目录
关联式容器与序列式容器
序列式容器 (Sequence Containers)
-
关注元素的位置和插入顺序
-
典型的"先来后到"顺序存储
关联式容器 (Associative Containers)
-
关注元素之间的关联关系
-
基于键值对(key-value)的快速查找
具体容器类型对比

关联式容器也是用来存储数据的,与序列式容器不同的是,其里面存储的是结构的 键值对 ,在数据检索时比序列式容器效率更高。
键值对:用来表示具有一一对应关系的一种结构,该结构中一般只包含两个成员变量key和value,key代 表键值,value表示与key对应的信息。
SGI-STL中关于键值对的定义:

根据应用场景的不同,STL总共实现了两种不同结构的管理式容器:树型结构与哈希结构。
树型结构的关联式容器主要有四种:map、set、multimap、multiset。这四种容器的共同点是:使用平衡搜索树(即红黑树)作为其底层结果。
set
set的介绍

set的模板参数列表
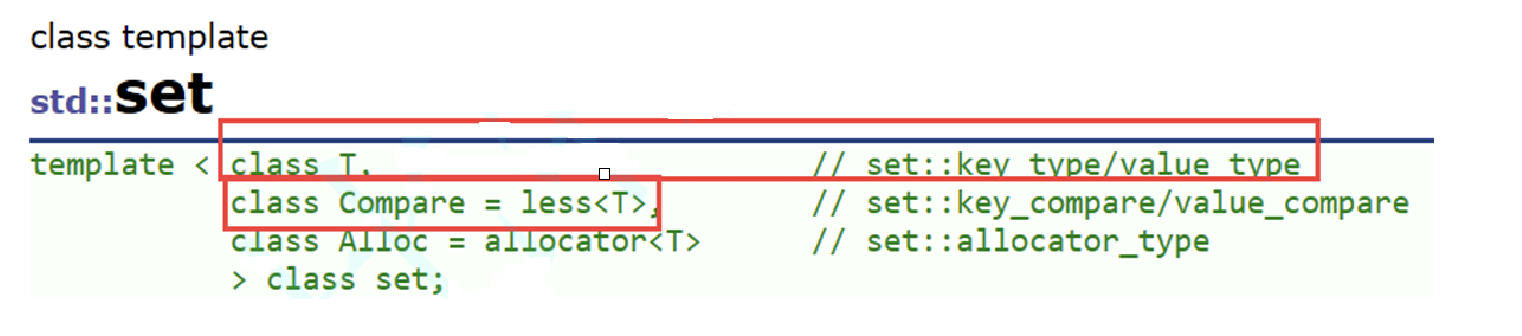
T:set中存放元素的类型,实际在底层存储<value, value>的键值对
Compare: set中元素默认按照小于来比较
Alloc: set中元素空间的管理方式,使用STL提供的空间配置管理器
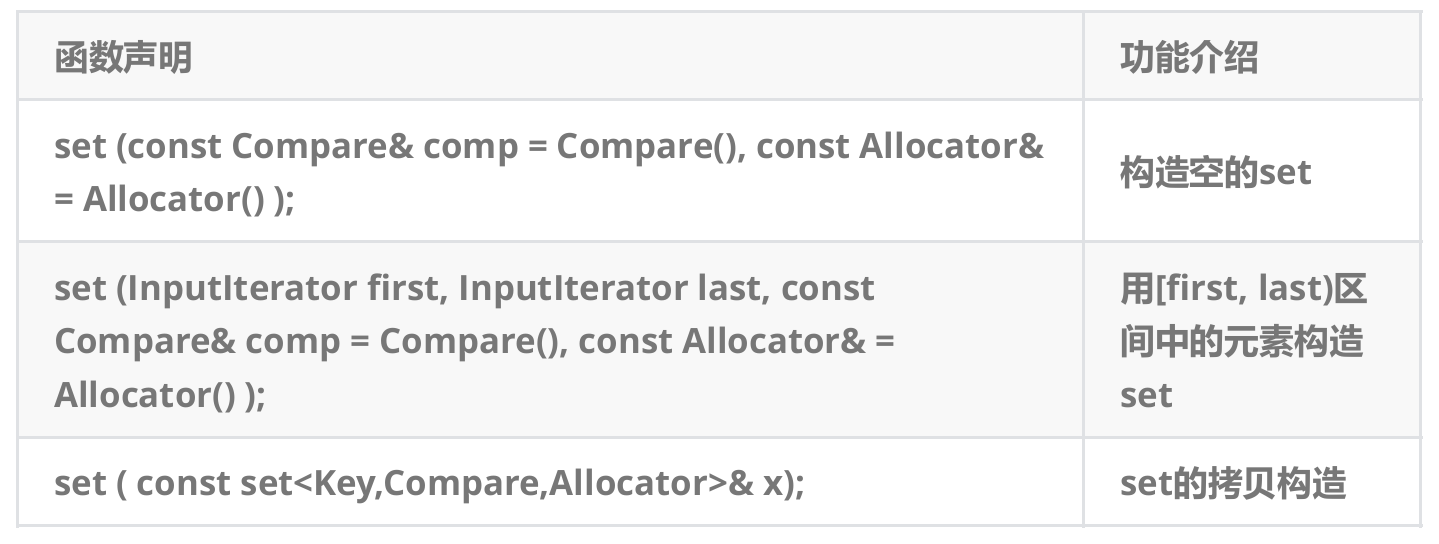
set的构造
set容器常见的接口
++基本构造和赋值:operator= 赋值操作++
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
void testAssignment() {
set<int> s1 = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};
set<int> s2;
s2 = s1; // 赋值操作
cout << "s2 after assignment: ";
for (int x : s2) cout << x << " "; // 1 3 5 7 9
cout << endl;
// 移动赋值
set<int> s3 = move(s2);
cout << "s3 after move: ";
for (int x : s3) cout << x << " "; // 1 3 5 7 9
cout << endl;
cout << "s2 size after move: " << s2.size() << endl; // 0
}++迭代器接口++:正向和反向迭代器
cpp
void testIterators() {
set<int> s = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
cout << "正向遍历: ";
for (auto it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); ++it) {
cout << *it << " "; // 10 20 30 40 50
}
cout << endl;
cout << "反向遍历: ";
for (auto it = s.rbegin(); it != s.rend(); ++it) {
cout << *it << " "; // 50 40 30 20 10
}
cout << endl;
// C++11引入的const迭代器
cout << "常量正向遍历: ";
for (auto it = s.cbegin(); it != s.cend(); ++it) {
// *it = 100; // 错误:不能修改常量迭代器指向的值
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}++容量查询++:empty() 和 size()
cpp
void testCapacity() {
set<int> s;
cout << "空set - empty: " << s.empty() << ", size: " << s.size() << endl;
s.insert({1, 2, 3});
cout << "插入后 - empty: " << s.empty() << ", size: " << s.size() << endl;
}++insert()++ 插入操作
++set::insert 的返回值是一个 pair类型++,具体定义为:

这是一个模板类,包含两个成员:
-
first: 迭代器(iterator),指向被插入的元素 -
second: 布尔值(bool),表示插入是否成功
cpp
void testInsert() {
set<int> s;
// 方式1:直接插入值
auto result1 = s.insert(10);
cout << "插入10: " << (result1.second ? "成功" : "失败")
<< ", 插入位置的值: " << *result1.first << endl;
// result1 的类型: pair<set<int>::iterator, bool>
// result1.first: 指向元素10的迭代器
// result1.second: true (因为10不存在,插入成功)
// 方式2:插入已存在值(会失败)
auto result2 = s.insert(10);
cout << "再次插入10: " << (result2.second ? "成功" : "失败") << endl;
// 方式3:批量插入
s.insert({5, 15, 25, 35});
cout << "最终set内容: ";
for (int x : s) cout << x << " "; // 5 10 15 25 35
cout << endl;
}++erase()++删除操作
cpp
void testErase() {
set<int> s = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
// 方式1:通过值删除
size_t count1 = s.erase(5); // 返回删除的元素个数
cout << "删除值5,删除了 " << count1 << " 个元素" << endl;
// 方式2:通过迭代器删除
auto it = s.find(3);
if (it != s.end()) {
s.erase(it); // 安全删除
cout << "通过迭代器删除3" << endl;
}
// 方式3:删除不存在的值(不会报错)
size_t count2 = s.erase(100);
cout << "删除不存在的值100,删除了 " << count2 << " 个元素" << endl;
// 方式4:删除范围
auto first = s.find(6);
auto last = s.find(8);
if (first != s.end() && last != s.end()) {
s.erase(first, last); // 删除[6, 8),注意是前闭后开
}
cout << "删除后set内容: ";
for (int x : s) cout << x << " "; // 1 2 4 8 9
cout << endl;
}返回值类型总结

++查找操作++(核心功能):find() 查找
cpp
void testFind() {
set<int> s = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
// set专用的find(二分查找 O(log n))
auto it = s.find(30);
if (it != s.end()) {
cout << "找到30: " << *it << endl;
} else {
cout << "未找到30" << endl;
}
// 与std::find对比(线性查找 O(n))
auto it2 = find(s.begin(), s.end(), 30);
if (it2 != s.end()) {
cout << "std::find也找到30: " << *it2 << endl;
}
// 查找不存在的值
auto it3 = s.find(100);
if (it3 == s.end()) {
cout << "100不存在于set中" << endl;
}
}++lower_bound() 和 upper_bound()++
cpp
void testBounds() {
set<int> s = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
// lower_bound: 第一个 >= 值的元素
auto lb = s.lower_bound(25);
if (lb != s.end()) {
cout << "lower_bound(25): " << *lb << endl; // 30
}
// upper_bound: 第一个 > 值的元素
auto ub = s.upper_bound(25);
if (ub != s.end()) {
cout << "upper_bound(25): " << *ub << endl; // 30
}
// 查找边界值
cout << "lower_bound(30): " << *s.lower_bound(30) << endl; // 30
cout << "upper_bound(30): " << *s.upper_bound(30) << endl; // 40
// 查找超出范围的值
auto beyond = s.upper_bound(60);
if (beyond == s.end()) {
cout << "upper_bound(60) 返回end()" << endl;
}
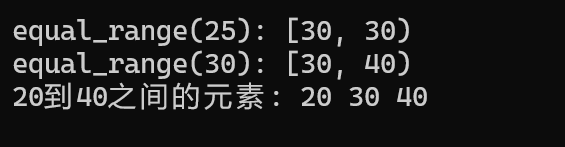
}++equal_range()++相等范围
cpp
void testEqualRange() {
set<int> s = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
// equal_range返回pair<lower_bound, upper_bound>
auto range = s.equal_range(25);
cout << "equal_range(25): [" << *range.first << ", " << *range.second << ")" << endl;
// 输出: [30, 30) 因为25不在set中
// 对于存在的值
range = s.equal_range(30);
cout << "equal_range(30): [" << *range.first << ", " << *range.second << ")" << endl;
// 输出: [30, 40)
// 可以用来遍历某个范围内的元素
cout << "20到40之间的元素: ";
range = s.equal_range(20);
range.second = s.upper_bound(40); // 手动调整上界
for (auto it = range.first; it != range.second; ++it) {
cout << *it << " "; // 20 30 40
}
cout << endl;
}
++count()++计数
cpp
void testCount() {
set<int> s = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// set中count只能返回0或1(因为元素唯一)
cout << "count(3): " << s.count(3) << endl; // 1
cout << "count(10): " << s.count(10) << endl; // 0
// 与multiset对比
multiset<int> ms = {1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3};
cout << "multiset count(2): " << ms.count(2) << endl; // 2
cout << "multiset count(3): " << ms.count(3) << endl; // 3
}++swap() 和 clear()++
cpp
void testSwapClear() {
set<int> s1 = {1, 3, 5};
set<int> s2 = {2, 4, 6};
cout << "交换前 - s1: ";
for (int x : s1) cout << x << " "; // 1 3 5
cout << ", s2: ";
for (int x : s2) cout << x << " "; // 2 4 6
cout << endl;
s1.swap(s2); // 交换两个set的内容
cout << "交换后 - s1: ";
for (int x : s1) cout << x << " "; // 2 4 6
cout << ", s2: ";
for (int x : s2) cout << x << " "; // 1 3 5
cout << endl;
s1.clear(); // 清空set
cout << "清空后s1的size: " << s1.size() << endl; // 0
}完整测试代码
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "=== set容器接口测试 ===" << endl;
testAssignment();
testIterators();
testCapacity();
testInsert();
testErase();
testFind();
testBounds();
testEqualRange();
testCount();
testSwapClear();
// 验证自动排序和去重特性
cout << "\n=== 自动排序和去重验证 ===" << endl;
set<int> s = {5, 2, 8, 2, 5, 1, 8, 9};
cout << "插入{5,2,8,2,5,1,8,9}后: ";
for (int x : s) cout << x << " "; // 1 2 5 8 9
cout << endl;
return 0;
}重要特性总结
- 自动排序和去重
cpp
set<int> s = {3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2, 6};
// 实际存储: 1 2 3 4 5 6 9(自动排序+去重)- 查找性能对比
cpp
set<int> large_set;
// 插入大量数据...
// 专用find - O(log n) - 推荐
auto it1 = large_set.find(target);
// 通用find - O(n) - 不推荐
auto it2 = find(large_set.begin(), large_set.end(), target);- 安全删除模式
cpp
// 安全删除模式
auto it = s.find(value);
if (it != s.end()) {
s.erase(it); // 安全,迭代器有效才删除
}
// 直接删除值(更简洁)
s.erase(value); // 如果值不存在,不会报错使用建议
-
需要快速查找时优先使用set专用find
-
需要范围查询时使用lower_bound/upper_bound/equal_range
-
删除元素时优先使用值删除,避免迭代器失效问题
-
需要保持插入顺序时不要使用set,选择vector或list
-
需要重复元素时使用multiset
set的这些特性使其成为需要快速查找、自动排序和唯一元素的理想选择!
multiset
multiset 确实与 set 的主要区别就是允许重复元素,其他接口基本一致。
++1.++
1.1 基本特性对比
cpp
void basicDifference() {
cout << "=== set vs multiset 基本区别 ===" << endl;
// set: 自动去重
set<int> s = {1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3};
cout << "set 内容: ";
for (int x : s) cout << x << " "; // 1 2 3
cout << ", 大小: " << s.size() << endl; // 3
// multiset: 允许重复
multiset<int> ms = {1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3};
cout << "multiset 内容: ";
for (int x : ms) cout << x << " "; // 1 2 2 3 3 3
cout << ", 大小: " << ms.size() << endl; // 6
}1.2 insert() 行为的区别
cpp
void testInsertDifference() {
cout << "\n=== insert() 行为区别 ===" << endl;
set<int> s;
multiset<int> ms;
// set插入重复元素
auto s_result1 = s.insert(10);
cout << "set第一次插入10: " << (s_result1.second ? "成功" : "失败") << endl; // 成功
auto s_result2 = s.insert(10);
cout << "set第二次插入10: " << (s_result2.second ? "成功" : "失败") << endl; // 失败
// multiset插入重复元素
auto ms_result1 = ms.insert(10);
cout << "multiset第一次插入10: 成功" << endl;
auto ms_result2 = ms.insert(10);
cout << "multiset第二次插入10: 成功" << endl;
cout << "set大小: " << s.size() << endl; // 1
cout << "multiset大小: " << ms.size() << endl; // 2
}++2. multiset 特有的应用场景++
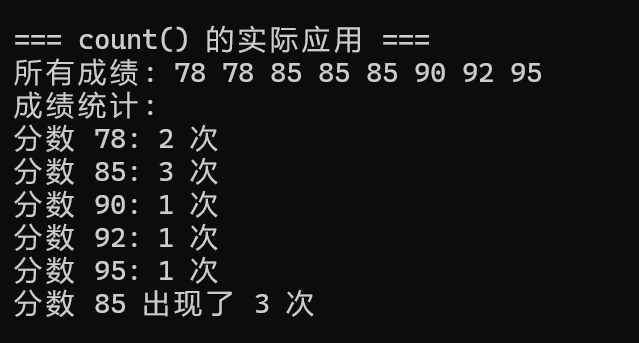
2.1 count() 的实际应用
cpp
void testCountUsage() {
cout << "\n=== count() 的实际应用 ===" << endl;
// 成绩统计示例
multiset<int> scores = {85, 92, 78, 85, 90, 85, 78, 95};
cout << "所有成绩: ";
for (int score : scores) cout << score << " ";
cout << endl;
// 统计每个分数出现的次数
cout << "成绩统计:" << endl;
auto it = scores.begin();
while (it != scores.end()) {
int current_score = *it;
int count = scores.count(current_score);
cout << "分数 " << current_score << ": " << count << " 次" << endl;
// 跳过相同的分数
advance(it, count);
}
// 查找特定分数的出现次数
int target_score = 85;
cout << "分数 " << target_score << " 出现了 "
<< scores.count(target_score) << " 次" << endl;
}
2.2 equal_range() 的实际应用
cpp
void testEqualRangeUsage() {
cout << "\n=== equal_range() 的实际应用 ===" << endl;
multiset<int> data = {10, 20, 20, 20, 30, 30, 40, 50, 50, 50};
// 查找所有等于20的元素
auto range = data.equal_range(20);
cout << "所有等于20的元素: ";
for (auto it = range.first; it != range.second; ++it) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 查找范围 [30, 50) 的元素
auto lower = data.lower_bound(30); // 第一个 >= 30 的元素
auto upper = data.upper_bound(49); // 第一个 > 49 的元素
cout << "范围 [30, 50) 的元素: ";
for (auto it = lower; it != upper; ++it) {
cout << *it << " "; // 30, 30, 40
}
cout << endl;
// 使用equal_range处理不存在的值
auto not_found_range = data.equal_range(25);
if (not_found_range.first == not_found_range.second) {
cout << "元素25不存在" << endl;
}
}
++3. multiset 专有操作示例++
3.1 删除特定数量的重复元素
cpp
void testMultisetErase() {
cout << "\n=== multiset 特有的删除操作 ===" << endl;
multiset<int> ms = {1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4};
cout << "原始multiset: ";
for (int x : ms) cout << x << " ";
cout << ", 大小: " << ms.size() << endl;
// 删除所有值为2的元素
size_t removed = ms.erase(2);
cout << "删除所有2,删除了 " << removed << " 个元素" << endl;
cout << "删除后: ";
for (int x : ms) cout << x << " "; // 1 3 3 4 4 4 4
cout << endl;
// 只删除第一个3
auto it = ms.find(3);
if (it != ms.end()) {
ms.erase(it); // 只删除迭代器指向的那个3
}
cout << "删除一个3后: ";
for (int x : ms) cout << x << " "; // 1 3 4 4 4 4
cout << endl;
}删除某个数字,就是删除所有这个数字。
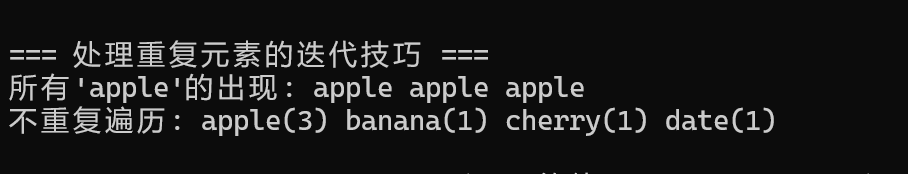
3.2 处理重复元素的迭代技巧
cpp
void testIterationTechniques() {
cout << "\n=== 处理重复元素的迭代技巧 ===" << endl;
multiset<string> words = {"apple", "banana", "apple", "cherry", "apple", "date"};
// 方法1:使用equal_range遍历特定值的所有出现
cout << "所有'apple'的出现: ";
auto apple_range = words.equal_range("apple");
for (auto it = apple_range.first; it != apple_range.second; ++it) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 方法2:跳过重复元素的遍历
cout << "不重复遍历: ";
auto it = words.begin();
while (it != words.end()) {
string current_word = *it;
cout << current_word << "(" << words.count(current_word) << ") ";
// 跳到下一个不同的单词
it = words.upper_bound(current_word);
}
cout << endl;
}
使用建议
cpp
void usageRecommendations() {
cout << "\n=== 使用建议 ===" << endl;
cout << "适合使用multiset的场景:" << endl;
cout << "1. 需要维护排序且允许重复的集合" << endl;
cout << "2. 需要频繁统计元素出现次数" << endl;
cout << "3. 需要快速查找某个范围内的所有元素" << endl;
cout << "4. 需要保持插入顺序但允许重复(与vector不同)" << endl;
cout << "\n不适合使用multiset的场景:" << endl;
cout << "1. 需要唯一元素 → 使用set" << endl;
cout << "2. 需要极快插入且不关心顺序 → 使用unordered_multiset" << endl;
cout << "3. 只需要简单集合操作 → 使用vector + sort" << endl;
}完整测试代码
cpp
int main()
{
//cout << " === set容器接口测试 === " << endl;
/*testAssignment();*/
/* testAssignment();*/
//testCapacity();
/*testInsert();*/
//testErase();
/*testFind();*/
/*testBounds();*/
//testEqualRange();
//testCount();
//testSwapClear();
basicDifference();
testInsertDifference();
testCountUsage();
testEqualRangeUsage();
testMultisetErase();
testIterationTechniques();
usageRecommendations();
return 0;
}multiset 的核心特点:
-
允许重复元素:与set最主要的区别
-
自动排序:保持元素有序
-
高效操作:插入、删除、查找都是O(log n)
-
特有功能:count()和equal_range()在multiset中特别有用
关键接口对比:
| 操作 | set | multiset |
|---|---|---|
insert(value) |
可能失败(重复时) | 总是成功 |
count(value) |
返回0或1 | 返回实际出现次数 |
equal_range(value) |
范围最多1个元素 | 可能包含多个元素 |
erase(value) |
删除0或1个元素 | 删除所有该值的元素 |
一句话总结 :当您需要维护一个有序且允许重复的集合时,multiset是最佳选择!
map
map的介绍

map与set的基本区别
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
void basicDifference() {
cout << "=== map vs set 基本区别 ===" << endl;
// set: 只存储键(key)
set<string> s = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"};
cout << "set内容: ";
for (const auto& key : s) cout << key << " "; // apple banana cherry
cout << endl;
// map: 存储键值对(key-value)
map<string, int> m = {{"apple", 3}, {"banana", 2}, {"cherry", 5}};
cout << "map内容: ";
for (const auto& pair : m) {
cout << pair.first << ":" << pair.second << " ";
// apple:3 banana:2 cherry:5
}
cout << endl;
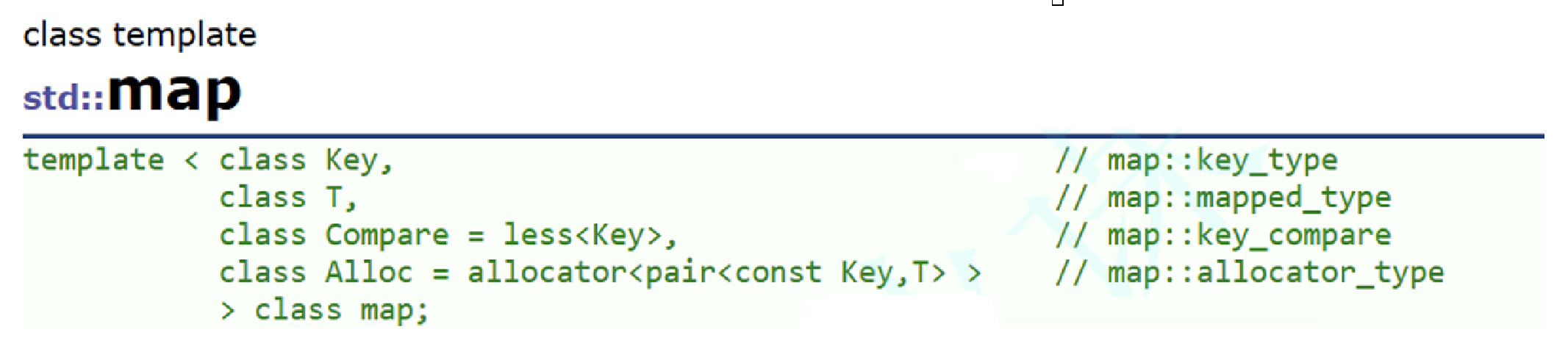
}map的模板参数列表
key: 键值对中key的类型
T: 键值对中value的类型
Compare: 比较器的类型。map中的元素是按照key来比较的,缺省情况下按照++小于++ 来比较,一般情况下(内置类型元素)该参数不需要传递。++如果无法比较时++ (自定义类型),++需要用户 自己显式传递比较规则++(一般情况下按照函数指针或者仿函数来传递)
Alloc:通过空间配置器来申请底层空间,不需要用户传递
注意:使用map时,需要包含头文件
map的构造
map的迭代器

map的容量与元素访问
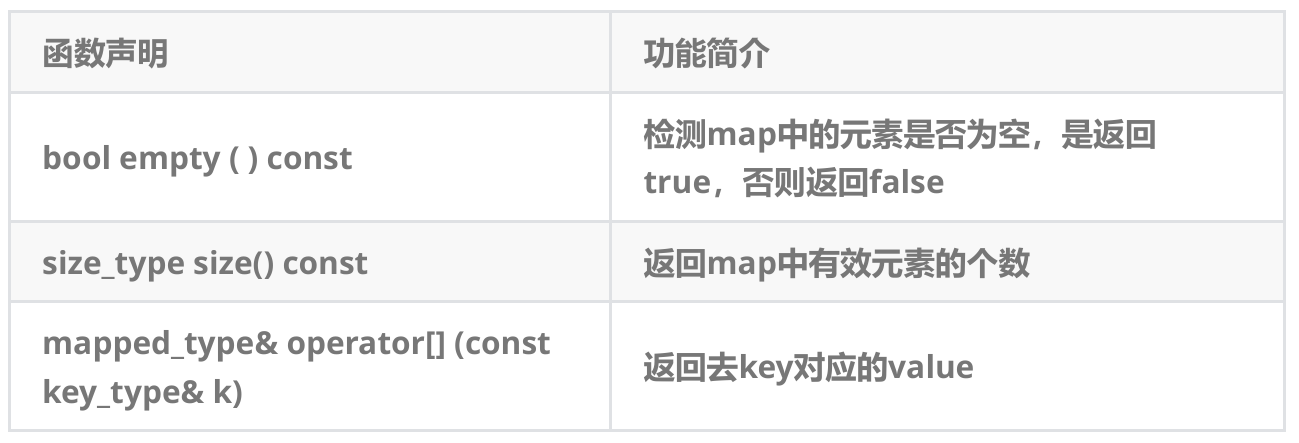
问题:当key不在map中时,通过operator获取对应value时会发生什么问题?
cpp
void testAutoInsertion() {
map<string, int> scores = {{"Alice", 90}, {"Bob", 85}};
cout << "操作前map大小: " << scores.size() << endl; // 2
// 访问不存在的key
cout << "Charlie的分数: " << charlie_score << endl; // 输出: 0
cout << "操作后map大小: " << scores.size() << endl; // 3 - 自动增加了!
}operator[]调用等价于:
cpp
(*((this->insert(make_pair(k, mapped_type()))).first)).second让我们分解理解
cpp
void explainEquivalentCode() {
map<string, int> scores;
// 分解operator["Charlie"]的等价操作
auto result = scores.insert(make_pair("Charlie", int()));
// 1. 尝试插入pair("Charlie", 0)
// 2. 如果key已存在,insert返回已存在元素的迭代器
// 3. 如果key不存在,插入新元素并返回新元素的迭代器
int& value_ref = (*(result.first)).second;
// 获取映射值的引用
cout << "插入结果: " << (result.second ? "成功" : "失败") << endl;
cout << "获取的值: " << value_ref << endl;
}当key不存在时,operator[]用默认 value与key构造键值对然后插入,返回该默认value。at()函数直接抛异常。
构造和初始化
cpp
void testMapConstruction() {
cout << "\n=== map的构造方式 ===" << endl;
// 方式1:默认构造
map<string, int> m1;
// 方式2:初始化列表
map<string, int> m2 = {
{"Alice", 90},
{"Bob", 85},
{"Charlie", 92}
};
// 方式3:拷贝构造
map<string, int> m3(m2);
// 方式4:范围构造
map<string, int> m4(m2.begin(), m2.end());
cout << "m2内容: ";
for (const auto& p : m2) {
cout << p.first << ":" << p.second << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}插入操作
cpp
void testInsertOperations() {
cout << "\n=== 插入操作对比 ===" << endl;
map<string, int> m;
// map插入:需要键值对
auto m_result = m.insert({ "apple", 3 }); // 使用pair
cout << "map插入结果: " << (m_result.second ? "成功" : "失败") << endl;
for (const auto& p : m) {
cout << p.first << ":" << p.second << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}访问操作(map特有功能)
cpp
void testAccessOperations() {
cout << "\n=== 访问操作(map特有)===" << endl;
map<string, int> scores = {{"Alice", 90}, {"Bob", 85}};
// 1. operator[](最重要、最常用)
cout << "Alice的分数: " << scores["Alice"] << endl; // 90
// operator[]的特殊行为:key不存在时自动插入
cout << "Charlie的分数: " << scores["Charlie"] << endl; // 0(自动插入)
cout << "map大小: " << scores.size() << endl; // 3
// 2. at()方法(安全访问)
try {
cout << "Bob的分数: " << scores.at("Bob") << endl; // 85
cout << "David的分数: " << scores.at("David") << endl; // 抛出异常
} catch (const out_of_range& e) {
cout << "异常: " << e.what() << endl;
}
// 3. 通过迭代器访问
auto it = scores.find("Alice");
if (it != scores.end()) {
cout << "通过迭代器访问: " << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;
}
}查找操作
cpp
void testFindOperations() {
cout << "\n=== 查找操作对比 ===" << endl;
set<string> s = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"};
map<string, int> m = {{"apple", 3}, {"banana", 2}, {"cherry", 5}};
// set查找:返回键的迭代器
auto s_it = s.find("banana");
if (s_it != s.end()) {
cout << "set找到: " << *s_it << endl;
}
// map查找:返回键值对的迭代器
auto m_it = m.find("banana");
if (m_it != m.end()) {
cout << "map找到: " << m_it->first << ":" << m_it->second << endl;
}
// map特有的查找模式
string key = "apple";
if (m.count(key) > 0) { // 检查键是否存在
cout << key << "的值为: " << m[key] << endl; // 安全访问
}
}删除操作
cpp
void testEraseOperations() {
cout << "\n=== 删除操作 ===" << endl;
map<string, int> m = {
{"A", 1}, {"B", 2}, {"C", 3}, {"D", 4}, {"E", 5}
};
// 1. 通过键删除
size_t count = m.erase("B"); // 返回删除的元素个数
cout << "删除了 " << count << " 个元素" << endl;
// 2. 通过迭代器删除
auto it = m.find("C");
if (it != m.end()) {
m.erase(it);
}
// 3. 删除范围
auto first = m.find("D");
if (first != m.end()) {
m.erase(first, m.end());
}
cout << "删除后剩余: ";
for (const auto& p : m) {
cout << p.first << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}map特有功能讲解
operator[] 的妙用
cpp
void testOperatorBracket() {
cout << "\n=== operator[] 的实用技巧 ===" << endl;
// 1. 单词计数(经典用法)
string text = "apple banana apple cherry banana apple";
map<string, int> wordCount;
stringstream ss(text);
string word;
while (ss >> word) {
wordCount[word]++; // 自动初始化为0然后递增
}
cout << "单词统计: ";
for (const auto& p : wordCount) {
cout << p.first << ":" << p.second << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 2. 默认值设置
map<string, string> config;
string value = config["timeout"]; // 自动插入空字符串
cout << "timeout配置: '" << value << "'" << endl;
// 3. 链式访问(需要谨慎)
map<string, map<string, int>> nestedMap;
nestedMap["user1"]["score"] = 100; // 自动创建内层map
cout << "嵌套访问: " << nestedMap["user1"]["score"] << endl;
}范围查询(map特有优势)
cpp
void testRangeQueries() {
cout << "\n=== 范围查询 ===" << endl;
map<int, string> students = {
{101, "Alice"}, {102, "Bob"}, {105, "Charlie"},
{108, "David"}, {110, "Eve"}
};
// 查找学号在[103, 109)范围内的学生
auto lower = students.lower_bound(103); // 第一个 >= 103
auto upper = students.upper_bound(109); // 第一个 > 109
cout << "学号103-109的学生: ";
for (auto it = lower; it != upper; ++it) {
cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << " "; // 105:Charlie 108:David
}
cout << endl;
// equal_range获取相等键的范围(在multimap中更有用)
auto range = students.equal_range(105);
if (range.first != range.second) {
cout << "学号105的学生: " << range.first->second << endl;
}
}mulimap
mulimap的介绍

mulimap的使用

operator[]的语义是"获取或设置指定键的值",但在multimap中,一个键对应多个值,这导致了根本性的语义歧义。所以multimap中没有重载operator[]操作。
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void oneToManyMapping() {
cout << "=== 一对多关系映射 ===" << endl;
// 学生与课程成绩的映射
multimap<string, string> studentCourses;
// 添加选课关系
studentCourses.insert({"Alice", "Math"});
studentCourses.insert({"Alice", "Physics"});
studentCourses.insert({"Bob", "Chemistry"});
studentCourses.insert({"Alice", "Computer Science"});
studentCourses.insert({"Bob", "Math"});
// 查询Alice的所有课程
cout << "Alice的课程: ";
auto range = studentCourses.equal_range("Alice");
for (auto it = range.first; it != range.second; ++it) {
cout << it->second << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 查询Bob的所有课程
cout << "Bob的课程: ";
range = studentCourses.equal_range("Bob");
for (auto it = range.first; it != range.second; ++it) {
cout << it->second << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
pair
想象一下 pair 就像一张名片:
-
名片上有两个主要信息:姓名 + 电话号码
-
这两个信息是相关的,总是一起出现
-
但名片就是一个独立的东西
注意:头文件是utility。pair就是一个"数据对",可以把任意两个值打包在一起,不管它们是什么类型。
代码中的基本形式
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <utility> // 包含pair的头文件
using namespace std;
int main() {
// 创建一个pair:就像创建一张名片
pair<string, string> businessCard = {"张三", "138-1234-5678"};
// 访问pair中的信息
cout << "姓名: " << businessCard.first << endl; // 张三
cout << "电话: " << businessCard.second << endl; // 138-1234-5678
return 0;
}pair 与 map 的根本区别,map是由很多pair组成的。
