系列文章目录
文章目录
- 系列文章目录
- 前言
- 1、nvidia-smi指令
- 2、nvcc
- [3、核函数(Kernel function)](#3、核函数(Kernel function))
- [4、GPU 和 CPU的区别](#4、GPU 和 CPU的区别)
- 5、GPU计算能力
- 6、设备信息查询和设置
-
- 1、运行时API查询GPU信息
- [2、设置GPU 设备](#2、设置GPU 设备)
前言
回顾计算机技术的发展,特别是摩尔定律的影响,计算能力的快速提升。然而,随着晶体管尺寸的缩小和频率的停滞,单线程性能增长放缓。为了继续提升性能,多核处理器开始普及,促使软件开发者开始考虑并行计算。
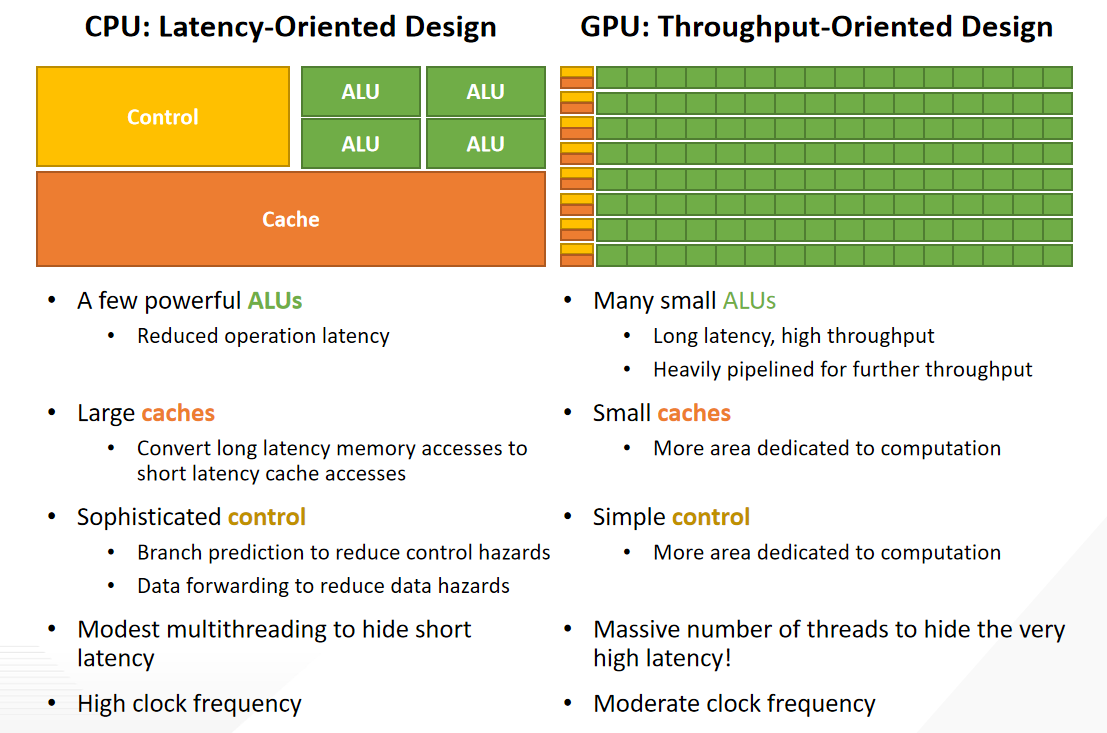
CPU和GPU分别代表了这两种设计方法。GPU是吞吐量导向的,拥有众多弱小的ALU,通过流水线处理提高算术吞吐量。GPU的成功在于其高并行性和高吞吐量,以及能够分摊高昂的固定成本的大量销售额。
随着CUDA的普及,GPU计算的应用领域迅速扩大,尤其是在机器学习领域。如今,GPU已经成为全球顶级超级计算机的重要组成部分,并且在能源效率方面表现出色。课程将关注如何以通用的方式编程GPU,以及如何利用GPU加速科学计算和深度学习工作负载。
1、nvidia-smi指令
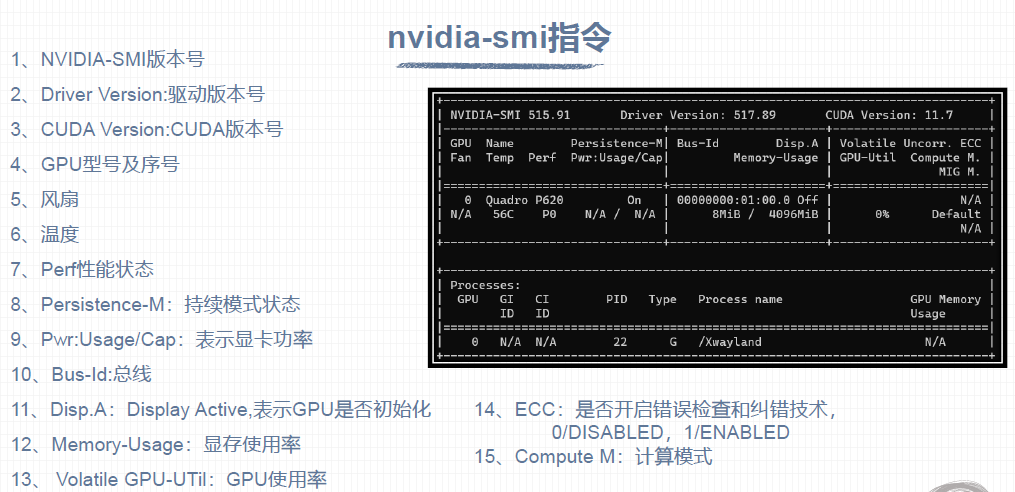
- 查询GPU 详细信息
nvidia-smi -q - 查询特定GPU 详细信息
nvidia-smi -h - 显示GPU 特定信息
nvidia-smi --q --i 0 --d MEMORY
2、nvcc
编译CUDA 文件指令:nvcc hello.cu -o hello
3、核函数(Kernel function)
1、核函数在GPU 上进行并行 执行
2、注意:
(1)限定词__global__ 修饰
(2)返回值必须是void
3、形式:
c
__global__ void kernel_function(argument arg)
{
printf("Hello World from the GPU!\n");
}
void __global__ kernel_function(argument arg)
{
printf("Hello World from the GPU!\n");
}kernel的限制:
- 仅能获取device memory 。
- 必须返回void类型。
- 不支持可变数目参数。
- 不支持静态变量。
- 不支持函数指针。
- 核函数具有异步性
4、GPU 和 CPU的区别
5、GPU计算能力
1、每款GPU 都有用于标识"计算能力"(compute capability )
的版本号
2、形式X.Y Y,X 标识主版本号,Y 表示次版本号
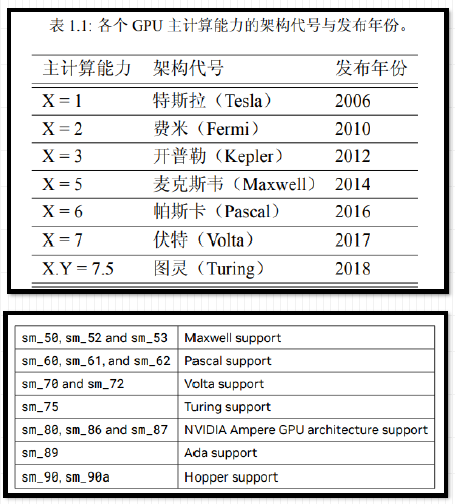
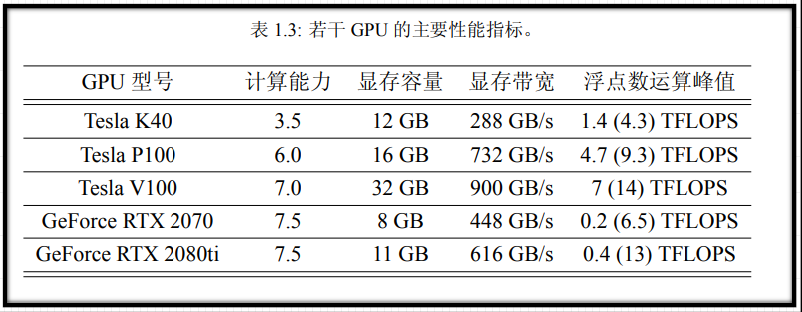
并非GPU 的计算能力越高,性能就越高
6、设备信息查询和设置
1、运行时API查询GPU信息
c
/*********************************************************************************************
* file name : query.cu
* brief : 运行时API查询GPU信息
***********************************************************************************************/
#include "../tools/common.cuh"
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int device_id = 0;
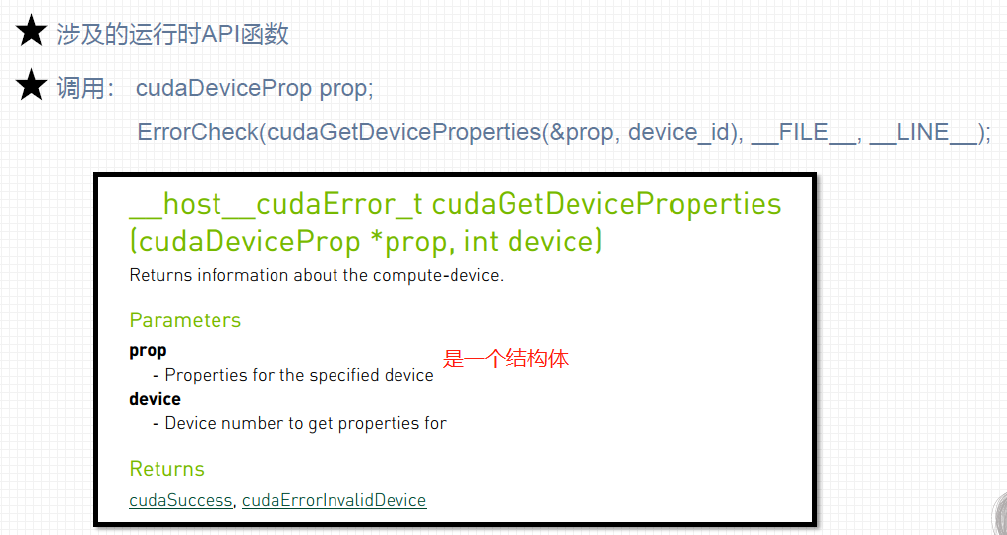
ErrorCheck(cudaSetDevice(device_id), __FILE__, __LINE__);
cudaDeviceProp prop;
ErrorCheck(**cudaGetDeviceProperties(&prop, device_id)**, __FILE__, __LINE__);
printf("Device id: %d\n",
device_id);
printf("Device name: %s\n",
prop.name);
printf("Compute capability: %d.%d\n",
prop.major, prop.minor);
printf("Amount of global memory: %g GB\n",
prop.totalGlobalMem / (1024.0 * 1024 * 1024));
printf("Amount of constant memory: %g KB\n",
prop.totalConstMem / 1024.0);
printf("Maximum grid size: %d %d %d\n",
prop.maxGridSize[0],
prop.maxGridSize[1], prop.maxGridSize[2]);
printf("Maximum block size: %d %d %d\n",
prop.maxThreadsDim[0], prop.maxThreadsDim[1],
prop.maxThreadsDim[2]);
printf("Number of SMs: %d\n",
prop.multiProcessorCount);
printf("Maximum amount of shared memory per block: %g KB\n",
prop.sharedMemPerBlock / 1024.0);
printf("Maximum amount of shared memory per SM: %g KB\n",
prop.sharedMemPerMultiprocessor / 1024.0);
printf("Maximum number of registers per block: %d K\n",
prop.regsPerBlock / 1024);
printf("Maximum number of registers per SM: %d K\n",
prop.regsPerMultiprocessor / 1024);
printf("Maximum number of threads per block: %d\n",
prop.maxThreadsPerBlock);
printf("Maximum number of threads per SM: %d\n",
prop.maxThreadsPerMultiProcessor);
return 0;
}2、设置GPU 设备
1、获取GPU设备数量
c
int iDeviceCount = 0;
cudaGetDeviceCount(&iDeviceCount);2、设置GPU执行时使用的设备
c
int iDev = 0;
cudaSetDevice(iDev)完整实例:
c
#pragma once
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
cudaError_t ErrorCheck(cudaError_t error_code, const char* filename, int lineNumber)
{
if (error_code != cudaSuccess)
{
printf("CUDA error:\r\ncode=%d, name=%s, description=%s\r\nfile=%s, line%d\r\n",
error_code, cudaGetErrorName(error_code), cudaGetErrorString(error_code), filename, lineNumber);
return error_code;
}
return error_code;
}
void setGPU()
{
// 检测计算机GPU数量
int iDeviceCount = 0;
cudaError_t error = ErrorCheck(cudaGetDeviceCount(&iDeviceCount), __FILE__, __LINE__);
if (error != cudaSuccess || iDeviceCount == 0)
{
printf("No CUDA campatable GPU found!\n");
exit(-1);
}
else
{
printf("The count of GPUs is %d.\n", iDeviceCount);
}
// 设置执行
int iDev = 0;
error = ErrorCheck(cudaSetDevice(iDev), __FILE__, __LINE__);
if (error != cudaSuccess)
{
printf("fail to set GPU 0 for computing.\n");
exit(-1);
}
else
{
printf("set GPU 0 for computing.\n");
}
}