一、实验题目
1.两数之和
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 target 的那 两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素在答案里不能重复出现。
你可以按任意顺序返回答案。
2.两数相加
给你两个 非空 的链表,表示两个非负的整数。它们每位数字都是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。
请你将两个数相加,并以相同形式返回一个表示和的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。
92.反转链表2
给你单链表的头指针 head 和两个整数 left 和 right ,其中 left <= right 。请你反转从位置 left 到位置 right 的链表节点,返回 反转后的链表 。
二、实验思路和方案
1.两数之和
方法一要求使用最简单暴力算法,即暴力枚举法,通过两个for循环将所有相加的可能性枚举出来,然后再通过if()条件判断语句筛选出符合条件的情况即可。
方法二要求设计一个时间复杂度小于o(n*2)的算法,我们可以采用哈希表的方法进行解决。先创建一个哈希表,对于每一个 x,我们会查询哈希表中是否存在 target - x,然后将 x 插入到哈希表中,这样做就可以保证不会让 x 和自己匹配。
2.两数相加
由于输入的两个链表都是逆序存储数字的位数的,因此两个链表中同一位置的数字可以直接相加。我们同时遍历两个链表,逐位计算它们的和,并与当前位置的进位值相加。
92.反转链表2
迭代法:由于要反转中间的链表,因此把链表分成三部分:前部分链表,反转链表和后部分链表。找到前部分链表的尾节点就可以开始反转,最后再把三个链表拼接。
递归法:将反转部分之间的距离保持不变,利用递归平移找到反转部分的首结点位置。将反转部分的首结点从前往后遍历,找到反转部分的尾结点,再通过外部保存该尾结点的下一结点位置,然后进行交换next递归处理层层替换,最后再将反转后的尾结点(反转前的头结点)接上之前保留的结点。
三、实验代码
1.两数之和
基本任务:
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int n = nums.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target) {
return new int[]{i, j};
}
}
}
return new int[0];
}
}进阶任务:
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Map<Integer, Integer> hashtable = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (hashtable.containsKey(target - nums[i])) {
return new int[]{hashtable.get(target - nums[i]), i};
}
hashtable.put(nums[i], i);
}
return new int[0];
}
}2.两数相加
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode head = null, tail = null;
int carry = 0;
while (l1 != null || l2 != null) {
int n1 = l1 != null ? l1.val : 0;
int n2 = l2 != null ? l2.val : 0;
int sum = n1 + n2 + carry;
if (head == null) {
head = tail = new ListNode(sum % 10);
} else {
tail.next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
tail = tail.next;
}
carry = sum / 10;
if (l1 != null) {
l1 = l1.next;
}
if (l2 != null) {
l2 = l2.next;
}
}
if (carry > 0) {
tail.next = new ListNode(carry);
}
return head;
}
}92.反转链表2
基本任务:
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {
int count = 1;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode node = dummy;
while (count != m) {
node = node.next;
count++;
}
node.next = reverse(node.next, n - m + 1);
return dummy.next;
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head, int num) {
ListNode next;
ListNode newNode = null;
ListNode reverseTail = head;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
next = head.next;
head.next = newNode;
newNode = head;
head = next;
}
reverseTail.next = head;
return newNode;
}
}进阶任务:
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) {
if (left == 1) {
return reberseN(head, right);
}
head.next = reverseBetween(head.next, left - 1, right - 1);
return head;
}
ListNode Rnext = null;
public ListNode reberseN(ListNode head, int right) {
if (right == 1) {
Rnext = head.next;
return head;
}
ListNode last = reberseN(head.next, right - 1);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = Rnext;
return last;
}
}四、实验结果及分析
1.两数之和
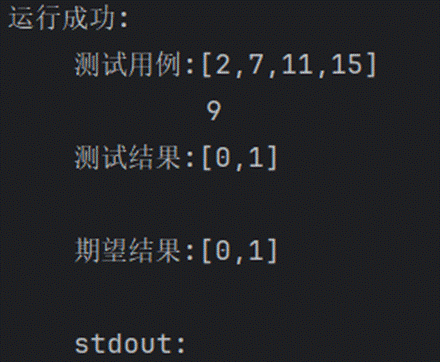
2.两数相加
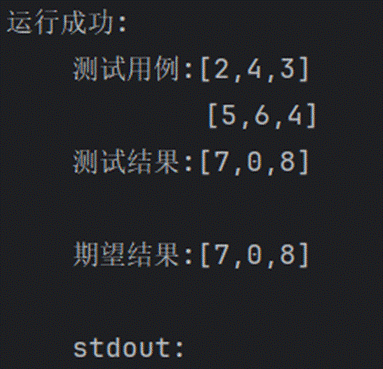
92.反转链表2
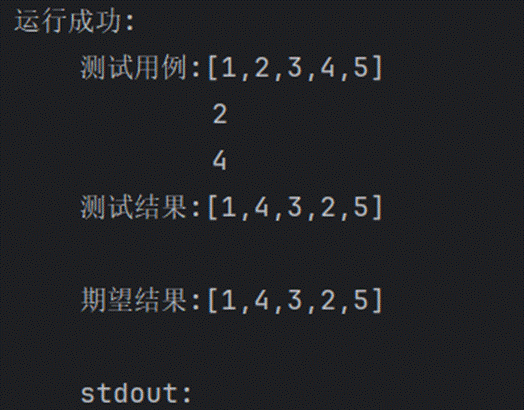
五、实验总结及体会
泛型让代码更具通用性,能适应不同类型的数据处理;数据结构则是算法的基础,选择合适的数据结构能显著提升算法效率。通过本次实验,我深刻体会到泛型的灵活性与数据结构的重要性,学会了如何利用泛型设计可复用的代码,以及如何根据问题特性选用最优数据结构。