引言:在上一章节中,我们详细介绍了页面路由与导航的相关知识点。今天我们讨论的是数据绑定与事件处理 ,深入研究数据是如何流动、用户交互如何响应的问题。我们平时用的app比如说输入框中打字,下方实时显示输入内容。这个看似简单的交互背后,隐藏着前端框架的核心思想------数据驱动视图。
对比:传统DOM操作 vs 数据驱动
在传统开发中,我们需要:
javascript
// 传统方式
const input = document.getElementById('myInput');
const display = document.getElementById('display');
input.addEventListener('input', function(e) {
// 手动更新DOM
display.textContent = e.target.value;
});而在 uni-app 中:
html
<template>
<input v-model="message">
<div>{{ message }}</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
// 只需关注数据,DOM自动更新
message: ''
}
}
}
</script>这种模式的转变,正是现代前端框架的核心突破。下面让我们深入研究其实现原理。
一、响应式数据绑定
1.1 数据劫持
Vue 2.x 使用 Object.defineProperty 定义对象属性实现数据响应式,让我们通过一段代码来加深理解这个机制:
javascript
// 响应式原理
function defineReactive(obj, key, val) {
// 每个属性都有自己的依赖收集器
const dep = new Dep()
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: function reactiveGetter() {
console.log(`读取属性 ${key}: ${val}`)
// 依赖收集:记录当前谁在读取这个属性
dep.depend()
return val
},
set: function reactiveSetter(newVal) {
console.log(`设置属性 ${key}: ${newVal}`)
if (newVal === val) return
val = newVal
// 通知更新:值改变时通知所有依赖者
dep.notify()
}
})
}
// 测试
const data = {}
defineReactive(data, 'message', 'Hello')
data.message = 'World' // 控制台输出:设置属性 message: World
console.log(data.message) // 控制台输出:读取属性 message: World1.2 完整的响应式系统架构
原理说明
- 当对响应式数据进行赋值操作时,会触发通过Object.defineProperty定义的setter方法。
- setter首先比较新旧值是否相同,如果相同则直接返回,避免不必要的更新。
- 如果值发生变化,则更新数据,并通过依赖收集器(Dep)通知所有观察者(Watcher)进行更新。
- 这个过程是同步的,但实际的DOM更新是异步的,通过队列进行批量处理以提高性能。
1.3 v-model 的双向绑定原理
v-model 不是魔法,而是语法糖:
html
<!-- 这行代码: -->
<input v-model="username">
<!-- 等价于: -->
<input
:value="username"
@input="username = $event.target.value"
>原理分解:
1.4 不同表单元素的双向绑定
文本输入框
html
<template>
<view class="example">
<text class="title">文本输入框绑定</text>
<input
type="text"
v-model="textValue"
placeholder="请输入文本"
class="input"
/>
<text class="display">实时显示: {{ textValue }}</text>
<!-- 原理展示 -->
<view class="principle">
<text class="principle-title">实现原理:</text>
<input
:value="textValue"
@input="textValue = $event.detail.value"
placeholder="手动实现的v-model"
class="input"
/>
</view>
</view>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
textValue: ''
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.example {
padding: 20rpx;
border: 2rpx solid #eee;
margin: 20rpx;
border-radius: 10rpx;
}
.title {
font-weight: bold;
color: #333;
display: block;
margin-bottom: 20rpx;
}
.input {
border: 1rpx solid #ccc;
padding: 15rpx;
border-radius: 8rpx;
margin-bottom: 20rpx;
}
.display {
color: #007AFF;
font-size: 28rpx;
}
.principle {
background: #f9f9f9;
padding: 20rpx;
border-radius: 8rpx;
margin-top: 30rpx;
}
.principle-title {
font-size: 24rpx;
color: #666;
display: block;
margin-bottom: 15rpx;
}
</style>单选按钮组
html
<template>
<view class="example">
<text class="title">单选按钮组绑定</text>
<radio-group @change="onGenderChange" class="radio-group">
<label class="radio-item">
<radio value="male" :checked="gender === 'male'" /> 男
</label>
<label class="radio-item">
<radio value="female" :checked="gender === 'female'" /> 女
</label>
</radio-group>
<text class="display">选中: {{ gender }}</text>
<!-- 使用v-model -->
<text class="title" style="margin-top: 40rpx;">v-model简化版</text>
<radio-group v-model="simpleGender" class="radio-group">
<label class="radio-item">
<radio value="male" /> 男
</label>
<label class="radio-item">
<radio value="female" /> 女
</label>
</radio-group>
<text class="display">选中: {{ simpleGender }}</text>
</view>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
gender: 'male',
simpleGender: 'male'
}
},
methods: {
onGenderChange(e) {
this.gender = e.detail.value
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.radio-group {
display: flex;
gap: 40rpx;
margin: 20rpx 0;
}
.radio-item {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
gap: 10rpx;
}
</style>复选框数组
html
<template>
<view class="example">
<text class="title">复选框数组绑定</text>
<view class="checkbox-group">
<label
v-for="hobby in hobbyOptions"
:key="hobby.value"
class="checkbox-item"
>
<checkbox
:value="hobby.value"
:checked="selectedHobbies.includes(hobby.value)"
@change="onHobbyChange($event, hobby.value)"
/>
{{ hobby.name }}
</label>
</view>
<text class="display">选中: {{ selectedHobbies }}</text>
<!-- v-model简化版 -->
<text class="title" style="margin-top: 40rpx;">v-model简化版</text>
<view class="checkbox-group">
<label
v-for="hobby in hobbyOptions"
:key="hobby.value"
class="checkbox-item"
>
<checkbox
:value="hobby.value"
v-model="simpleHobbies"
/>
{{ hobby.name }}
</label>
</view>
<text class="display">选中: {{ simpleHobbies }}</text>
</view>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
hobbyOptions: [
{ name: '篮球', value: 'basketball' },
{ name: '阅读', value: 'reading' },
{ name: '音乐', value: 'music' },
{ name: '旅行', value: 'travel' }
],
selectedHobbies: ['basketball'],
simpleHobbies: ['basketball']
}
},
methods: {
onHobbyChange(event, value) {
const checked = event.detail.value.length > 0
if (checked) {
if (!this.selectedHobbies.includes(value)) {
this.selectedHobbies.push(value)
}
} else {
const index = this.selectedHobbies.indexOf(value)
if (index > -1) {
this.selectedHobbies.splice(index, 1)
}
}
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.checkbox-group {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
gap: 20rpx;
}
.checkbox-item {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
gap: 10rpx;
}
</style>二、事件处理
2.1 事件流:从点击到响应
浏览器中的事件流包含三个阶段:
解释说明:
第一阶段: 捕获阶段(事件从window向下传递到目标元素) 传递路径:Window → Document → HTML → Body → 父元素 → 目标元素; 监听方式:addEventListener(event, handler, true)第三个参数设为true;
第二阶段: 目标阶段(事件在目标元素上触发处理程序) 事件处理:在目标元素上执行绑定的事件处理函数,无论是否使用捕获模式; 执行顺序:按照事件监听器的注册顺序执行,与捕获/冒泡设置无关;
第三阶段: 冒泡阶段(事件从目标元素向上冒泡到window) 传递路径:目标元素 → 父元素 → Body → HTML → Document → Window; 默认行为:大多数事件都会冒泡,但focus、blur等事件不会冒泡;
2.2 事件修饰符原理详解
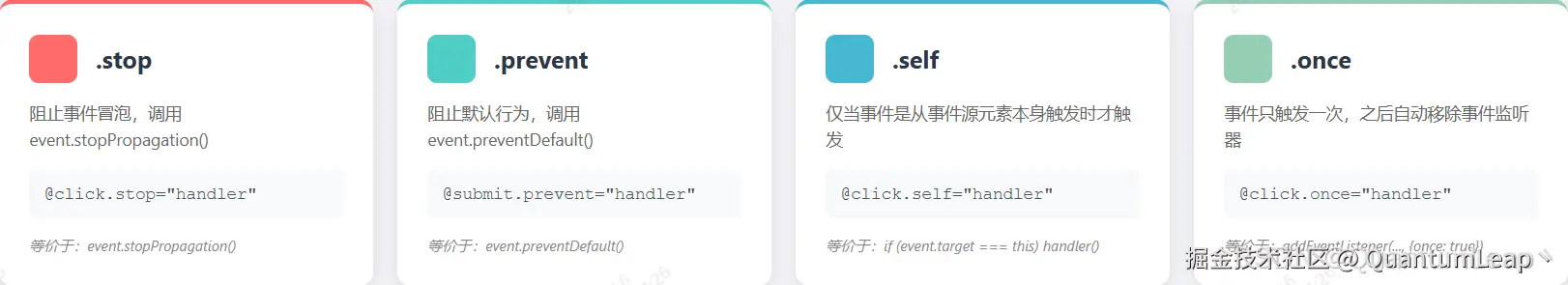
.stop 修饰符原理
javascript
// .stop 修饰符的实现原理
function handleClick(event) {
// 没有.stop时,事件正常冒泡
console.log('按钮被点击')
// 事件会继续向上冒泡,触发父元素的事件处理函数
}
function handleClickWithStop(event) {
console.log('按钮被点击,但阻止了冒泡')
event.stopPropagation()
// 事件不会继续向上冒泡
}事件修饰符对照表
| 修饰符 | 原生JS等价操作 | 作用 | 使用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
.stop |
event.stopPropagation() |
阻止事件冒泡 | 点击按钮不触发父容器点击事件 |
.prevent |
event.preventDefault() |
阻止默认行为 | 阻止表单提交、链接跳转 |
.capture |
addEventListener(..., true) |
使用捕获模式 | 需要在捕获阶段处理事件 |
.self |
if (event.target !== this) return |
仅元素自身触发 | 忽略子元素触发的事件 |
.once |
手动移除监听器 | 只触发一次 | 一次性提交按钮 |
2.3 综合案例
html
<template>
<view class="event-demo">
<!-- 1. .stop修饰符 -->
<view class="demo-section">
<text class="section-title">1. .stop 修饰符 - 阻止事件冒泡</text>
<view class="parent-box" @click="handleParentClick">
<text>父容器 (点击这里会触发)</text>
<button @click="handleButtonClick">普通按钮</button>
<button @click.stop="handleButtonClickWithStop">使用.stop的按钮</button>
</view>
<text class="log">日志: {{ logs }}</text>
</view>
<!-- 2. .prevent修饰符 -->
<view class="demo-section">
<text class="section-title">2. .prevent 修饰符 - 阻止默认行为</text>
<form @submit="handleFormSubmit">
<input type="text" v-model="formData.name" placeholder="请输入姓名" />
<button form-type="submit">普通提交</button>
<button form-type="submit" @click.prevent="handlePreventSubmit">
使用.prevent的提交
</button>
</form>
</view>
<!-- 3. .self修饰符 -->
<view class="demo-section">
<text class="section-title">3. .self 修饰符 - 仅自身触发</text>
<view class="self-demo">
<view @click.self="handleSelfClick" class="self-box">
<text>点击这个文本(自身)会触发</text>
<button>点击这个按钮(子元素)不会触发</button>
</view>
</view>
</view>
<!-- 4. 修饰符串联 -->
<view class="demo-section">
<text class="section-title">4. 修饰符串联使用</text>
<view @click="handleChainParent">
<button @click.stop.prevent="handleChainClick">
同时使用.stop和.prevent
</button>
</view>
</view>
</view>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
logs: [],
formData: {
name: ''
}
}
},
methods: {
handleParentClick() {
this.addLog('父容器被点击')
},
handleButtonClick() {
this.addLog('普通按钮被点击 → 会触发父容器事件')
},
handleButtonClickWithStop() {
this.addLog('使用.stop的按钮被点击 → 不会触发父容器事件')
},
handleFormSubmit(e) {
this.addLog('表单提交,页面可能会刷新')
},
handlePreventSubmit(e) {
this.addLog('使用.prevent,阻止了表单默认提交行为')
// 这里可以执行自定义的提交逻辑
this.submitForm()
},
handleSelfClick() {
this.addLog('.self: 只有点击容器本身才触发')
},
handleChainParent() {
this.addLog('父容器点击事件')
},
handleChainClick() {
this.addLog('按钮点击,但阻止了冒泡和默认行为')
},
addLog(message) {
this.logs.unshift(`${new Date().toLocaleTimeString()}: ${message}`)
// 只保留最近5条日志
if (this.logs.length > 5) {
this.logs.pop()
}
},
submitForm() {
uni.showToast({
title: '表单提交成功',
icon: 'success'
})
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.event-demo {
padding: 20rpx;
}
.demo-section {
margin-bottom: 40rpx;
padding: 20rpx;
border: 1rpx solid #e0e0e0;
border-radius: 10rpx;
}
.section-title {
font-weight: bold;
color: #333;
display: block;
margin-bottom: 20rpx;
font-size: 28rpx;
}
.parent-box {
background: #f5f5f5;
padding: 20rpx;
border-radius: 8rpx;
}
.log {
display: block;
background: #333;
color: #0f0;
padding: 15rpx;
border-radius: 6rpx;
font-family: monospace;
font-size: 24rpx;
margin-top: 15rpx;
max-height: 200rpx;
overflow-y: auto;
}
.self-box {
background: #e3f2fd;
padding: 30rpx;
border: 2rpx dashed #2196f3;
}
</style>三、表单数据处理
3.1 复杂表单设计
3.2 表单案例
html
<template>
<view class="form-container">
<text class="form-title">用户注册</text>
<!-- 用户名 -->
<view class="form-item" :class="{ error: errors.username }">
<text class="label">用户名</text>
<input
type="text"
v-model="formData.username"
placeholder="请输入用户名"
@blur="validateField('username')"
class="input"
/>
<text class="error-msg" v-if="errors.username">{{ errors.username }}</text>
</view>
<!-- 邮箱 -->
<view class="form-item" :class="{ error: errors.email }">
<text class="label">邮箱</text>
<input
type="text"
v-model="formData.email"
placeholder="请输入邮箱"
@blur="validateField('email')"
class="input"
/>
<text class="error-msg" v-if="errors.email">{{ errors.email }}</text>
</view>
<!-- 密码 -->
<view class="form-item" :class="{ error: errors.password }">
<text class="label">密码</text>
<input
type="password"
v-model="formData.password"
placeholder="请输入密码"
@blur="validateField('password')"
class="input"
/>
<text class="error-msg" v-if="errors.password">{{ errors.password }}</text>
</view>
<!-- 性别 -->
<view class="form-item">
<text class="label">性别</text>
<radio-group v-model="formData.gender" class="radio-group">
<label class="radio-item" v-for="item in genderOptions" :key="item.value">
<radio :value="item.value" /> {{ item.label }}
</label>
</radio-group>
</view>
<!-- 兴趣爱好 -->
<view class="form-item">
<text class="label">兴趣爱好</text>
<view class="checkbox-group">
<label
class="checkbox-item"
v-for="hobby in hobbyOptions"
:key="hobby.value"
>
<checkbox :value="hobby.value" v-model="formData.hobbies" />
{{ hobby.label }}
</label>
</view>
</view>
<!-- 提交按钮 -->
<button
@click="handleSubmit"
:disabled="!isFormValid"
class="submit-btn"
:class="{ disabled: !isFormValid }"
>
{{ isSubmitting ? '提交中...' : '注册' }}
</button>
<!-- 表单数据预览 -->
<view class="form-preview">
<text class="preview-title">表单数据预览</text>
<text class="preview-data">{{ JSON.stringify(formData, null, 2) }}</text>
</view>
</view>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
formData: {
username: '',
email: '',
password: '',
gender: 'male',
hobbies: ['sports']
},
errors: {
username: '',
email: '',
password: ''
},
isSubmitting: false,
genderOptions: [
{ label: '男', value: 'male' },
{ label: '女', value: 'female' },
{ label: '其他', value: 'other' }
],
hobbyOptions: [
{ label: '运动', value: 'sports' },
{ label: '阅读', value: 'reading' },
{ label: '音乐', value: 'music' },
{ label: '旅行', value: 'travel' },
{ label: '游戏', value: 'gaming' }
]
}
},
computed: {
isFormValid() {
return (
!this.errors.username &&
!this.errors.email &&
!this.errors.password &&
this.formData.username &&
this.formData.email &&
this.formData.password &&
!this.isSubmitting
)
}
},
methods: {
validateField(fieldName) {
const value = this.formData[fieldName]
switch (fieldName) {
case 'username':
if (!value) {
this.errors.username = '用户名不能为空'
} else if (value.length < 3) {
this.errors.username = '用户名至少3个字符'
} else {
this.errors.username = ''
}
break
case 'email':
if (!value) {
this.errors.email = '邮箱不能为空'
} else if (!/^[^\s@]+@[^\s@]+\.[^\s@]+$/.test(value)) {
this.errors.email = '邮箱格式不正确'
} else {
this.errors.email = ''
}
break
case 'password':
if (!value) {
this.errors.password = '密码不能为空'
} else if (value.length < 6) {
this.errors.password = '密码至少6个字符'
} else {
this.errors.password = ''
}
break
}
},
async handleSubmit() {
// 提交前验证所有字段
this.validateField('username')
this.validateField('email')
this.validateField('password')
// 报错直接返回
if (this.errors.username || this.errors.email || this.errors.password) {
uni.showToast({
title: '请正确填写表单',
icon: 'none'
})
return
}
this.isSubmitting = true
try {
// 接口调用
await this.mockApiCall()
uni.showToast({
title: '注册成功',
icon: 'success'
})
// 重置表单
this.resetForm()
} catch (error) {
uni.showToast({
title: '注册失败',
icon: 'error'
})
} finally {
this.isSubmitting = false
}
},
mockApiCall() {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('提交的数据:', this.formData)
resolve()
}, 2000)
})
},
resetForm() {
this.formData = {
username: '',
email: '',
password: '',
gender: 'male',
hobbies: ['sports']
}
this.errors = {
username: '',
email: '',
password: ''
}
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.form-container {
padding: 30rpx;
max-width: 600rpx;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.form-title {
font-size: 36rpx;
font-weight: bold;
text-align: center;
margin-bottom: 40rpx;
color: #333;
}
.form-item {
margin-bottom: 30rpx;
}
.label {
display: block;
margin-bottom: 15rpx;
font-weight: 500;
color: #333;
}
.input {
border: 2rpx solid #e0e0e0;
padding: 20rpx;
border-radius: 8rpx;
font-size: 28rpx;
}
.form-item.error .input {
border-color: #ff4757;
}
.error-msg {
color: #ff4757;
font-size: 24rpx;
margin-top: 8rpx;
display: block;
}
.radio-group {
display: flex;
gap: 40rpx;
}
.radio-item {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
gap: 10rpx;
}
.checkbox-group {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
gap: 20rpx;
}
.checkbox-item {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
gap: 10rpx;
min-width: 150rpx;
}
.submit-btn {
background: #007AFF;
color: white;
border: none;
padding: 25rpx;
border-radius: 10rpx;
font-size: 32rpx;
margin-top: 40rpx;
}
.submit-btn.disabled {
background: #ccc;
color: #666;
}
.form-preview {
margin-top: 50rpx;
padding: 30rpx;
background: #f9f9f9;
border-radius: 10rpx;
}
.preview-title {
font-weight: bold;
margin-bottom: 20rpx;
display: block;
}
.preview-data {
font-family: monospace;
font-size: 24rpx;
color: #666;
word-break: break-all;
}
</style>四、组件间通信-自定义事件
4.1 自定义事件原理
4.2 以计数器组件为例
html
<!-- 子组件:custom-counter.vue -->
<template>
<view class="custom-counter">
<text class="counter-title">{{ title }}</text>
<view class="counter-controls">
<button
@click="decrement"
:disabled="currentValue <= min"
class="counter-btn"
>
-
</button>
<text class="counter-value">{{ currentValue }}</text>
<button
@click="increment"
:disabled="currentValue >= max"
class="counter-btn"
>
+
</button>
</view>
<view class="counter-stats">
<text>最小值: {{ min }}</text>
<text>最大值: {{ max }}</text>
<text>步长: {{ step }}</text>
</view>
<!-- 操作 -->
<view class="quick-actions">
<button @click="reset" size="mini">重置</button>
<button @click="setToMax" size="mini">设为最大</button>
<button @click="setToMin" size="mini">设为最小</button>
</view>
</view>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'CustomCounter',
props: {
// 当前值
value: {
type: Number,
default: 0
},
// 最小值
min: {
type: Number,
default: 0
},
// 最大值
max: {
type: Number,
default: 100
},
// 步长
step: {
type: Number,
default: 1
},
// 标题
title: {
type: String,
default: '计数器'
}
},
data() {
return {
currentValue: this.value
}
},
watch: {
value(newVal) {
this.currentValue = newVal
},
currentValue(newVal) {
// 设置限制范围
if (newVal < this.min) {
this.currentValue = this.min
} else if (newVal > this.max) {
this.currentValue = this.max
}
}
},
methods: {
increment() {
const newValue = this.currentValue + this.step
if (newValue <= this.max) {
this.updateValue(newValue)
}
},
decrement() {
const newValue = this.currentValue - this.step
if (newValue >= this.min) {
this.updateValue(newValue)
}
},
updateValue(newValue) {
this.currentValue = newValue
// 触发自定义事件,通知父组件
this.$emit('input', newValue) // 用于 v-model
this.$emit('change', { // 用于普通事件监听
value: newValue,
oldValue: this.value,
type: 'change'
})
},
reset() {
this.updateValue(0)
this.$emit('reset', { value: 0 })
},
setToMax() {
this.updateValue(this.max)
this.$emit('set-to-max', { value: this.max })
},
setToMin() {
this.updateValue(this.min)
this.$emit('set-to-min', { value: this.min })
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.custom-counter {
border: 2rpx solid #e0e0e0;
border-radius: 15rpx;
padding: 30rpx;
margin: 20rpx 0;
background: white;
}
.counter-title {
font-size: 32rpx;
font-weight: bold;
text-align: center;
display: block;
margin-bottom: 25rpx;
color: #333;
}
.counter-controls {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
gap: 30rpx;
margin-bottom: 25rpx;
}
.counter-btn {
width: 80rpx;
height: 80rpx;
border-radius: 50%;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
font-size: 36rpx;
font-weight: bold;
}
.counter-value {
font-size: 48rpx;
font-weight: bold;
color: #007AFF;
min-width: 100rpx;
text-align: center;
}
.counter-stats {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-around;
margin-bottom: 25rpx;
padding: 15rpx;
background: #f8f9fa;
border-radius: 8rpx;
}
.counter-stats text {
font-size: 24rpx;
color: #666;
}
.quick-actions {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
gap: 15rpx;
}
</style>4.3 父组件使用
html
<!-- 父组件:parent-component.vue -->
<template>
<view class="parent-container">
<text class="main-title">自定义计数器组件演示</text>
<!-- 方式1:使用 v-model -->
<view class="demo-section">
<text class="section-title">1. 使用 v-model 双向绑定</text>
<custom-counter
v-model="counter1"
title="基础计数器"
:min="0"
:max="10"
:step="1"
/>
<text class="value-display">当前值: {{ counter1 }}</text>
</view>
<!-- 方式2:监听 change 事件 -->
<view class="demo-section">
<text class="section-title">2. 监听 change 事件</text>
<custom-counter
:value="counter2"
title="高级计数器"
:min="-10"
:max="20"
:step="2"
@change="onCounterChange"
/>
<text class="value-display">当前值: {{ counter2 }}</text>
<text class="event-log">事件日志: {{ eventLog }}</text>
</view>
<!-- 方式3:监听多个事件 -->
<view class="demo-section">
<text class="section-title">3. 监听多个事件</text>
<custom-counter
v-model="counter3"
title="多功能计数器"
@reset="onCounterReset"
@set-to-max="onSetToMax"
@set-to-min="onSetToMin"
/>
<text class="value-display">当前值: {{ counter3 }}</text>
</view>
<view class="demo-section">
<text class="section-title">4. 计数器联动</text>
<custom-counter
v-model="masterCounter"
title="主计数器"
@change="onMasterChange"
/>
<custom-counter
:value="slaveCounter"
title="从计数器"
:min="0"
:max="50"
readonly
/>
</view>
</view>
</template>
<script>
import CustomCounter from '@/components/custom-counter.vue'
export default {
components: {
CustomCounter
},
data() {
return {
counter1: 5,
counter2: 0,
counter3: 10,
masterCounter: 0,
slaveCounter: 0,
eventLog: ''
}
},
methods: {
onCounterChange(event) {
console.log('计数器变化事件:', event)
this.counter2 = event.value
this.addEventLog(`计数器变化: ${event.oldValue} → ${event.value}`)
},
onCounterReset(event) {
console.log('计数器重置:', event)
this.addEventLog(`计数器重置为: ${event.value}`)
},
onSetToMax(event) {
console.log('设置为最大值:', event)
this.addEventLog(`设置为最大值: ${event.value}`)
},
onSetToMin(event) {
console.log('设置为最小值:', event)
this.addEventLog(`设置为最小值: ${event.value}`)
},
onMasterChange(event) {
this.slaveCounter = Math.floor(event.value / 2)
},
addEventLog(message) {
const timestamp = new Date().toLocaleTimeString()
this.eventLog = `${timestamp}: ${message}\n${this.eventLog}`
// 增进日志长度
if (this.eventLog.split('\n').length > 5) {
this.eventLog = this.eventLog.split('\n').slice(0, 5).join('\n')
}
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.parent-container {
padding: 30rpx;
max-width: 700rpx;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.main-title {
font-size: 40rpx;
font-weight: bold;
text-align: center;
margin-bottom: 40rpx;
color: #333;
display: block;
}
.demo-section {
margin-bottom: 50rpx;
padding: 30rpx;
border: 2rpx solid #e0e0e0;
border-radius: 15rpx;
background: #fafafa;
}
.section-title {
font-size: 28rpx;
font-weight: bold;
color: #007AFF;
display: block;
margin-bottom: 25rpx;
}
.value-display {
display: block;
text-align: center;
font-size: 28rpx;
margin-top: 20rpx;
color: #333;
}
.event-log {
display: block;
background: #333;
color: #0f0;
padding: 20rpx;
border-radius: 8rpx;
font-family: monospace;
font-size: 22rpx;
margin-top: 15rpx;
white-space: pre-wrap;
max-height: 200rpx;
overflow-y: auto;
}
</style>五、性能优化
5.1 数据绑定性能优化
5.2 优化技巧
html
<template>
<view class="optimization-demo">
<text class="title">性能优化</text>
<!-- 1. 计算属性缓存 -->
<view class="optimization-section">
<text class="section-title">1. 计算属性 vs 方法</text>
<input v-model="filterText" placeholder="过滤文本" class="input" />
<view class="result">
<text>过滤后数量(计算属性): {{ filteredListLength }}</text>
<text>过滤后数量(方法调用): {{ getFilteredListLength() }}</text>
</view>
<button @click="refreshCount">刷新计数</button>
<text class="hint">打开控制台查看调用次数</text>
</view>
<!-- 2. v-once 静态内容优化 -->
<view class="optimization-section">
<text class="section-title">2. v-once 静态内容</text>
<view v-once class="static-content">
<text>这个内容只渲染一次: {{ staticTimestamp }}</text>
</view>
<button @click="updateStatic">更新静态内容(不会变化)</button>
</view>
<!-- 3. 大数据列表优化 -->
<view class="optimization-section">
<text class="section-title">3. 大数据列表渲染</text>
<button @click="loadBigData">加载1000条数据</button>
<button @click="loadOptimizedData">加载优化后的数据</button>
<!-- 普通渲染 -->
<view v-if="showNormalList">
<text>普通渲染({{ normalList.length }}条):</text>
<view v-for="item in normalList" :key="item.id" class="list-item">
<text>{{ item.name }}</text>
</view>
</view>
<!-- 虚拟滚动优化 -->
<view v-if="showOptimizedList">
<text>虚拟滚动渲染({{ optimizedList.length }}条):</text>
<view class="virtual-list">
<view
v-for="item in visibleItems"
:key="item.id"
class="list-item optimized"
>
<text>{{ item.name }}</text>
</view>
</view>
</view>
</view>
</view>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
filterText: '',
refreshCount: 0,
staticTimestamp: new Date().toLocaleTimeString(),
normalList: [],
optimizedList: [],
showNormalList: false,
showOptimizedList: false,
visibleItems: [],
bigData: []
}
},
computed: {
// 计算属性会自动缓存,只有依赖变化时才重新计算
filteredListLength() {
console.log('计算属性被执行')
const list = this.generateTestList()
return list.filter(item =>
item.name.includes(this.filterText)
).length
}
},
methods: {
// 方法每次调用都会执行
getFilteredListLength() {
console.log('方法被调用')
const list = this.generateTestList()
return list.filter(item =>
item.name.includes(this.filterText)
).length
},
generateTestList() {
return Array.from({ length: 100 }, (_, i) => ({
id: i,
name: `项目 ${i}`
}))
},
refreshCount() {
this.refreshCount++
},
updateStatic() {
this.staticTimestamp = new Date().toLocaleTimeString()
},
loadBigData() {
this.showNormalList = true
this.showOptimizedList = false
// 生成大量数据
this.normalList = Array.from({ length: 1000 }, (_, i) => ({
id: i,
name: `数据项 ${i}`,
value: Math.random() * 1000
}))
},
loadOptimizedData() {
this.showNormalList = false
this.showOptimizedList = true
// 使用 Object.freeze 避免不必要的响应式
this.optimizedList = Object.freeze(
Array.from({ length: 1000 }, (_, i) => ({
id: i,
name: `数据项 ${i}`,
value: Math.random() * 1000
}))
)
// 虚拟滚动:只渲染可见项
this.updateVisibleItems()
},
updateVisibleItems() {
// 简化的虚拟滚动实现
this.visibleItems = this.optimizedList.slice(0, 20)
},
// 防抖函数优化频繁触发的事件
debounce(func, wait) {
let timeout
return function executedFunction(...args) {
const later = () => {
clearTimeout(timeout)
func(...args)
}
clearTimeout(timeout)
timeout = setTimeout(later, wait)
}
}
},
// 组件销毁时清理资源
beforeDestroy() {
this.normalList = []
this.optimizedList = []
this.visibleItems = []
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.optimization-demo {
padding: 30rpx;
}
.title {
font-size: 36rpx;
font-weight: bold;
text-align: center;
display: block;
margin-bottom: 40rpx;
}
.optimization-section {
margin-bottom: 40rpx;
padding: 30rpx;
border: 1rpx solid #ddd;
border-radius: 10rpx;
}
.section-title {
font-weight: bold;
color: #007AFF;
display: block;
margin-bottom: 20rpx;
}
.input {
border: 1rpx solid #ccc;
padding: 15rpx;
border-radius: 6rpx;
margin-bottom: 15rpx;
}
.result {
margin: 15rpx 0;
}
.result text {
display: block;
margin: 5rpx 0;
}
.hint {
font-size: 24rpx;
color: #666;
display: block;
margin-top: 10rpx;
}
.static-content {
background: #e8f5e8;
padding: 20rpx;
border-radius: 6rpx;
margin: 15rpx 0;
}
.list-item {
padding: 10rpx;
border-bottom: 1rpx solid #eee;
}
.list-item.optimized {
background: #f0f8ff;
}
.virtual-list {
max-height: 400rpx;
overflow-y: auto;
}
</style>总结
通过以上学习,我们深入掌握了 uni-app 中数据绑定与事件处理的核心概念:
- 响应式原理 :理解了 Vue 2.x 基于
Object.defineProperty的数据劫持机制- 双向绑定 :
v-model的本质是:value+@input的语法糖- 事件系统:掌握了事件流、修饰符及其底层实现原理
- 组件通信:通过自定义事件实现子父组件间的数据传递
- 性能优化:学会了计算属性、虚拟滚动等优化技巧
至此数据绑定与时间处理就全部介绍完了,如果觉得这篇文章对你有帮助,别忘了一键三连~~~ 遇到任何问题,欢迎在评论区留言讨论。Happy Coding!