1.优先级队列
队列的元素指定"优先级"


2.堆(实现优先级队列)
JDK1.8中的PriorityQueue底层使用了堆这种数据结构,而堆实际就是在完全二叉树的基础上进行了一些调整。

2.1 概念
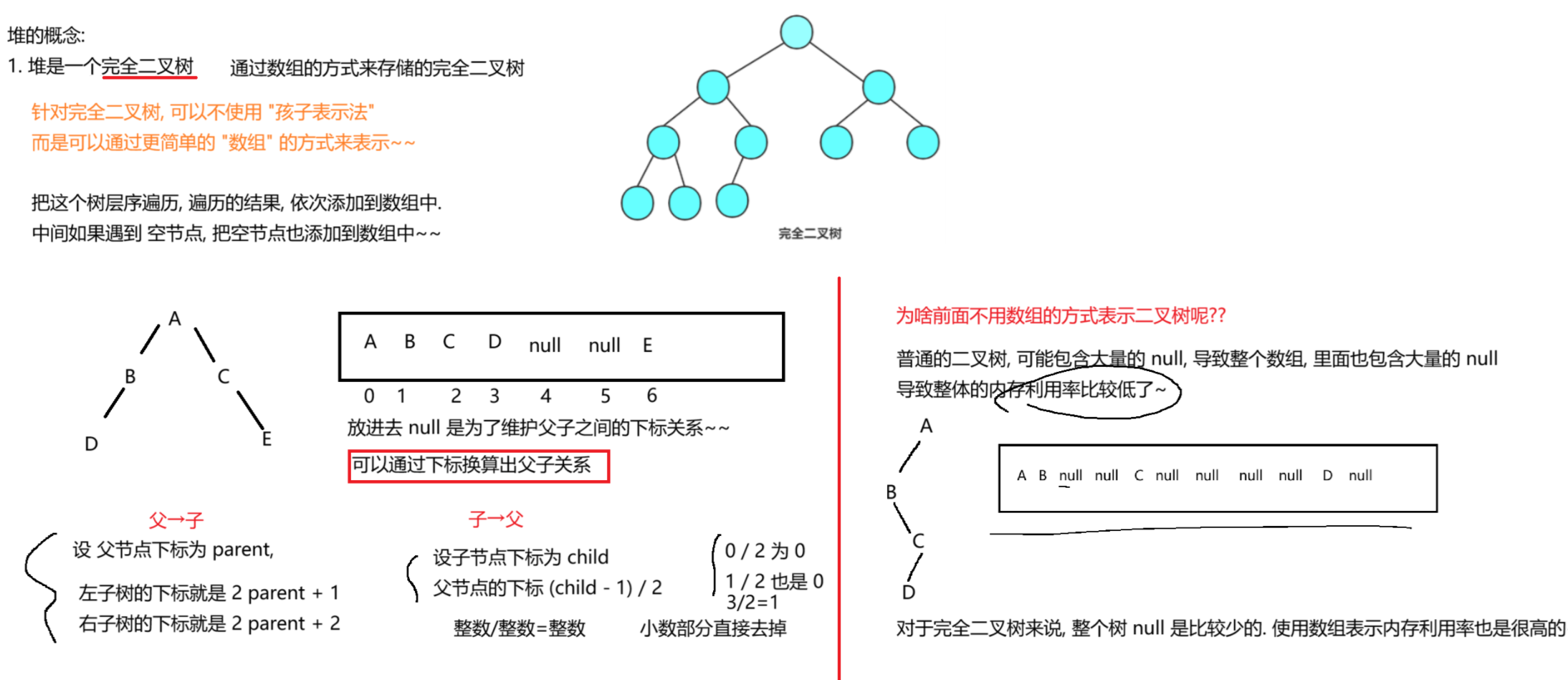
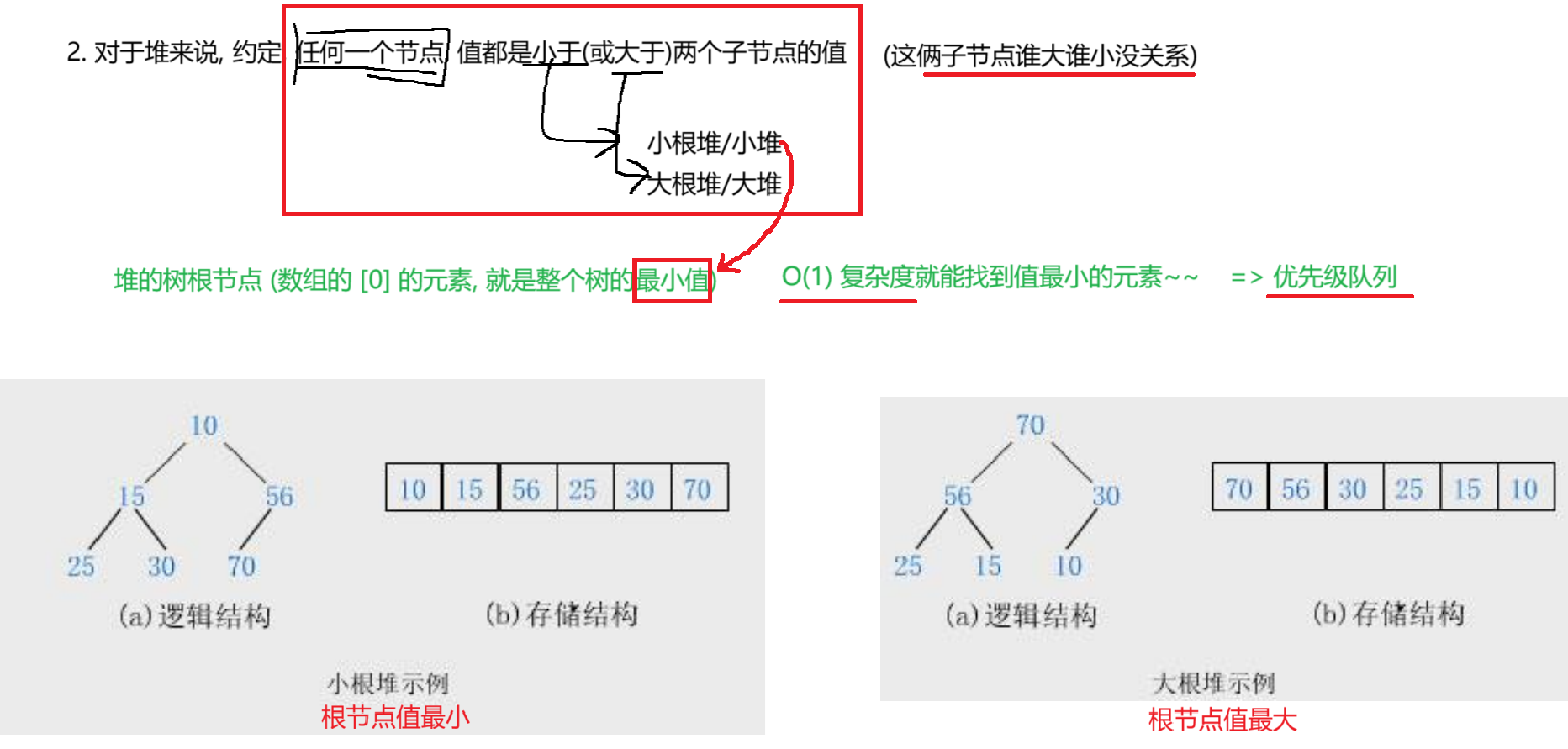

2.2 存储方式
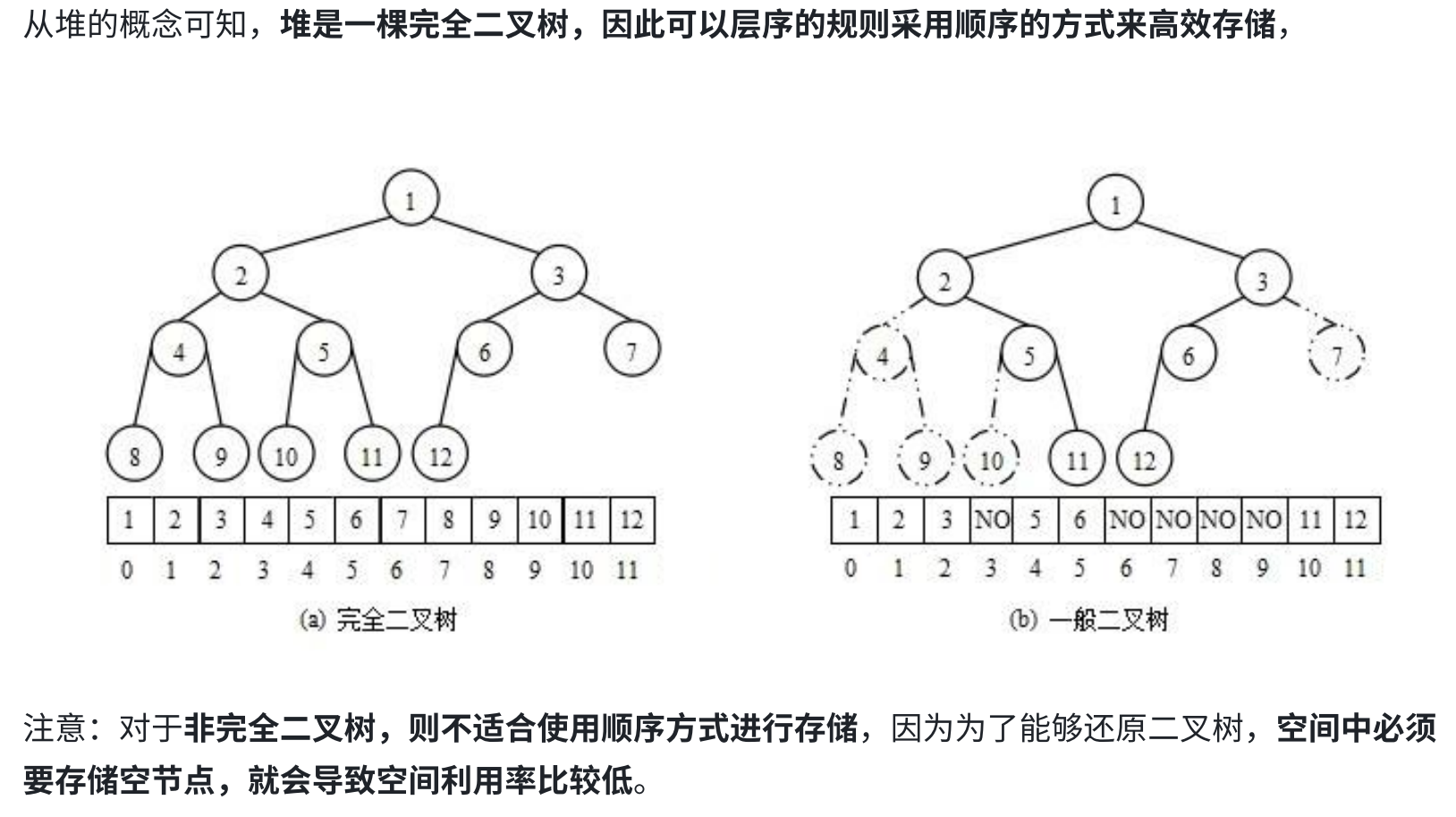
2.3 堆的向下调整、创建
(1)向下调整
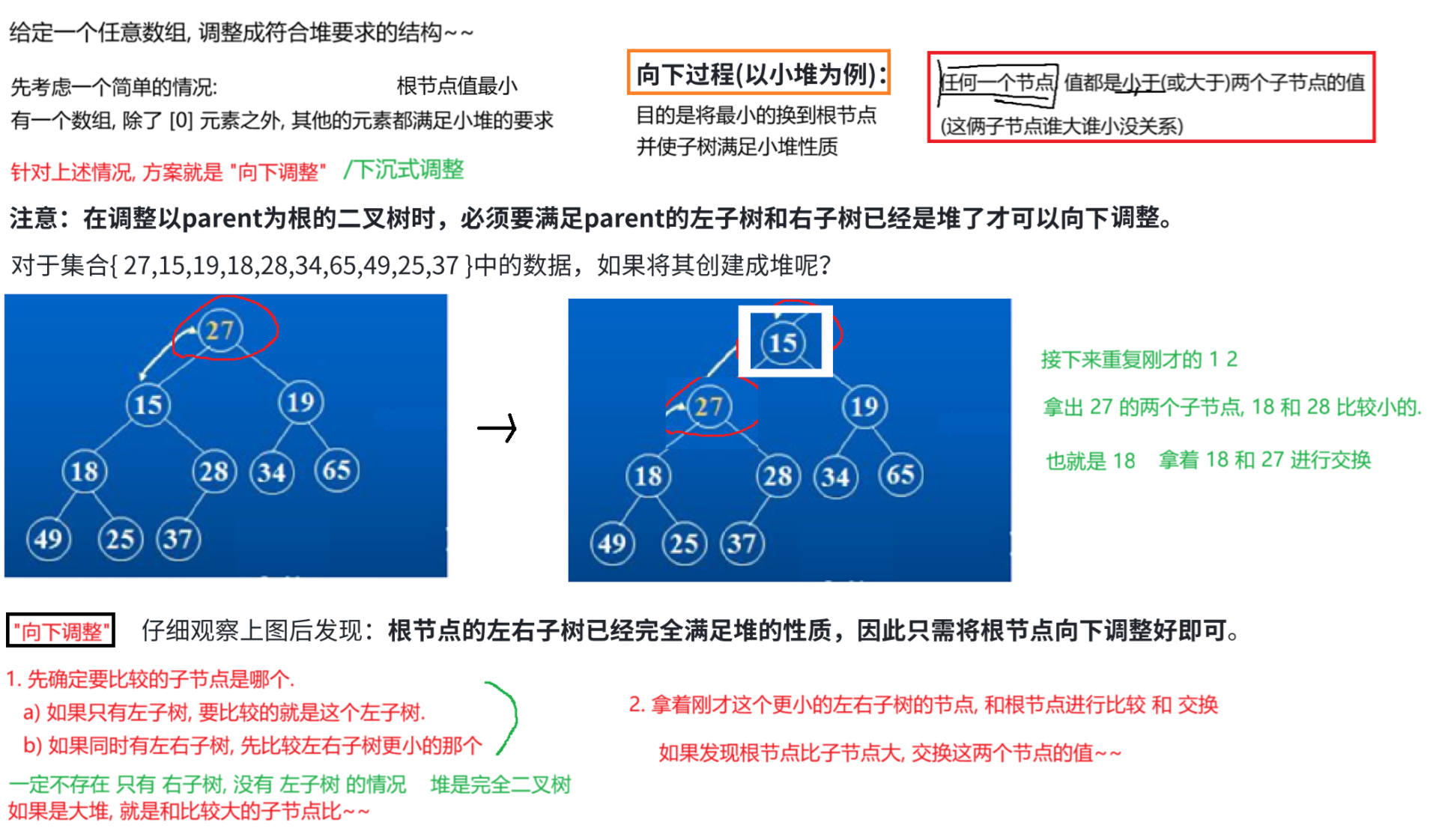
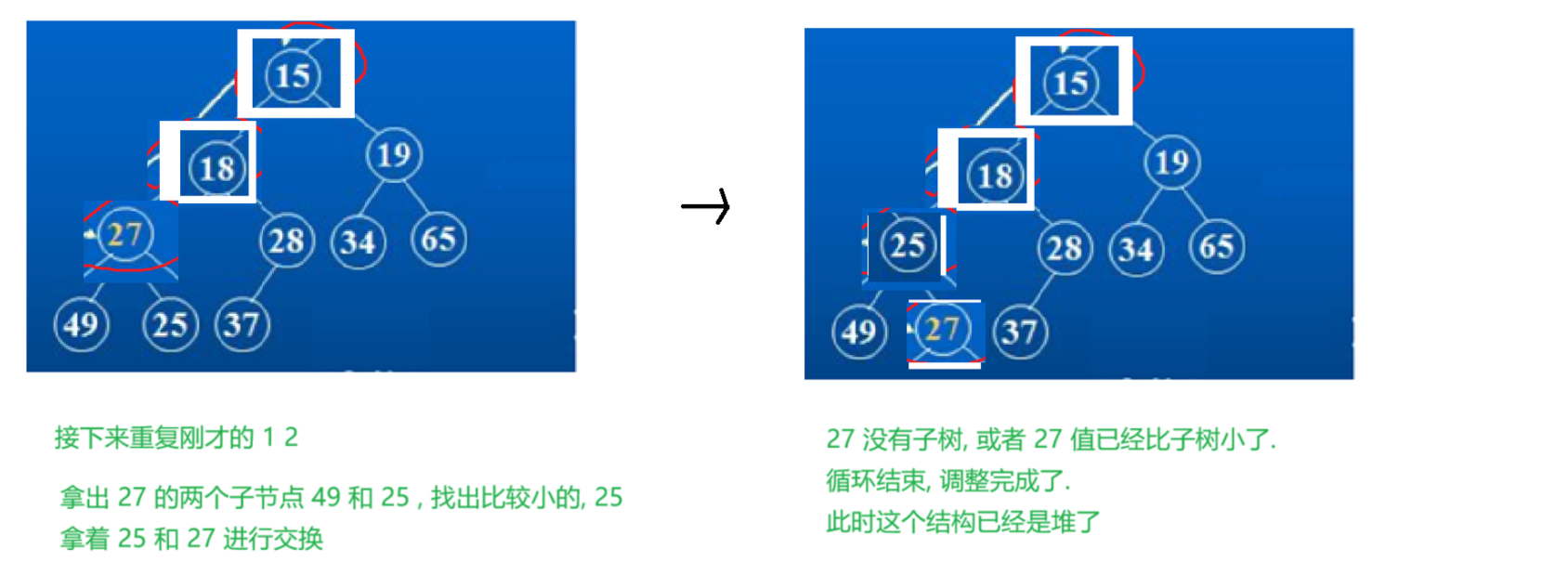
代码实现
java
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Heap {
/**
* 向下调整, 按照小堆的规则.
* @param array 要调整的堆
* @param size 堆的大小
* @param index 从哪个位置开始向下调整.
*/
public static void shiftDown(int[] array, int size, int index) {
// 要调整的父节点
int parent = index;
// 计算要调整的左孩子节点
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
// 如果子节点下标超出数组范围, 说明子节点就是不存在的!!
// 主循环就结束, 调整就完成了.
while (child < size) {
if (child + 1 < size && array[child + 1] < array[child]) {
child = child + 1;
}
// 通过上述判定, 就是要找出左右子树中, 更小的值, 用 child 下标指向更小值
// 然后比较 child 和 parent 的大小关系
if (array[parent] <= array[child]) {
// 当前的调整就结束了. 父亲已经比孩子小了, 已经符合小堆的规则了. 就不需要继续调整了.
break;
} else {
// 交换父子的值
int tmp = array[parent];
array[parent] = array[child];
array[child] = tmp;
// 更新 parent 和 child 的指向
parent = child;
child = 2 * parent + 1;
}
}
}
}下面是大堆示例
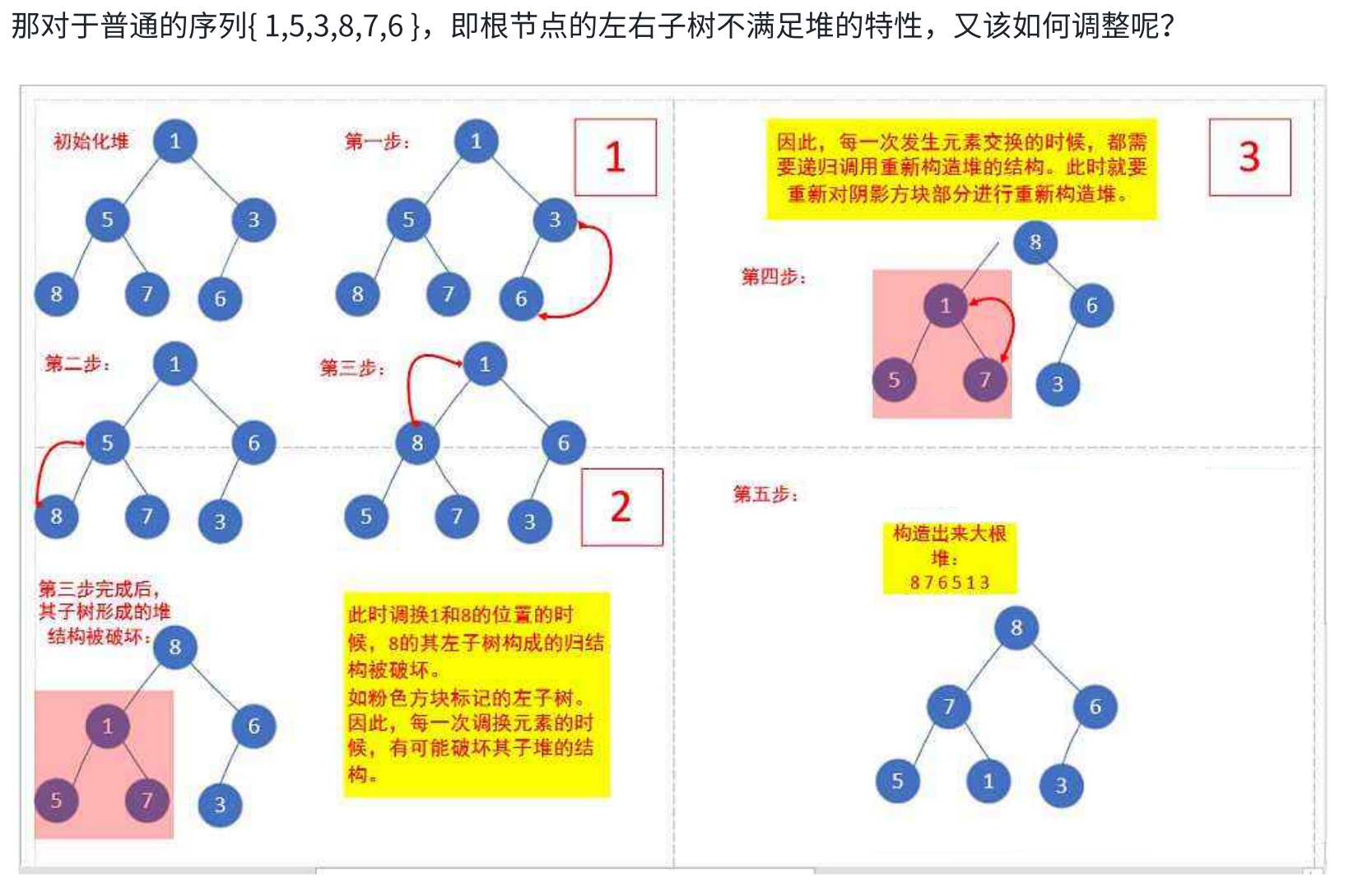
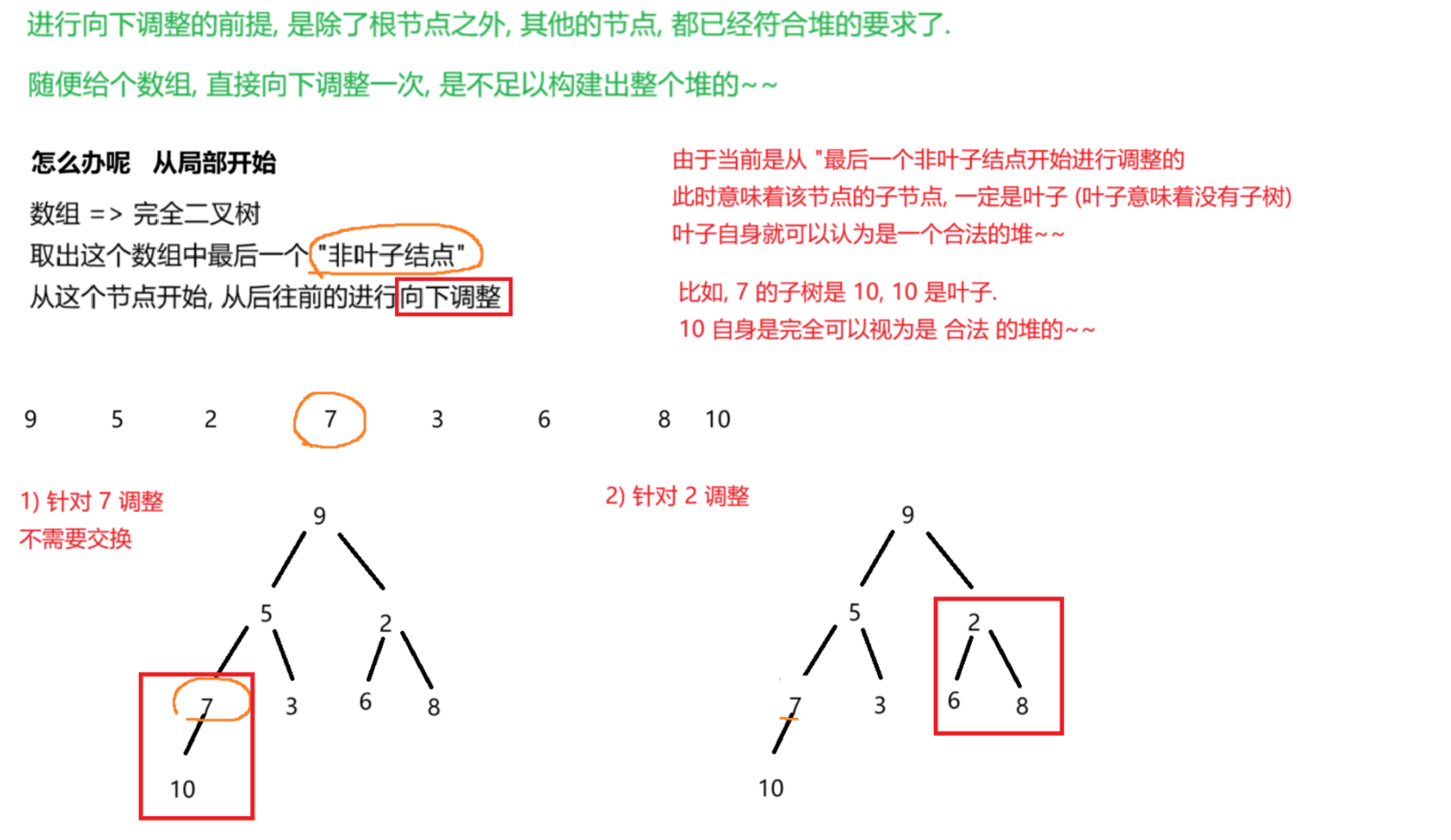
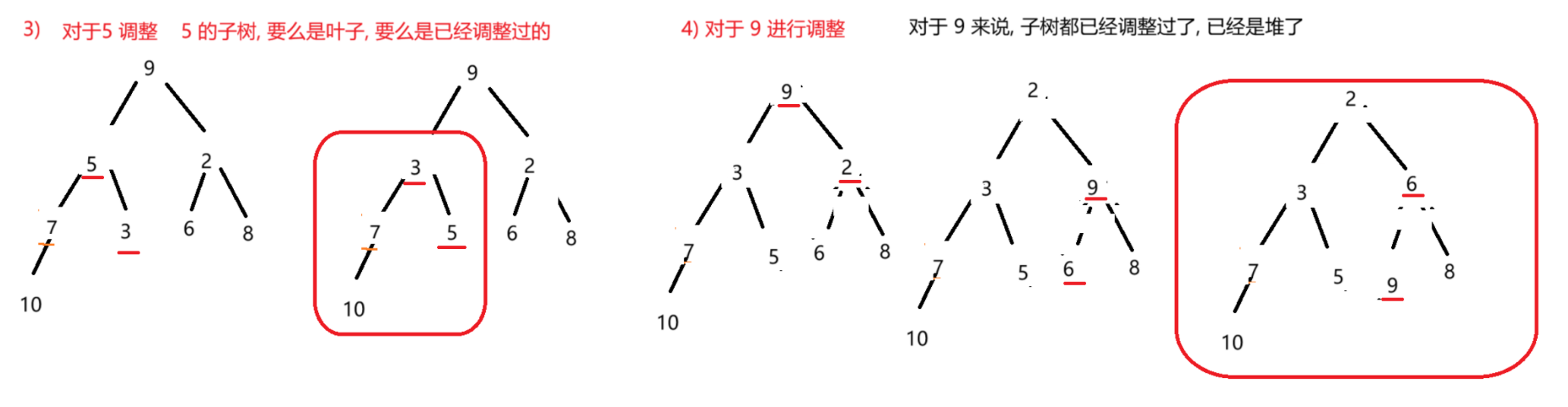
(2)创建
根据上述向下调整 内容进行建堆操作
代码实现
java
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Heap {
/**
* 向下调整, 按照小堆的规则.
* @param array 要调整的堆
* @param size 堆的大小
* @param index 从哪个位置开始向下调整.
*/
public static void shiftDown(int[] array, int size, int index) {
// 要调整的父节点
int parent = index;
// 计算要调整的左孩子节点
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
// 如果子节点下标超出数组范围, 说明子节点就是不存在的!!
// 主循环就结束, 调整就完成了.
while (child < size) {
if (child + 1 < size && array[child + 1] < array[child]) {
child = child + 1;
}
// 通过上述判定, 就是要找出左右子树中, 更小的值, 用 child 下标指向更小值
// 然后比较 child 和 parent 的大小关系
if (array[parent] <= array[child]) {
// 当前的调整就结束了. 父亲已经比孩子小了, 已经符合小堆的规则了. 就不需要继续调整了.
break;
} else {
// 交换父子的值
int tmp = array[parent];
array[parent] = array[child];
array[child] = tmp;
// 更新 parent 和 child 的指向
parent = child;
child = 2 * parent + 1;
}
}
}
/**
* 建堆操作
* @param array
*/
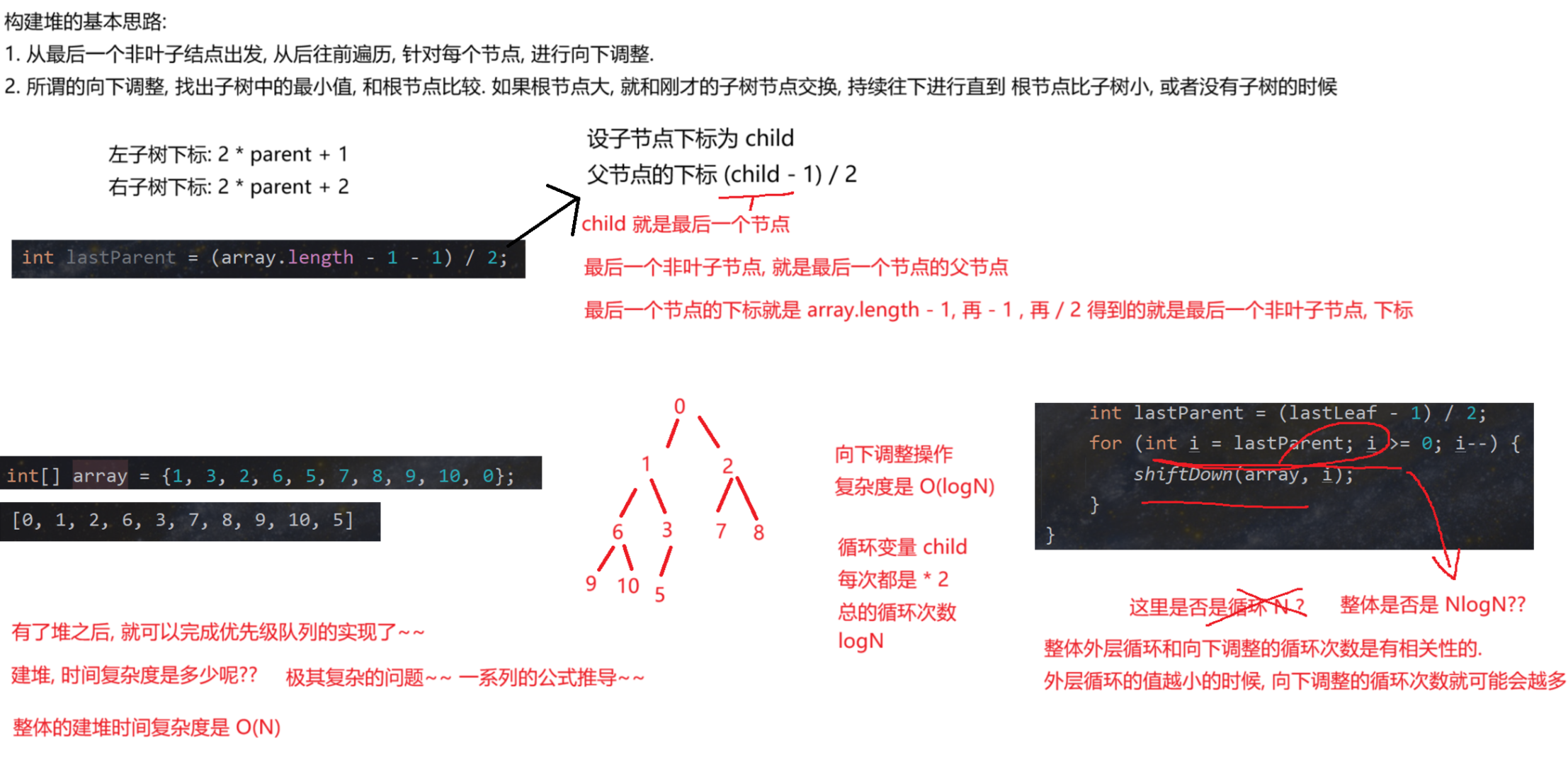
public static void createHeap(int[] array) {
// 1. 找到最后一个非叶子节点
// 2. 从后往前循环的进行向下调整.
int lastLeaf = array.length - 1;
// 这里不要写作 array.length - 2 这样的代码, 非常难读!!!
int lastParent = (lastLeaf - 1) / 2;
for (int i = lastParent; i >= 0; i--) {
shiftDown(array, array.length, i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {1, 3, 2, 6, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 0};
createHeap(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
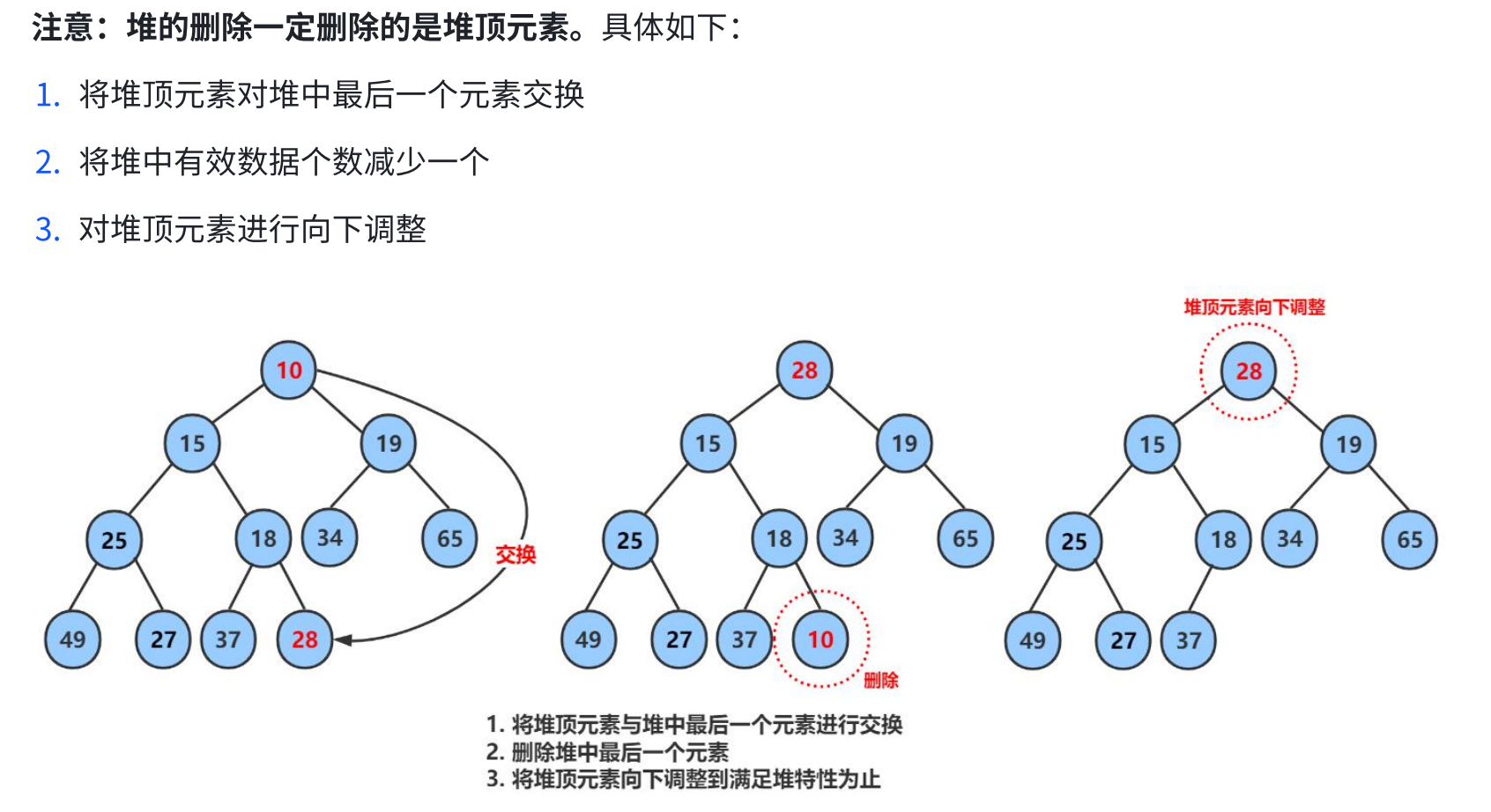
}2.4 堆的插入(向上调整)、删除、模拟实现优先级队列

向上调整代码实现
java
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Heap {
/**
* 向上调整堆. 整个数组, 只有最后一个元素不满足堆的要求, 其他部分都满足.
* 在这个前提下, 堆最后一个元素进行向上调整.
* 以小堆为例
* @param array
* @param index
*/
public static void shiftUp(int[] array, int index) {
int child = index;
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
// child 为 0, 说明已经调整到根节点了, 循环就结束了.
while (child > 0) {
if (array[parent] > array[child]) {
// 此时就应该要进行交换.
int tmp = array[parent];
array[parent] = array[child];
array[child] = tmp;
// 更新 child 和 parent 的指向
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
} else {
// 此时已经符合堆的要求了
break;
}
}
}
}优先级队列代码实现
java
public class MyPriorityQueue {
private int[] array;
private int size = 0;
public MyPriorityQueue() {
array = new int[1000];
}
public void offer(int value) {
// 先把新元素尾插, 然后向上调整.
if (size == array.length) {
// 此处还可以实现扩容.
return;
}
array[size] = value;
size++;
// 从最后这个元素开始向上进行调整.
Heap.shiftUp(array, size - 1);
}
public Integer poll() {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
// 先把第一个元素和最后一个元素交换.
int ret = array[0];
array[0] = array[size - 1];
array[size - 1] = ret;
// 这一步写不写不所谓, 因为马上要 size--, 相当于把这个元素给删了.
size--;
// 从 [0] 位置开始向下进行调整.
Heap.shiftDown(array, size, 0);
return ret;
}
public Integer peek() {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
return array[0];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyPriorityQueue queue = new MyPriorityQueue();
queue.offer(3);
queue.offer(4);
queue.offer(2);
queue.offer(1);
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue.poll());
}
}

2.5 常见习题
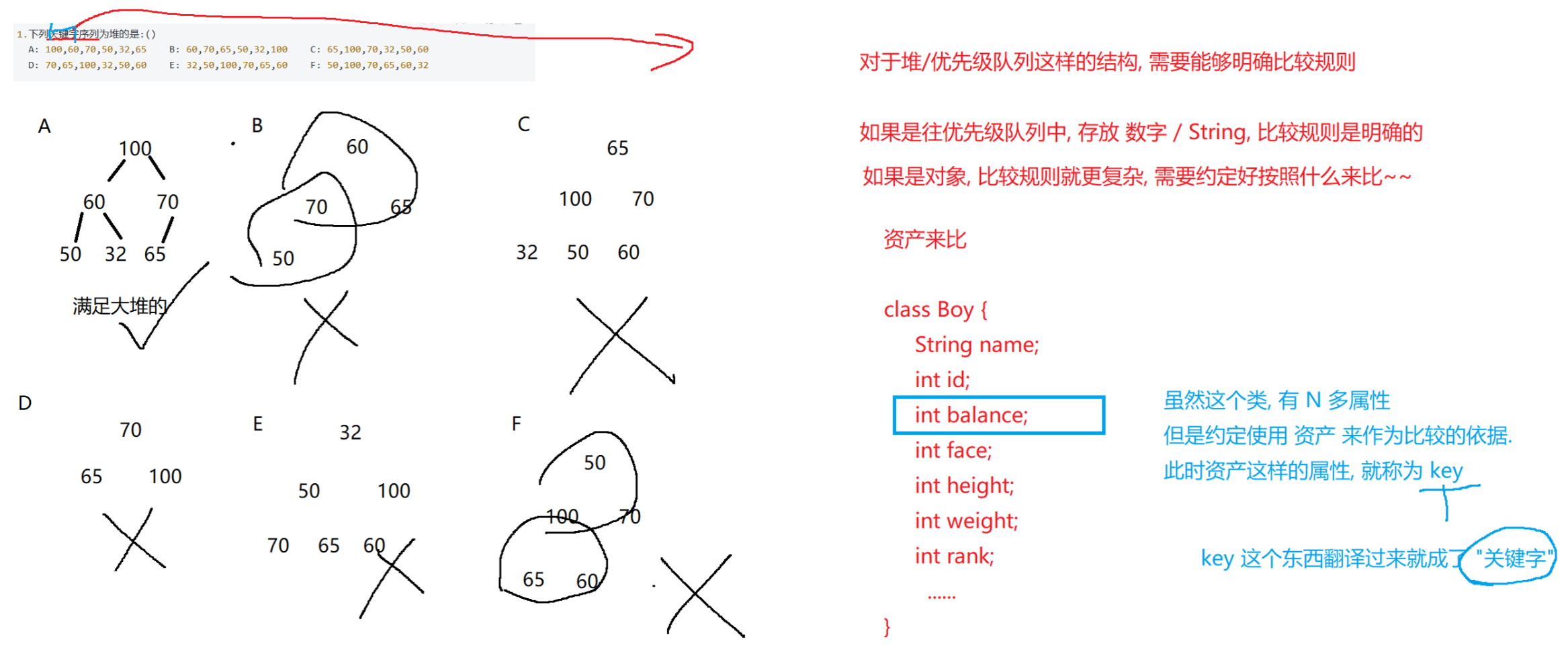
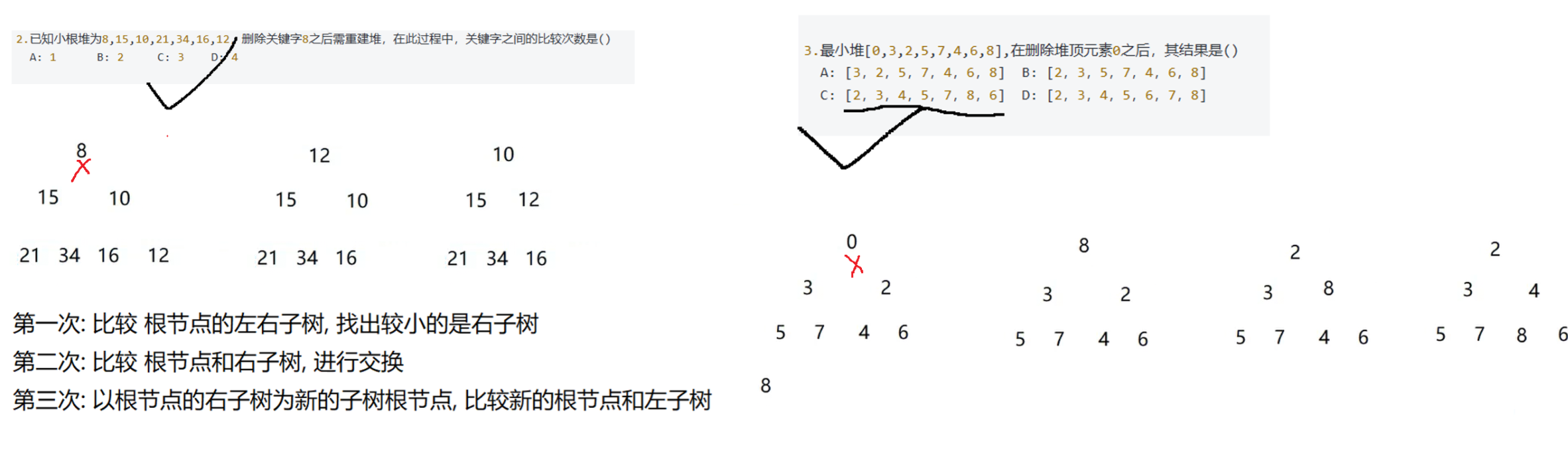
3.常用接口
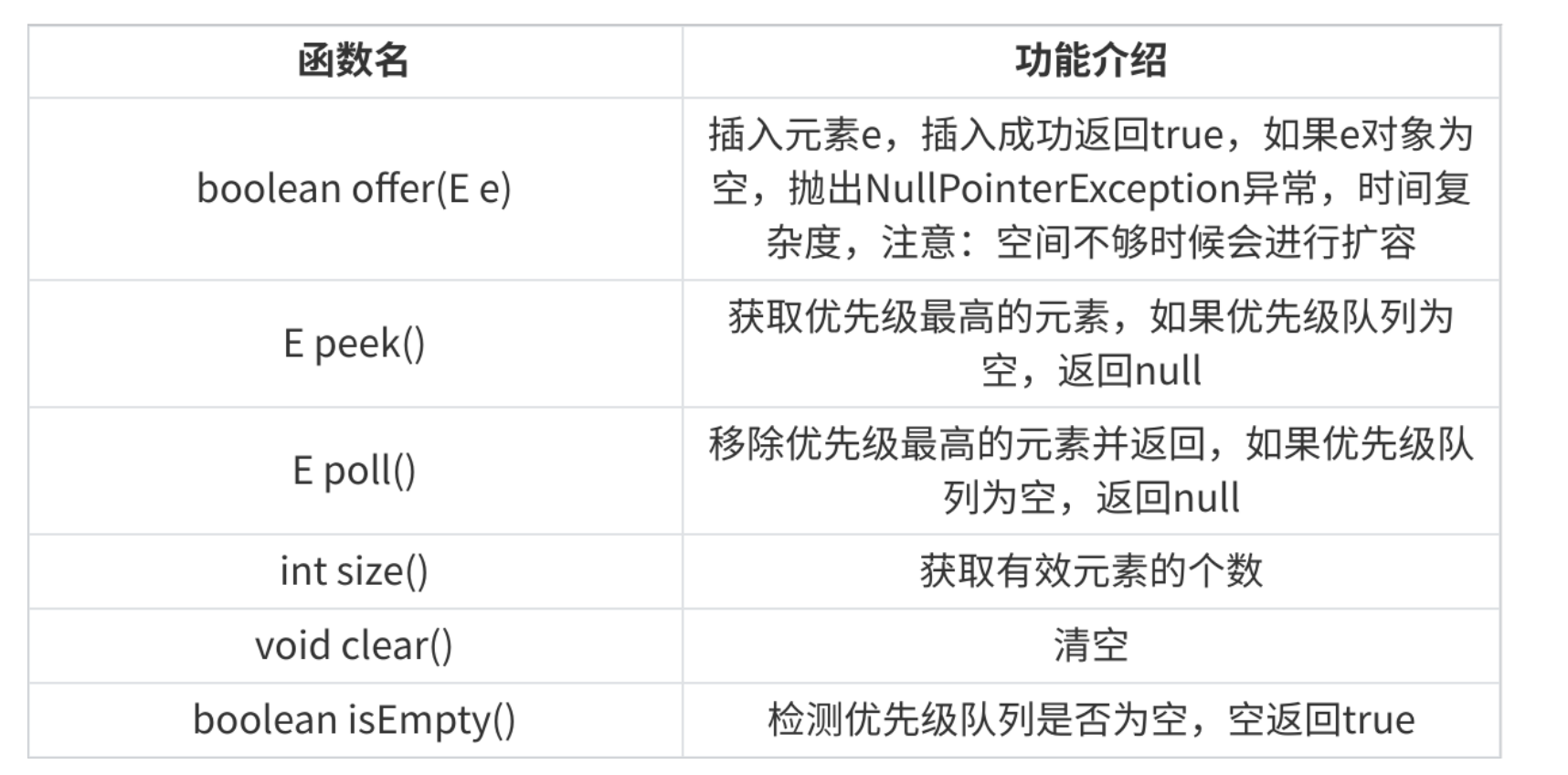
3.1 PriorityQueue特性、函数
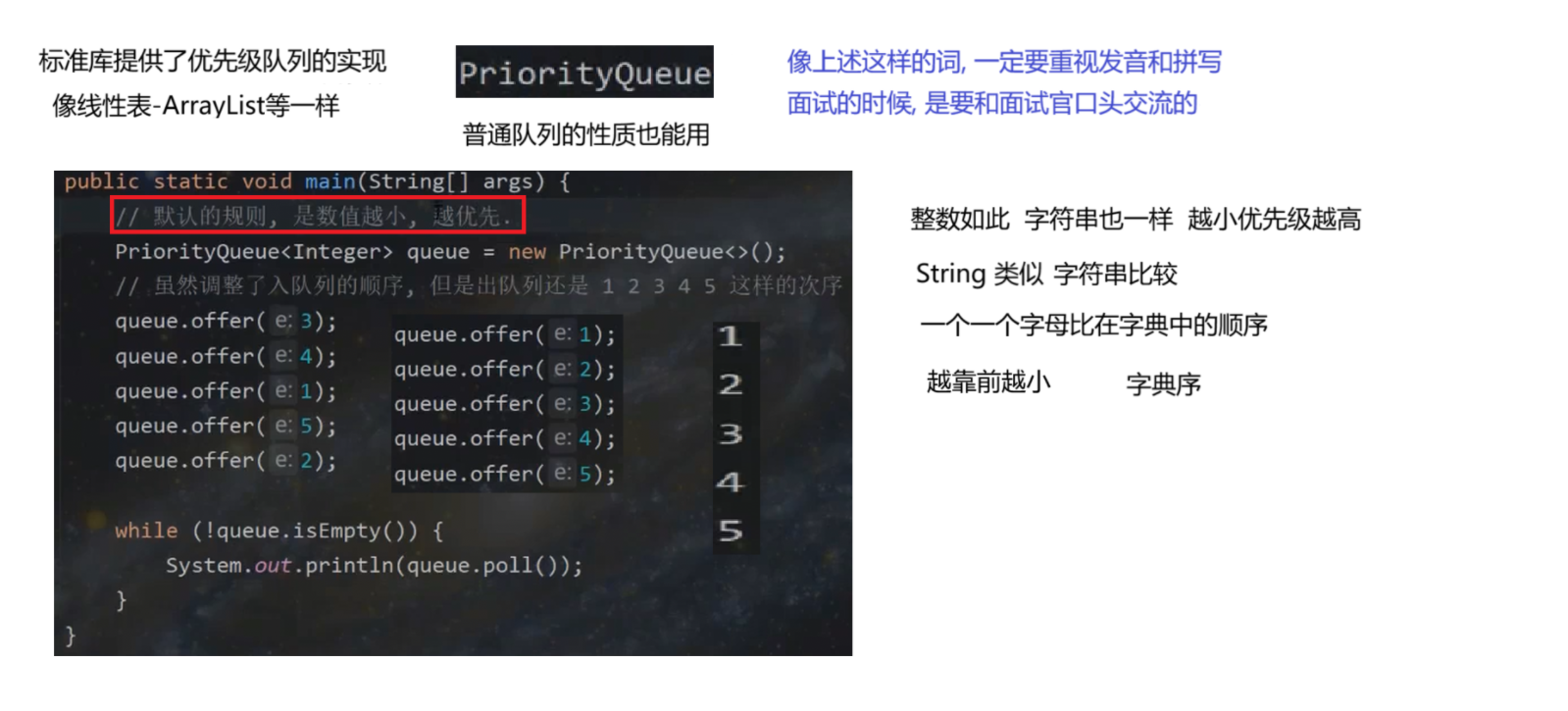
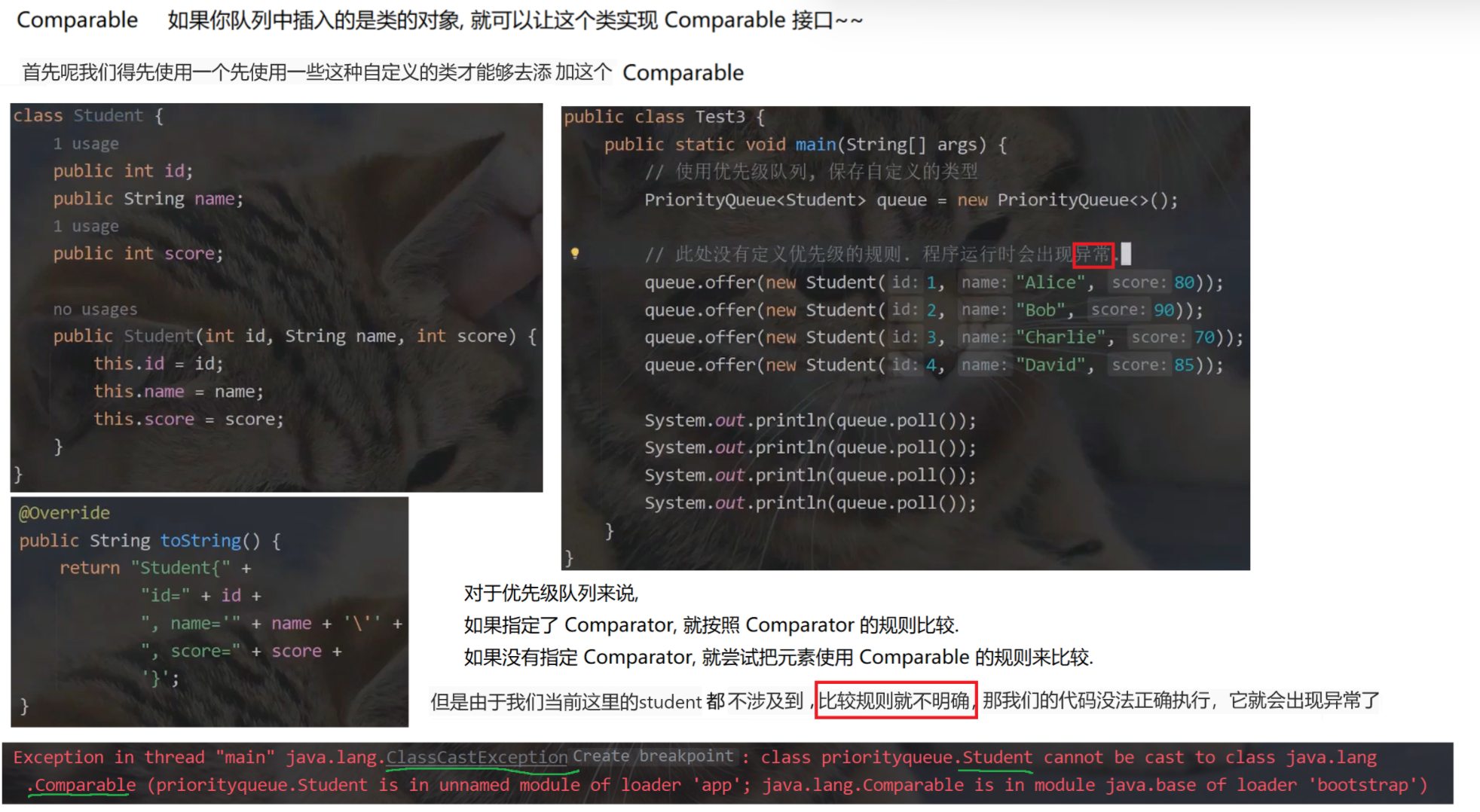
标准库提供了优先级队列的实现 PriorityQueue

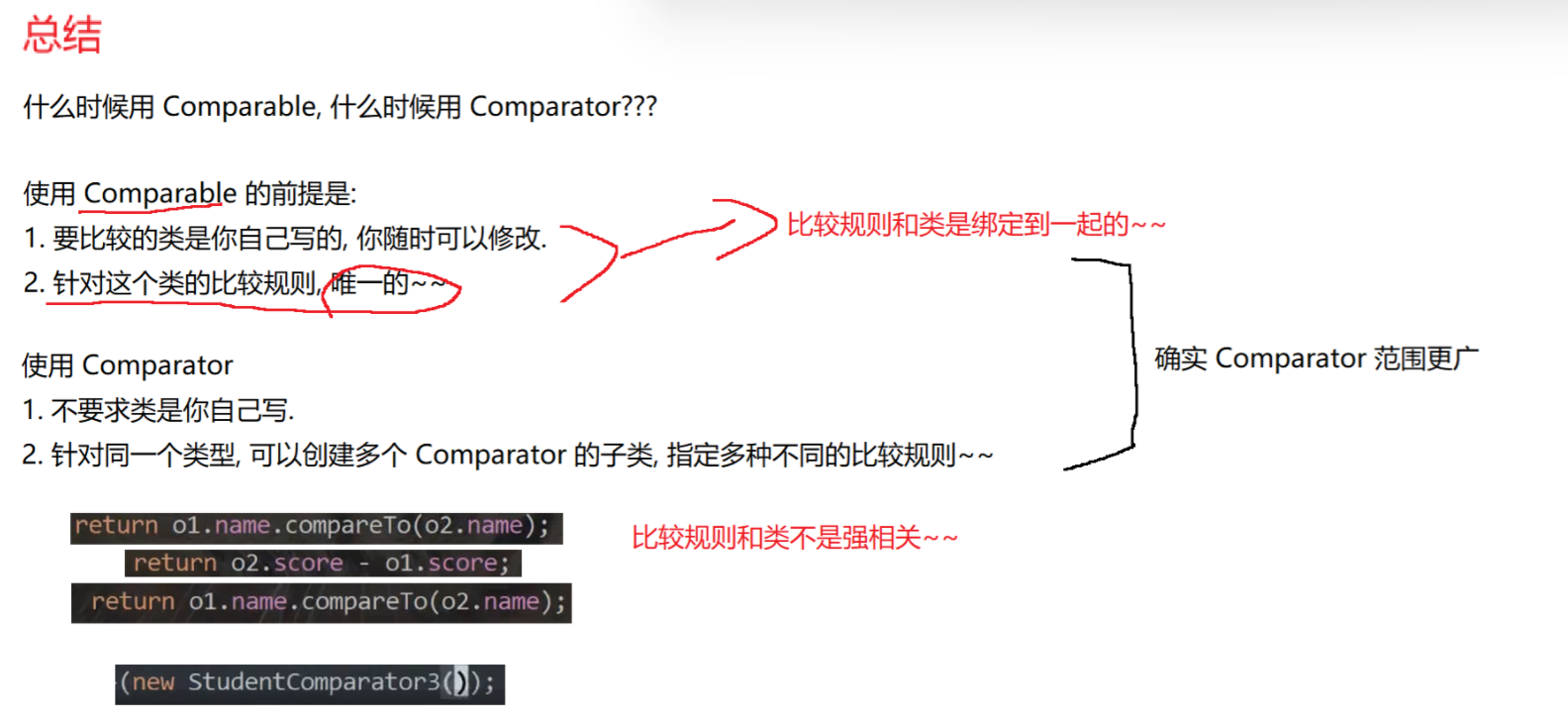
3.2 优先级队列的构造、比较器
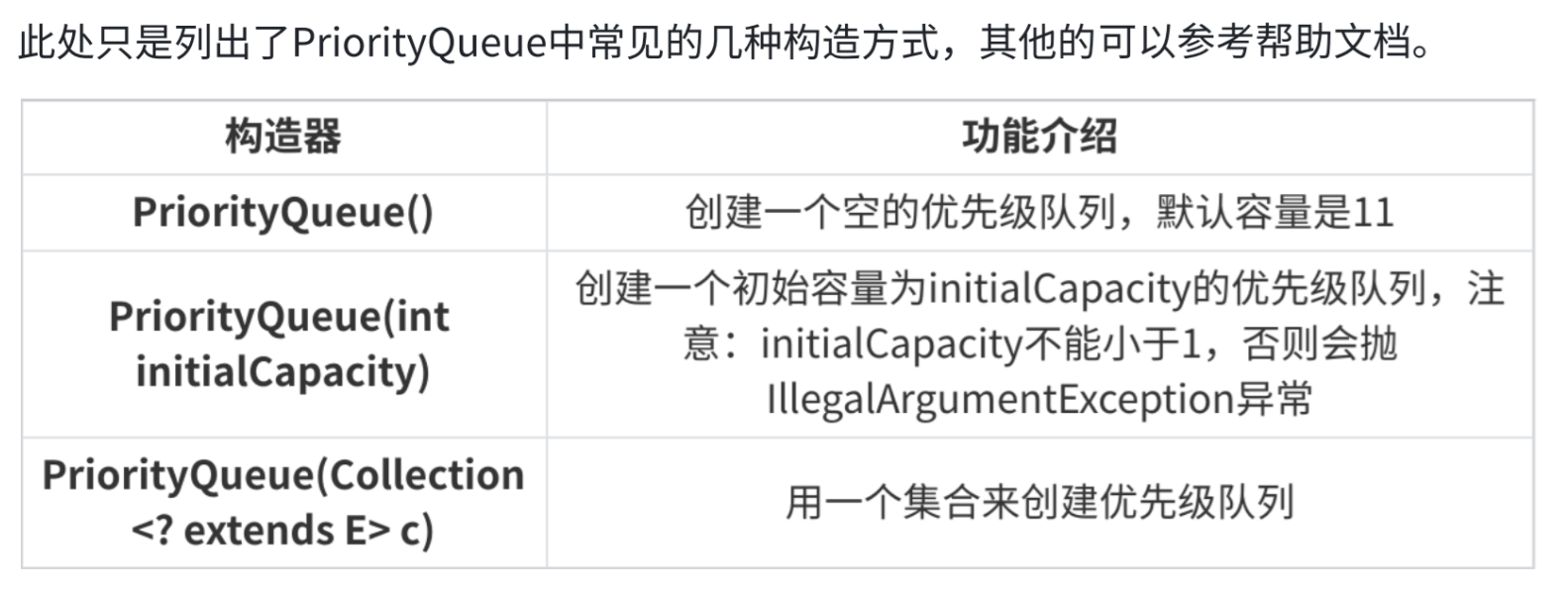
比较器


java
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
class IntComparator implements Comparator<Integer>{
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2 - o1;
}
}
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 需要创建上述的比较器实例, 通过构造方法传给优先级队列.
PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(new IntComparator());
queue.add(5);
queue.add(3);
queue.add(1);
queue.add(4);
queue.add(2);
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue.poll());
}
}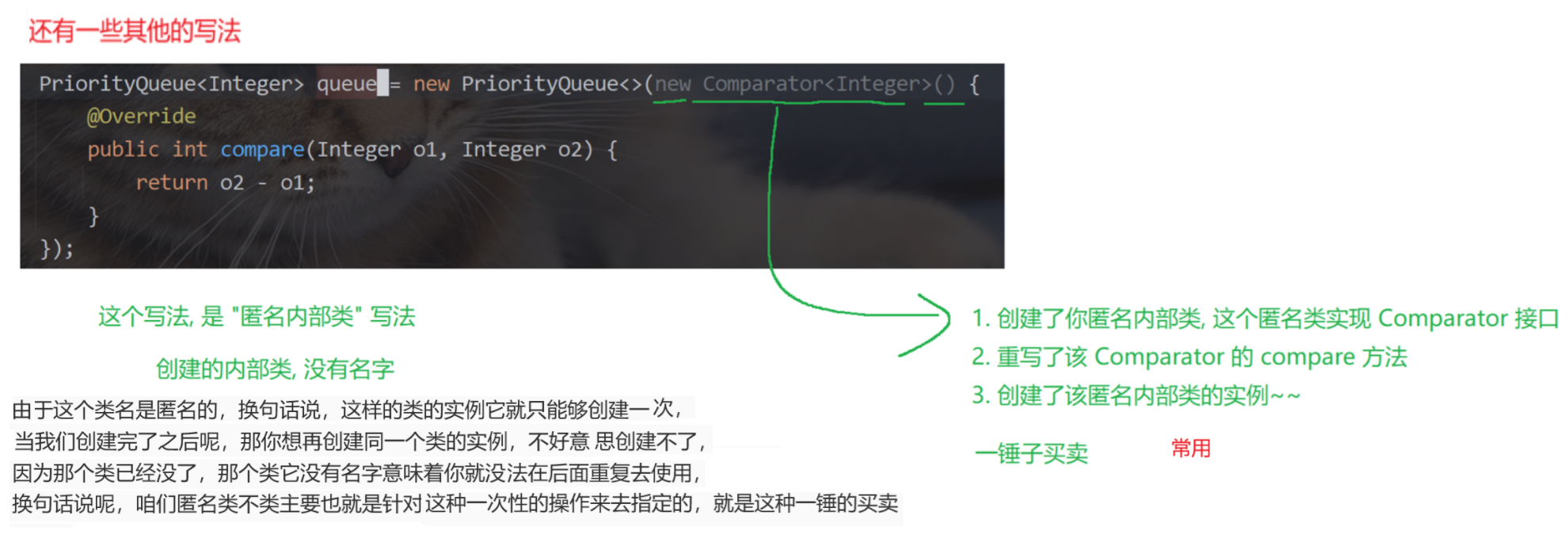

3.3 面试题
top-k问题:最大或者最小的前k个数据。 比如:世界前500强公司
https://leetcode.cn/problems/smallest-k-lcci/

java
class Solution {
public int[] smallestK(int[] arr, int k) {
// 参数检测
if(arr == null || k > arr.length) return null;
//创建优先级队列
PriorityQueue<Integer> quene = new PriorityQueue<>();
// 将数组中的元素依次放到堆中
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { quene.offer(arr[i]); }
// 将优先级队列的前k个元素放到数组中
int[] result = new int[k];
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++) { result[i] = quene.poll(); }
return result;
}
}该解法只是PriorityQueue的简单使用,并不是topK最好的做法,那topk该如何实现?

java
// 更优的做法, 消耗的空间更少
public int[] smallestK(int[] arr, int k) {
if (arr == null || k > arr.length) { return null; }
if (k == 0) { return new int[0]; }
// 创建一个大堆的优先级队列.
PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2 - o1;
}
});
// 把前 k 个元素添加到队列中.
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) { queue.offer(arr[i]); }
// 继续遍历剩余元素, 这个过程就需要进行比较了.
for (int i = k; i < arr.length; i++) {
int top = queue.peek();
if (arr[i] < top) {
// 新欢比旧爱更小. 弹出旧爱, 加入新欢
queue.poll();
queue.offer(arr[i]);
}
}
// 创建一个数组, 保存最终结果
int[] result = new int[k];
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) { result[i] = queue.poll(); }
return result;
}4.堆的应用
PriorityQueue的实现:用堆作为底层结构封装优先级队列
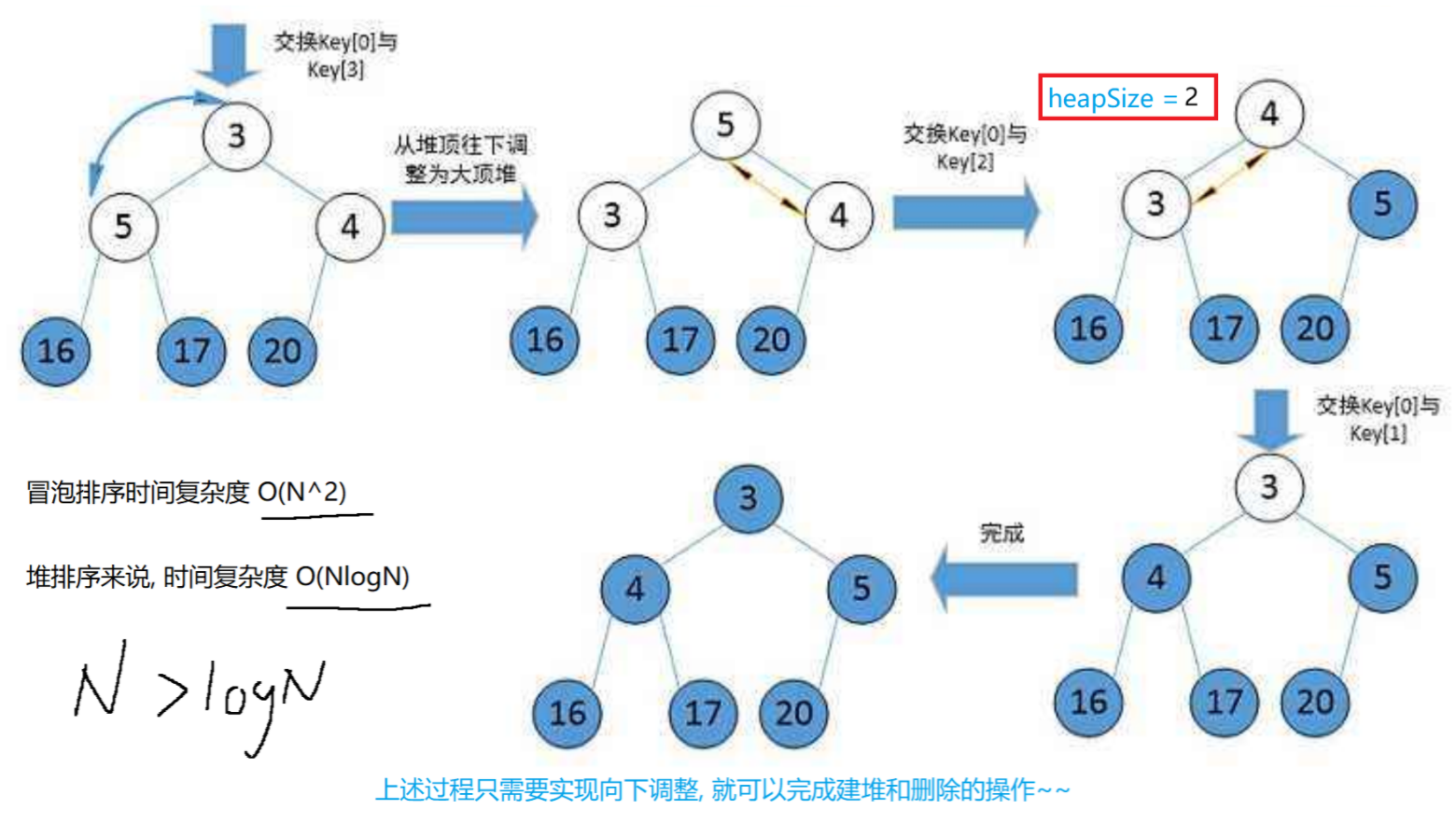
4.1 堆排序
堆排序即利用堆的思想来进行排序,总共分为两个步骤:
**1. 建堆:**升序--建大堆;降序--建小堆
2. 利用堆删除思想来进行排序 :建堆和堆删除中都用到了向下调整,因此掌握了向下调整,就可以完成堆排序。

4.2 Top-k问题


