MATH类:是一个帮助我们进行数学计算的工具类
私有化构造方法,所有的方法都是静态的

package com.jdL.day19classwork;
public class MathMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//abs绝对值
System.out.println(Math.abs(-11));
System.out.println(Math.abs(1));
System.out.println(Math.abs(0));
//celi向上取整
System.out.println(Math.ceil(-1.1));
System.out.println(Math.ceil(1.2));
System.out.println(Math.ceil(0.1));
//floor向下取整
System.out.println(Math.floor(-1.1));
System.out.println(Math.floor(0.1));
System.out.println(Math.floor(2.1));
//round四舍五入
System.out.println(Math.round(-1.461));
System.out.println(Math.round(0.453));
System.out.println(Math.round(2.462));
//max(a,b)求a,b中的最大值
System.out.println(Math.max(1,1.2));
System.out.println(Math.max(2,-1));
System.out.println(Math.max(2,0.99));
//pow(a,b)返回a的b次幂的值
System.out.println(Math.pow(1,2));
System.out.println(Math.pow(2,-1));
System.out.println(Math.pow(2,2));
//random返回值为double的随机值,范围为[0.0,1.0)
System.out.println(Math.random());
System.out.println("--------------------");
//写一个[1,100]
System.out.println(Math.floor(Math.random() * 100 + 1));
//开根号
System.out.println(Math.sqrt(4));
//开立方根
System.out.println(Math.cbrt(8));
}
}小练习:
1、判断一个数是否为质数
package com.jdL.day19classwork;
public class MathTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean result=getSqrt(16);
System.out.println(result);
}
public static boolean getSqrt(int number){
for (int i=2;i<=Math.sqrt(number);i++){
if(number%i==0){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}2、自幂数:一个n位自然数自身各个数位上数字的n次幂之和

package com.jdL.day19classwork;
public class MathTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//System.out.println(getNumberDigit(200));
int count=0;
for(int i=10000;i<100000;i++){
if(getNarcissisticNumber(i)!=0){
System.out.println(getNarcissisticNumber(i));
count++;
}
}
if(count==0){
System.out.println("不存在自幂数");
}
}
//判断一个数是否是自幂数
public static double getNarcissisticNumber(int number){
//计算三位数中有多少水仙花数
//先获取数字的位数
double digit=getNumberDigit(number);
double finalNumber=number;
double sum=0;
while(number!=0){
int ge=number%10;
number=number/10;
sum=sum+Math.pow(ge,digit);
}
if(sum==finalNumber){
return finalNumber;
}
return 0;
}
//判断一个整数是几位数
public static int getNumberDigit(int number){
int count=0;
while(number!=0){
number=number/10;
count++;
}
return count;
}
}
System:是一个帮助我们进行数学计算的工具类,提供了一些与系统相关的方法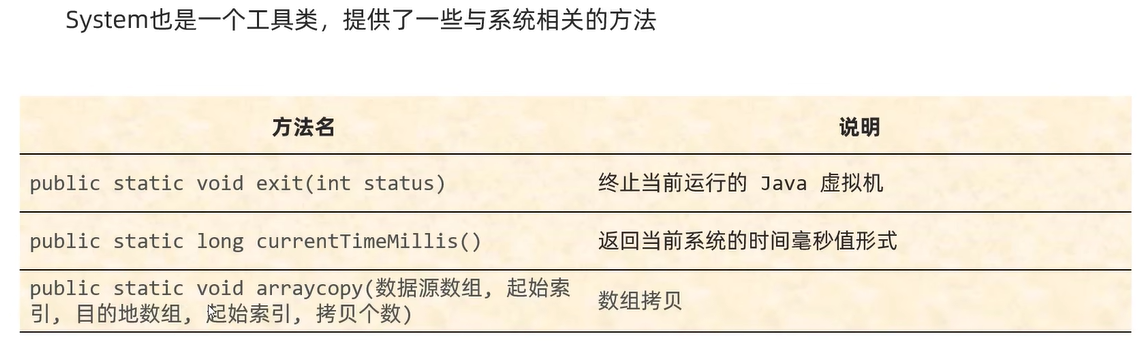
System.exit(0);
System.out.println("看看");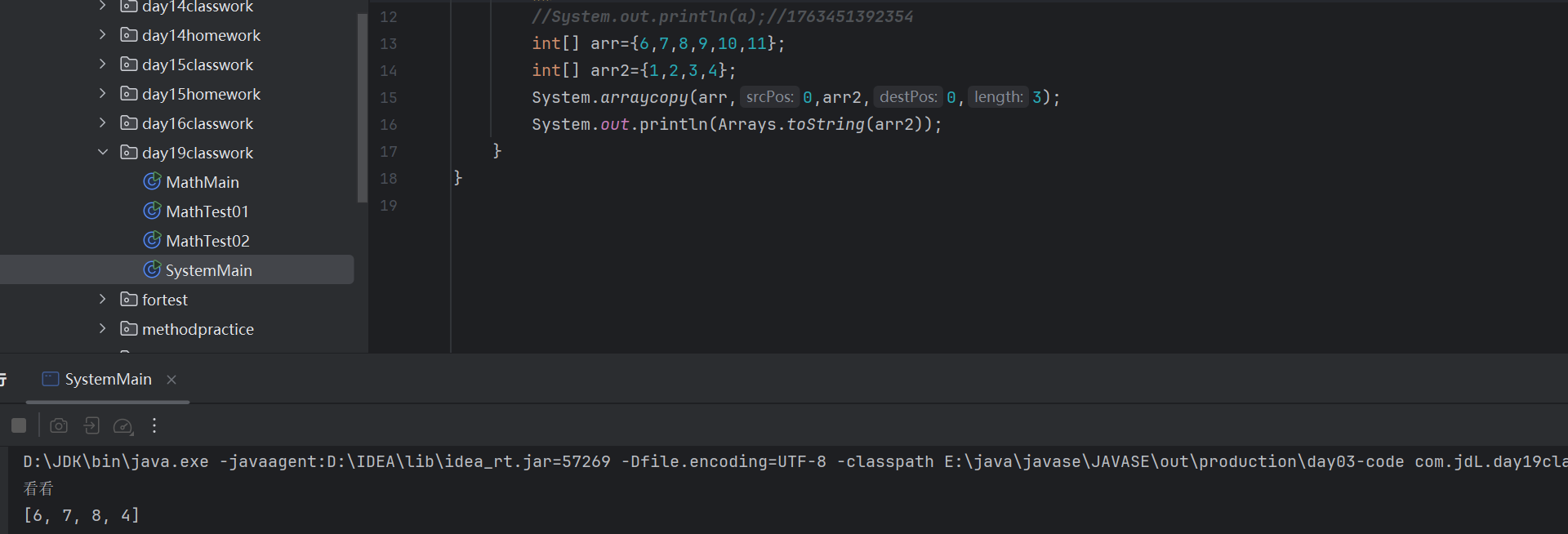
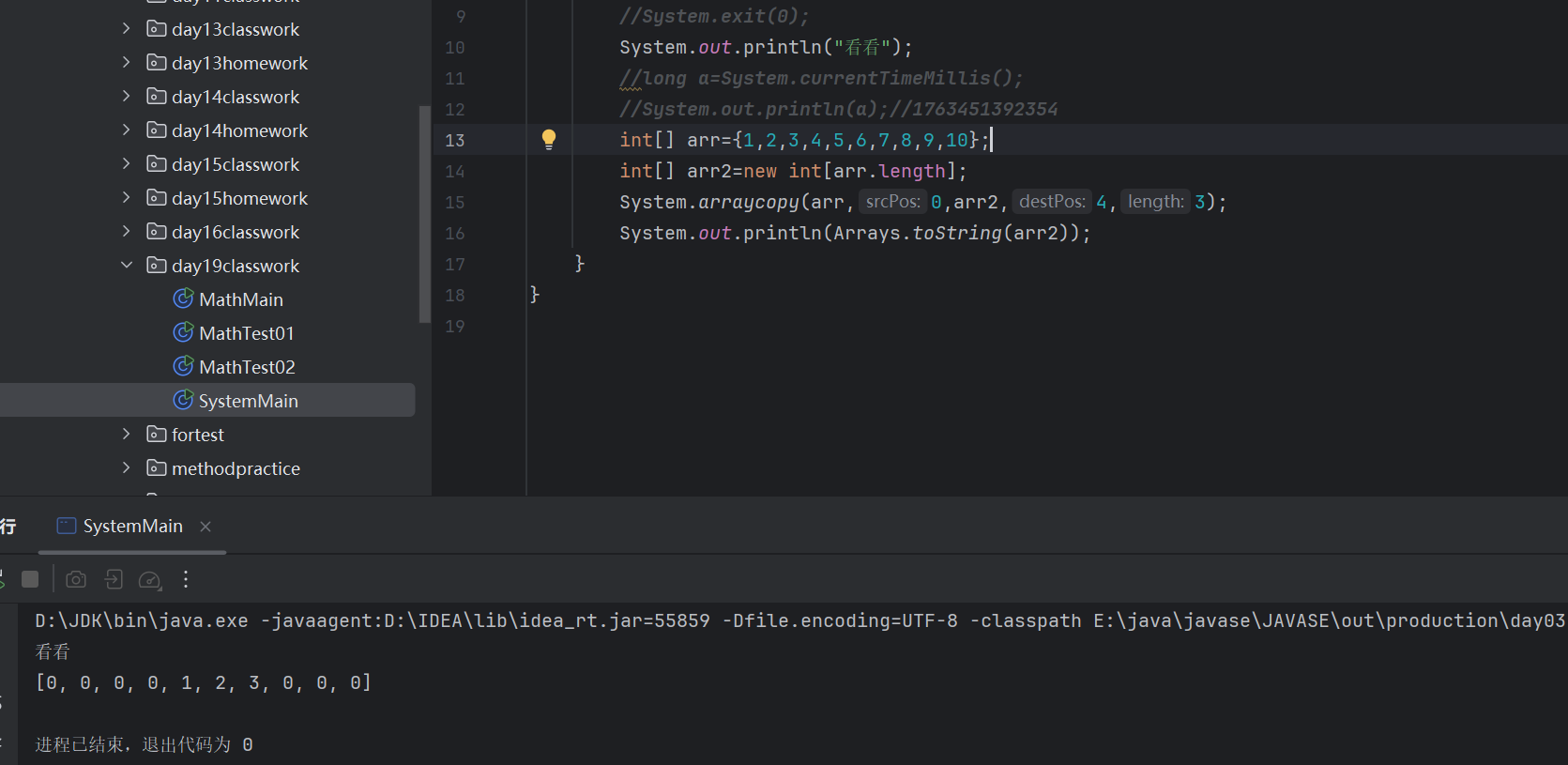
System.arraycopy(数据源数组,起始索引,目的地数组,起始索引,拷贝的元素个数)细节:
1、如果数据源数组和目的地数组都是基本数据类型,那么这两个数组的类型要完全一致,否则会报错;
2、在拷贝的时候需要考虑数组的长度,如果超出范围也会报错;
3、如果数据源数组和目的数组是引用数据类型的,那么子类类型可以赋值给父类类型
Runtime表示当前虚拟机运行的环境

Runtime没有办法直接new一个对象出来,因为Runtime表示虚拟机的运行环境,一台虚拟机只有一个运行环境,所以new出来的对象也没有意义
Runtime.getRuntime().exit(0);Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()Runtime.getRuntime().maxMemory()System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().exec("notepad");Object:
object是java中的顶级父类,所有的类都直接或者间接继承与object


public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
// ... 构造方法和其他代码 ...
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{name='" + name + "', age=" + age + "}";
}
}
equals中如果没有重写方法,比较的是地址值是否相等,equals如果想要比较对象的属性值,就需要重写里面的方法,重写也是类似的
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof User user)) return false;
return id == user.id && Objects.equals(username, user.username)
&& Objects.equals(password, user.password)
&& Objects.equals(path, user.path)
&& Objects.deepEquals(data, user.data);
}clone:对象克隆
把A对象中的属性值完全拷贝给B对象,也叫对象拷贝,或者是对象复制
JAVA中克隆有两种:
浅克隆:对于引用数据类型,克隆的两个对象都是记录的同一个地址值,这会导致如果一个对象改变了数据,会导致另外一个对象记录的数据也已经发生变化了
object中的clone是浅克隆
深克隆:深克隆对于引用数据类型,是会直接创建一个新的对象
//克隆 //方法在底层会帮我们创建一个对象,并把原对象中的数据拷贝过去 //细节: //1、重新Object中的clone方法 //2、让JavaBean类实现Cloneable接口 //3、创建原对象并调用clone方法

package com.jdL.day19classwork;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.StringJoiner;
//Cloneable这个接口里面没有抽象方法,说明这个接口是一个标记性接口
//Cloneable一旦实现了,就说明当前的类可以被克隆
public class User implements Cloneable{
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String path;
private int[] data;
public User() {
}
public User(int id, String username, String password, String path, int[] data) {
this.id = id;
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
this.path = path;
this.data = data;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public String getPath() {
return path;
}
public void setPath(String path) {
this.path = path;
}
public int[] getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(int[] data) {
this.data = data;
}
public String toString(){
return id+username+password+path+ arrToString();
}
//将数组变成字符串
public String arrToString(){
StringJoiner sj = new StringJoiner(",","[","]");
for(int i=0;i<data.length;i++){
sj.add(data[i]+"");
}
return sj.toString();
}
//重写clone
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
//调用父类的克隆方法
//让JAVA帮我们克隆一个对象,并且反馈克隆之后的对象
return super.clone();
}
}package com.jdL.day19classwork;
public class UserTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
//创建一个对象
int[] data={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
User u1 = new User(1,"zhangsan","123456","gir111",data);
//克隆
//方法在底层会帮我们创建一个对象,并把原对象中的数据拷贝过去
//细节:
//1、重新Object中的clone方法
//2、让JavaBean类实现Cloneable接口
//3、创建原对象并调用clone方法
User u2= (User) u1.clone();
System.out.println(u1);
System.out.println(u2);
}
}Objects类

BigInteger:
在JAVA中,整数有四种类型:byte,short,int long
在底层占用的字节个数:byte1个字节,short2个字节,int4个字节,long8个字节

package com.jdL.day19classwork;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.Random;
public class BigIntegerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random rand=new Random();
BigInteger big=new BigInteger(9,rand);//生成一个范围在0-2^9-1之间的一个大整数
System.out.println(big);
BigInteger big1=new BigInteger("12345");
System.out.println(big1);
BigInteger big2=new BigInteger("12345",8);
System.out.println(big2);
}
}BigInteger.valueOf(12345);BigInteger big1=new BigInteger("12345");
这两种范围表示的数据的区别是什么呢。
1、其中valueOf的话只能表示long范围的的;
2、valueOf对其中常用的-16到16之间的数字进行了优化,会提前创建好BigIntege的对象,如果多次获取就不会创建新的

注意:BigInteger里面的对象一旦创建,内部的数据不能发生改变
比如下面的这段,db1和db3是不同的对象
//验证BigInteger中对象一旦创建,内部的数据不能发生改变
BigInteger db1=BigInteger.valueOf(1);
BigInteger db2=BigInteger.valueOf(2);
BigInteger db3=db1.add(db2);
System.out.println(db3);
BigInteger中的成员方法:

注意:BigInteger的成员方法都是需要调用的
package com.jdL.day19classwork;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class BigIntegerTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//BigInteger的成员方法
BigInteger bd1=BigInteger.valueOf(3);
BigInteger bd2=BigInteger.valueOf(10);
BigInteger bd3=BigInteger.valueOf(3);
//加
System.out.println(bd2.add(bd1));
//减BigInteger
System.out.println(bd2.subtract(bd1));
//乘
System.out.println(bd2.multiply(bd1));
//除
System.out.println(bd2.divide(bd1));
//取余
System.out.println(bd2.mod(bd1));
//除法,获取商和余数
BigInteger[] arr=bd2.divideAndRemainder(bd1);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
//比较大小
System.out.println(bd1.equals(bd3));
//次幂
System.out.println(bd1.pow(2));
//返回最大值和最小值
System.out.println(bd1.max(bd2));
//转成int类型整数
System.out.println(bd2.intValue());
}
}
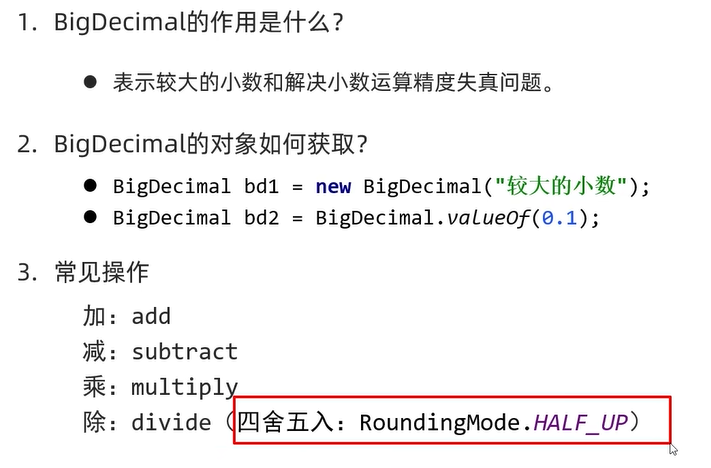
BigDecima:
构造方法和静态方法
用于小数的精确计算
用来表示很大的小数
package com.jdL.day19classwork;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class BigDecimaTets {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//BigDecimal通过构造方法获取
//方式1:通过double的方式来创建小数
//这种方式有可能是不精确的,不建议用
BigDecimal db1=new BigDecimal(1.222);
//方式2:通过字符串的方式创建小数
BigDecimal db2=new BigDecimal("1.333");
//通过valueof静态方法创建小数
BigDecimal db3=BigDecimal.valueOf(1.444);
System.out.println(db1+","+db2+","+db3);
}
}如果要表示的小数不大,没有超出double的范围,建议使用静态方法
如果要表示的小数很大,超出了double的方法,建议使用字符串
如果是创建0~10之间的数据,包含0,包含10,使用静态方法会返回已经创建好的对象,不会new一个对象

package com.jdL.day19classwork;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.math.RoundingMode;
public class BigDecimaTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigDecimal db1=BigDecimal.valueOf(10.0);
BigDecimal db2=BigDecimal.valueOf(2.0);
BigDecimal db3=BigDecimal.valueOf(10.0101);
BigDecimal db4=BigDecimal.valueOf(2.1);
//加
System.out.println(db1.add(db2));
//subtract
System.out.println(db1.subtract(db2));
//乘
System.out.println(db1.multiply(db2));
//除
System.out.println(db1.divide(db2));
//除
System.out.println(db4.divide(db3,2, RoundingMode.HALF_UP));
}
}注意:如果divide是刚好可以整除,可以不加舍入和参数,但是如果除不尽,就不能直接除
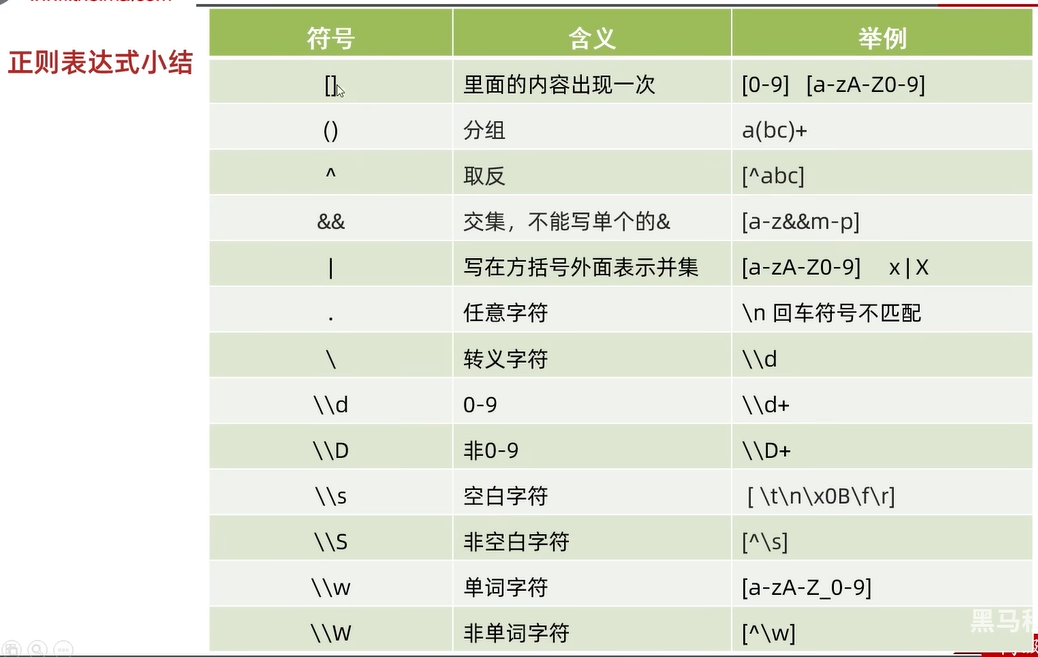
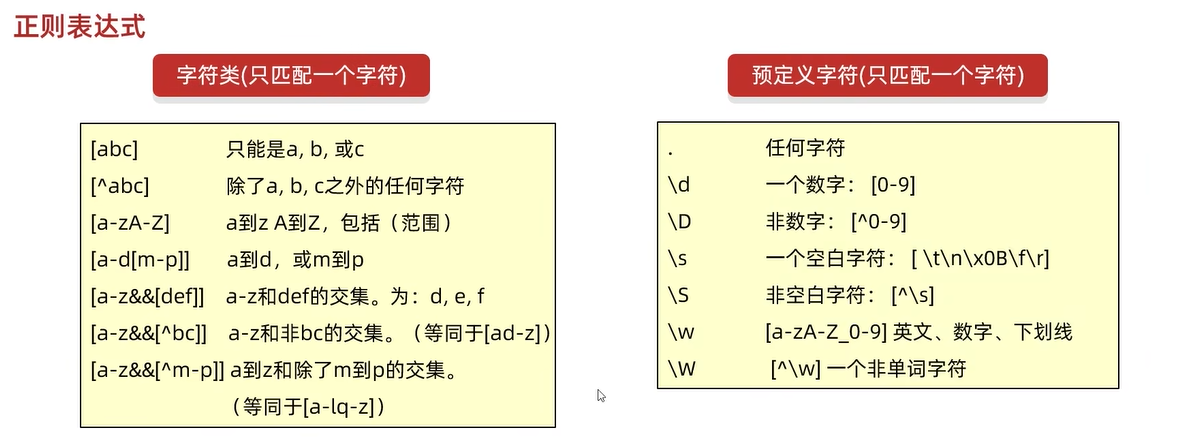
正则表达式:
正则表达式可以校验字符串是否满足一定的规则,并用来校验数据格式的合法性
QQ号的验证
package com.jdL.day19classwork;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class regularExpressionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//判断QQ号是否满足要求
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一个QQ号");
String QQnumber=sc.nextLine();
char[] qq=QQnumber.toCharArray();
if(qq.length<6||qq.length>20){
System.out.println("QQ号格式不符");
return;
}else if(qq[0]=='0'){
System.out.println("QQ号不能以0开头");
return;
}
for(int i=0;i<qq.length;i++){
if(!(qq[i]>='0'&&qq[i]<='9')){
System.out.println("QQ号必须全为数字");
return;
}
}
System.out.println("QQ号正确");
}
}正则表达式
package com.jdL.day19classwork;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class qqMatchs {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String qq="023456789";
System.out.println(qq.matches("[1,9]\\d{5,19}"));
}
}正则表达式的作用:
1、可以校验字符串是否满足一定的规则
2、在一段文本之中查找满足要求的内容

字符串匹配:
package com.jdL.day19classwork;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class qqMatchs {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("--------1--------");
System.out.println("a".matches("[abc]"));//true
System.out.println("d".matches("[abc]"));//false
System.out.println("0".matches("[abc]"));//false
System.out.println("aa".matches("[abc][abc]"));//true
System.out.println("--------2--------");
System.out.println("a".matches("[^abc]"));//false
System.out.println("d".matches("[^abc]"));//true
System.out.println("0".matches("[^abc]"));//true
System.out.println("dd".matches("[^abc][^abc]"));//true
System.out.println("--------3--------");
System.out.println("a".matches("[a-zA-Z]"));//true
System.out.println("A".matches("[a-zA-Z]"));//true
System.out.println("0".matches("[a-zA-Z]"));//false
System.out.println("AA".matches("[a-zA-Z]"));//false
System.out.println("--------4--------");
System.out.println("a".matches("[a-d[m-p]]"));//true
System.out.println("m".matches("[a-d[m-p]]"));//true
System.out.println("0".matches("[a-d[m-p]]"));//false
System.out.println("AA".matches("[a-d[m-p]]"));//false
System.out.println("--------5--------");
System.out.println("a".matches("[a-z&&[def]]"));//false
System.out.println("z".matches("[a-z&&[def]]"));//false
System.out.println("0".matches("[a-z&&[def]]"));//false
System.out.println("d".matches("[a-z&&[def]]"));//true
System.out.println("--------6--------");
System.out.println("a".matches("[a-z&&[^def]]"));//true
System.out.println("d".matches("[a-z&&[^def]]"));//false
System.out.println("z".matches("[a-z&&[^def]]"));//true
System.out.println("0".matches("[a-z&&[^def]]"));//false
System.out.println("--------7--------");
System.out.println("a".matches("[a-z&&[^d-f]]"));//true
System.out.println("d".matches("[a-z&&[^d-f]]"));//false
System.out.println("0".matches("[a-z&&[^d-f]]"));//false
}
}预定义字符
package com.jdL.day19classwork;
public class MatchTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//
System.out.println("-----------1-------------");
System.out.println("你".matches("."));//true
System.out.println("你好".matches("."));//false
System.out.println("你#".matches("."));//false
System.out.println("你好01".matches("...."));//true
//
System.out.println("-----------2-------------");
System.out.println("你".matches("\\d"));//false
System.out.println("1".matches("\\d"));//true
System.out.println("12".matches("\\d\\d"));//true
//
System.out.println("-----------3-------------");
System.out.println("你".matches("\\D"));//true
System.out.println("1".matches("\\D"));//false
System.out.println("1你".matches("\\D\\D"));//false
System.out.println("我你".matches("\\D\\D"));//true
//
System.out.println("-----------4-------------");
System.out.println("1".matches("\\w"));//true
System.out.println("a".matches("\\w"));//true
System.out.println("A".matches("\\w"));//true
System.out.println("Aa".matches("\\w\\w"));//true
System.out.println("你".matches("\\w"));//false
System.out.println("_".matches("\\w"));//true
//
System.out.println("-----------5-------------");
System.out.println("1".matches("\\W"));//false
System.out.println("a".matches("\\W"));//false
System.out.println("A".matches("\\W"));//false
System.out.println("Aa".matches("\\W\\W"));//false
System.out.println("你".matches("\\W"));//true
System.out.println("你我".matches("\\W\\W"));//true
System.out.println("_".matches("\\W"));//false
System.out.println("#".matches("\\W"));//true
System.out.println("-----------6-------------");
System.out.println(" ".matches("\\s"));//true
System.out.println("a".matches("\\s"));//false
System.out.println("A".matches("\\s"));//false
System.out.println("Aa".matches("\\s\\s"));//false
System.out.println("你".matches("\\s"));//false
System.out.println("0".matches("\\s"));//false
System.out.println("-----------7-------------");
System.out.println(" ".matches("\\S"));//false
System.out.println("a".matches("\\S"));//true
System.out.println("A".matches("\\S"));//true
System.out.println("Aa".matches("\\S\\S"));//true
System.out.println("你".matches("\\S"));//true
System.out.println("0".matches("\\S"));//true
}
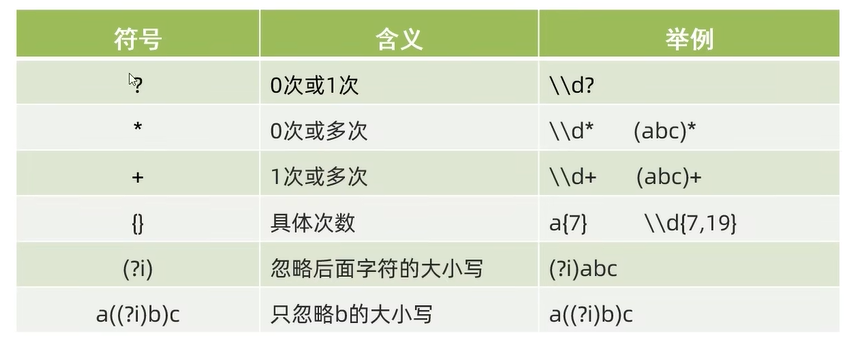
}System.out.println("------------数量词------------------");
System.out.println("024343dedfes".matches("\\w{6,}"));//true
System.out.println("dedfes".matches("\\w{6}"));//true
System.out.println("dedfed123s".matches("\\w{6,12}"));//true
System.out.println("dedfed".matches("[a-z]{6}"));//true
System.out.println("de1fEd".matches("[a-zA-Z0-9]{6}"));//true
System.out.println("de1fEd".matches("[\\w&&[^_]]{6}"));//true
System.out.println("de1_Ed".matches("[\\w&&[^_]]{6}"));//false正则表达式练习:
//正则表达式判断手机号
//心得:从左到右一位一位的书写
//15972909809
//String phone="1[3-9][0-9]{9}";
//判断输入的手机号
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("输入手机号");
String phone=sc.next();
System.out.println(phone.matches("1[3-9][0-9]{9}"));
}正确示例:
//020-2324243,021242424,027-42424
//String regist="0\\d{2,3}-?[1-9]\\d{4,9}";
System.out.println("输入座机号码");
String regist=sc.next();
System.out.println(regist.matches("0\\d{2,3}-?[1-9]\\d{4,9}"));System.out.println("输入邮箱号码");
String email="2272567531@qq.com";
//"\\W+@[\\w&&[^_]]{2,6}\\(.[a-zA-Z]{2,3}){1,2}";
System.out.println(email.matches("\\w+@[\\w&&[^_]]{2,6}(\\.[a-zA-Z]{2,3}){1,2}"));
package com.jdL.day19classwork;
public class MatchPractice02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//正则表达式校验用户名
//大写字母,小写字母,下划线,数字,一共4-16位
String userName="";
System.out.println(userName.matches("\\w{4,16}"));
//身份证号码
String idCard1="340823199507262112";
System.out.println(idCard1.matches("[1-9]\\d{16}[\\d|[xX]]"));
//身份证的严格要求
//前面6位:省份,市区,派出所等信息,第一位不能是0,后面5位是任意数字
//年份的前半段:18,19,20
//年份的后半段:任意数字出现两次
//月份01-09,11,12
//日期:0-31
//后面四位:前面三位是任意数字出现3次,最后一位:任意数字,x,X
String idCard="340823199507262112";
System.out.println(idCard.matches("[1-9]\\d{5}(18|19|20)\\d{2}(0[1-9]|1[0-2])(0[1-9]|1[0-9]|2[0-9]|3[0-1])\\d{3}[\\d[xX]]"));
}
}