本文旨在深度解析Java集合框架中最为核心的
List和Set接口。通过 源码分析、性能对比、实战场景**,彻底搞懂它们的设计哲学和使用场景。本文配有清晰的对比表格、代码示例、UML图,无论是面试准备还是项目开发,都能提供有力支持!
📊 一、核心区别总览
| 特性维度 | List接口 | Set接口 |
|---|---|---|
| 元素唯一性 | ✅ 允许重复元素 | ❌ 不允许重复元素 |
| 顺序保证 | ✅ 严格的插入顺序 | ❌ 不保证顺序(部分实现有特殊顺序) |
| 索引支持 | ✅ 支持基于索引的访问 | ❌ 不支持索引访问 |
| 实现类示例 | ArrayList, LinkedList, Vector | HashSet, TreeSet, LinkedHashSet |
| 判重机制 | 依赖equals()方法 | 依赖hashCode()和equals()方法 |
| 性能特点 | 随机访问快,插入删除慢 | 查找速度快,自动去重 |
🔍 二、源码级深度解析
2.1 List接口的核心特性
List的继承体系:
java
public interface List<E> extends Collection<E> {
// 核心方法:索引相关操作
E get(int index);
E set(int index, E element);
void add(int index, E element);
E remove(int index);
int indexOf(Object o);
}ArrayList的add方法源码分析:
java
// ArrayList.java
public boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
add(e, elementData, size);
return true;
}
private void add(E e, Object[] elementData, int s) {
if (s == elementData.length) // 容量检查
elementData = grow(); // 动态扩容
elementData[s] = e; // 直接放入数组
size = s + 1;
}LinkedList的节点结构:
java
// LinkedList的节点定义
private static class Node<E> {
E item; // 存储的元素
Node<E> next; // 指向下一个节点
Node<E> prev; // 指向上一个节点
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}2.2 Set接口的唯⼀性保证
HashSet的add方法源码:
java
// HashSet.java - 底层基于HashMap实现
public boolean add(E e) {
return map.put(e, PRESENT) == null; // PRESENT是虚拟值
}
// HashMap的putVal方法关键逻辑
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
// ...
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
// 关键:先比较hash,再比较equals
return p; // 已存在,返回旧值
// 不存在,插入新节点
if (++size > threshold)
resize(); // 扩容
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null; // 插入成功
}TreeSet的红黑树实现:
java
// TreeSet使用TreeMap实现
public TreeSet() {
this(new TreeMap<E,Object>()); // 基于红黑树
}
// 元素必须实现Comparable接口,或提供Comparator
public boolean add(E e) {
return m.put(e, PRESENT) == null;
}⚡ 三、性能对比实测
3.1 不同操作的性能测试
java
public class ListVsSetPerformanceTest {
private static final int SIZE = 100000;
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 测试数据准备
List<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
Set<Integer> hashSet = new HashSet<>();
Set<Integer> treeSet = new TreeSet<>();
// 1. 添加性能测试
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) {
arrayList.add(i);
}
System.out.println("ArrayList添加耗时: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + "ms");
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) {
hashSet.add(i); // HashSet的添加需要计算hash
}
System.out.println("HashSet添加耗时: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + "ms");
// 2. 查找性能测试
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
arrayList.contains(50000); // O(n)遍历
System.out.println("ArrayList查找耗时: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + "ms");
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
hashSet.contains(50000); // O(1)哈希查找
System.out.println("HashSet查找耗时: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + "ms");
// 3. 去重性能对比
List<Integer> listWithDuplicates = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4);
// 使用List去重(传统方式)
List<Integer> distinctList = new ArrayList<>();
for (Integer num : listWithDuplicates) {
if (!distinctList.contains(num)) { // 每次都要遍历!
distinctList.add(num);
}
}
// 使用Set去重(一行代码)
Set<Integer> distinctSet = new HashSet<>(listWithDuplicates);
}
}3.2 性能测试结果分析
| 操作类型 | ArrayList | LinkedList | HashSet | TreeSet |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 添加元素 | O(1) 摊销 | O(1) | O(1) 摊销 | O(log n) |
| 随机访问 | O(1) | O(n) | 不支持 | 不支持 |
| 包含检查 | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(log n) |
| 插入删除 | O(n) | O(1) | O(1) | O(log n) |
🎯 四、实战应用场景
4.1 List的典型使用场景
场景1:需要保持顺序的数据集合
java
// 电商订单列表 - 需要保持下单顺序
public class OrderService {
private List<Order> orderList = new ArrayList<>();
public void addOrder(Order order) {
orderList.add(order); // 按照时间顺序存储
}
public Order getLatestOrder() {
return orderList.get(orderList.size() - 1); // 获取最新订单
}
}场景2:需要索引操作的场景
java
// 分页查询实现
public class PaginationService {
public <T> List<T> getPage(List<T> data, int page, int size) {
int fromIndex = (page - 1) * size;
int toIndex = Math.min(fromIndex + size, data.size());
if (fromIndex >= data.size()) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
return data.subList(fromIndex, toIndex); // List特有的子列表操作
}
}4.2 Set的典型使用场景
场景1:快速去重
java
// 用户标签去重
public class TagService {
public Set<String> processTags(List<String> inputTags) {
return new HashSet<>(inputTags); // 自动去重!
}
// 统计独立访客
public int countUniqueUsers(List<User> users) {
Set<Long> userIds = users.stream()
.map(User::getId)
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
return userIds.size(); // 自动去重后的数量就是独立用户数
}
}场景2:关系判断和集合运算
java
// 社交网络好友关系
public class SocialNetworkService {
private Map<Long, Set<Long>> userFriends = new HashMap<>();
// 判断是否为好友
public boolean areFriends(long user1, long user2) {
return userFriends.getOrDefault(user1, Collections.emptySet())
.contains(user2);
}
// 获取共同好友
public Set<Long> getMutualFriends(long user1, long user2) {
Set<Long> friends1 = userFriends.getOrDefault(user1, Collections.emptySet());
Set<Long> friends2 = userFriends.getOrDefault(user2, Collections.emptySet());
Set<Long> mutualFriends = new HashSet<>(friends1);
mutualFriends.retainAll(friends2); // 集合交集运算
return mutualFriends;
}
}🔄 五、高级特性与注意事项
5.1 线程安全问题
java
// 不安全的做法
List<String> unsafeList = new ArrayList<>();
// 安全的做法
List<String> safeList = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>());
// 或者使用CopyOnWriteArrayList
List<String> concurrentList = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
// Set的线程安全版本
Set<String> safeSet = Collections.synchronizedSet(new HashSet<>());
Set<String> concurrentSet = new ConcurrentHashMap.newKeySet();5.2 equals和hashCode的重写要求
java
// 自定义对象在Set中使用的正确姿势
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private String email;
// 必须重写equals和hashCode
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
User user = (User) o;
return Objects.equals(id, user.id) &&
Objects.equals(email, user.email);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(id, email); // 使用业务唯一标识字段
}
}
// 测试
Set<User> userSet = new HashSet<>();
User user1 = new User(1L, "Alice", "alice@example.com");
User user2 = new User(1L, "Alice", "alice@example.com");
userSet.add(user1);
userSet.add(user2); // 不会重复添加,因为equals和hashCode相同
System.out.println(userSet.size()); // 输出:1💡 六、面试常见问题
Q1: ArrayList和LinkedList如何选择?
A: 根据操作类型选择:
- 查询多、增删少 → 选择
ArrayList(随机访问O(1)) - 增删多、查询少 → 选择
LinkedList(插入删除O(1)) - 需要线程安全 → 考虑
CopyOnWriteArrayList
Q2: HashSet如何保证元素唯一性?
A: 通过两个步骤:
-
首先 比较对象的
hashCode()值 -
如果hashCode相同 ,再比较
equals()方法 -
两者都相同则认为重复,不插入
Q3: TreeSet的排序规则?
A: 两种方式:
- 自然排序 :元素实现
Comparable接口 - 定制排序 :创建TreeSet时传入
Comparator
📚 七、总结与最佳实践
选择决策流程图:
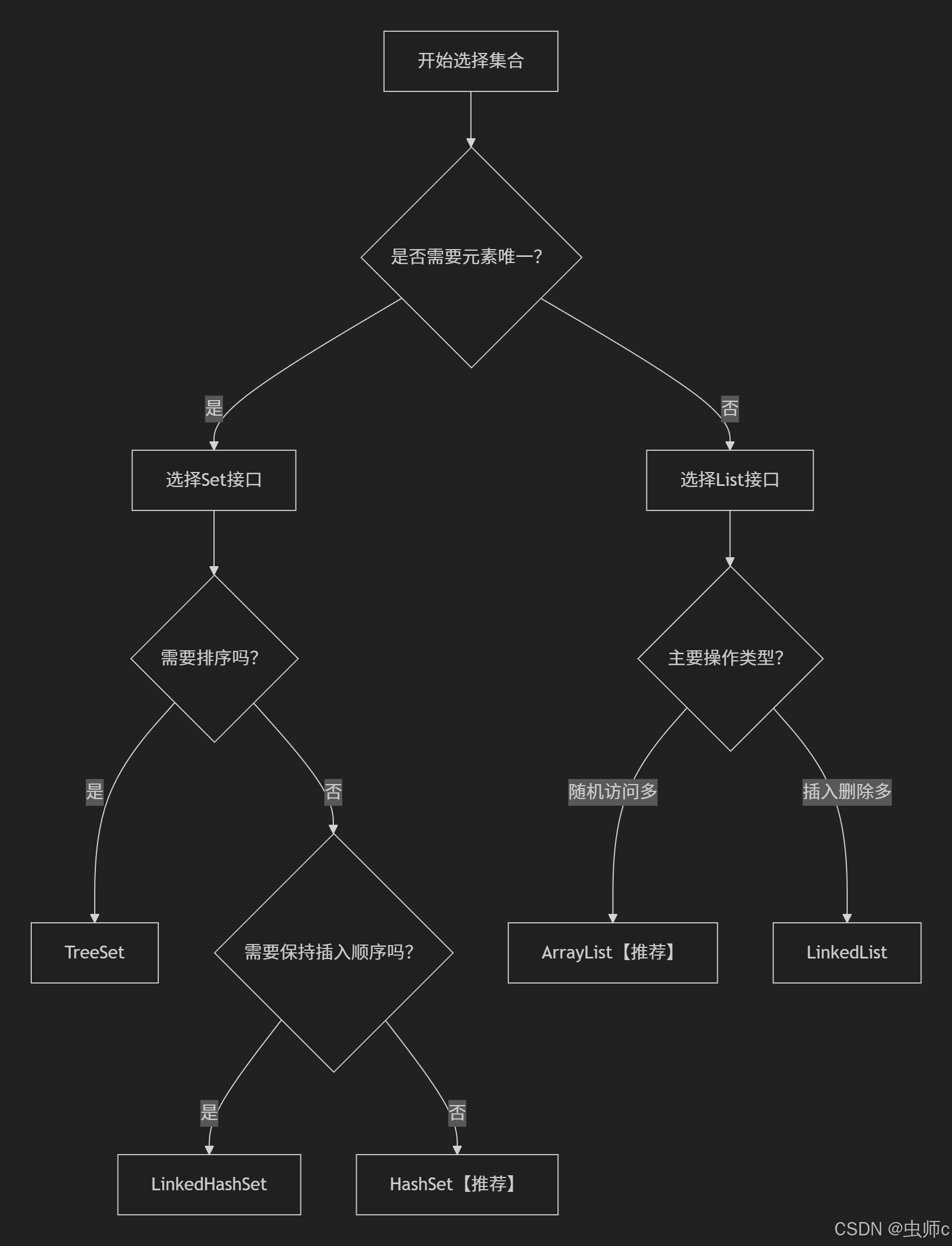
核心记忆要点:
- List:有序可重复,支持索引
- Set:唯一不重复,快速查找
- ArrayList:数组实现,查询快
- HashSet:哈希实现,去重快
- 根据业务需求选择最合适的实现
🎯 下期预告
《Map深度解析:HashMap、TreeMap、ConcurrentHashMap全对比》
- HashMap的扩容机制与线程安全问题
- TreeMap的红黑树实现原理
- ConcurrentHashMap的并发优化策略
📌 版权声明:本文为CSDN博主原创,转载请注明出处。欢迎点赞、收藏、关注!
💬 互动话题:你在项目中遇到过哪些因为错误选择集合类型导致的性能问题?欢迎在评论区分享你的经验!