Navigation3 相比 Navigation2 来说,区别主要有两点:
- 导航返回栈从由 Navigation 内部控制,变为由开发者控制。
- Navigation2 只适用于单页模式,一个屏幕只能显示一个路由对应的页面。而 Navigation3 可适配大屏。
添加依赖
kotlin
plugins {
// Kotlin serialization plugin
id("org.jetbrains.kotlin.plugin.serialization") version "2.0.21"
}
dependencies {
// Navigation3
implementation("androidx.navigation3:navigation3-runtime:1.0.0-rc01")
implementation("androidx.navigation3:navigation3-ui:1.0.0-rc01")
// Navigation3 Adaptive
implementation("androidx.compose.material3.adaptive:adaptive-navigation3:1.3.0-alpha03")
// Kotlin Serialization
implementation("org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-serialization-core:1.6.0")
// Navigation3 ViewModel
implementation("androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-viewmodel-navigation3:2.10.0-rc01")
}compileSdkVersion 需要 36 以上:
kotlin
android {
compileSdk = 36
}简单用法
我们以商品列表页和商品详情页为例:
kotlin
data object ProductList
data class ProductDetail(
val name: String,
val description: String
)
@Composable
fun ProductList(
products: List<ProductDetail>,
onProductClick: (ProductDetail) -> Unit,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier
) {
LazyColumn(modifier = modifier.fillMaxSize()) {
items(products) { product ->
Text(
text = product.name,
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.clickable { onProductClick(product) }
.padding(16.dp)
)
}
}
}
@Composable
fun ProductDetail(
product: ProductDetail,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier
) {
Column(
modifier = modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.padding(16.dp),
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally
) {
Text(
text = product.name,
fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold,
fontSize = 30.sp
)
Column(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.weight(1f),
verticalArrangement = Arrangement.Center,
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally
) {
Text(
text = product.description,
fontSize = 26.sp
)
}
}
}注意:ProductDetail 和 ProductList 有两重意思:既封装了页面的数据,又作为页面的导航节点。
然后是 MyApp 函数:
kotlin
class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
enableEdgeToEdge()
setContent {
ComposeNavigation3TestTheme {
MyApp()
}
}
}
}
@Composable
fun MyApp(modifier: Modifier = Modifier) {
// 返回栈,初始页面是商品列表
// Navigation3 会自动展示栈顶页面
val backStack = remember { mutableStateListOf<Any>(ProductList) }
NavDisplay( // 入口函数
backStack = backStack, // backStack参数是导航返回栈
onBack = { // onBack回调是返回的监听
// 返回逻辑为:移除栈顶元素
backStack.removeLastOrNull()
},
entryProvider = { key -> // entryProvider回调用于定义每个页面的NavEntry
when (key) {
// 商品列表页面
is ProductList -> NavEntry(key) {
val products = mutableListOf<ProductDetail>()
repeat(30) {
products.add(ProductDetail("Product $it", "Description of Product $it"))
}
ProductList(
products = products,
onProductClick = { product ->
// 跳转到商品详情页面
backStack.add(ProductDetail(product.name, product.description))
},
modifier
)
}
// 商品详情页面
is ProductDetail -> NavEntry(key) {
ProductDetail(
product = key,
modifier
)
}
else -> error("Unknown key: $key")
}
}
)
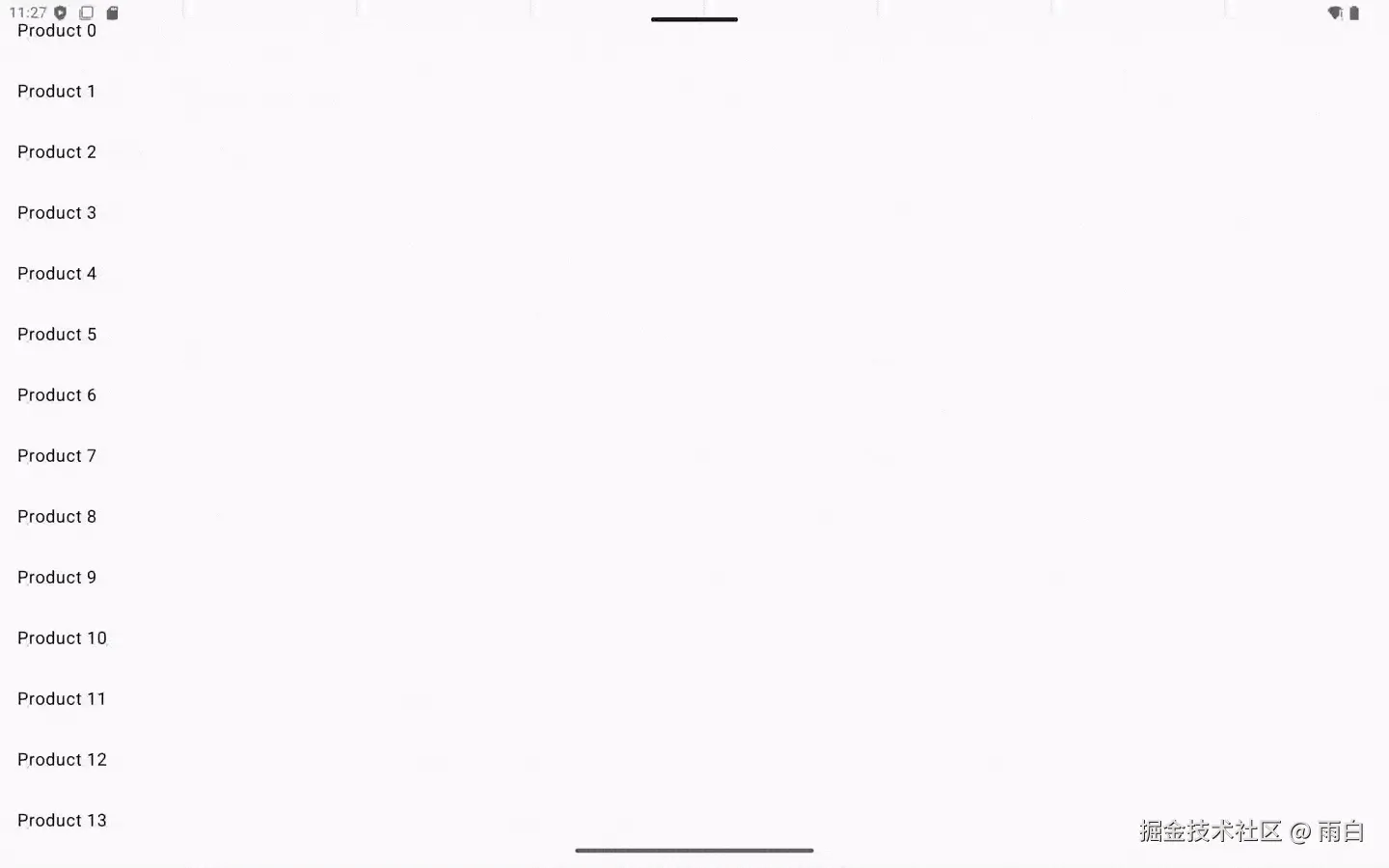
}运行效果:

可以看到,商品列表页向商品详情页传递数据非常容易,只需将数据加入到返回栈,详情页自然能在 entryProvider 回调中收到。
保存和管理导航状态
现在,我们旋转屏幕,会导致 Activity 的重建,导致返回栈被清空。
解决方法也很简单:只需给每一个 data class 加上 @Serializable 注解,然后实现 NavKey 接口。
状态恢复要求数据是可序列化的
kotlin
@Serializable
data object ProductList : NavKey
@Serializable
data class ProductDetail(
val name: String,
val description: String
) : NavKey再将返回栈的声明改为 val backStack = rememberNavBackStack(ProductList) 即可。
大屏适配
Navigation 3 中的场景(Scene)解决了大屏适配的问题,它可以显示一个或多个 NavEntry 实例,也就是同时显示多个 NavEntry 页面。
我们可以给 NavDisplay 函数传入一个 sceneStrategy 参数,来指定场景策略。默认策略是 SinglePaneSceneStrategy,单页场景模式。
我们来使用 ListDetailSceneStrategy,列表详情页面场景策略,它会自动根据当前屏幕大小进行页面分配。
kotlin
@OptIn(ExperimentalMaterial3AdaptiveApi::class)
@Composable
fun MyApp(modifier: Modifier = Modifier) {
val backStack = rememberNavBackStack(ProductList)
// 创建ListDetailSceneStrategy实例
val listDetailStrategy = rememberListDetailSceneStrategy<Any>()
NavDisplay(
backStack = backStack,
onBack = {
backStack.removeLastOrNull()
},
sceneStrategy = listDetailStrategy, // 使用ListDetailSceneStrategy
entryProvider = { key ->
when (key) {
is ProductList -> NavEntry(
key = key,
metadata = ListDetailSceneStrategy.listPane( // 修改处
detailPlaceholder = {
Column(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize(),
verticalArrangement = Arrangement.Center,
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally
) {
Text("Choose a product from the list", fontSize = 26.sp)
}
}
)
) {
val products = mutableListOf<ProductDetail>()
repeat(30) {
products.add(ProductDetail("Product $it", "Description of Product $it"))
}
ProductList(
products = products,
onProductClick = { product ->
backStack.add(ProductDetail(product.name, product.description))
},
modifier
)
}
is ProductDetail -> NavEntry(
key = key,
metadata = ListDetailSceneStrategy.detailPane() // 修改处
) {
ProductDetail(
product = key,
modifier
)
}
else -> error("Unknown key: $key")
}
}
)
}我们给列表页和详情页的 NavEntry 都传入了 metadata 参数,通过 listPane() 和 detailPane() 来告知了 Navigation 列表页和详情页的 NavEntry 分别是哪个。
我们还给 listPane() 传入了 detailPlaceholder(详情页占位符)参数,这样未选中列表项时,会默认显示占位的内容。
运行效果:

自定义场景
为了完成自定义场景,我们先来简单看看内置的单页模式场景的源码:
kotlin
internal data class SinglePaneScene<T : Any>(
override val key: Any, // 唯一标识符,用于动画
val entry: NavEntry<T>, // 当前页的 NavEntry
override val previousEntries: List<NavEntry<T>>, // 添加当前页之前的 NavEntry 列表,用于预测性返回动画
) : Scene<T> { // 实现 Scene 接口
override val entries: List<NavEntry<T>> = listOf(entry) // 当前场景需要显示的 NavEntry
override val content: @Composable () -> Unit = { entry.Content() } // 当前场景的内容
// equals、hashCode、toString 方法
}
public class SinglePaneSceneStrategy<T : Any> : SceneStrategy<T> {
// 返回场景类实例,它决定了最终界面的显示内容
override fun SceneStrategyScope<T>.calculateScene(entries: List<NavEntry<T>>): Scene<T> {
return SinglePaneScene(
key = entries.last().contentKey,
entry = entries.last(),
previousEntries = entries.dropLast(1),
)
}
}简单了解过后,我们来完成双页模式场景:
kotlin
data class DoublePaneScene<T : Any>(
override val key: Any,
override val previousEntries: List<NavEntry<T>>,
val startEntry: NavEntry<T>, // 左侧面板导航条目
val endEntry: NavEntry<T> // 右侧面板导航条目
) : Scene<T> {
override val entries: List<NavEntry<T>> = listOf(startEntry, endEntry)
override val content: @Composable (() -> Unit) = {
// 获取窗口大小信息
val windowSizeClass = currentWindowAdaptiveInfo().windowSizeClass
// 如果宽度大于等于中屏,则显示双列
if (windowSizeClass.isWidthAtLeastBreakpoint(WIDTH_DP_MEDIUM_LOWER_BOUND)) {
Row(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) {
Column(modifier = Modifier.weight(0.22f)) {
startEntry.Content()
}
Column(modifier = Modifier.weight(0.78f)) {
endEntry.Content()
}
}
} else {
endEntry.Content()
}
}
companion object {
internal const val START_PANE_KEY = "StartPane"
internal const val END_PANE_KEY = "EndPane"
fun startPane() = mapOf(START_PANE_KEY to true)
fun endPane() = mapOf(END_PANE_KEY to true)
}
}首先,我们接收了两个 NavEntry 实例,待会将会传递进来,分别代表了左侧和右侧的页面。
然后在 content 中,完成了页面的布局:如果是大屏设备,则双列显示;否则,只显示右侧页面。
kotlin
class DoublePaneSceneStrategy<T : Any> : SceneStrategy<T> {
override fun SceneStrategyScope<T>.calculateScene(entries: List<NavEntry<T>>): Scene<T>? {
// 过滤出拥有特定元数据的 NavEntry
val startPane =
entries.filter { it.metadata.containsKey(DoublePaneScene.START_PANE_KEY) }
val endPane =
entries.filter { it.metadata.containsKey(DoublePaneScene.END_PANE_KEY) }
if (startPane.isEmpty() || endPane.isEmpty()) {
// 不同时存在两个面板,说明当前场景策略无法处理
// 默认会被单页模式场景策略处理
return null
}
val startEntry = startPane.last()
val endEntry = endPane.last()
// 构建一个 Key 用于标识场景
val sceneKey = Pair(startEntry, endEntry)
return DoublePaneScene(
key = sceneKey,
previousEntries = entries.dropLast(1),
startEntry = startEntry,
endEntry = endEntry
)
}
}我们找到特定的两个 NavEntry(待会使用时,需要将指定的元数据传入),然后创建 DoublePaneScene 实例返回即可。
具体使用:
kotlin
@Composable
fun MyApp(modifier: Modifier = Modifier) {
val backStack = rememberNavBackStack(ProductList)
NavDisplay(
backStack = backStack,
onBack = {
backStack.removeLastOrNull()
},
sceneStrategy = DoublePaneSceneStrategy(), // 使用DoublePaneScene
entryProvider = { key ->
when (key) {
is ProductList -> NavEntry(
key = key,
// 传递特定元数据
metadata = DoublePaneScene.startPane()
) {
val products = mutableListOf<ProductDetail>()
repeat(30) {
products.add(ProductDetail("Product $it", "Description of Product $it"))
}
ProductList(
products = products,
onProductClick = { product ->
backStack.add(ProductDetail(product.name, product.description))
},
modifier
)
}
is ProductDetail -> NavEntry(
key = key,
// 传递特定元数据
metadata = DoublePaneScene.endPane()
) {
ProductDetail(
product = key,
modifier
)
}
else -> error("Unknown key: $key")
}
}
)
}运行效果:
可以看到,每次点击列表项时,左侧的列表页都会"闪烁"一下。并且按下返回键时,会回到上一个详情页。
这与官方的 ListDetailSceneStrategy 效果并不同,这是因为官方的 ListDetailSceneStrategy 会安装自己的 BackHandler,在大屏幕设备上,按下返回键会直接清空堆栈。而我们的 DoublePaneSceneStrategy 只负责显示,并不会有额外的优化。
"闪烁"是因为 NavDisplay 依靠 sceneKey 来判断是否是同一个场景,当我们点击了新的列表项后,NavDisplay 发现场景已经变化,会销毁并重建整个场景,而这个过程就是我们看到的"闪烁"。
参考
参考郭霖大佬的博客:写给初学者的Jetpack Compose教程,Navigation 3。