int binary_search(int x, int y)
//{
// // ⼤于等于 x 的最⼩元素
// int left = 1, right = n;
// while (left < right)
// {
// int mid = (left + right) / 2;
// if (a[mid] >= x) right = mid;
// else left = mid + 1;
// }
// if (a[left] < x) return 0;
// int tmp = left;
// // ⼩于等于 y 的最⼤元素
// left = 1, right = n;
// while (left < right)
// {
// int mid = (left + right + 1) / 2;
// if (a[mid] <= y) left = mid;
// else right = mid - 1;
// }
// if (a[left] > y) return 0;
// return left - tmp + 1;
//}
//int main()
//{
// cin >> n;
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
// int Q; cin >> Q;
// while (Q--)
// {
// int x, y; cin >> x >> y;
// cout << binary_search(x, y) << endl;
// }
// return 0;
//}
//#include <iostream>
//#include <algorithm>
//using namespace std;
//typedef long long LL;
//const int N = 2e5 + 10;
//LL n, c;
//LL a[N];
//int main()
//{
// cin >> n >> c;
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
// sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n);
// LL ret = 0;
// for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
// {
// // a[i]
// LL b = a[i] - c;
// ret += upper_bound(a + 1, a + i, b) - lower_bound(a + 1, a + i, b);
// }
// cout << ret << endl;
// return 0;
//}
//#include <iostream>
//#include <algorithm>
//using namespace std;
//typedef long long LL;
//const int N = 1e5 + 10;
//int n, m;
//LL a[N];
//int find(LL x)
//{
// int left = 1, right = m;
// while (left < right)
// {
// int mid = (left + right) / 2;
// if (a[mid] >= x) right = mid;
// else left = mid + 1;
// }
// return left;
//}
//int main()
//{
// cin >> m >> n;
// for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) cin >> a[i];
// sort(a + 1, a + 1 + m);
// // 加上左右护法
// a[0] = -1e7 + 10;
// LL ret = 0;
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
// {
// LL b; cin >> b;
// int pos = find(b);
// ret += min(abs(a[pos] - b), abs(a[pos - 1] - b));
// }
// cout << ret << endl;
// return 0;
//}
//#include <iostream>
//using namespace std;
//typedef long long LL;
//const int N = 1e5 + 10;
//LL n, k;
//LL a[N];
//// 当切割⻓度为 x 的时候,最多能切出来多少段
//LL calc(LL x)
//{
// LL cnt = 0;
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
// {
// cnt += a[i] / x;
// }
// return cnt;
//}
//int main()
//{
// cin >> n >> k;
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
// LL left = 0, right = 1e8;
// while (left < right)
// {
// LL mid = (left + right + 1) / 2;
// if (calc(mid) >= k) left = mid;
// else right = mid - 1;
// }
// cout << left << endl;
// return 0;
//}
//#include <iostream>
//using namespace std;
//typedef long long LL;
//const int N = 1e6 + 10;
//LL n, m;
//LL a[N];
//// 当伐⽊机的⾼度为 x 时,所能获得的⽊材
//LL calc(LL x)
//{
// LL ret = 0;
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
// {
// if (a[i] > x) ret += a[i] - x;
// }
// return ret;
//}
//int main()
//{
// cin >> n >> m;
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
// LL left = 1, right = 2e9;
// while (left < right)
// {
// LL mid = (left + right + 1) / 2;
// if (calc(mid) >= m) left = mid;
// else right = mid - 1;
// }
// cout << left << endl;
// return 0;
//}
//#include <iostream>
//using namespace std;
//typedef long long LL;
//const int N = 5e4 + 10;
//LL l, n, m;
//LL a[N];
//// 当最短跳跃距离为 x 时,移⾛的岩⽯数⽬
//LL calc(LL x)
//{
// LL ret = 0;
// for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
// {
// int j = i + 1;
// while (j <= n && a[j] - a[i] < x) j++;
// ret += j - i - 1;
// i = j - 1;
// }
// return ret;
//}
//int main()
//{
// cin >> l >> n >> m;
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
// a[n + 1] = l;
// n++;
// LL left = 1, right = l;
// while (left < right)
// {
// LL mid = (left + right + 1) / 2;
// if (calc(mid) <= m) left = mid;
// else right = mid - 1;
// }
// cout << left << endl;
// return 0;
//}