引言
在JavaScript的世界中,原型(Prototype)是一个核心概念,它构成了JavaScript面向对象编程的基石。对于许多初学者来说,原型和原型链可能是最令人困惑的概念之一,但一旦深入理解,就会发现它实际上是JavaScript最强大、最灵活的特性之一。本文将通过详细的理论解释和丰富的代码示例,全面剖析JavaScript中的原型对象、原型继承以及原型链机制。
一、原型对象:共享属性和方法的智慧
1.1 什么是原型对象
在JavaScript中,每个函数都有一个特殊的属性prototype,这就是我们所说的原型对象。这个属性指向一个对象,其主要目的是包含可以由特定类型的所有实例共享的属性和方法。
javascript
复制下载
javascript
function Star(uname){
this.uname = uname;
}
// 通过构造函数的prototype属性访问原型对象
console.log(Star.prototype); // 输出原型对象1.2 为什么需要原型对象
考虑以下场景:我们创建了一个构造函数,并实例化了多个对象。如果每个对象都有自己独立的方法副本,会造成内存的极大浪费。
javascript
复制下载
javascript
// 不推荐的方式:每个实例都有独立的方法副本
function Star(uname){
this.uname = uname;
this.sing = function(){
console.log(this.uname + '会唱歌');
}
}
const ldh = new Star('刘德华');
const zxy = new Star('张学友');
console.log(ldh.sing === zxy.sing); // false,方法是不同的函数实例使用原型对象可以优雅地解决这个问题:
javascript
复制下载
javascript
// 推荐的方式:方法定义在原型上,所有实例共享
function Star(uname){
this.uname = uname;
}
Star.prototype.sing = function(){
console.log(this.uname + '会唱歌');
}
const ldh = new Star('刘德华');
const zxy = new Star('张学友');
ldh.sing(); // 刘德华会唱歌
zxy.sing(); // 张学友会唱歌
console.log(ldh.sing === zxy.sing); // true,所有实例共享同一个方法1.3 原型对象的工作原理
当我们访问一个对象的属性或方法时,JavaScript引擎会首先在对象自身查找,如果找不到,就会沿着原型链向上查找,直到找到该属性或到达原型链的末端。
javascript
复制下载
javascript
function Star(uname){
this.uname = uname;
}
Star.prototype.sing = function(){
console.log(this.uname + '会唱歌');
}
const ldh = new Star('刘德华');
// ldh对象本身没有sing方法,但通过原型链可以访问到
console.log(ldh.hasOwnProperty('sing')); // false
console.log('sing' in ldh); // true
ldh.sing(); // 刘德华会唱歌1.4 原型对象中的this指向
一个重要的细节是:无论方法定义在构造函数中还是原型对象中,方法内部的this都指向调用该方法的实例对象。
javascript
复制下载
javascript
function Star(uname){
this.uname = uname;
}
Star.prototype.sing = function(){
// 这里的this指向调用该方法的实例对象
console.log(this.uname + '会唱歌');
}
const ldh = new Star('刘德华');
ldh.sing(); // 输出"刘德华会唱歌",this指向ldh实例二、constructor属性:连接实例与构造函数的桥梁
2.1 原型对象中的constructor属性
每个原型对象都有一个constructor属性,默认指向该原型对象所属的构造函数。
javascript
复制下载
ini
function Star(uname){
this.uname = uname;
}
console.log(Star.prototype.constructor === Star); // true2.2 实例对象中的constructor属性
通过实例对象访问constructor属性时,实际上是通过原型链访问到原型对象的constructor属性。
javascript
复制下载
ini
function Star(uname){
this.uname = uname;
}
const ldh = new Star('刘德华');
console.log(ldh.constructor === Star); // true2.3 重写原型对象时的constructor问题
当我们完全重写原型对象时,会丢失原有的constructor属性,需要手动重新指向。
javascript
复制下载
javascript
function Star(uname){
this.uname = uname;
}
// 完全重写原型对象
Star.prototype = {
sing: function(){
console.log(this.uname + '会唱歌');
},
dance: function(){
console.log(this.uname + '会跳舞');
}
};
console.log(Star.prototype.constructor === Star); // false
console.log(Star.prototype.constructor === Object); // true
// 正确的方式:重写原型对象时手动设置constructor
Star.prototype = {
constructor: Star, // 手动指向构造函数
sing: function(){
console.log(this.uname + '会唱歌');
},
dance: function(){
console.log(this.uname + '会跳舞');
}
};
console.log(Star.prototype.constructor === Star); // true三、对象原型:__proto__与原型链的纽带
3.1 什么是对象原型
每个JavaScript对象(除null外)都有一个内置属性[[Prototype]],在大多数浏览器中可以通过__proto__属性访问。这个属性指向创建该对象的构造函数的原型对象。
javascript
复制下载
ini
function Star(uname){
this.uname = uname;
}
const ldh = new Star('刘德华');
// 实例对象的__proto__指向构造函数的原型对象
console.log(ldh.__proto__ === Star.prototype); // true3.2 __proto__与prototype的关系
prototype是构造函数的属性,指向原型对象__proto__是实例对象的属性,指向构造函数的原型对象
javascript
复制下载
ini
function Star(uname){
this.uname = uname;
}
const ldh = new Star('刘德华');
// 三者关系
console.log(ldh.__proto__ === Star.prototype); // true
console.log(Star.prototype.constructor === Star); // true
console.log(ldh.constructor === Star); // true3.3 对象原型的实际意义
对象原型__proto__的主要意义在于为对象成员查找机制提供一个方向,或者说一条路线,这就是我们接下来要讨论的原型链。
四、原型继承:实现代码复用的优雅方式
4.1 什么是原型继承
原型继承是JavaScript中实现继承的主要方式。其核心思想是:让一个构造函数的原型对象等于另一个构造函数的实例,这样前者就可以继承后者的属性和方法。
4.2 原型继承的实现
javascript
复制下载
ini
// 父类
function Person(){
this.eyes = 2;
this.head = 1;
}
// 子类
function Woman(sex){
this.sex = sex;
}
function Man(sex){
this.sex = sex;
}
// 实现继承:子类的原型对象是父类的实例
Woman.prototype = new Person();
// 修复constructor指向
Woman.prototype.constructor = Woman;
Man.prototype = new Person();
Man.prototype.constructor = Man;
const red = new Woman('女');
console.log(red.eyes); // 2,继承自Person
console.log(red.head); // 1,继承自Person
console.log(red.sex); // 女,自身的属性
const blue = new Man('男');
console.log(blue.eyes); // 2,继承自Person
console.log(blue.head); // 1,继承自Person
console.log(blue.sex); // 男,自身的属性4.3 原型继承的内存效率
通过原型继承,所有子类实例共享父类原型上的方法,这大大提高了内存使用效率。
javascript
复制下载
ini
function Person(){
this.eyes = 2;
}
Person.prototype.breathe = function(){
console.log('呼吸');
};
function Woman(sex){
this.sex = sex;
}
Woman.prototype = new Person();
Woman.prototype.constructor = Woman;
const red = new Woman('女');
const pink = new Woman('女');
// 两个实例共享同一个breathe方法
console.log(red.breathe === pink.breathe); // true4.4 方法重写与属性屏蔽
子类可以重写父类的方法,或者在实例上定义与原型链上同名的属性,实现属性屏蔽。
javascript
复制下载
javascript
function Person(){
this.eyes = 2;
}
Person.prototype.see = function(){
console.log('用眼睛看');
};
function Superman(){
this.eyes = 3; // 属性屏蔽
}
Superman.prototype = new Person();
Superman.prototype.constructor = Superman;
// 方法重写
Superman.prototype.see = function(){
console.log('用超级眼睛看');
};
const clark = new Superman();
console.log(clark.eyes); // 3,访问的是自身属性
clark.see(); // "用超级眼睛看",调用的是重写后的方法五、原型链:JavaScript对象查找机制的核心
5.1 什么是原型链
原型链是JavaScript中实现继承和属性查找的机制。当访问一个对象的属性时,JavaScript引擎会执行以下步骤:
- 首先在对象自身查找该属性
- 如果找不到,则在该对象的原型(
__proto__指向的对象)上查找 - 如果还找不到,则继续在原型的原型上查找
- 依此类推,直到找到该属性或到达原型链的顶端(null)
5.2 原型链的图示与理解
考虑以下代码:
javascript
复制下载
ini
function Person(name){
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.sayHello = function(){
console.log('Hello, I am ' + this.name);
};
function Student(name, grade){
this.name = name;
this.grade = grade;
}
// 实现继承
Student.prototype = new Person();
Student.prototype.constructor = Student;
Student.prototype.study = function(){
console.log(this.name + ' is studying');
};
const tom = new Student('Tom', 5);此时的原型链关系为:
text
复制下载
javascript
tom -> Student.prototype -> Person.prototype -> Object.prototype -> null属性查找过程:
tom.grade:在tom对象自身找到tom.study:在Student.prototype中找到tom.sayHello:在Person.prototype中找到tom.toString:在Object.prototype中找到
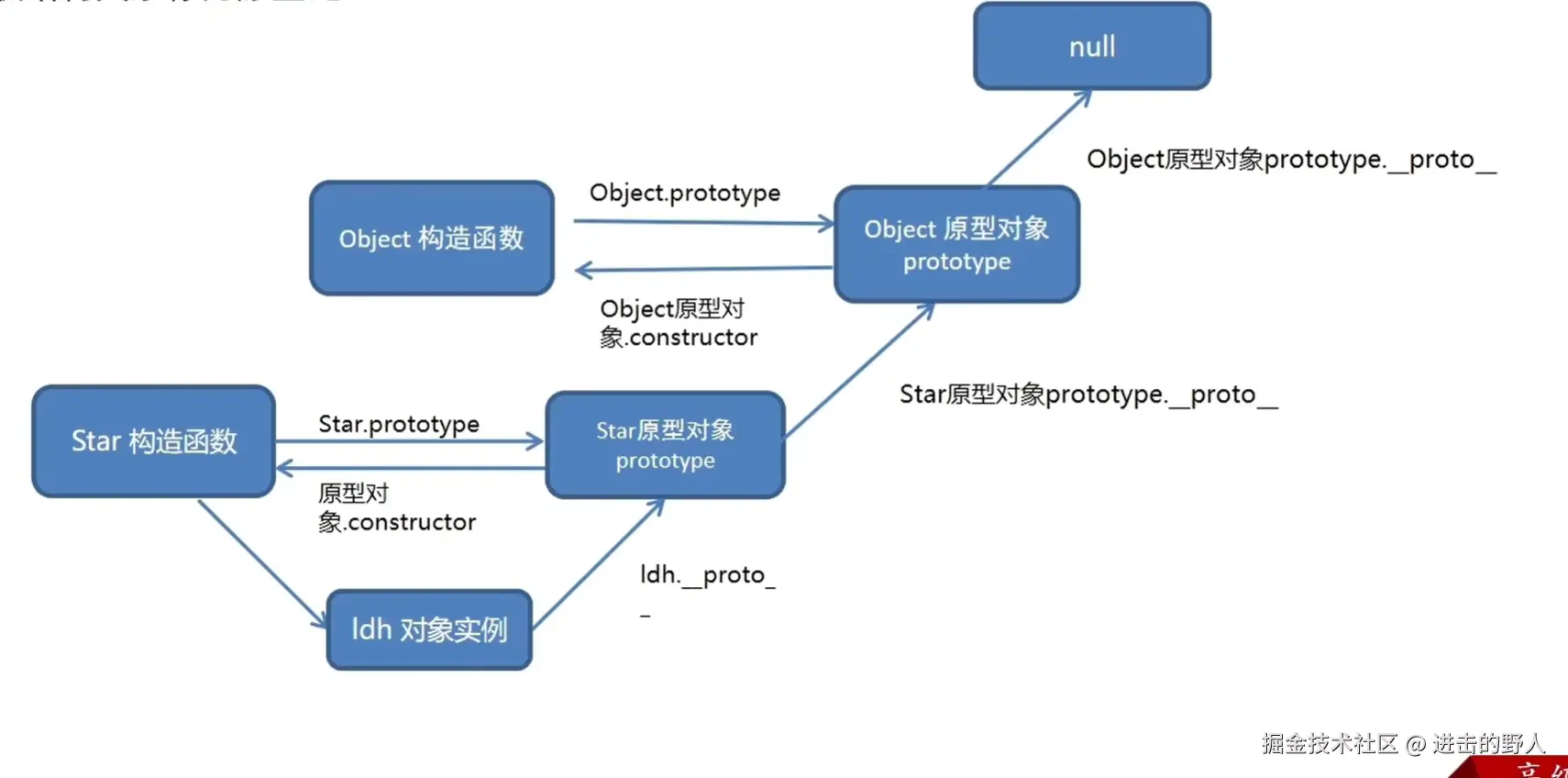
5.3 原型链的终点
所有普通的原型链最终都会指向Object.prototype,而Object.prototype的__proto__指向null,这是原型链的终点。
javascript
复制下载
javascript
function Person(){}
const person = new Person();
console.log(person.__proto__ === Person.prototype); // true
console.log(Person.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype); // true
console.log(Object.prototype.__proto__ === null); // true5.4 instanceof操作符
instanceof运算符用于检测构造函数的prototype属性是否出现在某个实例对象的原型链上。
javascript
复制下载
javascript
function Person(){}
function Student(){}
Student.prototype = new Person();
Student.prototype.constructor = Student;
const tom = new Student();
console.log(tom instanceof Student); // true
console.log(tom instanceof Person); // true
console.log(tom instanceof Object); // true
console.log(tom instanceof Array); // false5.5 原型链与性能考虑
虽然原型链提供了强大的继承机制,但过长的原型链可能会影响性能,因为属性查找需要遍历整个原型链。在实际开发中,应尽量避免过深的继承层次。
六、实际应用与最佳实践
6.1 组合使用构造函数和原型模式
这是创建自定义类型的最常见方式,通过构造函数定义实例属性,通过原型定义共享的方法和属性。
javascript
复制下载
javascript
// 最佳实践:组合使用构造函数和原型模式
function Person(name, age){
// 实例属性
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// 共享方法
Person.prototype.sayHello = function(){
console.log('Hello, I am ' + this.name);
};
Person.prototype.toString = function(){
return '[Person: ' + this.name + ', ' + this.age + ']';
};
const alice = new Person('Alice', 25);
const bob = new Person('Bob', 30);
alice.sayHello(); // Hello, I am Alice
bob.sayHello(); // Hello, I am Bob
console.log(alice.toString()); // [Person: Alice, 25]6.2 原型与对象创建性能
在需要创建大量相似对象的场景中,使用原型可以显著提高性能。
javascript
复制下载
javascript
// 性能对比:使用原型 vs 不使用原型
// 方式1:不使用原型(性能较差)
function createUserWithoutPrototype(name, email) {
return {
name: name,
email: email,
getInfo: function() {
return this.name + ' <' + this.email + '>';
}
};
}
// 方式2:使用原型(性能较好)
function User(name, email) {
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
}
User.prototype.getInfo = function() {
return this.name + ' <' + this.email + '>';
};
function createUserWithPrototype(name, email) {
return new User(name, email);
}
// 测试性能
console.time('Without Prototype');
for (let i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
createUserWithoutPrototype('user' + i, 'user' + i + '@example.com');
}
console.timeEnd('Without Prototype');
console.time('With Prototype');
for (let i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
createUserWithPrototype('user' + i, 'user' + i + '@example.com');
}
console.timeEnd('With Prototype');七、常见问题与解决方案
7.1 原型对象共享引用类型值的问题
当原型对象包含引用类型值时,所有实例会共享同一个引用,这可能导致意外的行为。
javascript
复制下载
ini
// 问题:共享引用类型值
function Person(name){
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.friends = []; // 引用类型值
const alice = new Person('Alice');
const bob = new Person('Bob');
alice.friends.push('Charlie');
console.log(bob.friends); // ['Charlie'],bob也受到了影响
// 解决方案:在构造函数中定义引用类型属性
function BetterPerson(name){
this.name = name;
this.friends = []; // 每个实例有自己的friends数组
}
BetterPerson.prototype.addFriend = function(friend){
this.friends.push(friend);
};
const carol = new BetterPerson('Carol');
const dave = new BetterPerson('Dave');
carol.addFriend('Eve');
console.log(carol.friends); // ['Eve']
console.log(dave.friends); // [],dave不受影响7.2 原型链与枚举属性
使用for...in循环时会遍历对象自身和原型链上的可枚举属性,这可能不是我们想要的行为。
javascript
复制下载
javascript
function Person(name){
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.sayHello = function(){
console.log('Hello');
};
const person = new Person('Alice');
// for...in会遍历原型链上的属性
for(let key in person){
console.log(key); // 输出: name, sayHello
}
// 解决方案:使用hasOwnProperty过滤
for(let key in person){
if(person.hasOwnProperty(key)){
console.log(key); // 只输出: name
}
}结论
JavaScript的原型机制是其面向对象编程的核心,理解原型对象、原型继承和原型链对于掌握JavaScript至关重要。通过原型,JavaScript实现了高效的代码复用和灵活的继承机制。虽然ES6引入了class语法,使其更接近传统面向对象语言,但底层仍然是基于原型的继承。
在实际开发中,我们应该:
- 理解原型链的工作原理,避免过深的继承层次
- 合理使用原型共享方法,提高内存效率
- 注意引用类型值的共享问题
- 掌握现代class语法,同时理解其背后的原型机制
通过深入理解和合理应用原型相关概念,我们能够编写出更加高效、可维护的JavaScript代码,充分利用JavaScript这门语言的强大特性。