硬件:
- ESP32,再用一个IO扩展板,板子的弹簧端子用起来不方便。
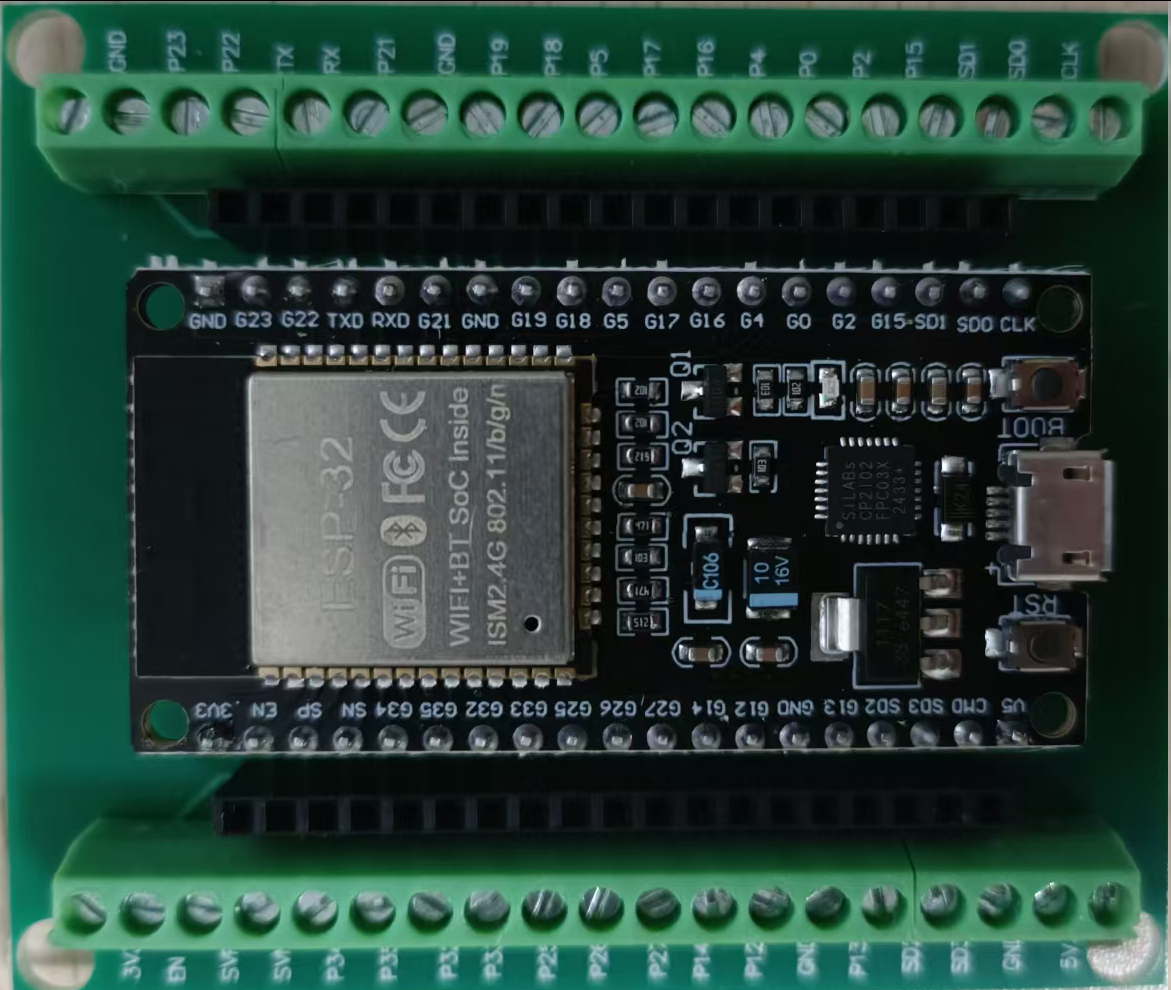

内侧两列针脚距离是26mm,开发板针脚丝印标记在前面的宽度都差不多。
-二氧化碳传感器MH-Z19E,是NDIR(非分散红外技术),需要预热2-3分钟后出正确数据,测量范围是400~5000。通电正常,会闪烁光芒。
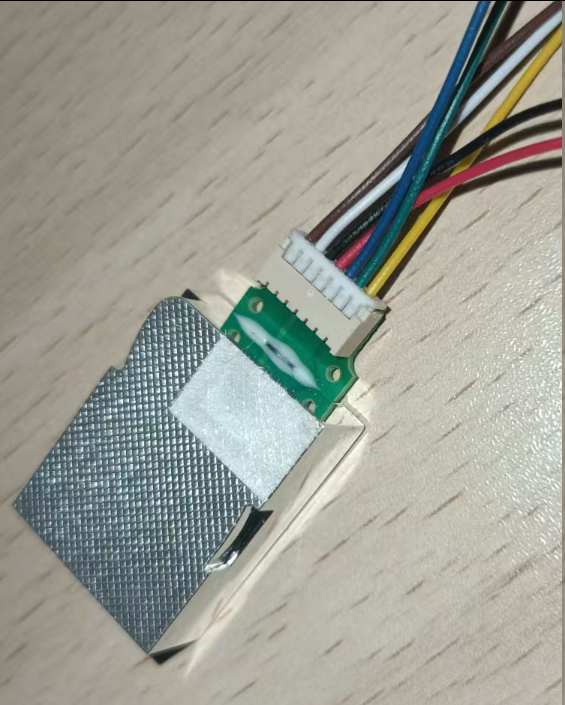

接4根线,两根是电源,用板子的5V.
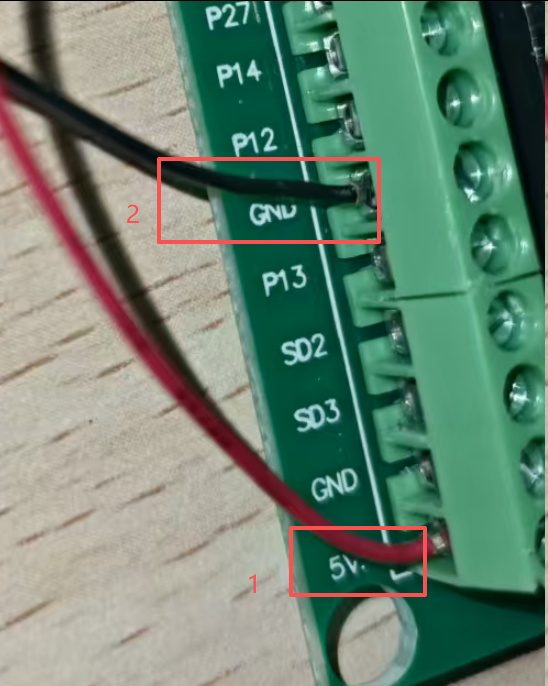
5V顶头的是CND,不能用。
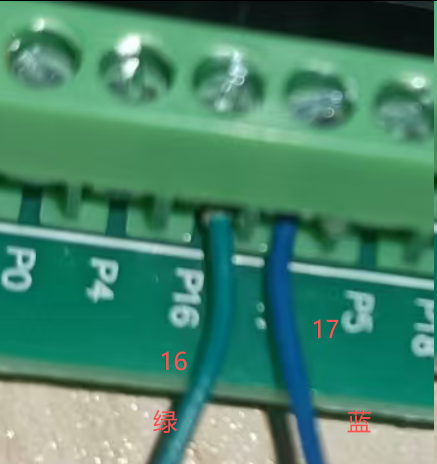
选择UART2,不能选择UART0(被USB调试占用)
- 电源,可以用5V充电器,也可以电脑USB供电。
软件
系统是micropython,用异步任务比较方便。Web框架还是microdot,用它自带的websocket类。
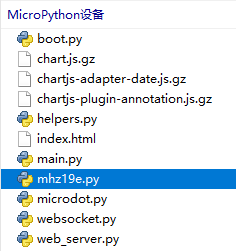
microdot的src目录找到microdot.py, websocket.py,helper.py上传。
chartjs的文件从web链接保存下来的。问智谱(GLM-4.6),让它写个chartjs的例子,代码会给出链接,或者到官方网站去。
按照惯例,使用7zip进行压缩,要选择"添加到压缩包...",注意后缀是.gz 。
使用F12查看控制台错误和websocket的响应。
代码
代码是描述给ai,让它给咱打工,咱只是负责检查、反馈。
wifi为简单起见,直接连自家路由,ip是在openwrt的DHCP里面直接看的。
- 主函数
python
from web_server import WebServerMicrodot
from mhz19e import MHZ19E
import uasyncio
import network
# main
async def main():
wlan = network.WLAN(network.STA_IF)
wlan.active(True)
if not wlan.isconnected():
print('connecting to network...')
try:
wlan.connect('fengy09', '01234567')
except:
ap = network.WLAN(network.WLAN.IF_AP)
ap.config(ssid='ESP-AP')
ap.config(max_clients=10)
ap.active(True)
else:
print('ip:', wlan.ifconfig()[0] )
co2_sensor=MHZ19E()
# 初始化 Web 服务器,并将传感器实例传入
web_server = WebServerMicrodot(co2=co2_sensor)
#启动服务器 (这个函数内部会启动生产者任务)
await web_server.start_server()
if __name__ == "__main__":
uasyncio.run(main())只有一个web task。
- 后端
读串口的函数也写在web类里。要求第1次websocket连接时,发送历史数据给web,然后就只发1个当前数据。
web_server.py
python
from microdot import Microdot, send_file
from websocket import with_websocket
from collections import deque
from mhz19e import MHZ19E
import ujson
import uasyncio
import time
MAX_HISTORY_POINTS = 500
class WebServerMicrodot:
def __init__(self, co2: MHZ19E):
self.app = Microdot()
self.co2 = co2
# 队列: 用于存储历史数据,供客户端首次连接时使用
self.history_queue = deque([], MAX_HISTORY_POINTS)
# 存储所有活动WebSocket连接的集合
self.connected_websockets = set()
self.setup_routes()
async def read_mhz19(self):
"""
任务:每5秒读取一次传感器数据,并将其放入队列。
"""
while True:
try:
# 1. 读取传感器数据
# mhz19e.py 中的 read_data 是一个 async 函数,所以需要 await
co2_value = await self.co2.read_data()
co2_value=round(co2_value,1)
if co2_value is not None:
# 2. 创建带时间戳的数据点
timestamp = time.time()
dt = time.gmtime(timestamp)
now_iso = f'{dt[0]:04d}-{dt[1]:02d}-{dt[2]:02d}T{dt[3]:02d}:{dt[4]:02d}:{dt[5]:02d}.000Z'
new_data_point = {'x': now_iso, 'y': co2_value}
print(now_iso,co2_value)
# 3. 将新数据点加入历史队列
self.history_queue.append(new_data_point)
# 2. 将新数据广播给所有连接的客户端
if self.connected_websockets:
message = ujson.dumps({'type': 'update', 'data': new_data_point})
# 创建一个副本进行迭代,防止在迭代过程中集合被修改
for ws in list(self.connected_websockets):
try:
await ws.send(message)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error sending to a client: {e}. Client might be disconnected.")
# 发送失败,从集合中移除
self.connected_websockets.discard(ws)
except Exception as e:
print(f'读传感器时错误:{e}')
# 5. 等待5秒
await uasyncio.sleep(5)
def setup_routes(self):
"""设置路由"""
@self.app.route('/')
async def index(request):
return send_file('index.html')
# ... 其他静态文件路由保持不变 ...
@self.app.route('/chart.js')
async def script_chart(request):
return send_file('chart.js.gz', compressed=True)
@self.app.route('/chartjs-adapter-date.js')
async def script_chart(request):
return send_file('/chartjs-adapter-date.js.gz', compressed=True)
@self.app.route('/chartjs-plugin-annotation.js')
async def script_chart(request):
return send_file('/chartjs-plugin-annotation.js.gz', compressed=True)
@self.app.errorhandler(404)
async def not_found(request):
return '页面未找到', 404
@self.app.route('/ws')
@with_websocket
async def handle_websocket(request, ws):
"""
处理WebSocket连接。
1. 首次连接时发送所有历史数据。
2. 将连接加入活动连接池。
3. 维持连接直到断开。
"""
print(f"New WebSocket connection from {request.client_addr}")
# 1. 发送历史数据
if self.history_queue:
initial_data = list(self.history_queue)
initial_message = ujson.dumps({'type': 'initial', 'data': initial_data})
await ws.send(initial_message)
print(f"Sent {len(initial_data)} historical data points to new client.")
else:
print("No historical data to send.")
# 2. 将连接加入活动连接池
self.connected_websockets.add(ws)
print(f"Total connected clients: {len(self.connected_websockets)}")
try:
# 3. 循环接收消息以保持连接活跃,并检测断开
while True:
# 使用 receive() 等待消息,如果客户端断开,会引发异常
msg = await ws.receive()
# 这里可以处理来自客户端的消息,例如心跳包
print(f"Received message from client: {msg}")
except Exception as e:
# 连接关闭时会触发异常
print(f"WebSocket connection closed or error: {e}")
finally:
# 4. 确保连接从池中移除
self.connected_websockets.discard(ws)
print(f"Client disconnected. Total connected clients: {len(self.connected_websockets)}")
async def start_server(self):
"""启动Microdot服务"""
print("启动Microdot服务...")
# 创建并启动数据任务
uasyncio.create_task(self.read_mhz19())
# 启动Web服务器,这会阻塞直到服务器停止
await self.app.start_server(port=80, debug=False)好多例子都是读了两个字节,直接计算二氧化碳值。这里需要进行转换,0对应400,0xff对应5000,为节省资源直接写了sclale值。
python
from machine import UART
#import time
import uasyncio
class MHZ19E:
"""
用于与 MH-Z19E CO2 传感器通信的驱动类。
该类封装了通过 UART 发送命令、读取响应、校验数据以及解析 CO2 和温度值的全部功能。
"""
def __init__(self, uart_id=2, tx=17, rx=16, baudrate=9600):
"""
初始化 MH-Z19E 传感器。
参数:
uart_id (int): 要使用的 UART 端口号,默认为 2。
tx (int): 连接到传感器 RXD 的 ESP32 引脚号,默认为 17。
rx (int): 连接到传感器 TXD 的 ESP32 引脚号,默认为 16。
baudrate (int): 通信波特率,默认为 9600。
"""
self.tx_pin = tx
self.rx_pin = rx
self.baudrate = baudrate
# 构建读取命令: 0xFF 0x01 0x86 ...
self.cmd = bytearray([0xFF, 0x01, 0x86, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00])
self.cmd.append(self._calculate_checksum(self.cmd))
# 初始化 UART,推荐使用 UART2 以避免与 REPL 冲突
self.uart = UART(uart_id, baudrate=self.baudrate, tx=self.tx_pin, rx=self.rx_pin)
print(f"MH-Z19E 传感器已在 UART{uart_id} (TX: {tx}, RX: {rx}) 上初始化。")
def convert(self, analog_value: int) -> float:
"""
将0-65535范围的模拟量线性转换为400-5000范围的物理量。
"""
# 定义输入和输出范围
in_min = 0
in_max = 65535 # 16位无符号整数的最大值
out_min = 400.0
out_max = 5000.0
# 计算比例因子
scale = 0.07019 # (out_max - out_min) / (in_max - in_min)
# 执行线性转换
physical_value = out_min + scale * (analog_value - in_min)
return physical_value
def _calculate_checksum(self, data):
"""
计算命令或响应的校验和。
这是 MH-Z19E 协议的内部方法。
"""
return 0xFF - (sum(data) & 0xFF)
async def read_data(self):
"""
从传感器读取 CO2 浓度和温度。
返回:
tuple: (co2_ppm, temperature_celsius) 如果读取成功。
None: 如果读取失败、校验错误或无响应。
"""
# 发送命令
self.uart.write(self.cmd)
# 3. 等待并读取响应
#time.sleep_ms(100) # 给传感器一些时间响应
await uasyncio.sleep_ms(100)
if self.uart.any() >= 9:
response = self.uart.read(9)
if response is None or len(response) != 9:
print("错误: 响应数据长度不正确。")
return None
# 4. 验证校验和
if response[8] != self._calculate_checksum(response[:8]):
print(f"错误: 校验和不匹配!")
return None
# 5. 解析数据
# 响应格式: 0xFF 0x01 0x86 <CO2_H> <CO2_L> <Temp> <Status> <...> <Checksum>
co2_raw = (response[2] << 8) | response[3]
co2_value=self.convert(co2_raw)
# 6. 检查状态
status_byte = response[5]
if status_byte == 0x40:
print("警告: 传感器正在预热中,读数可能不准确。")
elif status_byte != 0x00:
print(f"警告: 传感器状态异常,状态码: {hex(status_byte)}")
# print (f'Co2:{co2_value}',)
return co2_value
else:
print("错误: 未收到传感器响应。")
def calibrate_zero_point(self):
"""
在 400ppm 环境下进行零点校准。
请将传感器置于室外清新空气中(约400ppm)3分钟后执行此命令。
"""
print("开始零点校准... (请确保传感器在400ppm环境中)")
cmd = bytearray([0xFF, 0x01, 0x87, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00])
cmd.append(self._calculate_checksum(cmd))
self.uart.write(cmd)
print("零点校准命令已发送。")index.html
没有使用js和css库。
html
<!-- index.html -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>WebSocket 实时数据图表</title>
<!-- 1. 引入 Chart.js 库 -->
<script src="/chart.js"></script>
<!-- 引入日期适配器,用于处理时间轴 -->
<script src="/chartjs-adapter-date.js"></script>
<script src="/chartjs-plugin-annotation.js"></script>
<style>
body {
font-family: sans-serif;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
padding: 20px;
}
#chart-container {
width: 90%;
max-width: 900px;
height: 500px; /* 给容器一个固定高度 */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
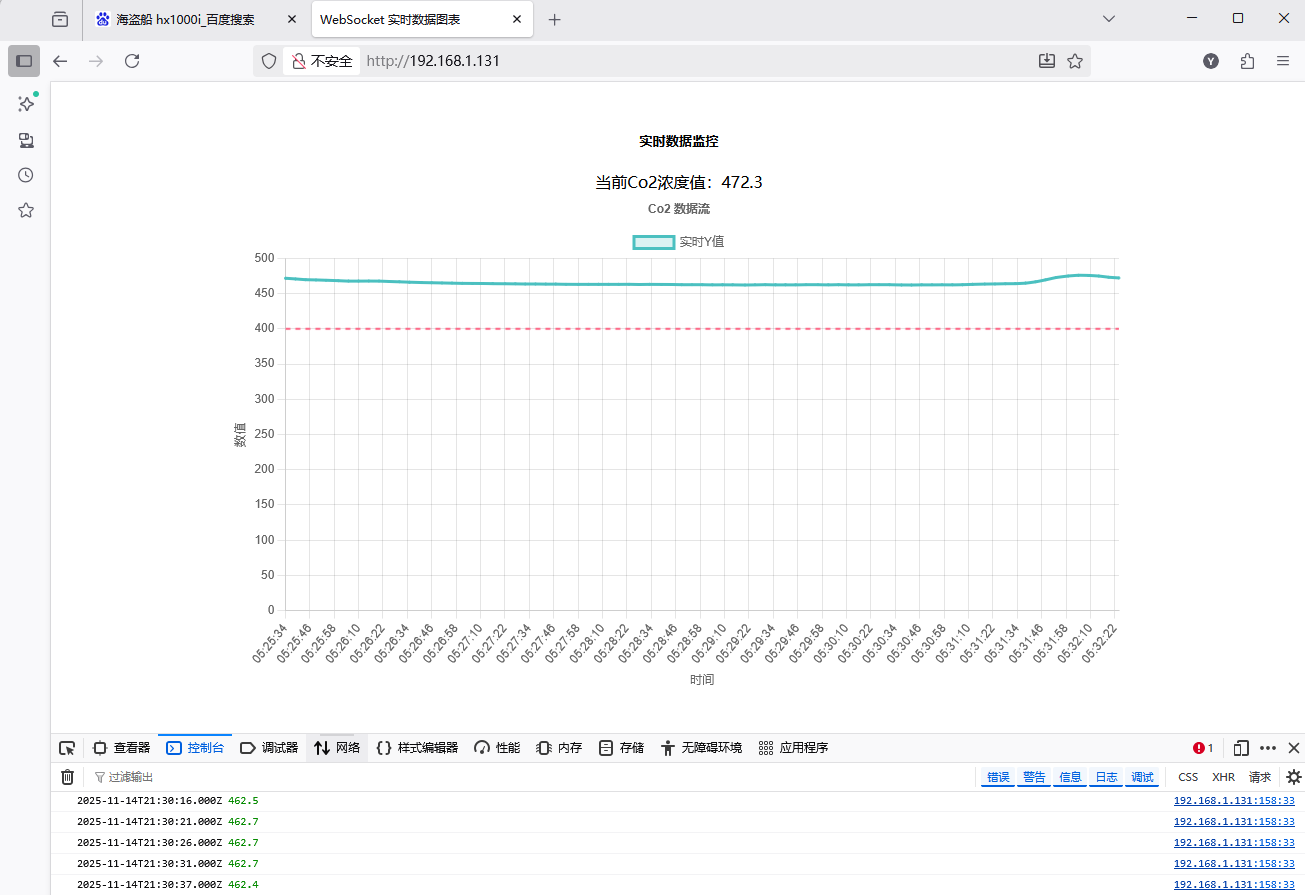
<h5>实时数据监控</h5>
<!-- Co2值 -->
<div id="co2_value">
</div>
<!-- 2. 用于绘制图表的 Canvas 元素 -->
<div id="chart-container">
<canvas id="myChart"></canvas>
</div>
<script>
const maxDataPoints = 2000;
// 3. 初始化 Chart.js 图表
const ctx = document.getElementById('myChart').getContext('2d');
const myChart = new Chart(ctx, {
type: 'line', // 图表类型为折线图
data: {
// 数据集
datasets: [{
label: '实时Y值', // 数据集的标签
data: [], // 初始数据为空,将由WebSocket填充
borderColor: 'rgb(75, 192, 192)', // 线条颜色
backgroundColor: 'rgba(75, 192, 192, 0.2)', // 填充区域颜色
tension: 0.1, // 线条弯曲度,0为直线
pointRadius: 1 // 数据点半径
}]
},
options: {
responsive: true,
maintainAspectRatio: false, // 允许图表填满容器
scales: {
// X轴配置
x: {
type: 'time', // 关键:设置X轴为时间轴
time: {
timezone: 'UTC',
unit: 'second', // 时间单位
displayFormats: {
second: 'HH:mm:ss' // 时间显示格式
}
},
title: {
display: true,
text: '时间'
}
},
// Y轴配置
y: {
beginAtZero: true, // Y轴从0开始
title: {
display: true,
text: '数值'
}
}
},
plugins: {
title: {
display: true,
text: 'Co2 数据流'
},
annotation: {
annotations: {
// 定义一个名为 'line1' 的注释
line1: {
type: 'line', // 类型是 'line'
yMin:400, // 线的起始 y 值
yMax: 400, // 线的结束 y 值 (与 yMin 相同即为水平线)
borderColor: 'rgb(255, 99, 132)', // 线的颜色
borderWidth: 2, // 线的宽度
borderDash: [5, 5], // 虚线样式 (可选)
label: {
// 为线条添加一个标签
content: 'y = 50',
enabled: true,
position: 'end', // 标签位置 ('start', 'center', 'end')
yAdjust: -10, // 微调标签y位置
backgroundColor: 'rgba(255, 99, 132, 0.8)',
font: {
size: 12
}
}
}
}
}
} //plugin
} //option
});
// 更新显示的CO2数值
const co2_value= document.getElementById('co2_value')
function updateCO2Display(currentCO2) {
// 更新div内容
co2_value.innerHTML = '当前Co2浓度值:' + currentCO2;
}
// 4. 创建 WebSocket 连接
// 注意:地址和端口必须与Python服务器匹配
let ws;
function connect() {
const ws = new WebSocket('ws://' + location.hostname + '/ws');
ws.onopen = function(event) {
console.log("WebSocket 连接已建立。");
// 可以在这里发送一条初始化消息给服务器,如果需要的话
ws.send("hi");
};
ws.onmessage = function(event) {
try {
// 解析收到的JSON数据
const message = JSON.parse(event.data);
// 检查数据类型
if (message.type === 'initial') {
// 处理数据队列(多个数据点)
const dataQueue = message.data;
if (Array.isArray(dataQueue)) {
// 将队列中的每个数据点添加到图表
dataQueue.forEach(point => {
myChart.data.datasets[0].data.push({
x: point.x,
y: point.y
});
});
}
} else if (message.type === 'update'){
// 处理单个数据点
// 限制数据点数量,避免内存溢出和图表卡顿
if (myChart.data.datasets[0].data.length >= maxDataPoints) {
myChart.data.datasets[0].data.shift(); // 移除最旧的数据点
}
console.log(message.data.x,message.data.y);
myChart.data.datasets[0].data.push({
x: message.data.x,
y: message.data.y
});
}
//显示当前值
updateCO2Display(message.data.y);
// 更新图表显示
myChart.update('none'); // 使用 'none' 模式可以提高性能,避免动画
} catch (error) {
console.error("处理WebSocket消息时出错:", error);
}
};
ws.onerror = function(error) {
console.error("WebSocket 错误:", error);
};
ws.onclose = function(event) {
console.log("WebSocket 连接已关闭。", event.code, event.reason);
// 可以在这里添加重连逻辑
};
}
// 页面加载完成后立即尝试连接
window.onload = connect;
</script>
</body>
</html>使用Chartjs,需要注意时区。返回的时间字符串末尾带z,会有时差。esp32没有校正时间,因此时间是不对的。
- 结论
冬天来了,新楼房密封好,睡一宿没有通风、净化,二氧化碳浓度还是很高的。
如果睡的不舒服,可以检查空气质量。
用esp32来做,打算让它控制松下空调的净化,结果松下空调净化只分解甲醛等,不吸收二氧化碳不送新风。