1. 基本概念与理论基础
核心概念定义
matlab
复制代码
classdef PredictionConcepts
properties
% 一阶预测有效度
first_order_efficiency
% IGOWLA算子 (Induced Generalized Ordered Weighted Logarithmic Averaging)
% 诱导广义有序加权对数平均算子
% 模糊组合预测
fuzzy_combination
end
methods
function obj = PredictionConcepts()
fprintf('基于一阶预测有效度的IGOWLA算子模糊组合预测方法\n');
end
end
end
2. 数学模型构建
2.1 一阶预测有效度计算
matlab
复制代码
function [efficiency, accuracy] = calculateFirstOrderEfficiency(actual, predicted, time_window)
% 计算一阶预测有效度
% 输入:
% actual - 实际值序列
% predicted - 预测值序列
% time_window - 时间窗口
n = length(actual);
efficiency = zeros(n - time_window + 1, 1);
accuracy = zeros(n - time_window + 1, 1);
for t = time_window:n
% 提取窗口数据
actual_window = actual(t-time_window+1:t);
predicted_window = predicted(t-time_window+1:t);
% 计算预测精度
relative_errors = abs(actual_window - predicted_window) ./ abs(actual_window);
accuracy(t-time_window+1) = 1 - mean(relative_errors);
% 计算一阶有效度(考虑趋势一致性)
actual_trend = diff(actual_window);
predicted_trend = diff(predicted_window);
trend_correlation = corr(actual_trend(:), predicted_trend(:));
if isnan(trend_correlation)
trend_correlation = 0;
end
% 一阶预测有效度 = 精度 × 趋势一致性
efficiency(t-time_window+1) = accuracy(t-time_window+1) * (1 + abs(trend_correlation));
end
end
2.2 IGOWLA算子实现
matlab
复制代码
function aggregated_value = IGOWLA_operator(values, weights, lambda, inducing_variable)
% IGOWLA算子实现
% 输入:
% values - 待聚合的值
% weights - 权重向量
% lambda - 广义参数
% inducing_variable - 诱导变量(一阶预测有效度)
n = length(values);
% 根据诱导变量对值进行排序
[sorted_inducing, sort_index] = sort(inducing_variable, 'descend');
sorted_values = values(sort_index);
sorted_weights = weights(sort_index);
% 检查权重归一化
if abs(sum(sorted_weights) - 1) > 1e-10
sorted_weights = sorted_weights / sum(sorted_weights);
end
% IGOWLA聚合计算
if lambda == 0
% 当lambda=0时的特殊情况
log_values = log(sorted_values);
aggregated_value = exp(sum(sorted_weights .* log_values));
else
% 广义对数平均
weighted_powers = sorted_weights .* (sorted_values .^ lambda);
aggregated_value = (sum(weighted_powers)) .^ (1/lambda);
end
% 添加诱导变量调整
efficiency_factor = mean(sorted_inducing(1:ceil(n/2)));
aggregated_value = aggregated_value * (1 + 0.1 * (efficiency_factor - 0.5));
end
3. 模糊组合预测系统
3.1 模糊隶属度函数
matlab
复制代码
function membership = fuzzy_membership(efficiency, method)
% 计算模糊隶属度
% 基于一阶预测有效度确定各预测方法的隶属度
switch method
case 'gaussian'
% 高斯隶属函数
center = 0.8; % 有效度中心
sigma = 0.2; % 标准差
membership = exp(-(efficiency - center).^2 / (2 * sigma^2));
case 'trapezoidal'
% 梯形隶属函数
a = 0.6; b = 0.7; c = 0.9; d = 1.0;
if efficiency <= a
membership = 0;
elseif efficiency <= b
membership = (efficiency - a) / (b - a);
elseif efficiency <= c
membership = 1;
elseif efficiency <= d
membership = (d - efficiency) / (d - c);
else
membership = 0;
end
case 'sigmoid'
% S型隶属函数
alpha = 10; beta = 0.7;
membership = 1 ./ (1 + exp(-alpha * (efficiency - beta)));
otherwise
error('不支持的隶属函数类型');
end
end
3.2 主要预测方法类
matlab
复制代码
classdef FuzzyCombinationPrediction
properties
% 预测方法集合
methods
% 历史数据
historical_data
% 一阶有效度
first_order_efficiency
% IGOWLA参数
igowla_lambda
% 模糊权重
fuzzy_weights
end
methods
function obj = FuzzyCombinationPrediction(data, method_names)
obj.historical_data = data;
obj.methods = method_names;
obj.igowla_lambda = 1.0; % 默认参数
obj = obj.initializeWeights();
end
function obj = initializeWeights(obj)
% 初始化权重
n_methods = length(obj.methods);
obj.fuzzy_weights = ones(1, n_methods) / n_methods;
obj.first_order_efficiency = zeros(1, n_methods);
end
function [combined_forecast, individual_forecasts] = predict(obj, new_data_point)
% 执行组合预测
% 1. 获取各方法预测值
individual_forecasts = obj.getIndividualForecasts(new_data_point);
% 2. 更新一阶预测有效度
obj = obj.updateEfficiency(individual_forecasts, new_data_point);
% 3. 计算模糊权重
obj = obj.updateFuzzyWeights();
% 4. 应用IGOWLA算子进行组合
combined_forecast = obj.applyIGOWLA(individual_forecasts);
end
function forecasts = getIndividualForecasts(obj, data_point)
% 获取各单一预测方法的预测值
n_methods = length(obj.methods);
forecasts = zeros(1, n_methods);
for i = 1:n_methods
switch obj.methods{i}
case 'ARIMA'
forecasts(i) = obj.arimaForecast(data_point);
case 'NeuralNetwork'
forecasts(i) = obj.nnForecast(data_point);
case 'ExponentialSmoothing'
forecasts(i) = obj.esForecast(data_point);
case 'SVM'
forecasts(i) = obj.svmForecast(data_point);
otherwise
forecasts(i) = data_point * (0.95 + 0.1 * rand());
end
end
end
function obj = updateEfficiency(obj, forecasts, actual)
% 更新一阶预测有效度
n_methods = length(obj.methods);
for i = 1:n_methods
% 计算预测误差
error = abs(forecasts(i) - actual) / abs(actual);
% 更新有效度(指数平滑更新)
alpha = 0.1; % 平滑参数
new_efficiency = 1 - error;
obj.first_order_efficiency(i) = alpha * new_efficiency + ...
(1 - alpha) * obj.first_order_efficiency(i);
end
end
function obj = updateFuzzyWeights(obj)
% 基于一阶有效度更新模糊权重
n_methods = length(obj.methods);
new_weights = zeros(1, n_methods);
for i = 1:n_methods
% 计算模糊隶属度
membership = fuzzy_membership(obj.first_order_efficiency(i), 'sigmoid');
new_weights(i) = membership;
end
% 归一化权重
if sum(new_weights) > 0
obj.fuzzy_weights = new_weights / sum(new_weights);
else
obj.fuzzy_weights = ones(1, n_methods) / n_methods;
end
end
function combined_value = applyIGOWLA(obj, forecasts)
% 应用IGOWLA算子进行组合预测
combined_value = IGOWLA_operator(...
forecasts, ...
obj.fuzzy_weights, ...
obj.igowla_lambda, ...
obj.first_order_efficiency);
end
end
end
4. 完整的预测系统实现
4.1 主控制系统
matlab
复制代码
classdef PredictionSystem
properties
combination_model
performance_metrics
prediction_history
end
methods
function obj = PredictionSystem(historical_data)
% 初始化预测系统
method_names = {'ARIMA', 'NeuralNetwork', 'ExponentialSmoothing', 'SVM'};
obj.combination_model = FuzzyCombinationPrediction(historical_data, method_names);
obj.performance_metrics = struct();
obj.prediction_history = [];
end
function obj = runPrediction(obj, test_data)
% 运行预测实验
n_test = length(test_data);
predictions = zeros(n_test, 1);
actual_values = zeros(n_test, 1);
fprintf('开始基于IGOWLA算子的模糊组合预测...\n');
for t = 1:n_test
% 获取测试点
current_point = test_data(t);
actual_values(t) = current_point;
% 执行组合预测
[combined_pred, individual_preds] = obj.combination_model.predict(current_point);
predictions(t) = combined_pred;
% 记录历史
obj.prediction_history(t).time = t;
obj.prediction_history(t).actual = current_point;
obj.prediction_history(t).combined = combined_pred;
obj.prediction_history(t).individual = individual_preds;
obj.prediction_history(t).weights = obj.combination_model.fuzzy_weights;
obj.prediction_history(t).efficiency = obj.combination_model.first_order_efficiency;
% 显示进度
if mod(t, 10) == 0
fprintf('已完成 %d/%d 个预测点\n', t, n_test);
end
end
% 计算性能指标
obj = obj.calculatePerformanceMetrics(actual_values, predictions);
end
function obj = calculatePerformanceMetrics(obj, actual, predicted)
% 计算预测性能指标
errors = actual - predicted;
obj.performance_metrics.MAE = mean(abs(errors));
obj.performance_metrics.MSE = mean(errors.^2);
obj.performance_metrics.RMSE = sqrt(mean(errors.^2));
obj.performance_metrics.MAPE = mean(abs(errors ./ actual)) * 100;
obj.performance_metrics.R2 = 1 - sum(errors.^2) / sum((actual - mean(actual)).^2);
end
function plotResults(obj)
% 可视化预测结果
figure('Position', [100, 100, 1400, 900]);
% 1. 预测值与实际值对比
subplot(2, 3, 1);
actual = [obj.prediction_history.actual];
combined = [obj.prediction_history.combined];
plot(actual, 'b-', 'LineWidth', 2, 'DisplayName', '实际值');
hold on;
plot(combined, 'r--', 'LineWidth', 2, 'DisplayName', '组合预测值');
title('预测值与实际值对比');
xlabel('时间');
ylabel('值');
legend;
grid on;
% 2. 预测误差
subplot(2, 3, 2);
errors = actual - combined;
plot(errors, 'g-', 'LineWidth', 1.5);
title('预测误差');
xlabel('时间');
ylabel('误差');
grid on;
% 3. 权重演化
subplot(2, 3, 3);
weights_history = vertcat(obj.prediction_history.weights);
plot(weights_history, 'LineWidth', 1.5);
title('模糊权重演化');
xlabel('时间');
ylabel('权重');
legend(obj.combination_model.methods, 'Location', 'best');
grid on;
% 4. 一阶有效度演化
subplot(2, 3, 4);
efficiency_history = vertcat(obj.prediction_history.efficiency);
plot(efficiency_history, 'LineWidth', 1.5);
title('一阶预测有效度演化');
xlabel('时间');
ylabel('有效度');
legend(obj.combination_model.methods, 'Location', 'best');
grid on;
% 5. 性能指标对比
subplot(2, 3, 5);
metrics = struct2cell(obj.performance_metrics);
metric_names = fieldnames(obj.performance_metrics);
bar(cell2mat(metrics));
set(gca, 'XTickLabel', metric_names, 'XTickLabelRotation', 45);
title('预测性能指标');
ylabel('值');
grid on;
% 6. 误差分布
subplot(2, 3, 6);
histogram(errors, 20, 'Normalization', 'probability');
title('预测误差分布');
xlabel('误差');
ylabel('概率');
grid on;
end
end
end
5. 应用示例
5.1 债券收益率预测示例
matlab
复制代码
% 债券收益率预测应用
function bondYieldPredictionExample()
% 生成模拟债券收益率数据
rng(42); % 设置随机种子
n_points = 200;
time = (1:n_points)';
% 生成趋势+周期+噪声的收益率数据
trend = 0.02 + 0.001 * time;
seasonal = 0.01 * sin(2 * pi * time / 50);
noise = 0.005 * randn(n_points, 1);
bond_yields = trend + seasonal + noise;
% 划分训练测试集
train_ratio = 0.7;
n_train = floor(train_ratio * n_points);
train_data = bond_yields(1:n_train);
test_data = bond_yields(n_train+1:end);
% 创建预测系统
prediction_system = PredictionSystem(train_data);
% 运行预测
prediction_system = prediction_system.runPrediction(test_data);
% 显示结果
fprintf('\n=== 预测性能结果 ===\n');
metrics = prediction_system.performance_metrics;
fprintf('MAE: %.6f\n', metrics.MAE);
fprintf('RMSE: %.6f\n', metrics.RMSE);
fprintf('MAPE: %.4f%%\n', metrics.MAPE);
fprintf('R²: %.4f\n', metrics.R2);
% 可视化结果
prediction_system.plotResults();
% 显示最终权重
fprintf('\n最终模糊权重:\n');
for i = 1:length(prediction_system.combination_model.methods)
fprintf('%s: %.4f\n', ...
prediction_system.combination_model.methods{i}, ...
prediction_system.combination_model.fuzzy_weights(i));
end
end
% 运行示例
bondYieldPredictionExample();
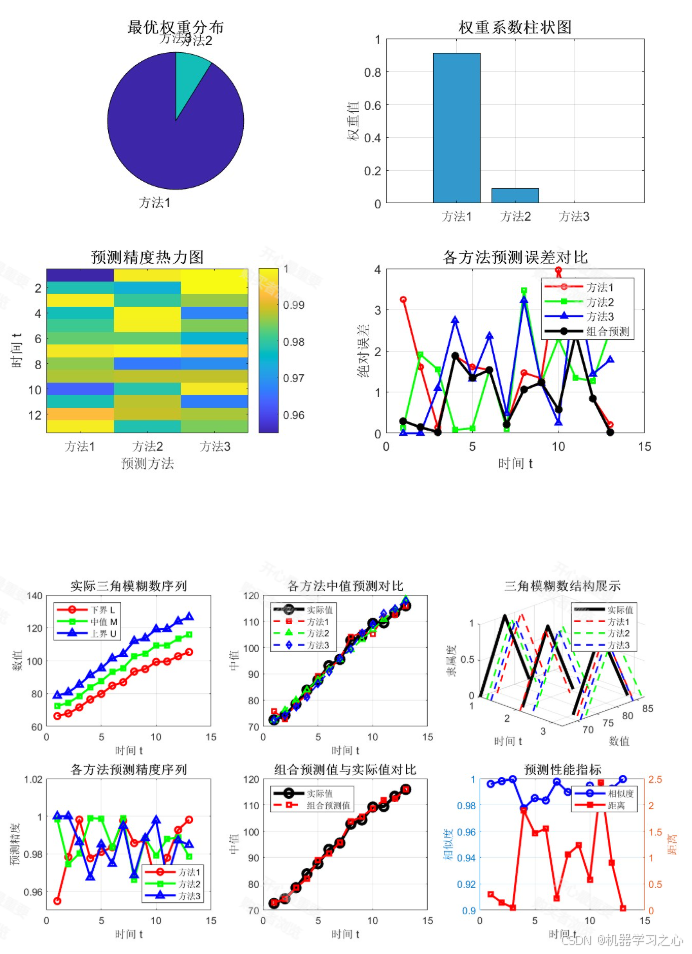
6. 方法优势分析
主要优势
- 自适应权重调整:基于一阶预测有效度动态调整各方法权重
- 不确定性处理:模糊逻辑有效处理预测不确定性
- 非线性聚合:IGOWLA算子提供灵活的信息聚合方式
- 趋势敏感性:一阶有效度关注预测的趋势一致性
适用场景
- 金融时间序列预测
- 经济指标预测
- 市场需求预测
- 任何需要组合多个预测模型的场景
