算法基础概念与实战应用(二) 基础算法(下)
文章目录
- [算法基础概念与实战应用(二) 基础算法(下)](#算法基础概念与实战应用(二) 基础算法(下))
- 一、贪心算法
- [8.1 简单贪⼼](#8.1 简单贪⼼)
-
- [8.1.1 货仓选址](#8.1.1 货仓选址)
- [8.1.2 最⼤⼦段和](#8.1.2 最⼤⼦段和)
- [8.1.3 纪念品分组](#8.1.3 纪念品分组)
- [8.1.4 排座椅](#8.1.4 排座椅)
- [8.1.5 矩阵消除游戏](#8.1.5 矩阵消除游戏)
- [8.2 推公式](#8.2 推公式)
-
- [8.2.1 拼数](#8.2.1 拼数)
- [8.2.2 保卫花园](#8.2.2 保卫花园)
- [8.2.3 奶⽜玩杂技](#8.2.3 奶⽜玩杂技)
- [8.3 哈夫曼编码](#8.3 哈夫曼编码)
-
- [8.3.1 哈夫曼编码](#8.3.1 哈夫曼编码)
- [8.3.2 合并果⼦](#8.3.2 合并果⼦)
- [8.4 区间问题](#8.4 区间问题)
-
- [8.4.1 线段覆盖](#8.4.1 线段覆盖)
- [8.4.2 Radar Installation](#8.4.2 Radar Installation)
- [8.4.3 Sunscreen](#8.4.3 Sunscreen)
- [8.4.4 ⽜栏预定](#8.4.4 ⽜栏预定)
- [9. 倍增思想](#9. 倍增思想)
-
- [9.1 快速幂](#9.1 快速幂)
- [9.2 ⼤整数乘法](#9.2 ⼤整数乘法)
- [10. 离散化](#10. 离散化)
- [11. 递归初阶](#11. 递归初阶)
- 总结
一、贪心算法
8.1 简单贪⼼
8.1.1 货仓选址

代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n;
LL a[N];
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n);
LL ret = 0;
// 利⽤中间值来计算
// for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
// {
// ret += abs(a[i] - a[n / 2]);
// }
// ⽤结论计算
for (int i = 1; i <= n / 2; i++)
{
ret += a[n - i + 1] - a[i];
}
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}8.1.2 最⼤⼦段和

代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int n;
LL a[N];
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
LL sum = 0, ret = -1e6;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
sum += a[i];
ret = max(ret, sum);
if (sum < 0) sum = 0;
}
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}8.1.3 纪念品分组


代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 3e4 + 10;
int w, n;
int a[N];
int main()
{
cin >> w >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n);
int l = 1, r = n, ret = 0;
while (l <= r)
{
if (a[l] + a[r] <= w) l++, r--;
else r--;
ret++;
}
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
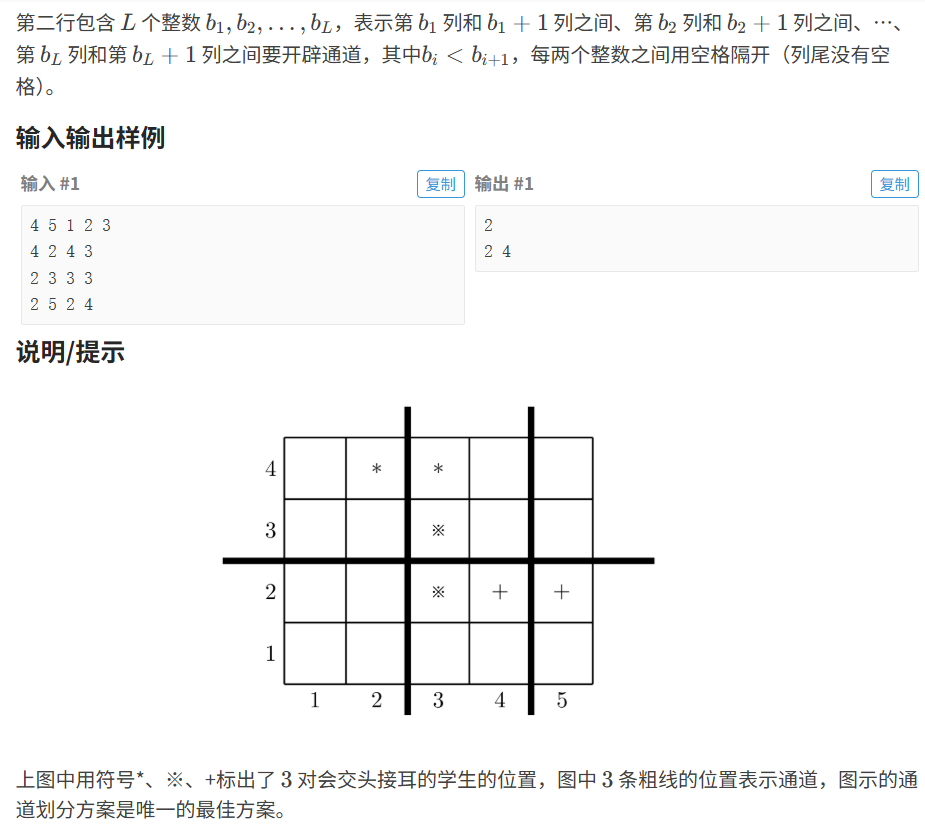
}8.1.4 排座椅


代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
struct node
{
int index;
int cnt;
}row[N], col[N];
int m, n, k, l, d;
// 按照 cnt 从⼤到⼩排序
bool cmp1(node& x, node& y)
{
return x.cnt > y.cnt;
}
// 按照 index 从⼩到⼤排序
bool cmp2(node& x, node& y)
{
return x.index < y.index;
}
int main()
{
cin >> m >> n >> k >> l >> d;
// 初始化结构体数组
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) row[i].index = i;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) col[i].index = i;
while (d--)
{
int x, y, p, q; cin >> x >> y >> p >> q;
if (x == p) col[min(y, q)].cnt++;
else row[min(x, p)].cnt++;
}
// 对两个数组按照 cnt 从⼤到⼩排序
sort(row + 1, row + 1 + m, cmp1);
sort(col + 1, col + 1 + n, cmp1);
// 对 row 数组,前 k 个元素,按照下标从⼩到⼤排序
sort(row + 1, row + 1 + k, cmp2);
// 对 col 数组,前 l 个元素,按照下标从⼩到⼤排序
sort(col + 1, col + 1 + l, cmp2);
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++)
{
cout << row[i].index << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (int i = 1; i <= l; i++)
{
cout << col[i].index << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}8.1.5 矩阵消除游戏
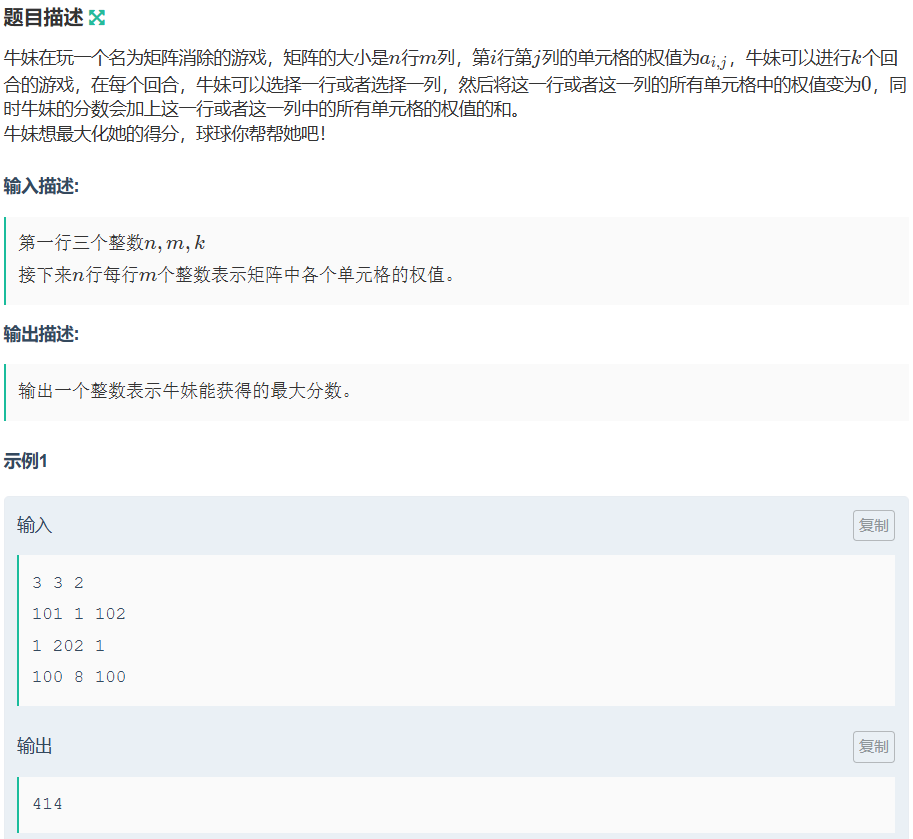

代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 20;
int n, m, k;
int a[N][N];
int col[N]; // 统计列和
// 统计 x 的⼆进制表⽰中 1 的个数
int calc(int x)
{
int ret = 0;
while (x)
{
ret++;
x -= x & -x;
}
return ret;
}
// 按照值从⼤到⼩排序
bool cmp(int a, int b)
{
return a > b;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m >> k;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
cin >> a[i][j];
int ret = 0;
// 暴⼒枚举出⾏的所有选法
for (int st = 0; st < (1 << n); st++)
{
int cnt = calc(st);
if (cnt > k) continue; // 不合法的状态
memset(col, 0, sizeof col);
int sum = 0; // 记录当前选法中的和
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
if ((st >> i) & 1) sum += a[i][j];
else col[j] += a[i][j];
}
}
// 处理列
sort(col, col + m, cmp);
// 选 k - cnt 列
for (int i = 0; i < k - cnt; i++) sum += col[i];
ret = max(ret, sum);
}
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}8.2 推公式

8.2.1 拼数
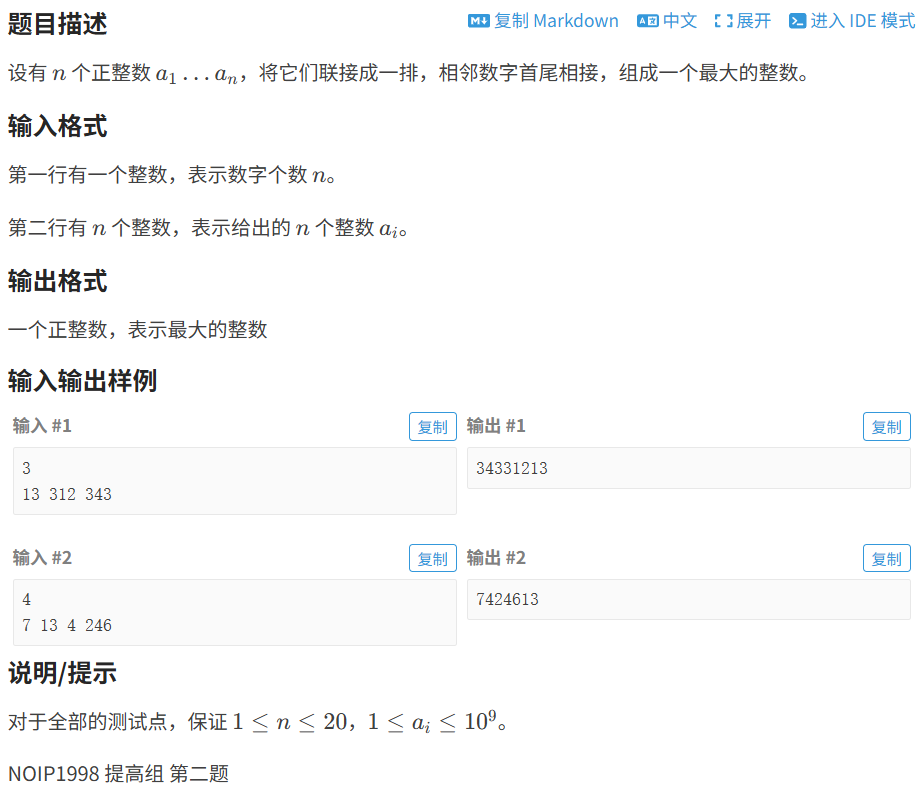

代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 25;
int n;
string a[N];
bool cmp(string& x, string& y)
{
return x + y > y + x;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
// 排序
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n, cmp);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cout << a[i];
return 0;
}8.2.2 保卫花园
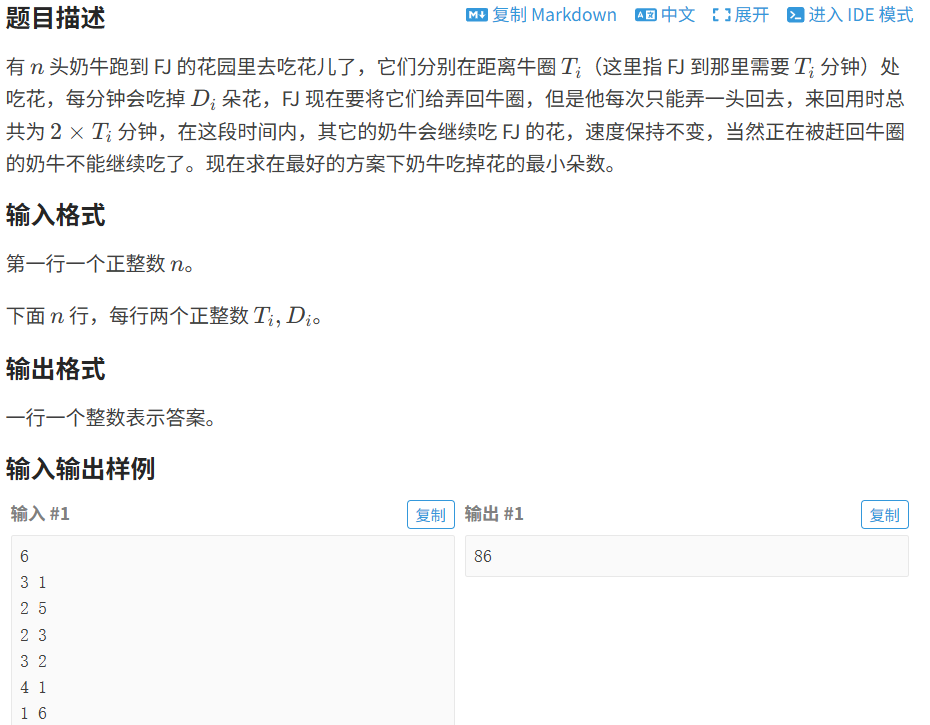

代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n;
struct node
{
int t;
int d;
}a[N];
bool cmp(node& x, node& y)
{
return x.t * y.d < y.t* x.d;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i].t >> a[i].d;
}
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n, cmp);
LL ret = 0, t = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
ret += a[i].d * t;
t += 2 * a[i].t;
}
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}8.2.3 奶⽜玩杂技

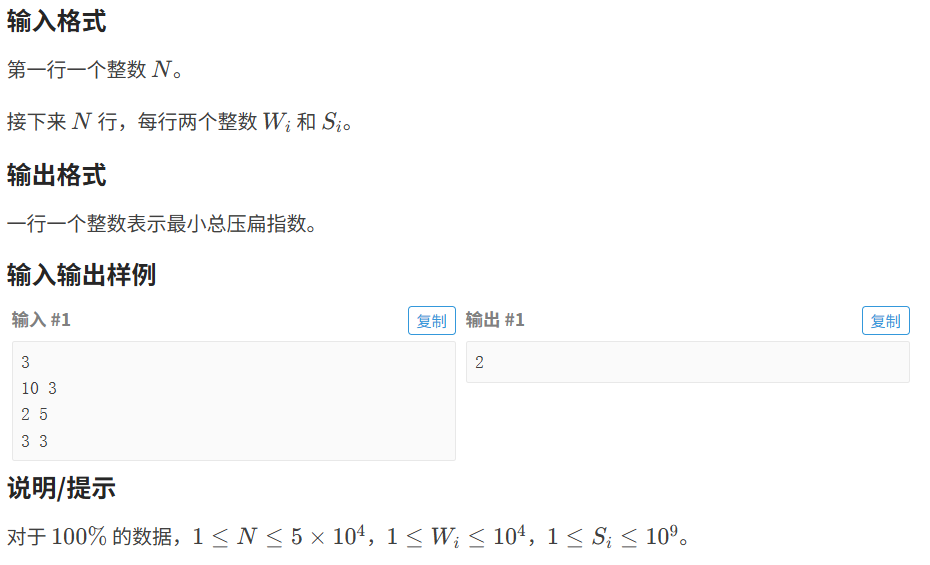

代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 5e4 + 10;
int n;
struct node
{
int w, s;
}a[N];
bool cmp(node& i, node& j)
{
return i.w + i.s < j.w + j.s;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i].w >> a[i].s;
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n, cmp);
LL ret = -1e9 - 10, w = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
ret = max(ret, w - a[i].s);
w += a[i].w;
}
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}8.3 哈夫曼编码
8.3.1 哈夫曼编码
代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int n;
priority_queue<LL, vector<LL>, greater<LL>> heap; // ⼩根堆
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
LL x; cin >> x;
heap.push(x);
}
LL len = 0;
while (heap.size() > 1)
{
// 每次拿出权值最⼩的两棵树合并
LL x = heap.top(); heap.pop();
LL y = heap.top(); heap.pop();
LL t = x + y;
len += t;
heap.push(t);
}
cout << len << endl;
return 0;
}8.3.2 合并果⼦
代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
int n;
priority_queue<LL, vector<LL>, greater<LL>> heap;
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
LL x;
cin >> x;
heap.push(x);
}
LL sum = 0;
while (heap.size() > 1)
{
// 取出最⼩的两堆合并
LL a = heap.top(); heap.pop();
LL b = heap.top(); heap.pop();
heap.push(a + b);
sum += a + b;
}
cout << sum << endl;
return 0;
}8.4 区间问题
8.4.1 线段覆盖

代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int n;
PII a[N];
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i].first >> a[i].second;
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n); // 默然按照⾸元素⽐较
int r = a[1].second, ret = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
int x = a[i].first, y = a[i].second;
if (r <= x) // 没有重叠
{
ret++;
r = y;
}
else // 有重叠,就选右边界最⼩的那⼀个
{
r = min(r, y);
}
}
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}8.4.2 Radar Installation


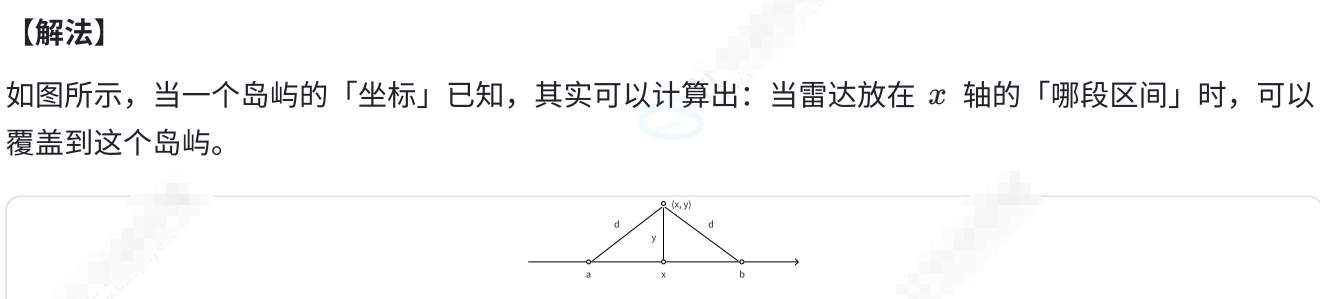

代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
int n, d;
struct node
{
double l, r;
}a[N];
bool cmp(node& x, node& y)
{
return x.l < y.l;
}
int main()
{
int cnt = 0;
while (cin >> n >> d, n && d)
{
cnt++;
bool flag = false; // 有可能岛屿太远,⽆论如何也覆盖不到
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
double x, y; cin >> x >> y;
if (y > d) flag = true;
else
{
double t = sqrt(d * d - y * y);
a[i].l = x - t, a[i].r = x + t;
}
}
cout << "Case " << cnt << ": ";
if (flag) cout << -1 << endl;
else
{
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n, cmp);
int ret = 1;
double r = a[1].r;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
double x = a[i].l, y = a[i].r;
if (x > r) // 没有重叠
{
ret++;
r = y;
}
else // 有重叠
{
r = min(r, y);
}
}
cout << ret << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}8.4.3 Sunscreen



代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2510;
int n, m;
struct node
{
int x, y;
}a[N], b[N];
bool cmp1(node& x, node& y)
{
return x.y < y.y;
}
bool cmp2(node& x, node& y)
{
return x.x < y.x;
}
bool cmp3(node & x, node & y)
{
return x.x > y.x;
}
// 所有区间按照右端点从⼩到⼤排序
// 所有点按照从⼩到⼤排序
void solve1()
{
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n, cmp1);
sort(b + 1, b + 1 + m, cmp2);
int ret = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int l = a[i].x, r = a[i].y;
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
// 选⼀个最⼩的,符合要求的点
int& sp = b[j].x, & cnt = b[j].y;
if (!cnt || sp < l) continue;
if (sp > r) break;
cnt--;
ret++;
break;
}
}
cout << ret << endl;
}
// 所有区间按照左端点从⼤到⼩排列
// 所有点从⼤到⼩排列
void solve2()
{
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n, cmp3);
sort(b + 1, b + 1 + m, cmp3);
int ret = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int l = a[i].x, r = a[i].y;
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
// 选⼀个最⼤的,符合要求的点
int& sp = b[j].x, & cnt = b[j].y;
if (!cnt || sp > r) continue;
if (sp < l) break;
ret++;
cnt--;
break;
}
}
cout << ret << endl;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i].x >> a[i].y;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) cin >> b[i].x >> b[i].y;
// solve1(); // 按照右端点排序
solve2(); // 按照左端点排序
}8.4.4 ⽜栏预定

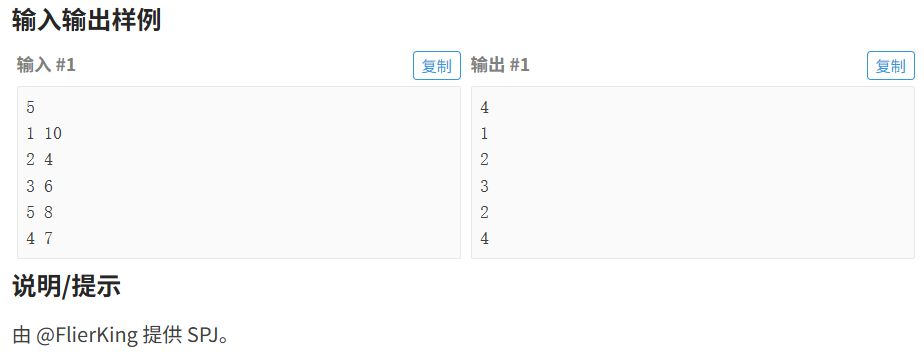


代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e4 + 10;
int n;
struct node
{
// 存每⼀头⽜的信息:开始时间,结束时间,排序之前的位置,分配的⽜棚号
int x, y, pos, num;
}a[N];
int cnt;
int ret[N];
multimap<int, int> st;
bool cmp(node& x, node& y)
{
return x.x < y.x;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i].x >> a[i].y;
a[i].pos = i;
}
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n, cmp);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int l = a[i].x, r = a[i].y;
auto it = st.upper_bound(l);
// 不能接在任何⼀个区间后⾯,那就新开⼀个区间
if (it == st.end())
{
st.insert({ r, ++cnt });
a[i].num = cnt;
}
else // 能接在某个区间后⾯,那就接上去
{
int p = it->second;
st.erase(it); // 把之前⽜删掉
st.insert({ r, p }); // 新来的⽜放进去
a[i].num = p;
}
}
cout << cnt << endl;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
ret[a[i].pos] = a[i].num;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cout << ret[i] << endl;
return 0;
}9. 倍增思想
9.1 快速幂
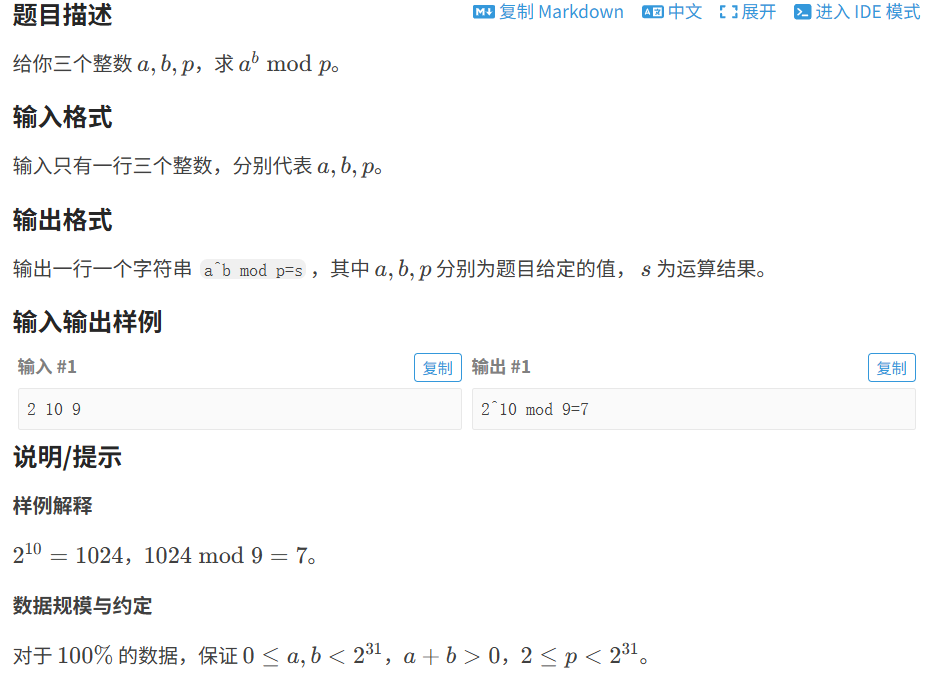


代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
// a^b % p 的值
LL quickpow(LL a, LL b, LL p)
{
LL ret = 1;
while (b)
{
if (b & 1) ret = ret * a % p;
a = a * a % p;
b >>= 1; // 提取 b 的⼆进制位
}
return ret;
}
int main()
{
LL a, b, p;
scanf("%lld%lld%lld", &a, &b, &p);
printf("%lld^%lld mod %lld=%lld\n", a, b, p, quickpow(a, b, p));
return 0;
}9.2 ⼤整数乘法
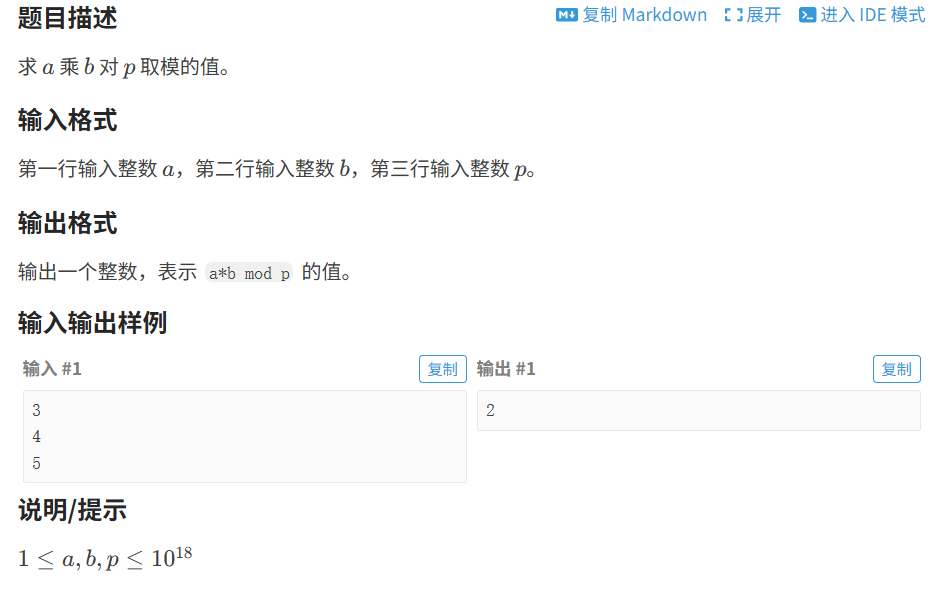

代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
// 加法⽐乘法快,⽽且防溢出
LL qmul(LL a, LL b, LL p)
{
LL sum = 0;
while (b) // 枚举 b 的⼆进制位
{
if (b & 1) sum = (sum + a) % p;
a = (a + a) % p; // 计算下⼀个权值
b >>= 1;
}
return sum % p;
}
int main()
{
LL a, b, p;
cin >> a >> b >> p;
cout << qmul(a % p, b, p) << endl;
return 0;
}10. 离散化
模板一:
代码如下(示例):
c
// 离散化⽅式⼀:排序 + 去重 + ⼆分查找离散化后的值
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n;
int a[N]; // 原始数据
int pos; // 记录离散化数组中元素的个数
int disc[N]; // 离散化需要的数组
// ⼆分查找离散化之后的值,其实就是排序之后的下标
int find(int x)
{
int l = 1, r = pos; // 注意查找的区间
while (l < r)
{
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (disc[mid] >= x) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
return l;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int x; cin >> x;
a[i] = x;
disc[++pos] = x; // 数据放进离散化数组中
}
// 离散化:排序 + 去重
sort(disc + 1, disc + 1 + pos);
pos = unique(disc + 1, disc + 1 + pos) - (disc + 1);
// 找到离散化之后的值
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int x = a[i];
cout << x << "离散化之后是: " << find(x) << endl; // ⼆分查找离散化之后的值
}
}模板二:
代码如下(示例):
c
// 离散化⽅式⼆:排序 + STL
// 本质是和⽅式⼀ 样的,只不过借助了 STL,去重以及查找更⽅便
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n;
int a[N]; // 原始数据
int tmp[N]; // ⽤来排序的数组
int cnt;
unordered_map<int, int> id; // 记录离散化之后的值
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int x; cin >> x;
a[i] = x;
tmp[i] = x; // 数据放进离散化数组中
}
// 离散化:排序 + 放进哈希表中
sort(tmp + 1, tmp + 1 + n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (id.count(tmp[i])) continue; // 如果已经存过这个数,不做处理
cnt++; // 这个数映射之后的值
id[tmp[i]] = cnt; // 放进哈希表中
}
// 找到离散化之后的值
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int x = a[i];
cout << x << "离散化之后是: " << id[a[i]] << endl; // ⼆分查找离散化之后的值
}
return 0;
}
10.1 火烧赤壁
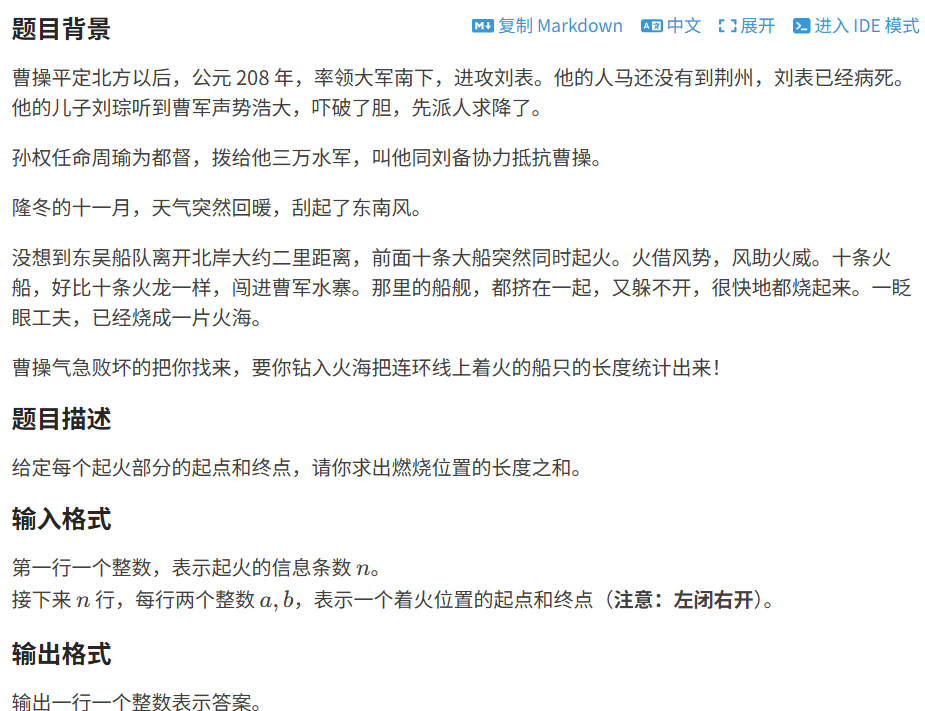
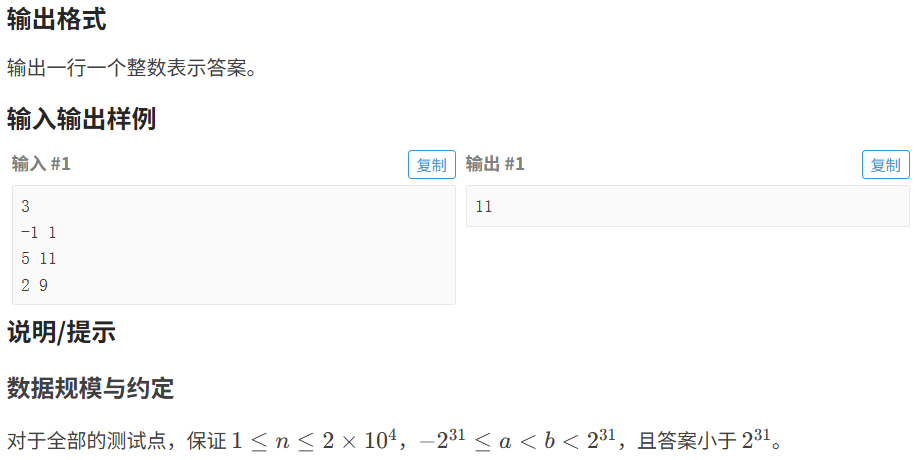

代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e4 + 10;
int n;
int l[N], r[N];
int m; // 离散数组的⼤⼩
int disc[N * 2]; // 离散之后的数组
int f[N * 2]; // 差分数组
int find(int x)
{
int l = 1, r = m;
while (l < r)
{
int mid = (l + r + 1) >> 1;
if (disc[mid] <= x) l = mid;
else r = mid - 1;
}
return l;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int x, y; cin >> x >> y;
l[i] = x, r[i] = y;
disc[++m] = l[i], disc[++m] = r[i];
}
// 离散化处理
sort(disc + 1, disc + 1 + m);
m = unique(disc + 1, disc + 1 + m) - disc - 1;
// 处理区间修改
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int x = find(l[i]), y = find(r[i]);
f[x] += 1, f[y] -= 1;
}
// 还原数组
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) f[i] += f[i - 1];
// 找出每⼀段⼤于0的区间,统计⻓度
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
if (f[i] <= 0) continue;
int j = i;
while (j <= m && f[j] > 0) j++;
// 累加⻓度的时候记得使⽤离散化之前的值
sum += disc[j] - disc[i];
i = j;
}
cout << sum << endl;
return 0;
}10.2 贴海报

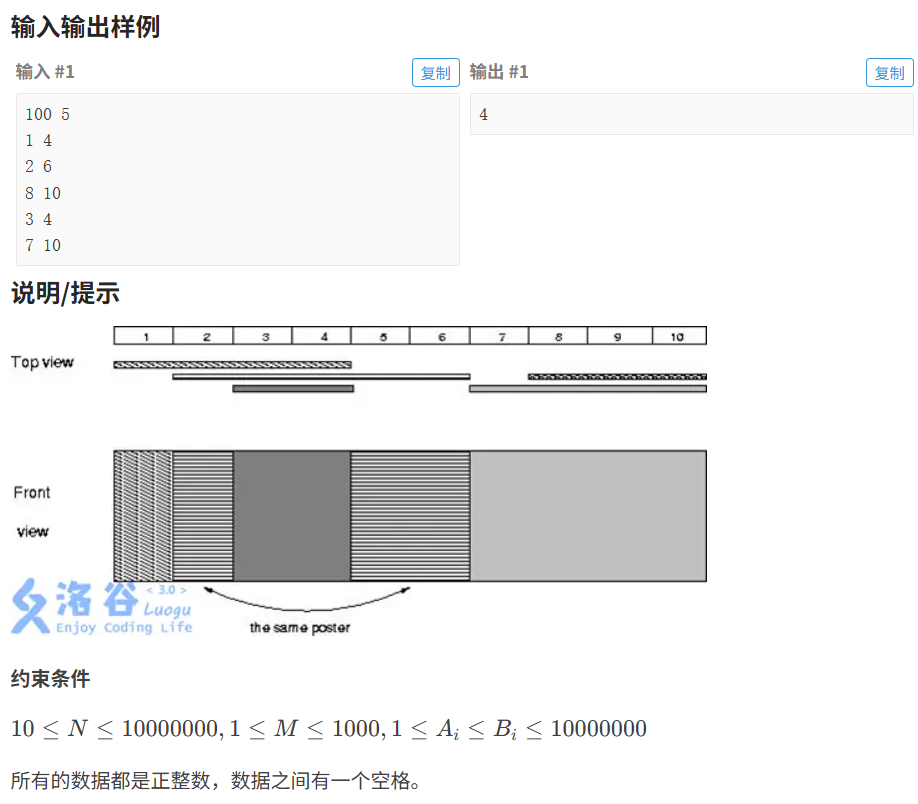



代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
int n, m;
int a[N], b[N];
int pos;
int disc[N * 4]; // 因为有两套位置
int w[N * 4];
bool mp[N];
// 找到 x 映射之后的数,也就是 x 的下标
int find(int x)
{
int l = 1, r = pos;
while (l < r)
{
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (disc[mid] >= x) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
return l;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
int x, y; cin >> x >> y;
a[i] = x, b[i] = y;
// 离散化之后有可能导致区间缩⼩,多加⼀个位置
disc[++pos] = x, disc[++pos] = x + 1;
disc[++pos] = y, disc[++pos] = y + 1;
}
// 离散化
sort(disc + 1, disc + 1 + pos);
pos = unique(disc + 1, disc + 1 + pos) - (disc + 1);
// ⽤离散化之后的值覆盖区间
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
int x = find(a[i]), y = find(b[i]);
for (int j = x; j <= y; j++) w[j] = i;
}
// 统计整个数组中,⼀共有多少个不同的数
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= pos; i++)
{
int x = w[i];
if (!x) continue; // 不要统计 0
if (mp[x]) continue;
cnt++;
mp[x] = true;
}
cout << cnt << endl;
return 0;
}