1 监控指标体系设计
性能监控说白了就是盯着系统的各种数据,看看哪里出问题了。就像医生给病人量体温、测血压一样,我们需要收集服务器的"生命体征"。
现代应用系统复杂得很,从硬件到软件,从网络到数据库,每个环节都可能出状况。建立完整的监控体系,就是要让这些潜在问题无处遁形。
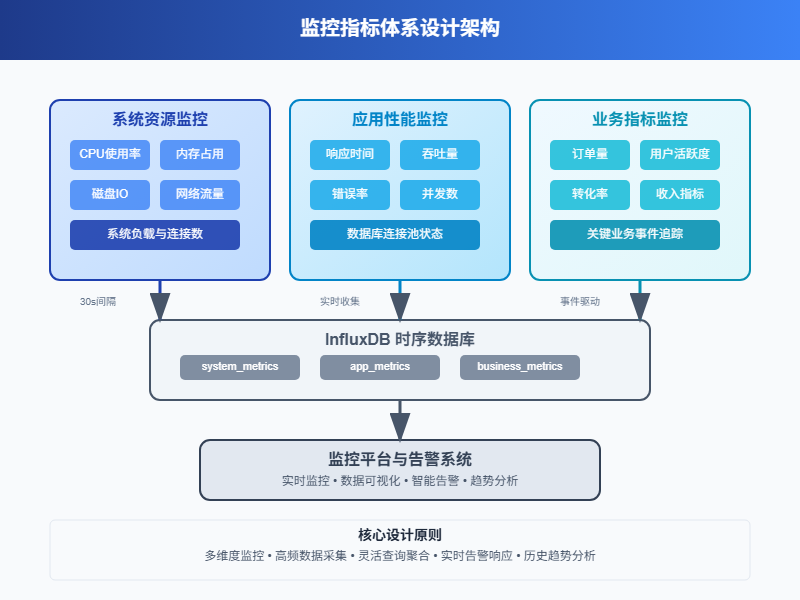
1.1 核心监控维度
系统资源监控
CPU使用率、内存占用、磁盘IO、网络流量这些基础指标必须要有。这就像人的基本生命体征,出问题了第一时间就能发现。
应用性能监控
响应时间、吞吐量、错误率、并发数等。这些指标直接反映用户体验,比如接口响应慢了,用户就会抱怨。
业务指标监控
订单量、用户活跃度、转化率等业务相关的数据。技术指标正常不代表业务就没问题,有时候需要从业务角度看问题。
1.2 数据模型设计
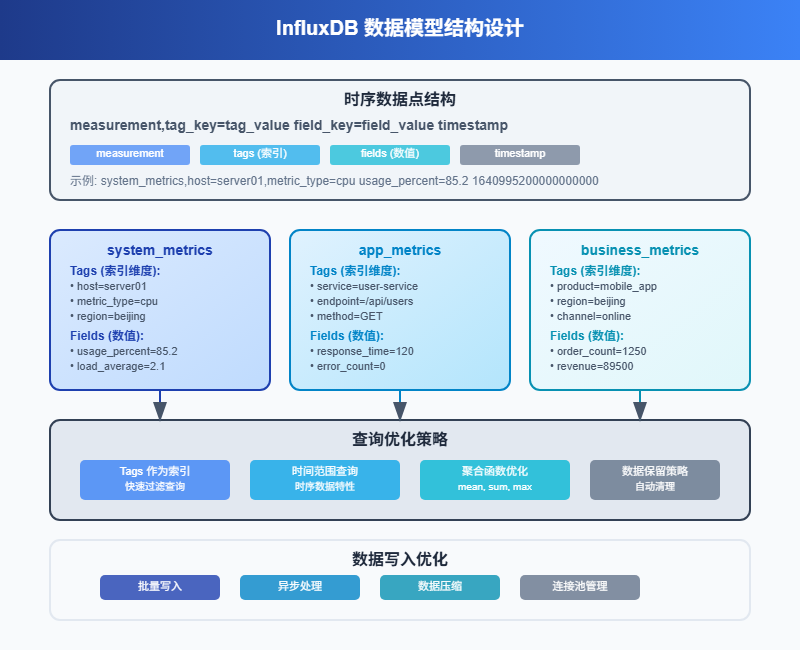
在InfluxDB中,我们按照不同的监控对象来设计measurement:
# 系统资源
system_metrics,host=server01,metric_type=cpu value=85.2 1640995200000000000
system_metrics,host=server01,metric_type=memory value=4096 1640995200000000000
# 应用性能
app_metrics,service=user-service,endpoint=/api/users response_time=120,error_count=0 1640995200000000000
# 业务指标
business_metrics,product=mobile_app,region=beijing order_count=1250,revenue=89500 1640995200000000000这样设计的好处是查询时可以灵活组合条件,比如查看某台服务器的所有指标,或者查看某个服务的性能趋势。
2 系统资源监控实现
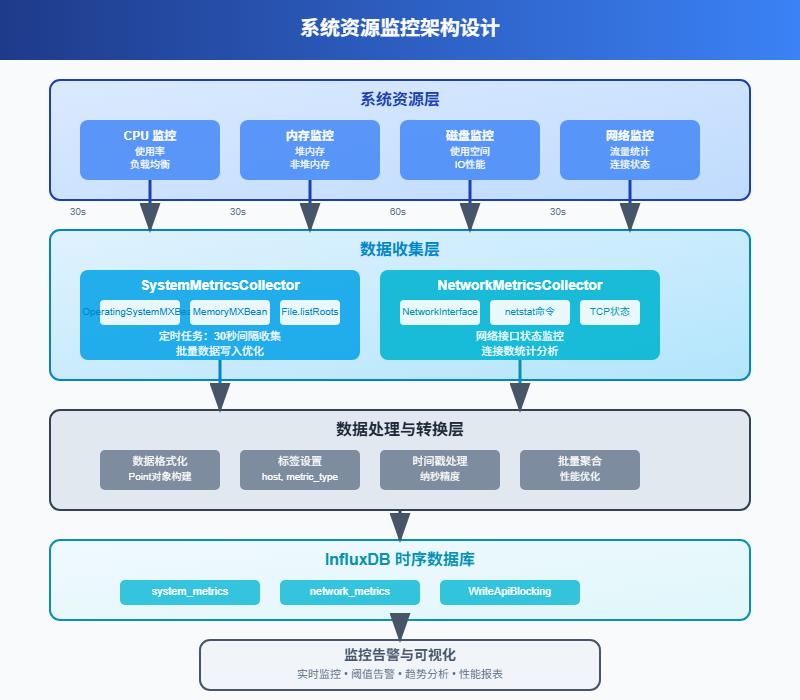
2.1 服务器基础指标收集
系统监控最基础的就是CPU、内存、磁盘、网络这四大件。我们用Java来实现一个完整的监控数据收集器。
java
import com.influxdb.client.InfluxDBClient;
import com.influxdb.client.InfluxDBClientFactory;
import com.influxdb.client.WriteApiBlocking;
import com.influxdb.client.domain.WritePrecision;
import com.influxdb.client.write.Point;
import com.sun.management.OperatingSystemMXBean;
import java.lang.management.ManagementFactory;
import java.lang.management.MemoryMXBean;
import java.lang.management.MemoryUsage;
import java.time.Instant;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Component
public class SystemMetricsCollector {
private final InfluxDBClient influxDBClient;
private final WriteApiBlocking writeApi;
private final ScheduledExecutorService scheduler;
private final String hostname;
public SystemMetricsCollector() {
this.influxDBClient = InfluxDBClientFactory.create(
"http://localhost:8086",
"your-token".toCharArray(),
"your-org",
"monitoring"
);
this.writeApi = influxDBClient.getWriteApiBlocking();
this.scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2);
this.hostname = getHostname();
}
public void startCollection() {
// 每30秒收集一次系统指标
scheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(this::collectSystemMetrics, 0, 30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 每60秒收集一次磁盘指标
scheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(this::collectDiskMetrics, 0, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
private void collectSystemMetrics() {
try {
OperatingSystemMXBean osBean = (OperatingSystemMXBean)
ManagementFactory.getOperatingSystemMXBean();
MemoryMXBean memoryBean = ManagementFactory.getMemoryMXBean();
Instant timestamp = Instant.now();
// CPU使用率
double cpuUsage = osBean.getProcessCpuLoad() * 100;
Point cpuPoint = Point.measurement("system_metrics")
.addTag("host", hostname)
.addTag("metric_type", "cpu")
.addField("usage_percent", cpuUsage)
.time(timestamp, WritePrecision.NS);
// 内存使用情况
MemoryUsage heapMemory = memoryBean.getHeapMemoryUsage();
long usedMemory = heapMemory.getUsed();
long maxMemory = heapMemory.getMax();
double memoryUsage = (double) usedMemory / maxMemory * 100;
Point memoryPoint = Point.measurement("system_metrics")
.addTag("host", hostname)
.addTag("metric_type", "memory")
.addField("used_bytes", usedMemory)
.addField("max_bytes", maxMemory)
.addField("usage_percent", memoryUsage)
.time(timestamp, WritePrecision.NS);
// 系统负载
double systemLoad = osBean.getSystemLoadAverage();
Point loadPoint = Point.measurement("system_metrics")
.addTag("host", hostname)
.addTag("metric_type", "load")
.addField("load_average", systemLoad)
.time(timestamp, WritePrecision.NS);
// 批量写入
writeApi.writePoints(Arrays.asList(cpuPoint, memoryPoint, loadPoint));
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("收集系统指标失败", e);
}
}
private void collectDiskMetrics() {
try {
File[] roots = File.listRoots();
Instant timestamp = Instant.now();
List<Point> diskPoints = new ArrayList<>();
for (File root : roots) {
long totalSpace = root.getTotalSpace();
long freeSpace = root.getFreeSpace();
long usedSpace = totalSpace - freeSpace;
double usagePercent = (double) usedSpace / totalSpace * 100;
Point diskPoint = Point.measurement("system_metrics")
.addTag("host", hostname)
.addTag("metric_type", "disk")
.addTag("mount_point", root.getAbsolutePath())
.addField("total_bytes", totalSpace)
.addField("used_bytes", usedSpace)
.addField("free_bytes", freeSpace)
.addField("usage_percent", usagePercent)
.time(timestamp, WritePrecision.NS);
diskPoints.add(diskPoint);
}
writeApi.writePoints(diskPoints);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("收集磁盘指标失败", e);
}
}
private String getHostname() {
try {
return InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostName();
} catch (Exception e) {
return "unknown";
}
}
}2.2 网络监控实现
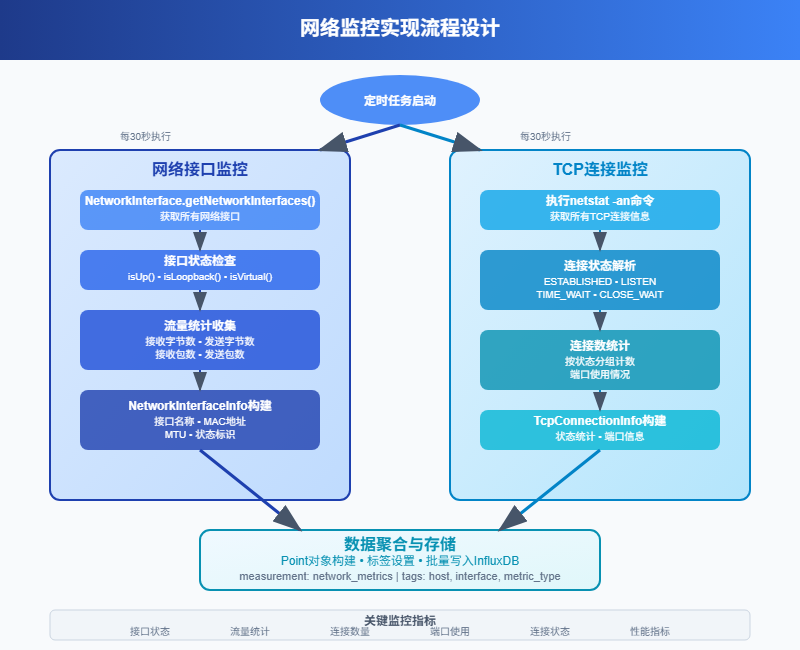
网络监控比较复杂,需要监控网络接口的流量、连接数、错误包等指标。
java
@Component
public class NetworkMetricsCollector {
private final InfluxDBClient influxDBClient;
private final WriteApiBlocking writeApi;
private final String hostname;
public NetworkMetricsCollector(InfluxDBClient influxDBClient) {
this.influxDBClient = influxDBClient;
this.writeApi = influxDBClient.getWriteApiBlocking();
this.hostname = getHostname();
}
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 30000) // 每30秒执行一次
public void collectNetworkMetrics() {
try {
// 获取网络接口信息
Enumeration<NetworkInterface> interfaces = NetworkInterface.getNetworkInterfaces();
Instant timestamp = Instant.now();
List<Point> networkPoints = new ArrayList<>();
while (interfaces.hasMoreElements()) {
NetworkInterface networkInterface = interfaces.nextElement();
if (networkInterface.isLoopback() || !networkInterface.isUp()) {
continue;
}
String interfaceName = networkInterface.getName();
// 这里简化处理,实际项目中可能需要读取/proc/net/dev文件
// 或者使用SNMP等方式获取更详细的网络统计信息
Point networkPoint = Point.measurement("network_metrics")
.addTag("host", hostname)
.addTag("interface", interfaceName)
.addField("status", networkInterface.isUp() ? 1 : 0)
.addField("mtu", networkInterface.getMTU())
.time(timestamp, WritePrecision.NS);
networkPoints.add(networkPoint);
}
// 收集TCP连接数
collectTcpConnections(timestamp, networkPoints);
writeApi.writePoints(networkPoints);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("收集网络指标失败", e);
}
}
private void collectTcpConnections(Instant timestamp, List<Point> points) {
try {
// 在Linux系统中可以读取/proc/net/tcp文件
// 这里提供一个简化的实现思路
ProcessBuilder pb = new ProcessBuilder("netstat", "-an");
Process process = pb.start();
try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(process.getInputStream()))) {
Map<String, Integer> connectionStates = new HashMap<>();
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
if (line.contains("tcp")) {
String[] parts = line.trim().split("\\s+");
if (parts.length >= 6) {
String state = parts[5];
connectionStates.merge(state, 1, Integer::sum);
}
}
}
// 写入连接状态统计
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : connectionStates.entrySet()) {
Point tcpPoint = Point.measurement("network_metrics")
.addTag("host", hostname)
.addTag("metric_type", "tcp_connections")
.addTag("state", entry.getKey())
.addField("count", entry.getValue())
.time(timestamp, WritePrecision.NS);
points.add(tcpPoint);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("收集TCP连接信息失败", e);
}
}
}3 应用性能监控
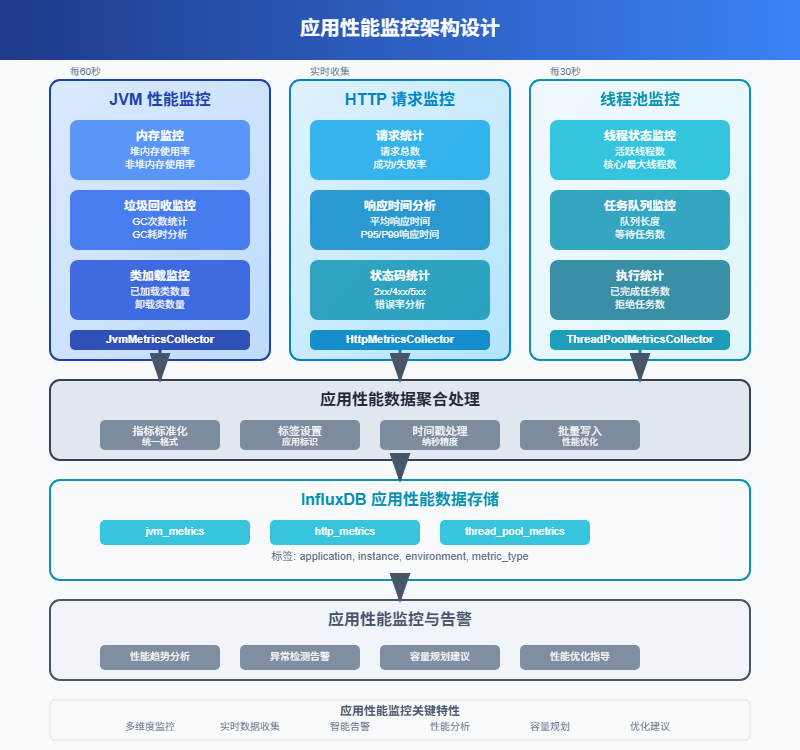
3.1 HTTP接口性能监控
对于Web应用,接口的响应时间和错误率是最重要的指标。我们可以通过拦截器来实现自动化的性能数据收集。
java
@Component
public class PerformanceInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
private final InfluxDBClient influxDBClient;
private final WriteApiBlocking writeApi;
private final ThreadLocal<Long> startTimeHolder = new ThreadLocal<>();
public PerformanceInterceptor(InfluxDBClient influxDBClient) {
this.influxDBClient = influxDBClient;
this.writeApi = influxDBClient.getWriteApiBlocking();
}
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler) throws Exception {
startTimeHolder.set(System.currentTimeMillis());
return true;
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler,
Exception ex) throws Exception {
try {
Long startTime = startTimeHolder.get();
if (startTime != null) {
long responseTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
String method = request.getMethod();
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
int statusCode = response.getStatus();
String userAgent = request.getHeader("User-Agent");
String clientIp = getClientIp(request);
Point performancePoint = Point.measurement("api_metrics")
.addTag("method", method)
.addTag("endpoint", uri)
.addTag("status_code", String.valueOf(statusCode))
.addTag("client_ip", clientIp)
.addField("response_time_ms", responseTime)
.addField("success", statusCode < 400 ? 1 : 0)
.addField("error", statusCode >= 400 ? 1 : 0)
.time(Instant.now(), WritePrecision.NS);
writeApi.writePoint(performancePoint);
// 如果响应时间超过阈值,记录慢查询
if (responseTime > 1000) {
recordSlowRequest(method, uri, responseTime, statusCode);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("记录性能指标失败", e);
} finally {
startTimeHolder.remove();
}
}
private void recordSlowRequest(String method, String uri, long responseTime, int statusCode) {
Point slowRequestPoint = Point.measurement("slow_requests")
.addTag("method", method)
.addTag("endpoint", uri)
.addTag("status_code", String.valueOf(statusCode))
.addField("response_time_ms", responseTime)
.time(Instant.now(), WritePrecision.NS);
writeApi.writePoint(slowRequestPoint);
}
private String getClientIp(HttpServletRequest request) {
String xForwardedFor = request.getHeader("X-Forwarded-For");
if (xForwardedFor != null && !xForwardedFor.isEmpty()) {
return xForwardedFor.split(",")[0].trim();
}
String xRealIp = request.getHeader("X-Real-IP");
if (xRealIp != null && !xRealIp.isEmpty()) {
return xRealIp;
}
return request.getRemoteAddr();
}
}3.2 数据库性能监控
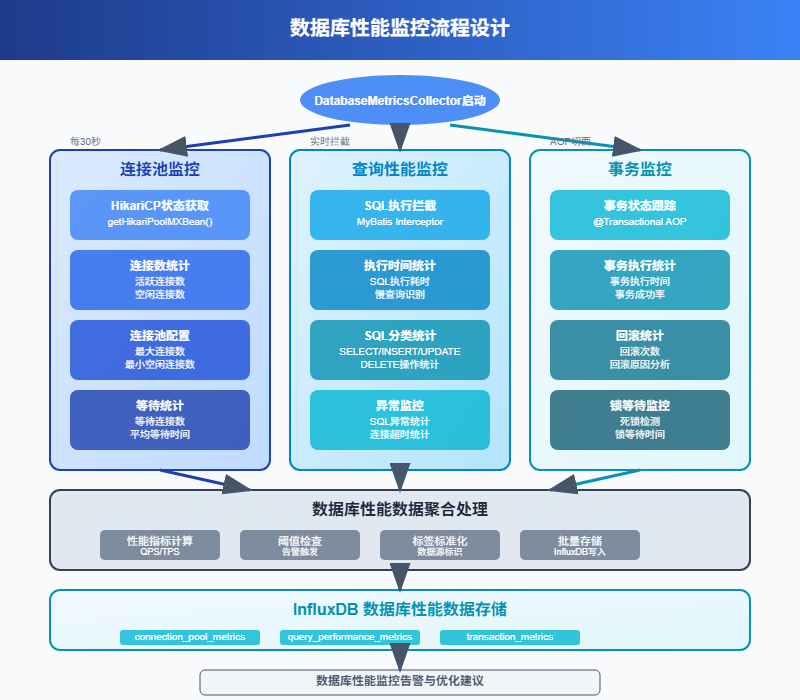
数据库是应用的核心,SQL执行时间、连接池状态、慢查询等都需要重点关注。
java
@Component
public class DatabaseMetricsCollector {
private final InfluxDBClient influxDBClient;
private final WriteApiBlocking writeApi;
private final DataSource dataSource;
public DatabaseMetricsCollector(InfluxDBClient influxDBClient, DataSource dataSource) {
this.influxDBClient = influxDBClient;
this.writeApi = influxDBClient.getWriteApiBlocking();
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 60000) // 每分钟收集一次
public void collectDatabaseMetrics() {
try {
Instant timestamp = Instant.now();
List<Point> dbPoints = new ArrayList<>();
// 收集连接池信息
if (dataSource instanceof HikariDataSource) {
HikariDataSource hikariDS = (HikariDataSource) dataSource;
HikariPoolMXBean poolBean = hikariDS.getHikariPoolMXBean();
Point poolPoint = Point.measurement("database_metrics")
.addTag("metric_type", "connection_pool")
.addTag("pool_name", hikariDS.getPoolName())
.addField("active_connections", poolBean.getActiveConnections())
.addField("idle_connections", poolBean.getIdleConnections())
.addField("total_connections", poolBean.getTotalConnections())
.addField("threads_awaiting_connection", poolBean.getThreadsAwaitingConnection())
.time(timestamp, WritePrecision.NS);
dbPoints.add(poolPoint);
}
// 收集数据库状态信息
collectDatabaseStatus(timestamp, dbPoints);
writeApi.writePoints(dbPoints);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("收集数据库指标失败", e);
}
}
private void collectDatabaseStatus(Instant timestamp, List<Point> points) {
try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection()) {
// 查询数据库连接数
String connectionCountSql = "SHOW STATUS LIKE 'Threads_connected'";
try (PreparedStatement stmt = connection.prepareStatement(connectionCountSql);
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery()) {
if (rs.next()) {
int connectionCount = rs.getInt("Value");
Point connectionPoint = Point.measurement("database_metrics")
.addTag("metric_type", "connections")
.addField("current_connections", connectionCount)
.time(timestamp, WritePrecision.NS);
points.add(connectionPoint);
}
}
// 查询慢查询数量
String slowQuerySql = "SHOW STATUS LIKE 'Slow_queries'";
try (PreparedStatement stmt = connection.prepareStatement(slowQuerySql);
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery()) {
if (rs.next()) {
int slowQueries = rs.getInt("Value");
Point slowQueryPoint = Point.measurement("database_metrics")
.addTag("metric_type", "slow_queries")
.addField("slow_query_count", slowQueries)
.time(timestamp, WritePrecision.NS);
points.add(slowQueryPoint);
}
}
// 查询查询缓存命中率
collectQueryCacheMetrics(connection, timestamp, points);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("收集数据库状态失败", e);
}
}
private void collectQueryCacheMetrics(Connection connection, Instant timestamp, List<Point> points) {
try {
String cacheSql = "SHOW STATUS WHERE Variable_name IN ('Qcache_hits', 'Qcache_inserts', 'Qcache_not_cached')";
try (PreparedStatement stmt = connection.prepareStatement(cacheSql);
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery()) {
Map<String, Long> cacheStats = new HashMap<>();
while (rs.next()) {
cacheStats.put(rs.getString("Variable_name"), rs.getLong("Value"));
}
long hits = cacheStats.getOrDefault("Qcache_hits", 0L);
long inserts = cacheStats.getOrDefault("Qcache_inserts", 0L);
long notCached = cacheStats.getOrDefault("Qcache_not_cached", 0L);
long totalQueries = hits + inserts + notCached;
double hitRate = totalQueries > 0 ? (double) hits / totalQueries * 100 : 0;
Point cachePoint = Point.measurement("database_metrics")
.addTag("metric_type", "query_cache")
.addField("cache_hits", hits)
.addField("cache_inserts", inserts)
.addField("cache_not_cached", notCached)
.addField("hit_rate_percent", hitRate)
.time(timestamp, WritePrecision.NS);
points.add(cachePoint);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("收集查询缓存指标失败", e);
}
}
}4 业务指标监控
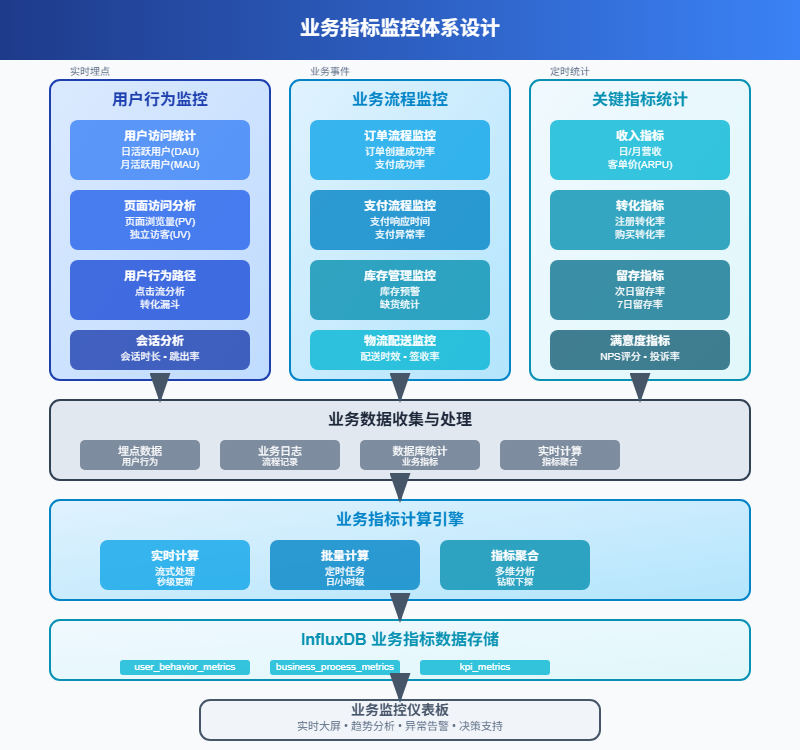
4.1 业务事件追踪
除了技术指标,业务指标同样重要。用户注册、订单创建、支付成功等关键业务事件都需要监控。
java
@Service
public class BusinessMetricsService {
private final InfluxDBClient influxDBClient;
private final WriteApiBlocking writeApi;
public BusinessMetricsService(InfluxDBClient influxDBClient) {
this.influxDBClient = influxDBClient;
this.writeApi = influxDBClient.getWriteApiBlocking();
}
public void recordUserRegistration(String userId, String source, String region) {
Point registrationPoint = Point.measurement("business_events")
.addTag("event_type", "user_registration")
.addTag("source", source)
.addTag("region", region)
.addField("user_id", userId)
.addField("count", 1)
.time(Instant.now(), WritePrecision.NS);
writeApi.writePoint(registrationPoint);
}
public void recordOrderCreated(String orderId, String userId, double amount, String productCategory) {
Point orderPoint = Point.measurement("business_events")
.addTag("event_type", "order_created")
.addTag("product_category", productCategory)
.addField("order_id", orderId)
.addField("user_id", userId)
.addField("amount", amount)
.addField("count", 1)
.time(Instant.now(), WritePrecision.NS);
writeApi.writePoint(orderPoint);
}
public void recordPaymentResult(String orderId, String paymentMethod, boolean success, double amount) {
Point paymentPoint = Point.measurement("business_events")
.addTag("event_type", "payment")
.addTag("payment_method", paymentMethod)
.addTag("status", success ? "success" : "failed")
.addField("order_id", orderId)
.addField("amount", amount)
.addField("success", success ? 1 : 0)
.addField("count", 1)
.time(Instant.now(), WritePrecision.NS);
writeApi.writePoint(paymentPoint);
}
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 300000) // 每5分钟统计一次
public void calculateBusinessMetrics() {
try {
Instant now = Instant.now();
Instant fiveMinutesAgo = now.minus(5, ChronoUnit.MINUTES);
// 计算最近5分钟的业务指标
calculateRecentMetrics(fiveMinutesAgo, now);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("计算业务指标失败", e);
}
}
private void calculateRecentMetrics(Instant start, Instant end) {
try {
QueryApi queryApi = influxDBClient.getQueryApi();
// 查询最近5分钟的注册数
String registrationQuery = String.format(
"from(bucket: \"monitoring\") " +
"|> range(start: %s, stop: %s) " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == \"business_events\" and r.event_type == \"user_registration\") " +
"|> count()",
start.toString(), end.toString()
);
List<FluxTable> registrationTables = queryApi.query(registrationQuery);
int registrationCount = extractCountFromQuery(registrationTables);
// 查询最近5分钟的订单金额
String orderAmountQuery = String.format(
"from(bucket: \"monitoring\") " +
"|> range(start: %s, stop: %s) " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == \"business_events\" and r.event_type == \"order_created\") " +
"|> sum(column: \"amount\")",
start.toString(), end.toString()
);
List<FluxTable> orderTables = queryApi.query(orderAmountQuery);
double totalOrderAmount = extractSumFromQuery(orderTables);
// 记录汇总指标
Point summaryPoint = Point.measurement("business_summary")
.addTag("time_window", "5min")
.addField("registration_count", registrationCount)
.addField("total_order_amount", totalOrderAmount)
.time(end, WritePrecision.NS);
writeApi.writePoint(summaryPoint);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("计算业务汇总指标失败", e);
}
}
private int extractCountFromQuery(List<FluxTable> tables) {
return tables.stream()
.flatMap(table -> table.getRecords().stream())
.mapToInt(record -> ((Number) record.getValue()).intValue())
.sum();
}
private double extractSumFromQuery(List<FluxTable> tables) {
return tables.stream()
.flatMap(table -> table.getRecords().stream())
.mapToDouble(record -> ((Number) record.getValue()).doubleValue())
.sum();
}
}4.2 实时告警机制
监控数据收集了,还需要及时发现异常。我们可以实现一个简单的告警系统。
java
@Service
public class AlertService {
private final InfluxDBClient influxDBClient;
private final NotificationService notificationService;
public AlertService(InfluxDBClient influxDBClient, NotificationService notificationService) {
this.influxDBClient = influxDBClient;
this.notificationService = notificationService;
}
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 60000) // 每分钟检查一次
public void checkAlerts() {
try {
checkCpuUsage();
checkMemoryUsage();
checkResponseTime();
checkErrorRate();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("检查告警失败", e);
}
}
private void checkCpuUsage() {
try {
QueryApi queryApi = influxDBClient.getQueryApi();
String query = "from(bucket: \"monitoring\") " +
"|> range(start: -5m) " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == \"system_metrics\" and r.metric_type == \"cpu\") " +
"|> mean()";
List<FluxTable> tables = queryApi.query(query);
for (FluxTable table : tables) {
for (FluxRecord record : table.getRecords()) {
double cpuUsage = ((Number) record.getValue()).doubleValue();
String host = (String) record.getValueByKey("host");
if (cpuUsage > 80) {
String message = String.format("服务器 %s CPU使用率过高: %.2f%%", host, cpuUsage);
notificationService.sendAlert("CPU_HIGH", message, AlertLevel.WARNING);
}
if (cpuUsage > 95) {
String message = String.format("服务器 %s CPU使用率严重过高: %.2f%%", host, cpuUsage);
notificationService.sendAlert("CPU_CRITICAL", message, AlertLevel.CRITICAL);
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("检查CPU使用率告警失败", e);
}
}
private void checkResponseTime() {
try {
QueryApi queryApi = influxDBClient.getQueryApi();
String query = "from(bucket: \"monitoring\") " +
"|> range(start: -10m) " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == \"api_metrics\") " +
"|> group(columns: [\"endpoint\"]) " +
"|> mean(column: \"response_time_ms\")";
List<FluxTable> tables = queryApi.query(query);
for (FluxTable table : tables) {
for (FluxRecord record : table.getRecords()) {
double avgResponseTime = ((Number) record.getValue()).doubleValue();
String endpoint = (String) record.getValueByKey("endpoint");
if (avgResponseTime > 2000) {
String message = String.format("接口 %s 平均响应时间过长: %.0fms", endpoint, avgResponseTime);
notificationService.sendAlert("RESPONSE_TIME_HIGH", message, AlertLevel.WARNING);
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("检查响应时间告警失败", e);
}
}
private void checkErrorRate() {
try {
QueryApi queryApi = influxDBClient.getQueryApi();
String query = "from(bucket: \"monitoring\") " +
"|> range(start: -10m) " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == \"api_metrics\") " +
"|> group(columns: [\"endpoint\"]) " +
"|> aggregateWindow(every: 10m, fn: sum) " +
"|> pivot(rowKey:[\"_time\"], columnKey: [\"_field\"], valueColumn: \"_value\") " +
"|> map(fn: (r) => ({ r with error_rate: float(v: r.error) / float(v: r.success + r.error) * 100.0 }))";
List<FluxTable> tables = queryApi.query(query);
for (FluxTable table : tables) {
for (FluxRecord record : table.getRecords()) {
Object errorRateObj = record.getValueByKey("error_rate");
if (errorRateObj != null) {
double errorRate = ((Number) errorRateObj).doubleValue();
String endpoint = (String) record.getValueByKey("endpoint");
if (errorRate > 5) {
String message = String.format("接口 %s 错误率过高: %.2f%%", endpoint, errorRate);
notificationService.sendAlert("ERROR_RATE_HIGH", message, AlertLevel.WARNING);
}
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("检查错误率告警失败", e);
}
}
}
enum AlertLevel {
INFO, WARNING, CRITICAL
}
@Service
public class NotificationService {
public void sendAlert(String alertType, String message, AlertLevel level) {
// 这里可以集成邮件、短信、钉钉、企业微信等通知方式
logger.warn("告警通知 [{}] {}: {}", level, alertType, message);
// 发送邮件通知
sendEmailAlert(alertType, message, level);
// 发送钉钉通知
sendDingTalkAlert(alertType, message, level);
}
private void sendEmailAlert(String alertType, String message, AlertLevel level) {
// 邮件发送逻辑
}
private void sendDingTalkAlert(String alertType, String message, AlertLevel level) {
// 钉钉机器人通知逻辑
}
}5 性能优化与最佳实践
5.1 数据写入优化
监控数据量通常很大,写入性能很关键。批量写入、异步处理、数据压缩都是常用的优化手段。
java
@Configuration
public class InfluxDBOptimizedConfig {
@Bean
public InfluxDBClient influxDBClient() {
return InfluxDBClientFactory.create(
"http://localhost:8086",
"your-token".toCharArray(),
"your-org",
"monitoring"
);
}
@Bean
public WriteApi writeApi(InfluxDBClient client) {
WriteOptions options = WriteOptions.builder()
.batchSize(1000) // 批量大小
.flushInterval(5000) // 刷新间隔5秒
.bufferLimit(10000) // 缓冲区大小
.retryInterval(1000) // 重试间隔
.maxRetries(3) // 最大重试次数
.build();
return client.makeWriteApi(options);
}
}
@Service
public class OptimizedMetricsCollector {
private final WriteApi writeApi;
private final BlockingQueue<Point> metricsQueue;
private final ScheduledExecutorService scheduler;
public OptimizedMetricsCollector(WriteApi writeApi) {
this.writeApi = writeApi;
this.metricsQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(50000);
this.scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2);
// 启动批量写入任务
startBatchWriter();
}
public void recordMetric(Point point) {
try {
if (!metricsQueue.offer(point)) {
logger.warn("指标队列已满,丢弃数据点");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("记录指标失败", e);
}
}
private void startBatchWriter() {
scheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
try {
List<Point> batch = new ArrayList<>();
metricsQueue.drainTo(batch, 1000);
if (!batch.isEmpty()) {
writeApi.writePoints(batch);
logger.debug("批量写入 {} 个数据点", batch.size());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("批量写入失败", e);
}
}, 0, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
@PreDestroy
public void shutdown() {
try {
scheduler.shutdown();
if (!scheduler.awaitTermination(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
scheduler.shutdownNow();
}
// 写入剩余数据
List<Point> remaining = new ArrayList<>();
metricsQueue.drainTo(remaining);
if (!remaining.isEmpty()) {
writeApi.writePoints(remaining);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("关闭指标收集器失败", e);
}
}
}5.2 查询性能优化
监控查询通常涉及大量数据,合理的索引设计和查询优化很重要。
java
@Service
public class OptimizedQueryService {
private final InfluxDBClient influxDBClient;
private final QueryApi queryApi;
public OptimizedQueryService(InfluxDBClient influxDBClient) {
this.influxDBClient = influxDBClient;
this.queryApi = influxDBClient.getQueryApi();
}
// 优化的时间范围查询
public List<MetricData> getMetricsInTimeRange(String measurement,
String host,
Instant start,
Instant end) {
// 使用参数化查询,避免字符串拼接
String query = "from(bucket: \"monitoring\") " +
"|> range(start: " + start + ", stop: " + end + ") " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == \"" + measurement + "\") " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r.host == \"" + host + "\") " +
"|> aggregateWindow(every: 1m, fn: mean, createEmpty: false)";
List<FluxTable> tables = queryApi.query(query);
return convertToMetricData(tables);
}
// 聚合查询优化
public Map<String, Double> getAggregatedMetrics(String measurement,
Duration timeWindow) {
Instant end = Instant.now();
Instant start = end.minus(timeWindow);
String query = "from(bucket: \"monitoring\") " +
"|> range(start: " + start + ", stop: " + end + ") " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == \"" + measurement + "\") " +
"|> group(columns: [\"host\"]) " +
"|> mean()";
List<FluxTable> tables = queryApi.query(query);
Map<String, Double> result = new HashMap<>();
for (FluxTable table : tables) {
for (FluxRecord record : table.getRecords()) {
String host = (String) record.getValueByKey("host");
Double value = ((Number) record.getValue()).doubleValue();
result.put(host, value);
}
}
return result;
}
// 分页查询大量数据
public PagedResult<MetricData> getMetricsPaged(String measurement,
int page,
int size,
Instant start,
Instant end) {
int offset = page * size;
String query = "from(bucket: \"monitoring\") " +
"|> range(start: " + start + ", stop: " + end + ") " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == \"" + measurement + "\") " +
"|> sort(columns: [\"_time\"], desc: true) " +
"|> limit(n: " + size + ", offset: " + offset + ")";
List<FluxTable> tables = queryApi.query(query);
List<MetricData> data = convertToMetricData(tables);
// 获取总数(简化实现)
long total = getTotalCount(measurement, start, end);
return new PagedResult<>(data, page, size, total);
}
private List<MetricData> convertToMetricData(List<FluxTable> tables) {
List<MetricData> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (FluxTable table : tables) {
for (FluxRecord record : table.getRecords()) {
MetricData data = new MetricData();
data.setTime(record.getTime());
data.setMeasurement(record.getMeasurement());
data.setValue(((Number) record.getValue()).doubleValue());
data.setHost((String) record.getValueByKey("host"));
result.add(data);
}
}
return result;
}
private long getTotalCount(String measurement, Instant start, Instant end) {
String countQuery = "from(bucket: \"monitoring\") " +
"|> range(start: " + start + ", stop: " + end + ") " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == \"" + measurement + "\") " +
"|> count()";
List<FluxTable> tables = queryApi.query(countQuery);
return tables.stream()
.flatMap(table -> table.getRecords().stream())
.mapToLong(record -> ((Number) record.getValue()).longValue())
.sum();
}
}
class MetricData {
private Instant time;
private String measurement;
private Double value;
private String host;
// getters and setters
}
class PagedResult<T> {
private List<T> data;
private int page;
private int size;
private long total;
private int totalPages;
public PagedResult(List<T> data, int page, int size, long total) {
this.data = data;
this.page = page;
this.size = size;
this.total = total;
this.totalPages = (int) Math.ceil((double) total / size);
}
// getters and setters
}这套监控系统涵盖了从系统资源到业务指标的全方位监控,通过Java代码实现了自动化的数据收集、存储和告警。关键是要根据实际业务需求调整监控指标和告警阈值,确保监控系统既能及时发现问题,又不会产生太多噪音。
记住,监控不是目的,快速发现和解决问题才是。好的监控系统应该让你在问题影响用户之前就能发现并处理。