算法基础概念与实战应用(三)搜索
文章目录
- 算法基础概念与实战应用(三)搜索
- [1.1 深度优先搜索 - DFS](#1.1 深度优先搜索 - DFS)
-
- [1.1.1 枚举⼦集](#1.1.1 枚举⼦集)
- [1.1.2 组合型枚举](#1.1.2 组合型枚举)
- [1.1.3 枚举排列](#1.1.3 枚举排列)
- [1.1.4 全排列问题](#1.1.4 全排列问题)
- [1.2 DFS](#1.2 DFS)
-
- [1.2.1 选数](#1.2.1 选数)
- [1.2.2 ⻜机降落](#1.2.2 ⻜机降落)
- [1.2.3 ⼋皇后](#1.2.3 ⼋皇后)
- [1.2.4 数独](#1.2.4 数独)
- [1.3 剪枝与优化](#1.3 剪枝与优化)
-
- [1.3.1 数的划分](#1.3.1 数的划分)
- [1.3.2 ⼩猫爬⼭](#1.3.2 ⼩猫爬⼭)
- [1.4 记忆化搜索](#1.4 记忆化搜索)
-
- [1.4.1 Function](#1.4.1 Function)
- [1.4.2 天下第⼀](#1.4.2 天下第⼀)
- [1.4.3 滑雪](#1.4.3 滑雪)
- [2. 宽度优先搜索 - BFS](#2. 宽度优先搜索 - BFS)
- 整体源代码总结

1.1 深度优先搜索 - DFS
1.1.1 枚举⼦集
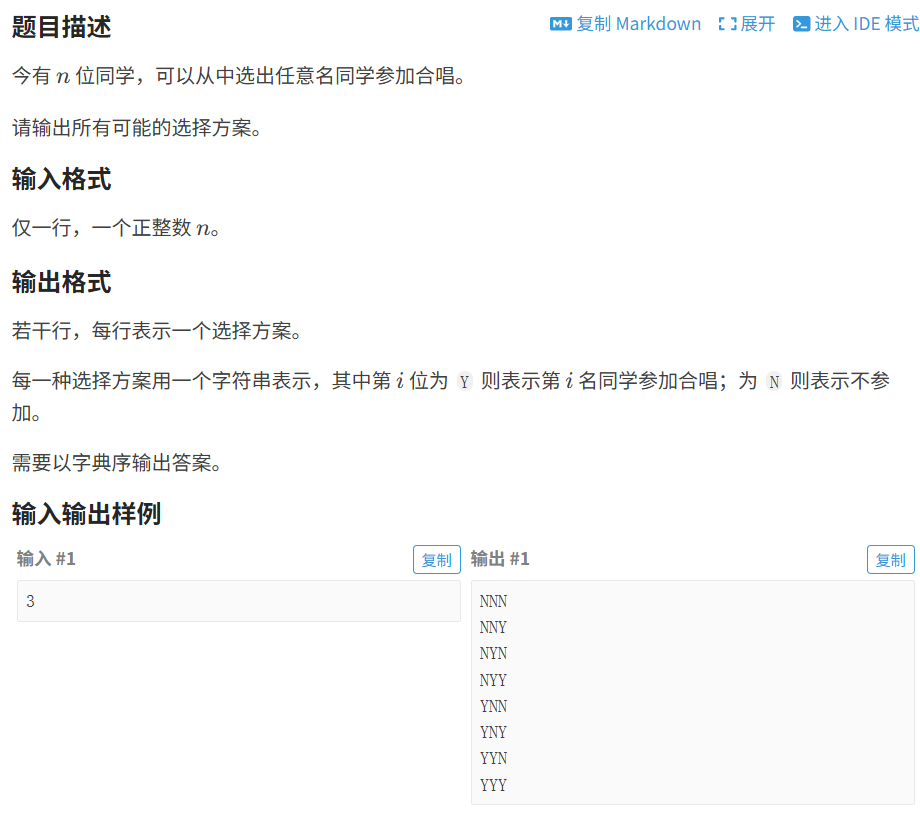
代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int n;
string path; // 记录递归过程中,每⼀步的决策
void dfs(int pos)
{
if (pos > n)
{
// path 就存着前 n 个⼈的决策
cout << path << endl;
return;
}
// 不选
path += 'N';
dfs(pos + 1);
path.pop_back(); // 回溯,清空现场
// 选
path += 'Y';
dfs(pos + 1);
path.pop_back(); // 清空现场
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
dfs(1);
return 0;
}1.1.2 组合型枚举
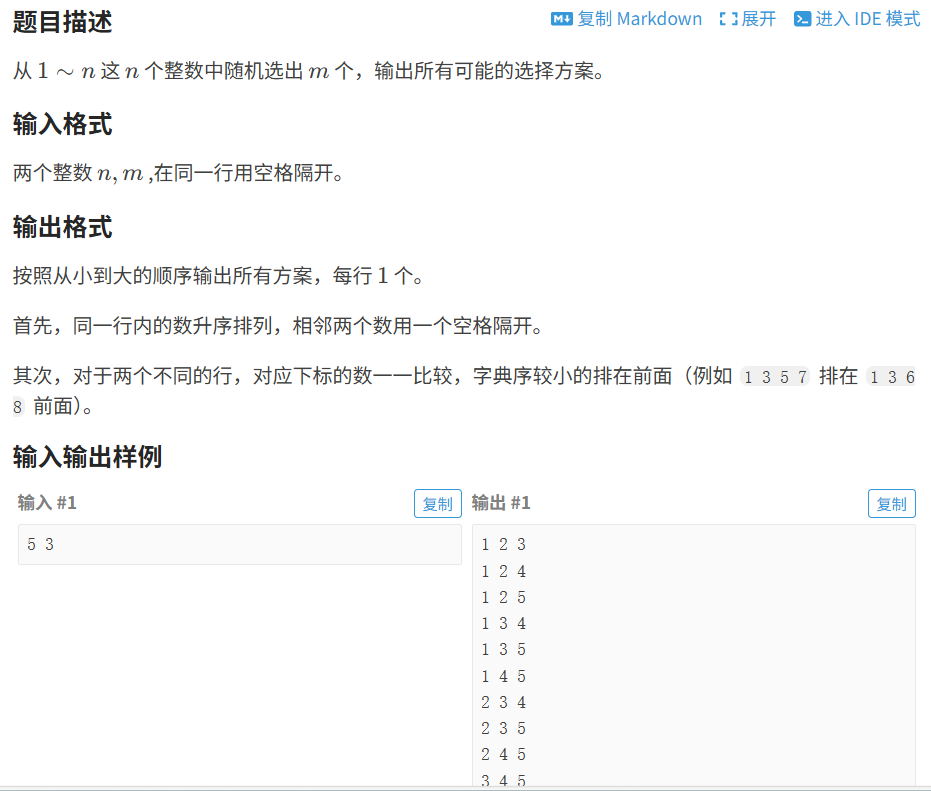
代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int n, m;
vector<int> path;
// path.size();
void dfs(int begin)
{
if (path.size() == m)
{
for (auto x : path) cout << x << " ";
cout << endl;
return;
}
for (int i = begin; i <= n; i++)
{
path.push_back(i);
dfs(i + 1);
path.pop_back(); // 清空现场
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
dfs(1);
return 0;
}1.1.3 枚举排列
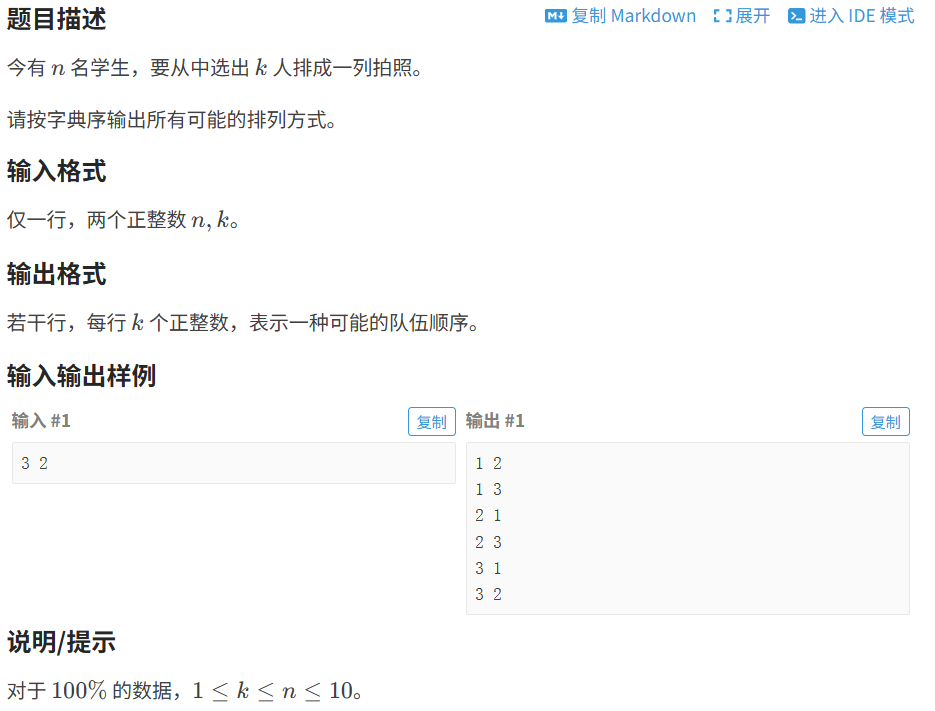
代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int N = 15;
int n, k;
vector<int> path;
bool st[N]; // 标记⼀下哪些数已经选过了
void dfs()
{
if (path.size() == k)
{
for (auto x : path) cout << x << " ";
cout << endl;
return;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (st[i]) continue;
path.push_back(i);
st[i] = true;
dfs();
// 恢复现场
path.pop_back();
st[i] = false;
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> k;
dfs();
return 0;
}1.1.4 全排列问题
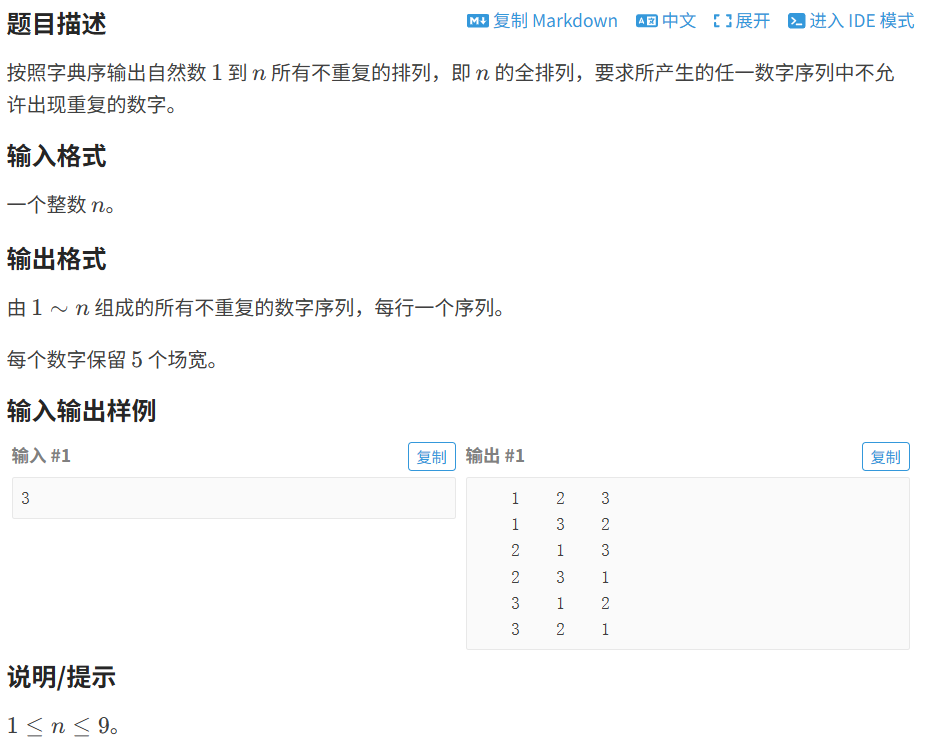
代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int N = 15;
int n;
bool st[N];
vector<int> path;
void dfs()
{
if (path.size() == n)
{
for (auto x : path)
{
printf("%5d", x);
}
cout << endl;
return;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (st[i]) continue;
path.push_back(i);
st[i] = true;
dfs();
// 恢复现场
path.pop_back();
st[i] = false;
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
dfs();
return 0;
}1.2 DFS
1.2.1 选数

代码如下(示例):
c
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 25;
int n, k;
int a[N];
int ret;
int path; // 记录路径中所选择的数的和
bool isprime(int x)
{
if (x <= 1) return false;
// 试除法
for (int i = 2; i <= x / i; i++)
{
if (x % i == 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
void dfs(int pos, int begin)
{
if (pos > k)
{
if (isprime(path)) ret++;
return;
}
for (int i = begin; i <= n; i++)
{
path += a[i];
dfs(pos + 1, i + 1);
path -= a[i]; // 恢复现场
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> k;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
dfs(1, 1);
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}1.2.2 ⻜机降落

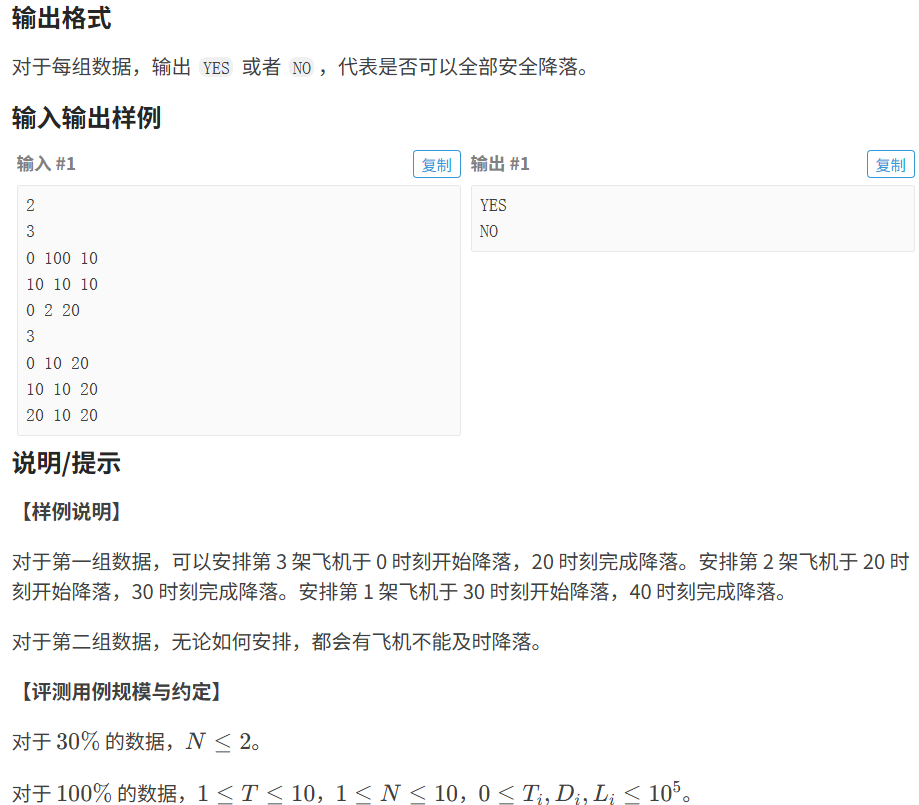

代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 15;
int n;
int t[N], d[N], l[N];
bool st[N]; // 标记路径中哪些⻜机已经摆放过
bool dfs(int pos, int end)
{
if (pos > n)
{
return true;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (st[i] == true) continue; // 剪枝
if (end > t[i] + d[i]) continue; // 剪枝
int newend = max(t[i], end) + l[i];
st[i] = true;
if (dfs(pos + 1, newend)) return true;
st[i] = false; // 回复现场
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
int T; cin >> T;
while (T--) // 多组测试数据的时候,⼀定要注意清空数据
{
memset(st, 0, sizeof st);
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> t[i] >> d[i] >> l[i];
if (dfs(1, 0)) cout << "YES" << endl;
else cout << "NO" << endl;
}
return 0;
}1.2.3 ⼋皇后
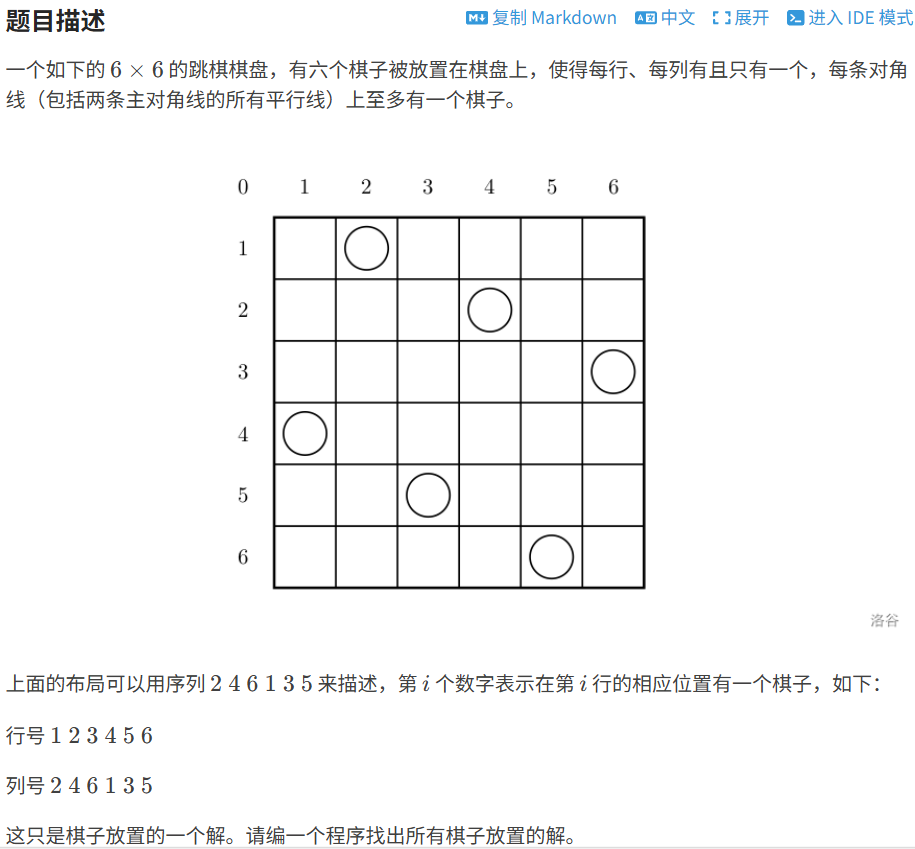
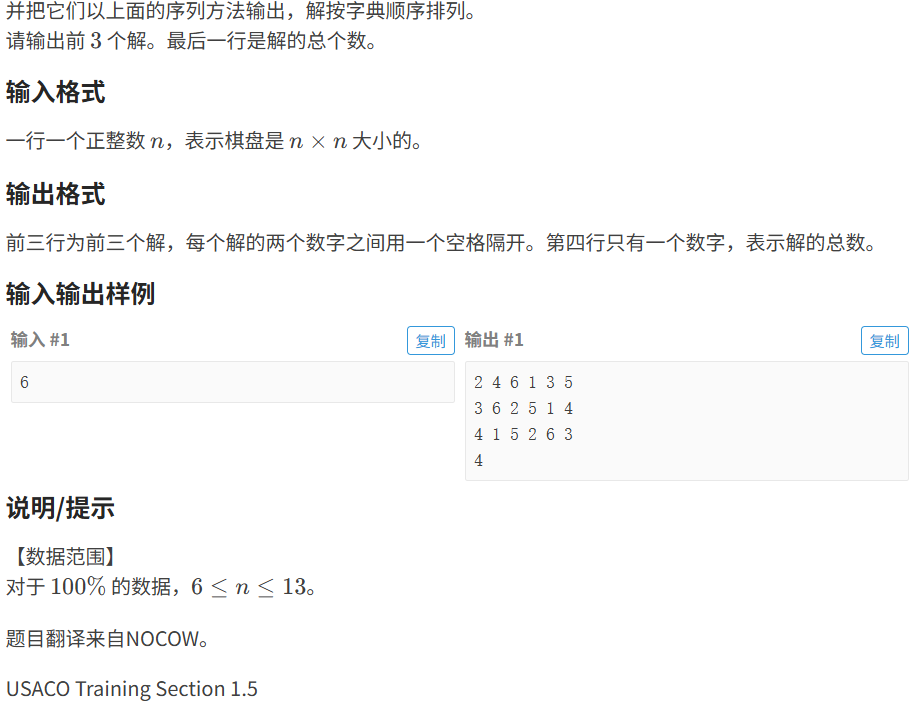

代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int N = 15;
int n;
bool col[N], st1[N * 2], st2[N * 2];
int ret;
vector<int> path;
void dfs(int x)
{
if (x > n)
{
ret++;
if (ret <= 3)
{
for (auto x : path) cout << x << " ";
cout << endl;
}
return;
}
for (int y = 1; y <= n; y++)
{
// 判断能不能摆在这⼀列
if (col[y] || st1[y - x + n] || st2[y + x]) continue; // 剪枝
col[y] = st1[y - x + n] = st2[y + x] = true;
path.push_back(y);
dfs(x + 1);
col[y] = st1[y - x + n] = st2[y + x] = false;
path.pop_back();
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
dfs(1);
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}1.2.4 数独

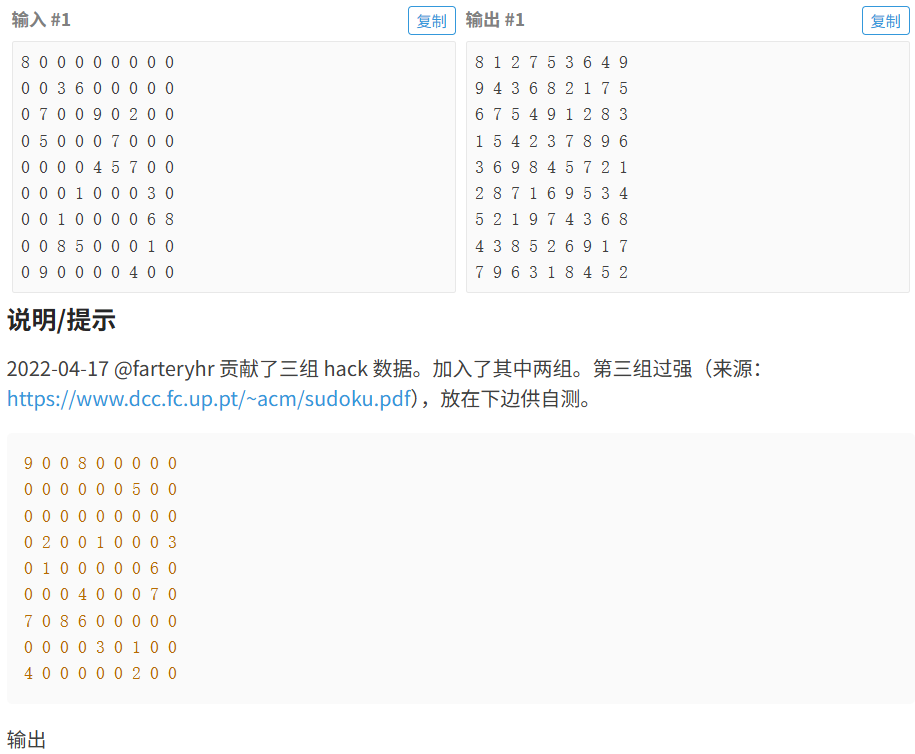


代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10;
int n = 9;
int a[N][N];
bool row[N][N], col[N][N], st[N][N][N];
bool dfs(int i, int j)
{
if (j == n)
{
// 当这⼀⾏填满之后
i++;
j = 0;
}
if (i == n) return true; // 找到⼀种合法的情况,就停⽌递归
if (a[i][j]) return dfs(i, j + 1);
for (int x = 1; x <= 9; x++)
{
if (row[i][x] || col[j][x] || st[i / 3][j / 3][x]) continue; // 剪枝
row[i][x] = col[j][x] = st[i / 3][j / 3][x] = true;
a[i][j] = x;
if (dfs(i, j + 1)) return true;
// 恢复现场
row[i][x] = col[j][x] = st[i / 3][j / 3][x] = false;
a[i][j] = 0;
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
cin >> a[i][j];
int x = a[i][j];
if (x)
{
// 标记⼀下
row[i][x] = col[j][x] = st[i / 3][j / 3][x] = true;
}
}
}
dfs(0, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
cout << a[i][j] << " ";
}
}
return 0;
}1.3 剪枝与优化

1.3.1 数的划分
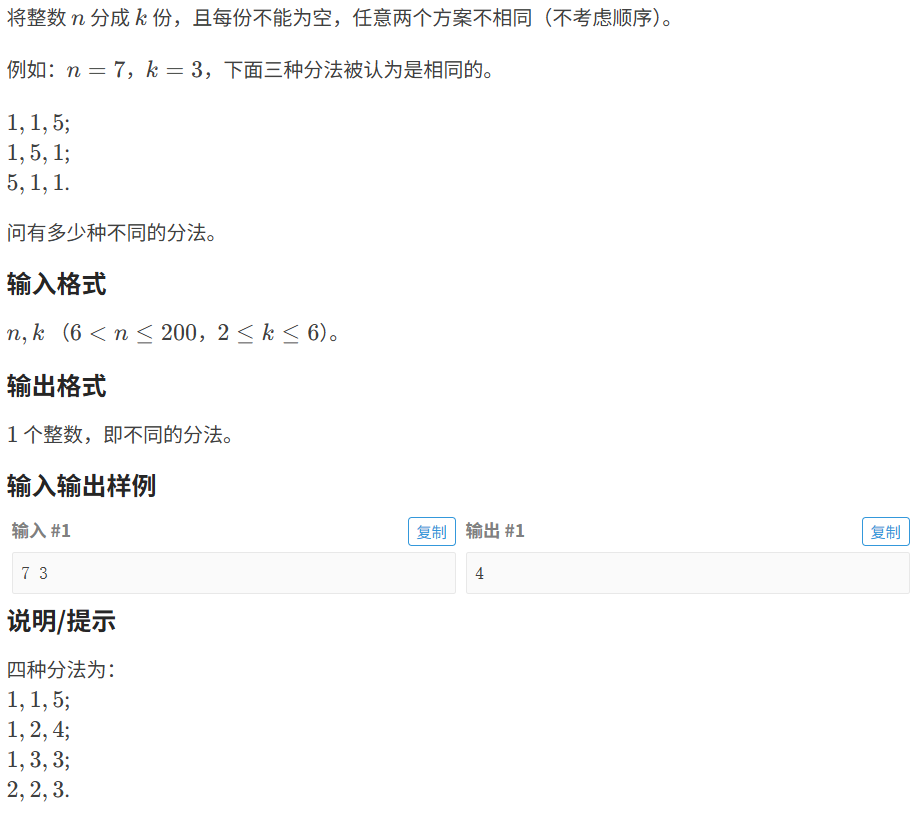

代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int n, k;
int path, ret;
void dfs(int pos, int begin)
{
if (pos == k)
{
if (path == n) ret++;
return;
}
// 可⾏性剪枝
// if(path + begin * (k - pos) > n) return;
for (int i = begin; i <= n; i++)
{
// 可⾏性剪枝
if (path + i * (k - pos) > n) return;
path += i;
dfs(pos + 1, i);
path -= i;
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> k;
dfs(0, 1);
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}1.3.2 ⼩猫爬⼭
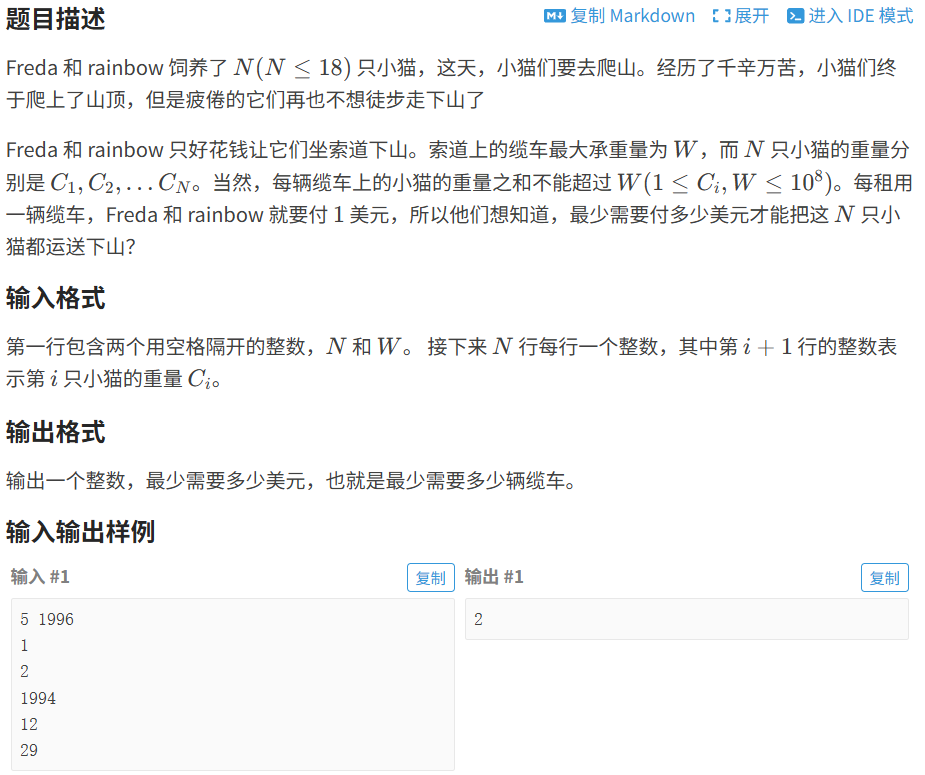

代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 20;
int n, w;
int c[N]; // ⼩猫的信息
int cnt; // 当前⽤了多少⻋
int s[N]; // 每⼀辆⻋⽬前的总重
int ret = N; // 最优解
bool cmp(int a, int b)
{
return a > b;
}
void dfs(int pos)
{
// 策略⼆:最优性剪枝
if (cnt >= ret) return;
if (pos > n)
{
ret = cnt;
return;
}
// 策略三:优化搜索顺序
// 先安排在已有的⻋辆上
for (int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++)
{
// 策略⼀:可⾏性剪枝
if (s[i] + c[pos] > w) continue;
s[i] += c[pos];
dfs(pos + 1);
s[i] -= c[pos]; // 恢复现场
}
// 重开⼀辆⻋
cnt++;
s[cnt] = c[pos];
dfs(pos + 1);
// 恢复现场
s[cnt] = 0;
cnt--;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> w;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> c[i];
// 策略三:优化搜索顺序
sort(c + 1, c + 1 + n, cmp);
dfs(1);
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}1.4 记忆化搜索
1.4.1 Function


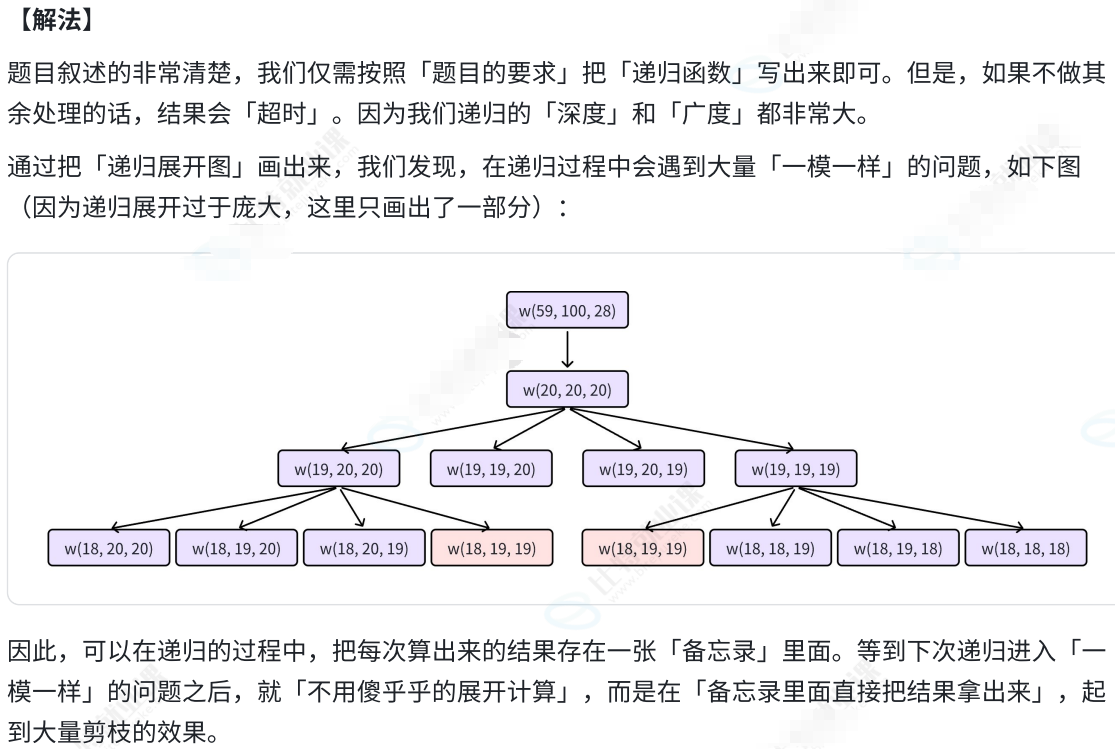
代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 25;
LL a, b, c;
LL f[N][N][N]; // 备忘录
LL dfs(LL a, LL b, LL c)
{
if (a <= 0 || b <= 0 || c <= 0) return 1;
if (a > 20 || b > 20 || c > 20) return dfs(20, 20, 20);
if (f[a][b][c]) return f[a][b][c];
if (a < b && b < c) return f[a][b][c] = dfs(a, b, c - 1) + dfs(a, b - 1, c
- 1) - dfs(a, b - 1, c);
else return f[a][b][c] = dfs(a - 1, b, c) + dfs(a - 1, b - 1, c) + dfs(a
- 1, b, c - 1) - dfs(a - 1, b - 1, c - 1);
}
int main()
{
while (cin >> a >> b >> c)
{
// 多组测试数据:不需要清空
if (a == -1 && b == -1 && c == -1) break;
printf("w(%lld, %lld, %lld) = %lld\n", a, b, c, dfs(a, b, c));
}
return 0;
}1.4.2 天下第⼀

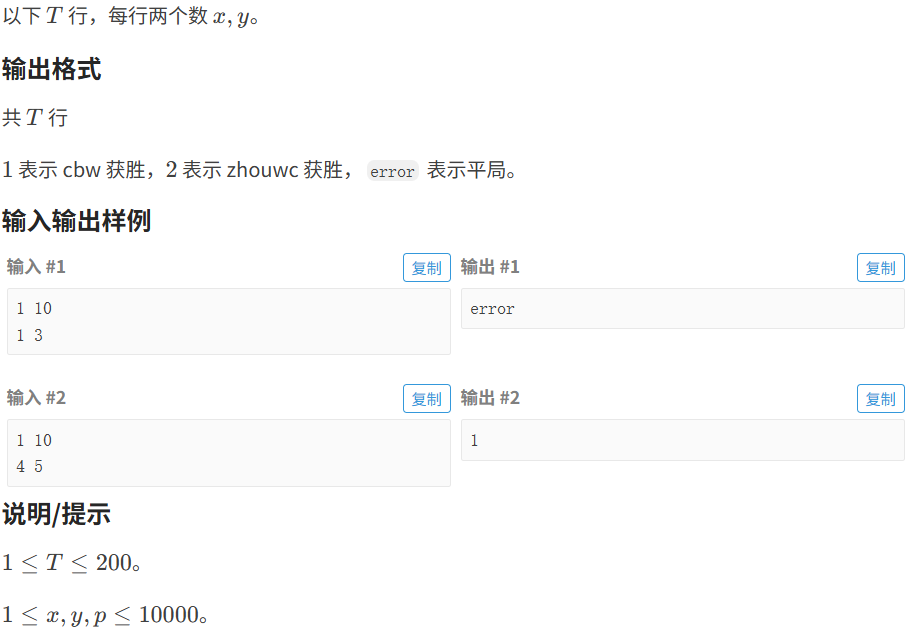

代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e4 + 10;
int x, y, p;
char f[N][N]; // 备忘录
char dfs(int x, int y)
{
if (f[x][y]) return f[x][y]; // 剪枝
f[x][y] = '3'; // 这个状态已经访问过了,之后再遇到时,表⽰平局
if (x == 0) return f[x][y] = '1';
if (y == 0) return f[x][y] = '2';
return f[x][y] = dfs((x + y) % p, (x + y + y) % p);
}
int main()
{
int T; cin >> T >> p;
while (T--)
{
cin >> x >> y;
char ret = dfs(x, y);
if (ret == '1') cout << 1 << endl;
else if (ret == '2') cout << 2 << endl;
else cout << "error" << endl;
}
}1.4.3 滑雪



代码如下(示例):
c
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
int n, m;
int a[N][N];
int f[N][N]; // 备忘录
int dx[] = { 0, 0, 1, -1 };
int dy[] = { 1, -1, 0, 0 };
int dfs(int i, int j)
{
if (f[i][j]) return f[i][j];
int len = 1;
// 上下左右四个⽅向搜
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int x = i + dx[k], y = j + dy[k];
if (x < 1 || x > n || y < 1 || y > m) continue;
if (a[i][j] <= a[x][y]) continue;
len = max(dfs(x, y) + 1, len);
}
return f[i][j] = len;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
cin >> a[i][j];
int ret = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
ret = max(ret, dfs(i, j));
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}2. 宽度优先搜索 - BFS
整体源代码总结
代码如下(示例):
c